
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM


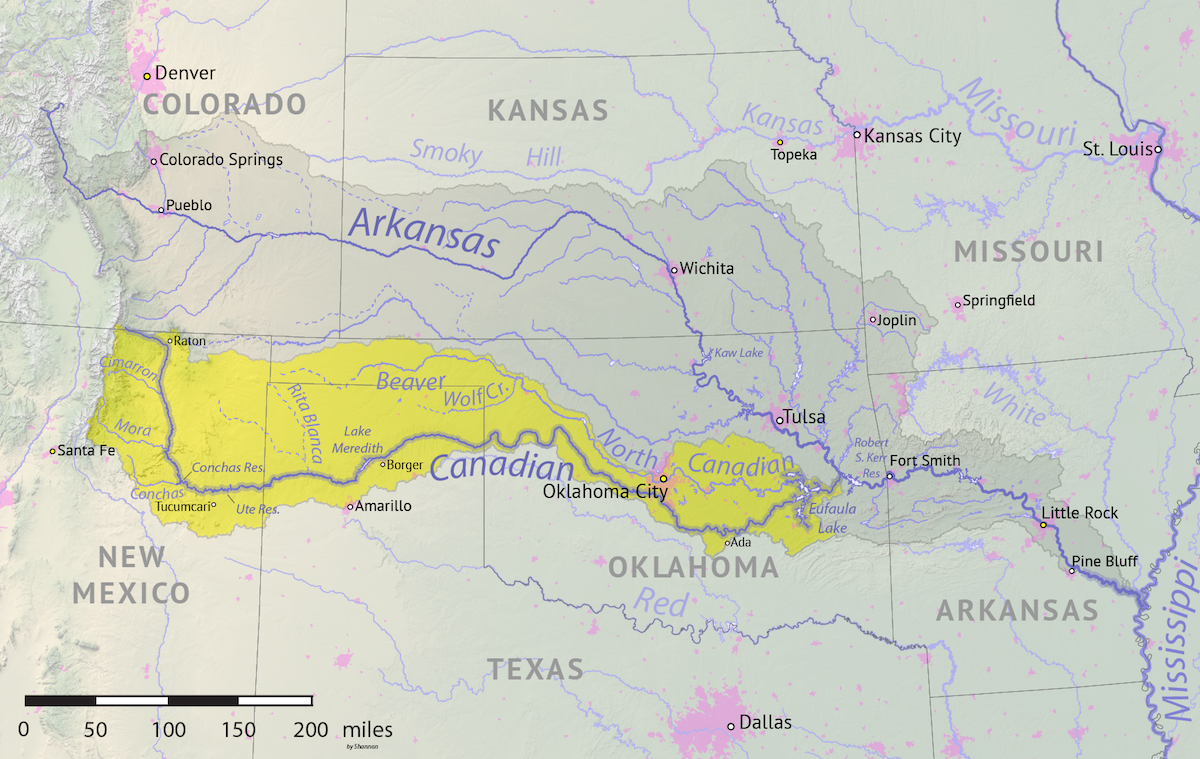

 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO
 Canada
Canada
 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB
 Mexico
Mexico
 Mississippi River
Mississippi River

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Saskatchewan-SK
Saskatchewan-SK

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX
 United States
United States

