漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
 1928 Summer Olympics
1928 Summer Olympics

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Important port
Important port
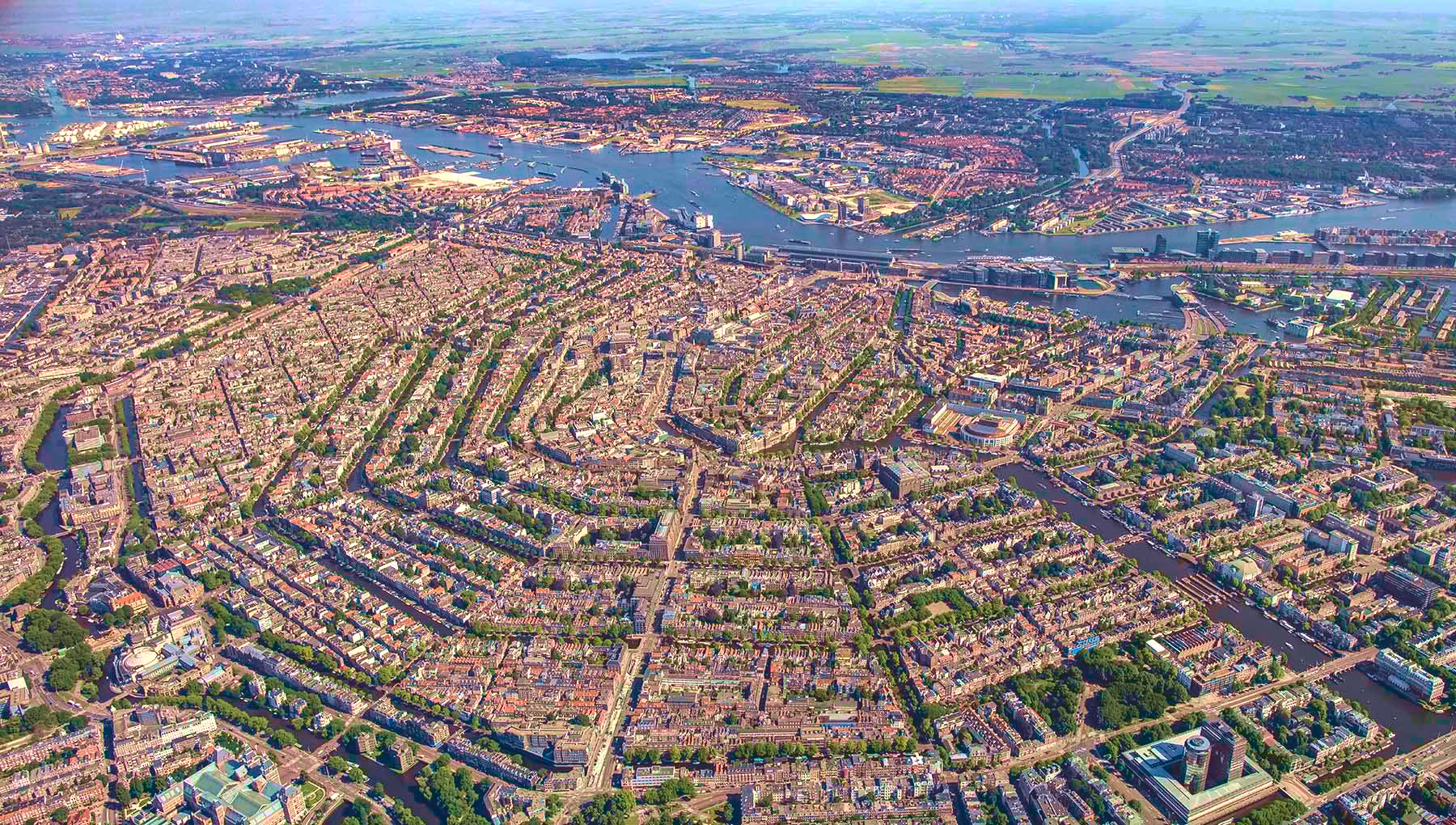

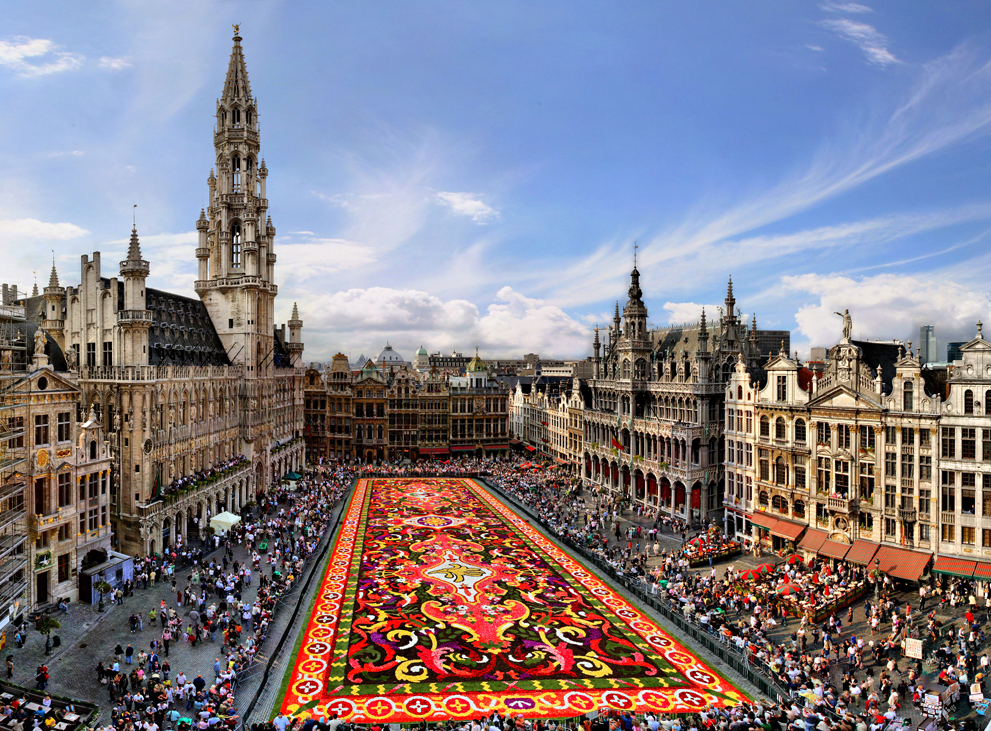
Amsterdam (niederländisch  Amsterdam?/i) ist die Hauptstadt und einwohnerstärkste Stadt des Königreichs der Niederlande. Die Gemeinde Amsterdam hat 851.223 Einwohner (Stand: 31. August 2017)[2] und als Agglomeration Groot-Amsterdam 1.362.270 Millionen (Stand: 28. Februar 2018).[3] Im Großraum Amsterdam, der den nördlichen Teil des niederländischen Verdichtungsraumes Randstad ausmacht, leben etwa 2,4 Millionen Menschen (2012).[4] Auch wenn sich der Regierungssitz des Landes sowie die Königsresidenz im 60 Kilometer entfernten Den Haag befinden, ist Amsterdam seit 1983 gemäß niederländischer Verfassung die Hauptstadt der Niederlande.[5]
Amsterdam?/i) ist die Hauptstadt und einwohnerstärkste Stadt des Königreichs der Niederlande. Die Gemeinde Amsterdam hat 851.223 Einwohner (Stand: 31. August 2017)[2] und als Agglomeration Groot-Amsterdam 1.362.270 Millionen (Stand: 28. Februar 2018).[3] Im Großraum Amsterdam, der den nördlichen Teil des niederländischen Verdichtungsraumes Randstad ausmacht, leben etwa 2,4 Millionen Menschen (2012).[4] Auch wenn sich der Regierungssitz des Landes sowie die Königsresidenz im 60 Kilometer entfernten Den Haag befinden, ist Amsterdam seit 1983 gemäß niederländischer Verfassung die Hauptstadt der Niederlande.[5]
Amsterdam liegt in der niederländischen Provinz Nordholland, wo Amstel und IJ direkt hintereinander in das IJsselmeer münden. Der Hafen der Stadt ist durch den Nordseekanal mit der Nordsee verbunden. Amsterdam ist für die vielen Grachten weltberühmt.
