
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV


 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA
 Canada
Canada

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 New Brunswick-NB
New Brunswick-NB

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 Newfoundland and Labrador-NL
Newfoundland and Labrador-NL

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 Nova Scotia-NS
Nova Scotia-NS

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC
 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV
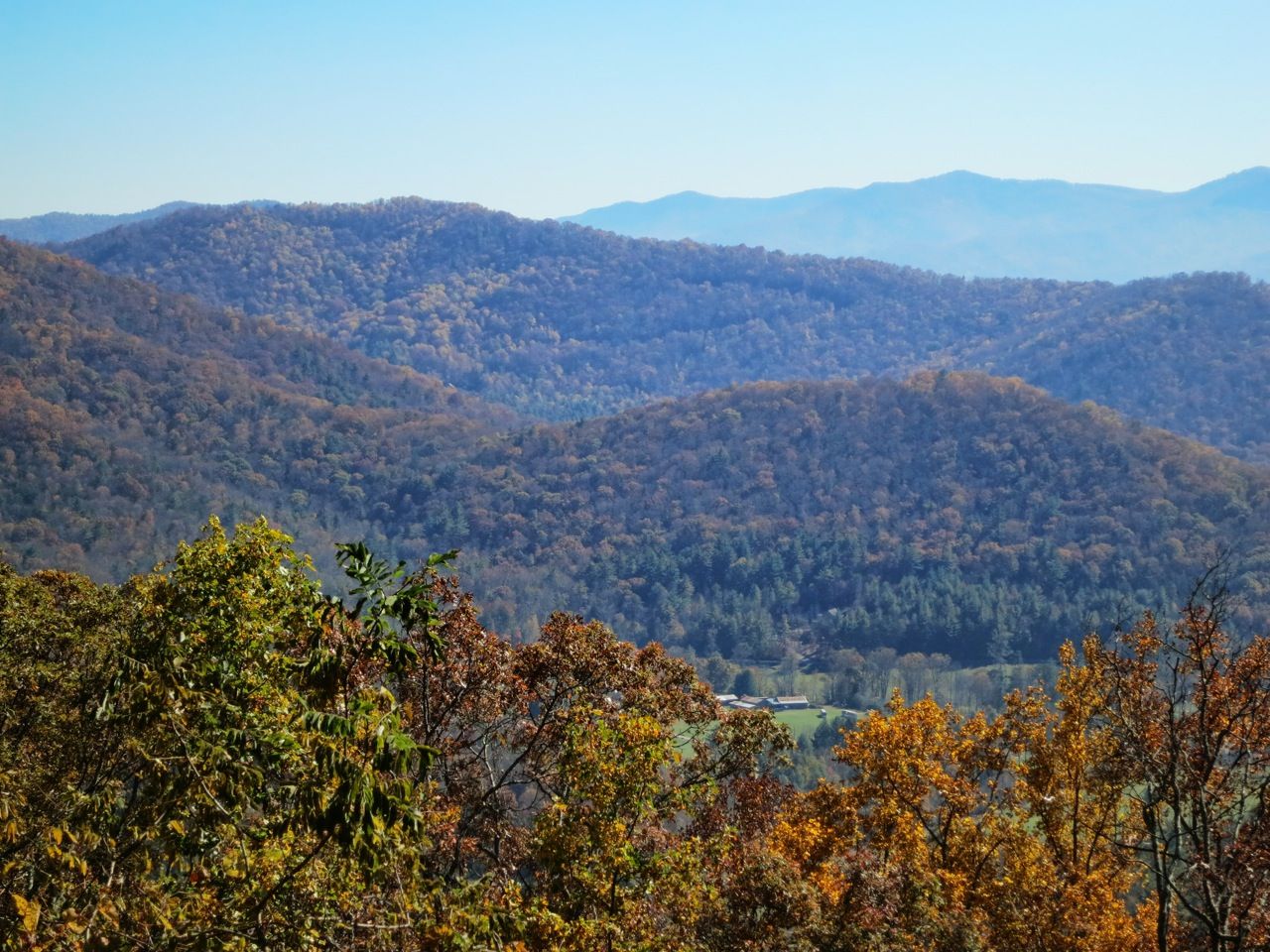