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY
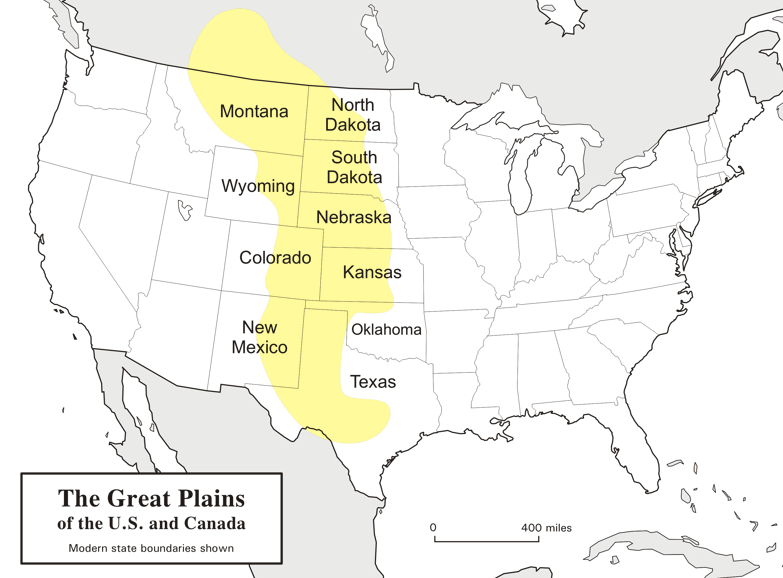
大平原(英语:Great Plains),多称北美大平原、北美大草原,是北美洲中部一块广袤的平原地区,大致位于密西西比河以西、洛基山脉以东、格兰德河以北。自然植被以草为主。
大平原东西长800千米,南北长3,200千米。另根据内布拉斯加-林肯大学大平原研究中心的定义,其总面积约130万平方千米。大平原主要包括了美国的科罗拉多州、堪萨斯州、蒙大拿州、内布拉斯加州、新墨西哥州 、北达科他州、俄克拉荷马州、南达科他州、得克萨斯州和怀俄明州,以及加拿大的草原三省(艾伯塔省、曼尼托巴省和萨斯喀彻温省)还有墨西哥的一小部分。
Die Great Plains (deutsch „Große Ebenen“) sind ein trockenes Gebiet östlich der Rocky Mountains in Nordamerika. Naturräumlich sind sie die klassischen Kurzgras-Prärien des amerikanischen Westens, heute werden sie intensiv landwirtschaftlich genutzt. Sie reichen von den kanadischen Prärieprovinzen (Alberta, Saskatchewan und Manitoba) bis nach Texas; manchmal wird auch ein kleiner Teil Mexikos dazu gezählt.
Die Great Plains umfassen (je nach Grenzziehung) eine Fläche von knapp 2 Millionen Quadratkilometern und erstrecken sich insgesamt etwa auf einer maximalen Breite von über 750 km und einer Länge von fast 3000 km. Während sie an den Rocky Mountains noch über 1800 m hoch sind, fallen sie nach Osten auf ca. 500 m ab. Damit sind sie insgesamt als Hochebene zu betrachten, die sich als „Piedmont-Plateau“, zum Teil in Schichtstufen ansteigend, vor dem Gebirge ausbreitet.
Man kann die Great Plains in zwei klimatische Regionen unterteilen, da man westlich des 100. Längengrades einen spärlichen Niederschlagsdurchschnitt vorfindet (weniger als 500 mm pro Jahr), wohingegen die östliche Region ein vergleichsweise humides Klima hat. Entsprechend dominiert im Westen die Viehwirtschaft und im Osten der Getreideanbau.

 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL
 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