阿姆斯特丹(荷兰语:Amsterdam[ɑmstərˈdɑm] ),是荷兰首都及最大城市,位于该国西部省份北荷兰省。根据2008年1月的统计数据,这座城市人口达747,290人;而该城市所处的兰斯台德都市圈,大约有670万人口,是欧洲第6大都市圈。
其名称源于Amstel dam,这表明了该城市的起源:一个位于阿姆斯特尔河上的水坝,即今水坝广场址。12世纪晚期一个小渔村建于此,而后由于贸易的迅猛发展,阿姆斯特丹在荷兰黄金时代一跃而成为世界上最重要的港口。在那个时代,该城是金融和钻石的中心。 19和20世纪,该城扩展,许多新的街坊与近郊住宅区形成。
阿姆斯特丹是荷兰的金融和文化首都。许多荷兰大型机构的总部都设于此,其中包括飞利浦和ING等7家世界500强企业的总部。作为泛欧交易所的一部分,阿姆斯特丹证券交易所坐落于城市中心。阿姆斯特丹有很多旅游景点,包括历史悠久的运河网、荷兰国家博物馆、凡·高博物馆、安妮之家、红灯区以及许多大麻咖啡馆。每年有大约420万游客来此观光。
作为当前荷兰第一大城市,阿姆斯特丹历经了从渔村到国际化大都市的发展过程,经历了辉煌与破坏,以及世界大战的洗礼,从一定程度上讲,她的历史也是荷兰历史的一个缩影。
アムステルダム(オランダ語: Amsterdam [ˌʔɑmstərˈdɑm] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、オランダの北ホラント州の基礎自治体(ヘメーンテ)であり、オランダ最大の都市である。人口820,654人(2012年)、都市圏人口は2,289,762人にのぼる。商業や観光が盛んなヨーロッパ屈指の世界都市である[6]。オランダ語での発音は片仮名で表記すると「アムスタダム」に近い。地名は「アムステル川のダム(堤防)」の意(「ダム広場」の項を参照)。
音声ファイル))は、オランダの北ホラント州の基礎自治体(ヘメーンテ)であり、オランダ最大の都市である。人口820,654人(2012年)、都市圏人口は2,289,762人にのぼる。商業や観光が盛んなヨーロッパ屈指の世界都市である[6]。オランダ語での発音は片仮名で表記すると「アムスタダム」に近い。地名は「アムステル川のダム(堤防)」の意(「ダム広場」の項を参照)。
憲法に規定されたオランダの首都だが、国会、中央官庁、王宮、各国の大使館など首都機能のほとんどはデン・ハーグにある[7]。
元々は小さな漁村だったが、13世紀にアムステル川の河口にダムを築き、町が築かれた。16世紀には海運貿易の港町として、ヨーロッパ屈指の都市へと発展した。現在のアムステルダムは、アムステルダム中央駅を中心に市内に網の目状に広がる運河や、その運河に沿って並ぶ無総督時代の豪商の邸宅、自転車、飾り窓の女性たち、アンネ・フランクの家などで広く知られる。
Amsterdam (/ˈæmstərdæm/, UK also /ˌæmstərˈdæm/;[9][10] Dutch: [ɑmstərˈdɑm] ( listen)) is the capital and most populous municipality of the Netherlands. Its status as the capital is mandated by the Constitution of the Netherlands,[11] although it is not the seat of the government, which is The Hague.[12] Amsterdam has a population of 851,373 within the city proper, 1,351,587 in the urban area,[13] and 2,410,960 in the Amsterdam metropolitan area.[8] The city is located in the province of North Holland in the west of the country but is not its capital, which is Haarlem. The metropolitan area comprises much of the northern part of the Randstad, one of the larger conurbations in Europe, with a population of approximately 8 million.[14]
listen)) is the capital and most populous municipality of the Netherlands. Its status as the capital is mandated by the Constitution of the Netherlands,[11] although it is not the seat of the government, which is The Hague.[12] Amsterdam has a population of 851,373 within the city proper, 1,351,587 in the urban area,[13] and 2,410,960 in the Amsterdam metropolitan area.[8] The city is located in the province of North Holland in the west of the country but is not its capital, which is Haarlem. The metropolitan area comprises much of the northern part of the Randstad, one of the larger conurbations in Europe, with a population of approximately 8 million.[14]
Amsterdam's name derives from Amstelredamme,[15] indicative of the city's origin around a dam in the river Amstel. Originating as a small fishing village in the late 12th century, Amsterdam became one of the most important ports in the world during the Dutch Golden Age (17th century), a result of its innovative developments in trade. During that time, the city was the leading centre for finance and diamonds.[16] In the 19th and 20th centuries the city expanded, and many new neighbourhoods and suburbs were planned and built. The 17th-century canals of Amsterdam and the 19–20th century Defence Line of Amsterdam are on the UNESCO World Heritage List. Since the annexation of the municipality of Sloten in 1921 by the municipality of Amsterdam, the oldest historic part of the city lies in Sloten (9th century).
