
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON




 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC
 Canada
Canada
 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB

 New Brunswick-NB
New Brunswick-NB

 Newfoundland and Labrador-NL
Newfoundland and Labrador-NL

 Nova Scotia-NS
Nova Scotia-NS

 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC

 Saskatchewan-SK
Saskatchewan-SK
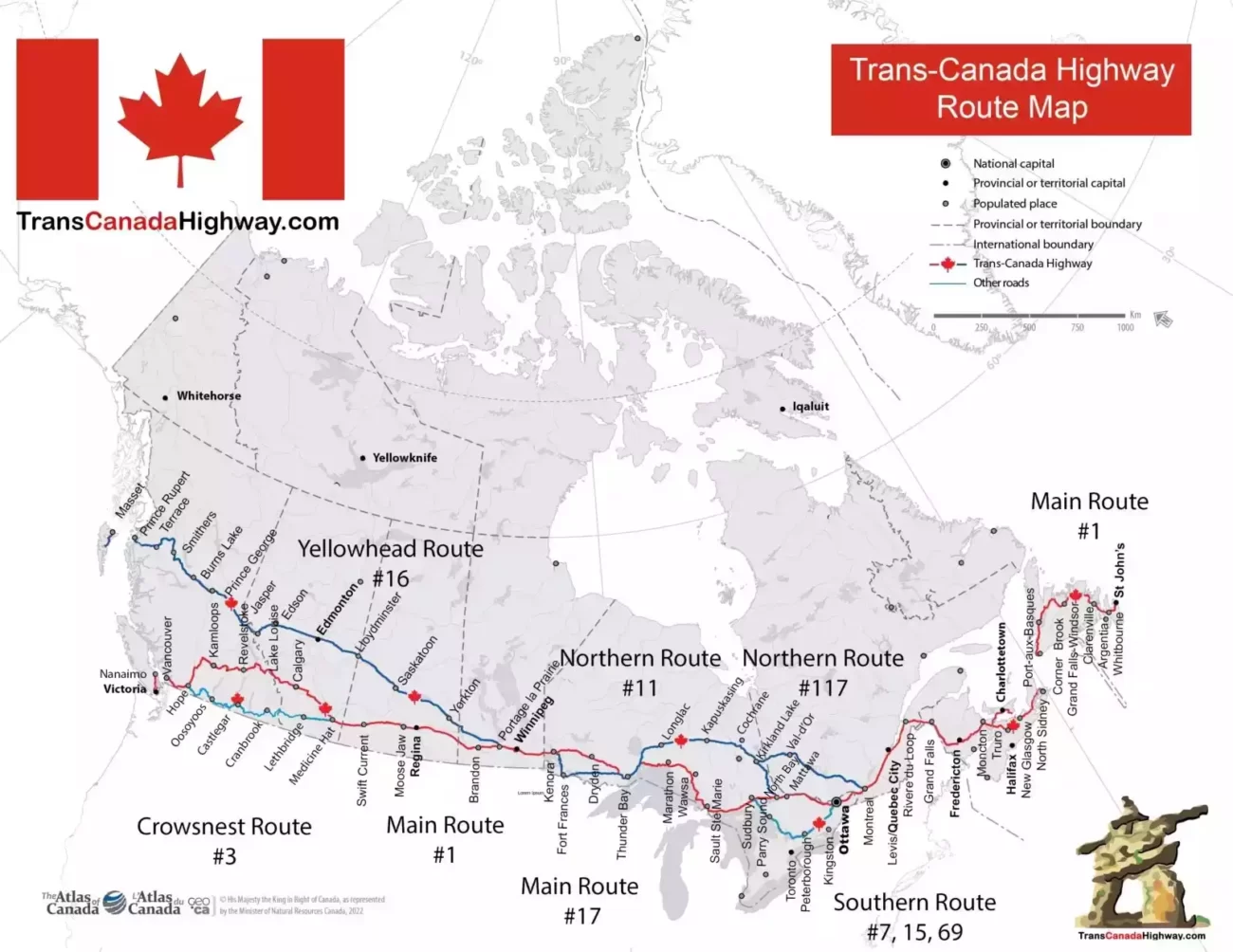
加拿大横贯公路 (英语:Trans-Canada Highway,法语:Route Transcanadienne),又称横加公路,是一个自西向东横贯加拿大全部十个省的公路系统。主线西起不列颠哥伦比亚省的省会维多利亚,东至纽芬兰和拉布拉多省的省会圣约翰斯,全长8,030公里[3]。系统另有数条支线,例如连接温尼伯和夏洛特皇后群岛的耶洛黑德公路。
《加拿大横贯公路法案》 (Trans-Canada Highway Act)在1948年获议会通过[4]。工程于1950年开始,[5]1962年启用,1971年完工。
由于加拿大国内公路系统的建造和管理都是由各省政府负责(而非联邦政府),横加公路系统中的干线编号亦因省而异。横加公路沿线设有绿底白枫叶的标记以作识别。
有别于美国的州际公路系统,横加公路并未全线达致高速公路标准,部分路段更只是双线行车。
トランスカナダハイウェイ(英語:Trans-Canada Highway、フランス語:Route transcanadienne)はカナダを東西に横断する幹線道路網。日本語では「カナダ大陸横断高速道路」と書かれることもある。
カナダの太平洋岸から大西洋岸まですべての州(準州は含まない)を通る。1948年のトランスカナダハイウェイ法にて制定され、1962年に供用開始、1970年に完成した。緑地に白のメイプルリーフ標識で表される。略称はTCH。
アメリカ合衆国の州間高速道路網と違い、トランスカナダハイウェイは交差点が点在する区間や片側一車線の対面通行の区間も多く、アメリカのUSハイウェイ道路網や日本の国道のように一般道路に割り当てられている区間も多い。
The Trans-Canada Highway (French: Route Transcanadienne; abbreviated as TCH or T-Can[3]) is a transcontinental federal-provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada from the Pacific Ocean on the west to the Atlantic on the east. The main route spans 7,821 km (4,860 mi) across the country, one of the longest routes of its type in the world.[4] The highway system is recognizable by its distinctive white-on-green maple leaf route markers, although there are small variations in the markers in some provinces.
Throughout much of Canada, there are at least two routes designated as part of the Trans-Canada Highway (TCH). For example, in the western provinces, both the main Trans-Canada route and the Yellowhead Highway are part of the Trans-Canada system. Although the TCH, being strictly a transcontinental route, does not enter any of Canada's three northern territories or run to the Canada–US border, the Trans-Canada Highway forms part of Canada's overall National Highway System (NHS), providing connections to the Northwest Territories, Yukon and the border, although the NHS (apart from the TCH sections) is unsigned.[5]
La route Transcanadienne est un système de voies routières à régime fédéral-provincial qui relie les dix provinces du Canada. Ce réseau n'est pas une simple route, car il est à certains endroits composé de deux, voire trois routes parallèles. Par exemple, dans l'ouest du pays, la Route Yellowhead est une branche de la Transcanadienne parallèle à la route originale. La construction de la route fut décidée en 1948, débuta en 1950 pour se terminer en 1970. La route fut inaugurée en 1962. Elle fait actuellement 7 821 kilomètres de long, s'étendant d'un océan à l'autre, du Pacifique à l'Atlantique. Elle est la route « nationale » la plus longue du monde. Il faut préciser que le Canada n'a pas de système routier national, car les routes sont de compétence provinciale. Toutefois, l'entretien de la Transcanadienne est financé par le gouvernement fédéral qui, chaque année, octroie de l'argent aux provinces.
Contrairement au système Interstate des États-Unis, la route Transcanadienne n'est pas toujours une autoroute ou même une route à 4 voies divisées. En 2000, le gouvernement de Jean Chrétien a étudié la possibilité de financer la transformation de la Transcanadienne en autoroute à 4 voies à la grandeur du pays. Finalement, cette idée fut abandonnée car certaines portions de la route ne sont pas assez achalandées pour justifier ce projet. Les provinces ont préféré investir dans des axes routiers plus achalandés et plus commerciaux, comme les liaisons avec les États-Unis. Malgré cela, certaines sections ont été ou seront transformées en autoroute, comme la Route 185 du Québec qui deviendra l'Autoroute 85. Un autre exemple est la Route 2 du Nouveau-Brunswick. Au milieu des années 1980, cette route de plus de 500 km était à deux voies et souvent à accès non limité. En 1987, le gouvernement de la province lança le projet de transformation de la route en autoroute à 4 voies à chaussées séparées. La transformation se termina 20 ans plus tard, à l'automne 2007.
