
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Madrid
Madrid


国际证监会组织(英語:International Organization of Securities Commissions,缩写:IOSCO)成立于1983年,总部位于西班牙马德里。IOSCO是由各国各地区证券期货监管机构组成的组织,是主要的金融监管国际标准制定机构之一。截至2022年9月,该组织共有233个会员,包括130个正式会员(ordinary member),34个联系会员(associate member)和69个附属会员(affiliate member)。
Die Internationale Organisation der Wertpapieraufsichtsbehörden (kurz IOSCO von engl. International Organization of Securities Commissions) wurde 1983 als internationale Vereinigung von Börsenaufsichtsbehörden in der Nachfolge einer gleichnamigen rein-amerikanischen Organisation aus dem Jahr 1973 gegründet.[1] Sie hat ihren Sitz im spanischen Madrid. Ihr Ziel ist die Förderung weltweiter einheitlicher Börsen- und Wertpapierzulassungsstandards.

 European Union
European Union

 Financial
Financial

 Financial
Financial
 *European Union economic data
*European Union economic data
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Madrid
Madrid

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade

La Agencia Estatal de Administración Tributaria (AEAT), comúnmente llamada Agencia Tributaria, es un organismo público español encargado de la gestión del sistema tributario y aduanero estatal, así como de los recursos de otras Administraciones y entes públicos nacionales o de la Unión Europea, cuya gestión se le encomiende.

 Madrid
Madrid
 Primera División
Primera División
 Primera División 2015/16
Primera División 2015/16
 Primera División 2017/18
Primera División 2017/18
 Primera División 2018/19
Primera División 2018/19
 UEFA Europa League 2019/20
UEFA Europa League 2019/20
 Group C
Group C