As the commercial capital of the Netherlands and one of the top financial centres in Europe, Amsterdam is considered an alpha world city by the Globalization and World Cities (GaWC) study group. The city is also the cultural capital of the Netherlands.[17] Many large Dutch institutions have their headquarters there, and seven of the world's 500 largest companies, including Philips, AkzoNobel, TomTom and ING, are based in the city.[18] Also, many leading technology companies have their European headquarters in Amsterdam, such as Uber, Netflix and Tesla.[19] In 2012, Amsterdam was ranked the second best city to live in by the Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU)[20] and 12th globally on quality of living for environment and infrastructure by Mercer.[21] The city was ranked 3rd in innovation by Australian innovation agency 2thinknow in their Innovation Cities Index 2009.[22] The Port of Amsterdam to this day remains the second in the country, and the fifth largest seaport in Europe.[23] Famous Amsterdam residents include the diarist Anne Frank, artists Rembrandt van Rijn and Vincent van Gogh, and philosopher Baruch Spinoza.
The Amsterdam Stock Exchange, the oldest stock exchange in the world, is located in the city centre. Amsterdam's main attractions, include its historic canals, the Rijksmuseum, the Van Gogh Museum, the Stedelijk Museum, Hermitage Amsterdam, the Anne Frank House, the Scheepvaartmuseum, the Amsterdam Museum, the Heineken Experience, the Royal Palace of Amsterdam, Natura Artis Magistra, Hortus Botanicus Amsterdam, NEMO Science Museum, its red-light district and its many cannabis coffee shops draw more than 5 million international visitors annually.[24] The city is also well known for its nightlife and festival activity; several of its nightclubs (Melkweg, Paradiso) are among the world's most famous. It is also one of the world's most multicultural cities, with at least 177 nationalities represented.[25]
Amsterdam (Écouter) est la commune la plus peuplée et la capitale du royaume des Pays-Bas, bien que le gouvernement ainsi que la plupart des institutions du pays siègent à La Haye. Sur la base des chiffres de l'année 2017, la commune d'Amsterdam compte plus de 850 000 habitants appelés Amstellodamois, au cœur de la région d'Amsterdam qui regroupe environ 1 350 000 habitants. L'aire urbaine, qui rassemble plus de 2 400 000 résidents3,4 fait elle-même partie d'une conurbation appelée Randstad Holland qui compte 7 100 000 habitants. La ville est située en Hollande-Septentrionale, mais n'est cependant pas la capitale de la province, cette dernière étant Haarlem, située à 19 kilomètres à l'ouest d'Amsterdam.
Le nom de la commune vient de l'ancien nom néerlandais Amstelredamme évoquant les origines de la ville : la digue (Dam) sur l'Amstel. Petit village de pêcheurs au XIIe siècle, la ville connaît une très forte croissance au Moyen Âge au point de devenir l'un des principaux ports du monde durant le Siècle d'or néerlandais. Le quartier De Wallen est la partie la plus ancienne de la ville, qui se développe autour d'un réseau concentrique de canaux semi-circulaires reliés par des canaux perpendiculaires, formant une « toile d'araignée ». Au centre de la vieille ville se trouve, sur la place du Dam, le palais royal d'Amsterdam, construit au XVIIe siècle, symbole de l'importance de la ville. Guillaume Ier en fait sa résidence en 1815. Depuis juillet 2010, le quartier du Grachtengordel, délimité par le Herengracht, Keizersgracht et Prinsengracht, figure sur la liste du patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO. Dans cette zone que se trouve le renommé béguinage d'Amsterdam, cour arborée et bordée d'habitations anciennes — la plus vieille datant de 1528 environ — abritant en son sein une chapelle anglicane.