阿巴拉契亚山脉(Appalachian Mountains),又譯阿帕拉契山脉,是北美洲东部的一座山系。南起美国的阿拉巴马州,北至加拿大的纽芬兰和拉布拉多省。最北部余脉则延伸到魁北克的加斯佩地区。最高峰在北卡罗莱纳州的米切尔峰(2037米)。
阿巴拉契亚山脉(英语:Appalachian Mountains),又译阿帕拉契山脉,是北美洲东部的一座山系。南起美国的阿拉巴马州,北至加拿大的纽芬兰和拉布拉多省。最北部余脉则延伸到魁北克的加斯佩地区。最高峰在北卡罗莱纳州的米切尔峰(2037米)。
构成阿巴拉契亚山脉的有纽芬兰省的长岭山、魁北克的圣母山、缅因州的朗费罗山、新罕布夏州的怀特山、佛蒙特州的格林山脉、塔库尼克山;马萨诸塞州的勃克夏山;跨宾夕法尼亚州、马里兰州和西佛吉尼亚州三州的阿勒格尼山脉;跨宾夕法尼亚州、马里兰州、西佛吉尼亚州以及佛吉尼亚州四州的阿巴拉契亚岭谷。还有从宾夕法尼亚州南部到佐治亚州北部的蓝岭山脉。
实际上阿巴拉契高地 严格的边界范围存有争议,阿第伦达克山脉一般被认为是属于加拿大地盾,而非阿巴拉契亚高地。
Die Appalachen (englisch Appalachian Mountains) sind ein bewaldetes Gebirgssystem im Osten Nordamerikas, das sich über eine Länge von 2400 Kilometer von den Long Range Mountains an der Westküste der kanadischen Insel Neufundland bis in den Norden des US-Bundesstaates Alabama erstreckt. Obwohl ihr höchster Gipfel mehr als 2000 Meter hoch ist, haben die Appalachen sowohl hinsichtlich ihrer Höhe als auch ihrer Morphologie einen Mittelgebirgscharakter. Nur wenige Berge erheben sich über mehr als 1200 m Höhe, und viele Bergkuppen bleiben deutlich unter 800 m.
Benannt sind die Appalachen nach dem indigenen Stamm der Apalachee. Für die Appalachenregion als Kultur- und Wirtschaftsraum wird auch die Bezeichnung Appalachia verwendet.[1]
アパラチア山脈(Appalachian Mountains)は、カナダ及びアメリカ合衆国東北部に位置し、北東から南西方向に全長約2,600kmにわたって延びる丘陵・山脈。狭義では、そのうちのウエストバージニア州、バージニア州、ケンタッキー州、テネシー州、ノースカロライナ州等の南側の部分のみを指すこともある。
複雑に褶曲した山脈で、侵食が進んだ丘陵性の古い山脈である。北端はカナダニューファンドランド島で、そこから北アメリカ大陸東部を南西方向に縦断し、南端はアラバマ州の中央に至る。また、その裾野はミシシッピ州北西部にまで及んでいる。個々の山の標高は平均して1,000m前後で、最高峰はノースカロライナ州にあるミッチェル山(標高2,037m)。
山脈の西部では石油・石炭が盛んに採掘されているなど地下資源が豊富。山脈の東側には都市が発達している。国立公園が多く、グレート・スモーキー山脈国立公園やシェナンドー国立公園が有名である。
The Appalachian Mountains,[a] often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion.[4][5] The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west.
Definitions vary on the precise boundaries of the Appalachians. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defines the Appalachian Highlands physiographic division as consisting of thirteen provinces: the Atlantic Coast Uplands, Eastern Newfoundland Atlantic, Maritime Acadian Highlands, Maritime Plain, Notre Dame and Mégantic Mountains, Western Newfoundland Mountains, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, Saint Lawrence Valley, Appalachian Plateaus, New England province, and the Adirondack areas.[6][7] A common variant definition does not include the Adirondack Mountains, which geologically belong to the Grenville Orogeny and have a different geological history from the rest of the Appalachians.[8][9][10]
Les Appalaches sont une chaîne de montagnes située dans l'Est de l'Amérique du Nord et s'étendant de Terre-Neuve (Canada), au nord, jusqu'au centre de l'État de l'Alabama, au sud (États-Unis). Elle culmine au mont Mitchell (2 037 mètres) en Caroline du Nord.
Les Appalaches séparent la plaine côtière atlantique (à l'est) du bassin du fleuve Mississippi et des Grands Lacs (à l'ouest). Elles s'étirent sur près de 2 000 km de longueur.
L'exploitation du charbon, qui fournit la moitié de l'électricité américaine, y a fortement périclité, et l'industrie métallurgique est en grande difficulté.
Les Appalaches ont donné leur nom à un type de relief, le relief appalachien, qui désigne les vestiges d'une ancienne montagne fortement arasée. De longs couloirs s'étendent parallèlement à des échines rectilignes. Les cluses appalachiennes forment des passages étroits à travers les chaînons de la montagne.
Le Sentier des Appalaches (AT) parcourt les sommets de la chaîne depuis le Maine jusqu'à la Géorgie et le Sentier international des Appalaches (SIA - IAT) passe par les sommets du nord du Maine jusqu'au cap Gaspé, en Gaspésie. Leur point d'intersection est le sommet du mont Katahdin.
Gli Appalachi (AFI: /appaˈlaki/) o Appalaci (/appaˈlaʧi/[1]; in inglese Appalachian Mountains, in francese Appalaches) sono una catena montuosa situata nella parte orientale dell'America del Nord.
Si sviluppa, quasi parallelamente alla costa orientale atlantica, dal golfo del fiume San Lorenzo fino all'Alabama, per almeno 2500 km con picchi non molto elevati (i più alti sono con 2037 m il monte Mitchell e con 1917 m il monte Washington). Gli Appalachi riguardano anche l'isola di Terranova (Canada) e l'isola francese di Miquelon parte della collettività territoriale di Saint-Pierre e Miquelon[2][3]. La porzione sud degli Appalachi viene chiamata monti Unakas.
Per via dell'età geologica, gli Appalachi sono la catena montuosa più vecchia delle Americhe. Gli Appalachi statunitensi sono una delle zone economicamente più depresse degli Stati Uniti.
Apalaches o montes Apalaches (en inglés: Appalachian Mountains o Appalachians; en francés: Appalaches1) es una importante cordillera ubicada en el este de Norteamérica. Se extiende desde la Isla de Terranova en Canadá, pasado por la colectividad de ultramar francés de San Pedro y Miquelón, hasta Alabama en los Estados Unidos, aunque su parte más septentrional termina en la península de Gaspé, en Quebec. Constituye el elemento morfológico más sobresaliente de la parte oriental de América del Norte.
Se originó en antiguas montañas formadas en el periodo Paleozoico con relieves suavizados por la prolongada acción de los agentes exógenos. El sistema está dividido en una serie de cordilleras, en las que la medida de altura de los picos es de unos 1000 m s. n. m. (metros sobre el nivel del mar). La cima más elevada es el monte Mitchell, en Carolina del Norte, mide 2037 m s. n. m. y es el punto más alto de los Estados Unidos al este del río Misisipi y de todo el este de Norteamérica.
Аппала́чи[2] (англ. Appalachian Mountains) — горная система на востоке Северной Америки, в США и Канаде. Длина — 2600 км.
Северные Аппалачи (к северу от рек Мохок и Гудзон) — холмистое плоскогорье с отдельными массивами высотой до 1916 м (гора Вашингтон), имеют следы древнего оледенения. Южные Аппалачи в осевой зоне состоят из параллельных хребтов и массивов, разделённых широкими долинами; к осевой зоне прилегают с востока плато Пидмонт, с запада — Аппалачское плато. Высота — до 2037 м (гора Митчелл). В горах имеются месторождения каменного угля, нефти и газа, железных руд, титана; широколиственные, хвойные и смешанные леса.
Горы образовались в пермский период в результате столкновения двух материков (возникновение Пангеи).

 *Democratic Party
*Democratic Party
 *United States Political System
*United States Political System
 *United States presidential election
*United States presidential election
 *U.S. foreign territories
*U.S. foreign territories
 Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Delaware-DE
Delaware-DE

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Political parties with more than a hundred years of history
*Political parties with more than a hundred years of history

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA
 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

