漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 重要港口
重要港口




利马(西班牙语:Lima)是南美洲国家秘鲁的首都,位于秘鲁西海岸线的中央,西临太平洋,与海港卡亚俄组成利马都会区,是南美洲最大的都市之一,全国约有三分之一的人口居住在此地区。
当代,利马被认为是该国最重要的政治、文化、金融和商业中心,城市的基础于1535年1月18日由西班牙殖民者法兰西斯克·皮泽洛所建,是秘鲁的西班牙文化重地,著名的天主教建筑还包括了16世纪的利马主教座堂和国立圣马尔科斯大学。在1500年代和1600年代,秘鲁是西班牙美洲殖民地仅次于波哥大和墨西哥城的经济中心。
Lima ist die Hauptstadt des südamerikanischen Andenstaates Peru und die mit Abstand größte Stadt des Landes. Im Verwaltungsgebiet der Stadt, der Provinz Lima, leben 8.574.974 Menschen (Stand 2017).[1] In der Konurbation Limas mit der Hafenstadt Callao leben insgesamt etwa 10.480.000 Einwohner.[1] Beide Städte bilden die Metropolregion Lima (Área Metropolitana de Lima).
Lima ist ein wichtiger Verkehrsknotenpunkt sowie das bedeutendste Wirtschafts- und Kulturzentrum von Peru mit zahlreichen Universitäten, Hochschulen, Museen und Baudenkmälern. Die Altstadt von Lima wurde 1991 von der UNESCO zum Weltkulturerbe erklärt.
リマ(スペイン語: Lima)は、ペルー共和国の首都で、政治、文化、金融、商業、工業の中心地。人口約1,035万人で、同国最大。南米有数の世界都市であり、近郊を含む都市圏人口は2016年では1,095万人で、世界第29位である[1]。チャラと呼ばれる海岸砂漠地帯に位置する。市街地は植民地時代に建てられた建物が多く残るリマ・セントロ地区(1988年、ユネスコの世界遺産に登録)、それより海岸側の新市街(サン・イシドロ地区・ミラフローレス地区など三輪モトタクシー乗入れ禁止の閑静で裕福な地域)、それらの新旧市街地を取り巻く複数の人口密集地域(第二次世界大戦後に発展)、以上の三つに分類できる。リマは1535年にインカ帝国を征服したスペイン人のコンキスタドール、フランシスコ・ピサロによって築かれた。リマの名前の由来は市内を流れるリマック川(río Rimacが訛ったもの)に由来すると言われているが、当初の名前は"La Ciudad de los Reyes"(諸王の街)であった。
Lima (/ˈliːmə/ LEE-mə; locally [ˈlima]), founded in 1535 as the Ciudad de los Reyes (locally [sjuˈdat de los ˈreʝes], Spanish for "City of Kings"), is the capital and largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón, Rímac and Lurín Rivers, in the desert zone of the central coastal part of the country, overlooking the Pacific Ocean. The city is considered the political, cultural, financial and commercial center of Peru. Due to its geostrategic importance, the Globalization and World Cities Research Network has categorized it as a "beta" tier city. Jurisdictionally, the metropolis extends mainly within the province of Lima and in a smaller portion, to the west, within the Constitutional Province of Callao, where the seaport and the Jorge Chávez Airport are located. Both provinces have regional autonomy since 2002.
The 2023 census projection indicates that the city of Lima has an estimated population of 10,092,000 inhabitants, making it the most populated city in the country, and the second most populous in the Americas after São Paulo.[5][6] Together with the seaside city of Callao, it forms a contiguous urban area known as the Lima Metropolitan Area, which encompasses a total of 10,151,200 inhabitants.[5][note 1] When considering the constitutional province of Callao, the total agglomeration reaches a population of 11,342,100 inhabitants, one of the thirty most populated urban agglomerations in the world.
Lima was named by natives in the agricultural region known by native Peruvians as Limaq. It became the capital and most important city in the Viceroyalty of Peru. Following the Peruvian War of Independence, it became the capital of the Republic of Peru (República del Perú). Around one-third of the national population now lives in its metropolitan area.
In October 2013, Lima was chosen to host the 2019 Pan American Games; these games were held at venues in and around Lima, and were the largest sporting event ever hosted by the country. It also hosted the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Meetings of 2008 and 2016, the Annual Meetings of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank Group in October 2015, the United Nations Climate Change Conference in December 2014, and the Miss Universe 1982 contest. In November 2024, it hosted the APEC summit for the third time.
Lima (prononcé [lima]) est la capitale et la plus grande ville du Pérou, ainsi que le chef-lieu de la région de Lima. Au milieu de la façade maritime du Pérou sur l'océan Pacifique, Lima s'étend au débouché des vallées de trois petits fleuves - plutôt des torrents - : Rímac, Chillón (es) et Lurín (es). Ses habitants s'appellent les Liméniens (Limeños) et Liméniennes (Limeñas).
Avec une agglomération d’environ dix millions d’habitants, Lima est la cinquième plus grande ville d'Amérique latine, derrière Mexico, São Paulo, Buenos Aires et Rio de Janeiro. C'est aussi la troisième ville du monde la plus peuplée qui soit située dans un désert, après Le Caire et Bagdad.
Lima est fondée le par le conquistador espagnol Francisco Pizarro. Sous le nom de « la Ciudad de los Reyes » (« la Cité des Rois »), elle devient la capitale et la ville principale de la vice-royauté du Pérou, puis celle de la République, après l’indépendance du pays vis-à-vis de l’Espagne en .
Lima est le cœur commercial, financier, culturel et politique du Pérou, tout en concentrant deux tiers de l’industrie, en relation avec le plus grand aéroport du pays : l'aéroport international Jorge Chávez desservant les principales villes d’Europe, des États-Unis et d'Amérique latine.
Son patrimoine architectural va de l’époque coloniale au XXe siècle et, pour cette raison, le centre-ville a été classé patrimoine mondial de l’UNESCO en 1991. La province de Lima est divisée en 43 districts, dont les plus importants sont : Miraflores, La Molina, San Isidro, Barranco, San Borja (es), Chorrillos, Villa El Salvador, Pachacamac et Los Olivos.
Rafael López Aliaga est l'actuel maire de Lima2
Lima (AFI: /ˈlima/; pronuncia spagnola: [ˈlima]) è la capitale e la città più grande del Perù. Si trova nelle valli dei fiumi Chillón, Rímac e Lurín, nella parte costiera centrale del paese, affacciata sull'Oceano Pacifico. Insieme al porto di Callao, forma un'area urbana contigua nota come area metropolitana di Lima. Con una popolazione di più di 9 milioni di abitanti[1], Lima è la quinta città più popolosa dell'America Latina dopo Città del Messico, San Paolo, Rio de Janeiro e Buenos Aires.
Lima è stata nominata dai nativi nella regione agricola conosciuta come Limaq. Fu la capitale e la città più importante del Vicereame del Perù. Dopo la guerra d'indipendenza peruviana divenne la capitale della Repubblica del Perù (República del Perú). Circa un terzo della popolazione nazionale vive nell'area metropolitana.
Lima ospita una delle più antiche istituzioni di istruzione superiore nel Nuovo Mondo: l'Università Nazionale di San Marcos, fondata il 12 maggio 1551, durante il Vicereame del Perù, è la prima università ufficialmente istituita e la più antica ininterrottamente funzionante nelle Americhe.
Oggigiorno la città è considerata il centro politico, culturale, finanziario e commerciale del paese. A livello internazionale, è uno dei trenta agglomerati urbani più popolati al mondo. Per la sua importanza geostrategica è stata definita una città "beta"[2].
Giurisdizionalmente, la metropoli si estende per lo più all'interno della provincia di Lima e in una porzione minore, a ovest, all'interno della provincia costituzionale di Callao, dove si trovano il porto marittimo e l'aeroporto Jorge Chávez. Entrambe le province hanno autonomia regionale dal 2002.
Nell'ottobre 2013 è stata scelta per ospitare i Giochi Panamericani del 2019; i giochi si sono svolti in sedi dentro e intorno a Lima e sono stati il più grande evento sportivo mai ospitato dal paese. Ha inoltre ospitato le riunioni APEC del 2008 e 2016, le riunioni annuali del Fondo monetario internazionale e del gruppo della Banca mondiale nell'ottobre 2015, la Conferenza delle Nazioni Unite sui cambiamenti climatici nel dicembre 2014 e il concorso Miss Universo 1982.
Lima, oficialmente, según la Constitución, Ciudad de Lima,10 Ciudad de los Reyes en su fundación, es la capital de la República del Perú.11 Está ubicada en la costa central del país, a orillas del océano Pacífico, integrando una extensa y poblada área urbana, flanqueada por el desierto costero, y extendida sobre los valles de los ríos Chillón, Rímac y Lurín.
La proyección censal de 2023, establece que la ciudad de Lima tiene una población estimada de 10 092 000 habitantes, lo que la convierte en la urbe más poblada del país. Según el INEI, Lima Metropolitana engloba a una cifra ligeramente superior con 10 151 200 habitantes. Esta área incluye los 43 distritos de la provincia de Lima. Asimismo, considerando la provincia constitucional del Callao, la aglomeración total alcanza una población de 11 342 100 habitantes. La organización urbana de Lima se estructura en 4 subregiones: Lima Norte, Lima Este, Lima Sur y Lima Centro.11213
En la actualidad, está considerada como el centro político, económico, industrial, cultural, financiero y comercial del país. En el plano internacional, es la quinta ciudad más grande de América Latina, la cuarta por PBI, la quinta por número de habitantes y una de las treinta aglomeraciones urbanas más pobladas del mundo.14 Por su importancia geoestratégica, ha sido definida como una ciudad global de «clase beta+».15
El 18 de enero de 1535, todavía durante la vigencia del Calendario juliano, la capital fue fundada por el conquistador español, Francisco Pizarro, con el nombre de Ciudad de los Reyes, en conmemoración a la festividad cristiana de la Epifanía, por la revelación a los Reyes Magos.16 La Ciudad de los Reyes fue capital del virreinato del Perú, y sustituyó la ciudad de Jauja como capital de la Gobernación de Nueva Castilla.
El virreinato, en su momento, fungió como la entidad administrativa más relevante de la Monarquía Hispánica dentro de América del Sur; mientras que, Lima a su vez, fue la ciudad más grande e importante en toda América Austral, durante el periodo colonial. Después del proceso de independencia, pasó a ser la capital de los departamentos libres, y posteriormente, de la República Peruana.17
Asimismo, fue capital del Estado Nor-Peruano. Lima es la sede de la institución más antigua de educación superior en el Nuevo Mundo, la Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos, fundada el 12 de mayo de 1551 durante el régimen virreinal español, es la universidad más antigua, reconocida e importante del Perú.18 Además, la primera fundada oficialmente y la más antigua en funcionamiento continuo en América.1920
En octubre de 2013, Lima fue elegida para albergar los Juegos Panamericanos 2019. Adicionalmente, fue sede de la Conferencia de las Naciones Unidas sobre el Cambio Climático en la edición de 2014. Además, fue sede del foro mundial APEC en las ediciones de 2008 y 2016, de las Reuniones Anuales del Fondo Monetario Internacional, y del Grupo del Banco Mundial en octubre de 2015, del concurso Miss Universo 1982.
Ли́ма (исп. Lima) — город на тихоокеанском побережье Южной Америки, столица Республики Перу. Административный центр автономной провинции Лима региона Лима. Главный политический, экономический и культурный центр страны.
Основана испанскими колонистами в 1535 году. Впоследствии стала центром испанских колоний в Южной Америке, после провозглашения независимости Перу в 1821 году — столица Республики Перу. Исторический центр Лимы в 1988 году внесён в список Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО.
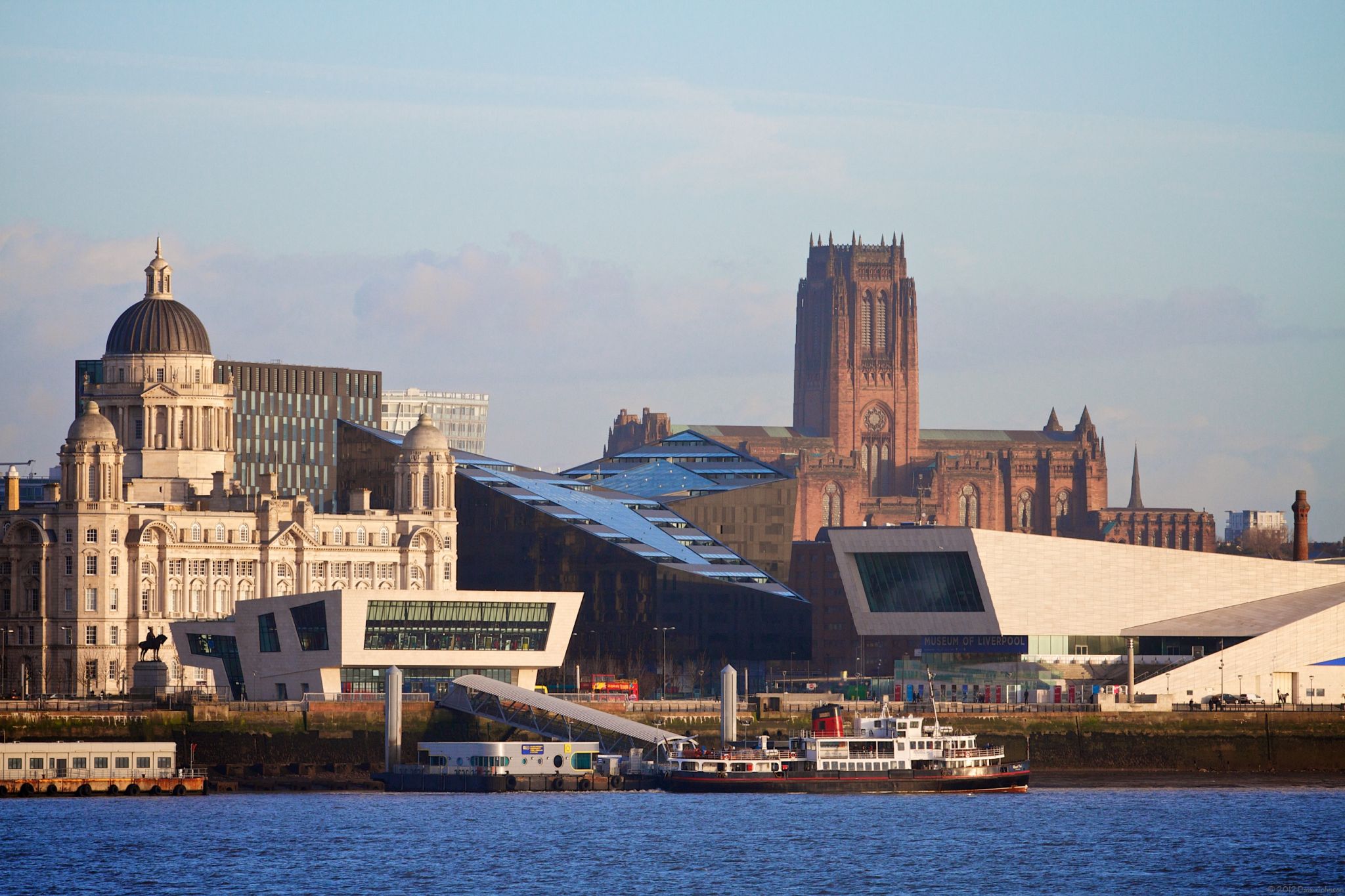

Liverpool [ˈlɪvəpuːl] ist eine Stadt und Metropolitan Borough im Nordwesten von England im Vereinigten Königreich Großbritannien und Nordirland, an der Mündung des Flusses Mersey. Im Jahr 2014 hatte die Stadt 473.073 Einwohner, im Ballungsraum Liverpool Urban Area lebten 817.000 Einwohner. Liverpool ist der zweitgrößte Exporthafen Großbritanniens.
Der historische Teil der Hafenstadt wurde 2004 zum Weltkulturerbe erklärt. Bekannt ist die Stadt durch die traditionsreichen Fußballvereine FC Everton und FC Liverpool sowie durch ihre pulsierende Musikszene, aus der in den 1960er Jahren unter anderem die Rockband The Beatles hervorging. 2008 war Liverpool (neben Stavanger in Norwegen) Europäische Kulturhauptstadt.
Die Einwohner Liverpools werden offiziell Liverpudlians genannt. Besser bekannt ist die Bezeichnung Scousers, nach dem in Liverpool gesprochenen Dialekt Scouse, dessen Name sich wiederum von der lokalen Eintopfspezialität Scouse herleitet.
利物浦(英语:Liverpool /ˈlɪvərpuːl/),是英格兰西北部著名港口城市,是默西赛德都市郡的5个自治市之一,由利物浦市议会治理。1207年时以自治市镇的身份成立,1880年获得城市地位。2011年人口约为466,415[4],是利物浦都会区的中心[5]。利物浦市区的人口约为2,200,000,英国第四大城市。[6]
利物浦居民称为Liverpudlians,但也称“Scousers”,后裔名称来自当地名吃炖汤“scouse”,同时这一词还指利物浦方言[7]。利物浦居民种族颇为丰富,有全英最古老的黑人社区和全欧最古老的华人社区。
吉尼斯世界纪录将利物浦评为“世界流行乐之都”[8],披头士、比利·弗里、格里和带头人及其他许多乐队都是在此发迹的。两支英超联球会:利物浦和埃弗顿也位于利物浦。2007年时利物浦庆祝其800岁诞辰,次年与斯塔万格一起成为欧洲文化之都[9]。
利物浦的历史建筑保护良好,其中许多都举世闻名。市中心的多个地区在2004年被联合国教科文组织评为世界遗产,并称利物浦海事商城。[10]
リヴァプール(Liverpool)は、イギリス・イングランド北西部マージーサイド州の中心都市である。面積は111.84平方キロメートル、2015年の人口は47万8580人[1]。かつてはイギリスの主要な港湾都市であったが、世界的ロック・バンドであるザ・ビートルズの出身地であることから、いまでは観光都市として知られる。2008年の欧州文化首都の一つ。
Liverpool (/ˈlɪvərpuːl/) is a city in North West England, with an estimated population of 491,500 in 2017.[5] Its metropolitan area is the fifth-largest in the UK, with a population of 2.24 million in 2011.[6] The local authority is Liverpool City Council, the most populous local government district in the metropolitan county of Merseyside and the largest in the Liverpool City Region.
Liverpool is on the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary, and historically lay within the ancient hundred of West Derby in the south west of the county of Lancashire.[7][8] It became a borough in 1207 and a city in 1880. In 1889, it became a county borough independent of Lancashire. Its growth as a major port was paralleled by the expansion of the city throughout the Industrial Revolution. Along with handling general cargo, freight, raw materials such as coal and cotton, the city merchants were involved in the Atlantic slave trade. In the 19th century, it was a major port of departure for Irish and English emigrants to North America. Liverpool was home to both the Cunard and White Star Line, and was the port of registry of the ocean liner RMS Titanic, the RMS Lusitania, RMS Queen Mary and RMS Olympic.
The popularity of the Beatles and other groups from the Merseybeat era contributes to Liverpool's status as a tourist destination. Liverpool is also the home of two Premier League football clubs, Liverpool and Everton, matches between the two being known as the Merseyside derby. The Grand National horse race takes place annually at Aintree Racecourse on the outskirts of the city.
The city celebrated its 800th anniversary in 2007. In 2008, it was nominated as the annual European Capital of Culture together with Stavanger, Norway.[9] Several areas of the city centre were granted World Heritage Site status by UNESCO in 2004. The Liverpool Maritime Mercantile City includes the Pier Head, Albert Dock, and William Brown Street.[10] Liverpool's status as a port city has attracted a diverse population, which, historically, was drawn from a wide range of peoples, cultures, and religions, particularly from Ireland and Wales. The city is also home to the oldest Black African community in the country and the oldest Chinese community in Europe.
Natives and residents of the city of Liverpool are referred to as Liverpudlians, and colloquially as "Scousers", a reference to "scouse", a form of stew. The word "Scouse" has also become synonymous with the Liverpool accent and dialect.
Liverpool est une cité et un district métropolitain du Merseyside dans la région de l'Angleterre du Nord-Ouest sur la rive est et nord de l'estuaire du fleuve Mersey. La ville faisait partie du comté du Lancashire jusqu'en 1974 avant la formation du comté de Merseyside.
La ville est fondée en 1207 et obtient le statut de cité en 1880. Avec une population de 491 500 habitants en 2017, c'est la sixième plus grande ville du Royaume-Uni, et la quatrième d'Angleterre ; l'aire urbaine de Liverpool comprend 864 122 habitants en 2011 (6e région urbaine du Royaume-Uni)1. Ses habitants s'appellent les Liverpuldiens (Liverpudlians en anglais)2.
L'ensablement progressif de l'estuaire de la Dee, sur lequel se tenait le port de Chester depuis l'époque romaine, a permis à Liverpool de devenir un port majeur. Au début du XIXe siècle, alors que l'Empire britannique était en pleine expansion économique, environ 40 % de son commerce passe par Liverpool, ce qui contribue grandement à l'importance de la ville. En 1930, la ville est à son apogée avec une population de plus de 850 000 habitants.
Bombardée durant la Seconde Guerre mondiale, la ville entame au lendemain de la guerre sa reconstruction, mais elle est rapidement touchée par la crise industrielle des années 1970 qui affecte son activité portuaire et dont elle se remet lentement. Liverpool a ainsi perdu de nombreux habitants mais demeure encore une métropole économique de premier rang pour le Nord-Ouest anglais. La ville a entamé un processus de reconversion dans le secteur tertiaire : services à l'industrie, activités commerciales (Liverpool One), et le tourisme (Albert Dock).
Liverpool est associée à la popularité des Beatles, un des plus grands phénomènes de l'industrie discographique mondiale, et développe son activité touristique principalement autour des groupes de musique des années 1960 et des galeries d'art et musées. Sixième ville la plus visitée du Royaume-Uni, Liverpool possède le deuxième plus grand nombre de musées après Londres. En 2004, plusieurs quartiers de la ville obtiennent le statut de Patrimoine mondial et la ville partage le titre de capitale européenne de la culture en 2008 avec Stavanger (Norvège) pour célébrer son 800e anniversaire.
Ville multi-culturelle (elle abrite une des plus anciennes communautés chinoises et africaines d'Europe), elle est aussi un important pôle universitaire, et est également célèbre pour ses deux principaux clubs de football, Everton et Liverpool, qui évoluent tous deux en Premier League.
L'accent propre aux habitants de Liverpool et du Merseyside est le « scouse » (terme anglais désignant également un ragoût à base de pommes de terre, de viande salée et d'oignons). Le mot « Scouser » est utilisé pour désigner les gens possédant cet accent ou, de façon plus générale, toute personne venant de Liverpool.
Liverpool (AFI: [ˈliverpul][2]; in inglese [ˈlɪvəpuːl]) è una città di 578 324 abitanti del Regno Unito e un distretto metropolitano, capoluogo della contea metropolitana inglese del Merseyside. Sorge lungo l'estuario della Mersey e affaccia sul Mare d'Irlanda, non lontano dal confine con il Galles.
Liverpool es una ciudad y municipio metropolitano del condado de Merseyside, en la región Noroeste de Inglaterra, sobre el lado este del estuario del río Mersey en Reino Unido. Limita al norte con el municipio metropolitano de Sefton, al este con el de Knowsley, al sur y oeste con el mencionado río. Fue fundada como villa en 1207 y tuvo ese estatus hasta 1880, cuando recibió el título de ciudad. Según el último censo oficial, que data de 2001, Liverpool tenía una población de 439 473 habitantes;2 esta cifra aumenta ligeramente hasta los 454 654 habitantes según estimaciones para el año 2009.1 La ciudad se encuentra en el centro del Área Metropolitana de Liverpool, cuya población asciende a 816 216 habitantes.
Históricamente perteneciente al condado de Lancashire, la urbanización y expansión de Liverpool se debió en gran parte a su condición de ciudad portuaria importante. En el siglo XVIII, el comercio con las Indias Occidentales, con la Europa continental y el tráfico de esclavos en el Atlántico promovió la expansión económica de la ciudad. A principios del siglo XIX, el 40% del comercio marítimo mundial pasaba por los muelles de Liverpool. Actualmente es el segundo puerto del Reino Unido en volumen de exportaciones tras Londres.
La popularidad de The Beatles (también destacaron otros grupos como por ejemplo The Scaffold3 ) y del equipo de fútbol Liverpool Football Club contribuyen a convertir a Liverpool en un destino turístico; el turismo juega un papel significante en la economía de la ciudad. En 2007 celebró su 800.º aniversario, y al año siguiente fue Capital Europea de la Cultura junto a la ciudad noruega de Stavanger.4
En 2004, varias zonas a lo largo del centro de la ciudad fueron declaradas Patrimonio de la Humanidad por la Unesco. Conocido como la «Ciudad mercantil marítima de Liverpool», el lugar comprende seis localizaciones separadas en la ciudad, incluyendo «Pier Head», «Albert Dock» y la «calle William Brown»; incluye la mayoría de los puntos de interés más famosos de la ciudad.5
Ливерпу́ль, также Ливерпул[2] (англ. Liverpool, МФА: [ˈlɪvəpuːl]) — город в Великобритании в графстве Мерсисайд, порт на северо-западном побережье Англии, в устье реки Мерси.
Население — 441 477 человек (2002 год) — пятый по величине город Великобритании (и третий — в Англии). Население Ливерпульской агломерации превышает 800 000 жителей. На протяжении 2-й половины XX века Ливерпуль имел славу депрессивного города: с 1930-х до начала 2000-х годов его население сократилось почти вдвое[3].



Während der Tang-Dynastie galt Lianyungang als Ausgangspunkt einer Handelslinie, die China mit anderen Ländern in Südostasien verband.
江蘇省の東北部にあって黄海に面し、北は山東省日照市、西は徐州市、淮安市、南は淮安市、塩城市に隣接。気候は海流の影響で温暖で、年平均気温は14℃、年間降水量は930mm。全体に海沿いの平坦な土地だが、西部には山地があり、その最高点である南雲台山の玉女峰(標高625m)は江蘇省の最高点でもある。 農業も盛んで、水稲や小麦、綿、大豆、落花生などが生産されている。
連雲港市(れんうんこう-し)は中華人民共和国江蘇省に位置する地級市。全国十大港湾の一つである貿易港を有し、中国に14ある沿海の経済技術開発区の一つでもある。連雲港の古い名は海州であり、春秋時代には呉を滅ぼした越王勾践がこの地を首都とし中原の覇者となった。秦朝以降は江蘇地方の重要港湾都市とされ、清末には税関が設置されている。改革開放政策が発表されてからは中国で最初に指定された14箇所の経済技術開発区の一つになった。
行政区画としては1935年(民国24年)に灌雲県連雲港地区に新設された連雲市を前身とする。1948年(民国37年)には東海県海州、新浦地区を統合し新海連特区と改編された。中華人民共和国が成立すると1949年に新海連市と改称し山東省の管轄とした。その後1952年に江蘇省に移管、1961年に連雲港市と改称され現在に至る。
Lianyungang (simplified Chinese: 连云港; traditional Chinese: 連雲港; pinyin: Liányúngǎng) is a prefecture-level city in northeastern Jiangsu province, China. It borders Yancheng to its southeast, Huai'an and Suqian to its south, Xuzhou to its southwest, and the province of Shandong to its north. Its name derives from Lian Island, the largest island in Jiangsu which lies off its coastline, and Yuntai Mountain, the highest peak in Jiangsu, a few miles from the town center, and the fact that it is a port. The name can be literally translated as the Port Connecting the Clouds.
Lianyungang (连云港 ; pinyin : Liányúngǎng) est une ville du nord-est de la province du Jiangsu en Chine.
Lianyungang (in cinese: 连云港; in pinyin: Liányúngǎng; letteralmente "il porto collegato alle nuvole") è una città della Cina nella provincia dello Jiangsu.
Lianyungang, léase: Lianyún-ka-áng (en chino 连云港市,pinyin: Liányúngǎngshí,literalmente,el puerto conectado a las nubes). Es una ciudad-prefectura en la provincia de Jiangsu, República Popular de China. Limita al norte con Shandong,al sur con Suqian,al oeste con Xuzhou y al este con el Mar de China Oriental. Su nombre deriva de la isla Lian (Isla Dongxilian) la isla más grande de la provincia de Jiangsu que se encuentra frente a sus costas, y de la montaña Yuntai, el pico más alto de la provincia de Jiangsu, a pocos kilómetros del centro de la ciudad.
Lianyungang fue uno de los cuatro puertos originales abiertos para el comercio exterior en la década de 1680 por el Gobierno de la Dinastía Qing. Los otros eran Ningbo, Xiamen y Guangzhou.
Ляньюньга́н (кит. упр. 连云港, пиньинь Liányúngǎng , переводится как «порт (ган) у острова Дунсилянь и горы Юньтай») — городской округ в провинции Цзянсу КНР.
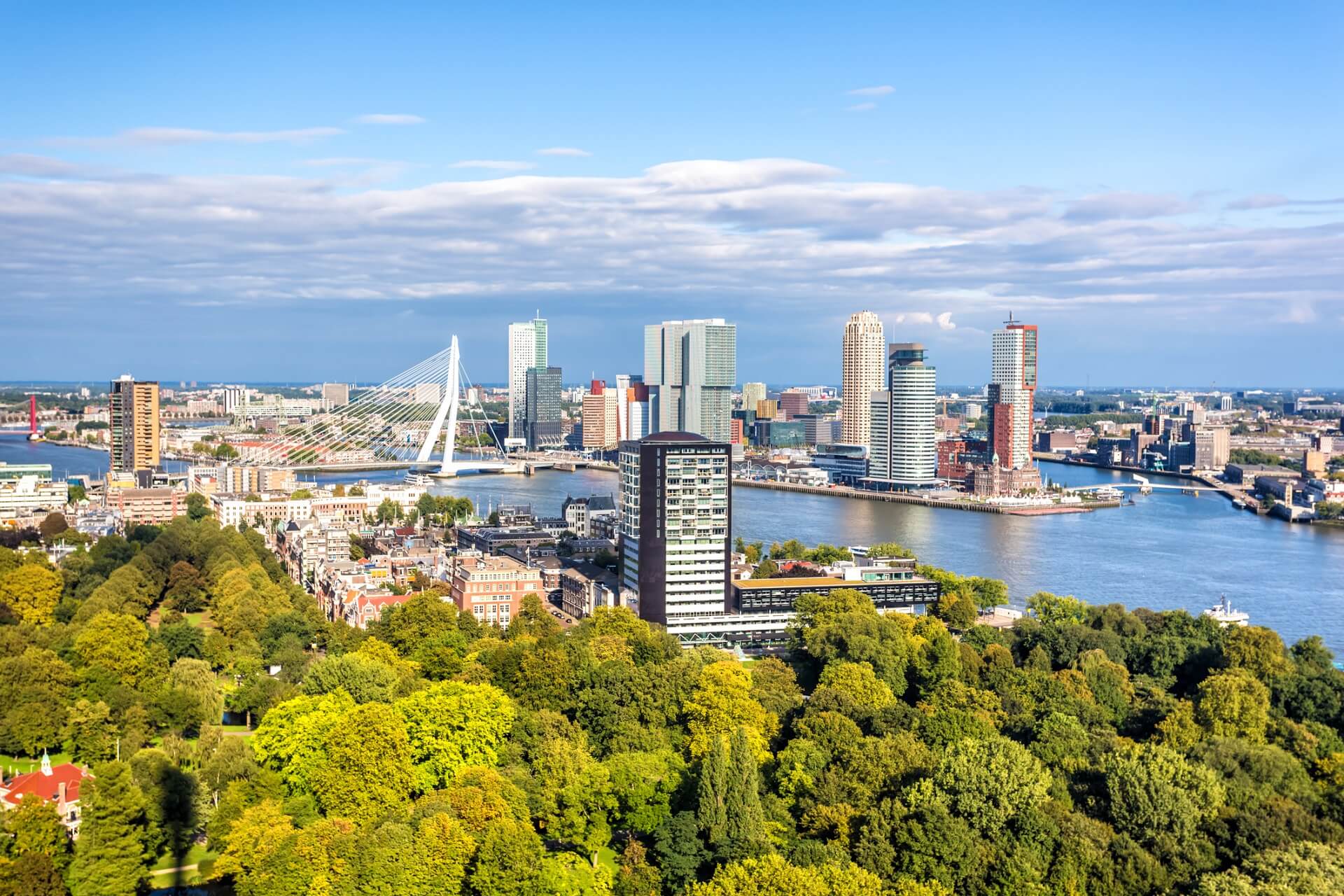

Rotterdam ist mit 635.389 Einwohnern (Stand: 31. August 2017) nach Amsterdam die zweitgrößte Stadt der Niederlande. Sie ist aufgrund des größten Seehafens Europas [2] ein bedeutender Verkehrsknotenpunkt für den Güterverkehr. Neben Amsterdam und Den Haag ist Rotterdam zudem eines der kulturellen Zentren der Niederlande. Rotterdam verfügt über eine traditionsreiche Universität, mehrere Fachhochschulen, eine Musikhochschule und eine Kunstakademie. Sie ist die führende Industrie- und Handelsstadt der Niederlande. Auffällig ist die Rotterdamer Wolkenkratzer-Silhouette, die sich seit Mitte der 1980er-Jahre entwickelt hat.
鹿特丹(荷兰语:Rotterdam 荷兰语读音:[ˌrɔtərˈdɑm] ![]() 聆听)是荷兰南荷兰省的城市,是荷兰第二大城市,位于荷兰的南荷兰省,新马斯河畔。其名称来自于在市中心注入新马斯河的小河鹿特河、以及荷兰语的“坝”(Dam)。鹿特丹长期为欧洲最大的海港,以集装箱运量计算,1980年代曾是世界上第一大港口,在2010年为世界第10。
聆听)是荷兰南荷兰省的城市,是荷兰第二大城市,位于荷兰的南荷兰省,新马斯河畔。其名称来自于在市中心注入新马斯河的小河鹿特河、以及荷兰语的“坝”(Dam)。鹿特丹长期为欧洲最大的海港,以集装箱运量计算,1980年代曾是世界上第一大港口,在2010年为世界第10。
ロッテルダム(オランダ語: Rotterdam [ˌrɔtərˈdɑm] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、オランダの南ホラント州にある基礎自治体(ヘメーンテ)。オランダ語での発音は「ロッタダム」または「ロターダム」と表記する方が近い。
音声ファイル))は、オランダの南ホラント州にある基礎自治体(ヘメーンテ)。オランダ語での発音は「ロッタダム」または「ロターダム」と表記する方が近い。
ロッテルダム港を擁する世界屈指の港湾都市で、人口規模はアムステルダムに次いでオランダ第2位である。世界都市であり、国内の他都市に比べて近代的なビルが立ち並ぶ。
Rotterdam (/ˈrɒtərdæm/, UK also /ˌrɒtərˈdæm/;[8][9] Dutch: [ˌrɔtərˈdɑm] ( listen)) is a city in the Netherlands, in South Holland within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt river delta at the North Sea. Its history goes back to 1270, when a dam was constructed in the Rotte river, after which people settled around it for safety. In 1340, Rotterdam was granted city rights by the Count of Holland.[10]
listen)) is a city in the Netherlands, in South Holland within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt river delta at the North Sea. Its history goes back to 1270, when a dam was constructed in the Rotte river, after which people settled around it for safety. In 1340, Rotterdam was granted city rights by the Count of Holland.[10]
A major logistic and economic centre, Rotterdam is Europe's largest port, and has a population of 633,471 (2017), the second-largest in the Netherlands, just behind Amsterdam.[11]
Rotterdam is known for the Erasmus University, its riverside setting, lively cultural life, and maritime heritage. The near-complete destruction of the city centre in the World War II Rotterdam Blitz has resulted in a varied architectural landscape, including sky-scrapers (an uncommon sight in other Dutch cities) designed by renowned architects such as Rem Koolhaas, Piet Blom, and Ben van Berkel.[12][13]
Rotterdam's logistic success is based on its strategic location by the North Sea, at the mouth of the Nieuwe Maas channel leading into the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. The rivers Rhine, Meuse, and Scheldt give waterway access into the heart of Western Europe, including the highly industrialized Ruhr. The extensive distribution system including rail, roads, and waterways have earned Rotterdam the nicknames "Gateway to Europe" and "Gateway to the World".[14][15][16]
Rotterdam (prononcé en néerlandais /ˌrɔtərˈdɑm/ Écouter) est une commune néerlandaise, située dans la province de Hollande-Méridionale. Au 1er juillet 2017, la commune comptait 634 253 habitants (environ 1 424 000 dans sa région urbaine). Son agglomération fait partie de la conurbation de la Randstad Holland (7 100 000 habitants entre Amsterdam, Haarlem, La Haye, Dordrecht et Utrecht). Ses habitants sont les Rotterdamois.
Deuxième ville des Pays-Bas en nombre d'habitants après Amsterdam, Rotterdam représente le cœur industriel du pays, et sa position géographique, à l'embouchure du Rhin et de la Meuse, à proximité de la mer du Nord, lui assure une place commerciale stratégique dans les échanges européens, notamment avec l'Allemagne.
Huitième port mondial en 2014, et premier port européen, ses infrastructures portuaires s'étendent sur près de 42 kilomètres. La capacité et la modernité de celles-ci lui garantissent un quasi-monopole sur les arrivées d'hydrocarbures, étant le seul port européen, avec Le Havre, en capacité d'accueillir des supertankers transportant jusqu'à 400 000 tonnes de pétrole. Le port est aussi un pôle important pour les matières premières et les conteneurs.
Fondée au XIIe siècle, Rotterdam s'est organisée autour de la digue de la rivière Rotte (qui donne son nom à la ville) et les premiers ports de pêcheurs : le vieux port, Oude Haven et les quais de Haringvliet. Elle reçoit son statut de ville en 1340. Le commerce y fleurit pendant plusieurs siècles, tandis que le port s'étend et que le commerce avec les Indes occidentales et orientales s'accroît. Ville natale du philosophe humaniste Érasme au XVIe siècle et du peintre Pieter de Hooch au XVIIe siècle, elle favorise la vie culturelle et participe au rayonnement néerlandais durant le Siècle d'or. Au XIXe siècle, après une stagnation de son commerce due au blocus continental et à l'inadaptation de son port, la ville grandit à nouveau vers 1870, avec le percement d'une nouvelle voie d'eau qui lui donne un accès direct à la mer du Nord, l'agrandissement de son port et l'industrialisation de ses infrastructures. Des années de récession résultent de la Première Guerre mondiale, suivie de la crise économique de 1929. La guerre de 1939-1945 met un coup d'arrêt à ce développement, le centre de Rotterdam étant totalement détruit par l'armée nazie, lors du bombardement aérien du 14 mai 1940 qui force le pays à capituler. La reconstruction reprend après-guerre, ainsi que l’expansion du port et des industries associées. Après une récession dans les années 1980, due aux chocs pétroliers successifs, la ville diversifie ses activités économiques et commerciales en lien avec l'expansion de son port dans les années 2000. Elle développe son architecture contemporaine, met en valeur ses musées et son art moderne, et augmente ainsi le potentiel touristique de la ville.
Rotterdam a souvent été confrontée à de nombreux défis politiques, économiques, historiques. La maîtrise des eaux et des risques liés aux changements climatiques reste, pour la ville, un enjeu primordial du XXIe siècle.
Rotterdam (AFI: /rotterˈdam/ o /ˈrɔtterdam/[1][2]; in olandese [ˌrɔtərˈdɑm], ascolta[?·info]) è la seconda città dei Paesi Bassi dopo la capitale Amsterdam, situata nella provincia dell'Olanda Meridionale. La città ha il più grande porto d'Europa[3], collocato sulle rive del fiume Nieuwe Maas. Il nome Rotterdam deriva da quello di una diga (dam) su un piccolo fiume, la Rotte, che si unisce alla Nieuwe Maas nel cuore della città.
Róterdam1 (en neerlandés Rotterdam AFI:  [ɾɔtər'dɑm] (?·i)) es una ciudad neerlandesa situada al oeste del país, en la provincia de Holanda Meridional, y puerto sobre el río Mosa, cerca de La Haya. Situada a 30 km del mar, tiene una población de 623 556 habitantes.2 El área metropolitana de Róterdam cuenta con una población de 2,82 millones de personas. La ciudad es conocida por la Universidad Erasmus, su vida cultural y su patrimonio marítimo.
[ɾɔtər'dɑm] (?·i)) es una ciudad neerlandesa situada al oeste del país, en la provincia de Holanda Meridional, y puerto sobre el río Mosa, cerca de La Haya. Situada a 30 km del mar, tiene una población de 623 556 habitantes.2 El área metropolitana de Róterdam cuenta con una población de 2,82 millones de personas. La ciudad es conocida por la Universidad Erasmus, su vida cultural y su patrimonio marítimo.
El puerto de Róterdam, Europoort, es el más grande de Europa y el segundo más grande del mundo. Está comunicado con el río Rin.
Роттерда́м (нидерл. Rotterdam [ˌrɔtərˈdɑm]  слушать) — город и община в Нидерландах. Расположен в провинции Южная Голландия при впадении реки Ньиве-Маас в Северное море. С населением 617 347 жителей (на 1 января 2012)[4] является вторым по количеству жителей городом в Нидерландах после Амстердама. Роттердам входит в состав крупной городской агломерации Рандстад.
слушать) — город и община в Нидерландах. Расположен в провинции Южная Голландия при впадении реки Ньиве-Маас в Северное море. С населением 617 347 жителей (на 1 января 2012)[4] является вторым по количеству жителей городом в Нидерландах после Амстердама. Роттердам входит в состав крупной городской агломерации Рандстад.
Девиз Роттердама — Sterker door strijd («Окреп в борьбе»).
Центр машиностроения. Крупный транспортный узел (железные и шоссейные дороги); морской (на Северном море) и речной (река Ньиве-Маас) порты; аэропорт Роттердам-Гаага. Порт Роттердама является самым большим в Европе, а с 1962 по 2004 года он являлся самым крупным в мире (в настоящий момент он уступил это звание Шанхаю).
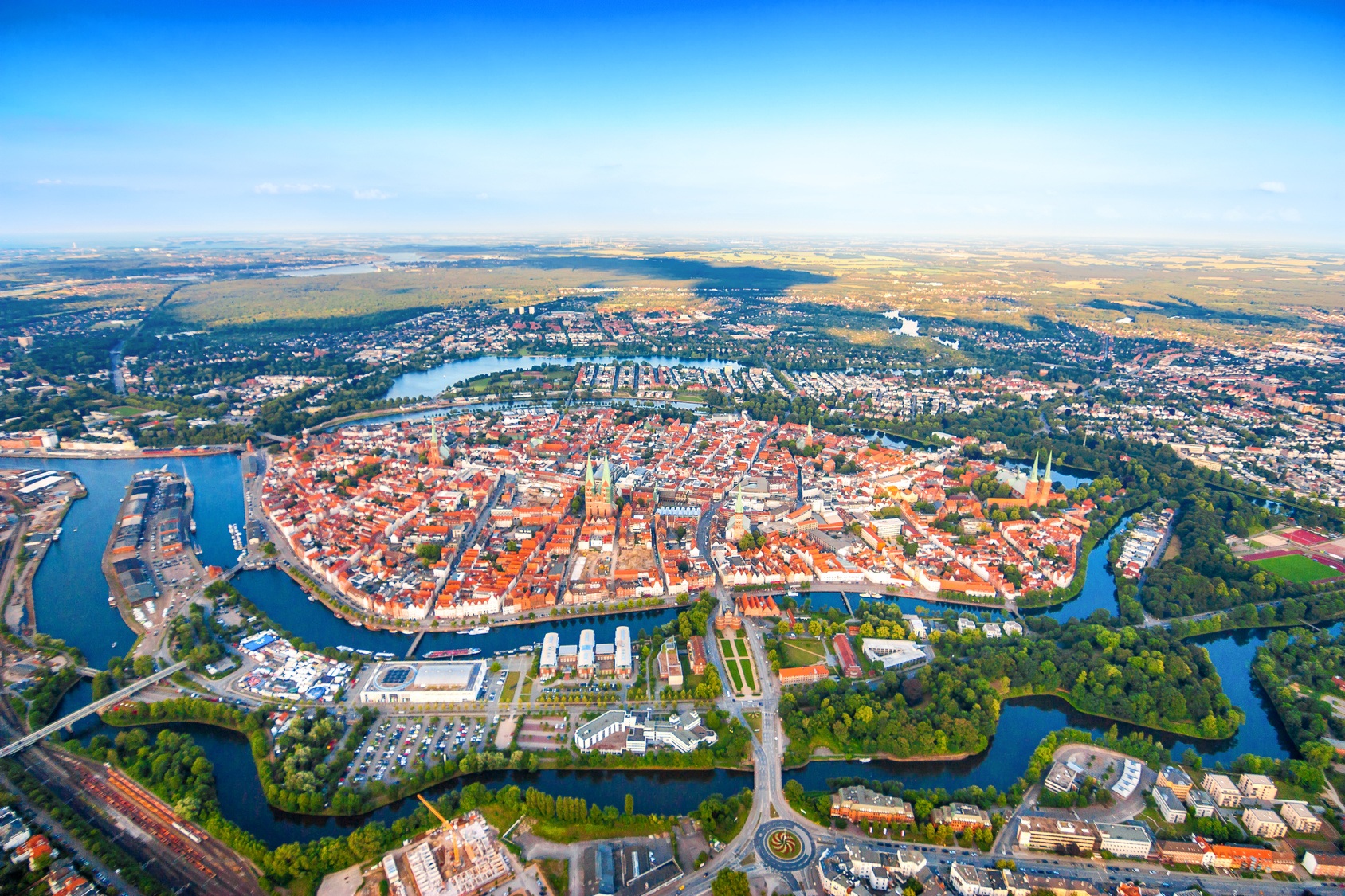

Die Hansestadt Lübeck[2] ( Anhören?/i) (niederdeutsch: Lübęk, Lübeek; Adjektiv: lübsch, lübisch, spätestens seit dem 19. Jahrhundert auch lübeckisch), lateinisch Lubeca, ist eine kreisfreie Großstadt im Norden Deutschlands und im Südosten Schleswig-Holsteins an der Ostsee (Lübecker Bucht). Mit etwa 220.000 Einwohnern[3] ist Lübeck nach der Landeshauptstadt Kiel die Stadt mit den meisten Einwohnern und eines der vier Oberzentren und eine Regiopole des Landes. Lübeck ist mit rund 214 km² die flächenmäßig größte Stadt Schleswig-Holsteins. Die nächstgelegenen großen Städte sind Hamburg etwa 65 Kilometer südwestlich, Kiel etwa 78 Kilometer nordwestlich und Schwerin etwa 68 Kilometer südöstlich. Lübeck gehört der europäischen Metropolregion Hamburg an.
Anhören?/i) (niederdeutsch: Lübęk, Lübeek; Adjektiv: lübsch, lübisch, spätestens seit dem 19. Jahrhundert auch lübeckisch), lateinisch Lubeca, ist eine kreisfreie Großstadt im Norden Deutschlands und im Südosten Schleswig-Holsteins an der Ostsee (Lübecker Bucht). Mit etwa 220.000 Einwohnern[3] ist Lübeck nach der Landeshauptstadt Kiel die Stadt mit den meisten Einwohnern und eines der vier Oberzentren und eine Regiopole des Landes. Lübeck ist mit rund 214 km² die flächenmäßig größte Stadt Schleswig-Holsteins. Die nächstgelegenen großen Städte sind Hamburg etwa 65 Kilometer südwestlich, Kiel etwa 78 Kilometer nordwestlich und Schwerin etwa 68 Kilometer südöstlich. Lübeck gehört der europäischen Metropolregion Hamburg an.
Die Hansestadt erhielt 1160 das Stadtrecht und wird auch „Stadt der Sieben Türme“ und „Tor zum Norden“ genannt. Sie gilt als „Königin“ und „Mutter der Hanse“, einer Handelsvereinigung, die seit dem 12. Jahrhundert bis in die Neuzeit durch Freihandel und friedliche Zusammenarbeit für großen Wohlstand in Lübeck und anderen Mitgliedsstädten sorgte. St. Marien zu Lübeck gilt als eines der Hauptwerke und als „Mutterkirche“ der Backsteingotik, die vom Wendischen Städtebund aus Verbreitung im nordeuropäischen Raum fand. Die mittelalterliche Lübecker Altstadt mit zahlreichen Kulturdenkmalen ist seit 1987 Teil des UNESCO-Welterbes. Lübeck hatte eine seit 1226 bestehende Tradition als Freie Reichsstadt im Heiligen Römischen Reich und als Freie Stadt bzw. Stadtstaat, diese endete im Jahr 1937 mit dem Gesetz über Groß-Hamburg und andere Gebietsbereinigungen.
吕贝克汉萨同盟旧城,文化遗产,1987年列入世界遗产名录。 著名的汉萨联盟的首府,建于12世纪,直到16世纪,一直是北欧的商业中心。现在保存着当时的城市布局和15到16世纪的许多建筑,如城墙、城门、碉堡、贵族住宅、记功碑、教堂以及盐库等。 吕贝克旧城位于德国石勒苏益格-荷尔斯泰因州的吕贝克市,是一座典型的中世纪山地城市。自1143年建城以来,一直是欧洲著名的港口及商业城市,它的影响与汉堡、哥本哈根、不来梅等其他汉莎同盟城市相当。回顾历史,早在819年,此地便建有一座城堡,称为"老吕贝克"。11世纪时,吕贝克改名为"留比斯",意为可爱之城。1143年,荷尔斯泰因伯爵阿道夫二世在"可爱之城"的基础上重建吕贝克,形成了如今旧城的雏形。1159年的一场大火之后,吕贝克城重新布局,其鱼骨状的大街和四通八达的小巷成为日后北欧城市布局的模式。1226年,该城成为自由城邦;1358年,吕贝克成为汉萨同盟的总部所在地,确定了它在欧洲的重要地位。16世纪,随着北欧诸国的逐渐强大,吕贝克失去了往日的辉煌。进入二十世纪后,该城早已风光不在,二战后盟军的空袭摧毁了旧城五分之一的建筑,其中包括著名的教堂和市政厅。战后德国政府努力修缮和保护残存的文物古迹,使得吕贝克旧城依旧成为北欧地区的一座保存良好的中世纪古城。 吕贝克旧城分为三部分,第一部分是旧城东部和北部区域,第二部分是旧城的西南区域,第三部分是圣玛丽教堂及市政厅。 旧城区的东部和北部现已被划为保护区,保持着中世纪的完整格局。这一区建筑的最大特点是将10世纪城市特有的宗教性和世俗性和谐地融为一体。城市上空轮廓由7座高耸的教堂塔楼构成,突出体现了该城特有的风格。它同时又是一座活的建筑博物馆:哥特式、巴洛克式、洛克克式、非经典式,从中世纪到现代的各种建筑风格都有。其中哥特式的圣玛丽教堂、罗马式的大教堂等众多教堂尖顶簇拥在旧城区上空,仿佛是一片教堂的森林。1942年,圣玛丽教堂和圣彼得教堂的尖塔曾在空袭中被毁,1956-1962年间重修。不足的是续建的建筑在结构、造型比例和组合形式上与相邻的原有建筑风格相异,未能与旧城传统形式相统一;但由于续建范围小,故未对整个城市景观造成损害。 旧城北区是中世纪城镇特色的典型代表,而这些特色主要通过当地独特的砖造房子和建筑阶梯形的山花显示出来。中世纪由于对空间需求的增长,建筑结构上出现了内院和背街,临街的房子将内院与大街隔离开来,形成了相对封闭的内向性格,同时也造就了旧城的独特风貌。城东区保存一些手工艺人的朴素住宅,这些住宅大都设有内院,有一定的虚实开阖变化。城内的贵族宅邸则更为讲究,它们结构坚固,设施完备,空间富于变化装饰精巧细致,艺术价值很高。其中颇具特色的有:变化丰富的大厅、古色古香的壁炉、彩绘的木制天花板、房间嵌板细工和拉毛粉饰吊顶,还有花园的侧厅。现在这些建筑都加以保护,精心修补。 旧城的西南区是幽静而略显拘谨的城区,也有一些浪漫的田园风格,吕贝克人将这里称为"画家角"。 在旧城中心的制高点,坐落着圣玛丽教堂和市政厅,这二者相毗邻,成为吕贝克最重要的建筑物,并因其艺术的高贵价值而在欧洲享有盛名。这两座建筑当时曾在整个北欧有广泛影响,以致波罗的海沿岸的大量建筑都纷纷模仿。其中圣玛丽教堂被作为哥特式砖构大教堂的典型;而市政厅则被当作该地区市政厅建筑的样板,具有独特的建筑风格,它的一半是哥特式的,而另一半是丽娜莎挪式。在后来的几个世纪,市政厅一直是远近城市争相效仿的典范。 旧城西侧坐落着荷尔斯坦因大门,这个13世纪建成的古城门一直是吕贝克城的象征。它建于1466-1477年,为晚期哥特式风格。登上城门,可以眺望整个吕贝克旧城。城堡现已成为博物馆,陈列着古代的作战地图、兵器和战船模型。二次大战中,吕贝克的许多古建筑遭到战火毁坏,但荷尔斯坦因门侥幸保存下来。 吕贝克旧城的建筑物组合自然,风格统一,有着动人的城市景观效果,表现了吕贝克城市艺术的高度成就。所以联合国教科文组织将这座包括近千座建筑的汉萨同盟古城列入世界遗产名录。
吕贝克(德语:Lübeck),位于德国北部波罗的海沿岸,是石勒苏益格-荷尔施泰因州第二大城市。历史上曾是汉萨同盟城市之一,也是同盟的“首都”。1987年,“汉萨同盟城市吕贝克”经联合国教科文组织列为世界文化遗产,是欧洲北部第一个入列世界文化遗产的城市。
吕贝克坐落于特拉维河沿岸,是德国在波罗的海最大的港口。旧城部分是被特拉维河和易北河-吕贝克运河围绕起来的一个岛屿。
リューベック(Lübeck)は、ドイツ連邦共和国の都市。シュレースヴィヒ=ホルシュタイン州に属する。トラヴェ川(英語版、ドイツ語版)沿岸、バルト海に面する北ドイツの代表都市。かつてはハンザ同盟の盟主として繁栄を誇った。正式名称をハンザ都市リューベック(Die Hansestadt Lübeck)という。"Lübeck"の発音は、標準ドイツ語ではドイツ語発音: [ˈlyːbɛk] (![]() 音声ファイル)(リューベックに近い)であるのに対し、地元では[ˈlyːbɛːk](リューベークに近い)となる傾向がある。面積214.14平方キロメートル、人口211,713人(2011年)。
音声ファイル)(リューベックに近い)であるのに対し、地元では[ˈlyːbɛːk](リューベークに近い)となる傾向がある。面積214.14平方キロメートル、人口211,713人(2011年)。
1143年、ホルシュタイン伯アドルフ2世によって建設された。一旦火事で荒廃したものの、ザクセンのハインリヒ獅子公によって再建された。1226年に帝国都市となる。北海・バルト海交易で一時期独占的な地位を築いたハンザ同盟の盟主でもあった。リューベック商人は、ノルウェーのベルゲンに商館を築き、ノルウェーの鱈を南に売却して大きな利益をあげた。また、リューネブルクの岩塩をおさえたことで、塩漬け鰊(ニシン)でも独占的な地位を誇った。近世にはいると、ハンザ同盟の衰退とともに、リューベックも衰退していった。
1806年の神聖ローマ帝国解体により主権国家となるが、ナポレオン戦争に巻き込まれ、1811年から1813年までフランス帝国に併合される。ナポレオンの没落にともない1813年に独立を回復するが、1815年にドイツ連邦に参加する。1867年には北ドイツ連邦に参加し、1871年のドイツ帝国成立に伴い、同国の州となる。ヴァイマル共和国時代も州の地位を保ったが、ナチス政権下の1937年にプロイセン州に併合され、同州の属州であるシュレースヴィヒ=ホルシュタインに編入される。
Lübeck (pronounced [ˈlyːbɛk] ( listen)) is a city in Schleswig-Holstein, northern Germany, and one of the major ports of Germany. On the river Trave, it was the leading city of the Hanseatic League, and because of its extensive Brick Gothic architecture, it is listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. In 2015, it had a population of 218,523.
listen)) is a city in Schleswig-Holstein, northern Germany, and one of the major ports of Germany. On the river Trave, it was the leading city of the Hanseatic League, and because of its extensive Brick Gothic architecture, it is listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. In 2015, it had a population of 218,523.
The old part of Lübeck is on an island enclosed by the Trave. The Elbe–Lübeck Canal connects the Trave with the Elbe River. Another important river near the town centre is the Wakenitz. Autobahn 1 connects Lübeck with Hamburg and Denmark. Travemünde is a sea resort and ferry port on the coast of the Baltic Sea. Lübeck Hauptbahnhof links Lübeck to a number of railway lines, notably the line to Hamburg.
Lübeck Écouter est une ville hanséatique d'Allemagne du Nord, dans le Land de Schleswig-Holstein. Avec une population de 212 000 habitants, c'est la deuxième ville du Schleswig-Holstein, après Kiel, la capitale du Land. Son code de plaque d'immatriculation est HL.
Ce port de la mer Baltique est également surnommé « la reine de la Hanse » : c'était en effet la capitale de la Ligue hanséatique.
La ville fait partie de la liste du patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO, notamment pour son architecture de briques rouges.
La Ciudad Hanseática de Lübeck (en alemán: Hansestadt Lübeck  [ˈlyːbɛk] (?·i)), que cuenta con 216 253 habitantes es la segunda ciudad en población del estado federado de Schleswig-Holstein, en el norte de Alemania, después de Kiel. El casco medieval de la ciudad fue nombrado Patrimonio de la Humanidad por la Unesco en el año 1987, destacando las construcciones de ladrillo en estilo gótico báltico como la Puerta de Holsten.1
[ˈlyːbɛk] (?·i)), que cuenta con 216 253 habitantes es la segunda ciudad en población del estado federado de Schleswig-Holstein, en el norte de Alemania, después de Kiel. El casco medieval de la ciudad fue nombrado Patrimonio de la Humanidad por la Unesco en el año 1987, destacando las construcciones de ladrillo en estilo gótico báltico como la Puerta de Holsten.1
La ciudad está dividida en diez municipios y 35 distritos. El municipio del Centro (Innenstadt) está localizado en una isla fluvial rodeada por los ríos Trave y Wakenitz. El municipio de Travemünde, a diecisiete kilómetros del centro, está a las orillas del mar Báltico y es un popular balneario y puerto en la desembocadura del río Trave.
Hamburgo se encuentra a unos 58 km al suroeste y Kiel, la capital de Schleswig-Holstein, a 62 km al noroeste. La autopista Autobahn 1 conecta a Lübeck con Hamburgo y Dinamarca.
Lübeck fue varios siglos la "capital" de la liga Hanseática y conocida como la "Reina de la Hansa". Actualmente es también conocida como "La ciudad de las siete torres" (Stadt der Sieben Türme) y como la "Puerta hacia el norte" (Tor zum Norden).
Лю́бек (нем. Lübeck [ˈlyːbɛk]) — город на севере Германии (юго-восток земли Шлезвиг-Гольштейн). Порт на Балтийском море вблизи устья реки Траве. В истории известен как крупнейший центр Ганзейского союза; основные достопримечательности включены в список объектов Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО в Германии. Население — ок. 220 тыс. человек[6] (данные на январь 2017 г.; в 1992 г. было 216 тыс.).

 建筑艺术
建筑艺术
 英格兰
英格兰
 欧洲流行歌曲大赛
欧洲流行歌曲大赛

 财政金融
财政金融
 ***全球金融中心
***全球金融中心
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020

 历史
历史
 公元 2000 - 2100
公元 2000 - 2100

 历史
历史
 公元 1500 - 2000
公元 1500 - 2000

 国际城市
国际城市
 ***全球城市经济竞争力
***全球城市经济竞争力
 国际铁人三项联盟冠军系列赛
国际铁人三项联盟冠军系列赛
 欧洲中世纪城市
欧洲中世纪城市
 夏季奥林匹克运动会
夏季奥林匹克运动会
 1908夏季奥林匹克运动会
1908夏季奥林匹克运动会
 1944夏季奥林匹克运动会
1944夏季奥林匹克运动会
 1948夏季奥林匹克运动会
1948夏季奥林匹克运动会
 2012夏季奥林匹克运动会
2012夏季奥林匹克运动会
 丝绸之路
丝绸之路

 体育
体育
 铁人三项
铁人三项
 英国
英国

 罗马人建立的城市
罗马人建立的城市

 文化遗产
文化遗产

 重要港口
重要港口
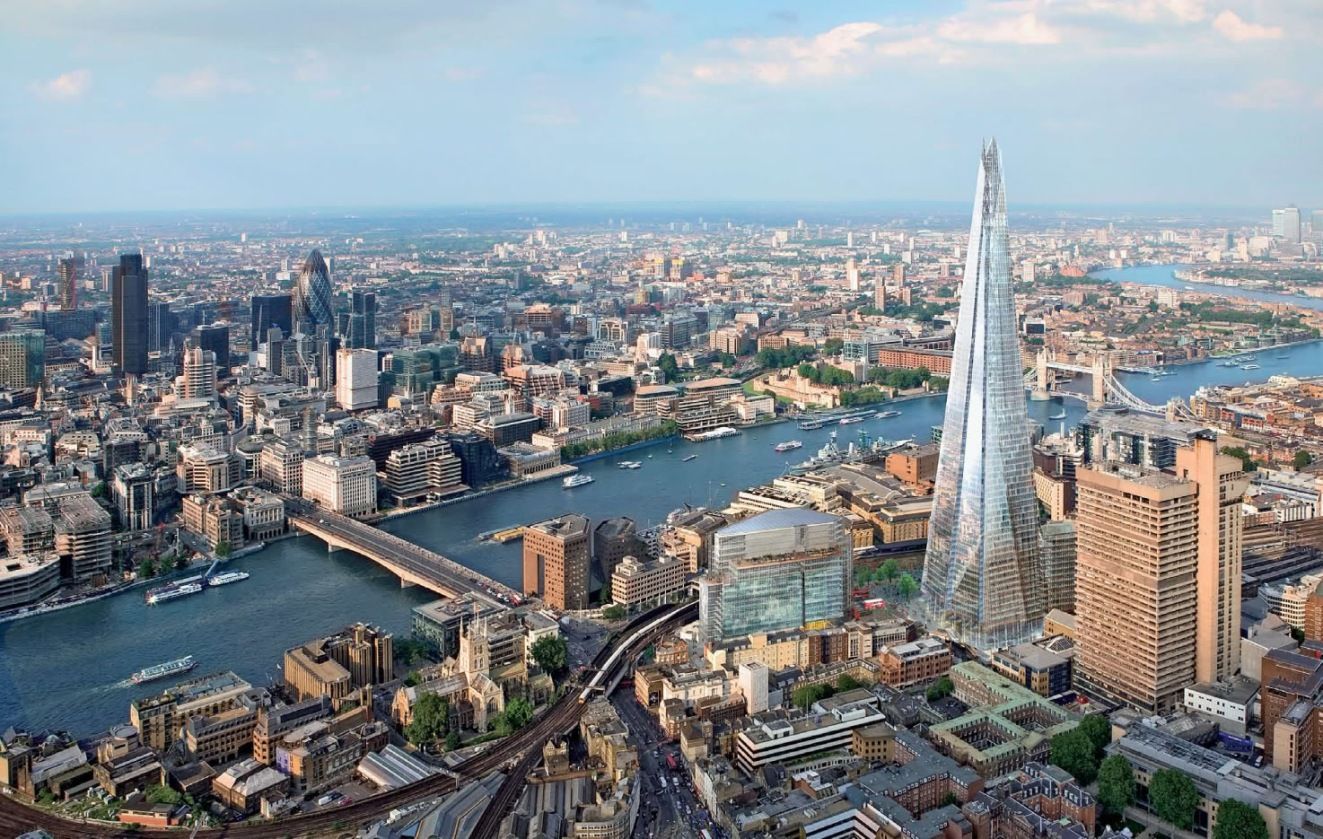


London (deutsche Aussprache [ˈlɔndɔn] oder gelegentlich [ˈlɔndən], englische Aussprache [ˈlʌndən]) ist zugleich die Hauptstadt des Vereinigten Königreiches und Englands. Die Stadt liegt an der Themse in Südostengland. Das heutige Verwaltungsgebiet mit 33 Stadtbezirken entstand im Jahr 1965 durch die Gründung von Greater London. Dort lebten 2022 rund 8,9 Millionen Menschen, davon rund 3,4 Millionen in den 13 Stadtbezirken Inner Londons.[2][4] In der gesamten Metropolregion London lebten 2019 knapp 14,4 Millionen Einwohner.[5]
Im Jahr 50 n. Chr. von den Römern als Londinium gegründet, wurde die Stadt nach der normannischen Eroberung 1066 Hauptstadt und Königssitz des Königreiches England. Bereits im Mittelalter entwickelte sich die Stadt zu einem bedeutenden internationalen Handelsplatz. Unter der Herrschaft von Elisabeth I. stieg ihre Bedeutung als Hafenstadt der Nordsee. Durch den Beginn der Industrialisierung im 18. Jahrhundert wuchs auch die Bevölkerung Londons, sodass es um 1800 eine der ersten Städte war, die mehr als eine Million Einwohner zählte. Bis 1900 versechsfachte sich die Bevölkerung, und London war bis zum Jahr 1925 die größte Stadt der Welt. Es entwickelte sich zu einem bedeutenden Zentrum der Technik und Industrie und wird bis heute zu den Weltstädten gerechnet.
London ist eines der bedeutendsten Kultur- und Handelszentren der Welt mit zahlreichen Universitäten, Hochschulen, Theatern und Museen. Mit einem BIP von 801,66 Mrd. € im Jahr 2017 ist London die größte städtische Wirtschaft Europas.[6] Die Stadt zählt außerdem neben New York City, Singapur und Hongkong zu den größten Finanzplätzen der Welt.[7] Historische Gebäude wie der Palace of Westminster oder Tower of London zählen zum UNESCO-Weltkulturerbe. Mit jährlich über 19 Millionen Touristen aus dem Ausland war London im Jahr 2016 nach Bangkok weltweit die zweitmeistbesuchte Stadt vor Paris.[8][9]
伦敦(英语:London;![]() i/ˈlʌndən/)[4]是英国首都,也是英国最大城市[5]以及其构成国英格兰的首府。位于泰晤士河流域,于公元50年由罗马人建立,取名为伦蒂尼恩,在此后两个世纪内为这一地区最重要的定居点之一[6]。伦敦的历史核心区——伦敦城仍旧维持其中世纪的界限,面积606.95平方英里(1,572.0平方千米),2019年人口为898.2万,为全英格兰最大的城市。自19世纪起,“伦敦”一称亦用于指称围绕这一核心区开发的周围地带[7]。这一城区集合自1965年起构成大伦敦行政区,由32个伦敦自治市加上伦敦城组成[8][9],由伦敦市长及伦敦议会管辖。[10][注 1]
i/ˈlʌndən/)[4]是英国首都,也是英国最大城市[5]以及其构成国英格兰的首府。位于泰晤士河流域,于公元50年由罗马人建立,取名为伦蒂尼恩,在此后两个世纪内为这一地区最重要的定居点之一[6]。伦敦的历史核心区——伦敦城仍旧维持其中世纪的界限,面积606.95平方英里(1,572.0平方千米),2019年人口为898.2万,为全英格兰最大的城市。自19世纪起,“伦敦”一称亦用于指称围绕这一核心区开发的周围地带[7]。这一城区集合自1965年起构成大伦敦行政区,由32个伦敦自治市加上伦敦城组成[8][9],由伦敦市长及伦敦议会管辖。[10][注 1]
伦敦亦是一个全球城市[11][12],[13]在文艺、商业、教育、娱乐、时尚、金融、健康、媒体、专业服务、研究与开发、旅游和交通方面都具有显著的地位[14][15][16][17],同时还是全球主要金融中心之一[18][19][20],根据计算,为全球国内生产总值第六大的都市区[注 2][21][22]。伦敦亦是全球文化首都之一[23][24][25][26],还是全球国际访客数量最多的城市[27],根据客流量计算则拥有全球最为繁忙的城市机场系统[28]。伦敦是全球领先投资地[29],吸引很多国际零售商来投资[30],个人净资产值高于其它城市[31]。伦敦拥有43所大学,其高等教育机构密集度在全欧洲最高[32]。2012年,伦敦成为史上首座三次举办现代夏季奥林匹克运动会的城市。[33]
伦敦的人口和文化十分多样,在大伦敦地区内使用的语言就超过300种[34]。这一区域2015年的官方统计人口为8,673,713[35],人口占全英国的12.5%[36]。在2020年英国脱离欧盟之前,伦敦的城市区为欧盟第二大,根据2011年普查其人口达到9,787,426,仅次于巴黎[37]。其都市区为欧洲最大,人口达13,614,409[注 3][38],而大伦敦政府则称伦敦都市区的总人口为2,100万[39]。1831年—1925年间,伦敦为世界最大的城市。[40]
有四项世界遗产位于伦敦,分别为:伦敦塔;邱园;威斯敏斯特宫、威斯敏斯特教堂和圣玛格丽特教堂;以及格林尼治历史区(其中的皇家天文台为本初子午线、0°经线和格林尼治标准时间所经之地)[41]。其他著名景点包括白金汉宫、伦敦眼、皮卡迪利圆环、圣保罗座堂、伦敦塔桥、特拉法加广场和碎片大厦。伦敦亦是诸多博物馆、画廊、图书馆、体育运动及其他文化机构的所在地,包括大英博物馆、国家美术馆、泰特现代艺术馆、大英图书馆以及40家西区剧院[42]。伦敦地铁是全球最古老的地下铁路网络。
ロンドン(英語: London [ˈlʌndən] (![]() 音声ファイル))はグレートブリテンおよび北アイルランド連合王国およびこれを構成するイングランドの首都。イギリスやヨーロッパ域内で最大の都市圏を形成している。ロンドンはテムズ川河畔に位置し、2,000年前のローマ帝国によるロンディニウム創建が都市の起源である[4]。ロンディニウム当時の街の中心部は、現在のシティ・オブ・ロンドン(シティ)に当たる地域にあった。シティの市街壁内の面積は約1平方マイルあり、中世以来その範囲はほぼ変わっていない。少なくとも19世紀以降、「ロンドン」の名称はシティの市街壁を越えて開発が進んだシティ周辺地域をも含めて用いられている[5]。ロンドンは市街地の大部分はコナベーションにより形成されている[6]。ロンドンを管轄するリージョンであるグレーター・ロンドンでは[7]、選挙で選出されたロンドン市長とロンドン議会により統治が行われている[8]。
音声ファイル))はグレートブリテンおよび北アイルランド連合王国およびこれを構成するイングランドの首都。イギリスやヨーロッパ域内で最大の都市圏を形成している。ロンドンはテムズ川河畔に位置し、2,000年前のローマ帝国によるロンディニウム創建が都市の起源である[4]。ロンディニウム当時の街の中心部は、現在のシティ・オブ・ロンドン(シティ)に当たる地域にあった。シティの市街壁内の面積は約1平方マイルあり、中世以来その範囲はほぼ変わっていない。少なくとも19世紀以降、「ロンドン」の名称はシティの市街壁を越えて開発が進んだシティ周辺地域をも含めて用いられている[5]。ロンドンは市街地の大部分はコナベーションにより形成されている[6]。ロンドンを管轄するリージョンであるグレーター・ロンドンでは[7]、選挙で選出されたロンドン市長とロンドン議会により統治が行われている[8]。
ロンドンは屈指の世界都市として、芸術、商業、教育、娯楽、ファッション、金融、ヘルスケア、メディア、専門サービス、調査開発、観光、交通といった広範囲にわたる分野において強い影響力がある[9]。また、ニューヨークと並び世界をリードする金融センターでもあり[10][11][12]、2009年時点の域内総生産は世界第5位で、欧州域内では最大である[13]。世界的な文化の中心でもある[14][15][16][17]。ロンドンは世界で最も来訪者の多い都市であり[18]、単一の都市圏としては世界で最も航空旅客数が多い[19]。欧州では最も高等教育機関が集積する都市であり、ロンドンには大学が43校ある[20]。2012年のロンドンオリンピック開催に伴い、1908年、1948年に次ぐ3度目のオリンピック開催となり、同一都市としては史上最多となる[21]。
ロンドンは文化的な多様性があり、300以上の言語が使われている[22]。2011年3月時点のロンドンの公式の人口は817万4,100人であり、欧州の市域人口では最大で[23][24]、イギリス国内の全人口の12.7%を占めている[25]。グレーター・ロンドンの都市的地域は、パリの都市的地域に次いで欧州域内で第2位となる8,278,251人の人口を有し[26]、ロンドンの都市圏の人口は1200万人[27]から1400万人[28]に達し、欧州域内では最大である。ロンドンは1831年から1925年にかけて、世界最大の人口を擁する都市であった[29]。2012年にマスターカードが公表した統計によると、ロンドンは世界で最も外国人旅行者が訪れる都市である[30]。
イギリスの首都とされているが、他国の多くの首都と同様、ロンドンの首都としての地位を明示した文書は存在しない[31]。
London (/ˈlʌndən/ ( listen) LUN-dən) is the capital and most populous city of England and the United Kingdom.[8][9] Standing on the River Thames in the south east of the island of Great Britain, London has been a major settlement for two millennia. It was founded by the Romans, who named it Londinium.[10] London's ancient core, the City of London, largely retains its 1.12-square-mile (2.9 km2) medieval boundaries. Since at least the 19th century, "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent and Hertfordshire,[11][12][13] which today largely makes up Greater London,[14][15][note 1] a region governed by the Mayor of London and the London Assembly.[16][note 2][17]
listen) LUN-dən) is the capital and most populous city of England and the United Kingdom.[8][9] Standing on the River Thames in the south east of the island of Great Britain, London has been a major settlement for two millennia. It was founded by the Romans, who named it Londinium.[10] London's ancient core, the City of London, largely retains its 1.12-square-mile (2.9 km2) medieval boundaries. Since at least the 19th century, "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent and Hertfordshire,[11][12][13] which today largely makes up Greater London,[14][15][note 1] a region governed by the Mayor of London and the London Assembly.[16][note 2][17]
London is one of the leading global cities[18][19] in the arts, commerce, education, entertainment, fashion, finance, healthcare, media, professional services, research and development, tourism and transportation.[20][21][22] It is the world's largest financial centre[23][24][25][26] and has the fifth or sixth largest metropolitan area GDP in the world.[note 3][27][28] London is often regarded as a world cultural capital.[29][30][31] It is the world's most-visited city as measured by international arrivals[32] and has the world's largest city airport system measured by passenger traffic.[33] It is the world's leading investment destination,[34][35][36][37] hosting more international retailers[38][39] and ultra high-net-worth individuals[40][41] than any other city. London's universities form the largest concentration of higher education institutes in Europe.[42] In 2012, London became the first city to have hosted the modern Summer Olympic Games three times.[43]
London has a diverse range of people and cultures, and more than 300 languages are spoken in the region.[44] Its estimated mid-2016 municipal population (corresponding to Greater London) was 8,787,892,[4] the largest of any city in the European Union[45] and accounting for 13.4% of the UK population.[46] London's urban area is the second most populous in the EU, after Paris, with 9,787,426 inhabitants at the 2011 census.[47] The city's metropolitan area is the most populous in the EU with 14,040,163 inhabitants in 2016,[note 4][3] while the Greater London Authority states the population of the city-region (covering a large part of the south east) as 22.7 million.[48][49] London was the world's most populous city from around 1831 to 1925.[50]
London contains four World Heritage Sites: the Tower of London; Kew Gardens; the site comprising the Palace of Westminster, Westminster Abbey, and St Margaret's Church; and the historic settlement of Greenwich (in which the Royal Observatory, Greenwich defines the Prime Meridian, 0° longitude, and GMT).[51] Other landmarks include Buckingham Palace, the London Eye, Piccadilly Circus, St Paul's Cathedral, Tower Bridge, Trafalgar Square and The Shard. London is home to numerous museums, galleries, libraries, sporting events and other cultural institutions, including the British Museum, National Gallery, Natural History Museum, Tate Modern, British Library and West End theatres.[52] The London Underground is the oldest underground railway network in the world.
Londres (prononcé [lɔ̃dʁ] ; en anglais London [ˈlʌn.dən]), située dans le Sud-Est de la Grande-Bretagne, est la capitale et la plus grande ville de l'Angleterre et du Royaume-Uni. Longtemps capitale de l'Empire britannique, elle est désormais le siège du Commonwealth of Nations.
Fondée il y a presque 2 000 ans par les Romains sous le nom de Londinium, Londres était au XIXe siècle la ville la plus peuplée du monde. Bien que largement dépassée dans ce domaine par de nombreuses mégapoles, elle reste une métropole de tout premier plan1, en raison de son rayonnement et de sa puissance économique, dû notamment à sa place de premier centre financier mondial2. Londres se place dans la triade des grands centres financiers du monde, avec New York et Hong Kong, en étant la principale place bancaire et financière d'Europe. Cette trilogie est appelée par les médias anglophones « Nylonkong »3.
La région de Londres, composée de l'Inner London et de l'Outer London, comptait environ 8 673 000 habitants en 2015 et réalise un cinquième du produit intérieur brut du Royaume-Uni4. En 2015, l'aire urbaine de Londres comptait 9 787 426 habitants et son aire métropolitaine 12 317 800 habitants. En Europe, seules les agglomérations de Moscou, Istanbul et Paris5 ont un poids démographique comparable. Ses habitants s'appellent les Londoniens (en anglais : Londoners).
Londres, la seule ville du monde à ce jour à avoir organisé trois fois les Jeux olympiques (1908, 1948, 2012), est dynamique et très diverse sur le plan culturel. Elle joue un rôle important dans l'art et dans la mode. Elle reçoit 28 millions de touristes par an et compte quatre sites inscrits au patrimoine mondial ainsi que de nombreux monuments emblématiques : le palais de Westminster, le Tower Bridge, la tour de Londres, l'abbaye de Westminster, le palais de Buckingham, Big Ben ainsi que des institutions renommées comme le British Museum ou la National Gallery.
Londra (AFI: [ˈlondra];[2] in inglese britannico: London, [ˈlʌndən][3]) è la capitale e maggiore città dell'Inghilterra e del Regno Unito, con i suoi 8 825 000 abitanti.
La sua estensione territoriale la rende la terza città più estesa d'Europa, preceduta da Mosca e Istanbul e seguita da Roma e Berlino. L'area metropolitana conta infatti circa 14 milioni di residenti e si estende per svariate decine di chilometri lungo la valle del Tamigi, fino al suo enorme estuario. Molti degli abitanti, chiamati londinesi (Londoners), provengono dall'estero o sono di origine straniera, risultando così una delle città più cosmopolite e multietniche del mondo. Londra è stata la capitale indiscussa dell'Impero britannico e, quindi, meta di flussi migratori durante e soprattutto dopo la fine dell'era coloniale.
Ha il più elevato PIL fra tutte le città europee, ed il quinto al mondo.[4] I suoi sei aeroporti internazionali ne fanno il più grande snodo del traffico aereo globale; è anche sede del più antico sistema di metropolitana del mondo, la London Underground (The Tube). È la seconda città più visitata al mondo dal turismo internazionale, dopo Bangkok in Asia.[5]
A Londra hanno sede numerose istituzioni, organizzazioni e società internazionali. Vi si trovano importanti musei, teatri e sale da concerto; la città contiene quattro patrimoni dell'umanità. Inoltre, vi risiede stabilmente il monarca del Regno Unito presso Buckingham Palace ed il parlamento; il primo ministro occupa l'abitazione al 10 Downing Street. Per tutte le caratteristiche elencate, Londra conquista il titolo di Città globale, classificandosi come l'unica città britannica nella lista delle Città Mondiali Alfa[6].
Dal 2000, con le riforme volute dal governo di Tony Blair, Londra è amministrata secondo una speciale legislazione sui generis[7] che determina e coordina i poteri della superiore Autorità della Grande Londra, composta dal Sindaco e dall'Assemblea di Londra, con quelli di 33 borghi londinesi a livello inferiore.[8
Londres (London en inglés,  ˈlʌndən (?·i)) es la capital y mayor ciudad de Inglaterra y del Reino Unido.23 Situada a orillas del río Támesis, Londres es un importante asentamiento humano desde que fue fundada por los romanos con el nombre de Londinium hace casi dos milenios.4 El núcleo antiguo de la urbe, la City de Londres, conserva básicamente su perímetro medieval de una milla cuadrada. Desde el siglo XIX el nombre «Londres» también hace referencia a toda la metrópolis desarrollada alrededor de este núcleo.5 El grueso de esta
ˈlʌndən (?·i)) es la capital y mayor ciudad de Inglaterra y del Reino Unido.23 Situada a orillas del río Támesis, Londres es un importante asentamiento humano desde que fue fundada por los romanos con el nombre de Londinium hace casi dos milenios.4 El núcleo antiguo de la urbe, la City de Londres, conserva básicamente su perímetro medieval de una milla cuadrada. Desde el siglo XIX el nombre «Londres» también hace referencia a toda la metrópolis desarrollada alrededor de este núcleo.5 El grueso de esta
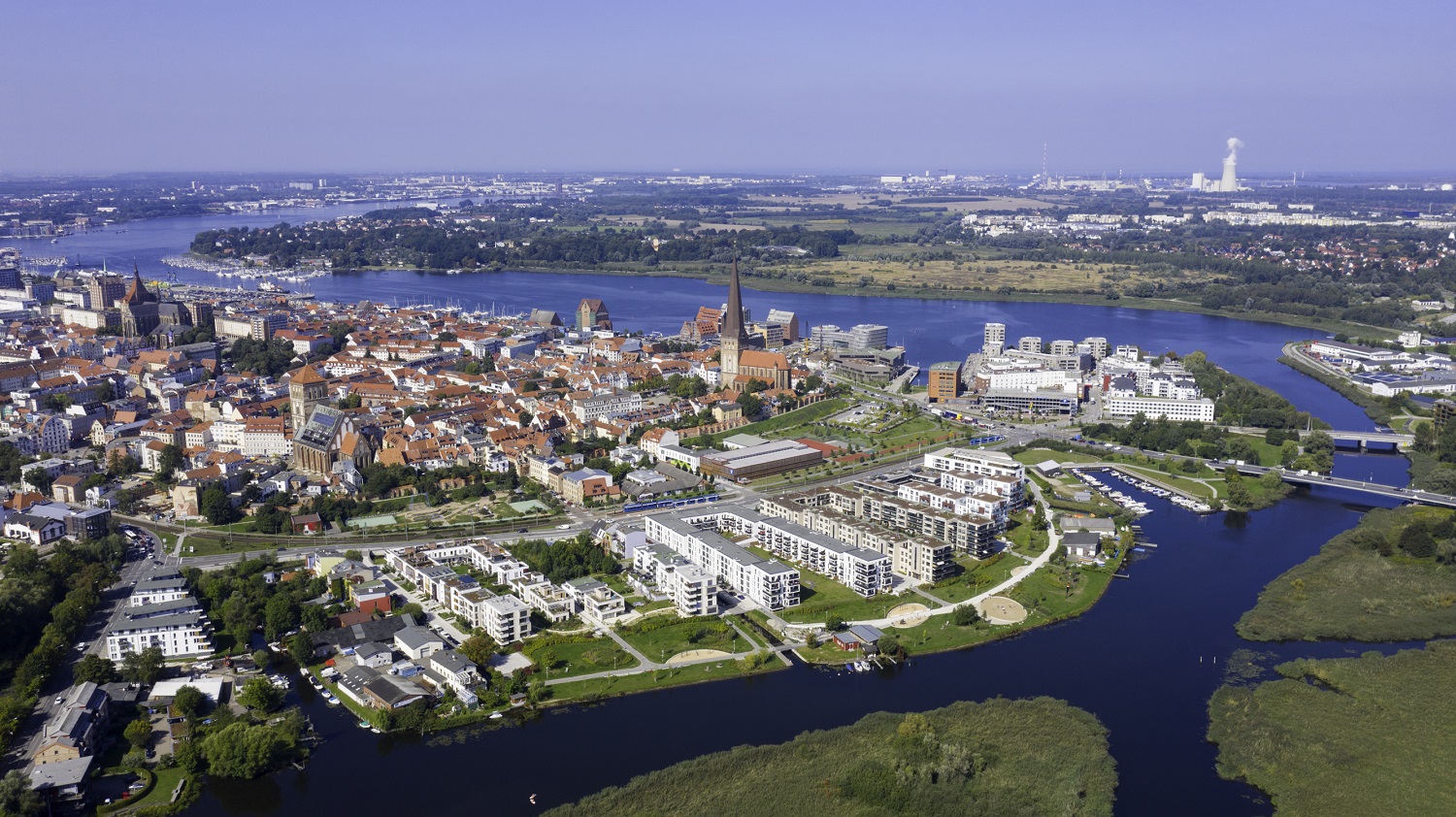
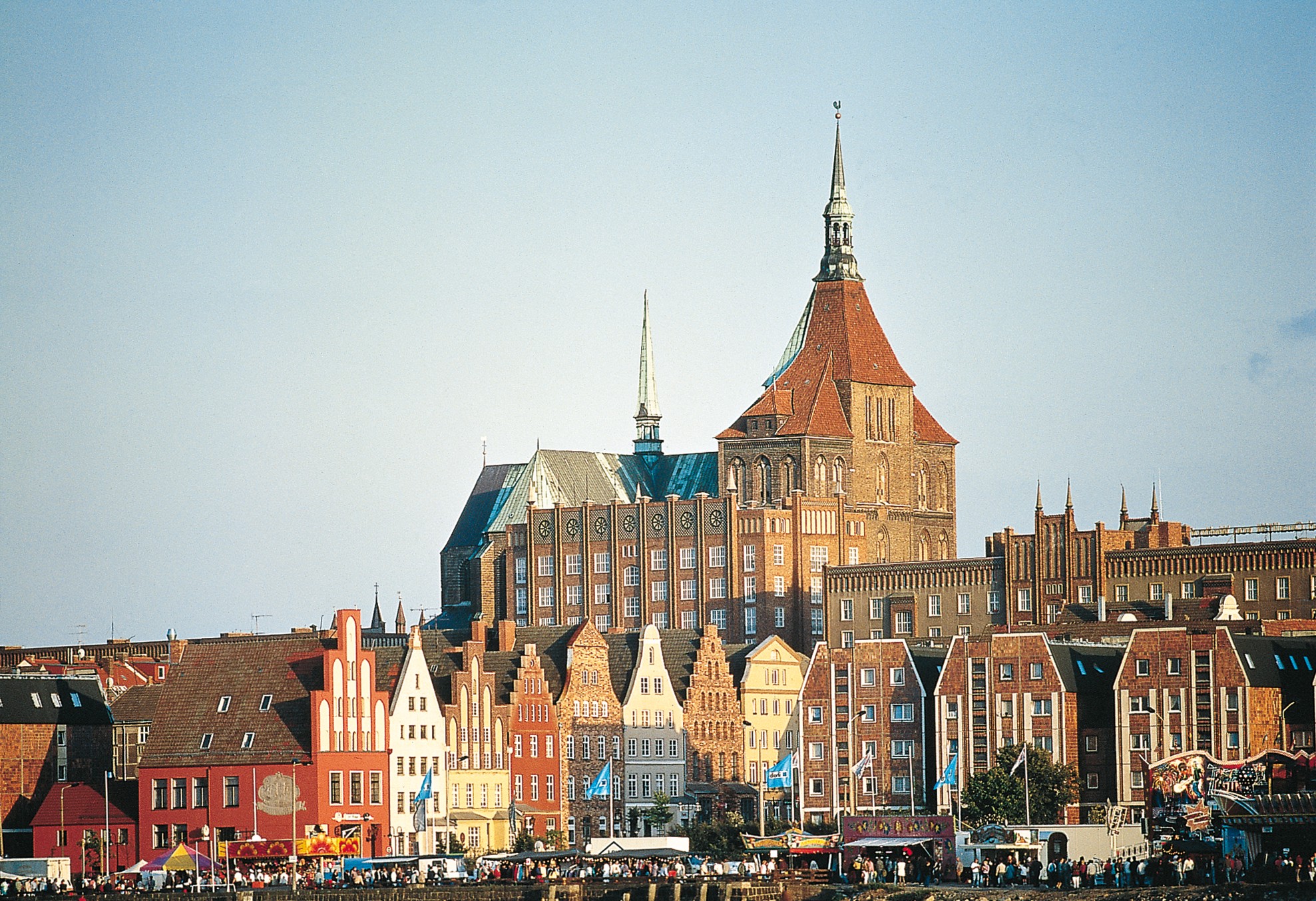


Rostock ([ˈʁɔstɔk]) ist eine norddeutsche kreisfreie Groß-, Universitäts- und Hansestadt an der Ostsee. Sie liegt im Landesteil Mecklenburg des Landes Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Mit 208.409 Einwohnern[2] ist sie die bevölkerungsreichste Stadt Mecklenburg-Vorpommerns und war neben Schwerin stets das wirtschaftlich-kulturelle urbane Zentrum in der Region Mecklenburg-Schwerin. Die Regiopole ist neben Schwerin, Neubrandenburg und Stralsund-Greifswald eines der vier Oberzentren des Landes und gilt kulturell wie wirtschaftlich als bedeutende Großstadt des südlichen Ostseeraumes.
Das Stadtgebiet erstreckt sich rund 16 Kilometer vor allem am Westufer der Warnow bis zu deren Mündung in die Ostsee zwischen den Stadtteilen Warnemünde und Hohe Düne. Geprägt wird Rostock durch seine Lage am Meer, seinen Hafen sowie die Universität Rostock, die 1419 gegründet wurde und die älteste Universität im Ostseeraum ist. Weitere akademische Einrichtungen Rostocks sind die Hochschule für Musik und Theater, die private Fachhochschule des Mittelstands und moderne Forschungseinrichtungen.
Der für den Fährverkehr und Güterumschlag bedeutende Rostocker Hafen sowie der größte deutsche Kreuzfahrthafen in Warnemünde liegen im Bereich der Stadt Rostock. Der südöstlich der Stadt gelegene Flughafen Rostock-Laage ist als Zubringer für Kreuzfahrten sowie für Urlaubs- und Geschäftsflüge von regionaler Bedeutung. Im Wirtschaftszentrum des Mittleren Mecklenburgs dominieren die Spitzentechnologien wie Luft- und Raumfahrttechnik, Biotechnologie und Informationstechnologie, Schiffbau und Schifffahrt, Maschinenbau, der Tourismus, der Dienstleistungssektor, die Kultur- und Kreativwirtschaft und die Universität samt der Universitätsmedizin als größte Arbeitgeber der Stadt. Innovative Startup-Unternehmen und die Gründerkultur Rostocks sind besonders dynamische Bestandteile des Standortes.[3]
Rostock erhielt am 24. Juni 1218 das Lübische Stadtrecht. Neun Jahre später wurde die Stadt zum Zentrum der bis 1327 bestehenden Herrschaft Rostock. Als ab 1283 wendisches Mitglied der Hanse blühte die Stadt durch den Freihandel auf. Aus jener Zeit sind wertvolle Werke der Backsteingotik erhalten. Viele weitere Baudenkmale in Rostock zeugen von der geschichtlichen Entwicklung der Stadt. Durch den Niedergang der Hanse, den Dreißigjährigen Krieg und den Großen Stadtbrand von 1677 wurde Rostock zurückgeworfen und die Einwohnerzahl verringerte sich auf ein Drittel, wovon sich die Stadt erst mit der Industrialisierung im 19. Jahrhundert vollständig erholen konnte.
Rostock gehörte bis 1918 zum Großherzogtum und dann zum Freistaat Mecklenburg-Schwerin. Mit der Gründung der Flugzeugwerke Arado 1921 und Heinkel 1922 wurde Rostock ein bedeutender deutscher Technologiestandort, was die Stadt in den 1940er Jahren zu einem Ziel des Luftkriegs im Zweiten Weltkrieg machte. In der DDR-Zeit war Rostock von 1952 bis 1990 DDR-Bezirksstadt und wurde systematisch durch neue Stadtgebiete erweitert, bis es auf über 250.000 Einwohner anwuchs. In dieser Zeit dominierte die maritime Wirtschaft. Seitdem hat sich die Rostocker Wirtschaft erheblich verändert und die 1991 begründete Hanse Sail in Rostock zu einer der großen maritimen Veranstaltungen im Ostseeraum entwickelt. Im Jahr 2018 feierte die Stadt das Doppeljubiläum 800 Jahre Rostock und 600 Jahre Universität mit vielen Veranstaltungen, darunter dem MV-Tag.[4] Anlässlich dieses Jubiläums gab die Deutsche Post AG ein Postwertzeichen im Nennwert von 70 Eurocent heraus. Der Entwurf stammt vom Grafiker Matthias Wittig aus Berlin.
罗斯托克(Rostock)有着八百年的历史,保留了很多古老的传统魅力,它与海滨浴场瓦尔内明德(Warnemünde)一起,向人们展现出多样化的文化氛围。海洋赋予了罗斯托克以独特的魅力,使它成为生机勃勃、胸襟开阔的港口和大学城。老城区的砖砌建筑是本地的一大特色。罗斯托克还有引人入胜的Warnemünde海滨浴场。
罗斯托克最重要的两座教堂位于市中心:圣玛利亚教堂(St. Marien)拥有一座1472年制造的天文钟,而从圣彼得利教堂(St. Petri-Kirche)的钟楼可以眺望老城和港口。在新集市广场(Neuer Markt)上矗立着老市政厅,而罗斯托克大学的主楼(Universitätshauptgebäude)就位于步行区。
老城的哥特式砖砌建筑
除了华丽的教堂外,哥特式、文艺复兴以及巴洛克风格的山墙向街的房子彰现着中世纪商人的富有;天文钟吸引着游客们前往哥特式大教堂圣玛利亚教堂(St. Marien);几步开外就是巴洛克风格的门廊突出的市政厅(Rathaus)。
老市政厅
老市政厅(Historisches Rathaus)在中世纪时是一座百货商店,商人们在那里出售他们的货物。二楼顶层的巴洛克风格的宴会大厅(Festsaal)则用于音乐会演出。近八百年来,这座市政厅一直是政府办公的地方。
瓦尔内明德海滨浴场
瓦尔内明德海滨浴场(Seebad Warnemünde)100米宽的沙滩和海边林荫道、灯塔、鱼市、渔民们住的漂亮小房子、味道独特的海鲜馆、航行在旧港口航道(Alten Strom)上的捕鱼船和帆船,这一切都带给人们真正的海滨生活感受。(Quelle:www.tctd.net)
汉萨城市罗斯托克(德语:Hansestadt Rostock)位于德国北部,人口接近二十万,是梅克伦堡-前波美拉尼亚州最大的城市。瓦尔诺河(Warnow)流经市区,在瓦尔诺明德(Warnemünde,意为瓦尔诺河口)汇入波罗的海。公元600年左右,开始有斯拉夫部落在瓦尔诺河下游定居,瓦尔诺河在入海前约13公里处由窄变宽,早期居民称这一景象为Roztoc,并以此命名其据点,这也是今天城市名称Rostock的起源。罗斯托克是德国在波罗的海沿岸的三大港城之一,也是梅克伦堡-前波美拉尼亚州文化上和经济上最重要的城市,主要经济部门包括造船业、海运业、旅游业和服务业。海滨,港口,汉萨城市的历史,砖石哥特建筑,以及建于1419年的古老的罗斯托克大学勾画出这座城市的特色。罗斯托克的城市格言是“城内一致,众生康乐”(拉丁语:SIT INTRA TE CONCORDIA, ET PUBLICA FELICITAS)。
ロストック (Rostock) は、ドイツ連邦共和国北部、メクレンブルク=フォアポンメルン州の都市である。バルト海に面する港湾都市で、中世のハンザ同盟の中心都市、また旧東ドイツ最大の港湾都市であった。人口は約21万人。ロストク、ロシュトック、ロシュトクとも表記される。
バルト海に面した北側を除いて周囲をロストック郡に囲まれているが、郡には属さない郡独立市である。
Rostock (German pronunciation: [ˈʁɔstɔk] (![]() listen)) is a city in the north German state Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Rostock is on the Warnow river; the district of Warnemünde, 12 kilometres (7 miles) north of the city centre, is directly on the Baltic Sea coast. Rostock is the largest city in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, as well as its only regiopolis.
listen)) is a city in the north German state Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Rostock is on the Warnow river; the district of Warnemünde, 12 kilometres (7 miles) north of the city centre, is directly on the Baltic Sea coast. Rostock is the largest city in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, as well as its only regiopolis.
Rostock is home to one of the oldest universities in the world, the University of Rostock, founded in 1419.
The city territory of Rostock stretches for about 20 km (12 mi) along the Warnow to the Baltic Sea. The largest built-up area of Rostock is on the western side of the river. The eastern part of its territory is dominated by industrial estates and the forested Rostock Heath.
Rostock (prononciation /'ʁɔstɔk/ du polabe Roz toc) est une ville-arrondissement du nord de l’Allemagne. C’est la plus grande ville de Mecklembourg-Poméranie occidentale. Rostock est située sur les bords de la rivière Warnow.
Rostock è una città extracircondariale (targa HRO) del Meclemburgo-Pomerania Anteriore, in Germania. Conta (dicembre 2010) 202.735 abitanti. È il centro maggiore, ma non la capitale, del Land.
Rostock ricevette nel 1218 il cosiddetto Diritto di Lubecca e si fregia del titolo di "città anseatica" (Hansestadt).
La città si sviluppa per circa venti chilometri lungo il corso del fiume Warnow, fino alle sue foci sul Mar Baltico. La porzione maggiormente costruita della città è quella posta ad ovest del fiume, mentre ad est sono presenti soprattutto gli insediamenti commerciali e la brughiera cittadina, detta Rostocker Heide.
Il porto di Rostock è uno dei più importanti del paese sia per trasporto dei passeggeri che per movimento merci, risultando anche uno dei principali porti crocieristici tedeschi. La città si impone all'interno del proprio Land anche come principale centro culturale ed economico. Elementi caratteristici della città sono la posizione strategica, il porto, il Gotico baltico, la storica appartenenza di Rostock alla Lega anseatica e l'importante università, che costituisce oggi il più grande datore di lavoro cittadino.
Rostock è situata nella regione geografica del Meclemburgo ed appartenne in passato al Granducato di Meclemburgo-Schwerin, ridenominato dal 1918 al 1934 "stato libero". Rappresenta, insieme a Neubrandenburg, Schwerin e a Stralsund-Greifswald, uno dei quattro "Oberzentren" del Land.
Rostock (![]() [ˈʁɔstɔk] (?·i)) es una ciudad de Alemania, en el Estado federado de Mecklemburgo-Pomerania Occidental, con 206.011 habitantes (2015). Está ubicada a orillas del mar Báltico, en la desembocadura del río Warnow. Formaba parte de la antigua República Democrática Alemana.
[ˈʁɔstɔk] (?·i)) es una ciudad de Alemania, en el Estado federado de Mecklemburgo-Pomerania Occidental, con 206.011 habitantes (2015). Está ubicada a orillas del mar Báltico, en la desembocadura del río Warnow. Formaba parte de la antigua República Democrática Alemana.
El municipio de Rostock incluye también el balneario de Warnemünde.
 加利福尼亚州高速公路一号
加利福尼亚州高速公路一号

 加利福尼亚州
加利福尼亚州

 2026年世界杯足球赛
2026年世界杯足球赛

 财政金融
财政金融
 ***全球金融中心
***全球金融中心

 历史
历史
 公元 2000 - 2100
公元 2000 - 2100

 历史
历史
 公元 1500 - 2000
公元 1500 - 2000

 国际城市
国际城市
 ***全球城市经济竞争力
***全球城市经济竞争力
 英雄联盟
英雄联盟
 英雄联盟全球总决赛
英雄联盟全球总决赛
 夏季奥林匹克运动会
夏季奥林匹克运动会
 美国
美国

 重要港口
重要港口
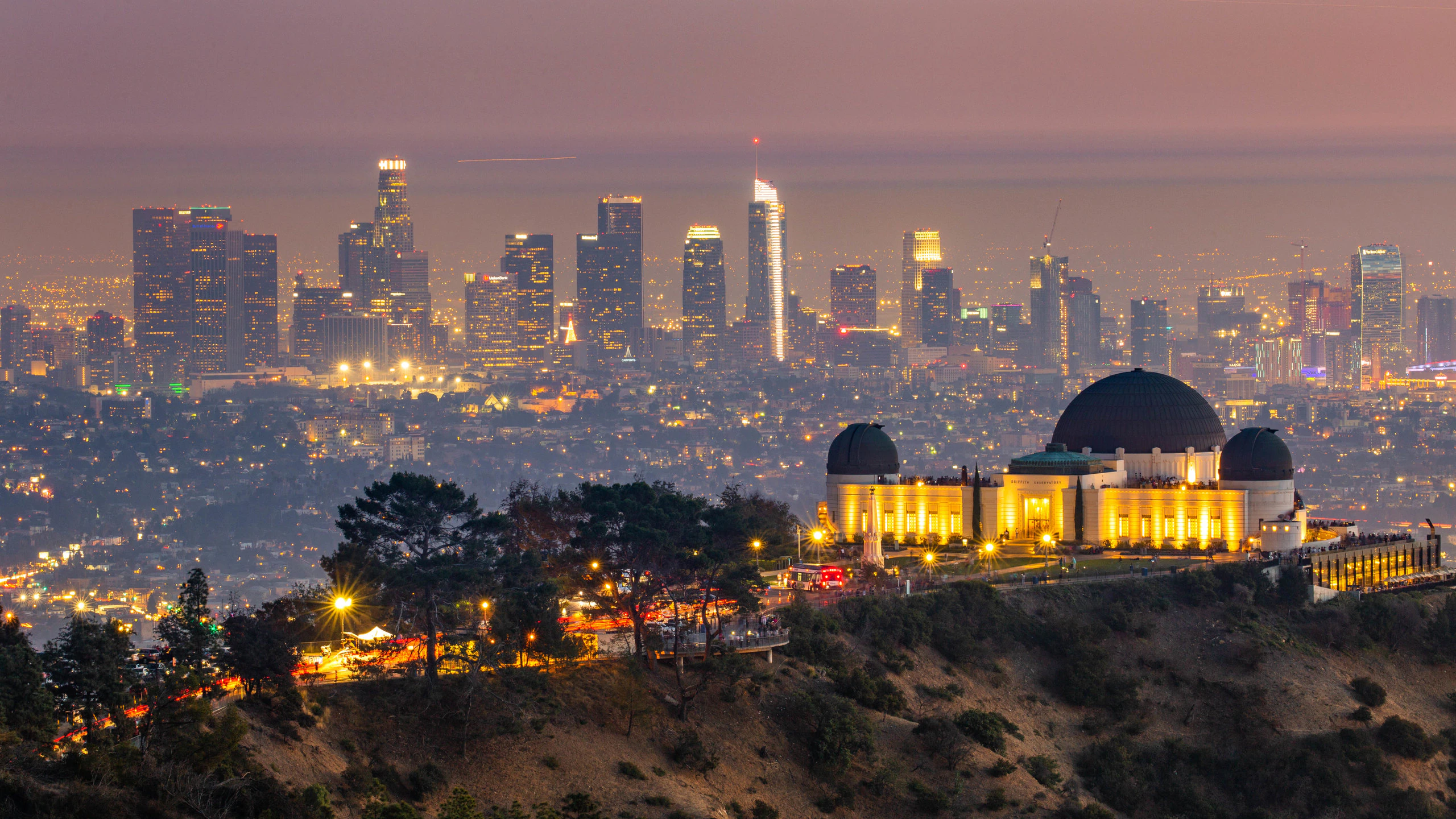
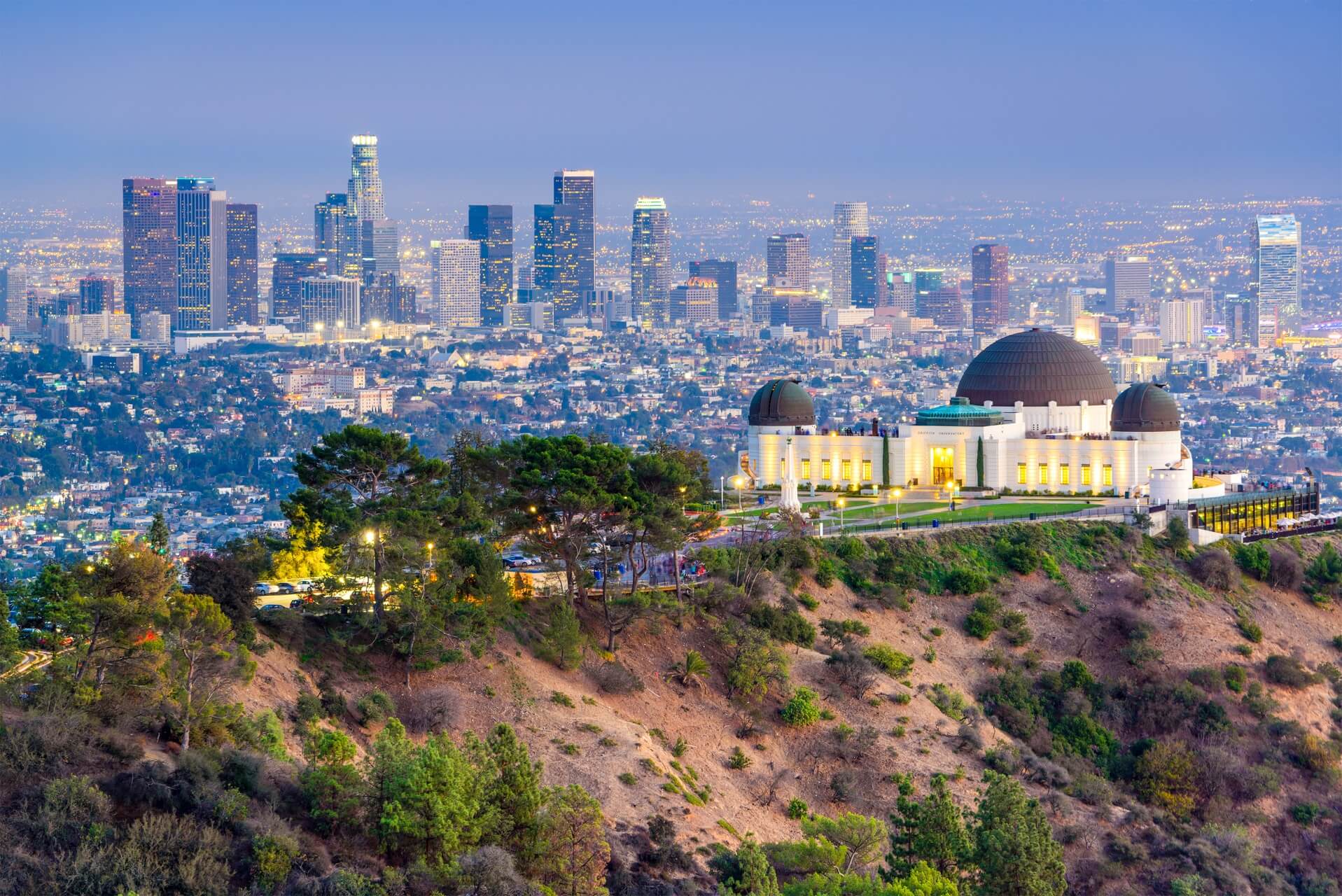




洛杉矶(英语:City of Los Angeles,缩写为L.A.),简称洛城,是位于美国加利福尼亚州南部的都市,也是洛杉矶县的县治,人口约397万[8],为加州第一大城,同时也是美国人口第二大都市,仅次于纽约市。全市面积为469.1平方英里(1214.9平方公里)。由洛杉矶、长滩、安那翰3市组成的洛杉矶都会区拥有约1331万的人口[9],涵盖范围更广的大洛杉矶地区则达到1870万[10],两者在统计上均次于纽约都会区,为全美国第二大都会区。
洛杉矶在1781年由西属上加利福尼亚总督费利佩·德·内维建立。它曾先后属于西班牙与墨西哥,但在1848年美墨战争结束后,墨西哥将包括洛杉矶在内的上加利福尼亚地区割让给美国。1850年4月4日,洛杉矶正式建市,比加州加入联邦的时间早了5个月。时至今日,洛杉矶已发展成为全世界的文化、科学、技术、体育、国际贸易和高等教育中心之一,还拥有世界知名的各种专业与文化领域的机构。整个大洛杉矶地区在电影、电视、音乐等文化娱乐产业的蓬勃发展,构成了洛杉矶的国际声誉和全球地位的基础。截至2014年,洛杉矶的大都市生产总值达8605亿美元,排名世界第三。
Los Angeles [lɔs ˈændʒələs] (aus dem spanischen Los Ángeles [losˈaŋxeles] ‚Die Engel‘) oder auch kurz L.A., ist die größte Stadt im US-Bundesstaat Kalifornien. Sie liegt am Pazifischen Ozean und am Los Angeles River.
Los Angeles ist mit 3.928.864 Einwohnern (2014)[1] im Stadtgebiet nach New York City und vor Chicago die zweitgrößte Stadt der Vereinigten Staaten.[2] Mit 11,8 Millionen Einwohnern in der Agglomeration[3] sowie über 12,8 Millionen Einwohnern in der Metropolregion (Metropolitan Statistical Area) und knapp 17,8 Millionen in der erweiterten Metropolregion steht die Greater Los Angeles Area unter den größten Metropolregionen der Welt an 17. Stelle.[4] Die Einwohner von Los Angeles werden Angelenos [ændʒəˈlinoʊz] genannt.
Los Angeles ist Hauptstadt und Verwaltungssitz des Los Angeles County. Die Stadt ist das Wirtschafts-, Geschäfts- und Kulturzentrum Kaliforniens mit zahlreichen Universitäten, Hochschulen, Forschungsinstituten, Theatern und Museen. Los Angeles ist weltgrößter Standort für die Flugzeug- und Raumfahrtindustrie und bekannt wegen der dort ansässigen Film- und Fernsehindustrie (Hollywood) und Musikszene.
Die Metropolregion Los Angeles erbrachte 2016 eine Wirtschaftsleistung von 1,001 Billionen US-Dollar. Unter den Städten der Welt belegt es damit den dritten Rang hinter Tokio und New York City.[5]
ロサンゼルス(英語: Los Angeles、スペイン語も同じ)は、アメリカ合衆国カリフォルニア州にある都市。同州最大の都市かつ全米有数の世界都市であり、国内ではニューヨークに次いで人口が多い[1]。
Los Angeles (US: /lɔːs ˈændʒələs/ ( listen);[16][a] Spanish for "The Angels"; Spanish: Los Ángeles; Spanish: [los ˈaŋxeles]; officially the City of Los Angeles, known colloquially by its initials L.A.) is the second-most populous city in the United States, after New York City, and the most populous city in the Western United States. With an estimated population of four million,[17] Los Angeles is the largest and most populous city in the state of California and the cultural, financial, and commercial center of Southern California. Nicknamed the "City of Angels" partly because of its name's Spanish meaning, Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic diversity, and sprawling metropolis.
listen);[16][a] Spanish for "The Angels"; Spanish: Los Ángeles; Spanish: [los ˈaŋxeles]; officially the City of Los Angeles, known colloquially by its initials L.A.) is the second-most populous city in the United States, after New York City, and the most populous city in the Western United States. With an estimated population of four million,[17] Los Angeles is the largest and most populous city in the state of California and the cultural, financial, and commercial center of Southern California. Nicknamed the "City of Angels" partly because of its name's Spanish meaning, Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic diversity, and sprawling metropolis.
Los Angeles is located in a large basin bounded by the Pacific Ocean on one side and by mountains as high as 10,000 feet (3,000 m) on the others. The city proper, which covers about 469 square miles (1,210 km2),[18] is the seat of Los Angeles County, the most populated county in the country. Los Angeles is the principal city of the Los Angeles metropolitan area; with a population of 13.1 million residents it is the second largest in the United States after that of New York City.[19] It is part of the Los Angeles-Long Beach combined statistical area, also the second most populous in the nation with a 2015 estimated population of 18.7 million.[20]
Los Angeles is one of the most substantial economic engines within the United States, with a diverse economy in a broad range of professional and cultural fields. Los Angeles is also famous as the home of Hollywood, a major center of the world entertainment industry. A global city, it has been ranked 6th in the Global Cities Index and 9th in the Global Economic Power Index. The Los Angeles combined statistical area also has a gross metropolitan product of $831 billion (as of 2008), making it the third-largest in the world, after the Tokyo and New York metropolitan areas. Los Angeles hosted the 1932 and 1984 Summer Olympics and will host the event for a third time in 2028. The city also hosted the Miss Universe pageant twice, in 1990 and 2006.
Historically home to the Chumash and Tongva, Los Angeles was claimed by Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo for Spain in 1542 along with the rest of what would become Alta California. The city was officially founded on September 4, 1781, by Spanish governor Felipe de Neve. It became a part of Mexico in 1821 following the Mexican War of Independence. In 1848, at the end of the Mexican–American War, Los Angeles and the rest of California were purchased as part of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, becoming part of the United States. Los Angeles was incorporated as a municipality on April 4, 1850, five months before California achieved statehood. The discovery of oil in the 1890s brought rapid growth to the city.[21] The completion of the Los Angeles Aqueduct in 1913, delivering water from Eastern California, later assured the city's continued rapid growth.
Los Angeles (prononcé en anglais américain [lɑs ˈæn.dʒə.ləs] Écouter)n 1 est la deuxième ville la plus peuplée des États-Unis après New York. Elle est située dans le sud de l'État de Californie, sur la côte pacifique. Les Américains l'appellent souvent par son diminutif, L.A. (prononcé [ˌɛlˈeɪ]). La ville est le siège du comté portant le même nom. Los Angeles signifie « les anges » en espagnol et ses habitants sont appelés Angelenos (quelquefois Angelinos) — les Angelins. Son nom complet est El Pueblo de Nuestra Señora la Reina de Los Ángeles del Río de Porciúncula, c'est-à-dire « le village de Notre-Dame la Reine des Anges du fleuve de Porciuncula », Porciuncula étant le nom donné au fleuve Los Angeles par les Amérindiens2.
Selon une estimation, la population de la commune est de 3 976 322 habitants en 2016, alors qu'elle n'était que de 11 500 en 1887. Le comté rassemble 10 179 716 habitants (en juillet 2004) alors que l'aire urbaine de Los Angeles compte environ 18,5 millions d’habitants3, ce qui en fait la deuxième agglomération des États-Unis après celle de New York. Mais la commune de Los Angeles est relativement restreinte face à son agglomération, même si elle est plus grande que New York et Chicago.
Los Angeles est une ville olympique : elle accueille les Jeux olympiques d'été deux fois (en 1932 et 1984), et les accueillera de nouveau en 2028. Mondialement connue pour son activité culturelle (notamment via la production cinématographique à Hollywood), elle a un statut de ville-région mondiale (world city-region)4 ; cosmopolite, elle demeure l'un des points d'entrée d'immigrants les plus importants aux États-Unis.
Los Angeles (pronuncia inglese [lɒs ˈændʒələs]; pronuncia italiana[4]: [loˈzɛndʒeles] o [loˈzandʒeles]; pronuncia spagnola [los ˈaŋxeles]), spesso abbreviata in L.A., è una città degli Stati Uniti d'America, capoluogo dell'omonima contea, situata nella California meridionale. Con 4 057 875 abitanti (nel 2017[3]), è la città più popolosa della California e la seconda più popolosa degli Stati Uniti d'America dopo New York.
Fondata dagli spagnoli come El Pueblo de Nuestra Señora la Reina de los Ángeles del Rio de la Porciúncula de Asís[5], ovvero "Il villaggio di santa Maria degli Angeli della Porziuncola di Assisi", assurse allo status di città il 9 giugno 1850, cinque mesi prima che la California diventasse il trentesimo Stato dell'Unione.
È un centro economico e scientifico di rilevanza internazionale. È inoltre la capitale mondiale dell'industria cinematografica, ospitata in uno dei sobborghi più famosi della città, Hollywood; a Los Angeles e dintorni risiedono numerosi personaggi del cinema e dello spettacolo americano e internazionale.
Los Ángeles (en inglés: Los Angeles, pronunciado AFI: [lɒs ˈændʒəˌləs]), oficialmente Ciudad de Los Ángeles y de manera abreviada L. A., es la ciudad más poblada del estado estadounidense de California y la segunda ciudad más poblada de Estados Unidos. Tiene, según el censo de 2010, una población de 3 792 621 habitantes.2 Está ubicada en el sur de California y abarca una superficie de 1215 km².
La ciudad es el centro del área estadística metropolitana de Los Ángeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana y del Gran Los Ángeles que, según el censo de 2010, sumaban una población de 13 y 18 millones de personas, respectivamente. Es, por tanto, una de las mayores áreas metropolitanas del mundo3 y la segunda de Estados Unidos.4 La ciudad también es la sede del condado de Los Ángeles, uno de los condados más poblados y étnicamente diversos del país;5 la propia ciudad de Los Ángeles es reconocida como una de las metrópolis más diversas del planeta.6 A sus habitantes les corresponde el gentilicio «angelinos/as».7
Los Ángeles fue fundada el 4 de septiembre de 1781 por el gobernador español Felipe de Neve con el nombre de «El Pueblo de Nuestra Señora la Reina de los Ángeles del Río de Porciúncula».8 En 1821, después de la guerra de independencia de México, la ciudad se integró como parte de México,9 pero en 1848, a consecuencia de la intervención estadounidense en México, Los Ángeles y el resto de la Alta California pasaron a ser parte de los Estados Unidos de América, de acuerdo con lo pactado en el Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo.10 La ciudad se incorporó a la Unión como municipio el 4 de abril de 1850, cinco meses antes de que California alcanzara la categoría de estado de los Estados Unidos.11
Los Ángeles es una ciudad global con gran influencia en ámbitos tan diversos como los negocios, el comercio internacional, el entretenimiento, la cultura, los medios de comunicación, la moda, la ciencia, los deportes, la tecnología, la educación, la medicina o la investigación. En la ciudad tienen su sede instituciones de renombre que abarcan diversos campos profesionales y culturales, y es uno de los motores económicos más importantes de Estados Unidos. El área estadística combinada de Los Ángeles sumaba en 2008 un producto regional bruto de 831 000 millones de USD, el tercero más importante del mundo tras Tokio y Nueva York.12 Los Ángeles, dentro de la cual se encuentra Hollywood, es líder mundial en la creación de producciones de televisión, videojuegos, música y cine que triunfan en todo el planeta. Además, la ciudad ha sido sede en dos ocasiones de los Juegos Olímpicos de Verano, en 1932 y en 1984, y lo será por tercera vez en 2028.
 假期和旅游
假期和旅游

 石勒苏益格-荷尔斯泰因州
石勒苏益格-荷尔斯泰因州
 梅克伦堡-前波莫瑞州
梅克伦堡-前波莫瑞州

 布列塔尼
布列塔尼