 Andalusia
Andalusia

 Aragón
Aragón
 Asturias
Asturias

 Cantabria
Cantabria

 Castilla y León
Castilla y León

 Castilla-La Mancha
Castilla-La Mancha
 Cataluña
Cataluña

 Comunidad Autónoma del País Vasco
Comunidad Autónoma del País Vasco

 Foral Community of Navarra
Foral Community of Navarra

 Valencian Community
Valencian Community

 Extremadura
Extremadura

 Galicia
Galicia

 Balearic Islands
Balearic Islands

 Canary Islands
Canary Islands

 La Rioja
La Rioja

 Madrid
Madrid

 Murcia
Murcia
 Spain
Spain
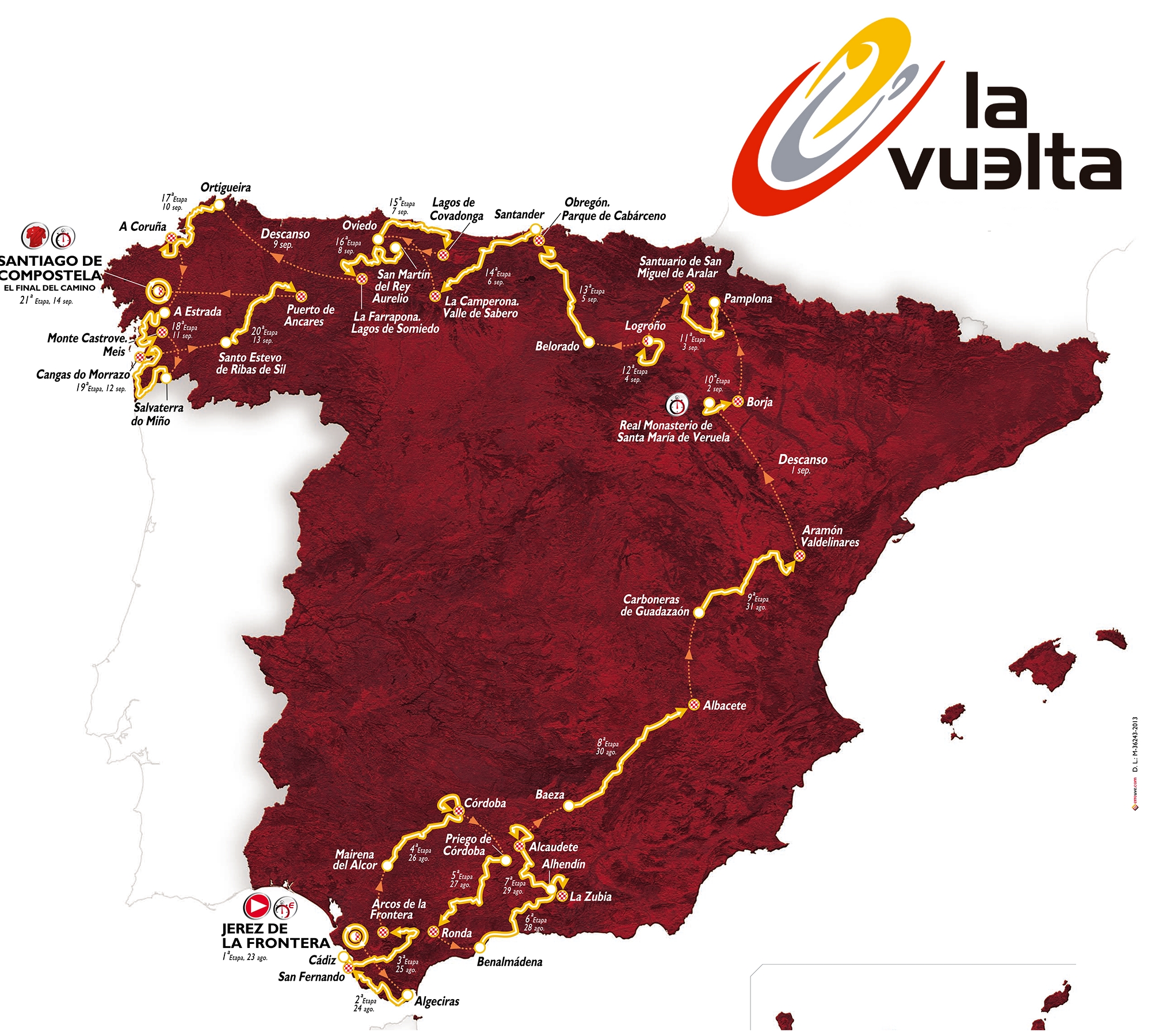
 UCI World Tour
UCI World Tour

 Audi Cup
Audi Cup
 Carlo Ancelotti
Carlo Ancelotti
 Fabio Capello
Fabio Capello
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025
 Group H
Group H
 José Mourinho
José Mourinho
 Jupp Heynckes
Jupp Heynckes

 Madrid
Madrid
 Primera División
Primera División
 Primera División 2015/16
Primera División 2015/16
 Primera División 2016/17
Primera División 2016/17
 Primera División 2017/18
Primera División 2017/18
 Primera División 2018/19
Primera División 2018/19
 Rafael Benítez
Rafael Benítez
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Europa League
(F)UEFA Europa League
 UEFA Champions League 2015/16
UEFA Champions League 2015/16
 UEFA Champions League 2016/17
UEFA Champions League 2016/17
 Group F
Group F
 UEFA Champions League 2017/18
UEFA Champions League 2017/18
 Group H
Group H
 UEFA Champions League 2018/19
UEFA Champions League 2018/19
 Group G
Group G
 UEFA Champions League 2019/20
UEFA Champions League 2019/20
 Group A
Group A
 UEFA Champions League 2025/26
UEFA Champions League 2025/26
 Vicente del Bosque
Vicente del Bosque
 Zinédine Zidane
Zinédine Zidane



























 AIRBUS
AIRBUS
 Airbus Helicopters
Airbus Helicopters
 AIRBUS
AIRBUS
 Airbus
Airbus
 AIRBUS
AIRBUS
 Airbus Defence and Space
Airbus Defence and Space
 Airbus A300
Airbus A300
 Airbus A310
Airbus A310
 Airbus A320
Airbus A320
 Airbus A330
Airbus A330
 Airbus A340
Airbus A340
 Airbus A350
Airbus A350
 Airbus A380
Airbus A380
 Airbus Group
Airbus Group
 Airbus
Airbus

 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL

 Andalusia
Andalusia

 Bremen
Bremen

 Castilla-La Mancha
Castilla-La Mancha
 China
China
 Germany
Germany
 England
England