民主党(英语:Democratic Party)是美国的主要政党,与共和党并列为美国两大主要政党。当前是美国最大在野党,并拥有美国国会众议院多数党地位,而该党的州长多在东海岸的新英格兰和西海岸主政。
1828年第七任美国总统安德鲁·杰克逊创建民主党,1848年成立民主党全国委员会,本杰明·富兰克林·哈利特为首任主席,但它的起源最早可以追溯至托马斯·杰斐逊于1792年创立的民主共和党[11]。
民主党在建立之初主要代表美国南部和西部农场主的利益。因此民主党在19世纪中期通过法案强制驱逐印第安人,发动美墨战争,获得大量土地以供农耕。在美国内战中则支持奴隶制以维护成型的农业体制。民主党长期支持奴隶制,获得南方各州的支持。20世纪初,民主党加入民粹主义的农本主义,支持维护白人的工人权利,创建了联邦储备系统,并通过了反垄断法,限制大企业的垄断。自从1930年代以来,富兰克林·德拉诺·罗斯福总统推行新政并称之为美国的自由主义,成为了之后民主党的主要政策走向。新政一直到1960年代的民权运动。1960年代的民权运动以及越战导致在民主党内部引发了对国外军事干预的立场及国内政策严重分歧,这种分歧导致之后民主党失去执政地位,但民主党维持对国会两院的控制权直至至1995年。而民主党的根基也逐渐从倾向白人、蓝领、工人阶级和农民利益,转变为以东西岸的都会居民、富裕阶层、女性和少数族裔为主。
Die Demokratische Partei (englisch Democratic Party, auch als Demokraten (Democrats) bezeichnet) ist neben der Republikanischen Partei eine der beiden großen Parteien in den USA. Ursprünglich eine Partei, die für Rassentrennung eintrat, gelten die Demokraten heute im Vergleich zu den Republikanern als liberaler, weniger konservativ und mehr am Progressivismus orientiert. Ihr inoffizielles Wappentier ist der Esel, obwohl er im Gegensatz zum Elefanten der Republikaner nie offiziell als solches angenommen wurde. Sein Ursprung geht, ebenso wie der Elefant der Republikaner, auf den Karikaturisten Thomas Nast zurück. Die ebenfalls inoffizielle Parteifarbe der Demokraten ist blau. In TV-Sendungen oder Medienberichten werden Senatoren und Parteimitglieder der Demokratischen Partei meistens mit einem „(D)“ hinter ihrem Namen dargestellt. Die Demokraten sind die älteste noch bestehende politische Partei der Welt.
Die Gründung der Partei geht auf Thomas Jefferson und das Jahr 1792 zurück. 1828 bauten Andrew Jackson und andere eine Massenpartei auf. Bis ins frühe 20. Jahrhundert galten die Demokraten als die konservativere der beiden großen Parteien. Das änderte sich ansatzweise während der Präsidentschaft Woodrow Wilsons (1913–1921), dann durch die Reformen des New Deal (1933–1938) und besonders nach dem Parteitag von 1948, als viele zumeist aus den Südstaaten stammende Vertreter einer Rassentrennung die Partei im Streit verließen. Die Demokraten wandten sich immer mehr liberalen und sozialliberalen Werten zu. Da die ursprünglich progressiven Republikaner spätestens seit 1964 ihrerseits nach rechts rückten, haben die beiden Parteien ihre Position im politischen Spektrum gewissermaßen getauscht.
Wie Parteien in den USA allgemein, sind die Demokraten wesentlich anders organisiert als europäische Parteien. So werden Bezirksvorstände, je nach Bundesstaat, zum Teil durch die allgemeine Wahlbevölkerung in Vorwahlen und nicht etwa durch Parteimitglieder allein gewählt. Wichtigstes Organ für die Gesamtpartei ist das Democratic National Committee (DNC, „Demokratisches Nationalkomitee“), das auch die Democratic National Convention (den vierjährlich zur Kür des jeweiligen Präsidentschaftskandidaten stattfindenden Parteitag) veranstaltet; derzeitiger Vorsitzender des DNC ist Tom Perez.
In sechs der letzten sieben Präsidentschaftswahlen gewannen die demokratischen Kandidaten die Mehrheit der abgegebenen Stimmen (Popular Vote); nur 2004 bildete eine Ausnahme. Mit Barack Obama stellte die Partei zuletzt von 2009 bis 2017 den 44. US-Präsidenten. Bei den Kongresswahlen im November 2010 verloren die Demokraten ihre Mehrheit im Repräsentantenhaus und konnten diese auch bei den Wahlen 2012, 2014 und 2016 nicht wiedererlangen. Auch im Senat verfügen sie seit Anfang 2015 nicht mehr über eine Mehrheit. In den Wahlen 2018 konnten sie dann allerdings wieder eine deutliche Mehrheit im Repräsentantenhaus erringen.
民主党(みんしゅとう、Democratic Party)は、アメリカ合衆国の政党。共和党と共に二大政党制を構成している。
一般的に保守の立場を取る共和党に対し、リベラルの立場を取る政党である。進歩同盟加盟。
21世紀においては、2011年以降で連邦議会下院の多数派の地位を失っていたが、2018年の中間選挙(共和党:ドナルド・トランプ大統領)において多数議席を回復した。また、直近では、2007年から2015年まで連邦議会上院において多数議席を占め、2009年から2017年まで大統領(バラク・オバマ政権)を擁した。
労働運動やマイノリティの集票力が大きく、外交面では、国際主義的で国際連合(UN)へのスタンスも好意的である。
内政面では、人工妊娠中絶完全自由化、死刑制度廃止、不法移民容認、労働組合重視、伝統的結婚制度維持反対(同性結婚賛成)同性愛容認、LGBTの権利擁護容認、宗教多様化容認などが特徴であり、リベラル思想の政党である。
The Democratic Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with its main rival, the Republican Party. Tracing its heritage back to Thomas Jefferson and James Madison's Democratic-Republican Party, the modern-day Democratic Party was founded around 1828 by supporters of Andrew Jackson, making it the world's oldest active political party.[18]
In its early years, the Party supported limited government, state sovereignty and opposed banks and the abolition of slavery. Since Franklin D. Roosevelt and his New Deal coalition in the 1930s, the Democratic Party has promoted a social liberal platform.[3][19] Well into the 20th century, the party had conservative pro-business and Southern conservative-populist wings; following the New Deal, however, the conservative wing of the party largely withered outside the South. The New Deal Coalition of 1932–1964 attracted strong support from voters of recent European extraction—many of whom were Catholics based in the cities.[20][21][22] After the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, the core bases of the two parties shifted, with the Southern states becoming more reliably Republican in presidential politics and the Northeastern states becoming more reliably Democratic. The once-powerful labor union element became smaller and less supportive after the 1970s. White evangelicals and Southerners have become heavily Republican at the state and local levels since the 1990s. People living in urban areas, women, college graduates, sexual and gender minorities, millennials, and black, Latino, Jewish, and Asian Americans tend to support the Democratic Party.[23][24][25]
The Democratic Party's philosophy of modern liberalism advocates social and economic equality, along with the welfare state.[26] It seeks to provide government regulation in the economy.[27] Policies such as environmental protection, support for organized labor and labor unions, the introduction of social programs, affordable college tuition, universal health care, equal opportunity, and consumer protection form the core of the party's economic policy.[26][28] On social issues, it advocates campaign finance reform,[29] LGBT rights,[30] police and immigration reform,[31] stricter gun laws,[32] and the legalization of marijuana.[33]
There have been 15 Democrats who have served as president of the United States. The first was Andrew Jackson, who was the seventh president and served from 1829 to 1837. The most recent was Barack Obama, who was the 44th and held office from 2009 to 2017. As of 2019, the Democrats hold a majority in the House of Representatives, 15 state government trifectas (governorship and both legislative chambers),[34] the mayoralty of most major American cities,[35] and 19 total state legislatures. Four of the nine sitting justices of the Supreme Court were appointed by Democratic presidents.
