
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Switzerland
Switzerland

国际雪车联合会(Fédération Internationale de Bobsleigh et de Tobogganing,简称FIBT,2015年6月后改名为International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Federation,简称IBSF)又称国际有舵雪橇和俯式冰橇联合会,为国际间的雪车和钢架雪车运动管理组织,于1923年在法国巴黎成立,总部位于瑞士洛桑[1]。截至2007年,有14个会员协会。
Der Internationale Bob & Skeleton Verband (englisch International Bobsleigh & Skeleton Federation, Abk. IBSF) ist der Weltverband aller Bobsportler und Skeletonfahrer und deren Landesverbände. Er hat seinen Sitz im Maison du Sport International in Lausanne.
 AFC Champions League 2015
AFC Champions League 2015
 AFC Champions League 2017
AFC Champions League 2017
 AFC Champions League 2017
AFC Champions League 2017
 AFC Champions League 2018
AFC Champions League 2018
 AFC Champions League 2019
AFC Champions League 2019
 Asian Football Confederation
Asian Football Confederation
 CONCACAF
CONCACAF
 Confederación Sudamericana de Fútbol
Confederación Sudamericana de Fútbol
 Confederation of African Football
Confederation of African Football
 FIFA
FIFA
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1998
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1998
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2002
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2002
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2006
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2006
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2010
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2010

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2014
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2014

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2018
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2018

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2022
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2022

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 FIFA-Konföderationen-Pokal 2013
FIFA-Konföderationen-Pokal 2013
 FIFA-Konföderationen-Pokal 2017
FIFA-Konföderationen-Pokal 2017
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1991
Women's Soccer World Cup 1991
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1995
Women's Soccer World Cup 1995
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1999
Women's Soccer World Cup 1999
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2003
Women's Soccer World Cup 2003
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2007
Women's Soccer World Cup 2007
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2011
Women's Soccer World Cup 2011
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2019
Women's Soccer World Cup 2019
 Oceania Football Confederation
Oceania Football Confederation
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Zurich
Zurich

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Football Women's World Cup
(F)Football Women's World Cup

 Sport
Sport
 (F)International soccer leagues
(F)International soccer leagues

 Sport
Sport
 (F)AFC Champions League
(F)AFC Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)CAF Champions League
(F)CAF Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)CONCACAF Champions League
(F)CONCACAF Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Copa Libertadores
(F)Copa Libertadores

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Champions League
(F)UEFA Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)European football championship
(F)European football championship

 Sport
Sport
 (F)FIFA U-20 World Cup
(F)FIFA U-20 World Cup

 Sport
Sport
 (F)FIFA Confederations Cup
(F)FIFA Confederations Cup

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Soccer Asia Cup
(F)Soccer Asia Cup

 Sport
Sport
 (F)African Cup of Nations
(F)African Cup of Nations
 UEFA Champions League 2015/16
UEFA Champions League 2015/16
 UEFA Champions League 2016/17
UEFA Champions League 2016/17
 UEFA Champions League 2017/18
UEFA Champions League 2017/18
 UEFA Champions League 2018/19
UEFA Champions League 2018/19
 UEFA Champions League 2019/20
UEFA Champions League 2019/20
 UEFA Europa League 2017/18
UEFA Europa League 2017/18
 UEFA Europa League 2018/19
UEFA Europa League 2018/19
 UEFA Europa League 2019/20
UEFA Europa League 2019/20
 UEFA Nations League
UEFA Nations League
 Union of European Football Associations
Union of European Football Associations

