
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 信息时代
信息时代



Ethernet ([ˈeːtɐˌnɛt][1] oder englisch [ˈiθəɹˌnɛt]) ist eine Technik, die Software (Protokolle usw.) und Hardware (Kabel, Verteiler, Netzwerkkarten usw.) für kabelgebundene Datennetze spezifiziert, welche ursprünglich für lokale Datennetze (LANs) gedacht war und daher auch als LAN-Technik bezeichnet wird. Sie ermöglicht den Datenaustausch in Form von Datenframes zwischen den in einem lokalen Netz (LAN) angeschlossenen Geräten (Computer, Drucker und dergleichen).[2] Derzeit sind Übertragungsraten von 1, 10, 100 Megabit/s (Fast Ethernet), 1000 Megabit/s (Gigabit-Ethernet), 2,5, 5, 10, 25, 40, 50, 100, 200 und 400 Gigabit/s spezifiziert, 800 Gigabit/s und 1,6 Terabit/s werden entwickelt. In seiner ursprünglichen Form erstreckt sich das LAN dabei nur über ein Gebäude; Ethernet-Standard-Varianten über Glasfaser haben eine Link-Reichweite von bis zu 80 km, proprietäre auch mehr.
Die Ethernet-Protokolle umfassen Festlegungen für Kabeltypen und Stecker sowie für Übertragungsformen (Signale auf der Bitübertragungsschicht, Paketformate). Im OSI-Modell ist mit Ethernet sowohl die physische Schicht (OSI Layer 1) als auch die Data-Link-Schicht (OSI Layer 2) festgelegt. Ethernet entspricht weitestgehend der IEEE-Norm 802.3. Es wurde ab den 1990ern zur meistverwendeten LAN-Technik und hat andere LAN-Standards wie Token Ring verdrängt oder, wie im Falle von ARCNET in Industrie- und Fertigungsnetzen oder FDDI in hoch verfügbaren Netzwerken, zu Nischenprodukten für Spezialgebiete gemacht. Ethernet kann die Basis für Netzwerkprotokolle, wie z. B. AppleTalk, DECnet, IPX/SPX und TCP/IP, bilden.
Für Anwendungen, in denen hohe Anforderungen an die Zuverlässigkeit der Kommunikation gestellt werden, kommt Echtzeit-Ethernet zum Einsatz.
以太网(英语:Ethernet)是一种计算机局域网技术。IEEE组织的IEEE 802.3标准制定了以太网的技术标准,它规定了包括物理层的连线、电子信号和介质访问控制的内容。以太网是目前应用最普遍的局域网技术,取代了其他局域网标准如令牌环、FDDI和ARCNET。
以太网的标准拓扑结构为总线型拓扑,但目前的快速以太网(100BASE-T、1000BASE-T标准)为了减少冲突,将能提高的网络速度和使用效率最大化,使用交换机(Switch hub)来进行网络连接和组织。如此一来,以太网的拓扑结构就成了星型;但在逻辑上,以太网仍然使用总线型拓扑和CSMA/CD(Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection,即载波多重访问/碰撞侦测)的总线技术。
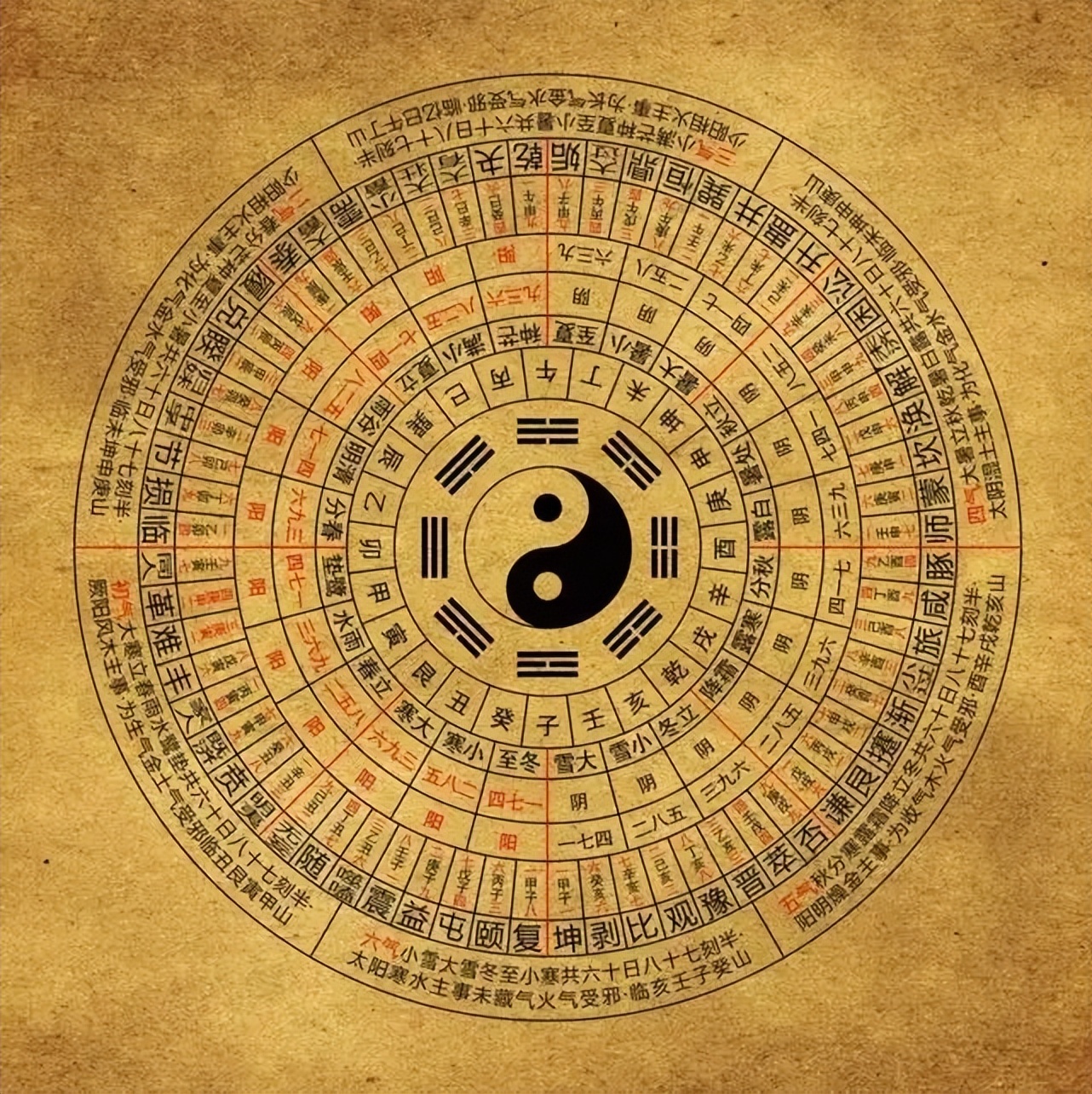

Das I Ging, hist. Romanisierung, heute: Yijing (chinesisch 易經 / 易经, Pinyin Yìjīng, W.-G. I-Ching ‚Buch der Wandlungen od. Klassiker der Wandlungen‘) ist eine Sammlung von Strichzeichen und zugeordneten Sprüchen. Es ist der älteste der klassischen chinesischen Texte. Seine legendäre Entstehungsgeschichte wird traditionell bis in das 3. Jahrtausend v. Chr. zurückgeführt. Das Werk ist im Chinesischen allgemein auch als Zhouyi (周易, Zhōuyì ‚Wandlungen der Zhou‘) bekannt.
《易经》是中国汉族最古老的文献之一[1],并被儒家尊为“五经”之始;一般说上古三大奇书包括《黄帝内经》、《易经》、《山海经》,但它们成书都较晚。《易经》以一套符号系统来描述状态的简易、变易、不易,表现了中国古典文化的哲学和宇宙观。它的中心思想,是以阴阳的交替变化描述世间万物。《易经》最初用于占卜和预报天气,但它的影响遍及中国的哲学、宗教、医学、天文、算术、文学、音乐、艺术、军事和武术等各方面,是一部无所不包的巨著。自从17世纪开始,《易经》也被介绍到西方。在四库全书中为经部,十三经中未经秦始皇焚书之害,它是最早哲学书。自从十七世纪开始,《易经》也被介绍到西方。
《易》原有三种版本:《连山》、《归藏》和《周易》[2],《连山》和《归藏》已经失传,一般所称《易经》即源于《周易》发展而来。
《易经》包括狭义的《周易》与《易传》。《周易》相传是依循周文王主编《易》的著述而来,成书大约在西周时期。由于随时代演变,《周易》文字含义到了春秋战国时代已经不便读懂,因此孔子撰写了“十翼”,后世又称为《易传》并列入《易经》。
『易経』(えききょう、正字体:易經、拼音: )は、古代中国の書物。『卜』が動物である亀の甲羅や牛や鹿の肩甲骨に入ったヒビの形から占うものであるのに対して、『筮』は植物である『蓍[1]』の茎の本数を用いた占いである。商の時代から蓄積された卜辞を集大成したものとして易経は成立した。易経は儒家である荀子の学派によって儒家の経典として取り込まれた。現代では、哲学書としての易経と占術のテキストとしての易経が、一部重なりながらも別のものとなっている。中心思想は、陰陽二つの元素の対立と統合により、森羅万象の変化法則を説く。著者は伏羲とされている[2]。
中国では『黄帝内經』・『山海經』と合わせて「上古三大奇書」とも呼ぶ。
The I Ching (/ˈiː ˈdʒɪŋ/),[2] also known as Classic of Changes or Book of Changes, is an ancient Chinese divination text and the oldest of the Chinese classics. Possessing a history of more than two and a half millennia of commentary and interpretation, the I Ching is an influential text read throughout the world, providing inspiration to the worlds of religion, psychoanalysis, literature, and art. Originally a divination manual in the Western Zhou period (1000–750 BC), over the course of the Warring States period and early imperial period (500–200 BC) it was transformed into a cosmological text with a series of philosophical commentaries known as the "Ten Wings".[3] After becoming part of the Five Classics in the 2nd century BC, the I Ching was the subject of scholarly commentary and the basis for divination practice for centuries across the Far East, and eventually took on an influential role in Western understanding of Eastern thought.
The I Ching uses a type of divination called cleromancy, which produces apparently random numbers. Six numbers between 6 and 9 are turned into a hexagram, which can then be looked up in the I Ching book, arranged in an order known as the King Wen sequence. The interpretation of the readings found in the I Ching is a matter of centuries of debate, and many commentators have used the book symbolically, often to provide guidance for moral decision making as informed by Taoism and Confucianism. The hexagrams themselves have often acquired cosmological significance and paralleled with many other traditional names for the processes of change such as yin and yang and Wu Xing.
Le Yi Jing (sinogrammes 易经simpl./易經trad., pinyin yì jīng, Wade-Giles i4 ching1, également orthographié Yi King ou Yi-King), prononcé en français i ting est un manuel chinois dont le titre peut se traduire par « Classique des changements » ou « Traité canonique des mutations ». Il s'agit d'un système de signes binaires qui peut être utilisé pour faire des divinations. Le Yi Jing s'appelle aussi Zhou Yi (周易, pinyin : Zhōu Yì, Wade-Giles : Chou1 I4) c'est-à-dire « changements de Zhou » pour la raison que son élaboration date du Ier millénaire avant l'ère chrétienne, époque des Zhou (1027, 256 av. J.-C.).
Il occupe une place fondamentale dans l'histoire de la pensée chinoise et peut être considéré comme un traité unique en son genre dont la finalité est de décrire les états du monde et leurs évolutions. Premier des cinq classiques, il est donc considéré comme le plus ancien texte chinois.
Le Yi Jing est le fruit d'une recherche spéculative et cosmogonique élaborée, dont les articulations ont influencé durablement la pensée chinoise. Sa structure mathématique a impressionné Leibniz qui y aurait vu la première formulation de l'arithmétique binaire. De fait, partant d'une opposition/complémentarité entre les principes d'engendrement Yin et Yang (yin // réceptif // lune // femelle // passif alors que yang // créatif // soleil // mâle // actif) et subdivisant cette dualité de façon systématique (adret = côté au Soleil alors qu'ubac = côté à l'ombre ; vents favorables opposés aux nuages contraires), le Yi Jing arrive à la série des 64 figures qui peuvent interpréter toutes les transformations possibles.
« Le Yi-King ou Livre des transformations de l'archaïque magie chinoise apporte l'image la plus exemplaire de l'identité du Génésique et du Génétique. La boucle circulaire est un cercle cosmogonique symboliquement tourbillonnaire par le S intérieur qui à la fois sépare et unit le Yin et le Yang. La figure se forme non à partir du centre mais de la périphérie et naît de la rencontre de mouvements de directions opposés. Le Yin et le Yang sont intimement épousés l'un dans l'autre, mais distincts, ils sont à la fois complémentaires, concurrents, antagonistes. La figure primordiale du Yi-King est donc une figure d'ordre, d'harmonie, mais portant en elle l'idée tourbillonnaire et le principe d'antagonisme. C'est une figure de complexité. »
— Edgar Morin, La Méthode 1. La Nature de la Nature, p. 228, Seuil, Paris, 1977.
Il Libro dei Mutamenti[2] (易經T, 易经S, YìjīngP, I ChingW[3]), conosciuto anche come Zhou Yi 周易 o I Mutamenti (della dinastia) Zhou, è ritenuto il primo dei testi classici cinesi sin da prima della nascita dell'impero cinese. È sopravvissuto alla distruzione delle biblioteche operata dal Primo imperatore, Qin Shi Huang Di.
L'Yi Jing è diviso in due porzioni, jing 經 o 'classico' e zhuan 傳 o 'commentario', composti in momenti differenti ma tramandati come testo unico da due millenni circa. La porzione jing è composta da sessantaquattro unità, ognuna basata su un esagramma (gua 卦) composto di sei linee che sono o continue (⚊) rappresentanti il principio yang o interrotte (⚋) rappresentanti il principio yin. Per ogni esagramma vi è una spiegazione chiamata 卦辞 guaci, accompagnata dalla spiegazione delle singole linee costituenti il trigramma chiamate 爻辞 yaoci. I primi due esagrammi del testo 乾 qian e 坤 kun sono accompagnati da due ulteriori testi chiamati 用六 yongliu e 用九 yongjiu.
Considerato da Confucio libro di saggezza, è utilizzato a livello popolare a scopo divinatorio, e dagli studiosi per approfondire aspetti matematici, filosofici e fisici. I metodi per ottenere i responsi sono vari e si passa dai gusci di tartaruga al lancio di 3 monete. Quando si utilizzano gli steli di achillea per estrarre i responsi, l'arte divinatoria è chiamata achilleomanzia.
El I Ching, Yijing o I King (en chino tradicional: 易經; en chino simplificado: 易经; en pinyin: yì jīng) es un libro oracular chino cuyos primeros textos se suponen escritos hacia el 1200 a. C. Es uno de los Cinco Clásicos confucianos.
El término i ching significa ‘libro de las mutaciones’. El texto fue aumentado durante la dinastía Zhou y posteriormente por comentaristas de la escuela de Confucio, pero su contenido original es de procedencia taoísta, y no confucianista. Se cree que describe la situación presente de quien lo consulta y predice el modo en que se resolverá en el futuro si se adopta ante ella la posición correcta. Es un libro adivinatorio y también un libro moral, a la vez que por su estructura y simbología es un libro filosófico y cosmogónico.
«И цзин» (кит. трад. 易經, упр. 易经, пиньинь: Yì Jīng), или «Чжоу И»[1] (周易) — наиболее ранний из китайских философских текстов. Наиболее ранний слой, традиционно датируемый ок. 700 г. до. н. э.[2] и предназначавшийся для гадания, состоит из 64 гексаграмм. Во II веке до н. э. был принят конфуцианской традицией как один из канонов конфуцианского Пятикнижия.
«Кни́га Переме́н» — название, закрепившееся за «И цзин» на Западе. Более правильный, хоть и не столь благозвучный вариант — «Кано́н Переме́н».
 财政金融
财政金融


 科学技术
科学技术
 加利福尼亚州
加利福尼亚州
 游戏
游戏
 企业
企业

 马萨诸塞州
马萨诸塞州

 历史
历史
 建筑艺术
建筑艺术
 天文
天文
 生肖星座
生肖星座
 文学
文学
 传统医学
传统医学
 能源
能源
 拉齐奥大区
拉齐奥大区
 经济和贸易
经济和贸易




 汽车
汽车