Le Parti démocrate est un parti politique américain qui s'oppose, dans le contexte du système bipartite, au Parti républicain. Il est l'une des plus grandes organisations politiques mondiales avec plus de 44 millions d'adhérents en 2017.
Le Parti démocrate conçoit la société américaine comme une union des communautés de citoyens. Il veut assurer la protection égale de leurs droits particuliers, notamment pour les moins puissants. Il est donc traditionnellement la « grande tente » dans laquelle les minorités se retrouvent23, qu'elles soient ethniques (Afro-Américains depuis le New Deal, Hispaniques et Latino-Américains, Asio-Américains), religieuses (catholiques, musulmans et juifs) ou sociologiques (intellectuels, artistes). Son principal adversaire, le Parti républicain, est considéré a contrario comme un parti White Anglo-Saxon Protestant visant à imposer la force de l'Union par le respect des valeurs centrales qui permettent la réussite des meilleurs, proche des milieux d'affaires et financiers, soutenu par les professions libérales et les entrepreneurs.
Le Parti démocrate est issu de la scission du Parti républicain-démocrate fondé par Thomas Jefferson en 179224. Doyen des partis américains et mondiaux, il est à l'origine un parti anti-fédéraliste défendant la liberté des États face au pouvoir fédéral, et celle des propriétaires individuels face aux intérêts bancaires et industriels. À l'époque de la Guerre de Sécession, il défend également l'esclavage face au parti républicain de Lincoln, abolitionniste. Il évolue nationalement vers une vision moins conservatrice25 et moins méfiante du pouvoir fédéral dès les années 1890, et plus nettement dans les années 1930 avec le président Franklin Delano Roosevelt, en valorisant le rôle de l'État dans la protection des minorités. Dans les années 1960 et 1970, il s'inscrit à gauche sous l'impulsion des sénateurs Hubert Humphrey, George McGovern ou Edward Moore Kennedy, puis se place vers le centre sous les mandats de Jimmy Carter et Bill Clinton avant de se réorienter à gauche sous la présidence de Barack Obama avec l'influence de Bernie Sanders, Elizabeth Warren, Jesse Jackson, Keith Ellison et Nancy Pelosi.
À l'échelle internationale, le Parti démocrate est, depuis 2013, membre de l'Alliance progressiste qui regroupe l'ensemble des partis politiques progressistes, sociaux-démocrates et socialistes proche de l'Internationale socialiste. Il est dirigé par le Comité national démocrate.
Il Partito Democratico (in inglese: Democratic Party) è un partito politico liberale statunitense, nonché uno dei due principali partiti del sistema politico statunitense insieme al Partito Repubblicano. Nel contesto politico statunitense odierno è considerato come il partito di centro-sinistra e della sinistra liberale (pur con le sue fazioni interne più conservatrici di centro e centro-destra e più socialdemocratiche di sinistra) in contrapposizione al Partito Repubblicano, che è invece diventato il partito della destra conservatrice, un'unione del liberalismo con il conservatorismo sociale e il tradizionalismo. Nel Congresso in carica il Partito Democratico detiene la maggioranza alla Camera dei rappresentanti (riconquistata nel 2018 dopo averla persa nel 2010), avendo perso il controllo del Senato nel 2014 e della presidenza nel 2016.
Fondato col nome moderno nel 1828 dai sostenitori di Andrew Jackson, il Partito Democratico è il più antico del mondo tra quelli attivi, originando dal Partito Democratico-Repubblicano fondato da Thomas Jefferson, James Madison e altri influenti anti-Federalisti nel 1792. Dopo la spaccatura dei Democratici-Repubblicani nel 1828 si è posizionato alla destra dei centristi Whig, partito predecessore del Partito Repubblicano di sinistra per quanto riguarda la questione della schiavitù che dominò quegli anni, soprattutto a partire dagli anni 1840 fino agli anni 1860, con i vari compromessi dei Whig che alla fine si sono rivelati inefficaci e che portarono alla fondazione del Partito Repubblicano nel 1854 da ex esponenti dei Whig e del Suolo Libero nonché militanti di preesistenti movimenti antischiavisti per opporre l'allora governo Democratico e contrastare la temuta espansione a ovest del sistema schiavistico degli Stati meridionali dominato dai Democratici.
L'elezione del Repubblicano Abraham Lincoln nel 1860 portò a una cruenta guerra civile tra i Democratici secessionisti schiavisti sudisti che formarono gli Stati Confederati d'America e i Repubblicani a favore dell'Unione. Ciò causò diversi dissidi interni al partito, con fazioni in favore dell'Unione e fazioni schiaviste intransigenti (già alle elezioni presidenziali del 1860 vinte da Lincoln i Democratici proposero due candidati, uno del nord e uno del sud). Il Democratico Andrew Johnson in favore dell'Unione fu scelto come vicepresidente da Lincoln per le elezioni presidenziali del 1864, con i due che si presentarono insieme come il Partito dell'Unione Nazionale così da favorire il consenso dei Democratici che non avrebbero votato per un duo Repubblicano mentre i Democratici presentarono l'intransigente generale filo-sudista George McClellan, uscendo sconfitti e poi perdendo definitivamente la guerra di secessione. Il Proclama di emancipazione abolì la schiavitù, ma Lincoln fu assassinato nel 1865 e Johnson prese il suo posto. Ciò causò fastidi ai Repubblicani, soprattutto alla fazione più liberale e radicale in fatto di diritti civili per gli ex schiavi afroamericani, arrivando alla fallita messa in stato di accusa del 1868 per un solo voto. Durante l'era della ricostruzione i Democratici cercarono di bloccare l'emancipazione civile e politica degli afroamericani, soprattutto nel Sud, riuscendoci nel 1877 come parte di un accordo bilaterale per eleggere il Repubblicano Rutherford B. Hayes alla carica di presidente a seguito delle controverse e dibattute elezioni presidenziali del 1876, con le truppe militari che non poterono più sostenere i governi statali Repubblicani nel Sud.
Nonostante la questione schiavista, il Partito Democratico proponeva certe politiche egalitarie, era a favore della democrazia e si proclamava partito della gente comune. Si spostò più a sinistra nelle questioni economiche dopo la vittoria dell'ala populista di William Jennings Bryan nel 1896 e con il New Deal («nuovo corso»), sebbene fino agli anni sessanta del Novecento molti Democratici conservatori e populisti degli Stati meridionali erano ancora favorevoli alla segregazione razziale. Di fatto il supporto dei sudisti che erano a favore di politiche economiche di sinistra fu importante nell'attuare la legislazione del New Deal di Franklin Delano Roosevelt. Pur favorendo le politiche sociali del Repubblicano Barry Goldwater, essi rigettarono le sue proposte economiche liberiste e di privatizzazione dello Stato sociale. La filosofia attivista a favore della classe lavoratrice di Roosevelt chiamata liberalismo (un'unione del liberalismo sociale e del progressismo) ha infatti rappresentato gran parte del programma del partito sin dal 1932. A partire dal 1948, con la desegregazione delle Forze armate statunitensi attuata dal presidente Harry Truman, i Democratici si sono spostati a sinistra anche sulle questione sociali. Dagli anni 1970 l'ambientalismo è diventato un importante corrente nel partito.