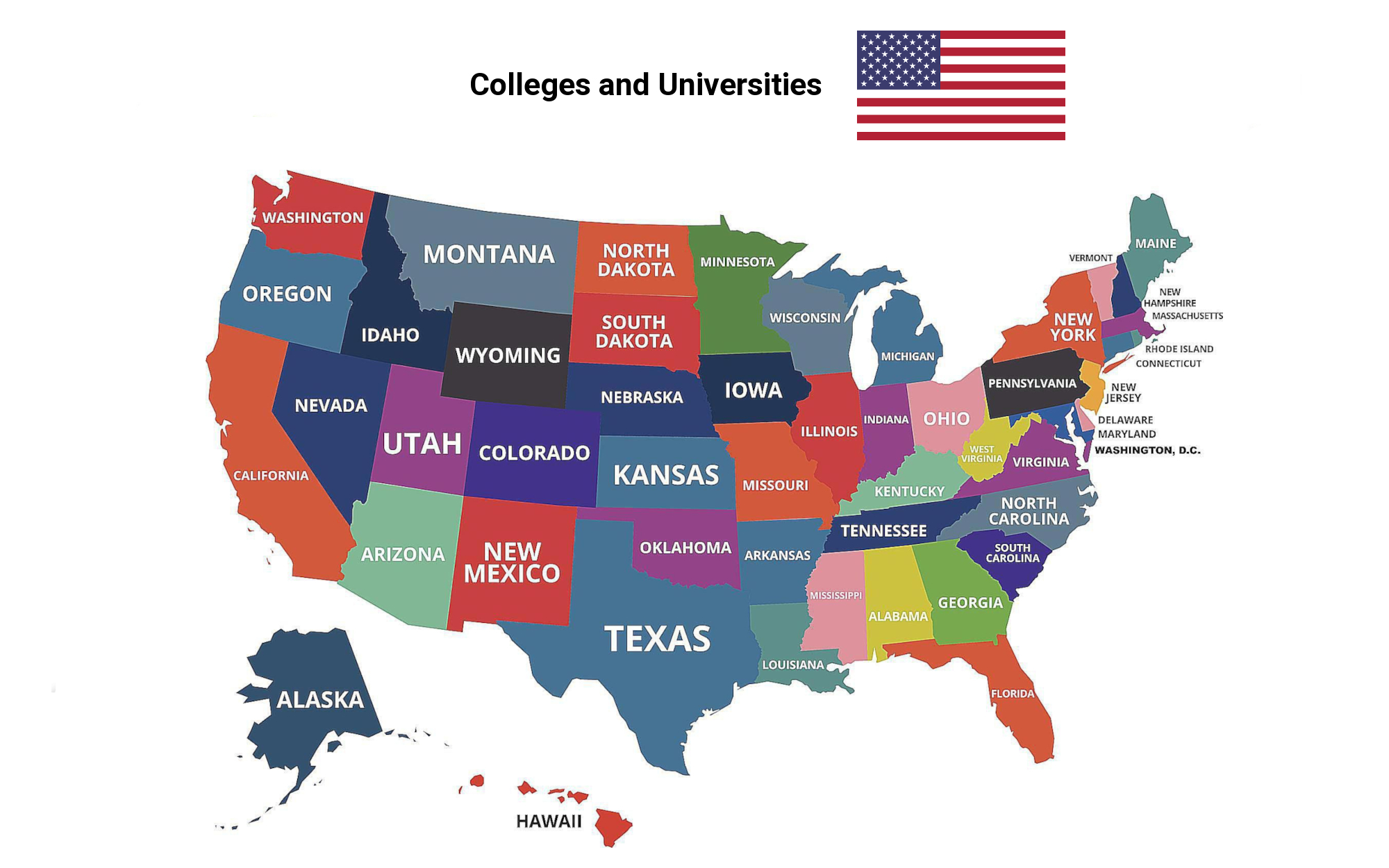
 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Universities and colleges in the United States of America
Universities and colleges in the United States of America

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Delaware-DE
Delaware-DE

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI
 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Universities in the USA
Universities in the USA

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA
 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

 Wisconsin-WI
Wisconsin-WI

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY

 Energy resource
Energy resource


 IT-Times
IT-Times


 Aerospace
Aerospace

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 *World famous research institutions
*World famous research institutions

洛斯阿拉莫斯国家实验室(英语:Los Alamos National Laboratory,缩写:LANL;前称“Y计划”、洛斯阿拉莫斯实验室、洛斯阿拉莫斯科学实验室)是美国承担核子武器设计工作的两个国家实验室之一,另一个是劳伦斯利弗莫尔国家实验室(始于1952年)。[2][3]洛斯阿拉莫斯国家实验室建立于1943年曼哈顿计划期间,最初负责原子弹的制造、由伯克利加州大学负责管理,首任主任是“原子弹之父”罗伯特·奥本海默。[2][4][5]
该国家实验室位于新墨西哥州洛斯阿拉莫斯,隶属美国能源部,目前的管理和运行则归由加州大学等机构组成的国家安全公司(Triad National Security, LLC)负责。[5][6]洛斯阿拉莫斯国家实验室是世界上最大的科学和技术研究机构之一,它在国家安全、太空探索、 可再生能源、医药、纳米技术和超级计算机等多个学科领域开展研究。