Étant donné que les routes relèvent des provinces, la numérotation de la Transcanadienne relève de celles-ci. Les provinces de l'Ouest (Colombie-Britannique, Alberta, Saskatchewan et Manitoba) ont harmonisé leurs numéros de routes, ainsi l'axe principal de la Transcanadienne, l'axe sud, est appelé Route 1. L'axe nord, la Route Yellowhead, pour sa part est désignée Route 16. Dans l'est du pays, la situation est complètement différente, le numéro de la route change à chaque frontière provinciale. Ceci est dû au fait que la Transcanadienne est composée de sections de routes importantes qui existaient avant son introduction. Il est peu probable que la route ait un jour une désignation uniforme à la grandeur du pays. Ceci serait incompatible avec le système de numérotation des provinces, comme celui du Québec qui est basé sur la géographie (voir Routes provinciales du Québec).
L'autostrada Transcanadese (TCH) (in inglese: Trans-Canada Highway; in francese: Route Transcanadienne) è un sistema di autostrade misto a strade di giurisdizione federale e provinciale che unisce le dieci province del Canada.
Si contende il titolo di autostrada più lunga del mondo con l'autostrada Trans-Siberiana e la Highway 1 dell'Australia. È una delle più lunghe autostrade nazionali del mondo, con una rotta principale che si estende per 8.030 km (4.990 miglia)[1]. Il sistema venne approvato grazie al Trans-Canada Highway Act del 1948,[2] e vide l'inizio della costruzione nel 1950.[3] Ufficialmente l'autostrada venne aperta nel 1962, e venne completata nel 1971. Il sistema di autostrade è riconoscibile per il logo verde su bianco a forma di foglia d'acero (maple leaf) che marca gli accessi, e i numeri delle strade. La Trans-Canada Highway viene spesso abbreviata come TCH.
Attraverso il Canada, vi sono almeno due percorsi designati come facenti parte della Trans-Canada Highway. Ad esempio, nelle province occidentali, sia la Trans-Canada route principale che la Yellowhead Highway formano parte del sistema della Trans-Canada.
La Carretera Transcanadiense (en inglés: Trans-Canada Highway, en francés: Route Transcanadienne) es un sistema vial de carreteras federal-provincial que enlaza las diez provincias de Canadá. Esta carretera es, después de la Australia's Highway 1 y de la Carretera transiberiana, la tercera autopista nacional más larga del mundo, ya que su ruta principal atraviesa 7821 kilómetros. El sistema fue aprobado mediante la Ley de la Carretera Transcanadiense de 1948 (Trans-Canada Highway Act of 1948), si bien la construcción no comenzó hasta 1950. Fue abierta al tráfico oficialmente en 1962 y terminada en 1971.
Atraviesa algunas de las principales ciudades del país como son Vancouver, Calgary, Montreal, Winnipeg, Ottawa, Quebec, Victoria y Edmonton.
Транскана́дское шоссе́ (англ. Trans-Canada Highway, TCH, фр. Route Transcanadienne) — федерально-провинциальная сеть автомобильных дорог, соединяющая десять провинций Канады. Вместе с Транссибирским шоссе и австралийским шоссе 1 оно является одной из самых длинных в мире национальных скоростных автострад: длина магистрали составляет 8030 км. Сеть была одобрена Законом о Трансканадском шоссе 1948 г., а строительство началось в 1950 г. Официально шоссе было открыто в 1962 г., а завершено в 1971 г. Эта сеть автомобильных дорог отличается от других шоссе легко узнаваемыми бело-зелёными дорожными указателями с кленовым листом.
На протяжении всей Канады существует не менее двух трасс, считающихся частью Трансканадского шоссе. Например, в западных провинциях частью трансканадской сети являются Трансканадская магистраль и Йеллоухедское шоссе.