Sulle questioni di politica estera entrambi i partiti Democratici e Repubblicani hanno cambiato diverse volte le rispettive politiche. Inizialmente promotori del destino manifesto e dell'espansione a ovest, i Democratici sono diventati anti-imperialisti e isolazionisti sotto la presidenza di Grover Cleveland (liberista) e poi interventisti e internazionalisti a partire dalla presidenza di Thomas Woodrow Wilson (liberal-progressista). Durante la guerra fredda furono promotori dell'anticomunismo, ma avversari dell'ultraconservatore Repubblicano Joseph McCarthy. Molti attivisti Democratici si opposero alla guerra del Vietnam, alienati dal crescente militarismo e promotori della controcultura e della nuova sinistra. Da allora il partito è diventato più pragmatico e aperto al multilateralismo, sebbene la fazione neoconservatrice in politica estera mantenne la presidenza, approvando l'interventismo in Jugoslavia negli anni 1990 e quello in Medio Oriente negli anni 2010, ma rigettando la guerra in Iraq a inizi anni 2000. La fazione opposta in politica estera è rappresentata tra gli altri da Bernie Sanders, Tulsi Gabbard e per certi versi anche da Elizabeth Warren, oltre che dalla cosiddetta Squad.
La coalizione del New Deal di Roosevelt controllò spesso il governo nazionale fino al 1964 e il movimento per i diritti civili degli anni 1950 e 1960 lo confermò nel centro-sinistra mentre i Repubblicani si spostarono sempre più a destra, facendogli tuttavia perdere parte dei consensi negli Stati meridionali e perdendo le successive due elezioni presidenziali, anche se a livello locale e statale ciò non si realizzò almeno sino angli anni 1980 e 1990 in quanto i sudisti preferivano le politiche economiche Democratiche, ma ciò venne meno quando entrambi i partiti appoggiarono il neoliberismo. A partire dagli anni 1990 i Democratici hanno infatti approvato il programma di Bill Clinton della più centrista terza via, cui anche il presidente Barack Obama ha aderito come Nuovo Democratico, per provare a vincere le elezioni dopo dodici anni, cosa che ha avuto successo con Clinton (1993–2001) e Obama (2009–2017), ma che fallì con Al Gore (2000) e Hillary Clinton (2016).
El Partido Demócrata (en inglés: Democratic Party) es un partido político progresista, que junto con el Partido Republicano, es uno de los dos partidos más grandes de los Estados Unidos. Traza sus orígenes al Partido Demócrata-Republicano de Thomas Jefferson y James Madison. Fue fundado alrededor de 1828 por seguidores de Andrew Jackson, convirtiéndolo en el partido político activo más antiguo del mundo.11
La filosofía del partido fue en sus inicios, el conservadurismo, siendo el populismo su característica principal en las zonas rurales del sur de los Estados Unidos.12.13 Hasta bien entrado el siglo XX, el partido tenía alas conservadoras pro-negocios y alas sureñas conservador-populistas anti-negocios. Gracias al New Deal, sin embargo, el ala conservadora del partido se extinguió fuera del Sur. La Coalición New Deal de 1932 a 1964 atrajo fuerte apoyo de votantes con orígenes europeos recientes, muchos de los cuales eran católicos que habitaban grandes ciudades.141516 Después de la conmoción racial de la década de 1960, la mayor parte de los sureños blancos y católicos del norte mudaron sus ideologías al Partido Republicano. El otrora poderoso sindicato se volvió más pequeño y menos comprensivo después de los años setenta. Evangélicos caucásicos y sureños por igual, se volvieron arduos republicanos a nivel local y estatal desde los años noventa. La gente que habita áreas metropolitanas, mujeres, minorías sexuales, milenials, graduados universitarios y minorías raciales y étnicas1718 tienden a apoyar al Partido Demócrata mucho más de lo que apoyan al Partido Republicano rival.
La filosofía del Partido Demócrata del liberalismo moderno aboga por la igualdad social junto con el estado del bienestar.19 20
Políticas como la introducción de programas sociales, el apoyo a los sindicatos, matrícula universitaria asequible, atención médica universal, igualdad de oportunidades, protección del consumidor y del medio ambiente constituyen el núcleo de la política económica del partido.1921 En cuestiones sociales, el partido apoya los derechos reproductivos, los derechos LGBT, la reforma migratoria, la reforma de financiación de campañas, el control de armas y la legalización de la marihuana.
Quince demócratas han servido como presidente de los Estados Unidos. El primero fue el presidente Andrew Jackson, que fue el séptimo presidente y se desempeñó desde 1829 hasta 1837. El más reciente fue el presidente Barack Obama, quien fue el 44º presidente y ocupó el cargo desde 2009 hasta 2017. Después de las elecciones intermedias de 2018, los demócratas obtuvieron la mayoría en la Cámara de Representantes, "trifectas" (poder ejecutivo y ambas cámaras del poder legislativo) en 14 estados,22 y la alcaldía de numerosas grandes ciudades estadounidense.23 Veintitrés gobernadores estatales son demócratas, y el partido forma minoría en el Senado y en la mayoría de las legislaturas estatales (control total de 18/50, control dividido de los demás). En abril de 2019, cuatro de los nueve jueces de la Corte Suprema habían sido nombrados por presidentes demócratas.
Демократическая партия (англ. Democratic Party) — наряду с Республиканской, одна из двух крупнейших современных политических партий США. Является самой старой партией в США. Её неофициальный символ — ослик (символ упрямого преодоления препятствий и выносливости), неофициальный цвет — голубой.
Начиная с 1930-х годов партия занимает социально-либеральные и прогрессивные позиции,[2][3][4] объединяя в своих рядах прогрессистов, либералов и центристов.[5] В результате смещения Демократической партии в сторону либерализма и прогрессивизма, произошедшего в 1930-х—1960-х годах, изменилась и география поддержки демократов. Если во второй половине XIX — первой половине XX века партия наибольшим влиянием пользовалась на юго-востоке США, в настоящее время она наиболее сильна на северо-востоке (Средне-Атлантические штаты и Новая Англия), в районе Великих озёр и на Тихоокеанском побережье (включая Гавайи), а также в крупных городах независимо от региона.
44-й Президент США Барак Обама являлся пятнадцатым демократом, занимавшим эту должность. По итогам выборов 2016 года Демократическая партия уступила республиканцам как по количеству мест в сенате и Палате представителей, так и по количеству губернаторов штатов и контролируемых законодательным собраниям штатов.