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

Die Fédération Internationale de Football Association (deutsch Internationaler Verband des Association Football), kurz FIFA oder Fifa, ist ein privater Verband, der „die Kontrolle des Association Football in all seinen Formen“ zum Zweck hat.[3] Der Weltfußballverband ist ein gemeinnütziger Verein im Sinne der Artikel 60 ff. des Schweizerischen Zivilgesetzbuches mit Sitz in Zürich und im Handelsregister eingetragen.[4][5][6] Die FIFA muss als nicht steuerbefreiter Verein im Kanton Zürich eine reduzierte Gewinnsteuer von 4 % entrichten.[1][2]
Die FIFA erwirtschaftet in ihrer aktuellen Vierjahresertragsperiode 5,66 Milliarden Dollar, die zu 89 % aus der Vermarktung der von ihr organisierten Männer-Fußball-WM stammen. Darüber hinaus organisiert sie auch die Frauen-Fußball-WM und zahlreiche weitere Turniere. Ihr Präsident ist Gianni Infantino.
国际足球联合会(法语:Fédération Internationale de Football Association;英语:International Federation of Association Football[注 1]),简称国际足联(FIFA),是管理英式足球、室内五人足球和沙滩足球的国际体育组织,下辖211个会员协会。总部设于瑞士苏黎世。现任主席为吉安尼·因凡蒂诺。国际足联负责组织世界重大足球赛事,当中最著名的是4年举行一次的世界杯。[3]
国際サッカー連盟(こくさいサッカーれんめい、仏: Fédération Internationale de Football Association)は、サッカー(アソシエーション式フットボール)の国際競技連盟であり、スイスの法律に基づいた自立法人である。略称はFIFA(フランス語発音: [fifa] フィファ、英語発音: [ˈfiːfə] フィーファ)。本部はスイスのチューリッヒに置かれている。
2018年時点で全211の国内競技連盟が加盟し[1]、国際競技連盟としては世界最大である[3]。FIFAワールドカップ・FIFA女子ワールドカップの主催が、もっとも大きな任務となっている。
The Fédération Internationale de Football Association[a] (FIFA /ˈfiːfə/ FEE-fə; French for International Federation of Association Football; Spanish: Federación Internacional de Fútbol Asociación; German: Internationaler Verband des Association Football) is a non-profit organization which describes itself as an international governing body of association football, fútsal, beach soccer, and efootball. It is the highest governing body of football.
FIFA was founded in 1904[3] to oversee international competition among the national associations of Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland. Headquartered in Zürich, its membership now comprises 211 national associations. Member countries must each also be members of one of the six regional confederations into which the world is divided: Africa, Asia, Europe, North & Central America and the Caribbean, Oceania, and South America.
Today, FIFA outlines a number of objectives in the organizational Statues, including growing football internationally, providing efforts to ensure football is accessible to everyone, and advocating for integrity and fair play.[4] FIFA is responsible for the organization and promotion of football's major international tournaments, notably the World Cup which commenced in 1930 and the Women's World Cup which commenced in 1991. Although FIFA does not solely set the rules of football, that being the responsibility of the International Football Association Board of which FIFA is a member, it applies and enforces the rules across all FIFA competitions.[5] All FIFA tournaments generate revenue from sponsorship; in 2018, FIFA had revenues of over US $4.6 billion, ending the 2015–2018 cycle with a net positive of US$1.2 billion, and had cash reserves of over US$2.7 billion.[6]
Reports by investigative journalists have linked FIFA leadership with corruption, bribery, and vote-rigging related to the election of FIFA president Sepp Blatter and the organization's decision to award the 2018 and 2022 World Cups to Russia and Qatar, respectively. These allegations led to the indictments of nine high-ranking FIFA officials and five corporate executives by the U.S. Department of Justice on charges including racketeering, wire fraud, and money laundering. On 27 May 2015, several of these officials were arrested by Swiss authorities, who were launching a simultaneous but separate criminal investigation into how the organization awarded the 2018 and 2022 World Cups. Those among these officials who were also indicted in the U.S. are expected to be extradited to face charges there as well.[7][8][9] Many officials were suspended by FIFA's ethics committee including Sepp Blatter[10] and Michel Platini.[11] In early 2017 reports became public about FIFA president Gianni Infantino attempting to prevent the re-elections[12] of both chairmen of the ethics committee, Cornel Borbély and Hans-Joachim Eckert, during the FIFA congress in May 2017.[13][14] On 9 May 2017, following Infantino's proposal,[15] FIFA Council decided not to renew the mandates of Borbély and Eckert.[15] Together with the chairmen, 11 of 13 committee members were removed.[16]
