
English Encyclopedia
 France
France
 America´s Cup 2017
America´s Cup 2017
 Australia
Australia

 California-CA
California-CA

 China
China

 Valencian Community
Valencian Community
 England
England
 France
France
 Greece
Greece

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Kyūshū
Kyūshū
 New Zealand
New Zealand

 New York-NY
New York-NY
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI
 Russia
Russia

 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 Sweden
Sweden
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport
 America´s Cup
America´s Cup

 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Western Australia-WA
Western Australia-WA

The America's Cup, affectionately known as the Auld Mug, is a trophy awarded to the winner of the America's Cup match races between two sailing yachts. One yacht, known as the defender, represents the yacht club that currently holds the America's Cup and the second yacht, known as the challenger, represents the yacht club that is challenging for the cup. The timing of each match is determined by an agreement between the defender and the challenger. The America's Cup is the oldest international sporting trophy.[1][2][3] It will next be raced for in the southern summer, in the early part of 2021.[4]
The cup was originally awarded in 1851 by the Royal Yacht Squadron for a race around the Isle of Wight in the United Kingdom, which was won by the schooner America. The trophy, originally named the '£100 Cup', was renamed the America's Cup after the yacht and was donated to the New York Yacht Club (NYYC) under the terms of the Deed of Gift, which made the cup available for perpetual international competition.
Any yacht club that meets the requirements specified in the deed of gift has the right to challenge the yacht club that holds the cup. If the challenging club wins the match, it gains stewardship of the cup.
The history and prestige associated with the America's Cup attracts not only the world's top sailors and yacht designers but also the involvement of wealthy entrepreneurs and sponsors. It is a test not only of sailing skill and boat and sail design, but also of fundraising and management skills.
The trophy was held by the NYYC from 1857 (when the syndicate that won the cup donated the trophy to the club) until 1983. The NYYC successfully defended the trophy twenty-four times in a row before being defeated by the Royal Perth Yacht Club, represented by the yacht Australia II. The NYYC's reign was the longest winning streak (in terms of date) in the history of all sports.[5]
From the first defence of the cup in 1870 through the twentieth defence in 1967, there was always only one challenger. In 1970, for the first time, there were multiple challengers, so the NYYC agreed that the challengers could run a selection series with the winner becoming the official challenger and competing against the defender in the America's Cup match. Since 1983, Louis Vuitton has sponsored the Louis Vuitton Cup as a prize for the winner of the challenger selection series.
Early matches for the cup were raced between yachts 65–90 ft (20–27 m) on the waterline owned by wealthy sportsmen. This culminated with the J-Class regattas of the 1930s. After World War II and almost twenty years without a challenge, the NYYC made changes to the deed of gift to allow smaller, less expensive 12-metre class yachts to compete; this class was used from 1958 until 1987. It was replaced in 1990 by the International America’s Cup Class which was used until 2007.
After a long legal battle, the 2010 America's Cup was raced in 90 ft (27 m) waterline multihull yachts in a best of three "deed of gift" match in Valencia, Spain. The victorious Golden Gate Yacht Club then elected to race the 2013 America's Cup in AC72 foiling, wing-sail catamarans. Golden Gate Yacht Club successfully defended the cup. The 35th America's Cup match was announced to be sailed in 50 ft foiling catamarans.[6]
The history of the America's Cup has included legal battles and disputes over rule changes including most recently over the rule changes for the 2017 America's Cup.[7]
The America's Cup is currently held by the Royal New Zealand Yacht Squadron,[8] who will stage the 36th defence of the Cup in 2021.
 Chancellerie des universités de Paris
Chancellerie des universités de Paris

 Colleges and Universities in Europe
Colleges and Universities in Europe

 Ile-de-France
Ile-de-France
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Literature
Nobel Prize in Literature
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Physics
Nobel Prize in Physics
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences
Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 University/Institute
University/Institute
 Universities in France
Universities in France

The École normale supérieure of Paris (French pronunciation: [ekɔl nɔʁmal sypeʁjœʁ]; also known as ENS, Normale sup', Ulm or ENS Paris) is a grande école in Paris, France. It is one of the constituent members of PSL University.[6]
Originally conceived during the French Revolution,[7] the school was founded in 1794 to provide homogeneous training of high-school teachers in France but it later closed. The school was subsequently reestablished by Napoleon I as pensionnat normal from 1808 to 1822, before being recreated in 1826 and taking the name of École normale in 1830. When institutes for primary teachers training called écoles normales were created in 1845, the word supérieure (meaning upper) was added to form the current name. It has since developed into an institution which has become a platform for French students to pursue careers in government and academia.
The ENS has a highly competitive selection process consisting of written and oral examinations.[8] During their studies, many ENS students hold the status of paid civil servants.[9][10]
The ENS is a grande école and, as such, is not part of the mainstream university system. However, the vast majority of the academic staff hosted at ENS belong to external institutions such as one of the Parisian universities, the CNRS and the EHESS. This mechanism for constant scientific turnover allows ENS to benefit from a continuous stream of researchers in all fields. ENS full professorships are rare and competitive. Generalistic in its recruitment and organisation, the ENS is the only grande école in France to have departments of research in all the natural, social, and human sciences.
Due to the selectivity of its entrance exam and its turnover among French researchers, it has a high proportion of prize laureates and therefore a very good reputation. The school has achieved particular recognition in the fields of mathematics and physics. Its alumni include 14 Nobel Prize laureates, of which 8 are in Physics (ENS has the highest proportion of Nobel laureates among its alumni of any institution worldwide[11]), 12 Fields Medalists (the third most of any university in the world), more than half the recipients of the CNRS's Gold Medal (France's highest scientific prize) and several hundred members of the Institut de France, and scores of politicians and statesmen.[12][13] The school has achieved particular recognition in the fields of mathematics and physics as one of France's foremost scientific training grounds, along with notability in the human sciences as the spiritual birthplace of authors such as Julien Gracq, Jean Giraudoux, Assia Djebar, and Charles Péguy, philosophers such as Henri Bergson, Jean-Paul Sartre, Louis Althusser, Simone Weil, Maurice Merleau-Ponty and Alain Badiou, social scientists such as Émile Durkheim, Raymond Aron, and Pierre Bourdieu, and "French theorists" such as Michel Foucault and Jacques Derrida.[14][15][16] The school's students are often referred to as normaliens. [9][17]
Its model has been replicated elsewhere, in France (at the ENSes of Lyon, Paris-Saclay, and Rennes), in Italy (at the Scuola Normale Superiore in Pisa[18]), in Romania, in China and in former French colonies such as Morocco, Mali, Mauritania, and Cameroon.
 *European Union
*European Union
 Belgium
Belgium
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia

 European Union
European Union
 Member States of the European Union
Member States of the European Union
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Holland
Holland
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malta
Malta
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 2012
2012
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Peace Prize
Nobel Peace Prize
 Austria
Austria

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Sweden
Sweden
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Hungary
Hungary

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Free trade agreement
Free trade agreement
 Cyprus
Cyprus
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 28 member states that are located primarily in Europe.[13] It has an area of 4,475,757 km2 (1,728,099 sq mi) and an estimated population of over 510 million. The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters (only) where members have agreed to act as one. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market,[14] enact legislation in justice and home affairs and maintain common policies on trade,[15] agriculture,[16] fisheries and regional development.[17] For travel within the Schengen Area, passport controls have been abolished.[18] A monetary union was established in 1999 and came into full force in 2002 and is composed of 19 EU member states which use the euro currency.
The EU and European citizenship were established when the Maastricht Treaty was enacted in 1993.[19] The EU traces its origins to the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) and the European Economic Community (EEC), established, respectively, by the 1951 Treaty of Paris and 1957 Treaty of Rome. The original members of what came to be known as the European Communities were the Inner Six: Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany. The Communities and its successors have grown in size by the accession of new member states and in power by the addition of policy areas to its remit. The latest major amendment to the constitutional basis of the EU, the Treaty of Lisbon, came into force in 2009. While no member state has left the EU or its predecessors, the United Kingdom signified an intention to leave after a membership referendum in June 2016 and is negotiating its withdrawal.
The European Union provides more foreign aid than any other economic union.[20] Covering 7.3% of the world population,[21] the EU in 2017 generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of 19.670 trillion US dollars, constituting approximately 24.6% of global nominal GDP[22] and 16.5% when measured in terms of purchasing power parity.[23] Additionally, 27 out of 28 EU countries have a very high Human Development Index, according to the United Nations Development Programme. In 2012, the EU was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize.[24] Through the Common Foreign and Security Policy, the EU has developed a role in external relations and defence. The union maintains permanent diplomatic missions throughout the world and represents itself at the United Nations, the World Trade Organization, the G7 and the G20. Because of its global influence, the European Union has been described as an emerging superpower.[25]
 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Brazil
Brazil

 China
China
 Germany
Germany
 England
England

 European Union
European Union
 France
France

 Hamburg
Hamburg

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Mexico
Mexico
 Nicolas Sarközy
Nicolas Sarközy

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 Queensland-QLD
Queensland-QLD
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 South Africa
South Africa
 Turkey
Turkey
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
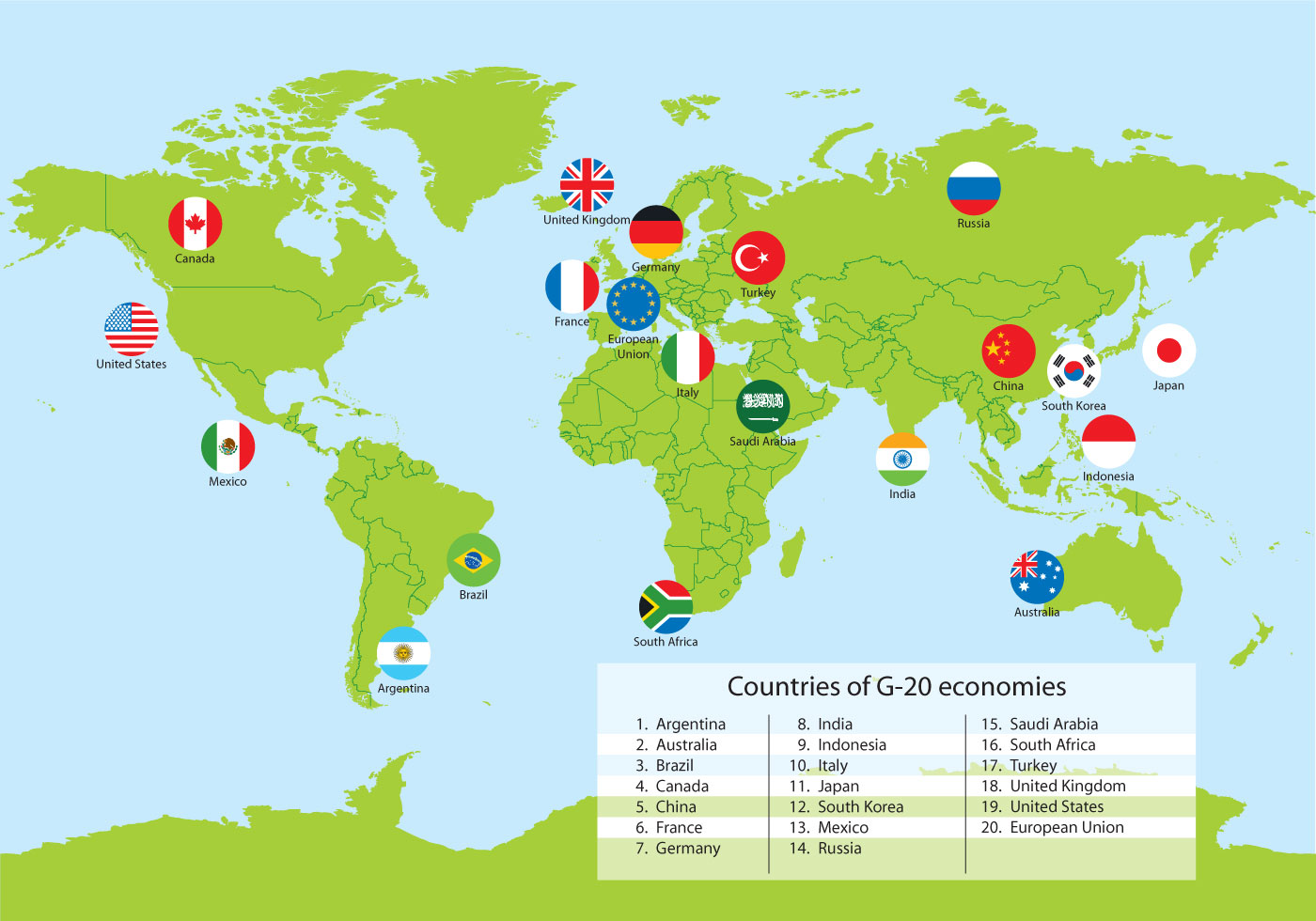
The G20 (or Group of Twenty) is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU). Founded in 1999 with the aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability,[3] the G20 has expanded its agenda since 2008 and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers, foreign ministers and think tanks[4], have periodically conferred at summits ever since. It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one organization.[3]
Membership of the G20 consists of 19 individual countries plus the European Union. The EU is represented by the European Commission and by the European Central Bank. Collectively, the G20 economies account for around 90%[5] of the gross world product (GWP), 80% of world trade (or, if excluding EU intra-trade, 75%), two-thirds of the world population,[2] and approximately half of the world land area.
With the G20 growing in stature[6] after its inaugural leaders' summit in 2008, its leaders announced on 25 September 2009 that the group would replace the G8 as the main economic council of wealthy nations.[7] Since its inception, the G20's membership policies have been criticized by some intellectuals,[8][9] and its summits have been a focus for major protests.[10][11]
The heads of the G20 nations held summits twice in 2009 and twice in 2010. Since the November 2011 Cannes summit, G20 summits have been held annually.[12]
 *Institut de France
*Institut de France
 Académie des sciences
Académie des sciences
 *Institut de France
*Institut de France
 Académie des inscriptions et belles-lettres
Académie des inscriptions et belles-lettres
 *Institut de France
*Institut de France
 Académie des Beaux-Arts
Académie des Beaux-Arts
 *Institut de France
*Institut de France
 Académie des Sciences morales et politiques
Académie des Sciences morales et politiques
 *Institut de France
*Institut de France
 Académie française
Académie française

 Ile-de-France
Ile-de-France
 Sinology
Sinology

The Institut de France (French pronunciation: [ɛ̃stity də fʁɑ̃s], Institute of France) is a French learned society, grouping five académies, the most[citation needed] famous of which is the Académie française.
The Institute, located in Paris, manages approximately 1,000 foundations, as well as museums and châteaux open for visit. It also awards prizes and subsidies, which amounted to a total of over €5 million for 2002.[citation needed] Most of these prizes are awarded by the Institute on the recommendation of the académies.
 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil

 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 France
France
 Holland
Holland
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Camille Gutt
Camille Gutt
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Christine Lagarde
Christine Lagarde
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Dominique Strauss-Kahn
Dominique Strauss-Kahn
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Horst Köhler
Horst Köhler
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Ivar Rooth
Ivar Rooth
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Jacques de Larosière
Jacques de Larosière
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Johan Witteveen
Johan Witteveen
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Michel Camdessus
Michel Camdessus
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Per Jacobsson
Per Jacobsson
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Pierre-Paul Schweitzer
Pierre-Paul Schweitzer
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Rodrigo Rato
Rodrigo Rato
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa

 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research

The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 189 countries working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world while periodically depending on the World Bank for its resources.[1] Formed in 1944 at the Bretton Woods Conference primarily by the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes,[6] it came into formal existence in 1945 with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international payment system. It now plays a central role in the management of balance of payments difficulties and international financial crises.[7] Countries contribute funds to a pool through a quota system from which countries experiencing balance of payments problems can borrow money. As of 2016, the fund had XDR 477 billion (about US$ 667 billion).[8]
Through the fund and other activities such as the gathering of statistics and analysis, surveillance of its members' economies, and the demand for particular policies,[9] the IMF works to improve the economies of its member countries.[10] The organization's objectives stated in the Articles of Agreement are:[11] to promote international monetary co-operation, international trade, high employment, exchange-rate stability, sustainable economic growth, and making resources available to member countries in financial difficulty.[12] IMF funds come from two major sources: quotas and loans. Quotas, which are pooled funds of member nations, generate most IMF funds. The size of a member's quota depends on its economic and financial importance in the world. Nations with larger economic importance have larger quotas. The quotas are increased periodically as a means of boosting the IMF's resources in the form of special drawing rights.[13]
The current Managing Director (MD) and Chairwoman of the IMF is Bulgarian Economist Kristalina Georgieva, who has held the post since October 1, 2019.[14]
Gita Gopinath was appointed as Chief Economist of IMF from 1 October 2018. She received her PhD in economics from Princeton University. Prior to her IMF appointment she was economic adviser to the Chief Minister of Kerala, India.[15]
 China
China

 European Union
European Union
 France
France
 Japan
Japan

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia


 Science and technology
Science and technology

ITER (initially the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor, iter meaning "the way" or "the path" in Latin[1][2][3]) is an international nuclear fusion research and engineering megaproject aimed at replicating the fusion processes of the Sun to create energy on the Earth. Upon completion of construction of the main reactor and first plasma, planned for late 2025,[4] it will be the world's largest magnetic confinement plasma physics experiment and the largest experimental tokamak nuclear fusion reactor. It is being built next to the Cadarache facility in southern France.[5][6] ITER will be the largest of more than 100 fusion reactors built since the 1950s, with ten times the plasma volume of any other tokamak operating today.[7][8]
The long-term goal of fusion research is to generate electricity. ITER's stated purpose is scientific research, and technology demonstration of a large fusion reactor, without electricity generation.[9][7] ITERs goals are: to achieve enough fusion to produce 10 times as much thermal output power as thermal power absorbed by the plasma for short time periods; to demonstrate and test technologies that would be needed to operate a fusion power plant including cryogenics, heating, control and diagnostics systems, plus remote maintenance; to achieve and learn from a burning plasma; to test tritium breeding; and to demonstrate the safety of a fusion plant.[8][6]
ITER's thermonuclear fusion reactor will use over 300MW of electrical power to cause the plasma to absorb 50 MW of thermal power, creating 500 MW of heat from fusion for periods of 400 to 600 seconds.[10] This would mean a ten-fold gain of plasma heating power (Q), as measured by heating input to thermal output, or Q ≥ 10.[11] As of 2021, the record for energy production using nuclear fusion is held by the National Ignition Facility reactor, which achieved a Q of 0.70 in August 2021.[12] Beyond just heating the plasma, the total electricity consumed by the reactor and facilities will range from 110 MW up to 620 MW peak for 30-second periods during plasma operation.[13] As a research reactor, the heat energy generated will not be converted to electricity, but simply vented.[6][14][15]
ITER is funded and run by seven member parties: China, the European Union, India, Japan, Russia, South Korea and the United States. The United Kingdom participates through EU's Fusion for Energy (F4E), Switzerland participates through Euratom and F4E, and the project has cooperation agreements with Australia, Canada, Kazakhstan and Thailand.[16]
Construction of the ITER complex started in 2013,[17] and assembly of the tokamak began in 2020.[18] The initial budget was close to €6 billion, but the total price of construction and operations is projected to be from €18 to €22 billion;[19][20] other estimates place the total cost between $45 billion and $65 billion, though these figures are disputed by ITER.[21][22] Regardless of the final cost, ITER has already been described as the most expensive science experiment of all time,[23] the most complicated engineering project in human history,[24] and one of the most ambitious human collaborations since the development of the International Space Station (€100 billion budget) and the Large Hadron Collider (€7.5 billion budget).[25][26]
ITER's planned successor, the EUROfusion-led DEMO, is expected to be one of the first fusion reactors to produce electricity in an experimental environment.
 United Nations
United Nations
 Energy resource
Energy resource