洛斯阿拉莫斯国家实验室是新墨西哥州北部最大的研究机构和最大的雇主,拥有大约9,000名的直接雇员和774人左右的合同雇员[7]。此外还有大约120名的美国能源部员工驻扎在实验室,负责监督那里的工作和运行情况。实验室约三分之一的技术人员是物理学家,四分之一是工程师,六分之一为化学家和材料科学家,其余的则在数学和计算科学、生物学、地球科学等其他学科的工作。外部的科学家和学生也会访问洛斯阿拉莫斯国家实验室参与科研项目。实验室联合大学和业界进行能源方面的基础和应用研究。洛斯阿拉莫斯国家实验室2016年的预算约为22亿美元[1]。
Das Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL, zuvor Los Alamos Laboratory und Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory) ist eine amerikanische Großforschungseinrichtung in Los Alamos (New Mexico). Das LANL betreibt multidisziplinäre Grundlagenforschung mit einem Schwerpunkt auf der nationalen Sicherheit für den Erhalt der Kernwaffenfähigkeiten ohne Nukleartests (Stockpile Stewardship). Die multidisziplinäre Forschung findet unter anderem auf den Gebieten Physik, Chemie, Biologie und Informationstechnologie statt.
Ursprünglich wurde am LANL während des Manhattan-Projekts die erste Atombombe entwickelt. Teile des Gebietes sind weiterhin militärische Sperrzone.
Das LANL hat insgesamt über 14.000 Mitarbeiter (Stand 2023) und ist damit eines der größten Forschungsinstitute der Welt. Es liegt abgelegen etwa 60 km nordwestlich von Santa Fe, New Mexico, auf einer Hochebene in etwa 2200 m Höhe. Der Standort des LANL in New Mexico sollte nicht verwechselt werden mit Los Alamos, Kalifornien, einer Kleinstadt im Nordwesten von Santa Barbara.