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL
 France
France

 Hamburg
Hamburg

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS


 Aerospace
Aerospace
 Civil aircraft
Civil aircraft

 Madrid
Madrid



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Military aircraft
Military aircraft

 Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony

 Occitania
Occitania

 Pays-de-la-Loire
Pays-de-la-Loire
 Spain
Spain
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA
 Wales
Wales
 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 Science and technology
Science and technology

空客集团,正式名称为空客欧洲股份公司(英语:Airbus SE)是一家由欧洲多国政府所合资、专营航空器与航天器之开发及销售的综合企业。注册于荷兰莱顿、总部位于法国图卢兹,旗下企业包括空中客车集团、空客国防航天公司和空客直升机公司等[3]。2000年7月10日成立,当时名为欧洲航空国防航天公司(European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company,简称EADS),2004年改名为空客集团公司(Airbus Group SE),2017年改为现名。
空客集团是目前全世界仅有三间能生产大型宽体客机的制造商其中之一,与美国制造商波音共同主导全球的民用航空器市场。同时空客集团也生产诸多军用机及飞行武器。
Die Airbus SE (von 2000 bis 2013 EADS für European Aeronautic Defence and Space) ist Europas größter Luft- und Raumfahrt- sowie (nach BAE Systems) zweitgrößter Rüstungskonzern. Mit einem Umsatz von rund 52 Milliarden Euro war Airbus im Jahr 2021 das drittgrößte Luft- und Raumfahrtunternehmen der Welt. Zum Jahreswechsel 2013/14 übernahm der Konzern den Namen seiner Tochtergesellschaft Airbus S.A.S., die als Flugzeughersteller im Bereich Verkehrsflugzeuge tätig ist. Das Unternehmen beschäftigt an mehr als 70 Entwicklungs- und Produktionsstandorten in Europa sowie in 35 Außenbüros weltweit rund 138.000 Mitarbeiter. Seit der Gründung im Jahr 2000 werden die Aktien des Konzerns an den Börsen Paris und Frankfurt gehandelt und in den französischen Leitindex CAC 40 sowie seit dem 20. September 2021 in den DAX einbezogen.
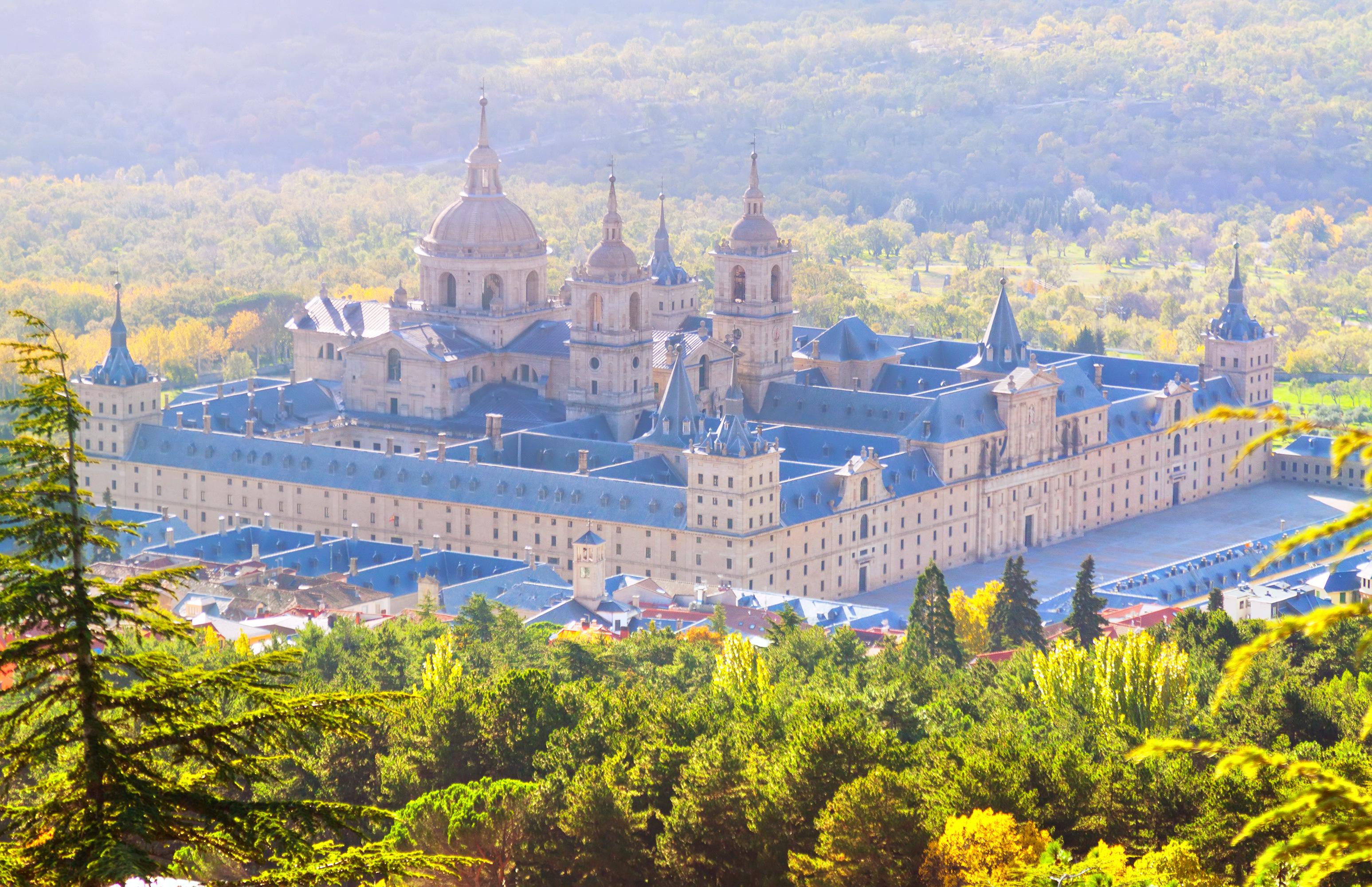