加拿大林业产品协会(FPAC)是一个行业协会,在政府、贸易和环境事务中代表加拿大国内和国际的木材、纸浆和纸张生产商。加拿大的林产品行业每年的产值达 800 亿美元,占加拿大国内生产总值的 2%。
Die Forest Products Association of Canada (FPAC) ist ein Handelsverband, der die kanadischen Holz-, Zellstoff- und Papierhersteller sowohl auf nationaler als auch auf internationaler Ebene in Regierungs-, Handels- und Umweltangelegenheiten vertritt. Die kanadische Forstindustrie ist ein Wirtschaftszweig mit einem Jahresumsatz von 80 Milliarden Dollar, der 2 % des kanadischen BIP ausmacht.


加拿大农业联合会(CFA)是加拿大最大的综合性农业组织,代表着 20 万农民和农业家庭。该组织总部位于安大略省渥太华市,其任务是在国家层面提供统一的行业声音。加拿大农业协会成立于 1935 年,至今仍是一个由农民出资的全国性伞式组织,代表着省级综合农场组织和全国性商品团体。
Der Kanadische Landwirtschaftsverband (Canadian Federation of Agriculture, CFA) ist Kanadas größter allgemeiner Landwirtschaftsverband, der 200.000 Landwirte und Landwirtsfamilien vertritt. Die Organisation hat ihren Sitz in Ottawa, Ontario, und hat den Auftrag, der Branche auf nationaler Ebene eine einheitliche Stimme zu geben. Der CFA wurde 1935 gegründet und ist auch heute noch ein von Landwirten finanzierter, nationaler Dachverband, der die allgemeinen landwirtschaftlichen Organisationen der Provinzen und die nationalen Rohstoffgruppen vertritt.