 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Review
Review

 Saskatchewan-SK
Saskatchewan-SK

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY
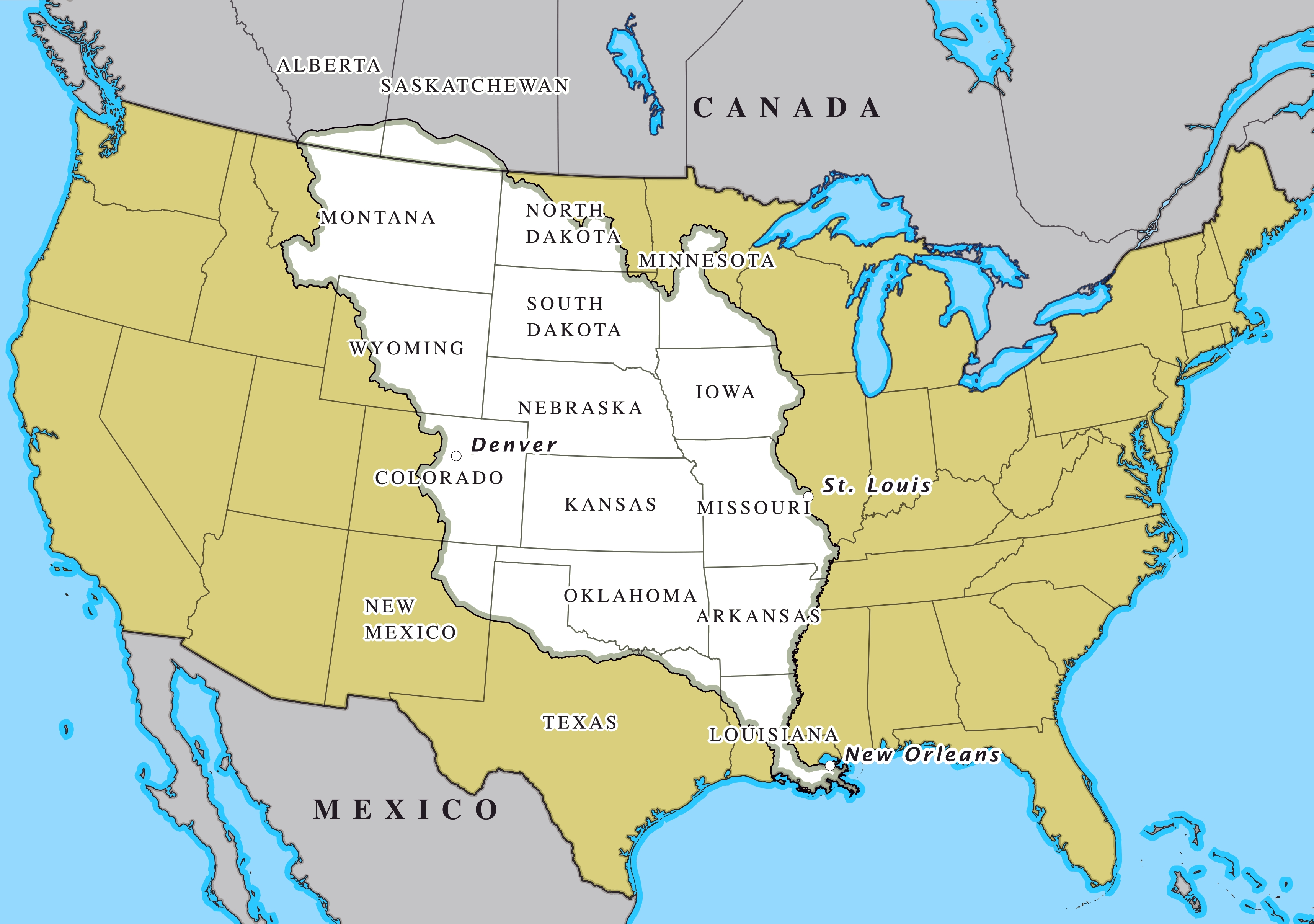
Der Louisiana Purchase (Louisiana-Kauf; im Französischen vente de la Louisiane, d. h. Verkauf von Louisiana) war der Kauf von 2.144.476 km² Land, das die USA 1803 von Frankreich erwarben. Der Kaufpreis betrug damals 15 Millionen US-Dollar oder 80 Millionen französische Francs (7 US-Dollar pro km²). Gemessen an der Kaufkraft entspricht das einem heutigen Wert von circa 251 Millionen US-Dollar oder knapp 117 Dollar pro km² (Stand 2018).[1]
Verkauft wurde das Gebiet der ehemaligen Kolonie Louisiana, das westlich des Mississippi River lag. Dieses Gebiet ist viel größer als der heutige Staat Louisiana: Es umfasst außer Teilen des heutigen Louisiana auch die heutigen Staaten Arkansas, Missouri, Iowa, Oklahoma, Kansas und Nebraska sowie Teile von Minnesota, North Dakota, South Dakota, Texas, New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, außerdem noch Randgebiete der kanadischen Provinzen Manitoba, Saskatchewan und Alberta.
Der Louisiana Purchase war das größte Grundstücksgeschäft der Geschichte. Das gekaufte Land verdoppelte damals das Territorium der Vereinigten Staaten und macht fast ein Viertel des heutigen Staatsgebiets aus.
路易斯安那购地(英语:Louisiana Purchase;法语:Vente de la Louisiane)是美国于1803年以每英亩三美分向法国购买超过529,911,680英亩(2,144,476平方公里)土地的交易案,该交易的总价为1500万美元或相当于8000万法郎;若计算通货膨胀等因素,此数额在今日相当于3亿100万美元。如以国内生产总值相对比例计算,此数额在2004年相当于4,178亿美元。而土地上所有后续条约和财务结算的总成本,估计约为26亿美元。[1]。
法属路易斯安那的版图远超今日美国的路易斯安那州。从南至北,该属地范围包括了现今美国路易斯安那州密西西比河两岸(包括新奥尔良市)、阿肯色州、奥克拉荷马州、德克萨斯州北部边界地带、新墨西哥州东北角、密苏里州、堪萨斯州、科罗拉多州洛基山脉以东、爱荷华州、内布拉斯加州、怀俄明州大部(落基山脉以东)、明尼苏达州密西西比河以西、南达科他州、北达科他州大部、蒙大拿州大部(除西端),以及现今加拿大马尼托巴、萨斯喀彻温、艾伯塔各省之密苏里河流域地区(也即南部边境地带)。购地所涉土地面积是今日美国国土的22.3%,与当时美国原有国土面积大致相当,因此使得当时美国的国土翻倍。
 *U.S. foreign territories
*U.S. foreign territories
 Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico

 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK

 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA



 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL

 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 California-CA
California-CA