La Fédération internationale de football association2 (souvent désignée par l'acronyme FIFA) est la fédération sportive internationale du football, du futsal et du football de plage. Association des fédérations nationales fondée le 21 mai 1904 à Paris, elle a pour vocation de gérer et de développer le football dans le monde. La Coupe du monde de football est créée en 1924 par Jules Rimet3, président de la fédération internationale de 1920 à 1954. Le terme Football Association est le nom originel du football, utilisé pour le distinguer des autres sports de ballon.
Fondée par les fédérations d'Allemagne, de Belgique, du Danemark, d'Espagne, de France, des Pays-Bas, de Suède et de Suisse, elle compte au 13 mai 2016 211 associations nationales affiliées à travers le monde, qui doivent être reconnues par l'une des six confédérations continentales. Son siège est situé depuis 1932 à Zurich, en Suisse.
Bien qu'étant officiellement une association à but non lucratif, la FIFA brasse un chiffre d'affaires très important du fait de l'organisation des compétitions et de leur sponsoring. En 2013, la FIFA génère 1,3 milliard de dollars de chiffre d'affaires, et dispose de réserves évaluées à 1,4 milliard de dollars4. La FIFA est chargée de l'organisation des grands tournois mondiaux, et notamment des Coupes du monde masculines, depuis le 13 juillet 1930, et féminines, depuis le 30 novembre 1991.
Après plusieurs années de rumeurs et d'enquêtes de journalistes sur les affaires financières au sein de la FIFA, notamment autour de l'attribution de l'organisation des Coupes du monde de 2018 et 2022 à la Russie et au Qatar, une enquête lancée par le département de la Justice des États-Unis pour des faits de corruption aboutit à un grand scandale en 2015, à la suite duquel le président Sepp Blatter, le 2 juin 2015, trois jours après sa réélection pour un cinquième mandat, annonce qu'il convoque un congrès extraordinaire, prévu en février 2016, afin de remettre son mandat de président à disposition. Le 8 octobre 2015, la commission d'éthique de la FIFA suspend Sepp Blatter de manière provisoire, pendant 90 jours5. Le 21 décembre 2015, la commission suspend Sepp Blatter pour 8 ans6. Cette suspension est ramenée à six ans le 24 février 2016, peu avant l'élection de son successeur, Gianni Infantino, le 26 février 2016.
La Fédération Internationale de Football Association (in italiano "Federazione internazionale di calcio"[Nota 1]), più nota con l'acronimo FIFA, è la federazione internazionale che governa gli sport del calcio, del calcio a 5 e del beach soccer. La sua sede si trova a Zurigo, in Svizzera, e il presidente è Gianni Infantino, eletto nel 2016.
La federazione fu fondata a Parigi il 21 maggio 1904 e si occupa dell'organizzazione di tutte le manifestazioni intercontinentali degli sport sopraccitati, tra le quali la più importante è sicuramente il Campionato mondiale di calcio, che premia il vincitore con il trofeo della Coppa del Mondo. Tale torneo viene disputato ogni quattro anni dal 1930, eccetto che per il 1942 e il 1946 a causa della Seconda guerra mondiale, e la federazione ha il compito di scegliere il paese organizzatore che ospita la fase finale della manifestazione.
La Fédération Internationale de Football Association2 (en español: Federación Internacional de Fútbol Asociación),3 universalmente conocida por sus siglas FIFA, es la institución que gobierna las federaciones de fútbol en todo el planeta. Se fundó el 21 de mayo de 1904 y tiene su sede en Zúrich, Suiza. Forma parte del IFAB, organismo encargado de modificar las reglas del juego. Además, la FIFA organiza la Copa Mundial de Fútbol, los otros campeonatos del mundo en sus distintas categorías, ramas y variaciones de la disciplina, y los Torneos Olímpicos a la par del COI.
La FIFA agrupa 211 asociaciones o federaciones de fútbol de distintos países, contando con 17 países afiliados más que la Organización de las Naciones Unidas, tres menos que la Asociación Internacional de Federaciones de Atletismo y dos menos que la Federación Internacional de Baloncesto.45
Междунаро́дная федера́ция футбо́ла[1] (фр. Fédération Internationale de Football Association, сокращённо FIFA, в русской транслитерации — ФИФА́) — главная футбольная организация, являющаяся крупнейшим международным руководящим органом в футболе, мини-футболе и пляжном футболе. Штаб-квартира ФИФА находится в швейцарском городе Цюрихе.
Под эгидой ФИФА проходят все футбольные турниры всемирного масштаба, в числе которых чемпионат мира ФИФА, аналогичный турнир среди женщин, молодёжные и юношеские турниры, Кубок конфедераций и клубный чемпионат мира.



 Switzerland
Switzerland

 Companies
Companies

 Companies
Companies
 *Centuries-old companies in the world
*Centuries-old companies in the world

 Companies
Companies
 Germany, Austria, Switzerland
Germany, Austria, Switzerland



 Disaster relief
Disaster relief

 Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 1963
1963
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Peace Prize
Nobel Peace Prize
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 1944
1944
 Useful info
Useful info

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

红十字国际委员会(法语:Comité International de la Croix Rouge, CICR;英语:International Committee of the Red Cross, ICRC)是一个总部设于瑞士日内瓦的人道主义机构。根据《日内瓦公约》以及习惯国际法的规定,国际社会赋予红十字国际委员会特权和法律豁免权,保护国内武装冲突和国际性武装冲突的受难者。这些受难者包括战伤者、战俘、难民、平民和其他非战斗员。
红十字国际委员会的委员只能是瑞士公民,而且新委员由委员会推选。长期以来,红十字国际委员会的雇员只能是瑞士公民,并特别强调以日内瓦市民、白人、男性、新教徒为主。但自1990年代初以来,红十字国际委员会开始聘用非瑞士籍员工。长期以来,瑞士官方认定红十字国际委员会为私人机构。1993年3月19日,瑞士政府和红十字国际委员会签署了一份正式协议,保护红十字国际委员会在瑞士的财产豁免权、委员及其员工的法律豁免权,免除各项税费,提供与外国使馆同等级别的安全通讯特权并简化红十字国际委员会在瑞士的出入境手续。
根据瑞士法律,红十字国际委员会被定义为私人协会。与普遍看法相反,红十字国际委员会不是一个最常见的非政府组织,也不是一个国际组织。由于它仅向瑞士国民限制其成员(称为合作的过程),因此对于像其他法律界定的非政府组织这样的个人而言,它没有公开和不受限制的成员资格政策。其名称中的“国际”一词并不是指其成员资格,而是指日内瓦公约所界定的其活动的全球范围。红十字国际委员会根据这些国家的法律或通过委员会与各自国家政府之间的协议,在许多国家享有特权和法律豁免权。
红十字国际委员会与红十字会与红新月会国际联合会(下文简称“联合会”)以及190个国家红十字/红新月/红水晶会共同组成国际红十字与红新月运动。根据1997年的塞维利亚协议,在武装冲突中红十字国际委员会是占主导地位的红十字组织;在非冲突情况下,联合会为运动的领导机关。
红十字国际委员会是运动中历史最为悠久且最负盛誉的组织,它也是世界上获得最广泛认可的组织之一,并在1917年、1944年和1963年三次荣获诺贝尔和平奖。而红十字会的创办人亨利·杜南则在1901年荣获首届诺贝尔和平奖。
Die Internationale Rotkreuz- und Rothalbmond-Bewegung umfasst das Internationale Komitee vom Roten Kreuz (IKRK) (englisch offiziell International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC)), die Internationale Föderation der Rotkreuz- und Rothalbmond-Gesellschaften (englisch offiziell International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC)) sowie die nationalen Rotkreuz- und Rothalbmond-Gesellschaften.[1] Das IKRK und die Internationale Föderation sind voneinander organisatorisch und rechtlich unabhängig und innerhalb der Bewegung durch gemeinsame Grundsätze, Ziele und Symbole miteinander verbunden. Als Föderation der nationalen Rotkreuz- und Rothalbmond-Gesellschaften wird die Internationale Föderation der Rotkreuz- und Rothalbmond-Gesellschaften von den 191 Mitgliedsorganisationen gesteuert und ist nicht von ihnen unabhängig.[2] Die weltweit gleichermaßen geltende Mission der Bewegung – unabhängig von staatlichen Institutionen und auf der Basis freiwilliger Hilfe – sind der Schutz des Lebens, der Gesundheit und der Würde sowie die Verminderung des Leids von Menschen in Not ohne Ansehen von Nationalität und Abstammung oder religiösen, weltanschaulichen oder politischen Ansichten der Betroffenen und Hilfeleistenden.
Das auf Anregung von Henry Dunant 1863 gegründete Internationale Komitee vom Roten Kreuz (IKRK) besteht aus bis zu 25 Schweizer Staatsbürgern, ist die älteste internationale medizinische Hilfsorganisation[3] und die einzige Organisation, die im humanitären Völkerrecht erfasst und als dessen Kontrollorgan genannt ist. Es ist die älteste Organisation der Bewegung und neben dem Heiligen Stuhl sowie dem Souveränen Malteser-Ritterorden eines der wenigen originären nichtstaatlichen Völkerrechtssubjekte. Seine ausschließlich humanitäre Mission ist, basierend auf den Prinzipien der Unparteilichkeit, Neutralität und Unabhängigkeit, der Schutz des Lebens und der Würde der Opfer von Kriegen und innerstaatlichen Konflikten.
Die Internationale Föderation der Rotkreuz- und Rothalbmond-Gesellschaften, Nachfolgeorganisation der 1919 entstandenen Liga der Rotkreuz-Gesellschaften, koordiniert innerhalb der Bewegung die Kooperation zwischen den nationalen Rotkreuz- und Rothalbmond-Gesellschaften und leistet Unterstützung beim Aufbau neuer nationaler Gesellschaften. Auf internationaler Ebene leitet und organisiert sie, in Zusammenarbeit mit den nationalen Gesellschaften, Hilfsmissionen nach nicht kriegsbedingten Notsituationen wie zum Beispiel Naturkatastrophen und Epidemien.
Die nationalen Rotkreuz- und Rothalbmond-Gesellschaften sind Organisationen in fast allen Ländern der Welt, die jeweils in ihrem Heimatland im Sinne des humanitären Völkerrechts sowie der Statuten der Internationalen Bewegung tätig sind und die Arbeit des IKRK sowie der Föderation unterstützen. Ihre wichtigsten Aufgaben in ihren Heimatländern sind die Katastrophenhilfe und die Verbreitung der Genfer Konventionen. Im Rahmen ihrer Möglichkeiten können sie darüber hinaus weitere soziale und humanitäre Aufgaben wahrnehmen, die nicht unmittelbar durch völkerrechtliche Bestimmungen oder die Prinzipien der Bewegung vorgegeben sind. Hierzu zählen in vielen Ländern beispielsweise das Blutspendewesen und der Rettungsdienst sowie die Altenpflege und andere Bereiche der Sozialarbeit.
Von der Gründung im Jahr 1928 als Dachorganisation des IKRK und der Föderation bis zur Umbenennung 1986 lautete der offizielle Name der Bewegung Internationales Rotes Kreuz. Diese bis in die Gegenwart weit verbreitete Bezeichnung und die daraus resultierende Abkürzung IRK sollten jedoch nach Möglichkeit nicht mehr verwendet werden, da sie zu Problemen bei der Unterscheidung zwischen dem IKRK und der Föderation in der öffentlichen Wahrnehmung führen können.

 Disaster relief
Disaster relief

 Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 1963
1963
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Peace Prize
Nobel Peace Prize
 Switzerland
Switzerland

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
红十字会与红新月会国际联合会(英语:International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, IFRC;阿拉伯语:الإتحاد الدولي لجمعيات الصليب الأحمرِ والهلال الأحمرِ;初创时名为红十字会联盟,旧译作“国际红十字协会”,英语:League of Red Cross Societies)是一个国际人道主义组织,与红十字国际委员会(ICRC)、各国家协会(红十字会或红新月会)共同组成了国际红十字与红新月运动[1]。该组织成立于1919年,总部设在瑞士日内瓦。它负责协调各国家协会的活动,以“通过动员人道力量改善弱势群体的生活”[2]。在国际层面上,该联合会与国家协会密切合作,领导和组织大规模紧急救援。该组织于1963年获得诺贝尔和平奖。
一般而言,依照七项基本原则(见下文)中的“普遍”原则,几乎所有国家都有国家协会(红十字会或红新月会),而在“统一”原则下,一个国家只有一个国家协会[来源请求]。由亨利·杜南创立的“红十字国际委员会”依照《日内瓦公约》及相关议定书的规定,提供战俘人道协助、监察战俘待遇。“红十字会与红新月会国际联合会”则负责协调国家协会,跨国救援和平时期的受害者。
红十字会与红新月会国际联合会及红十字国际委员会现在都是联合国的观察员。
Die Internationale Föderation der Rotkreuz- und Rothalbmondgesellschaften (IFRC) ist eine weltweite Organisation für humanitäre Hilfe, die über ihre 191 nationalen Mitgliedsgesellschaften jährlich 160 Millionen Menschen erreicht. Sie wird vor, während und nach Katastrophen und gesundheitlichen Notlagen tätig, um die Bedürfnisse der bedürftigen Menschen zu erfüllen und ihre Lebensbedingungen zu verbessern. Sie tut dies unabhängig und unparteiisch in Bezug auf Nationalität, Ethnie, Geschlecht, religiöse Überzeugungen, Klasse und politische Ansichten.
Die IFRC ist zusammen mit dem Internationalen Komitee vom Roten Kreuz (IKRK) und 191 nationalen Gesellschaften Teil der internationalen Rotkreuz- und Rothalbmondbewegung. Die Stärke der IFRC liegt in ihrem Netzwerk von Freiwilligen, ihrem Fachwissen auf Gemeindeebene sowie ihrer Unabhängigkeit und Neutralität. Sie setzt sich für die Verbesserung der humanitären Standards ein, als Partner in der Entwicklung und bei der Reaktion auf Katastrophen. Sie überzeugt die Entscheidungsträger, im Interesse der bedürftigen Menschen zu handeln. Sie arbeitet daran, gesunde und sichere Gemeinschaften zu ermöglichen, Schwachstellen zu verringern, die Widerstandsfähigkeit zu stärken und eine Kultur des Friedens in der ganzen Welt zu fördern.
 Belgium
Belgium
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Italy
Italy
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Russia
Russia
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Hungary
Hungary
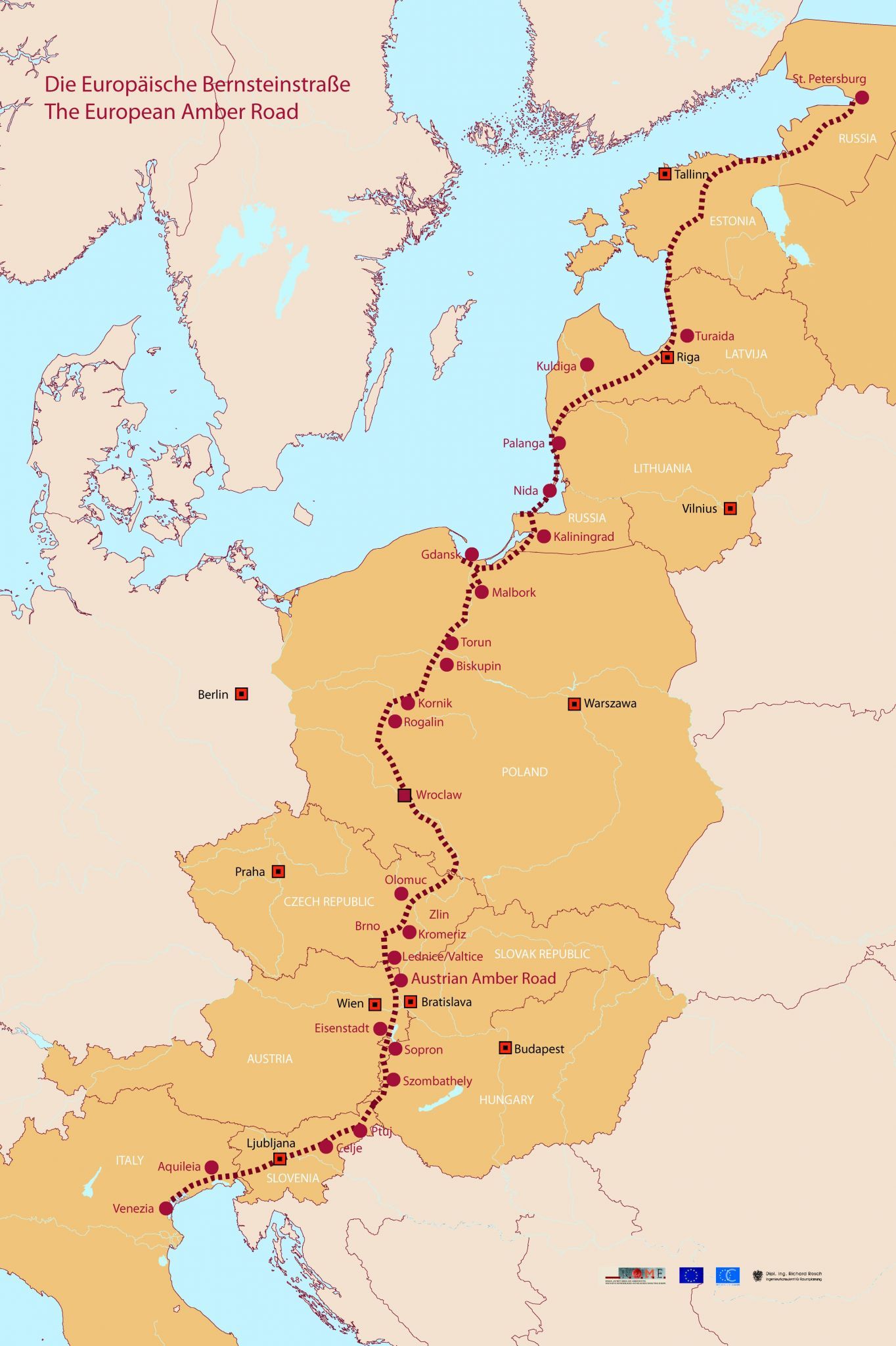
琥珀之路(英语:Amber Road)是一条古代运输琥珀的贸易道路,这条水路和陆路结合而成的通商道路,从欧洲北部的北海和波罗的海通往欧洲南部的地中海,连结了欧洲的多个重要城市,维持了多个世纪。
在公元前后的很长一段时间,琥珀作为装饰品中的重要组成部分,被从北海和波罗的海海岸的产地,经由维斯瓦河和第聂伯河运输到意大利、希腊、黑海和埃及。琥珀之路连结了琥珀的产地和在欧洲、中东地区和远东地区的消费地,并经由另一条通商道路丝绸之路继续通往亚洲。
Als Bernsteinstraße werden verschiedene Handelswege des Altertums (Altstraßen) bezeichnet, auf denen (unter anderem) Bernstein von der Nord- und Ostsee nach Süden in den Mittelmeerraum gelangte. Genau genommen handelt es sich nicht um eine Straße, sondern um unabhängige Handelswege, die für verschiedene Handelsgüter genutzt wurden. Die Bezeichnung „Bernsteinstraße“ tritt etwa ab dem Ende des 18. Jahrhunderts auf und hat in antiken Quellen keine Entsprechung.


 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Life and Style
Life and Style
 History
History
 Architecture
Architecture