Das Canadian Global Affairs Institute (CGAI; französisch Institut canadien des affaires mondiales, deutsch „Kanadisches Institut für globale Angelegenheiten“, vormals Canadian Defence and Foreign Affairs Institute CDFAI) ist eine unabhängige und überparteiliche Denkfabrik (englisch think tank) mit Hauptsitz in Calgary in der Provinz Alberta und einem weiteren Sitz in der kanadischen Hauptstadt Ottawa .
Es berichtet durch zahlreiche Veröffentlichungen umfassend über wichtige nationale und internationale Themen, wie Verteidigung, Diplomatie, Handel und Entwicklungen.
加拿大全球事务研究院(CGAI)是一个独立的无党派智库,总部设在阿尔伯塔省卡尔加里市,在加拿大首都渥太华设有办事处。它通过众多出版物对国防、外交、贸易和发展等重要的国家和国际问题进行广泛报道。
 Architecture
Architecture

 Aerospace
Aerospace
 Museum
Museum
 Exhibition
Exhibition



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Companies
Companies
 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
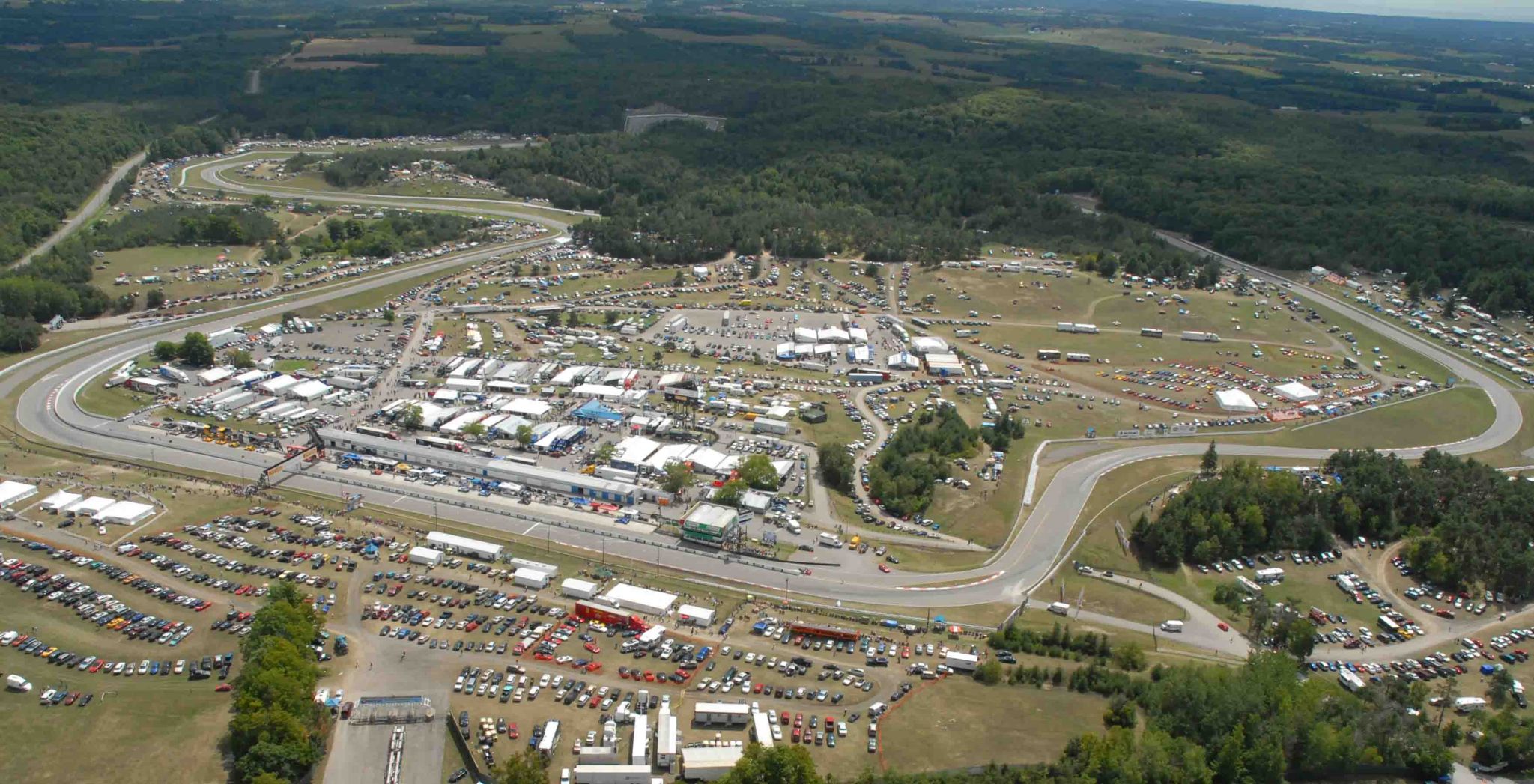
 Motorsport
Motorsport
 Ski vacation
Ski vacation