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Companies
Companies

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

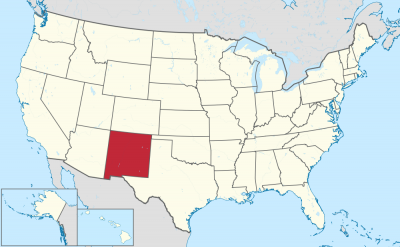


New Mexico ist geprägt durch die Lage auf einer Hochebene. Diese ist jedoch nicht uniform, sondern der Übergangsbereich von vier geologischen Provinzen Nordamerikas. Von Osten steigt das Gelände aus den Prärien der High Plains flach an. Der Südwesten des Staates ist Teil der Chihuahua-Wüste, die zur Basin and Range-Provinz gehört. Von Nordwesten ragt das Colorado-Plateau bis nach New Mexico und im Norden reichen mit der Sangre de Cristo Range die südlichsten Teile der Rocky Mountains bis Santa Fe. Die großen Teile des Lands auf der windabgewandten Seite (Lee) der Rocky Mountains sind arid. Die Trockenheit prägt die Landschaft in der Ebene wie im Gebirge. Ausnahmen sind die Berge nördlich von Santa Fe und das Gebiet im Westen jenseits der Kontinentalscheide, wo es ausgedehnte Wälder gibt. In den Bergen nördlich von Santa Fe ist die Niederschlagsmenge im Winter so groß, dass dort eine Wintersportregion entstanden ist. Außerdem gibt es Gebiete, die von Menschen nahezu unberührt sind, wie zum Beispiel die Gila Wilderness im Südwesten. Höchster Berg ist der Wheeler Peak nördlich von Santa Fe mit 4011 m.
Der Reichtum an Landschaftsformen, die klare Luft mit dem meist blauen Himmel und die abwechslungsreichen bunten Gesteine sind charakteristisch für New Mexico.
新墨西哥州(纳瓦霍语:Yootó Hahoodzo;英语:New Mexico;西班牙语:Nuevo México),简称新墨州,是美国西南方的一州,它曾是墨西哥的一省。该州有许多西班牙裔的居民,亦有不少的美国原住民。因此具有相当独特的文化。它也是美国唯一官方州名有两个语言的州份。该州邮政简写为NM,它的首府是圣菲。
该州早在公元前即有人类活动,州内一些地区发现了史前人类活动遗址。公元三世纪后半定居活动出现,出现了建筑遗址。公元16至17世纪后半叶,虽然欧洲探险者已经开始出现,但当地依然保留了传统文化和独特的社会组织。
18世纪随着西班牙殖民势力拓展,新墨西哥州所在的地区逐步被纳入新西班牙总督区的统治。
1821年墨西哥摆脱西班牙的殖民统治,民族主义情绪高涨,加上美国购买的路易斯安那领地西部与墨西哥的边界不清晰,墨西哥政府遂移民北部各地区,其中包括新墨西哥。
1845年爆发的美墨战争中,美国军队进入这一地区,但因没有稳定的后勤通道无法长期占领据守。1848年新墨西哥领地(包括今天亚利桑那东部、新墨西哥、科罗拉多南部和犹他东南部)被割让给美国,美国政府随后建立新墨西哥领地。
1853年为修建横贯大陆铁路南线而发起的加兹登购地为新墨西哥增加了埃尔帕索以西的地区,包括西南角向南突出的方形区域。
内战期间,新墨西哥忠于北方的联邦政府,但同时也有很多居民支持奴隶制的邦联。邦联军队曾试图占领新墨西哥和亚利桑那来缓解西部战线的威胁,但没能成功。与此同时,有不少黑奴逃亡于此。战后美国政府拆分了新墨西哥领地,在其西部建立了亚利桑那领地。东北部少量地区划入科罗拉多,西北角部分地区划入内华达州,包括今天的拉斯维加斯。
1912年,新墨西哥与亚利桑那分别建州,开始时州府定在阿尔伯克基,但后来迁址圣菲。
ニューメキシコ州(英: New Mexico、西: Nuevo México、"ヌエボ・メヒコ")は、アメリカ合衆国南西部にある州である。州の北はコロラド州に接し、東側にはオクラホマ州とテキサス州に、西側はアリゾナ州に、南側はテキサス州およびメキシコとの国境に接している。また州の北西にはフォー・コーナーズがあり、そこでユタ州とも一点で接している。面積ではアメリカ合衆国で5番目に大きいが、人口では36番目であり、人口密度では45番目になっている。美しい景観から「Land of Enchantment(魅惑/魔法の土地)」と通称される[1]。
州都は1607年にスペイン人が建設した歴史ある町サンタフェ市である。
New Mexico (Spanish: Nuevo México; Spanish pronunciation: [ˈnweβo ˈmexiko] (![]() listen), Navajo: Yootó Hahoodzo; Navajo pronunciation: [jòːtxó xɑ̀xòːtsò]) is a state in the Southwestern region of the United States of America; its capital is Santa Fe, which was founded in 1610 as capital of Nuevo México (itself established as a province of New Spain in 1598), while its largest city is Albuquerque with its accompanying metropolitan area. It is one of the Mountain States and shares the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. New Mexico is also bordered by the state of Texas to the east-southeast, Oklahoma to the northeast, and the Mexican states of Chihuahua to the south and Sonora to the southwest. With an estimated population of 2,096,829 as of the July 1, 2019, U.S. Census Bureau estimate, New Mexico is the 36th largest state by population. With a total area of 121,590 sq mi (314,900 km2), it is the fifth-largest and sixth-least densely populated of the 50 states. Due to their geographic locations, northern and eastern New Mexico exhibit a colder, alpine climate, while western and southern New Mexico exhibit a warmer, arid climate.
listen), Navajo: Yootó Hahoodzo; Navajo pronunciation: [jòːtxó xɑ̀xòːtsò]) is a state in the Southwestern region of the United States of America; its capital is Santa Fe, which was founded in 1610 as capital of Nuevo México (itself established as a province of New Spain in 1598), while its largest city is Albuquerque with its accompanying metropolitan area. It is one of the Mountain States and shares the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. New Mexico is also bordered by the state of Texas to the east-southeast, Oklahoma to the northeast, and the Mexican states of Chihuahua to the south and Sonora to the southwest. With an estimated population of 2,096,829 as of the July 1, 2019, U.S. Census Bureau estimate, New Mexico is the 36th largest state by population. With a total area of 121,590 sq mi (314,900 km2), it is the fifth-largest and sixth-least densely populated of the 50 states. Due to their geographic locations, northern and eastern New Mexico exhibit a colder, alpine climate, while western and southern New Mexico exhibit a warmer, arid climate.
The economy of New Mexico is dependent on oil drilling, mineral extraction, dryland farming, cattle ranching, lumber milling, and retail trade. As of 2018, its total gross domestic product (GDP) was $101 billion[8] with a GDP per capita of $45,465. State tax policy results in low to moderate taxation of resident personal income compared to most U.S. states, with special consideration for military personnel, and gives tax credits and exemptions to favorable industries. Because of this, its film industry has grown and contributed $1.23 billion to its overall economy. Due to its large area and economic climate, New Mexico has a large U.S. military presence marked notably with the White Sands Missile Range. Various U.S. national security agencies base their research and testing arms in New Mexico, such as the Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratories. During the 1940s, Project Y of the Manhattan Project developed and built the country's first atomic bomb and nuclear test, Trinity.
Inhabited by Native Americans for many thousands of years before European exploration, it was colonized by the Spanish in 1598 as part of the Imperial Spanish viceroyalty of New Spain. In 1563, it was named Nuevo México after the Aztec Valley of Mexico by Spanish settlers, more than 250 years before the establishment and naming of the present-day country of Mexico; thus, the present-day state of New Mexico was not named after the country today known as Mexico.[9][10] After Mexican independence in 1821, New Mexico became a Mexican territory with considerable autonomy. This autonomy was threatened, however, by the centralizing tendencies of the Mexican government from the 1830s onward, with rising tensions eventually leading to the Revolt of 1837. At the same time, the region became more economically dependent on the United States. At the conclusion of the Mexican–American War in 1848, the United States annexed New Mexico as the U.S. New Mexico Territory. It was admitted to the Union as the 47th state on January 6, 1912.
Il Nuovo Messico[2] (in inglese New Mexico; in spagnolo Nuevo México; in navajo Yootó Hahoodzo) è uno Stato federato del sud-ovest degli Stati Uniti. La sua capitale è Santa Fe, mentre la città più popolosa è Albuquerque. Considerato uno degli Stati delle Montagne Rocciose, è il 5º per grandezza e il 36º per popolazione tra i 50 Stati dell'Unione. È detto «lo Stato spagnolo d'America», poiché mentre giuridicamente il Nuovo Messico non ha nessuna lingua ufficiale, lo spagnolo è di uso corrente accanto all'inglese. È inoltre lo stato con la più alta percentuale di ispanici di qualunque altra parte degli Stati Uniti perché i suoi abitanti sono sia discendenti di coloni spagnoli sia di immigrati dal Messico, Centro e Sud America. Lo Stato ha anche la 2ª più alta percentuale di nativi americani (dopo l'Alaska), oltre al 4° più alto numero totale degli stessi (dopo California, Oklahoma, Arizona), principalmente di etnia navajo, pueblo e apache.[3]