 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL
 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Universities and colleges in the United States of America
Universities and colleges in the United States of America

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Delaware-DE
Delaware-DE

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI

 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Universities in the USA
Universities in the USA

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

 Wisconsin-WI
Wisconsin-WI

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY
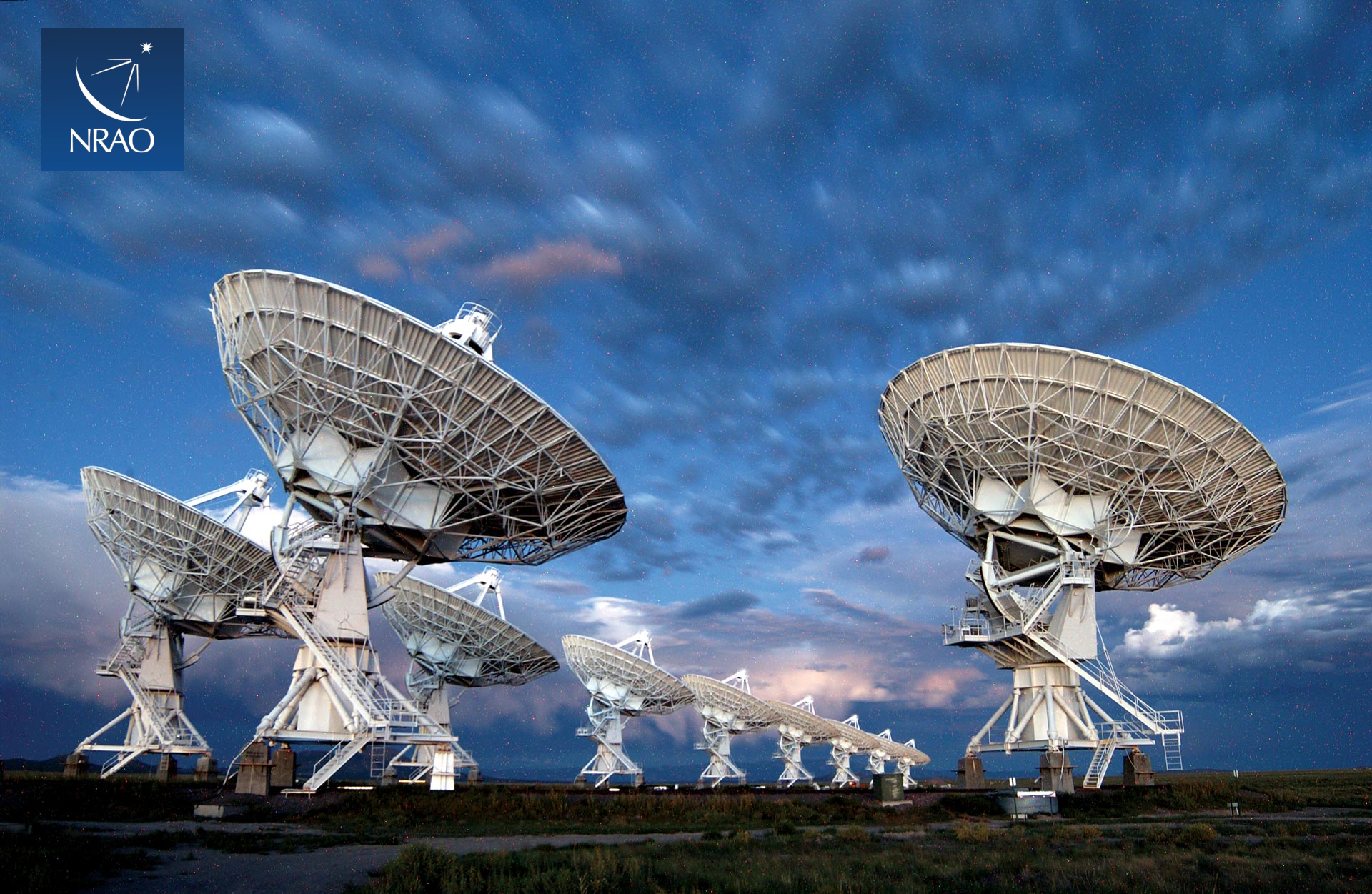
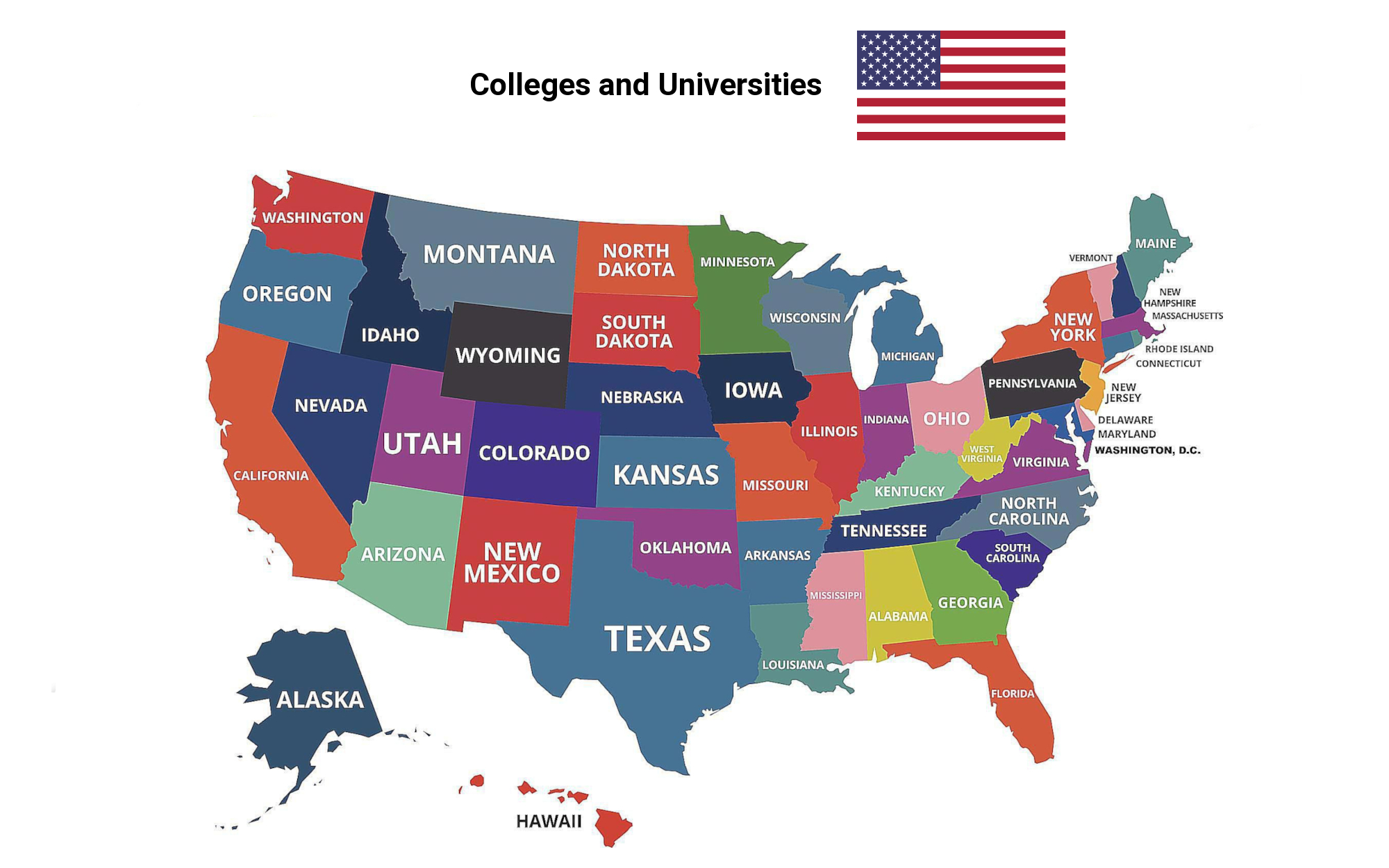


 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL

 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 California-CA
California-CA

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Companies
Companies

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV
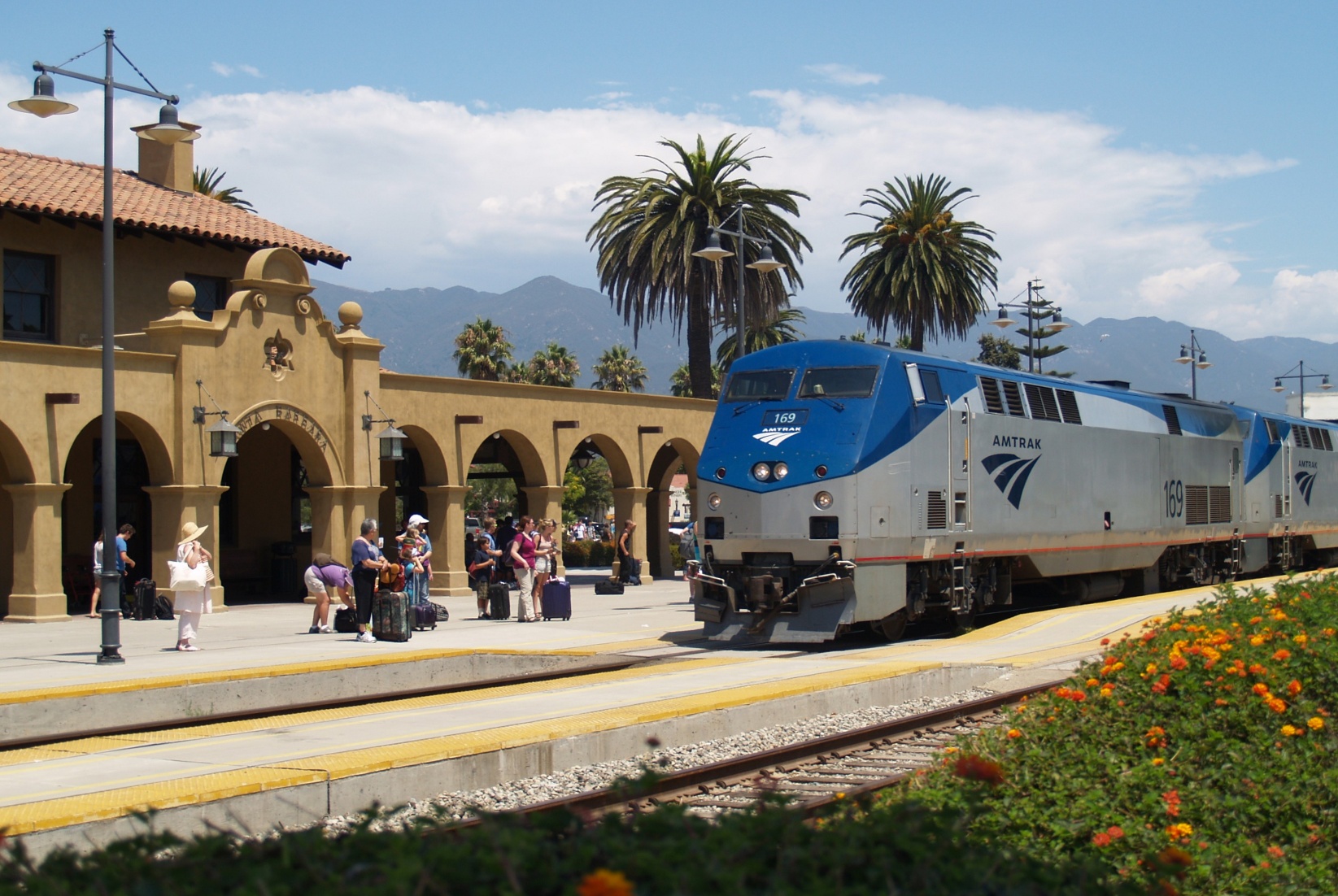
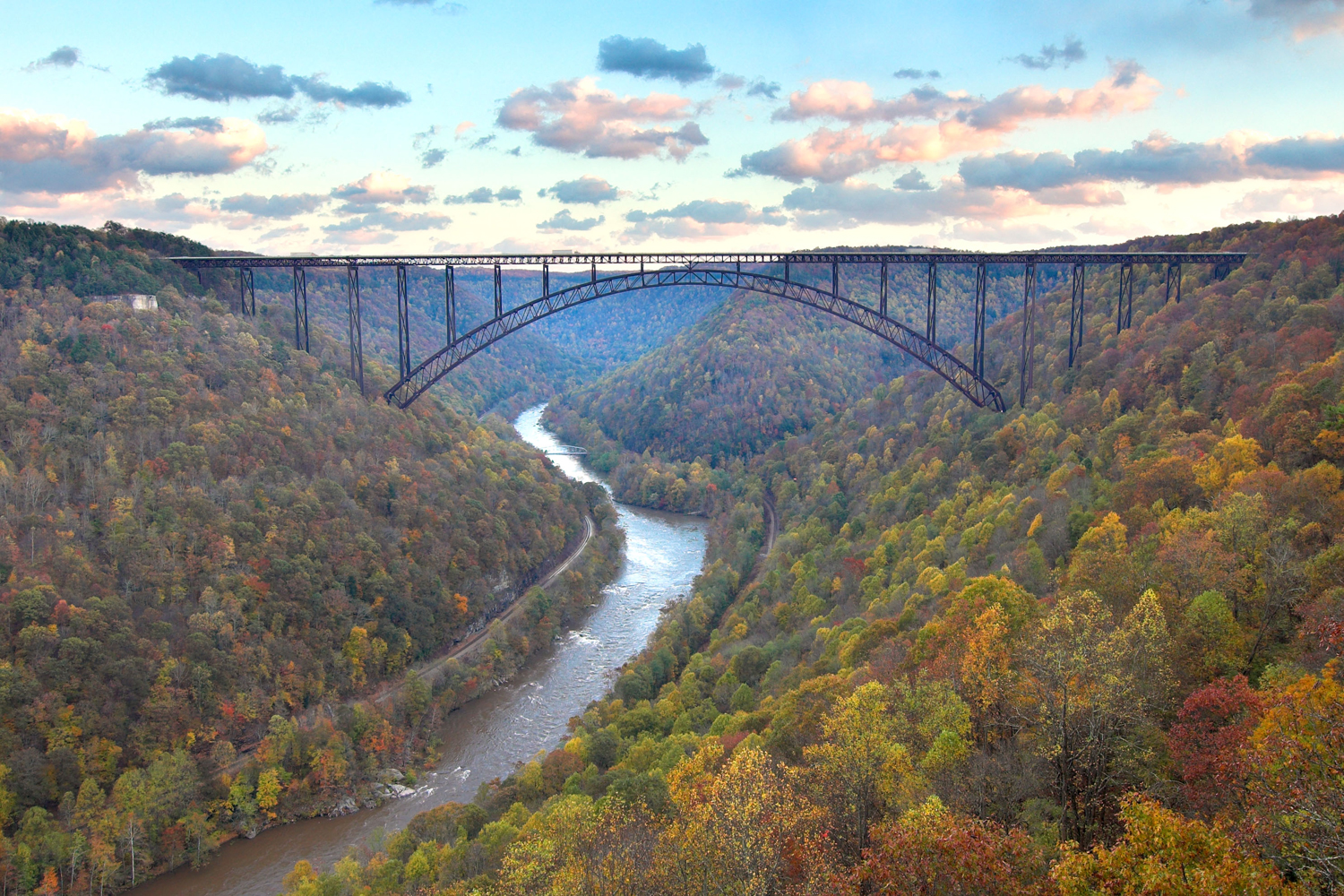



 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY
 Mississippi River
Mississippi River

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA
 United States
United States

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

俄亥俄河(英语:Ohio River)是美国东部的一条河流,是密西西比河最东的支流。发源于匹兹堡,初向西北流,在宾夕法尼亚州、西维吉尼亚州和俄亥俄州的边界以下转向西南方,并流经肯塔基州北界(同时是印地安那州和伊利诺伊州南界),在肯塔基州与田纳西河汇合,最后在开罗与密西西比河汇合。全长1,579公里,流域面积490,603平方公里。
Der Ohio (Irokesisch: Ohi:yo' bzw. Uhíyu' – „guter Fluss“, englisch Ohio River) ist der größte linke Nebenfluss des Mississippi. Er entsteht durch die Vereinigung der beiden Flüsse Allegheny (Hauptquellfluss) und Monongahela in Pittsburgh. Nahe der Stadt Cairo mündet der Ohio in den bis dahin sogenannten Oberen Mississippi (Upper Mississippi). Der Ohio ist auf seiner gesamten Länge von 1579 km schiffbar.
Der Ohio entwässert den größten Teil des Ostens der Vereinigten Staaten. Das Einzugsgebiet umfasst 14 Bundesstaaten, darunter die meisten südlichen Staaten an der Ostküste. An seiner Mündung führt der Ohio rund ein Drittel mehr Wasser als der Mississippi und ist damit hydrologisch der Hauptfluss des Mississippi-Flusssystems.
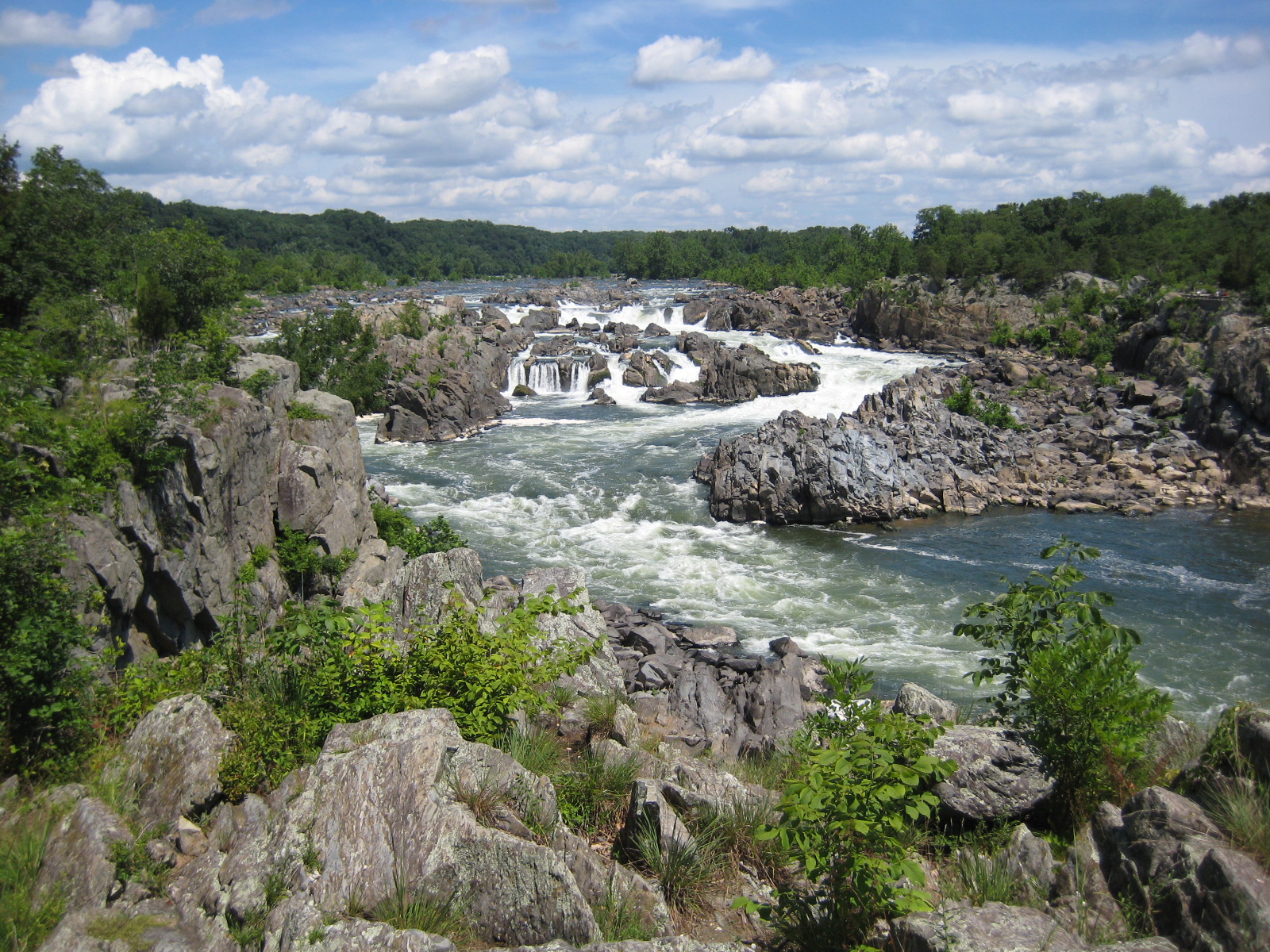
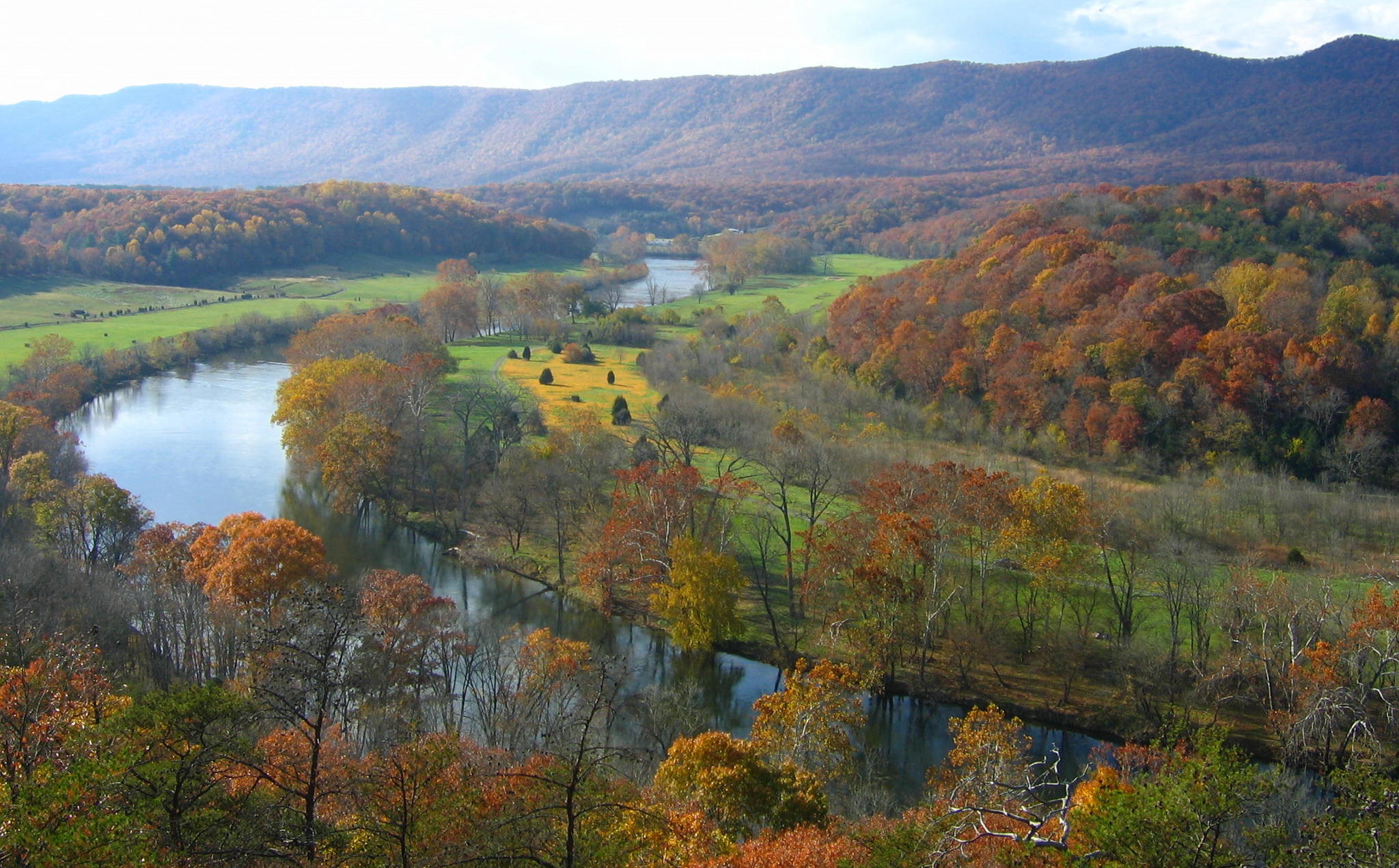
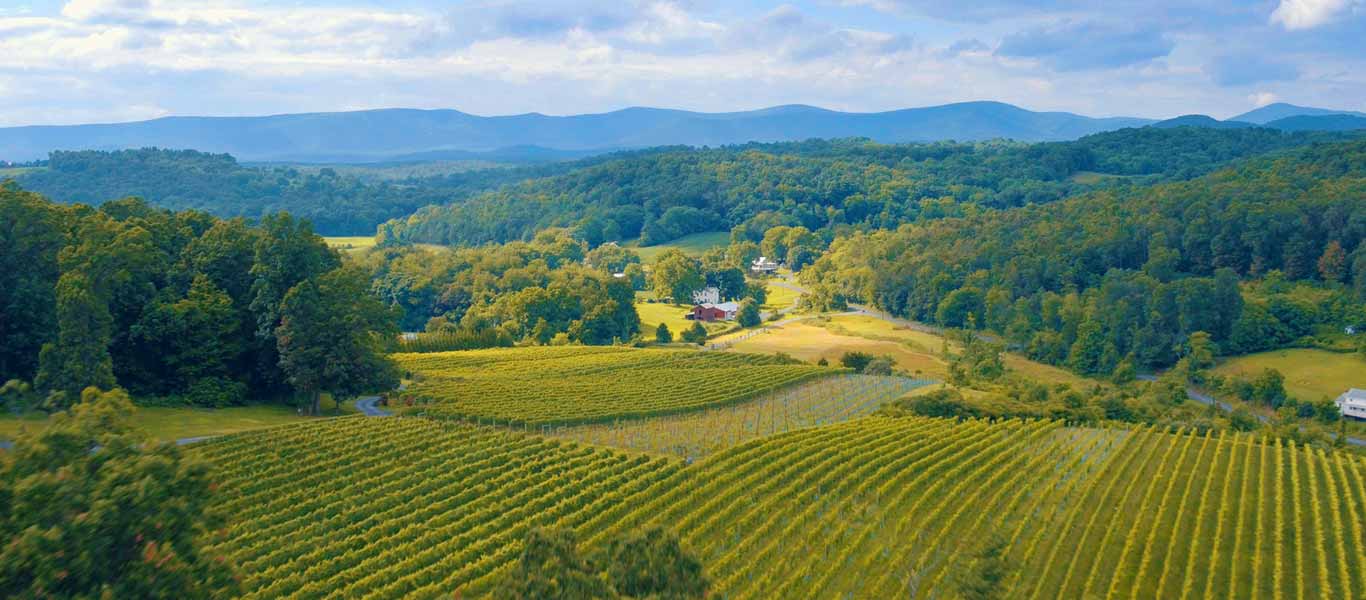



 Geography
Geography
 International cities
International cities
 Astronomy
Astronomy

 Aerospace
Aerospace
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Architecture
Architecture
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink