
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2023
Women's Soccer World Cup 2023
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 New Zealand
New Zealand

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon

 Sport
Sport
 The Ocean Race
The Ocean Race

 Important port
Important port
 France
France

 History
History

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon

 World Heritage
World Heritage
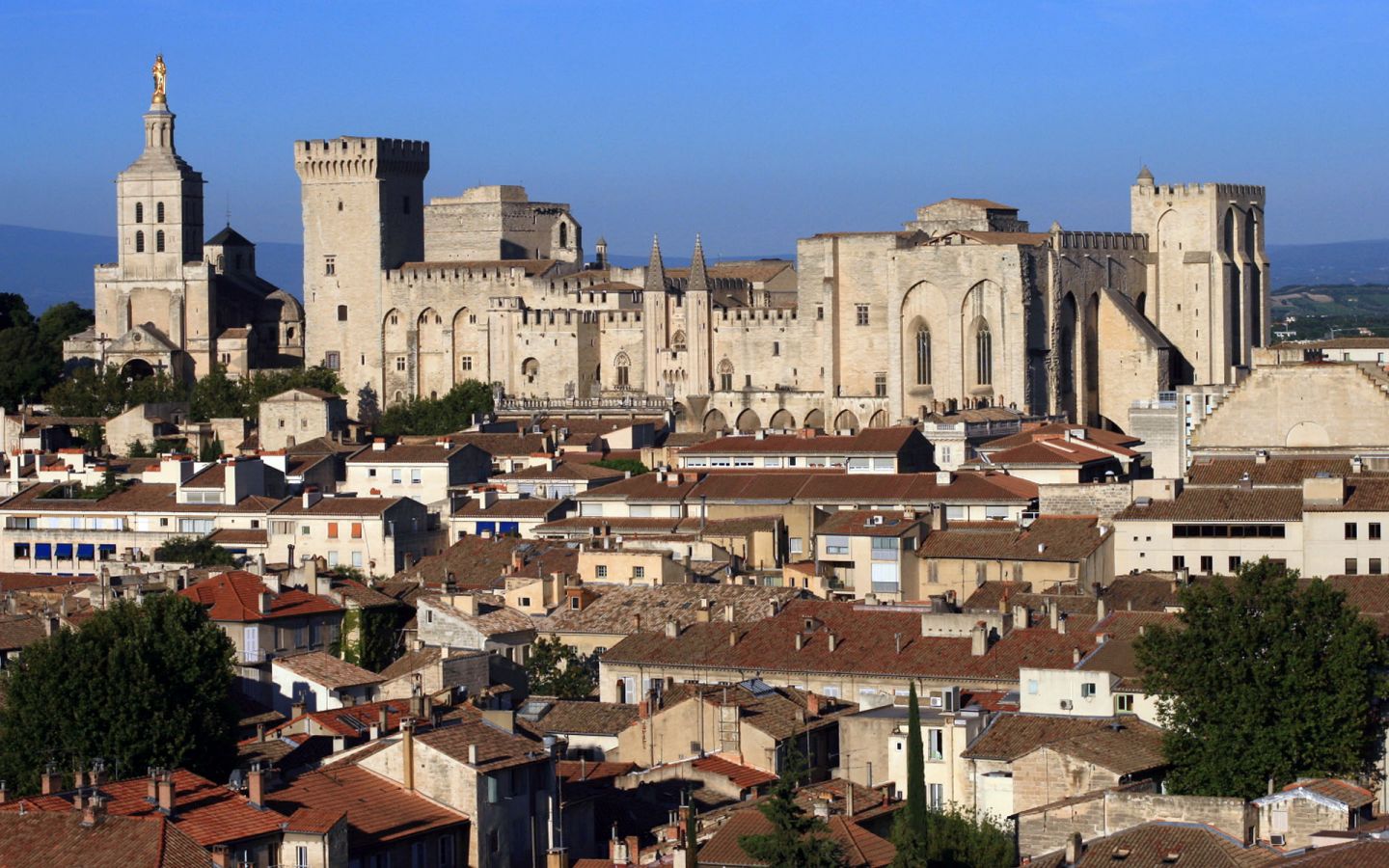

阿维尼翁(法语:Avignon; 加斯科:Avinhon)是位于法国南部普罗旺斯-阿尔卑斯-蓝色海岸大区沃克吕兹省,罗讷河左岸的一座城市。阿维尼翁始建于罗马时 期。现今是法国南部的旅游胜地之一。阿维尼翁城区住户在2011年初为90194人,其中有大约12000人仍居住在古城墙内,已被划为观光区域的老城区 (intra-muros)。如算上四周郊区和附属村镇,阿维尼翁地区的人口超过50万,是法国排名第16位的城市聚落。
在1309到1377年之间,天主教教廷从罗马梵缔冈迁移至此,前后一共有七位教宗在阿维尼翁教廷生活,直到格利高里十一世迁都罗马。后来更出现两地各立教宗的情形(史称“大分裂”)。这段时期也被后世称为阿维尼翁分裂时期。阿维尼翁城原是乔万娜一世的属地,在1348年售予教廷。教廷对阿维尼翁的统治一直延续到1791年法国大革命之时,其后阿维尼翁成为法国的一部分。阿维尼翁是沃克吕兹省的省会,也是法国少见的保留了城墙的城市。城墙内有为教宗修筑的教皇宫。此外著名古迹还有阿维尼翁圣母大教堂、圣贝内泽桥等。1995年以阿维尼翁历史城区之名被列入世界文化遗产。
Avignon [aviˈɲɔ̃] (oc. Avinhon bzw. Avignoun [aviˈɲũn]) ist eine Stadt und Gemeinde in der Provence in Südfrankreich am östlichen Ufer der Rhône mit 92.130 Einwohnern (Stand 1. Januar 2015), von denen etwa 15.000 innerhalb der Stadtmauern wohnen. Avignon ist Sitz der Präfektur und die größte Stadt des Départements Vaucluse.
Da Avignon von 1309 bis 1376 – und während des nachfolgenden Abendländischen Schismas – Papstsitz war, trägt die Stadt den Beinamen „Stadt der Päpste“. Die Altstadt von Avignon mit ihren prächtigen, mittelalterlichen Häusern ist von einer intakten und imposanten Befestigungsmauer umgeben. Die Altstadt mit dem gotischen Papstpalast (Palais des Papes) aus dem 14. Jahrhundert, der Bischofsanlage, dem Rocher des Doms und der berühmten Brücke, der Pont Saint-Bénézet, zählt zum UNESCO-Weltkulturerbe.
Künstlerisch und kulturell ist die Stadt durch das Festival von Avignon auch weit über die französischen Landesgrenzen hinaus bekannt. Im Jahr 2000 war Avignon Kulturhauptstadt Europas.
アヴィニョン(Avignon)は、フランスの南東部に位置する都市(コミューン)で、ヴォクリューズ県の県庁所在地である。ローマ帝国時代にはガリア・ナルボネンシス属州の主要都市の一つであった。5世紀に蛮族の侵入によって荒廃した後、737年にカール・マルテル率いるフランク人によって滅ぼされた。カール・マルテルが戦っていたアラブ人の側についたことによる。その後、ブルグント王国、ついでアルル王国領となる。12世紀末、都市は独立を宣言し、共和制をとる都市国家となるが、長くは続かず、アヴィニョンはプロヴァンス伯領、次いでトゥールーズ伯領となった。中世末のカタリ派運動の中ではカタリ派を支持した結果、1226年にアルビジョア十字軍を率いたフランス王ルイ8世によって占領され、武装解除された。カタリ派を支持した街への処罰として、市の城壁は破壊された。
キリスト教が入ったのは早く、70年に司教座が置かれた。1309年にローマ教皇クレメンス5世がアヴィニョンを居所に定め、1377年まで教皇庁所在地とした(アヴィニョン捕囚)。1426年に大司教座がおかれた。1303年にアヴィニョン大学が開かれ、フランス革命まで続き、法学で知られた。
アヴィニョン捕囚時代の半ば、1348年に領主プロヴァンス伯(兼ナポリ女王)ジョアンナから教皇クレメンス6世にアヴィニョンが売却された。以後、フランス革命で没収されるまでアヴィニョンは教皇領となった。何人かの対立教皇は、アヴィニョンに教皇座を置いている。
Avignon (French pronunciation: [avi'ɲɔ̃]; Latin: Avenio; Provençal: Avignoun, Occitan: Avinhon pronounced [aviˈɲun]) is a commune in south-eastern France in the department of Vaucluse on the left bank of the Rhône river. Of the 90,194 inhabitants of the city (as of 2011), about 12,000 live in the ancient town centre enclosed by its medieval ramparts.
Between 1309 and 1377, during the Avignon Papacy, seven successive popes resided in Avignon and in 1348 Pope Clement VI bought the town from Joanna I of Naples. Papal control persisted until 1791 when, during the French Revolution, it became part of France. The town is now the capital of the Vaucluse department and one of the few French cities to have preserved its ramparts.
The historic centre, which includes the Palais des Papes, the cathedral, and the Pont d'Avignon, became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1995. The medieval monuments and the annual Festival d'Avignon have helped to make the town a major centre for tourism.
Avignon [a.viˈɲɔ̃] est une ville du Sud de la France, située au confluent du Rhône et de la Durance. C'est la ville où siège le conseil du Grand Avignon. Avignon est le chef-lieu de l'arrondissement d'Avignon et du département de Vaucluse. Ses habitants s'appellent les Avignonnais.
Par sa population, Avignon constitue la seizième aire urbaine de France et fait partie des villes moyennes, elle est la 45e ville de France sur les 34 672 villes et communes du pays. Elle comptait 92 209 habitants lors de son dernier recensement.
Surnommée la « cité des papes » en raison de la présence des papes de 1309 à 1423, elle est actuellement la plus grande ville et la préfecture du département de Vaucluse.
C'est l'une des rares villes françaises à avoir conservé ses remparts, son centre historique, composé du Palais des Papes, de l'ensemble épiscopal, du Rocher des Doms et du pont d’Avignon. Elle a été classée patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO sous les critères I, II et IV.
La renommée de son festival, le plus grand du monde et véritable vitrine artistique et culturelle de la ville, a largement dépassé les frontières françaises. La ville fut capitale européenne de la culture en 2000.
Avignon comporte un cœur étudiant important, notamment grâce à son quartier étudiant : Agroparc ainsi que de son université : l'Université d'Avignon et des Pays de Vaucluse.
Avignone (Avignon in francese, Avignoun in provenzale in grafia mistraliana, Avinhon in occitano in grafia classica), è una città della Francia meridionale, la prefettura del dipartimento di Vaucluse, di cui è il capoluogo, nella regione amministrativa della Provenza-Alpi-Costa Azzurra. Si affaccia sulla riva sinistra del Rodano. I suoi abitanti si chiamano avignonesi (avignonnais).
Aviñón3 (en francés Avignon, en occitano provenzal Avinhon [en norma clásica] o Avignoun [en norma mistralense]) es una ciudad y comuna francesa, capital del departamento de Vaucluse, en la región de Provenza-Alpes-Costa Azul.
Авиньо́н[2][3] (фр. Avignon [aviˈɲɔ̃], окс. Avinhon, лат. Aven(n)io) — коммуна на юго-востоке Франции, префектура (главный город) округа Авиньон и департамента Воклюз в регионе Прованс — Альпы — Лазурный Берег, кантоны Авиньон-1, Авиньон-2, Авиньон-3[4]. Город расположен на левом берегу Роны, является местом проведения одного из крупнейших международных ежегодных театральных фестивалей.
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 China
China
 Chinese Super League 2019
Chinese Super League 2019

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 L 1000 - 1500 AD
L 1000 - 1500 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal
Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal
 League of Legends
League of Legends
 League of Legends World Championship
League of Legends World Championship
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
 2022 Winter Olympics
2022 Winter Olympics
 Silk road
Silk road
 Shanghai Cooperation Organization
Shanghai Cooperation Organization

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon

 World Heritage
World Heritage
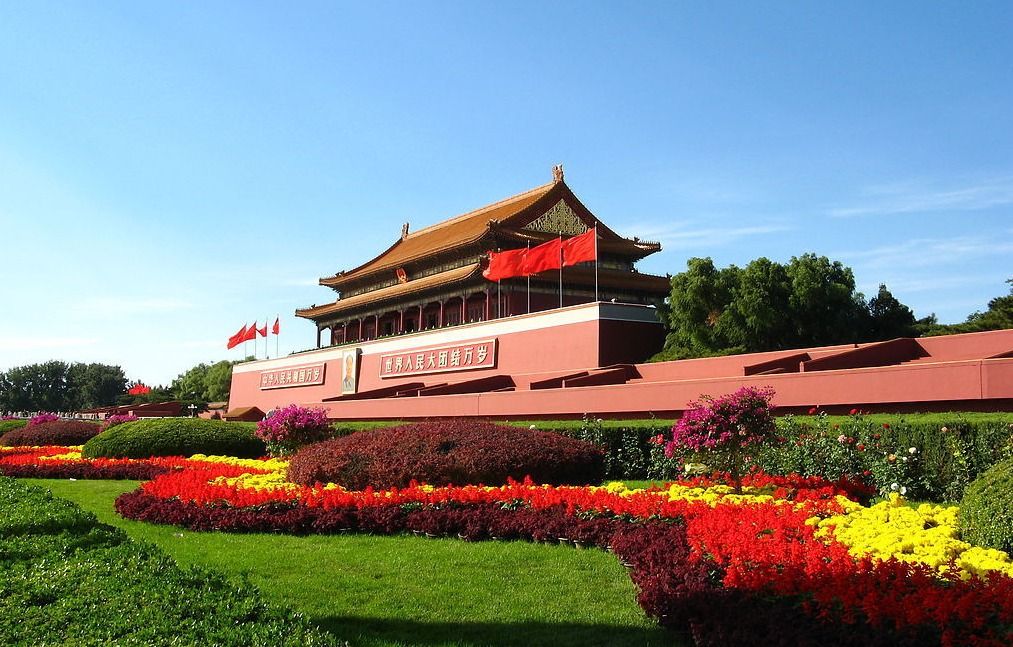

北京,简称“京”,是中华人民共和国的首都、直辖市、国家中心城市、超大城市、国际大都市,全国政治中心、文化中心、国际交往中心、科技创新中心,是中国共产党中央委员会、中华人民共和国中央人民政府、全国人民代表大会、中国人民政治协商会议全国委员会、中华人民共和国中央军事委员会所在地,也是中部战区司令部驻地。
北京位于华北平原北部,背靠燕山,毗邻天津市和河北省。北京的气候为典型的北温带半湿润大陆性季风气候。
北京是首批国家历史文化名城和世界上拥有世界文化遗产数最多的城市,三千多年的历史孕育了故宫、天坛、八达岭长城、颐和园等众多名胜古迹。早在七十万年前,北京周口店地区就出现了原始人群部落“北京人”。公元前1045年,北京成为蓟、燕等诸侯国的都城。公元938年以来,北京先后成为辽陪都、金中都、元大都、明、清国都。1949年10月1日成为中华人民共和国首都。
北京被全球权威机构GaWC评为世界一线城市 。联合国报告指出,北京人类发展指数居中国城市第二位 。2017年,北京人均可支配收入达到57230元,社会消费品零售总额11575.4亿元 。北京住户存款总额和人均住户存款均居全国第一 。2017年,北京高新技术企业达到20183家。 福布斯2017年“中国大陆最佳商业城市排行榜”排第3位。
2015年7月31日,国际奥委会主席巴赫宣布北京携手张家口获得2022年冬季奥林匹克运动会的举办权。北京由此成为全球首个既举办过夏季奥运会又将举办冬季奥运会的城市。
北京是一座有着三千多年历史的古都,在不同的朝代有着不同的称谓,大致算起来有二十多个别称。
燕都,据史书记载,公元前1122年,周武王灭商以后,在燕封召公。燕都因古时为燕国都城而得名。战国七雄中有燕国,据说是因临近燕山而得国名,其国都称为“燕都”。
幽州,远古时代的九州之一。幽州之名,最早见于《尚书·舜典》:“燕曰幽州。”两汉、魏、晋、唐代都曾设置过幽州,所治均在今天的北京一带。
京城,京城泛指国都,北京成为国都后,也多将其称为京城。
南京,辽太宗会同元年(938年),将原来的幽州升为幽都府,建号南京,又称燕京,作为辽的陪都。当时辽的首都在上京。
大都,元代以金的离宫今北海公园为中心重建新城,元世祖至元九年(1272年)改称大都,俗称元大都。
北平,明代洪武元年(1368年),朱元璋灭掉元朝后,为了记载平定北方的功绩,将元大都改称北平。
北京,明永乐元年(1403年),明成祖朱棣永乐皇帝取得皇位后,将他做燕王时的封地北平府改为顺天府,建北京城,并准备迁都城于此,这是正式命名为北京的开始,至今已有600余年的历史。
京师,明成祖于永乐十八年(1420年)迁都北京,改称京师,直至清代。
京兆,民国二年(1913年)废顺天府,翌年置京兆地方,直隶中央,其范围包括今天的北京大部分地区,民国十七年(1928年)废京兆地方,改北京为北平。
Peking (chinesisch 北京, Pinyin Běijīng, W.-G. Pei-ching auch Beijing,  [pei˨˩tɕiŋ˥˥], deutsch historisch Pekingen[2]) ist die Hauptstadt der Volksrepublik China. Der Name bedeutet Nördliche Hauptstadt (vgl. Nanjing für Südliche Hauptstadt). Peking hat eine über dreitausendjährige Geschichte und ist heute eine regierungsunmittelbare Stadt, das heißt, sie ist direkt der Zentralregierung unterstellt und damit Provinzen, autonomen Gebieten und Sonderverwaltungszonen gleichgestellt.
[pei˨˩tɕiŋ˥˥], deutsch historisch Pekingen[2]) ist die Hauptstadt der Volksrepublik China. Der Name bedeutet Nördliche Hauptstadt (vgl. Nanjing für Südliche Hauptstadt). Peking hat eine über dreitausendjährige Geschichte und ist heute eine regierungsunmittelbare Stadt, das heißt, sie ist direkt der Zentralregierung unterstellt und damit Provinzen, autonomen Gebieten und Sonderverwaltungszonen gleichgestellt.
Das gesamte 16.807 Quadratkilometer große (etwas größer als Schleswig-Holstein) Verwaltungsgebiet Pekings hat 21,5 Millionen Einwohner (Stand: März 2016).[3] Es stellt kein zusammenhängendes Stadtgebiet dar, mit seiner dominierenden ländlichen Siedlungsstruktur ist es eher mit einer Provinz vergleichbar.[4] Von der Gesamtbevölkerung sind 11,8 Millionen registrierte Bewohner mit ständigem Wohnsitz (戶口 / 户口, hùkǒu) und 7,7 Millionen temporäre Einwohner (流動人口 / 流动人口, liúdòng rénkǒu) mit befristeter Aufenthaltsgenehmigung (暫住證 / 暂住证, zànzhùzhèng).[5] Wird die Kernstadt (hohe Bebauungsdichte und geschlossene Ortsform) als Grundlage genommen, leben in Peking 7,7 Millionen Menschen mit Hauptwohnsitz (2007).[6] Der Ballungsraum (einschließlich Vororte) hat 11,8 Millionen Einwohner (2007).[7] Ab 2017 soll die Metropole Kern einer Megalopolis von 130 Millionen Einwohnern namens Jing-Jin-Ji werden.
Peking stellt als Hauptstadt das politische Zentrum Chinas dar. Aufgrund der langen Geschichte beherbergt Peking ein bedeutendes Kulturerbe. Dies umfasst die traditionellen Wohnviertel mit Hutongs, den Tian’anmen-Platz (chinesisch Platz am Tor des Himmlischen Friedens), die 1987 von der UNESCO zum Weltkulturerbe erklärte Verbotene Stadt, den neuen und alten Sommerpalast und verschiedene Tempel, wie z. B. den Himmelstempel, den Lamatempel und den Konfuziustempel.(2012)
北京市(ペキンし、中国語: 北京市、拼音: Běijīng)は、中華人民共和国の首都である。
行政区画上は直轄市であり、中国の華北の中央に位置する。人口は2152万(2014年)であり、中国では上海に次ぐ第二の都市。世界有数のメガシティであり、極めて高い影響力を有する世界都市でもある。古くは大都・燕京・北平とも呼ばれた。
春秋戦国時代には燕の首都で薊(けい)と称された。周の国都洛陽からは遠く離れ、常に北方の匈奴などの遊牧民族の侵入による被害を受ける辺境であった。秦漢代には北平(ほくへい)と称されるが、満州開発が進み、高句麗など周辺国の勢力が強大となると、戦略上、また交易上の重要な拠点として重視されるようになった。北京市に隣接する河北省涿郡(たくぐん)は三国志の英雄劉備の故郷で知られるとともに隋の煬帝が築いた大運河の北の起点とされている。
唐末五代の騒乱期、内モンゴルから南下してきた遼朝は、後晋に対し軍事支援を行った代償として北京地方を含む燕雲十六州を割譲された。遼はこの都市を副都の一つ南京と定めた。その後金朝が遼を滅ぼし支配権を獲得すると、金は北京に都城を定め中都とした。更にモンゴル帝国(元朝)が金を滅ぼすと大都として元朝の都城となり、カラコルムに代わってモンゴル帝国の中心となった。
朱元璋が元を北方に駆逐し明朝が成立すると、名称は北平に戻され、都城は南京に定められた。しかし、燕王に封じられ北京を拠点とした朱棣(後の永楽帝)は、1402年に建文帝に対し軍事攻撃を行い政権を奪取。皇帝に即位した後北京遷都を実行し地名を北京に改めた。辛亥革命後は中華民国北洋政府は北京を首都と定めたが、南京を首都と定めた蒋介石を中心とする国民政府は、「政府直轄地域」を意味する直隷省を1928年6月15日に河北省へ、北の首都を意味する北京を北平(ほくへい、ベイピンBěipíng)へと、それぞれ改称した。1937年から1945年まで続いた日本軍占領期は北京の名称が用いられ(公式には1940年に改名)、日本の敗戦によって再び北平に改称された。
1949年10月1日の中華人民共和国成立により新中国の首都とされた北京(北平)は再び北京と改称され現在に至っている。しかし、中華人民共和国の存在を承認せず、南京を公式な首都として大陸地区への統治権を主張する中華民国(台湾)では、現在でも公式名称として「北平」の名称が用いられている。
Beijing (/beɪˈdʒɪŋ/;[10] Mandarin: [pèi.tɕíŋ] ( listen)), formerly romanized as Peking,[11] is the capital of the People's Republic of China, the world's third most populous city proper, and most populous capital city. The city, located in northern China, is governed as a municipality under the direct administration of central government with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.[12] Beijing Municipality is surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighboring Tianjin Municipality to the southeast; together the three divisions form the Jingjinji metropolitan region and the national capital region of China.[13]
listen)), formerly romanized as Peking,[11] is the capital of the People's Republic of China, the world's third most populous city proper, and most populous capital city. The city, located in northern China, is governed as a municipality under the direct administration of central government with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.[12] Beijing Municipality is surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighboring Tianjin Municipality to the southeast; together the three divisions form the Jingjinji metropolitan region and the national capital region of China.[13]
Beijing is an important capital and global power city, and one of the world's leading centers for politics, economy and business, finance, education, culture, innovation and technology, architecture, language, and diplomacy. A megacity, Beijing is the second largest Chinese city by urban population after Shanghai and is the nation's political, cultural, and educational center.[14] It is home to the headquarters of most of China's largest state-owned companies and houses the largest number of Fortune Global 500 companies in the world.[15] It is also a major hub for the national highway, expressway, railway, and high-speed rail networks. The Beijing Capital International Airport has been the second busiest in the world by passenger traffic since 2010,[16] and, as of 2016, the city's subway network is the busiest and second longest in the world.
Combining both modern and traditional architecture, Beijing is one of the oldest cities in the world, with a rich history dating back three millennia. As the last of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China, Beijing has been the political center of the country for most of the past eight centuries,[17] and was the largest city in the world by population for much of the second millennium A.D.[18] Encyclopædia Britannica notes that "few cities in the world have served for so long as the political headquarters and cultural center of an area as immense as China."[19] With mountains surrounding the inland city on three sides, in addition to the old inner and outer city walls, Beijing was strategically poised and developed to be the residence of the emperor and thus was the perfect location for the imperial capital. The city is renowned for its opulent palaces, temples, parks, gardens, tombs, walls and gates.[20] It has seven UNESCO World Heritage Sites – the Forbidden City, Temple of Heaven, Summer Palace, Ming Tombs, Zhoukoudian, and parts of the Great Wall and the Grand Canal – all popular locations for tourism.[21] Siheyuans, the city's traditional housing style, and hutongs, the narrow alleys between siheyuans, are major tourist attractions and are common in urban Beijing.
Pékin2 (en chinois : 北京 ; pinyin : běijīng ; API : [pe˨˩˦i.tɕi˥ŋ] Écouter la prononciation en mandarin, littéralement « capitale du nord »), également appelée Beijing, est la capitale de la République populaire de Chine. Située dans le nord du pays, la municipalité de Pékin (北京市, abrégé en 北京), d'une superficie de 16 800 km2, borde la province du Hebei ainsi que la municipalité de Tianjin. Pékin est considérée comme le centre politique et culturel de la Chine, tandis que Hong Kong et Shanghai dominent au niveau économique.
D'abord ville périphérique de l'empire chinois sous les Han et les Tang, elle prend de l'importance lorsque les Jurchen, qui fondent la dynastie Jin, la choisissent comme leur capitale principale en 1153. Le prince mongol Kubilai Khan en fait de même sous le nom de Dadu (« grande métropole »), enfin les Ming y transfèrent leur administration en 1421, parachevant le choix de Pékin comme capitale de la Chine. Située à proximité de la Grande Muraille, Pékin abrite des monuments célèbres comme la Cité interdite et le Temple du ciel, qui sont inscrits au patrimoine mondial. De nombreuses réalisations architecturales et structurelles ont modifié la ville à l'occasion des Jeux olympiques d'été dont elle a été l'hôte en 2008. Beijing a été choisie par le CIO pour organiser les Jeux olympiques d'hiver de 2022 et sera la première ville à avoir accueilli les deux éditions de l'évènement sportif international.
Avec 21,15 millions d'habitants en 2013, Pékin est la deuxième ville la plus peuplée de Chine après Shanghai. La zone urbaine compte quant à elle 18 millions d'habitants. Le parler pékinois forme la base du mandarin standard. D'un point de vue économique, Pékin est la troisième ville de Chine par le PIB total derrière Shanghai et Hong Kong. Elle connaît une croissance économique très rapide, nettement plus de 10 % par an dans les années 2000. Un nouveau Central business district (CBD) est en construction.
Pechino (AFI: /peˈkino/[1]; in cinese 北京S, BěijīngP, letteralmente "capitale del nord", pronuncia in mandarino[?·info]) è la capitale della Cina e della municipalità omonima.
L'intera municipalità ha dimensioni pari a poco più della metà del Belgio avendone però quasi il doppio degli abitanti (21.516.000[senza fonte]). Pechino è la seconda città più popolata della Cina dopo Shanghai, la capitale di Stato più popolata al mondo, e la seconda città del mondo per popolazione. Confina esclusivamente con la provincia dell'Hebei e a sud-est con la municipalità di Tientsin.
Pekín, Pequín o Beijing (chino simplificado y tradicional: 北京, pinyin: Běijīng, Wade-Giles: Pei-ching, pronunciado: [pèi.tɕíŋ](![]() escuchar), literalmente «capital del Norte») es uno de los cuatro municipios que, junto con las veintidós provincias, cinco regiones autónomas y dos regiones administrativas especiales, conforman la República Popular China. Además Pekín es la capital del país y una de las ciudades más pobladas del mundo con 21 150 000 personas en 2013.2
escuchar), literalmente «capital del Norte») es uno de los cuatro municipios que, junto con las veintidós provincias, cinco regiones autónomas y dos regiones administrativas especiales, conforman la República Popular China. Además Pekín es la capital del país y una de las ciudades más pobladas del mundo con 21 150 000 personas en 2013.2
Situada en la periferia de la antigua civilización china, Pekín se convirtió en el baluarte de las potencias extranjeras que ocuparon China del Norte entre los siglos X y XII. La dinastía Liao estableció aquí su capital meridional, la más acreditada de las cinco del reino. La dinastía Jin, la siguiente dinastía "bárbara" emprendió un amplio proyecto urbanístico a imagen de la capital de los Song septentrionales, Kaifeng. En 1215 los mongoles arrasaron la ciudad, pero 50 años después Kublai Kan decidió edificar en ella la nueva capital.
En la zona centro-sur del trazado hipodámico se hallaba la colosal villa imperial que contenía el complejo de palacios imperiales. El emperador Yongle, el tercer Ming, decidió trasladar la capitalidad a Pekín. Las murallas del lado septentrional fueron trasladadas más hacia el Sur para que el complejo palaciego imperial, la llamada Ciudad Prohibida, quedase exactamente en el centro del plano. Así la estructura del nuevo Pekín representa la cima del urbanismo tradicional chino, basado en la organización introducida por los mongoles así como en la estructura de los palacios imperiales de Kaifeng y Nankín además de tomar en consideración las normas de la geomancia china (風水).
Pekín es uno de los cuatro municipios de China que poseen un estatus provincial y están bajo el control directo del gobierno central. Pekín ha sido municipalidad desde la creación de la República Popular China. Es una de las ciudades más pobladas de China, tan sólo superada por Shanghái en cuanto a población. Es considerada el corazón cultural, político y social de China.
Пеки́н (кит. 北京, пиньинь: Běijīng, палл.: Бэйцзин, буквально: «Северная столица») — столица и один из городов центрального подчинения Китайской Народной Республики. Пекин с трёх сторон окружён провинцией Хэбэй и граничит с Тяньцзинем на юго-востоке.
Это крупнейший железно- и автодорожный узел и один из основных авиаузлов страны. Кроме того, Пекин является политическим, образовательным и культурным центром КНР, в то время как главными экономическими центрами считаются Шанхай и Гонконг. Вместе с тем, в последнее время всё больше берёт на себя роль локомотива предпринимательской деятельности и основного поля для создания инновационных предприятий.
Входит в число четырёх древних столиц Китая. В 2008 году в городе прошли Летние Олимпийские игры. В 2022 году в городе пройдут Зимние Олимпийские игры.
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 History
History
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
 Hungary
Hungary

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 World Heritage
World Heritage
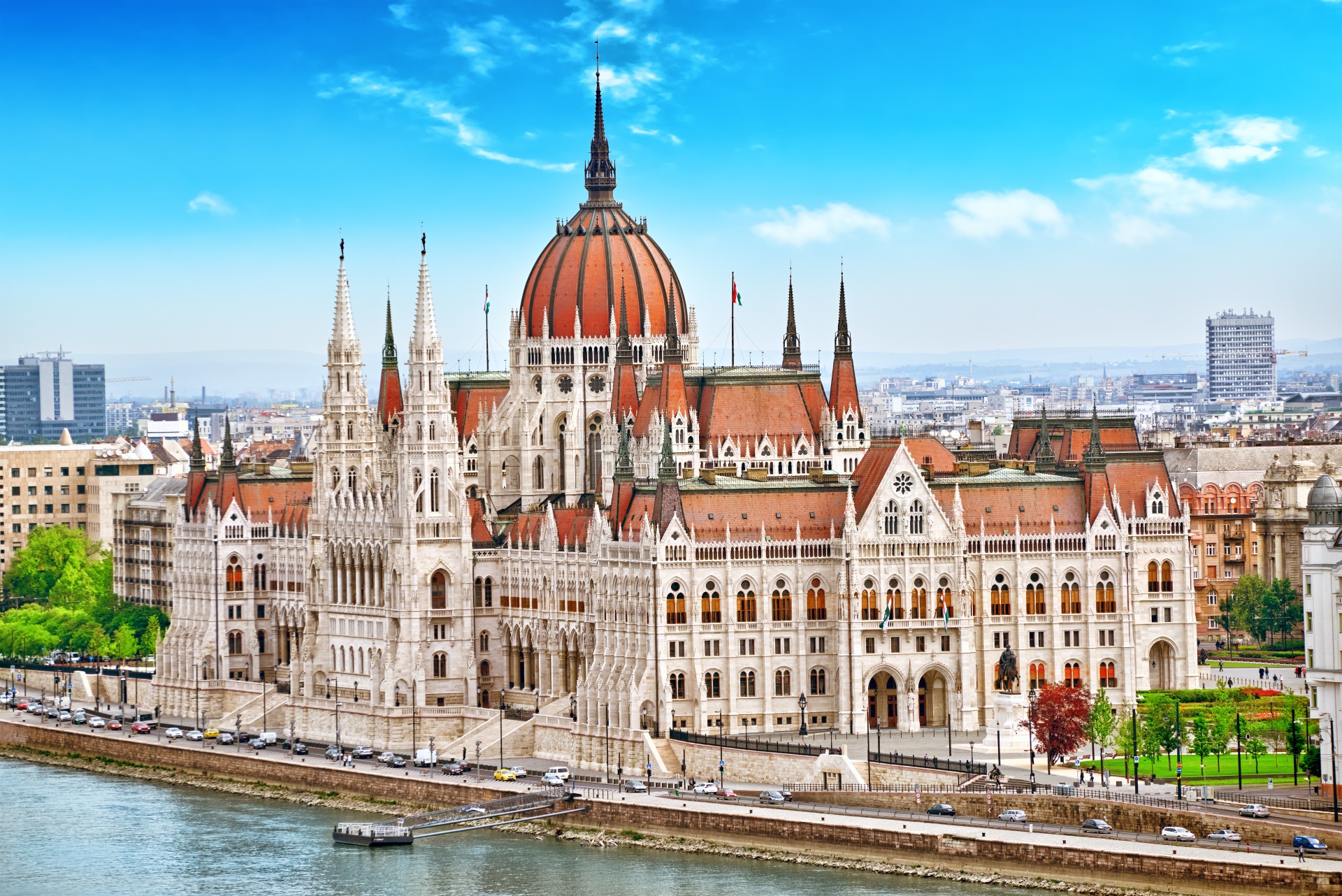

ブダペストまたはブダペシュト(ハンガリー語: Budapest, 英語:[ˈbuːdəpɛst], [ˈbuːdəpɛʃt] or [ˈbʊdəpɛst]; ハンガリー語発音: [ˈbudɒpɛʃt] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、ハンガリーの首都であり、同国最大の都市である[2]。
音声ファイル))は、ハンガリーの首都であり、同国最大の都市である[2]。
「ブダペスト」として一つの市でドナウ川の両岸を占めるようになったのは1873年11月17日に西岸のブダとオーブダ、東岸のペストが合併してからである[3][4]。
ドナウ川河畔に位置し、ハンガリーの政治、文化、商業、産業、交通の一大中心都市で[5]、東・中央ヨーロッパ (en) では最大、欧州連合の市域人口では8番目に大きな都市である。しばしばハンガリーのプライメイトシティとも表現される[6]。
ブダペストの市域面積は525km2 (202.7 sq mi)[3]で、2011年の国勢調査によるブダペストの人口は174万人[7]、ピークであった1989年の210万人より減少している[8]。これは、ブダペスト周辺部の郊外化によるものである[9]。ブダペスト都市圏(通勤圏)の人口は330万人である[10][11]。
ブダペストの歴史の始まりはローマ帝国のアクインクムとしてで、もともとはケルト人の集落であった[12][13]。アクインクムは古代ローマの低パンノニア属州の首府となっている[12]。マジャル人がブダペスト周辺にやって来たのは[14]9世紀頃である。最初の集落は1241年から1242年にかけてモンゴルの襲来 (en) により略奪された[15]。15世紀に[16]町が再建されるとブダペストはルネサンス期の人文主義者文化の中心となった[17]。続いてモハーチの戦いが起こり、オスマン帝国による150年間の支配が続き[18]、18世紀、19世紀に新しい時代に入ると町は発展し繁栄する。ブダペストは1873年にドナウ川を挟んだ都市の合併が行われると、世界都市となる[19]。また、1848年から1918年の第一次世界大戦勃発まで列強に含まれたオーストリア=ハンガリー帝国のウィーンに続く第二の首都であった。1920年のトリアノン条約によりハンガリーは国土の72%を失い、ハンガリーの文化や経済をブダペストがすべてを占めるようになった。ブダペストはその大きさや人口で圧倒的に優位に立ち、ハンガリーの他の都市を小さく見せていた[20]。ブダペストはハンガリー革命 (1848年)や1919年のハンガリー評議会共和国、1944年のパンツァーファウスト作戦、1945年のブダペスト包囲戦、1956年のハンガリー動乱など数々の歴史的な舞台の場でもあった。
ブダペストはヨーロッパでも最も美しい街の一つで[2][21][22]、ドナウ川河岸を含め世界遺産が広がりブダ城やアンドラーシ通り、英雄広場は良く知られている。ブダペスト地下鉄1号線Millenniumi Földalatti Vasútはロンドン地下鉄に次いで世界で2番目に古い地下鉄である[21][23]。ブダペストの他のハイライトはセーチェーニ温泉を含めた80の温泉で[24]世界でも最大の地下熱水系統がある[25]。世界で3番目に大きなシナゴーグであるドハーニ街シナゴーグや国会議事堂などもブダペストの見所である。ブダペストの観光客数は年間270万人に上り、ロンドンにある民間調査機関ユーロモニターによればブダペストは世界で37番目に旅行者が多い観光地であるとされている[26]。
Budapest /ˈbuːdəpɛst/ is the capital and the most populous city of Hungary, and the tenth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits.[9][10][11] The city had an estimated population of 1,752,704 in 2016 distributed over a land area of about 525 square kilometres (203 square miles).[12] Budapest is both a city and county, and forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of 7,626 square kilometres (2,944 square miles) and a population of 3,303,786, comprising 33 percent of the population of Hungary.[13][14]
The history of the city began when an early Celtic settlement transformed into a Roman town of Aquincum,[15][16] the capital of Lower Pannonia.[15] The Hungarians arrived in the territory in the late 9th century.[17] By the 11th century, Buda and Óbuda (Old Buda) became the names of their settlements on the west bank of the river Danube, with a formerly Slavic and then German settlement Pest on the opposite side.[3][18] The area was pillaged by the Mongols in 1241.[18] The Battle of Mohács in 1526 was followed by nearly 150 years of Ottoman rule.[19] After the reconquest of Buda in 1686, the region entered a new age of prosperity. Pest-Buda became a global city with the unification of Buda, Óbuda, and Pest on November 17, 1873, with the name 'Budapest' given to the new capital.[12][20] Budapest also became the co-capital of the Austro-Hungarian Empire,[21] a great power that dissolved in 1918, following World War I. The city was the focal point of the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Battle of Budapest in 1945, and the Hungarian Revolution of 1956.[22][23]
Budapest is a Beta+ global city with strengths in commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and entertainment.[24][25] It is Hungary's financial centre[26] and the highest ranked Central and Eastern European city on Innovation Cities Top 100 index,[27][28][29] as well ranked as the second fastest-developing urban economy in Europe.[30] Budapest is host to many major international organization's regional offices, including the United Nations and ICDT,[31] furthermore it is the headquarters of the European Institute of Innovation and Technology,[32] the European Police College[33] and the first foreign office of the China Investment Promotion Agency.[34] Over 40 colleges and universities are located in Budapest, including the Eötvös Loránd University, Semmelweis University and the notable Budapest University of Technology and Economics.[35][36] Opened in 1896,[37] the city's subway system, the Budapest Metro, serves 1.27 million, while the Budapest Tram Network serves 1.08 million passengers daily.[38]
Budapest is cited as one of the most beautiful cities in Europe,[9][39][40] ranked as "the world's second best city" by Condé Nast Traveler,[41] and "Europe's 7th most idyllic place to live" by Forbes.[42] Among Budapest's important museums and cultural institutions is the Museum of Fine Arts. Further famous cultural institutions are the Hungarian National Museum, House of Terror, Franz Liszt Academy of Music, Hungarian State Opera House and National Széchényi Library. The central area of the city along the Danube River is classified as a UNESCO World Heritage Site and has many notable monuments, including the Hungarian Parliament, Buda Castle, Fisherman's Bastion, Gresham Palace, Széchenyi Chain Bridge, Matthias Church and the Liberty Statue.[43] Other famous landmarks include Andrássy Avenue, St. Stephen's Basilica, Heroes' Square, the Great Market Hall, the Nyugati Railway Station built by the Eiffel Company of Paris in 1877 and the second-oldest metro line in the world, the Millennium Underground Railway.[39] The city also has around 80 geothermal springs,[44] the largest thermal water cave system,[45] second largest synagogue, and third largest Parliament building in the world.[46] Budapest attracts 4.4 million international tourists per year, making it a popular destination in Europe.[47]
Budapest (prononcé [by.da.ˈpɛst] , hongrois : Budapest [ˈbu.dɒ.pɛʃt] Écouter ; allemand : Budapest ou anciennement Ofen-Pesth) est la plus grande ville et la capitale de la Hongrie. Elle se situe en aval du coude du Danube entre le massif de Transdanubie et l'Alföld. Ses habitants sont les Budapestois (en hongrois, budapesti, -ek).
La ville actuelle est créée en 1873 par la fusion de Buda — alors capitale de la Hongrie — de Pest et d'Óbuda1. Elle a pour origine le site d'Aquincum2, un point de peuplement celte3 devenu capitale de la Pannonie inférieure pendant l'époque romaine3. Les Magyars arrivent dans la région au IXe siècle. Leur premier point d'implantation est pillé par les Mongols en 1241-12424. La ville est reconstruite et devient l'un des centres de la culture humaniste de la Renaissance5 au XVe siècle6. Après près de 150 ans de domination ottomane, elle poursuit son développement et connaît son apogée avec l'épanouissement de l'ère industrielle aux XVIIIe et XIXe siècles. Après la fusion de 1873 et l'accession de la ville au rang de seconde capitale de l'Autriche-Hongrie, Budapest atteint les proportions et les caractéristiques d'une ville mondiale7. Marquée par les différentes traces léguées par l'histoire, Budapest a notamment été l'épicentre de la révolution hongroise de 1848, de la République des conseils de Hongrie de 1919, de l'opération Panzerfaust en 1944, de la bataille de Budapest de 1945 et de l'insurrection de 1956.
Considérée comme l'une des plus belles villes d'Europe et comme la « perle » du Danube8,1,9, son panorama, le quartier du château de Buda, l'avenue Andrássy et le métropolitain du Millénaire figurent au patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO8,10. Destination touristique importante, la ville attire plus de 4,3 millions de visiteurs par an11.
Plus grande ville du pays, elle en est le principal centre politique, culturel, commercial et industriel. Elle abrite le Parlement hongrois, les bâtiments ministériels et les ambassades du pays ainsi que les sièges sociaux des entreprises installées en Hongrie. Son ancien statut de cocapitale de l'Autriche-Hongrie lui confère un rayonnement important dans la Mitteleuropa. La partition du royaume de Hongrie à la suite du traité de Trianon en 1920 en fait une ville démesurée pour la Hongrie dans ses frontières actuelles. La macrocéphalie dont est atteinte la ville se concrétise par la convergence de la plupart des réseaux routiers et ferroviaires du pays en son centre et des écarts démographiques et économiques disproportionnés entre la capitale et la province12 (près de 20 % de la population hongroise est budapestoise). Avec ses 1 702 297 habitants13 (l'aire urbaine en compte 2 524 697), Budapest est également la ville la plus peuplée d'Europe centrale (si l'on exclut Berlin de l'Europe centrale). Elle en est également considérée du point de vue des échanges économiques comme une importante plaque tournante14. Budapest abrite le siège de l'Institut européen d'innovation et de technologie (IET)15.
Budapest (IPA: [ˈbudɒpɛʃt]; pronuncia italiana moderna: /ˈbudapest/[1]) è la capitale e la maggiore città dell'Ungheria.
Amministrata come un comune autonomo, costituisce inoltre il centro primario del Paese per la vita politica, economica e culturale; al 2016 conta 1 759 407 abitanti, mentre la popolazione residente nell'area metropolitana ammonta a oltre 3 300 000 persone.
Budapest nacque ufficialmente nel 1873 dall'unione delle città storiche di Buda e Óbuda, ubicate sulla sponda destra del Danubio, con l'abitato di Pest, situato sulla riva opposta del fiume e anch'esso di antiche origini; fino al 1918 fu una delle due capitali dell'Impero austro-ungarico, dissoltosi al termine della prima guerra mondiale.
Nel XXI secolo, Budapest è diventata una metropoli globale e si è affermata come una popolare destinazione turistica: nel 2011, secondo i dati forniti da Euromonitor International, la capitale ungherese è stata la 25ª città più visitata del mondo[2].
Budapest (![]() /ˈbudɒpɛʃt/ (?·i)) es la capital y ciudad más poblada de Hungría,2 así como su principal centro industrial, comercial y de transportes.3 La ciudad posee 1,74 millones de habitantes (2011),4 una disminución significativa respecto de los casi 2,1 millones con que contaba a mediados de los años 1980,5 que representan un quinto de la población total de Hungría. Es la ciudad más poblada de Europa central-oriental y la séptima de la Unión Europea. La ciudad ocupa una superficie de 525 km²6 y su área metropolitana cuenta con una población de 2,38 millones de habitantes. Budapest se convirtió en una única ciudad cuando ocupó las dos orillas del río Danubio, unificando las ciudades de Buda y Óbuda, en la orilla oeste, con Pest, en la orilla este, el 17 de noviembre de 1873.67
/ˈbudɒpɛʃt/ (?·i)) es la capital y ciudad más poblada de Hungría,2 así como su principal centro industrial, comercial y de transportes.3 La ciudad posee 1,74 millones de habitantes (2011),4 una disminución significativa respecto de los casi 2,1 millones con que contaba a mediados de los años 1980,5 que representan un quinto de la población total de Hungría. Es la ciudad más poblada de Europa central-oriental y la séptima de la Unión Europea. La ciudad ocupa una superficie de 525 km²6 y su área metropolitana cuenta con una población de 2,38 millones de habitantes. Budapest se convirtió en una única ciudad cuando ocupó las dos orillas del río Danubio, unificando las ciudades de Buda y Óbuda, en la orilla oeste, con Pest, en la orilla este, el 17 de noviembre de 1873.67
La historia de Budapest comenzó con Aquincum, originalmente un asentamiento celta89 que se convirtió en la capital romana de Panonia Inferior.8 Los húngaros llegaron al territorio en el siglo IX.10 Su primer asentamiento fue saqueado por los mongoles en 1241-42.11 La ciudad restablecida se convirtió en uno de los centros de la cultura del Renacimiento humanista en el siglo XV.1213 Después de la batalla de Mohács y tras casi 150 años de dominio otomano,14 el desarrollo de la región entró en una nueva era de prosperidad en los siglos XVIII y XIX, y Budapest se convirtió en una ciudad global después de la unificación de 1873.15 También se convirtió en la segunda capital de Austria-Hungría, una gran potencia que se disolvió en 1918. Budapest fue el punto focal de la revolución húngara de 1848, la República Soviética Húngara de 1919, la Operación Panzerfaust en 1944, la batalla de Budapest de 1945 y la Revolución de 1956.
Considerada como una de las ciudades más bellas de Europa,21617 Budapest cuenta con varios sitios que son Patrimonio de la Humanidad, entre los que se incluyen, a orillas del Danubio, el barrio del Castillo de Buda, la avenida Andrássy, la Plaza de los Héroes y el Metropolitano del Milenio, el segundo más antiguo del mundo.1618 Otros puntos destacados incluyen un total de 80 manantiales geotérmicos,19 el mayor sistema de cuevas de aguas termales del mundo,20 la segunda sinagoga más grande y el tercer edificio del Parlamento más grande del mundo. La ciudad atrae a alrededor de 4,3 millones de turistas al año, convirtiéndola en la 25.ª ciudad más popular del mundo, según Euromonitor.21
Budapest es, también, un importante centro financiero de Europa Central. La ciudad se situó tercera (de un total de 65 ciudades) en el Índice de Mercados Emergentes elaborado por Mastercard,22 y clasificada como la ciudad mejor habitable de Europa Central y Europa del Este por índice de calidad de vida según Economist Intelligence Unit.2324 También se clasificó como el "séptimo lugar idílico de Europa para vivir" por la revista Forbes,25 y como la novena ciudad más bella del mundo por UCityGuides.26 Es, también, la mejor ciudad de Europa Central y del Este en el índice Innovation Cities' Top 100.2728
Будапе́шт (венг. Budapest [ˈbudɒpɛʃt]) — столица Венгрии и самый крупный город страны. По численности населения, составлявшей на январь 2014 года 1,745 млн жителей[2], в Европейском союзе Будапешт занимает восьмое место. Город образовался в 1873 году в результате слияния нескольких венгерских городов: Пешта, расположенного на восточной стороне реки Дунай, Буды и Обуды, занимающих западный берег Дуная.

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1999
Women's Soccer World Cup 1999

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
 United States
United States
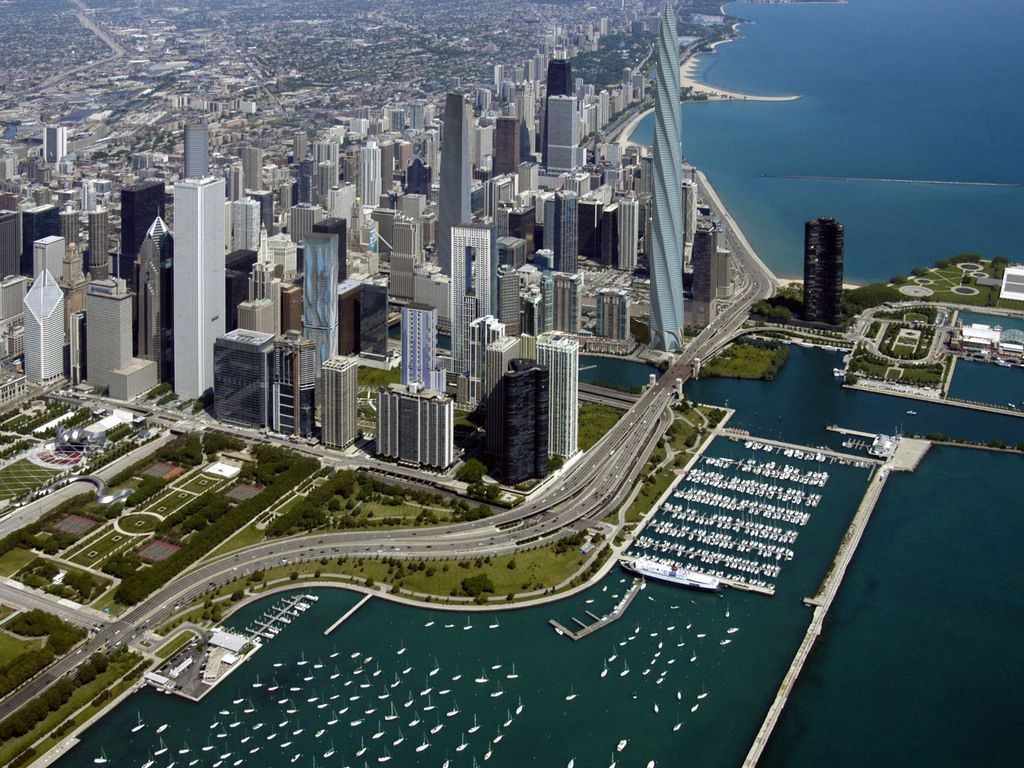

十七世纪时为法国皮毛商交易地,后归美国。1834年建市。1848年伊利诺伊·密歇根运河开通和铁路相继修建后,发展极速。全国最大的铁路 枢纽,32条干线交会于此。现为全国性的重要农畜产品贸易市场和钢铁冶炼基地。肉类加工、面粉、罐头、冷冻食品加工等发达。此外还有农机制造、机车、货 车、电话机、电视机、收音机、印刷、塑料等。包括卫星城市格里、南芝加哥,为美国第二个重工业地带。多大银行、商业企业,有芝加哥大学(1891年建)与 科学研究机构等。
芝加哥市内保存着早期传统式的西欧古建筑,又有壮观巍峨的现代摩天大楼。市区沿着宽阔壮丽的大道连绵数十公里,规划布局井井有条。现在的城市是 1871年的大火之后重建的,新城各种形状新奇、色彩各异的高层建筑使其成为一建筑艺术博物馆。芝加哥市区内摩天大楼之多,仅次于纽约。
芝加哥市内保存着早期传统式的西欧古建筑,又有壮观巍峨的现代摩天大楼。市区沿着宽阔壮丽的大道连绵数十公里,规划布局井井有条。现在的城市是1871年 的大火之后重建的,新城各种形状新奇、色彩各异的高层建筑使其成为一建筑艺术博物馆。芝加哥市区内摩天大楼之多,仅次于纽约。当今全世界5座最高的摩天大 楼有3座在芝加哥,市中心的西尔斯大厦是美国第一高楼,有110层,高443米。
19世纪开通的伊利诺伊-密歇根运河,把处于内陆的芝加哥同五大湖和大西洋连接起来,变为港口城市。海洋巨轮从加拿大的圣劳伦斯湾直驶芝加哥码头。芝加哥是美国的铁路枢纽,几十条铁路交汇于此,连接美国各大城市;它还有世界上最繁忙国际机场之一的奥黑尔国际机场;因此,芝加哥可以称得上美国东西交通、水、陆、空运输的中心。
Wie die meisten amerikanischen Städte ist Chicago am Reißbrett entworfen worden. Das Schachbrettmuster kann man z.B. von der Aussichtsplattform des Sears-Towers gut erkennen. Die Aussicht von diesem Punkt aus ist atemberaubend. Genießen Sie das Panorama des Lake Michigan und beobachten Sie die Flugzeuge die am Chicago-International-Airport landen.
Chicago (deutsche Schreibweise: Chikago,[1] Aussprache: [ʃɪˈkɑːgoʊ]; ) ist eine Stadt am Südwestufer des Michigansees im Bundesstaat Illinois in den Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika. Mit einer Einwohnerzahl von 2.722.389 (2014)[2] ist sie die drittgrößte Stadt der Vereinigten Staaten. In der Agglomeration leben 8,7 Millionen, in der Metropolregion Chicago 9,7 Millionen Menschen (2007).[3]
Chicago ist seit der Mitte des 19. Jahrhunderts eine wichtige Handelsstadt in den Vereinigten Staaten. Diese Funktion wird durch ihre Eigenschaft als Eisenbahnknotenpunkt und ihre Lage an der Mündung des Illinois Waterways begünstigt. Die Stadt liegt an wichtigen Eisenbahnstrecken, die die Ost- mit der Westküste verbinden und ist über die Großen Seen und den Sankt-Lorenz-Seeweg bzw. den Eriekanal mit dem Atlantik und mit New York City verbunden. Der Illinois Waterway stellt über den Mississippi die Verbindung zum Golf von Mexiko her.
Chicago ist Sitz der Chicago Mercantile Exchange, der größten Warenterminbörse der Vereinigten Staaten, und der Chicago Board of Trade, der größten Rohstoff-, Futures- und Optionsbörse der Vereinigten Staaten. Außerdem befindet sich hier die größte Regionalbörse der Vereinigten Staaten, die Chicago Stock Exchange.
Die Metropolregion von Chicago erbrachte 2016 eine Wirtschaftsleistung von 651,2 Milliarden US-Dollar.[4] Bei einer Studie aus dem Jahr 2014 belegte Chicago Platz 9 unter den wirtschaftsstärksten Metropolregionen weltweit und Platz 3 innerhalb der Vereinigten Staaten.[5]
シカゴ(英: Chicago [ʃɨˈkɑːɡoʊ, ʃɨˈkɔːɡoʊ, tʃɨˈkɑːɡoʊ] (![]() 音声ファイル)))は、アメリカ合衆国イリノイ州にある都市。同州最大の都市であり、国内では、ニューヨーク、ロサンゼルスに次ぐ人口を持つ。
音声ファイル)))は、アメリカ合衆国イリノイ州にある都市。同州最大の都市であり、国内では、ニューヨーク、ロサンゼルスに次ぐ人口を持つ。
シカゴはクック郡内にあり、同郡の郡庁所在地である。同郡には他にアーリントンハイツなどが含まれる。2012年の人口は271万人。
19世紀後半から20世紀中盤まで、アメリカ国内における鉄道・航空・海運の拠点として、また五大湖工業地帯の中心として発展し、ニューヨークに次ぐアメリカ第2の都市となっていた歴史を持つ。摩天楼がそびえ立つアメリカ型都市の発祥とされ、ダウンタウンの高層建築は、シカゴ派として知られ、近代建築史における重要局面をなした。1973年に建てられたシアーズ・タワー(現在はウィリス・タワーに改称)は、1998年まで世界一の高層建築であった。マコーミック・プレイスコンプレックスは、北米最大のコンベンション・センターであり、オヘア空港は全米有数の過密な空港として知られる。
アメリカのシンクタンクが2017年に発表した総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界12位の都市と評価された[1]。アメリカの都市ではニューヨーク、ロサンゼルスに次ぐ3位である。2017年3月の調査によると、世界7位の金融センターである[2]。2014年の都市の経済規模(GDP)では、世界9位となっている[3]。
日本語の漢字表記は「市俄古」。また、シカゴに住む人々は「Chicagoans(シカゴアンズ)」と呼ばれている[4]。
Chicago (/ʃɪˈkɑːɡoʊ/ (![]() listen), locally also /-ˈkɔː-/), officially the City of Chicago, located on the shores of freshwater Lake Michigan, is the third most populous city in America after New York and Los Angeles. As of the 2017 census-estimate, Chicago has a population of 2,716,450, which makes it the most populous city in both the state of Illinois and the Midwestern United States. It is the county seat of Cook County, the second most populous county in the U.S. Chicago is the principal city of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is often referred to as "Chicagoland." The Chicago metropolitan area has nearly 10 million people, is the third-largest in the United States, the fourth largest in North America, and the third largest metropolitan area in the world by land area. Chicago is the birthplace of the skyscraper, and considered the most influential architectural city of the 20th century.[6] In finance, the city saw the creation of the first standardized futures contracts at the Chicago Board of Trade; which today is the largest and most diverse derivatives market in the world, generating 20% of all volume in commodities and financial futures.[7]
listen), locally also /-ˈkɔː-/), officially the City of Chicago, located on the shores of freshwater Lake Michigan, is the third most populous city in America after New York and Los Angeles. As of the 2017 census-estimate, Chicago has a population of 2,716,450, which makes it the most populous city in both the state of Illinois and the Midwestern United States. It is the county seat of Cook County, the second most populous county in the U.S. Chicago is the principal city of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is often referred to as "Chicagoland." The Chicago metropolitan area has nearly 10 million people, is the third-largest in the United States, the fourth largest in North America, and the third largest metropolitan area in the world by land area. Chicago is the birthplace of the skyscraper, and considered the most influential architectural city of the 20th century.[6] In finance, the city saw the creation of the first standardized futures contracts at the Chicago Board of Trade; which today is the largest and most diverse derivatives market in the world, generating 20% of all volume in commodities and financial futures.[7]
Chicago was incorporated as a city in 1837 near a portage between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River watershed and grew rapidly in the mid-nineteenth century.[8] After the Great Chicago Fire of 1871, which destroyed several square miles and left more than 100,000 homeless, the city made a concerted effort to rebuild.[9] The construction boom accelerated population growth throughout the following decades, and by 1900 Chicago was one of the five largest cities in the world.[10] During this period, Chicago made noted contributions to urban planning and zoning standards, which included creating new construction styles (including the Chicago School of architecture), the development of the City Beautiful Movement, and the steel-framed skyscraper.[11]
Positioned along Lake Michigan, the city is an international hub for finance, commerce, industry, technology, telecommunications, and transportation. O'Hare International Airport is the one of the busiest airports in the world, and the region also has the largest number of U.S. highways and railroad freight.[12] In 2012, Chicago was listed as an alpha global city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network,[13] and it ranked seventh in the entire world in the 2017 Global Cities Index.[14] Chicago has the fourth-largest gross metropolitan product in the world — generating about $670.5 billion according to September 2017 estimates — ranking it after the metropolitan areas of Tokyo, New York City, and Los Angeles, and ranking ahead of number five London and number six Paris.[15] Chicago has one of the world's largest and most diversified and balanced economies, not being dependent on any one industry, with no single industry employing more than 14% of the workforce.[16]
Chicago was the second most visited city in the United States with 55 million domestic and international visitors,[17][18] not far behind the 62 million visitors to New York City in 2017.[19] The city ranked first place in the 2018 Time Out City Life Index, a global quality of life survey of 15,000 people in 32 cities.[20][21][22][23][24] Landmarks in the city include Millennium Park, Navy Pier, the Magnificent Mile, the Art Institute of Chicago, Museum Campus, the Willis (Sears) Tower, the Museum of Science and Industry, and Lincoln Park Zoo. Chicago's culture includes the visual arts, literature, film, theater, comedy (especially improvisational comedy), food, and music, particularly jazz, blues, soul, hip-hop, gospel,[25] and electronic dance music including house music. There are many colleges and universities in the Chicago area, of which the University of Chicago, Northwestern University, and the University of Illinois at Chicago are classified as "highest research" doctoral universities.
Chicago has professional sports teams in each of the major professional leagues, including two Major League Baseball teams. The city has had several nicknames throughout its history such as the Windy City, Chi-Town, Second City, and the City of the Big Shoulders, referring to its numerous towers and skyscrapers.[26]
Chicago (en anglais [ʃɪˈkɑːɡoʊ] ou [ʃɪˈkɔːɡoʊ]) est la troisième ville des États-Unis par sa population et se situe dans le nord-est de l'État de l'Illinois. C'est la plus grande ville de la région du Midwest, dont elle forme le principal centre économique et culturel2. Chicago se trouve sur la rive sud-ouest du lac Michigan, un des cinq Grands Lacs d'Amérique du Nord. Les rivières Chicago et Calumet traversent la ville.
Comptoir commercial fondé à la fin du XVIIIe siècle par Jean Baptiste Pointe du Sable, un mulâtre d'origine française, Chicago devient une municipalité en 18333 et acquiert officiellement le statut de ville en 18374. Elle est le siège du comté de Cook. Chicago est aussi le siège d'une paroisse catholique francophone, signe de son histoire liée à la France5.
La ville de Chicago compte 2 716 450 habitants et s'étend sur une superficie de 606 km2. Ses habitants s'appellent les Chicagoans6 (ou plus rarement Chicagolais7). Troisième ville des États-Unis par sa population, l'agglomération de Chicago est également la troisième du pays avec une population de 8 711 000 habitants s'étendant sur 5 498 km2. L'aire métropolitaine de Chicago (Chicago metropolitan area), communément appelée « Chicagoland », compte 9 526 434 habitants et s'étend sur 28 163 km28,9 à travers trois États (Illinois, Indiana et Wisconsin), ce qui en fait la quatrième aire urbaine d'Amérique du Nord après Mexico, New York et Los Angeles10.
Chicago est une ville de classe mondiale alpha11. Elle constitue le deuxième centre industriel des États-Unis et appartient à la « Ceinture des industries » (Manufacturing Belt), mais la ville est aussi une des principales places financières du monde12 et la première bourse de matières premières agricoles au monde13. C'est à Chicago que sont fixés les prix du blé et du soja aux États-Unis14. La ville se classe au troisième rang national pour le nombre d'entreprises implantées dans son agglomération15, dont les plus importantes sont Motorola, Boeing, United Airlines, McDonald's, Sears, Kraft Foods, Mondelēz ou encore les laboratoires Abbott. D'autres entreprises y ont été créées, comme Hertz, l'une des plus grandes enseignes de location de voitures. L'industrie emploie plus d'un million de personnes dans l'agglomération de Chicago15.
Grâce à sa situation exceptionnelle, la ville constitue un centre de communication majeur de voies terrestres (l'un des plus importants en Amérique du Nord), et de transports aériens avec ses deux aéroports internationaux, O'Hare et Midway. Elle acquiert une grande renommée culturelle grâce à son architecture moderne de gratte-ciel16 et attire des millions de visiteurs chaque année17. En effet, la Willis Tower (appelée « Sears Tower » jusqu'au mois de juillet 2009) a été de 1973 à 1998, le plus haut gratte-ciel du monde18 et est à ce jour le deuxième immeuble le plus haut du continent américain après le One World Trade Center à New York. Enfin, la ville compte de nombreux établissements d'enseignement supérieur, des musées prestigieux, des théâtres réputés et un orchestre symphonique de renommée mondiale.
Chicago (AFI: /ʧiˈkaɡo/[4]; in inglese /ʃɪˈkɑɡoʊ/) è la più grande città dell'Illinois, la più grande metropoli dell'entroterra statunitense e la terza per popolazione di tutti gli Stati Uniti d'America dopo New York e Los Angeles, con i suoi 2.722.389 abitanti.[3] La sua area metropolitana (detta Chicagoland) conta 9.554.598 abitanti distribuiti in un'ampia area pianeggiante situata lungo le rive del lago Michigan. Trasformatasi da cittadina in una importante metropoli, Chicago è stata definita come una delle 10 città più influenti al mondo. Oggi è una città multietnica, nonché un importante centro finanziario e industriale ed uno dei maggiori centri fieristico/espositivi mondiali.
Il centro della città (denominato "the Loop") è dominato da imponenti grattacieli che arrivano anche ai 108 piani (per un'altezza di 442 m) della Willis Tower. Questa tipologia architettonica è nata proprio a Chicago che, se da tempo ha dovuto perdere il primato di città con più grattacieli nel paese a favore di New York, vanta ancora oggi il secondo grattacielo più alto statunitense (dopo il nuovo World Trade Center) e tre grattacieli nella classifica dei primi 15 al mondo. Venti dei suoi grattacieli superano i 200 metri d'altezza e ben 240 superano i 100 metri. La città si estende per 50 km sul lago Michigan da nord a sud.
Chicago è la città con il maggior numero di ponti mobili al mondo (attualmente 45) ed è un punto di riferimento mondiale per il blues.
La città di Chicago ha diversi soprannomi, tra i quali "Windy City" e "Second City".
Chicago, conocida coloquialmente como «la Segunda Ciudad» o «la Ciudad de los Vientos», es la tercera ciudad con mayor número de habitantes en Estados Unidos, detrás de Nueva York y Los Ángeles.
Chicago se encuentra en el estado de Illinois, a lo largo de la costa suroeste del lago Míchigan, y es la sede del condado de Cook.2 Forma parte del área metropolitana de Chicago, una conurbación integrada además por los condados periféricos.
Чика́го (англ. Chicago, МФА: [ʃɪˈkɑːgoʊ] или [ʃɪˈkɔːgoʊ]) — третий по числу жителей (после Нью-Йорка и Лос-Анджелеса) город США, второй по значимости финансовый центр страны (после Нью-Йорка) и крупнейший транспортный узел Северной Америки. Расположен на юго-западном побережье озера Мичиган в штате Иллинойс; административный центр округа Кук.
Население Чикаго (по данным переписи 2010 года) составляет 2 695 000 человек. Агломерация Чикаго (с различными пригородами) называется «Большой Чикаго» или «Страна Чикаго» (англ. Chicagoland; название предложено газетой Chicago Tribune в начале XX века); в ней проживает более 9 млн человек. Агломерация Чикаго занимает 37-е место в мире по числу жителей.
Чикаго по праву считается экономической, промышленной, транспортной и культурной столицей Среднего Запада. Неофициально его иногда также называют «Второй Город» и «Город ветров». Впервые Чикаго был назван «Городом ветров» в статье в Chicago Tribune за 1858 год.
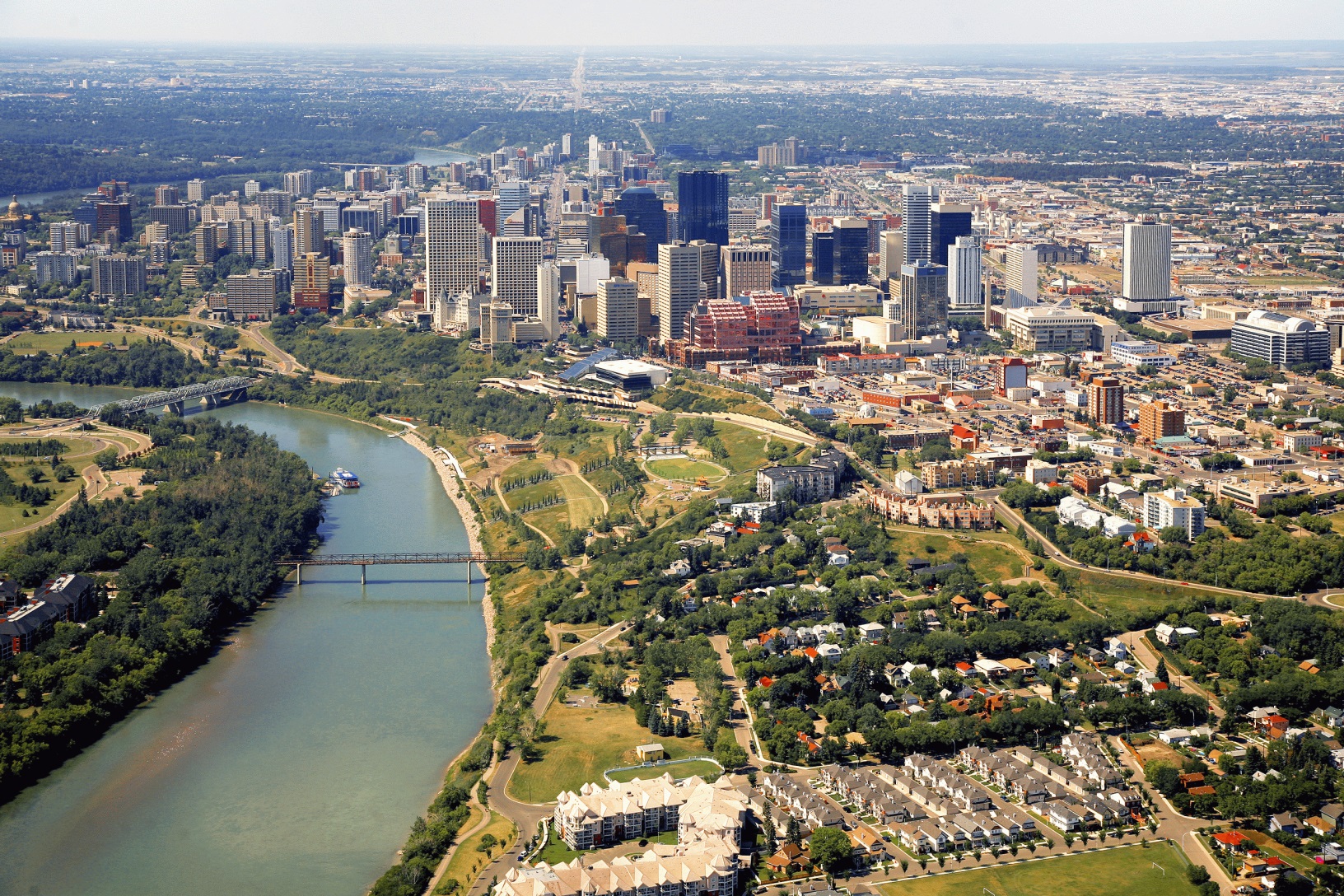


埃德蒙顿(英语:Edmonton,香港作爱民顿,台湾作艾德蒙顿,台山话作点问顿)是加拿大阿尔伯塔省的首府,该省的第二大城市(仅次于卡尔加里),城市人口为 899,447人(2016年数据),而大埃德蒙顿地区(CMA)人口为1,363,300(2015年数据)。埃德蒙顿是加拿大人口第二多的省会城市(排在多伦多之后)。埃德蒙顿是阿尔伯塔省的文化、政府和教育中心,城市拥有轻轨运输,一年有许多节日,大多集中在夏季,并有北美最大的室内购物中心——西部埃德蒙顿购物中心和加拿大最大的历史公园——埃德蒙顿炮台公园(Fort Edmonton Park)。2004年,埃德蒙顿庆祝其建市100周年(1904年)。
Edmonton [ˈedməntən] ist die Hauptstadt der kanadischen Provinz Alberta. Sie hat 932.546 Einwohner, hingegen hat die Metropolregion (CMA) 1.411.945 Einwohner (2017).[2] Damit ist Edmonton nach Calgary die zweitgrößte Stadt der Provinz und die fünftgrößte in Kanada. Mit 683 km² Gesamtfläche ist sie eine der flächengrößten Städte Nordamerikas, hat damit aber auch eine der niedrigsten Bevölkerungsdichten.
Indianische Siedlungen reichen mindestens 11.000 Jahre zurück, doch führt sich die Stadt auf ein Fort, das 1795 errichtet wurde, zurück. 1905 wurde Edmonton Hauptstadt der Provinz, die etwa bis zum Zweiten Weltkrieg stark von der Landwirtschaft abhing. Kriegsproduktion und Bodenschätze brachten der Stadt trotz des unwirtlichen Klimas einen lange anhaltenden industriellen Boom. Den bedeutendsten Wirtschaftszweig stellen heute die Dienstleistungsgewerbe dar, deren größter Arbeitgeber neben der Regierung die University of Alberta ist.
エドモントン(英: Edmonton[2])は、カナダのアルバータ州にある都市。同州の州都であり、州内ではカルガリーに次ぐ第2の都市である(国内5位)。また、カナダの州都としてはトロントに次ぐ第2位の人口規模を持つ。肥沃な農業地帯が広がるプレーリーに位置し、ノースサスカチュワン川が周辺地域の中心を流れている。
市内人口はおよそ81万人、広域圏人口はおよそ116万人で、北米の100万人都市としては最北端に位置する。州北部で盛んなオイルサンド産業と、ノースウエスト準州で運営されている大規模なダイヤモンド鉱への玄関口となっている。文化や行政、教育が盛んな地域でもある。「ザ・フェスティバル・シティ」[3]と呼ばれるほど年間を通してイベント行事が開催され、市内には北米最大のショッピングモール「ウェスト・エドモントン・モール」と最大の歴史公園「フォート・エドモントン(Fort Edmonton)」がある。
Edmonton (/ˈɛdməntən/ (![]() listen); Cree: ᐊᒥᐢᑲᐧᒋᐊᐧᐢᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ;[13] Blackfoot: Omahkoyis[14]) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the north end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor".[15]
listen); Cree: ᐊᒥᐢᑲᐧᒋᐊᐧᐢᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ;[13] Blackfoot: Omahkoyis[14]) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the north end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor".[15]
The city had a population of 932,546 in 2016, making it Alberta's second-largest city and Canada's fifth-largest municipality.[5] Also in 2016, Edmonton had a metropolitan population of 1,321,426, making it the sixth-largest census metropolitan area (CMA) in Canada.[7] Edmonton is North America's northernmost metropolitan area with a population over one million. A resident of Edmonton is known as an Edmontonian.[16]
Edmonton's historic growth has been facilitated through the absorption of five adjacent urban municipalities (Strathcona, North Edmonton, West Edmonton, Beverly and Jasper Place)[17] in addition to a series of annexations through 1982,[18] and the annexation of 8,260 ha (82.6 km2) of land from Leduc County and the city of Beaumont on January 1, 2019.[8] Known as the "Gateway to the North",[19] the city is a staging point for large-scale oil sands projects occurring in northern Alberta and large-scale diamond mining operations in the Northwest Territories.[20]
Edmonton is a cultural, governmental and educational centre. It hosts a year-round slate of festivals, reflected in the nickname "Canada's Festival City".[1] It is home to North America's largest mall, West Edmonton Mall (the world's largest mall from 1981 until 2004),[21] and Fort Edmonton Park, Canada's largest living history museum.[22]
Edmonton (![]() /ˈɛdməntən/ (?·i)) es la capital de la provincia canadiense de Alberta, así como sede de sus poderes y su administración. Está ubicada en la parte central de la provincia, una de las zonas más fértiles de las llanuras canadienses, en torno al río Saskatchewan Norte. 812 201 personas viven en Edmonton,1 lo que la convierte en la segunda ciudad más populosa de la provincia, detrás de Calgary, la segunda capital de provincia con más habitantes tras Toronto y la quinta de Canadá. Además, su área metropolitana es la sexta más poblada del país, con una población de 1 034 945 habitantes.2
/ˈɛdməntən/ (?·i)) es la capital de la provincia canadiense de Alberta, así como sede de sus poderes y su administración. Está ubicada en la parte central de la provincia, una de las zonas más fértiles de las llanuras canadienses, en torno al río Saskatchewan Norte. 812 201 personas viven en Edmonton,1 lo que la convierte en la segunda ciudad más populosa de la provincia, detrás de Calgary, la segunda capital de provincia con más habitantes tras Toronto y la quinta de Canadá. Además, su área metropolitana es la sexta más poblada del país, con una población de 1 034 945 habitantes.2
La ciudad abarca 683 km², una superficie mayor que la de Chicago, Filadelfia, Toronto o Montreal. Sin embargo, tiene una de las densidades de población más bajas de América del Norte, alrededor del 9,4 % de la de Nueva York. El residente de Edmonton es conocido como edmontoniano.
Edmonton sirve como enlace a la zona norte del «Corredor Calgary-Edmonton», una de las cuatro regiones que en conjunto comprenden el 50 % de la población de Canadá. Desde ella se organizan proyectos a gran escala de arenas de alquitrán que se desarrollan en el norte de Alberta, así como para proyectos de minería de diamantes en los Territorios del Noroeste.
Es el centro cultural, gubernamental y educativo de Alberta. Es sede de varios festivales de talla mundial, lo que le ha valido para ganarse el título de «La ciudad festival» (The Festival City).3 En Edmonton está el centro comercial más grande de Norteamérica, el West Edmonton Mall (que fue el más grande del mundo desde 1981 hasta 2004), y el museo de historia viva más grande de Canadá, el Fort Edmonton Park. En 2004, la ciudad celebró el centenario de su fundación como ciudad.
Edmonton è il capoluogo della provincia canadese dell'Alberta. Si trova nella parte centro settentrionale della provincia, un'area che conta alcune delle più fertili terre agricole delle praterie canadesi. Dopo Calgary, è la seconda città dell'Alberta, con 932.546 abitanti. La sua area metropolitana, con una popolazione stimata nel 2016 in 1.392.600 abitanti,[2] è la quinta del Canada. Tra le città delle Americhe con più di un milione di abitanti è quella situata più a nord.
Edmonton (![]() /ˈɛdməntən/ (?·i)) es la capital de la provincia canadiense de Alberta, así como sede de sus poderes y su administración. Está ubicada en la parte central de la provincia, una de las zonas más fértiles de las llanuras canadienses, en torno al río Saskatchewan Norte. 812 201 personas viven en Edmonton,1 lo que la convierte en la segunda ciudad más populosa de la provincia, detrás de Calgary, la segunda capital de provincia con más habitantes tras Toronto y la quinta de Canadá. Además, su área metropolitana es la sexta más poblada del país, con una población de 1 034 945 habitantes.2
/ˈɛdməntən/ (?·i)) es la capital de la provincia canadiense de Alberta, así como sede de sus poderes y su administración. Está ubicada en la parte central de la provincia, una de las zonas más fértiles de las llanuras canadienses, en torno al río Saskatchewan Norte. 812 201 personas viven en Edmonton,1 lo que la convierte en la segunda ciudad más populosa de la provincia, detrás de Calgary, la segunda capital de provincia con más habitantes tras Toronto y la quinta de Canadá. Además, su área metropolitana es la sexta más poblada del país, con una población de 1 034 945 habitantes.2
La ciudad abarca 683 km², una superficie mayor que la de Chicago, Filadelfia, Toronto o Montreal. Sin embargo, tiene una de las densidades de población más bajas de América del Norte, alrededor del 9,4 % de la de Nueva York. El residente de Edmonton es conocido como edmontoniano.
Edmonton sirve como enlace a la zona norte del «Corredor Calgary-Edmonton», una de las cuatro regiones que en conjunto comprenden el 50 % de la población de Canadá. Desde ella se organizan proyectos a gran escala de arenas de alquitrán que se desarrollan en el norte de Alberta, así como para proyectos de minería de diamantes en los Territorios del Noroeste.
Es el centro cultural, gubernamental y educativo de Alberta. Es sede de varios festivales de talla mundial, lo que le ha valido para ganarse el título de «La ciudad festival» (The Festival City).3 En Edmonton está el centro comercial más grande de Norteamérica, el West Edmonton Mall (que fue el más grande del mundo desde 1981 hasta 2004), y el museo de historia viva más grande de Canadá, el Fort Edmonton Park. En 2004, la ciudad celebró el centenario de su fundación como ciudad.
Эдмонтон (англ. Edmonton [ˈɛdməntən]) — административный центр канадской провинции Альберта.
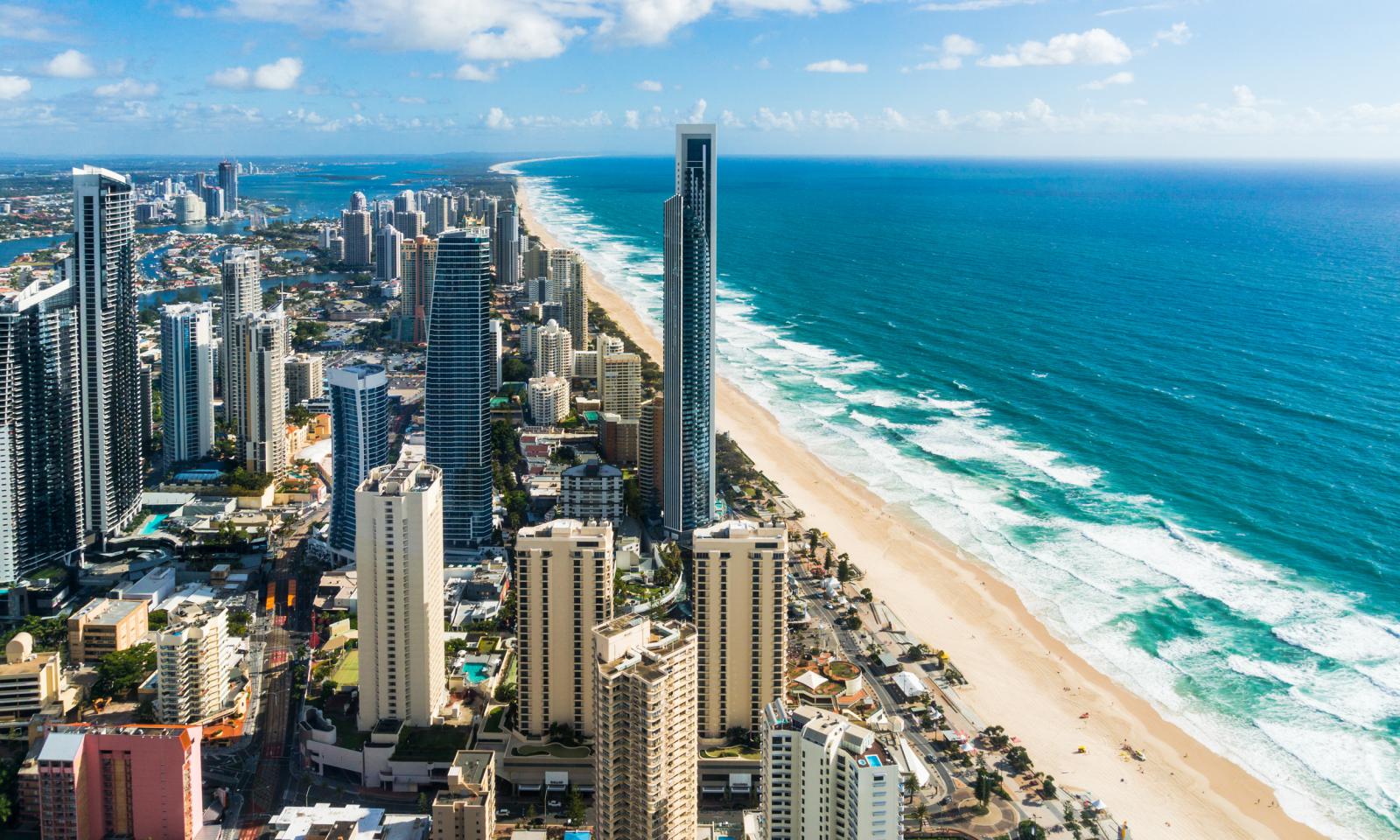


黄金海岸(英语:Gold Coast)是澳大利亚昆士兰州的太平洋沿岸城市,人口为569,997人(2016年),北与府城布里斯本(Brisbane)相邻,南与新南威尔士州堤维德岬(Tweed Heads)接壤。[1]
黄金海岸市如今是澳大利亚第六大城和国际著名的观光都市,其滨海风光和山林景观吸引了世界各地不少新移民和观光客。其文化创意产业、渔业、都市规划、资讯建设、赛车、水上运动和生物科技方面也在全球引领风骚。
Gold Coast ist eine Stadt an der Südostküste von Queensland in Australien, ca. 70 km südlich von Brisbane. Sie hat sich im Laufe von 50 Jahren aus einer losen Ansammlung kleinerer Orte zur zweitgrößten Stadt Queenslands mit knapp 600.000 Einwohnern (Stand 2016)[1] entwickelt. Sie ist Australiens sechstgrößte Stadt und gleichzeitig die für Touristen attraktivste Region des Landes.
Der „South Coast Town Council“ benannte sich 1958 in „Gold Coast Town Council“ um, und am 16. Mai 1959 wurde er von Queensland offiziell zur Großstadt Gold Coast erklärt.
Das subtropische Klima, die attraktiven Sandstrände (57 km), die oft von Surfern genutzt werden, und das Marketing haben Millionen von australischen und internationalen Touristen angelockt, und eine große Industrie ist entstanden, um dies zu unterstützen. In manchen Teilen – vor allem um Surfers Paradise – ist der schmale Küstenstreifen deshalb voller Nachtklubs, Hotels, Apartments und Touristen-Läden, was der Gold Coast lange ein billiges Image verliehen hat. Wie die Küste des US-Bundesstaats Florida zieht die Gegend viele Rentner an. Das Bild der Stadt selbst ist geprägt von zahllosen künstlichen Kanälen und Inseln.
Dank der neuen Verbindung zur Landeshauptstadt Brisbane durch den Pacific Motorway, der im Jahr 2000 nach drei Jahren Bauzeit mit knapp einer Milliarde australische Dollar Baukosten erweitert wurde, wird die Gold Coast jetzt von zwei größeren Flughäfen bedient, dem rund 100 km entfernten Brisbane International Airport, und dem Flughafen Gold Coast in Coolangatta am südlichen Ende. Außerdem ist Coolangatta der Endbahnhof der Strecke Casino-Coolangatta. In Casino erhält man Anschluss an die Hauptstrecke Brisbane–Sydney. Eine Straßenbahnlinie mit einer Länge von 13 Kilometern wurde im Juni 2014 in Betrieb genommen. Sie verbindet die Küstenabschnitte und Stadtzentren in Queenslands Süden miteinander – Main Beach, Surfers Paradise und Broadbeach. Insgesamt gibt es auf der Strecke zwischen dem Gold Coast University Hospital, Southport und Broadbeach South 16 Haltestellen.
Im Ortsteil Surfers Paradise steht der derzeit höchste Wolkenkratzer der Südhalbkugel, der Q1 Tower. Im Ortsteil Robina liegt der Campus der ersten Privatuniversität Australiens, der Bond University, in Southport der Campus der Griffith University.
 Germany
Germany
 Elbe
Elbe
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2006
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2006

 UEFA European Championship 2024
UEFA European Championship 2024

 Hamburg
Hamburg
 Hansestadt
Hansestadt
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
 Umwelthauptstadt Europas
Umwelthauptstadt Europas
 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel

 Important port
Important port
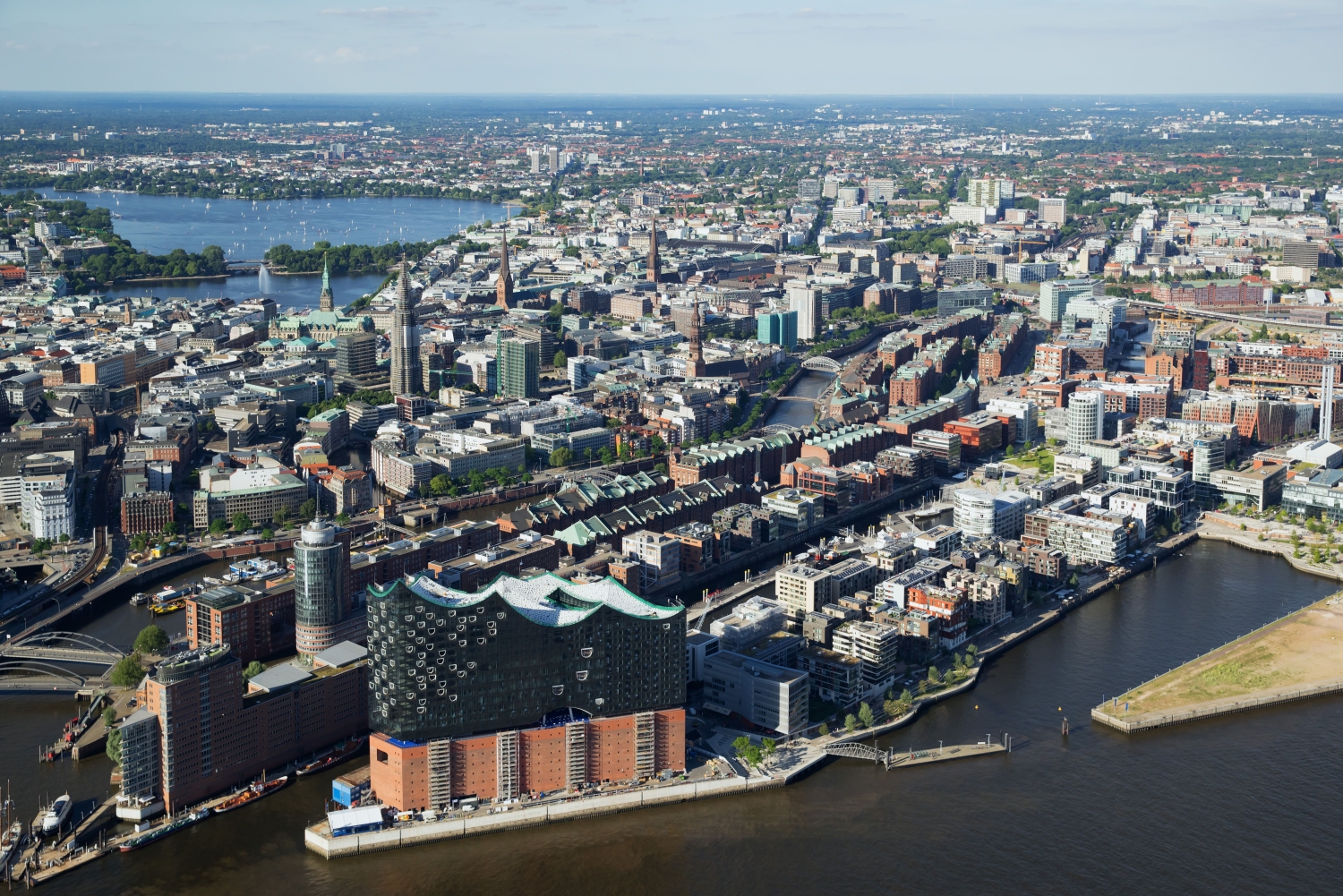

汉堡是德国三大州级市(柏林,汉堡,不来梅)之一,德国第二大城市,也是德国最重要的海港和最大的外贸中心、德国第二金融中心,同时是德国北部的经济和文化大都市。有着“世界桥城”的美称。
汉堡是德国北部重要的交通枢纽,是欧洲最富裕的城市之一,也已成为德国的新闻传媒与工业制造业中心。汉堡是世界大港,被誉为“德国通往世界的大门”。世界各地的远洋轮来德国时,都会在汉堡港停泊。
除美国西雅图外,汉堡是世界上第二大飞机制造区,生产“空中客车”。汉堡大多数工业和外贸有关。
汉堡(/ˈhæmbɜːrɡ/; 德语发音:[ˈhambʊʁk](![]() 发音), 当地发音:[ˈhambʊɪ̯ç]
发音), 当地发音:[ˈhambʊɪ̯ç] ![]() 聆听; 低地德语/低地撒克逊语:Hamborg -[ˈhambɔːx]
聆听; 低地德语/低地撒克逊语:Hamborg -[ˈhambɔːx] ![]() 聆听)),全称为汉堡汉萨自由市(德语:Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg)[3],位于德国北部的一个港口城市。汉堡拥有近180万人口,是仅次于柏林的德国第二大城市,欧盟第八大城市。作为一个城市州,其行政级别有其联邦州议会和州立法委员会。汉堡及其周围城镇共有274万人口,而汉堡大城市群则有500万人口。
聆听)),全称为汉堡汉萨自由市(德语:Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg)[3],位于德国北部的一个港口城市。汉堡拥有近180万人口,是仅次于柏林的德国第二大城市,欧盟第八大城市。作为一个城市州,其行政级别有其联邦州议会和州立法委员会。汉堡及其周围城镇共有274万人口,而汉堡大城市群则有500万人口。
汉堡港位于易北河出海口,是德国最大的港口,也是世界上第20大港口。同时因为包括汉堡机场和众多轨道交通,汉堡是欧洲物流的最重要的枢纽之一。汉堡经济主要为高科技经济,包括航空航天工程企业(空中客车)、生命科学企业、信息技术企业、制成品企业(拜尔斯道夫和联合利华),同时作为一个媒体中心其拥有发达的文化产业。
Die Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg ( [ˈhambʊʁk]; regional auch
[ˈhambʊʁk]; regional auch  [ˈhambʊɪ̯ç], niederdeutsch Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg[1] [ˈhambɔːχ], Ländercode: HH, Abkürzung: FHH oder FuHH) ist ein Stadtstaat und ein Land der Bundesrepublik Deutschland.[15] Der amtliche Name geht auf die Geschichte Hamburgs als Freie Reichsstadt und als führendes Mitglied der Hanse zurück.
[ˈhambʊɪ̯ç], niederdeutsch Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg[1] [ˈhambɔːχ], Ländercode: HH, Abkürzung: FHH oder FuHH) ist ein Stadtstaat und ein Land der Bundesrepublik Deutschland.[15] Der amtliche Name geht auf die Geschichte Hamburgs als Freie Reichsstadt und als führendes Mitglied der Hanse zurück.
Hamburg ist mit ca. 1,8 Millionen Einwohnern aus 183 Ländern die zweitgrößte Stadt Deutschlands nach Berlin und die größte Stadt in der Europäischen Union, die keine Hauptstadt ist. Die Metropolregion Hamburg hat über fünf Millionen Einwohner,[9] der städtische Ballungsraum zählt 2,7 Millionen Einwohner. Das Stadtgebiet ist in sieben Bezirke und 104 Stadtteile gegliedert.[12][16]
Der Hamburger Hafen ist einer der größten Umschlaghäfen weltweit[17] und macht Hamburg zusammen mit seinem internationalen Flughafen zu einem der bedeutendsten Logistikstandorte in Europa. Aktuell wird ein Strukturwandel zu einem Kreativ-, Wissenschafts- und Finanzplatz angestrebt.[18] Wirtschaftlich und wissenschaftlich ist die Metropole vor allem im Bereich der Spitzentechnologien wie der Luft- und Raumfahrttechnik, der Biowissenschaften und der Informationstechnik, sowie für die Konsumgüterbranche bedeutend. Hamburg hat eine in Mitteleuropa führende Medienlandschaft und Videospielbranche, ein wachsendes Startup-Ökosystem sowie eine dynamische Kultur- und Kreativszene. Der Bildungs- und Forschungsstandort Hamburg ist Zentrum mehrerer renommierter Bildungseinrichtungen, Institute und Forschungszentren.
Am 5. Juli 2015 wurden die Speicherstadt aus der Zeit der Industrialisierung und das angrenzende Kontorhausviertel von der UNESCO als Weltkulturerbe in die Welterbeliste aufgenommen.[19][20] Weitere bekannte Kulturdenkmäler sind das Rathaus und die markanten Hauptkirchen. Typisch für das Stadtbild sind Klinkerfassaden und viele Wasserlagen an den Flüssen Elbe und Alster sowie zahlreichen Fleeten und Kanälen. Europaweit bekannt sind auch der „Kiez“ als Vergnügungsviertel und Türöffner für Musiker und andere Künstler, sowie das Konzerthaus der Elbphilharmonie. Der Musicalstandort Hamburg ist der bedeutendste auf dem europäischen Kontinent. Hamburg verzeichnet ein verstärktes Wachstum im Bereich des internationalen Stadttourismus und gilt als eine der Städte mit der höchsten Lebensqualität der Welt.[21]
Hamburg ist seit 1996 Sitz des Internationalen Seegerichtshofs (ISGH). Seit 2004 findet mit dem Hamburg Summit ein bedeutendes chinesisch-europäisches Gipfeltreffen statt.[22] Im Juli 2017 fand in der Hansestadt der G20-Gipfel statt.
ハンブルク(ドイツ語: Hamburg、低ザクセン語・低地ドイツ語: Hamborg (Hamborch) [ˈhaˑmbɔːχ])は、ドイツの北部に位置し、エルベ川河口から約100kmほど入った港湾都市。正式名称は自由ハンザ都市ハンブルク(Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg、フライエ・ウント・ハンゼシュタット・ハンブルク)。行政上では、ベルリン特別市と同様に、一市単独で連邦州(ラント)を構成する特別市(都市州)なので、ハンブルク特別市やハンブルク州と呼ばれる。人口約175万人。国際海洋法裁判所がある。
Hamburg (English: /ˈhæmbɜːrɡ/; German: [ˈhambʊɐ̯k] ( listen); Low German: Hamborg [ˈhambɔːç] (
listen); Low German: Hamborg [ˈhambɔːç] ( listen); officially: Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg; German: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; Low German: Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg)[5] is, with a population of roughly 1.8 million people, the second-largest city of Germany after Berlin, the eighth-largest city in the European Union, as well as the union's largest city which is not one of its member states' capital cities. It is one of Germany's 16 federal states, surrounded by the states of Schleswig-Holstein to the north, and Lower Saxony to the south, and is the largest city of Northern Germany. The city's metropolitan region is home to more than five million people. Hamburg lies on the River Elbe and two of its tributaries, the River Alster, which forms two large lakes within the city, and the River Bille. It is the third-largest German-speaking city after Berlin and Vienna, and the largest city in the Low German dialect area.
listen); officially: Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg; German: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; Low German: Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg)[5] is, with a population of roughly 1.8 million people, the second-largest city of Germany after Berlin, the eighth-largest city in the European Union, as well as the union's largest city which is not one of its member states' capital cities. It is one of Germany's 16 federal states, surrounded by the states of Schleswig-Holstein to the north, and Lower Saxony to the south, and is the largest city of Northern Germany. The city's metropolitan region is home to more than five million people. Hamburg lies on the River Elbe and two of its tributaries, the River Alster, which forms two large lakes within the city, and the River Bille. It is the third-largest German-speaking city after Berlin and Vienna, and the largest city in the Low German dialect area.
The official name reflects Hamburg's history as a member of the medieval Hanseatic League, a free imperial city of the Holy Roman Empire, a city-state and one of the 16 states of Germany. Before the 1871 Unification of Germany, it was a fully sovereign state. Prior to the constitutional changes in 1919 it formed a civic republic headed constitutionally by a class of hereditary grand burghers or Hanseaten. The city has repeatedly been beset by disasters such as the Great Fire of Hamburg, exceptional coastal flooding and military conflicts including World War II bombing raids. Historians remark that the city has managed to recover and emerge wealthier after each catastrophe.
Situated on the Elbe river, Hamburg is home to Europe's second-largest port and a broad corporate base. In media, the major regional broadcasting firm NDR, the printing and publishing firm Gruner + Jahr and the newspapers Der Spiegel and Die Zeit are based in the city. Hamburg remains an important financial center, the seat of Germany's oldest stock exchange and the world's oldest merchant bank, Berenberg Bank. Media, commercial, logistical, and industrial firms with significant locations in the city include multinationals Airbus, Blohm + Voss, Aurubis, Beiersdorf, and Unilever.
The city hosts specialists in world economics and international law, including consular and diplomatic missions as the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea, the EU-LAC Foundation, and the UNESCO Institute for Lifelong Learning. In recent years, the city has played host to multipartite international political conferences and summits such as Europe and China and the G20. Former German Chancellor Helmut Schmidt, who governed Germany for eight years, and Angela Merkel, German chancellor since 2005, come from Hamburg.
The city is a major international and domestic tourist destination. It ranked 18th in the world for livability in 2016.[6] The Speicherstadt and Kontorhausviertel were declared World Heritage Sites by UNESCO in 2015.[7]
Hamburg is a major European science, research, and education hub, with several universities and institutions. Among its most notable cultural venues are the Elbphilharmonie and Laeiszhalle concert halls. It gave birth to movements like Hamburger Schule and paved the way for bands including The Beatles. Hamburg is also known for several theatres and a variety of musical shows. St. Pauli's Reeperbahn is among the best-known European entertainment districts.
Hambourg est une ville et l'un des 16 Länder composant l'Allemagne. Située au nord du pays, près de l'embouchure de l'Elbe et à proximité de la mer du Nord, Hambourg est la deuxième plus grande ville d'Allemagne (après Berlin) et le premier port du pays. Elle est également le deuxième port d'Europe en termes de volume de marchandises échangées, derrière Rotterdam.
La ville s'étend sur 755 km2 et compte 1,78 million d'habitants1 ; l'agglomération environ 3,5 millions. Hambourg était membre fondateur de la ligue hanséatique. Cette ancienne appartenance est encore aujourd'hui revendiquée par la ville, comme élément caractéristique de son identité. C'est ainsi que le code de la ville sur les plaques d'immatriculation est HH, qui signifie Hansestadt Hamburg et que le nom officiel de la ville est Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg (ville libre et hanséatique de Hambourg).
C'est également une ville au tourisme actif, ce qu'elle doit notamment à son architecture, à son réseau de canaux et aux abords luxuriants de l'Alster, rivière formant un lac artificiel au cœur de la ville. Elle présente de très nombreux théâtres et musées, notamment la célèbre Kunsthalle ou le jeune Bucerius Kunst Forum, qui accueille des expositions temporaires. Hambourg dispose d'un quartier entier dédié à la vie nocturne : Sankt Pauli et sa Reeperbahn, lieu de toutes les extravagances et libéralités.
Amburgo (in tedesco Hamburg, pronunciato [ˈhamˌbʊɐ̯k]; in basso-tedesco Hamborg, pronunciato [ˈhaˑmbɔːχ]) è una città della Germania, posta sull'estuario del fiume Elba.
È la seconda città più popolosa della Germania, dopo la capitale Berlino, ed è anche la città non-capitale più popolosa dell'Unione europea. Il suo porto è il maggiore della Germania e il secondo nell'Unione europea (non a caso la città ospita ITLOS, il tribunale della Convenzione delle Nazioni Unite sul diritto del mare).
Amburgo, coerentemente con il suo passato anseatico, costituisce ancora oggi una città-stato e si fregia ufficialmente del titolo di Freie- und Hansestadt Hamburg [ˈfʁaɪ̯ə ʔʊnt ˈhansəˌʃtat ˈhambʊɐ̯k] ("Città libera ed anseatica di Amburgo").
Hamburgo (en alemán, Hamburg; pronunciación:  [ˈham.bʊʁk] (?·i); localmente:
[ˈham.bʊʁk] (?·i); localmente:  [ˈham.bʊɪç] (?·i); en bajo alemán Hamborg,
[ˈham.bʊɪç] (?·i); en bajo alemán Hamborg,  [ˈham.bɔːx] (?·i)), oficialmente la Ciudad Libre y Hanseática de Hamburgon. 1 (en alemán, Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg) es una ciudad-estadon. 2 situada en el norte de Alemania. Tiene una extensión de 755 km² y 1 828 123 habitantes (septiembre de 2017). Hamburgo encabeza un área metropolitana de 5,3 millones de personas y ocupa estados vecinos de Baja Sajonia y Schleswig-Holstein. Hamburgo es la segunda ciudad más poblada en Alemania, después de Berlín,2 la tercera de Europa Central y la séptima de la Unión Europea. El puerto de Hamburgo es el segundo más grande de Europa, solo tras el puerto de Róterdam; y el noveno del mundo. Se encuentra a 290 kilómetros de Berlín.
[ˈham.bɔːx] (?·i)), oficialmente la Ciudad Libre y Hanseática de Hamburgon. 1 (en alemán, Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg) es una ciudad-estadon. 2 situada en el norte de Alemania. Tiene una extensión de 755 km² y 1 828 123 habitantes (septiembre de 2017). Hamburgo encabeza un área metropolitana de 5,3 millones de personas y ocupa estados vecinos de Baja Sajonia y Schleswig-Holstein. Hamburgo es la segunda ciudad más poblada en Alemania, después de Berlín,2 la tercera de Europa Central y la séptima de la Unión Europea. El puerto de Hamburgo es el segundo más grande de Europa, solo tras el puerto de Róterdam; y el noveno del mundo. Se encuentra a 290 kilómetros de Berlín.
El nombre completo de Hamburgo es «Ciudad libre y hanseática de Hamburgo» (Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg en alemán). Esto se debe a su historia como miembro de la liga medieval hanseática y como Ciudad Imperial Libre del Sacro Imperio Romano Germánico, y también por el hecho de que es una ciudad-estado y uno de los dieciséis estados federados de Alemania.
Га́мбург (нем. Hamburg [ˈhambʊɐ̯k], местн. [ˈhambʊɪç], н.-нем. Hamborg [ˈhambɔːx]; произношение (инф.)) — город на севере Германии. Как Во́льный и ганзе́йский го́род Га́мбург (нем. Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg) является одной из 16 земель Федеративной Республики Германия, городом-государством в её составе. Это второй по величине город в стране (после Берлина), седьмой по величине в Европейском союзе и самый населённый нестоличный город в Европейском союзе. По оценке на 31 декабря 2014 года население города составило 1 803 752 человека.[5]
Гамбург один из самых больших портовых городов в Европе, расположен у места впадения реки Эльбы в Северное море. Девиз города, который можно прочитать в виде надписи над порталом городской ратуши гласит: «Libertatem quam peperere maiores digne studeat servare posteritas». Принятый стихотворный перевод этой фразы на немецкий язык звучит, как «Die Freiheit, die erwarben die Alten, möge die Nachwelt würdig erhalten» («Свободу, что добились для нас наши предки, достойно пусть с честью хранят потомки»). Латинским названием города, используемым, например, в гимне города, является лат. Hammonia. На гербе и флаге Гамбурга изображены ворота городской крепости, и Гамбург часто называют за это «воротами в мир» (нем. Tor zur Welt). Кроме того, у Гамбурга есть свой гимн. Им стала песня, восхваляющая город и сочинённая в 1828 году, когда Гамбург был независимым городом-государством, Георгом Николаусом Берманом (нем. Georg Nikolaus Bärmann). Этот поэт написал много песен на нижненемецком языке, слыл большим знатоком истории Гамбурга. Песня в честь Гамбурга прозвучала впервые в финале его пьесы «Гражданская верность», поставленной по случаю 300-летия Реформации.

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH
 Geography
Geography
 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB
 Queensland-QLD
Queensland-QLD