La demografia e la cultura dello Stato sono uniche, per le forti influenze ispaniche e dei nativi americani; entrambe si riflettono nella bandiera dello Stato: i colori sono rosso e oro, presi dalla bandiera della Spagna, e vi è raffigurato l'antico simbolo del Sole degli indigeni zia, parte dell'etnia pueblo.
Nuevo Méxiconota 1 (en inglés: New Mexico) es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C. forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Santa Fe y su ciudad más poblada, Albuquerque.
Está ubicado en la región Oeste del país, división Montañas Rocosas. Limita al norte con Colorado, al noreste con Oklahoma, al este y sureste con Texas, al suroeste con Chihuahua (México), al oeste con Arizona y al noroeste con Utah. Con 314 915 km² es el quinto estado más extenso —por detrás de Alaska, Texas, California y Montana— y con 6.54 hab/km², el sexto menos densamente poblado, por delante de Dakota del Sur, Dakota del Norte, Montana, Wyoming y Alaska, el menos densamente poblado. Fue el cuadragésimo séptimo estado en ser admitido a la Unión, el 6 de enero de 1912, como el estado número 47, por delante de Arizona, Alaska y Hawái, último estado en ser admitido.
Habitado por Nativos Americanos desde miles de años antes de la Exploración Europea, fue colonizado por los españoles en 1598 y anexionado al Virreinato de la Nueva España. Después, fue parte del México Independiente hasta convertirse en territorio estadounidense y, eventualmente, un estado, como resultado de la guerra mexicano-estadounidense. Tiene el mayor porcentaje de hispanos, incluyendo a los descendientes de los colonizadores españoles. Tiene el segundo mayor porcentaje de Nativos Americanos como proporción con la población después de Alaska y la cuarta más grande población de Nativos Americanos después de California, Oklahoma y Arizona. Las naciones nativas norteamericanas más grandes son la Navajo, Pueblo y Apache, vinculadas étnica y lingüísticamente con naciones indígenas del norte de México. La demografía y cultura del estado están fuertemente influenciadas por estas raíces hispanas y nativoamericanas, expresadas en la bandera estatal. Los colores escarlata y amarillo de la misma fueron tomados de los estandartes reales de España, junto al antiguo símbolo del Sol de los Zia, una tribu Pueblo.
Los exploradores españoles registraron esta región como Nuevo México en 1563 y de nuevo en 1581, cuando creyeron incorrectamente que contenía ricas y diversas culturas relacionadas con la mexica, del Imperio azteca. El nombre se quedó, incluso cuando el área no tenía conexión alguna al Imperio Mexica o su cultura, más que la remota relación lingüística con los pueblos Ute. Nuevo México formaba parte de la Nueva España como provincia y posteriormente fue parte del Primer Imperio Mexicano y la República Federal Mexicana durante veintisiete años (desde 1821 hasta 1848).
Нью-Ме́ксико[1][2] (англ. New Mexico, МФА: [nuː ˈmɛksɨkoʊ], исп. Nuevo México [nwebo 'mexiko]) — штат[3] на юго-западе США, один из так называемых Горных штатов. Население — 2 085 287 человек (36-е место среди штатов; данные 2013 года). Столица — Санта-Фе, крупнейший город — Альбукерке. Другие крупные города — Лас-Крусес, Розуэлл, Фармингтон и Рио-Ранчо.
Официальный девиз штата — «Растёт на ходу» (лат. Crescit Eundo). Официальное прозвище — «Земля очарования» (англ. Land of Enchantment, исп. Tierra de Encanto).
 Sport
Sport
 Geography
Geography
 Animal world
Animal world
 History
History
 Astronomy
Astronomy
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic