
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
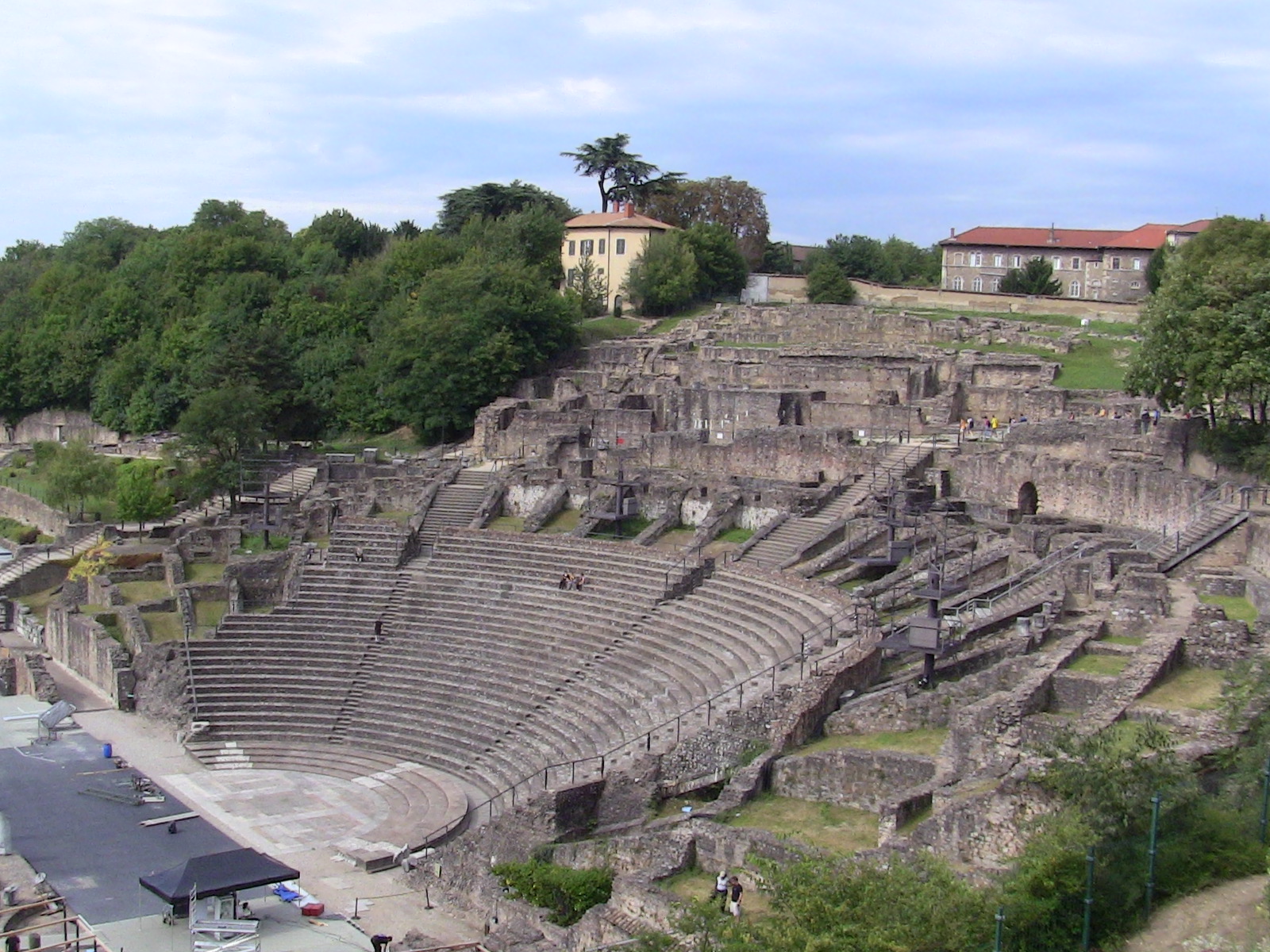
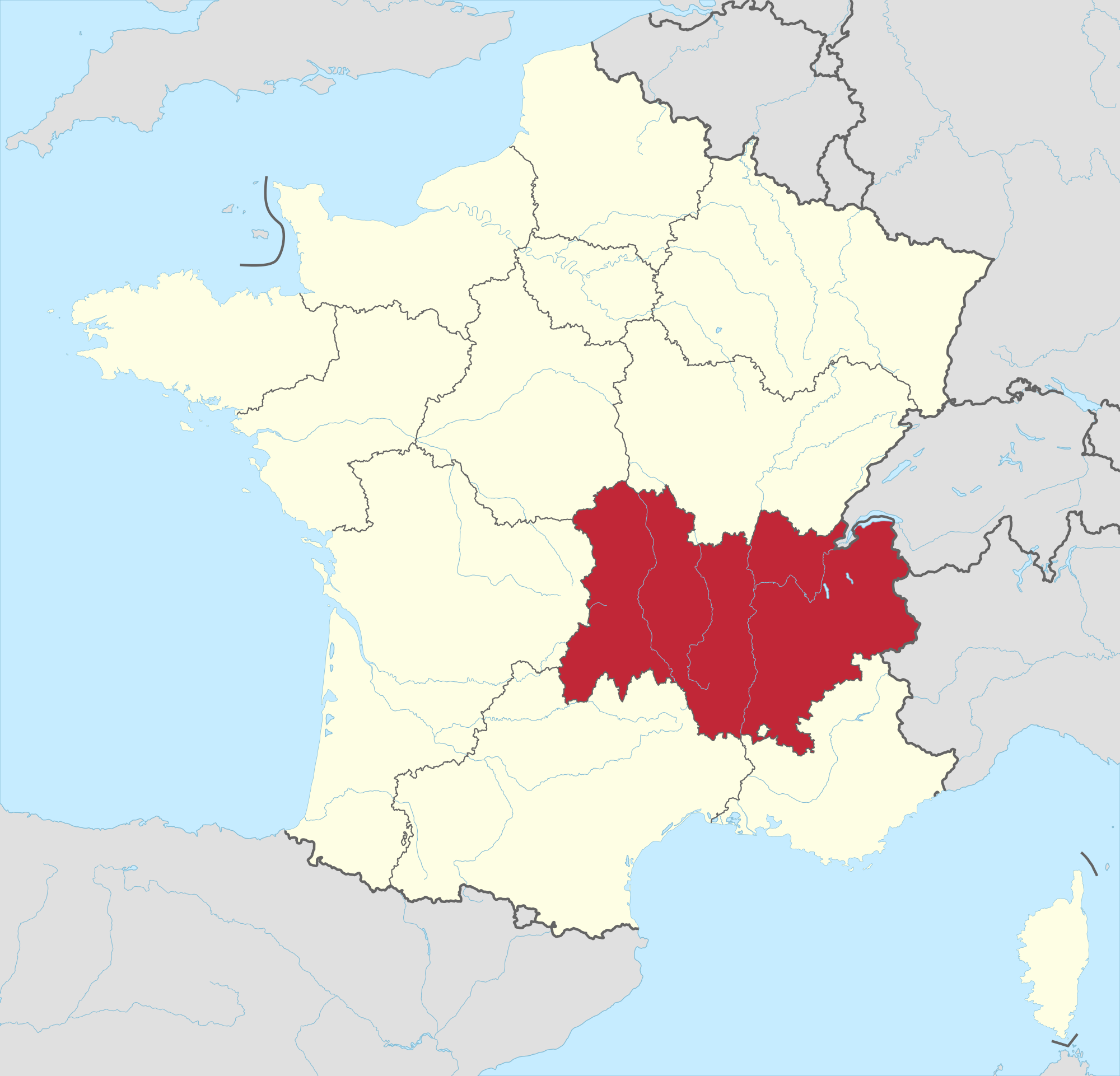
 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
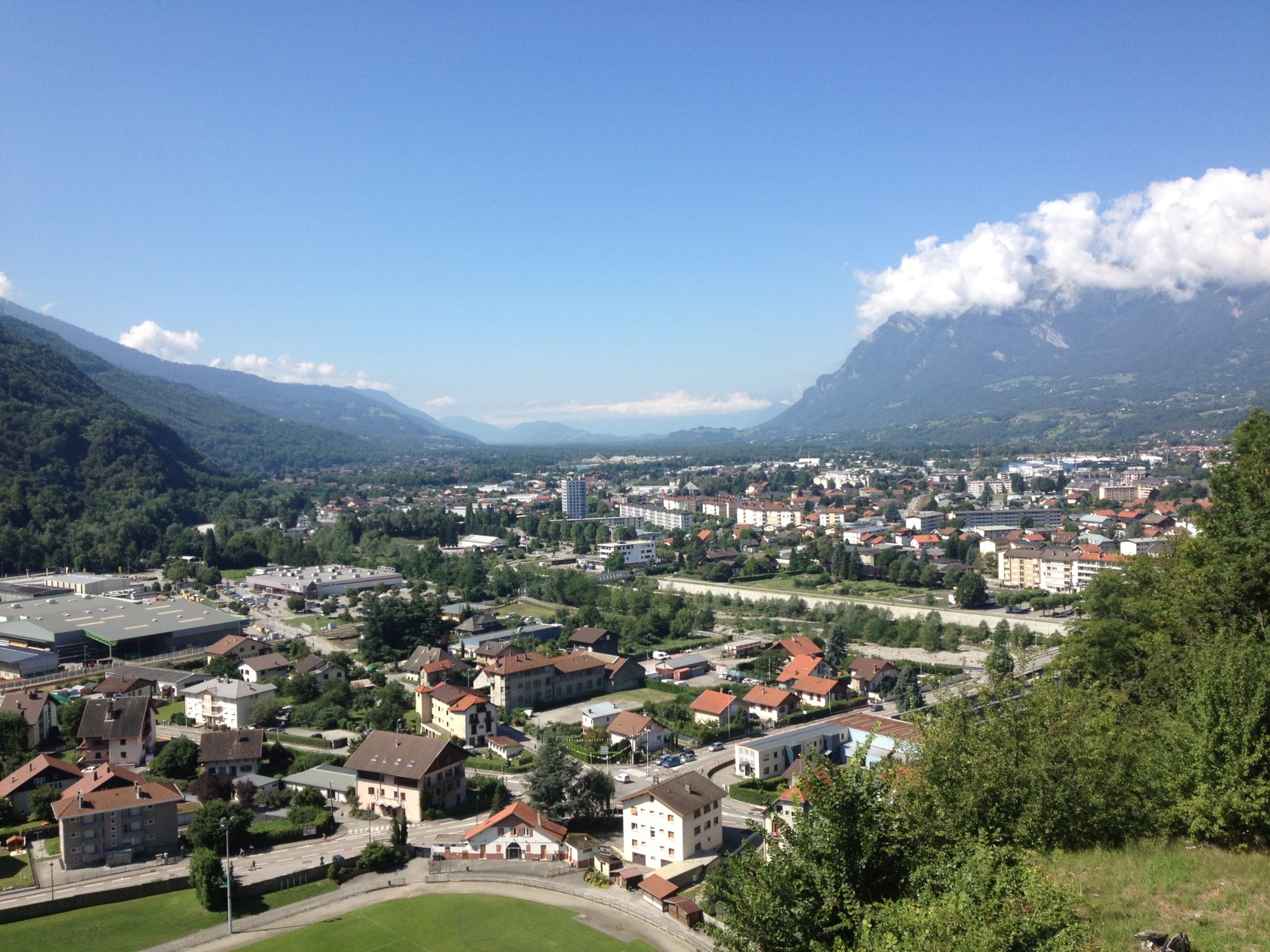



 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes

 Baden-Wuerttemberg
Baden-Wuerttemberg

 Bavaria
Bavaria
 Germany
Germany
 France
France

 Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
 Italy
Italy
 Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein

 Lombardia
Lombardia
 Monaco
Monaco
 Austria
Austria

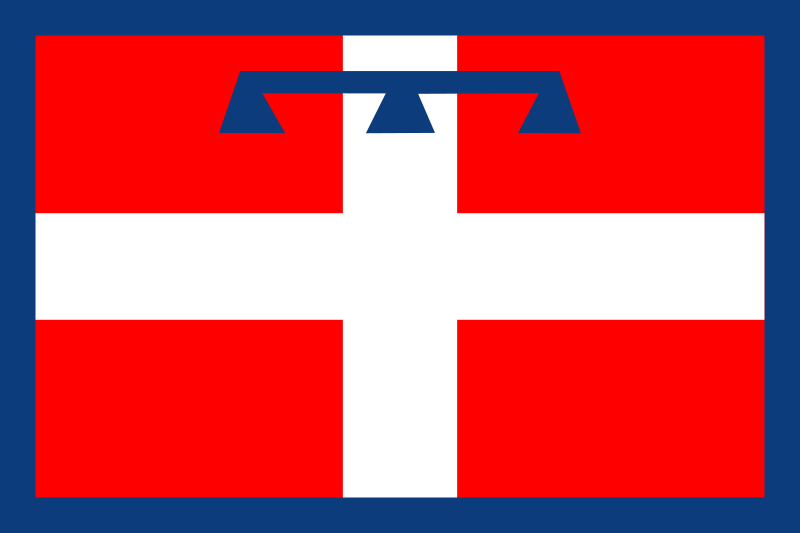 Piemonte
Piemonte

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovenia
Slovenia

 Tyrol
Tyrol

 Trentino-Alto Adige
Trentino-Alto Adige
 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel

 Valle d´Aosta
Valle d´Aosta
 Veneto
Veneto

 Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg
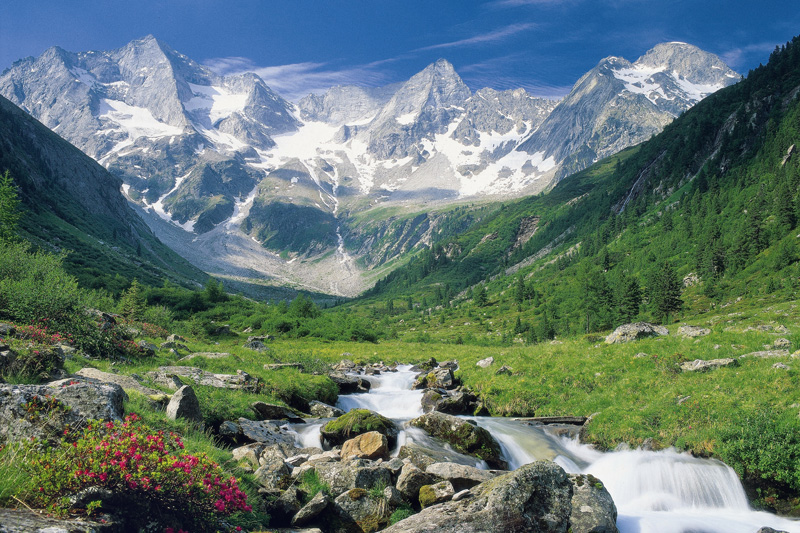

欧洲南部高大的山脉。西起法国尼斯附近地中海海岸,呈弧形向北、东延伸,经意大利北部、瑞士南部、列支敦士登、德国西南部,东止奥地利的维也纳盆地。总面积约22万平方千米。长约1200千米,宽130~260千米,东宽西窄。平均海拔3000米左右。 山脉主干向西南方向延伸为比利牛斯山脉,向南延伸为亚平宁山脉,向东南方向延伸为迪纳拉山脉,向东延伸为喀尔巴阡山脉。阿尔卑斯山脉可分为3段。西段西阿尔卑斯山从地中海岸,经法国东南部和意大利的西北部,到瑞士边境的大圣伯纳德山口附近,为山系最窄部分,也是高峰最集中的山段。勃朗峰(4810米)是整个山脉的最高点,位于法国和意大利边界。中段中阿尔卑斯山,介于大圣伯纳德山口和博登湖之间,宽度最大。有马特峰(4479米)和蒙特罗莎峰( 4634米)。东段东阿尔卑斯山在博登湖以东,海拔低于西、中两段阿尔卑斯山。
阿尔卑斯山(德语:Alpen;法语:Alpes;意大利语:Alpi;斯洛文尼亚语:Alpe)是一座位于欧洲中心的山脉,它覆盖了意大利北部边界、法国东南部、瑞士、列支敦士登、奥地利、德国南部及斯洛文尼亚。它可以被细分为三个部分,从地中海到勃朗峰的西阿尔卑斯山,从瓦莱达奥斯塔到布伦纳山口(奥地利和意大利交界处)的中阿尔卑斯山,从布伦纳山口到斯洛文尼亚的东阿尔卑斯山。欧洲许多大河都发源于此,水力资源丰富,为旅游、度假、疗养胜地。
阿尔卑斯山共有128座海拔超过4000米的山峰,其中最高峰勃朗峰海拔4810.45米[1],位于法国和意大利的交界处。山脉呈弧形,长1200千米,宽130~260千米,平均海拔约3000米,总面积约22万平方千米[2]。阿尔卑斯山北边是水汽较多的气候,而南边则较为干燥,雨量很少。
Die Alpen sind das höchste Gebirge im Inneren Europas. Es erstreckt sich in einem 1200 Kilometer langen und zwischen 150 und 250 Kilometer[1] breiten Bogen vom Ligurischen Meer bis zum Pannonischen Becken.
Die gesamte Alpenregion nimmt eine Fläche von etwa 200.000 Quadratkilometern ein.[2] Sie dehnt sich etwa 750 km von West nach Ost und ca. 400 km von Süd nach Nord aus und wird vom Rhonetal, dem Schweizer Mittelland, dem Oberlauf der Donau, der Kleinen Ungarischen Tiefebene, der Po-Ebene und dem Golf von Genua umgrenzt.
Der Alpenbogen schließt im Südwesten am Golf von Genua an den Apennin an, umfasst die Po-Ebene, verzweigt sich zum Französischen und Schweizer Jura und endet fächerförmig im Osten vor dem westpannonischen Berg- und Hügelland. Im Nordosten an der Donau bei Wien sind die Alpen durch das Wiener Becken von den geologisch verwandten Karpaten getrennt, im Südosten gehen sie in das stark verkarstete Dinarische Gebirge über. Im Norden fallen die Alpen allmählich zum österreichischen und deutschen Alpenvorland ab. Im Süden ist der Abfall zur Po-Ebene steiler. Der Gebirgszug, zu dem die Alpen gehören, erstreckt sich vom afrikanischen Atlas bis nach Südostasien.[3]
Die Gipfelhöhen in den westlichen Gebirgsstöcken liegen meist zwischen 3000 und 4300 Meter über dem Meeresspiegel, in den Ostalpen sind die Berge etwas niedriger. Der höchste Gipfel der Alpen ist der Mont Blanc mit 4810 Metern. 128 Berge der Alpen sind Viertausender, etliche Berge mehr oder weniger vergletschert. Die Alpen sind in zahlreiche Gebirgsgruppen und -ketten gegliedert.
Die Alpen bilden im „Herzen Europas“[4] eine wichtige Klima- und Wasserscheide. Sie trennen den zentralen Mittelmeerraum mit dem Etesienklima vom atlantisch beeinflussten nördlichen Mitteleuropa und stehen am Ostrand unter kontinentalem Einfluss. Auch die Entwässerung folgt diesen Großrichtungen zu Mittelmeer, Nordsee und Schwarzem Meer.
Der Alpenraum umfasst Gebiete der acht Alpenstaaten Frankreich, Monaco, Italien, Schweiz, Liechtenstein, Deutschland, Österreich und Slowenien. Er bildet den Lebensraum von 13 Millionen Menschen und genießt europäische Bedeutung als Erholungsraum.[4] Ungarn hat Anteile an Mittelgebirgen, die zu den Alpen gezählt werden, beispielsweise an Günser und Ödenburger Gebirge, wird in der Regel jedoch nicht zum Alpenraum gezählt. Seit der Frühgeschichte stellen Alpentäler und -pässe auch wichtige transeuropäische Verkehrsverbindungen dar.
アルプス山脈(アルプスさんみゃく、羅: Alpes アルペース、仏: Alpes、伊: Alpi、独: Alpen、英: Alps)は、アルプス・ヒマラヤ造山帯に属し、ヨーロッパ中央部を東西に横切る「山脈」である。オーストリア、スロベニアを東端とし、イタリア、ドイツ、リヒテンシュタイン、スイス各国にまたがり、フランスを南西端とする多国にまたがっている。アルプ(スイスの高山山腹の夏季放牧場;英語: alp,フランス語: alpe,ドイツ語: Alpe)がいっぱいであるからアルプスであると考える説と、ケルト語の alp「岩山」を語源とし、ラテン語を経由したと考える説がある。最高峰のモンブランは標高4,810.9m(2007年)で、フランスとイタリアの国境をなし、ヨーロッパの最高峰[1]でもある。
アルプス山脈はヨーロッパの多数の河川の水源地となっており、ここからドナウ川、ライン川、ローヌ川、ポー川、といった大河川が流れ出て、それぞれ黒海、北海、地中海、アドリア海へと注ぐ。
The Alps (/ælps/; French: Alpes [alp]; German: Alpen [ˈalpn̩]; Italian: Alpi [ˈalpi]; Romansh: Alps; Slovene: Alpe [ˈáːlpɛ]) are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe,[2][note 1] stretching approximately 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Switzerland, Italy, Monaco, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia.[3] The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrusting and folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at 4,810 m (15,781 ft) is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains about a hundred peaks higher than 4,000 metres (13,000 ft).
The altitude and size of the range affects the climate in Europe; in the mountains precipitation levels vary greatly and climatic conditions consist of distinct zones. Wildlife such as ibex live in the higher peaks to elevations of 3,400 m (11,155 ft), and plants such as Edelweiss grow in rocky areas in lower elevations as well as in higher elevations. Evidence of human habitation in the Alps goes back to the Palaeolithic era. A mummified man, determined to be 5,000 years old, was discovered on a glacier at the Austrian–Italian border in 1991.
By the 6th century BC, the Celtic La Tène culture was well established. Hannibal famously crossed the Alps with a herd of elephants, and the Romans had settlements in the region. In 1800, Napoleon crossed one of the mountain passes with an army of 40,000. The 18th and 19th centuries saw an influx of naturalists, writers, and artists, in particular, the Romantics, followed by the golden age of alpinism as mountaineers began to ascend the peaks.
The Alpine region has a strong cultural identity. The traditional culture of farming, cheesemaking, and woodworking still exists in Alpine villages, although the tourist industry began to grow early in the 20th century and expanded greatly after World War II to become the dominant industry by the end of the century. The Winter Olympic Games have been hosted in the Swiss, French, Italian, Austrian and German Alps. At present, the region is home to 14 million people and has 120 million annual visitors.[4]
Les Alpes (prononcé [alp]) sont une chaîne de montagnes qui s'étend en Europe, recouvrant la frontière nord de l'Italie, le Sud-Est de la France, Monaco, la Suisse, le Liechtenstein, l'Autriche, le Sud de l'Allemagne et la Slovénie.
Les Alpes culminent à 4 809 mètres, au sommet du mont Blanc. On recense 82 sommets majeurs de plus de 4 000 m d'altitude (Suisse : 48, Italie : 38, France : 24). Les cols de montagne reliant les vallées ou les pays dépassent souvent les 2 000 m d'altitude. Les Alpes forment une barrière de 1 200 km entre la Méditerranée et le Danube.
Le Alpi sono la catena montuosa più importante d'Europa, situate nell'Europa centrale a cavallo dei confini di Italia, Francia, Svizzera, Liechtenstein, Germania, Austria, Slovenia e Ungheria, separando l'Europa settentrionale da quella meridionale con lo stivale italiano. Suddivise in varie sezioni e svariati sottogruppi racchiudono in sé le vette più alte del continente centrale europeo, rivestendo anche un'importanza storica, naturalistica, idrografica e turistico-economica per i rispettivi paesi.
Los Alpes son una importante cadena de montañas situada en la Europa Central. Su cumbre más alta es el Mont Blanc, con 4.810 metros de altitud. Alrededor de los Alpes, favorecidos por ríos importantes de caudal uniforme y ricas tierras de cultivo, se ubicaron desde la prehistoria diversos pueblos, principalmente celtas, como los borgoñones, leucos, lombardos, helvecios, y posteriormente germánicos en el noreste y pueblos itálicos después de la conquista de la Galia Cisalpina por Julio César. Actualmente viven unos 14 millones de personas en la región de los Alpes.
А́льпы (фр. Alpes, нем. Alpen, итал. Alpi, романш. Alps, словен. Alpe) — самый высокий и протяжённый горный хребет среди систем, целиком лежащих в Европе. При этом Кавказские горы выше, а Уральские — протяжённей, но они лежат также и на территории Азии (в зависимости от выбранного определения границы между Европой и Азией).
Альпы представляют собой сложную систему хребтов и массивов, протянувшуюся выпуклой к северо-западу дугой от Лигурийского моря до Среднедунайской низменности. Альпы располагаются на территории 8 стран: Франции, Монако, Италии, Швейцарии, Германии, Австрии, Лихтенштейна и Словении. Общая длина альпийской дуги составляет около 1200 км (по внутреннему краю дуги — около 750 км), ширина — до 260 км. Самой высокой вершиной Альп является гора Монблан высотой 4810 метров над уровнем моря, расположенная на границе Франции и Италии[1]. Всего в Альпах сосредоточено около 100 вершин-четырёхтысячников[2].
Альпы являются международным центром альпинизма, горнолыжного спорта и туризма. Туризм в Альпах начал активно развиваться в XX веке и получил большой толчок после окончания Второй мировой войны, став одним из главных направлений в конце столетия. Пять стран из восьми (Швейцария, Франция, Италия, Австрия и Германия) были хозяйками Зимних Олимпийских игр, которые проводились в альпийских объектах[3]. Несмотря на активное развитие туризма, в альпийском регионе по-прежнему существует самобытная традиционная культура, включая сельское хозяйство, деревообработку и сыроварение.
Благодаря расположению в центре Западной Европы, Альпы являются одной из наиболее изученных горных систем. Многие понятия названы по имени Альп, в частности, альпийский климатический пояс, период альпийской складчатости, альпийский тип рельефа, альпийские луга, альпинизм.
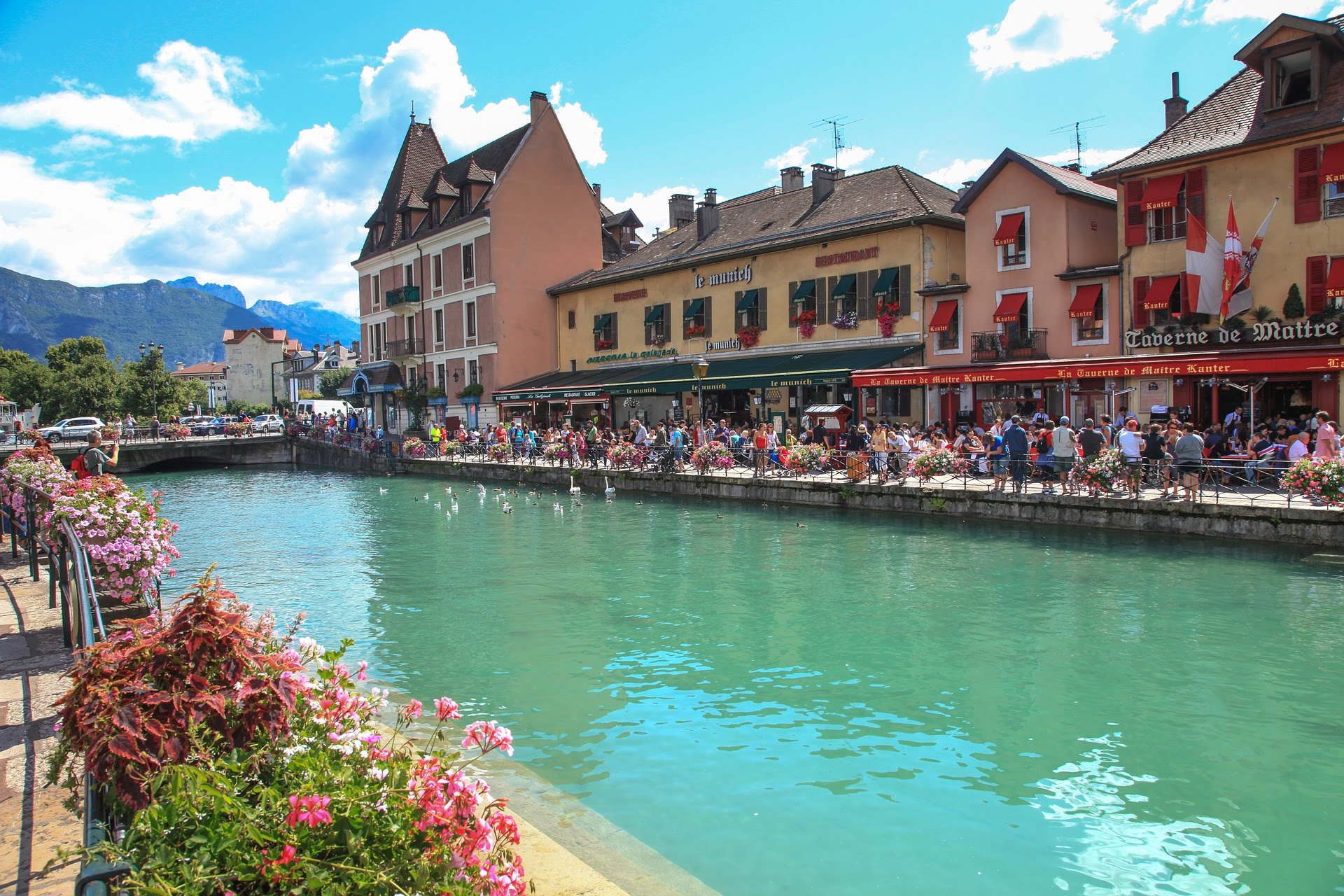


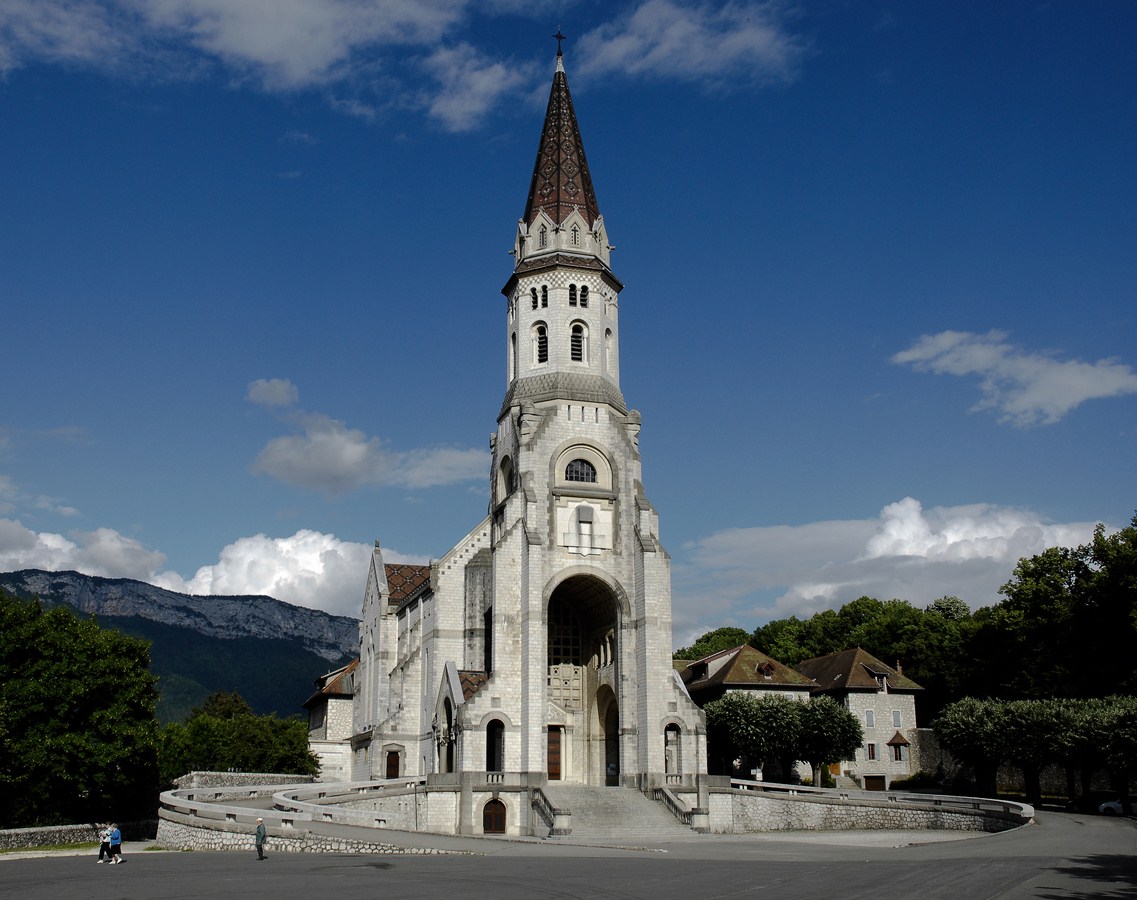
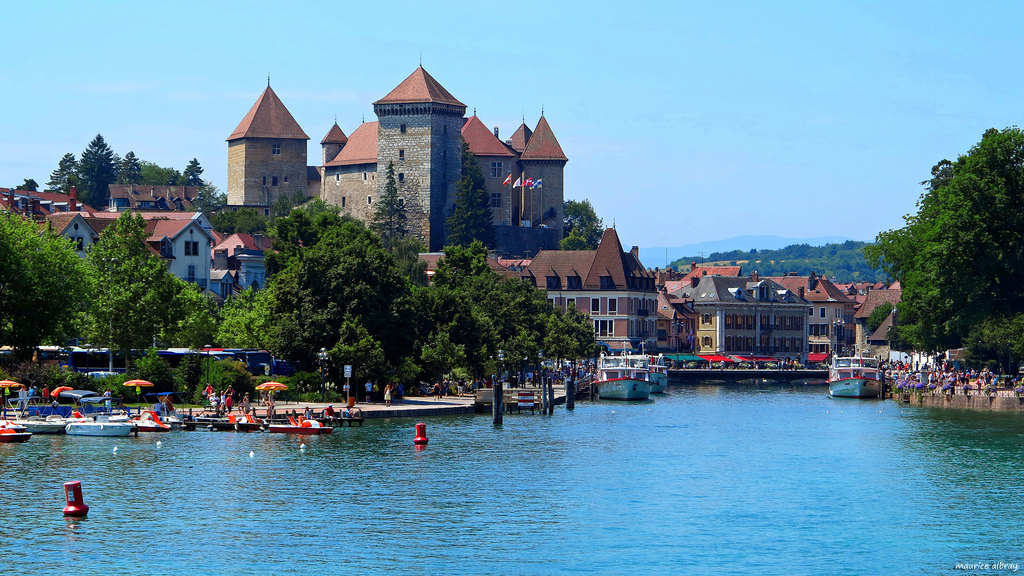
安锡(法语:Annecy, 台湾译作安锡,中国大陆译为阿讷西或安讷西)是法国罗讷-阿尔卑斯大区上萨瓦省的首府。阿纳西地处阿尔卑斯山脉西北麓,安纳西湖北岸,位于尚贝里和瑞士日内瓦之间,历史上长期受到这两个城市的影响。1401年起由萨伏依王朝统治。加尔文主义在日内瓦兴起后,这里成为反宗教改革的据点。法国大革命期间,安纳西被法国吞并,波旁王朝复辟后又归还萨丁尼亚王国。1860年,萨伏依被让与法国,阿讷西成为上萨瓦省的首府。
Annecy ist eine ostfranzösische Stadt mit 125.694 Einwohnern (Stand 1. Januar 2015) und die Hauptstadt des Départements Haute-Savoie in der Region Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes.
Sie wurde zur Alpenstadt des Jahres 2012 gekürt.
Annecy (French pronunciation: [ansi]; Arpitan: Èneci or Ènneci) is the largest city of Haute-Savoie department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France. It lies on the northern tip of Lake Annecy, 35 kilometers (22 mi) south of Geneva.
Nicknamed the "Pearl of French Alps" in Raoul Blanchard's monograph describing its location between lake and mountains, the city controls the northern entrance to the lake gorge. Due to a lack of available building land between the lake and the protected Semnoz mountain, its population remained stagnant, around 50,000 inhabitants, since 1950. However, the 2017 city merge extended the city population to 124,401 inhabitants, and 203,078 for its urban area, 6th regional position below Annemasse, which counts 292,000 inhabitants in the northern department.
Switching from counts of Geneva’s dwelling in the 13th century, to counts of Savoy’s in the 14th century, the city became Savoy's capital in 1434 during the Genevois-Nemours prerogative until 1659. Its role increased in 1536, during the Calvinist Reformation in Geneva, while the bishop took refuge in Annecy. Saint Francis de Sales gave Annecy its advanced Catholic citadel role known as Counter-Reformation. The annexation of Savoy merged the city to France in 1860.
Sometimes called "Venice of the Alps", this idyllic and touristic representation comes from the three canals and the Thiou river lying through the old city and whose initial role was to protect the city and to empower its handicrafts. The city experienced an industrial development in the 19th century with silk manufacturing. Some of its industrial legacy remains today with the headquarters of NTN-SNR bearings, Salomon, Entremont and Dassault Aviation.
Since the end of the 19th century, Annecy developed tourism around its lake summer facilities, winter resorts proximity and cultural attraction with its castle renovation and fine art museum opening in 1956 and the Animated Film Festival since 1960, hosted in Bonlieu's cultural Center. The municipal environmental policy managed to keep 40.3% of green spaces and the city and was awarded the "Golden Flower" in 2015, given to the nine most-flowered French cities. Its educational area is growing since the University of Savoy establishment in 1973.
Annecy (prononcé /an.si/ ; en francoprovençal Èneci1) est une ville française, chef-lieu et préfecture du département de la Haute-Savoie en région Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. Au nord des Alpes françaises, après Genève à 40 km au Nord, Annecy fait partie de l'axe des agglomérations du sillon alpin en alignement avec Chambéry puis Valence et Grenoble.
La « Perle des Alpes », comme décrite dans la monographie urbaine de Raoul Blanchard, est en situation de cluse de contact entre la plaine des Fins et les Préalpes, ce qui limita sa zone constructible et sa population des années 60 à la fusion communale de 2017. Après l'extension de son territoire sur Annecy-le-Vieux, Cran-Gevrier, Meythet, Pringy et Seynod, Annecy se range à la 29e rang place des villes françaises2 avec 125 694 habitants, ainsi qu'en 6e position régionale si l'on prend son aire urbaine de 234 085 habitants, derrière Annemasse et devant Chambéry.
Résidence historique des comtes de Genève au XIIIe siècle, puis des comtes de Savoie au XVe siècle, la bourgade gagne, lors de l'apanage de Genevois-Nemours, le statut de capitale de province de Savoie en 1434 avec les possessions du Genevois, du Faucigny et du Beaufortain jusqu'en 1659. Son rôle religieux s'intensifie en 1536, lors de la Réforme calviniste ; alors que l'évêque de Genève s'y réfugie, François de Sales en fait une citadelle avancée de la Contre-Réforme catholique, lui valant le surnom de « Rome des Alpes ». Le traité de Turin conduit à l'Annexion du duché de Savoie et rattache la ville à la France en 1860.
La « Venise des Alpes » fait référence aux canaux du Vassé, Saint Dominique et la rivière du Thiou prenant sa source dans son lac, dont le rôle passe de protection de la cité à celui de force hydraulique pour son artisanat. L'industrie se développe au XIXe siècle avec les manufactures de soies et subsiste encore de nos jours à travers la présence de sièges sociaux industriels tel SNR, Salomon, Entremont ou Alcatel, et de son bassin d'emploi considéré comme le 2e plus dynamique de France3. Au XXe siècle, le secteur du tourisme tire parti de l'image de pureté du lac, la proximité des stations de sports d'hiver, la conservation des espaces verts4 et du patrimoine avec, notamment, la rénovation de son château. Cette politique culturelle s'affirme en 1960 avec l'organisation du festival international du film d'animation d'Annecy au Centre culturel de Bonlieu. L'Université Savoie Mont Blanc en partenariat avec 3 autres villes de Savoie, ouvre ses portes en 1973.
Annecy es una comuna nueva francesa situada en el departamento de Alta Saboya, de la región de Auvernia-Ródano-Alpes.

 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
 Ligue 1
Ligue 1
 Ligue 1 2016/17
Ligue 1 2016/17
 Ligue 1 2017/18
Ligue 1 2017/18
 Ligue 1 2018/19
Ligue 1 2018/19
 UEFA Europa League 2019/20
UEFA Europa League 2019/20
 Group I
Group I
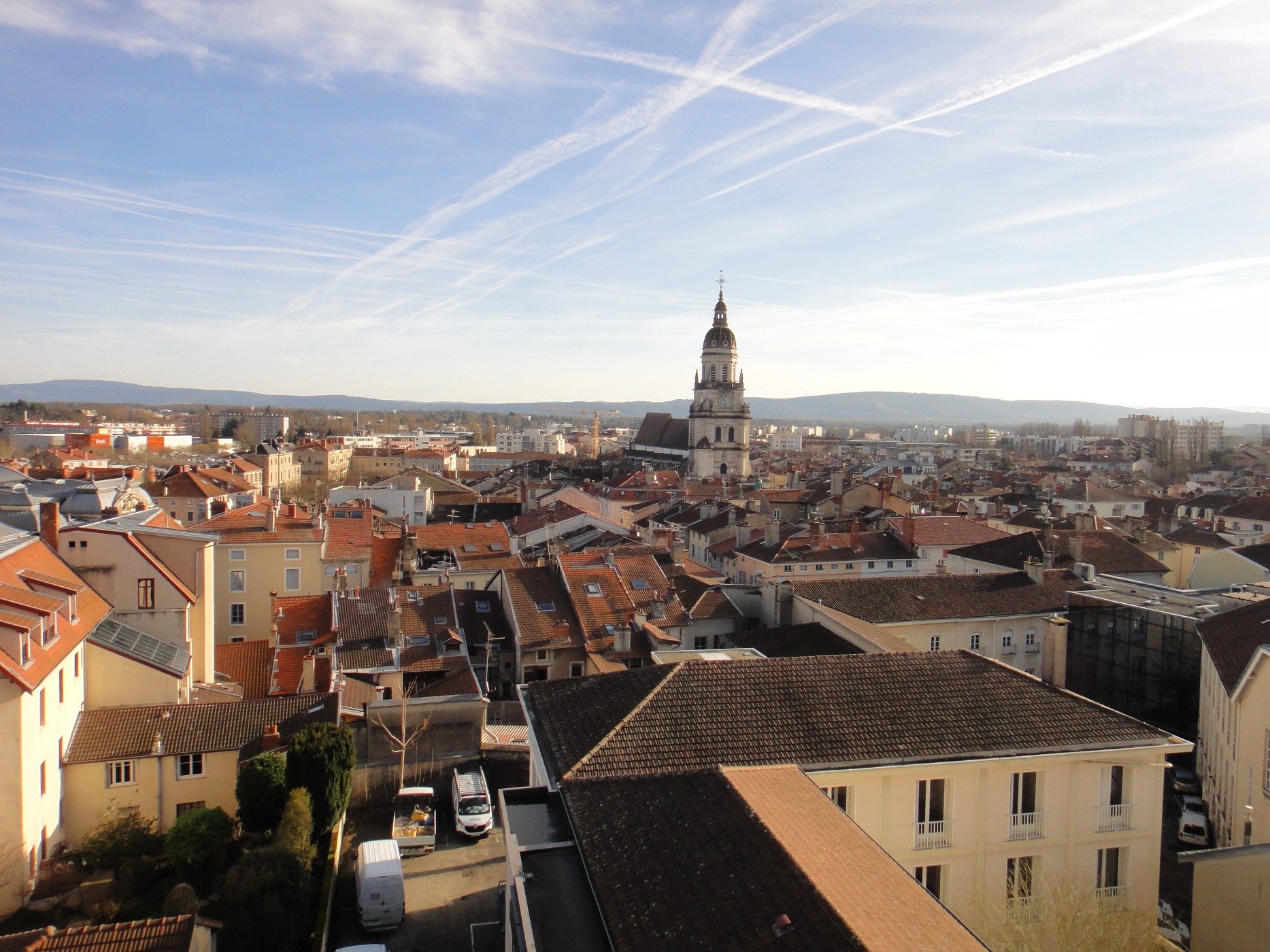
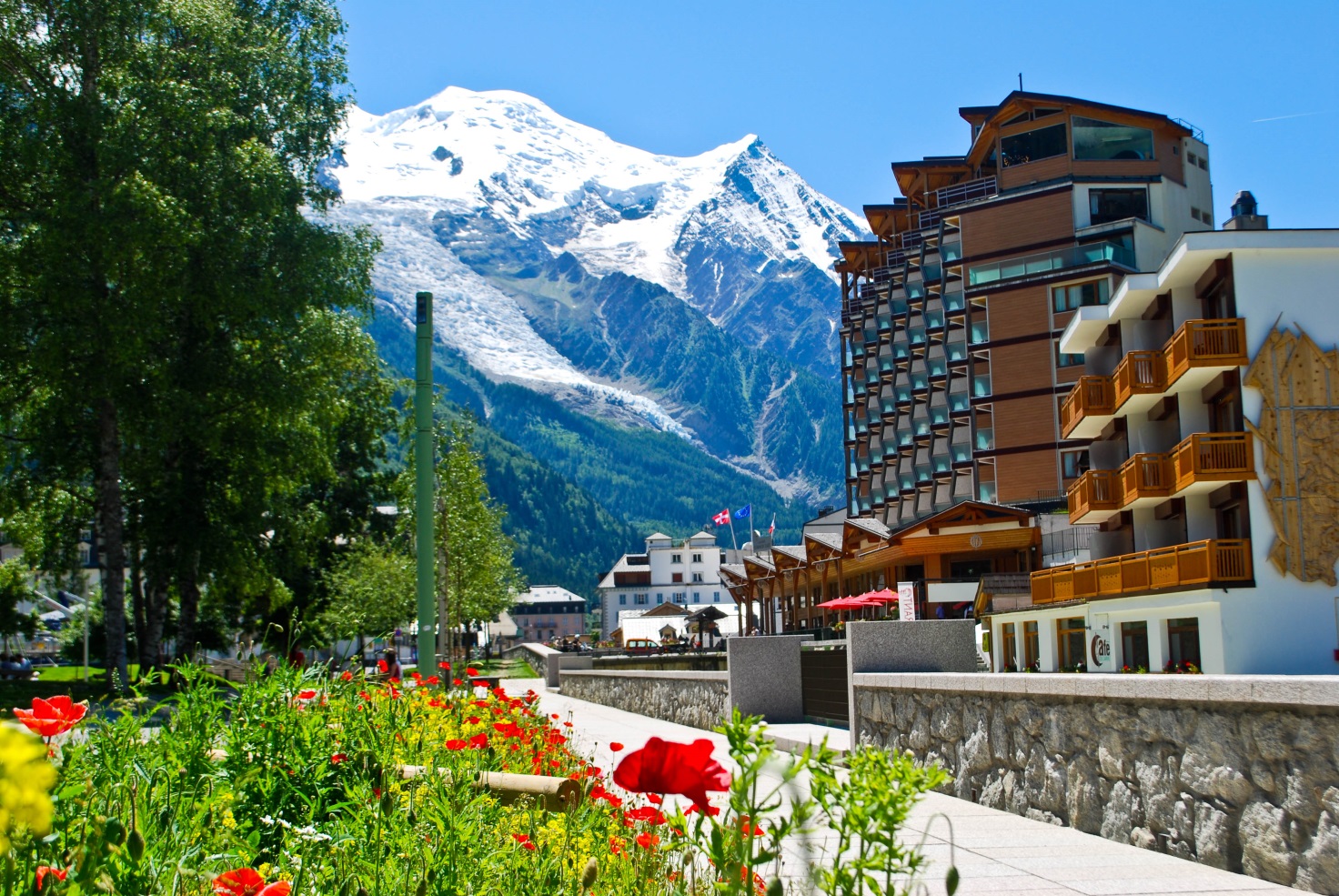








霞慕尼勃朗峰(法语:Chamonix-Mont-Blanc)是法国东南方接近瑞士与意大利国界的一个山中小镇,处于罗纳-阿尔卑斯大区上萨瓦省的勃朗峰山脚下,常住居民约9830人,是法国人口第865名的城镇[1],由16个村庄组成。
1091年日内瓦的伯爵把周边的谷地赠送给位于皮埃蒙特的一座本笃会修道院,这是首次提到阿尔沃河右岸的一些小建筑,即霞慕尼的前身。它后来属于萨伏依,后来随之被合并入萨丁王国。法国大革命和拿破仑帝国后它被并入法国。1860年3月24日按照都灵条约[2]萨伏依公国正式合并入法国,由此霞慕尼也于1860年4月4日正式成为法国一镇,1921年11月21日它更名为今天的名字。
霞慕尼是法国高度最高的镇之一,欧洲最高的高峰勃朗峰(海拔4810米)位于其境内,因此它是欧洲知名滑雪胜地,一般游客和体育登山攀登勃朗峰起点,因此是一座旅游业很兴旺的镇[3],这使得这座镇显得非常世界主义。霞慕尼的面积为245.46平方公里,是法国面积第四大的镇。
在1924年,第一届冬季奥林匹克运动会曾在这个城市举行。
Chamonix-Mont-Blanc (seit 1921 der offizielle Name), meistens kurz Chamonix genannt, ist ein Skiort und Zentrum des Alpinismus in Frankreich. Die Gemeinde liegt im Département Haute-Savoie in der Region Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. Sie erlangte weltweite Bekanntheit als Austragungsort der I. Olympischen Winterspiele.
Chamonix-Mont-Blanc wurde im Rahmen der Alpenkonvention zur Alpenstadt des Jahres 2015 gekürt.[1]
シャモニー=モン=ブラン(Chamonix-Mont-Blanc)はフランス東部、オート=サヴォワ県のコミューン。モンブランの麓にある標高1036mの登山とスキーのリゾート地である。日本では単にシャモニーと表記する場合が多い。
シャモニーはモンブランから続くモンブラン山群のふもとの渓谷の町であり、世界でも有数のスキーリゾートとして観光客を集めている。
1786年8月8日にモンブランが初登頂されてから、現在の登山というスポーツが始まったとされているため、登山発祥の地として登山家の聖地とも呼ばれている。
1924年に開催された冬季オリンピックの記念すべき第1回大会、シャモニーオリンピックがここで開催された。これにより冬季五輪・発祥の地と呼ばれる。
モンブランが西ヨーロッパ最高峰であるため、多くの登山家がここから山頂を目指した。各種クライミング、エクストリームスキー、パラグライダー、ラフティング、キャニオニング、マウンテンバイク、ウルトラトレイル(UTMB)など、その他の厳しい山岳スポーツの中心地でもある。
Chamonix-Mont-Blanc,[note 1] more commonly known as Chamonix[note 2] (formerly spelled Chamounix), is a commune in the Haute-Savoie département in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France. It was the site of the first Winter Olympics in 1924. The commune's population of around 8,900 ranks 1,089th within the country of France.[1]
Situated near the massive peaks of the Aiguilles Rouges and most notably the Aiguille du Midi, Chamonix is one of the oldest ski resorts in France. The north side of the summit of Mont Blanc, and therefore a summit half is part of the village of Chamonix. To the south side, the situation is different depending on the country. Italy considers that the border passes through the top. France considers that the boundary runs along the rocky Tournette under the summit cap, placing it entirely in French territory. The south side was in France, assigned to the commune of Saint-Gervais-les-Bains sharing the summit with its neighbor Chamonix. It is this situation "for France," which is found on the French IGN maps. The Chamonix commune is popular with skiers and mountain enthusiasts, and via the cable car lift to the Aiguille du Midi it is possible to access the off-piste (backcountry) ski run of the Vallée Blanche. With an area of 245 km2 (95 sq mi), Chamonix is the fourth largest commune, in area, in mainland France.
Chamonix-Mont-Blanc (prononcé [ ʃa.mɔ.ˈni mɔ̃ blɑ̃]1,Note 1) ou plus communément Chamonix, est une commune française située dans le département de la Haute-Savoie, en région Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. La commune de Chamonix-Mont-Blanc recouvre du nord au sud seize villages ou hameaux : le Tour, Montroc, le Planet, Argentière, les Chosalets, le Lavancher, les Tines, les Bois, les Praz de Chamonix, Chamonix-Mont-Blanc, les Pècles, les Mouilles, les Barrats, les Pélerins, les Gaillands, les Bossons.
Chamonix entre dans l'histoire en 1091, lorsque le comte Aymon Ier de Genève fait dotation de la vallée à l'abbaye bénédictine de Saint-Michel de la Cluse, en Piémont. Des moines s'installent sur la rive droite de l'Arve. C'est la naissance du prieuré de Chamonix. La commune est un territoire du duché de Savoie qui fait partie des États de Savoie, eux-mêmes intégrés par la suite au royaume de Sardaigne. Puis sous la Révolution française et le Premier Empire, elle devient un territoire français. Le 24 mars 1860, par le traité de Turin, le duché de Savoie est cédé à la France. Le 4 avril 1860, la commune de Chamonix devient alors définitivement française. Elle prend le nom de Chamonix-Mont-Blanc le 21 novembre 1921 : l'extension Mont-Blanc résulte d'un accord avec la commune de Saint-Gervais-les-Bains.
Enserrée entre les massifs montagneux des Aiguilles rouges et du mont Blanc, Chamonix partage avec Saint-Gervais-les-Bains le record de la commune ayant l'altitude la plus haute de France et d'Europe occidentale (ce point fait l'objet d'une discussion transfrontalière avec l'Italie. Il n'est pas réglé à ce jour du point de vue du droit international). Elle le doit à la présence sur son territoire du sommet le plus haut des Alpes : le mont Blanc qui culmine à 4 810 mètres. La commune est très prisée des amateurs d'alpinisme et des sportifs de montagne en général. Le site du mont Blanc étant le troisième site naturel le plus visité au monde5, cet atout touristique confère un visage très cosmopolite à la ville.
Chamonix-Mont-Blanc (pronuncia: ʃa.mɔ.ni mɔ̃ blɑ̃], in arpitano savoiardo Chamônix e in grafia Conflans Shamoni, pronuncia: θamuni) è un comune francese di 9.378 abitanti situato nel dipartimento dell'Alta Savoia della regione dell'Alvernia-Rodano-Alpi. È una grande stazione sciistica conosciuta in tutto il mondo. La città ha ottenuto nel 2015 il titolo Città alpina dell'anno.
Attraverso il Traforo del Monte Bianco la città francese è collegata al comune di Courmayeur (AO), in Italia, quindi all'autostrada A5 per Torino.
Chamonix es una población y comuna francesa, en la región de Auvernia-Ródano-Alpes, departamento de Alta Saboya, en el distrito de Bonneville. Es el chef-lieu del cantón de su nombre. Se encuentra a los pies del Mont Blanc.
Шамони́-Мон-Блан[2][3][4], или просто Шамони (фр. Chamonix-Mont-Blanc [ ʃa.mɔ.ni mɔ̃ blɑ̃ ], франкопров. Chamônix) — город и коммуна на востоке Франции, в департаменте Верхняя Савойя (историческая область Савойя).
Население — 9830 жителей (1999 год).
Расположен в Альпах, в узкой долине реки Арв (приток Роны), у подножия горы Монблан, в которой у Шамони прорыт тоннель, соединяющий Францию с Италией.
Шамони — центр популярного горнолыжного региона Шамони-Монблан.
 Ski vacation
Ski vacation
 International cities
International cities
 Geography
Geography
 Architecture
Architecture
 Sport
Sport
 Religion
Religion
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 History
History