埃斯科里亚尔修道院全称“埃斯科里亚尔圣洛伦索王家修道院”,位于西班牙马德里市西北约50公里处的瓜达拉马山南坡。是世界上最大最美的宗教建筑之一。该 建筑名为修道院,实为修道院、宫殿、陵墓、教堂、图书馆、慈善堂、神学院、学校八位一体的庞大建筑群,气势磅礴,雄伟壮观,并珍藏欧洲各艺术大师的名作, 有“世界第八大奇迹”之称。
埃斯科里亚尔的外观过于庄严肃穆,朴实无华,就像它的总设计师腓力二世一样缺乏情趣。这里集合着王宫、教堂、墓地、图书馆等重要建筑。当同年代的中国明朝万历皇帝在骄奢淫逸时,西班牙的宫廷却像灰暗的“僧侣们的花园”。(Quelle: www.tripdv.com/view/v/zl_34510.html)
The Royal Site of San Lorenzo de El Escorial (Spanish: Monasterio y Sitio de El Escorial en Madrid), commonly known as El Escorial (Spanish pronunciation: [el eskoˈɾi̯al]), is a historical residence of the King of Spain, in the town of San Lorenzo de El Escorial, about 45 kilometres (28 miles) northwest of the capital, Madrid, in Spain. It is one of the Spanish royal sites and has functioned as a monastery, basilica, royal palace, pantheon, library, museum, university, school and hospital. It is situated 2.06 km (1.28 mi) up the valley (4.1 km [2.5 mi] road distance) from the town of El Escorial.
El Escorial comprises two architectural complexes of great historical and cultural significance: the royal monastery itself and La Granjilla de La Fresneda, a royal hunting lodge and monastic retreat about five kilometres away. These sites have a dual nature; that is to say, during the 16th and 17th centuries, they were places in which the power of the Spanish monarchy and the ecclesiastical predominance of the Roman Catholic religion in Spain found a common architectural manifestation.[1] El Escorial was, at once, a monastery and a Spanish royal palace. Originally a property of the Hieronymite monks, it is now a monastery of the Order of Saint Augustine. It is also a boarding school (Real Colegio de Alfonso XII).[2]
Philip II of Spain, reacting to the changes of the 16th century, dedicated much of his lengthy reign (1556–1598) and much of his seemingly inexhaustible supply of New World gold to stemming the tide. His protracted efforts were, in the long run, partly successful; however, the same impulse had a much more benign expression thirty years earlier in Philip's decision to build the complex at El Escorial.
Philip engaged the Spanish architect, Juan Bautista de Toledo, to be his collaborator in the design of El Escorial. Juan Bautista had spent the greater part of his career in Rome, where he had worked on the basilica of St. Peter's, and in Naples, where he had served the king's viceroy, whose recommendation brought him to the king's attention. Philip appointed him architect-royal in 1559, and together they designed El Escorial as a monument to Spain's role as a center of the Christian world.[3]
On 2 November 1984, UNESCO declared The Royal Seat of San Lorenzo of El Escorial a World Heritage Site. It is a popular tourist attraction, often visited by day-trippers from Madrid – more than 500,000 visitors come to El Escorial every year.
Le site royal de Saint-Laurent-de-l'Escurial (en castillan : Real Sitio de San Lorenzo de El Escorial) est un grand complexe (monastère, musée, collège bibliothèque, et palais) qui se trouve sur le territoire de la commune de San Lorenzo de El Escorial, située à 45 kilomètres au nord-ouest de Madrid, dans la Communauté autonome de Madrid (Espagne). C'est une ancienne résidence du roi d'Espagne. La Bibliothèque sera la source de tensions diplomatique entre l'Espagne et le Maroc, après que la précieuse collection du Sultan du Maroc Zaidan El-Nasir a été capturée par des vaisseaux espagnols au large du Maroc, elle sera offerte au roi Philippe II qui, sans doute, connaissait l'importance d'un tel trésor et qui l’incorporera dans la bibliothèque de l'Escurial, mais une grande partie de la collection est perdue après l'incendie de 16711.
Le site royal de Saint-Laurent-de-l'Escurial a été inscrit sur la liste du patrimoine mondial de l'Unesco en 1984.
Il monastero dell'Escorial, anche detto di San Lorenzo del Escorial, si trova in Spagna, nella comunità autonoma di Madrid, nel comune di San Lorenzo de El Escorial. Fu fatto costruire da Filippo II come residenza e pantheon dei re di Spagna, fu anche convento e chiesa dal 1563 al 1584. Nel 1984 è stato dichiarato Patrimonio dell'Umanità dell'UNESCO.
El Real Monasterio de San Lorenzo de El Escorial es un complejo que incluye un palacio real, una basílica, un panteón, una biblioteca , un colegio y un monasterio. Se encuentra en la localidad española de San Lorenzo de El Escorial, en la Comunidad de Madrid, y fue construido entre 1563 y 1584.
El palacio fue residencia de la Familia Real Española, la basílica es lugar de sepultura de los reyes de España y el monasterio –fundado por monjes de la Orden de San Jerónimo– está ocupado actualmente por frailes de la Orden de San Agustín. Es una de las más singulares arquitecturas renacentistas de España y de Europa. Situado en San Lorenzo de El Escorial, ocupa una superficie de 33.327 m², sobre la ladera meridional del monte Abantos, a 1028 m de altitud, en la Sierra de Guadarrama. Está gestionado por Patrimonio Nacional.
Conocido también como Monasterio de San Lorenzo El Real, o, sencillamente, El Escorial, fue ideado en la segunda mitad del siglo XVI por el rey Felipe II y su arquitecto Juan Bautista de Toledo, aunque posteriormente intervinieron Juan de Herrera, Juan de Minjares, Giovanni Battista Castello El Bergamasco y Francisco de Mora. El rey concibió un gran complejo multifuncional, monacal y palaciego que, plasmado por Juan Bautista de Toledo según el paradigma de la Traza Universal, dio origen al estilo herreriano.
Fue considerado, desde finales del siglo XVI, la Octava Maravilla del Mundo, tanto por su tamaño y complejidad funcional como por su enorme valor simbólico. Su arquitectura marcó el paso del plateresco renacentista al clasicismo desornamentado. Obra ingente, de gran monumentalidad, es también un receptáculo de las demás artes.
Sus pinturas, esculturas, cantorales, pergaminos, ornamentos litúrgicos y demás objetos suntuarios, sacros y áulicos hacen que El Escorial sea también un museo. Su compleja iconografía e iconología ha merecido las más variadas interpretaciones de historiadores, admiradores y críticos. El Escorial es la cristalización de las ideas y de la voluntad de su impulsor, el rey Felipe II, un príncipe renacentista.

 Party and government
Party and government
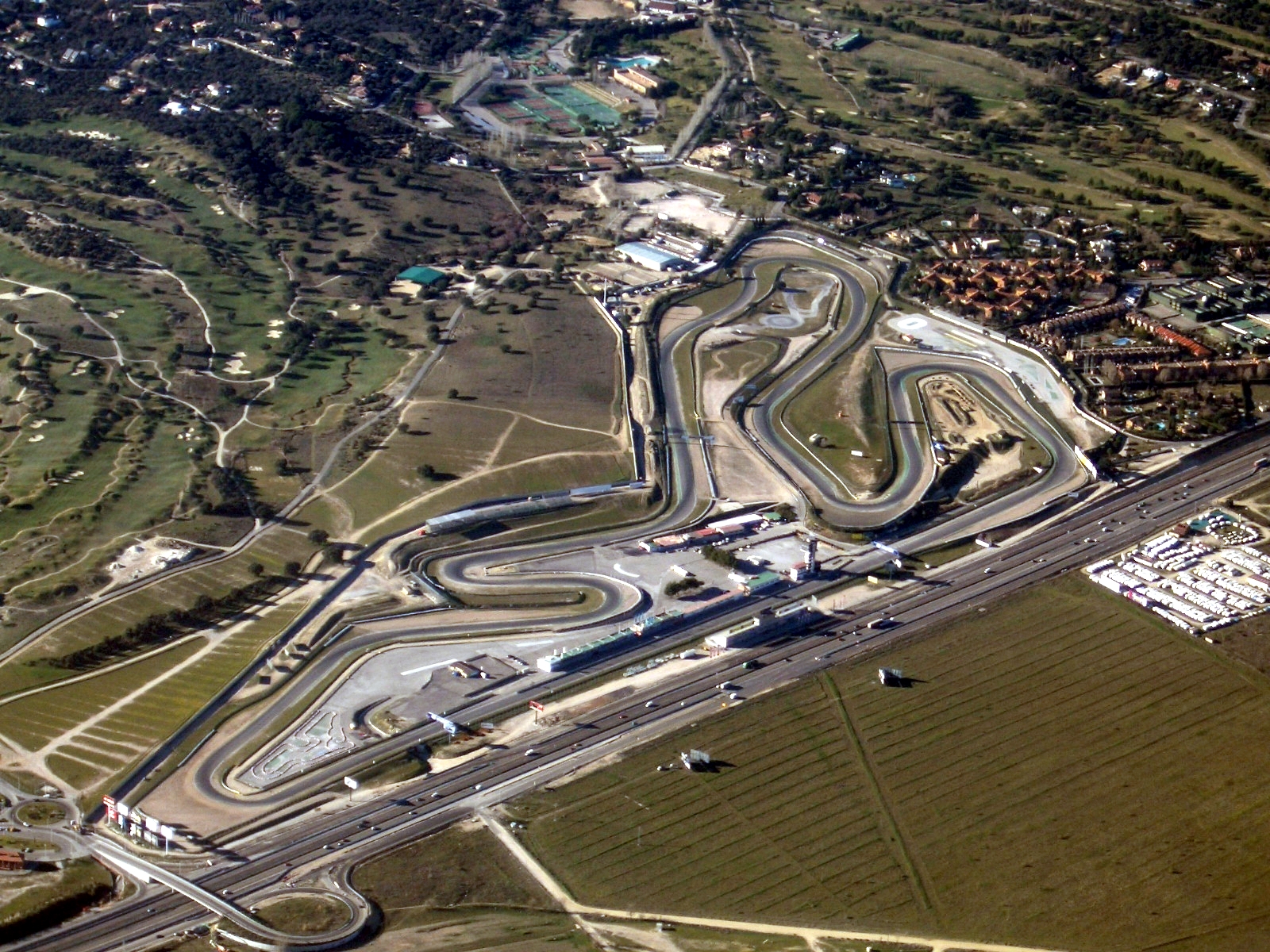
 Motorsport
Motorsport
 Companies
Companies
 Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Architecture
Architecture
 History
History
 Religion
Religion