Amsterdam est l'un des centres économiques majeurs des Pays-Bas et l'un des principaux centres financiers d'Europe. Les sièges sociaux de plusieurs firmes multinationales (Philips, AkzoNobel, ING et TomTom notamment) sont situés dans la ville et d'autres ont leurs bureaux européens basés à Amsterdam (principalement Netflix, Uber et Tesla). La ville est également la première destination touristique et culturelle néerlandaise, notamment du fait de la renommée ses principaux musées concentrés autour du Museumplein : le musée d'État, la fondation d'art moderne Stedelijk Museum et le Van Gogh Museum figurent parmi les plus visités au monde. D'autres lieux culturels d'importance sont le musée scientifique NEMO, l'Institut royal des Tropiques, le musée d'art Hermitage, l'institut du cinéma EYE, le musée maritime néerlandais et la Maison Anne Frank.
Divers classements placent Amsterdam parmi les métropoles mondiales offrant le meilleur confort de vie5, le magazine américain Forbes la positionnant à la première place en 20166. Selon l'Economist Intelligence Unit, elle est également la deuxième ville la plus sûre d'Europe après Stockholm7. La majorité des déplacements en ville s'effectue grâce aux quinze lignes de tramway, aux cinq lignes de métro, à pied ou à vélo. La ville est réputée pour ses événements festivaliers (particulièrement l'Amsterdam Music Festival, Sensation, In Qontrol et Uitmarkt), ses discothèques (spécifiquement Paradiso et Melkweg) et ses salles de concert (notamment le Ziggo Dome, Concertgebouw, Heineken Music Hall et Stadsschouwburg). Amsterdam est aussi connue pour son quartier rouge, ainsi que pour ses nombreux coffee shops possédant une licence leur permettant de commercialiser le cannabis, reflétant le progressisme politique des Pays-Bas8.
Amsterdam (pron. /ˈamsterdam/[1]; in olandese: /ˌɑmstər'dɑm/, pronuncia[?·info]) è la capitale e la maggiore città dei Paesi Bassi, nella provincia dell'Olanda Settentrionale. La municipalità di Amsterdam ha 851.573 residenti (al 2017) di oltre 170 nazionalità, mentre la popolazione che risiede nell'area metropolitana è di circa 2.289.762 persone. L'area al centro della città circondata dai canali del XII secolo è dal 2010 Patrimonio dell'umanità.
Amsterdam possiede uno dei maggiori centri rinascimentali di tutta l'Europa. Numerose costruzioni che risalgono al periodo tra il XVI e XVII secolo, conosciuto anche come Secolo d'oro, sono ora considerate monumenti storici e sono collocate intorno ad una serie di canali poligonali concentrici. Questi cingono il vecchio porto che un tempo era affacciato sullo Zuiderzee, oggi un lago separato dal resto del mare e noto con il nome di IJsselmeer. La città è famosa per ospitare il Rijksmuseum (museo statale), il museo Van Gogh, il Concertgebouw, il Rembrandthuis, la casa di Anna Frank e un enorme numero di biciclette.
Amsterdam è anche famosa per il suo quartiere a luci rosse, il De Wallen, e i suoi numerosi coffee-shop autorizzati alla vendita di marijuana e di derivati della cannabis.
Il motto ufficiale della città è "Heldhaftig, Vastberaden, Barmhartig" ("valorosa, decisa, misericordiosa"). Le tre croci di Sant'Andrea sulla bandiera sono associate a queste tre parole, benché siano entrate in uso prima del motto.
Ámsterdam5 o Amsterdam, según la pronunciación etimológica ( Amsterdam (?·i) [ɑmstər'dɑm]), es la capital oficial de los Países Bajos. La ciudad está situada entre la bahía del IJ, al norte, y a las orillas del río Amstel, al sureste. Fue fundada en el siglo XII como un pequeño pueblo pesquero. Sin embargo, en la actualidad es la ciudad más grande del país y un gran centro financiero y cultural de proyección internacional.
Amsterdam (?·i) [ɑmstər'dɑm]), es la capital oficial de los Países Bajos. La ciudad está situada entre la bahía del IJ, al norte, y a las orillas del río Amstel, al sureste. Fue fundada en el siglo XII como un pequeño pueblo pesquero. Sin embargo, en la actualidad es la ciudad más grande del país y un gran centro financiero y cultural de proyección internacional.
Tiene una población de unos 810 000 habitantes y en su área metropolitana residen aproximadamente 1,5 millones. Cabe destacar que Ámsterdam forma parte de la gran conurbación neerlandesa llamada Randstad (junto con las ciudades de La Haya, Róterdam y Utrecht), que cuenta con más de 6,5 millones de habitantes. Este núcleo es una de las conurbaciones más grandes de Europa.
El centro histórico de la ciudad fue construido en gran parte en el siglo XVII y es hoy en día uno de los centros históricos más grandes de Europa. En aquella época se construyeron una serie de canales semicirculares alrededor del casco antiguo ya existente de la ciudad. Después se edificaron las nuevas calles que ahora habían sido creadas con casas y almacenes en un estilo típico neerlandés que es una de las imágenes más famosas de Ámsterdam y del país. Al igual que otras ciudades de Europa septentrional con abundancia de agua, como Brujas, Hamburgo y Estocolmo, es conocida coloquialmente como la «Venecia del norte».
Aunque durante casi toda su historia (excepto entre 1808–1810) ha sido la capital oficial de los Países Bajos, nunca ha sido la sede de la justicia, el gobierno o el parlamento neerlandés, ya que todos estos órganos se encuentran en la ciudad de La Haya, que por tanto es la principal ciudad del país con respecto a política y justicia. Ámsterdam tampoco es la capital de la provincia de Holanda Septentrional, que siempre ha sido Haarlem.
Амстерда́м (нидерл. Amsterdam [ˌɑmstərˈdɑm]) — столица и крупнейший город Нидерландов. Является столицей королевства с 1814 года. Расположен в провинции Северная Голландия на западе страны в устье рек Амстел и Эй. Амстердам соединён Нордзе-каналом с Северным морем.
По состоянию на 1 января 2012 года население муниципалитета Амстердам составляет 801 847 человек[1], вместе с пригородами (городской округ) — 2,3 млн жителей. Амстердам является частью агломерации Рандстад, которая является 6-й по величине в Европе.
Название города произошло от двух слов: «Амстел» — название реки и «дам» — «дамба». В XII веке это была небольшая рыбачья деревня, но во времена Золотого века Нидерландов Амстердам стал одним из наиболее значимых портов мира и крупным торговым центром.
Город является местом концентрации различных культур — в апреле 2009 года здесь проживали представители 177 национальностей.
Амстердам также является финансовой и культурной столицей Нидерландов. Здесь расположились штаб-квартиры 7 из 500 наиболее крупных мировых компаний, например, Philips и ING Groep. Также в центре города расположена старейшая в мире фондовая биржа.
В Амстердаме расположен главный офис Гринпис.
Множество достопримечательностей: Рейксмюзеум, Музей Винсента Ван Гога, Городской музей, Эрмитаж на Амстеле, квартал красных фонарей (Де Валлен) — ежегодно привлекает в город около 4,2 миллиона туристов.
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD
 Medieval cities in Europe
Medieval cities in Europe
 Schottland
Schottland
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
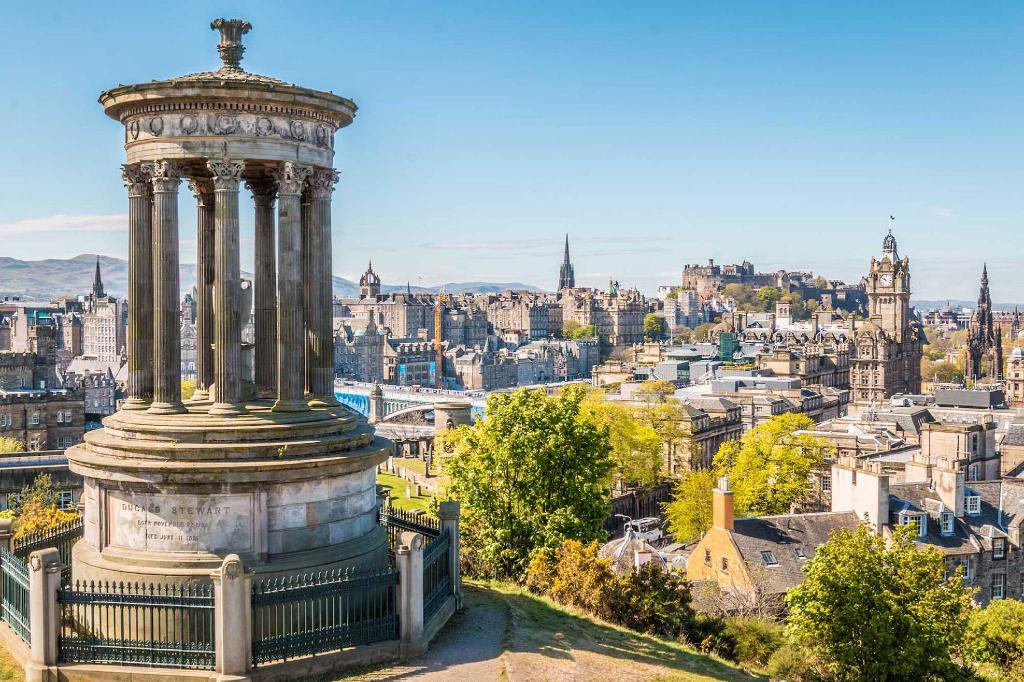

Edinburgh  [ˈɛdɪnb(ə)ɹə][2] (schottisch-gälisch Dùn Èideann [tuːn ˈeːtʃən]; dt. Edinburg; amtlich City of Edinburgh) ist seit dem 15. Jahrhundert die Hauptstadt von Schottland (bis dahin war es Perth). Seit 1999 ist Edinburgh außerdem Sitz des Schottischen Parlaments. Edinburgh ist mit etwa 493.000 Einwohnern nach Glasgow die zweitgrößte Stadt Schottlands und seit 1996 eine der 32 schottischen Council Areas. Die Stadt liegt an Schottlands Ostküste auf der Südseite des Firth of Forth gegenüber von Fife.
[ˈɛdɪnb(ə)ɹə][2] (schottisch-gälisch Dùn Èideann [tuːn ˈeːtʃən]; dt. Edinburg; amtlich City of Edinburgh) ist seit dem 15. Jahrhundert die Hauptstadt von Schottland (bis dahin war es Perth). Seit 1999 ist Edinburgh außerdem Sitz des Schottischen Parlaments. Edinburgh ist mit etwa 493.000 Einwohnern nach Glasgow die zweitgrößte Stadt Schottlands und seit 1996 eine der 32 schottischen Council Areas. Die Stadt liegt an Schottlands Ostküste auf der Südseite des Firth of Forth gegenüber von Fife.
爱丁堡(英语:Edinburgh, i/ˈɛdɪnbərə/[4]、苏格兰盖尔语:Dùn Èideann),是英国苏格兰首府,也是继格拉斯哥后苏格兰的第二大城市,位于苏格兰东海岸福斯湾南岸。截止到2013年,全市人口为487,500。[3]
i/ˈɛdɪnbərə/[4]、苏格兰盖尔语:Dùn Èideann),是英国苏格兰首府,也是继格拉斯哥后苏格兰的第二大城市,位于苏格兰东海岸福斯湾南岸。截止到2013年,全市人口为487,500。[3]
自15世纪以来爱丁堡就被当做苏格兰首府,但在1603年和1707年政治力量多次南移到伦敦。1999年苏格兰议会的自治权利才得以确立。苏格兰国家博物馆、苏格兰国家图书馆和苏格兰国家画廊等重要文化机构也位于爱丁堡。在经济上,现在的爱丁堡主要依靠金融业,是伦敦以外英国最大的金融中心。[5]
爱丁堡有着悠久的历史,许多历史建筑亦完好保存下来。爱丁堡城堡、荷里路德宫、圣吉尔斯大教堂等名胜都位于此地。爱丁堡的旧城和新城一起被联合国教科文组织列为世界遗产。[6]2004年爱丁堡成为世界第一座文学之城。[7]爱丁堡的教育也很发达,英国最古老的大学之一爱丁堡大学就坐落于此,为一所历史超过四百年的世界顶尖名校。[8]加上爱丁堡国际艺术节等文化活动,爱丁堡成为了英国仅次于伦敦的第二大旅游城市。
エディンバラ(英語: Edinburgh [ˈɛdɪnbərə] (![]() 音声ファイル)、スコットランド・ゲール語: Dùn Éideann [ˈt̪uːn ˈɛːtʲɛn̪ˠ])は、スコットランドの首都であり、ロージアン州の州都。日本語では「エジンバラ」とも表記される。
音声ファイル)、スコットランド・ゲール語: Dùn Éideann [ˈt̪uːn ˈɛːtʲɛn̪ˠ])は、スコットランドの首都であり、ロージアン州の州都。日本語では「エジンバラ」とも表記される。
Edinburgh (/ˈɛdɪnbərə/ ( listen);[6][7][8] Scottish Gaelic: Dùn Èideann [ˈt̪uːn ˈeːtʲən̪ˠ]; Scots: Edinburgh) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (or Edinburghshire), it is located in Lothian on the Firth of Forth's southern shore.
listen);[6][7][8] Scottish Gaelic: Dùn Èideann [ˈt̪uːn ˈeːtʲən̪ˠ]; Scots: Edinburgh) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (or Edinburghshire), it is located in Lothian on the Firth of Forth's southern shore.
Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the supreme courts of Scotland. The city's Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scots law, literature, the sciences and engineering. It is the second largest financial centre in the United Kingdom (after London)[9] and the city's historical and cultural attractions have made it the United Kingdom's second most popular tourist destination, attracting over one million overseas visitors each year.[10]
Edinburgh is Scotland's second most populous city and the seventh most populous in the United Kingdom. The official population estimates are 464,990 (2012) for the Locality of Edinburgh (Edinburgh pre 1975 regionalisation plus Currie and Balerno),[1] 513,210 (2017) for the City of Edinburgh,[2] and 1,339,380 (2014) for the city region.[2][3] Edinburgh lies at the heart of the Edinburgh and South East Scotland city region comprising East Lothian, Edinburgh, Fife, Midlothian, Scottish Borders and West Lothian.[11]
The city is the annual venue of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland. It is home to national institutions such as the National Museum of Scotland, the National Library of Scotland and the Scottish National Gallery. The University of Edinburgh, founded in 1582 and now one of four in the city, was placed 23rd in the QS World University Rankings in 2018.[12] The city is also famous for the Edinburgh International Festival and the Fringe, the latter being the world's largest annual international arts festival. Historic sites in Edinburgh include Edinburgh Castle, the Palace of Holyroodhouse, the churches of St. Giles, Greyfriars and the Canongate, and the extensive Georgian New Town, built in the 18th/19th centuries. Edinburgh's Old Town and New Town together are listed as a UNESCO World Heritage site,[13] which has been managed by Edinburgh World Heritage since 1999.
Édimbourg (prononcé [e.dɛ̃.buʁ] ; Edinburgh [ˈɛ.dɪn.bərə] Écouter en anglais britannique, Dùn Èideann [ˈt̪uːnˈeːtʲən̪ˠ] en gaélique écossais, Embra, Edinburrie, Edinburra et Edimbra en scots) est une ville d'Écosse au Royaume-Uni. Elle est sa capitale depuis 1532, ainsi que le siège du Parlement écossais depuis le rétablissement de celui-ci en 1999. Sa population était de 457 830 habitants en 2005 (c’est la deuxième ville d’Écosse derrière Glasgow). Ses habitants s'appellent les Édimbourgeois. Depuis 1329, Édimbourg possède officiellement le statut de cité. Elle a aussi le statut de council area (depuis le 31 mars 1996) et de région de lieutenance, après avoir eu celui de district au sein de la région du Lothian (du 15 mai 1975 au 31 mars 1996) dont elle était le siège.
La ville est construite sur des collines volcaniques qui fournissent chacune un point de vue différent sur la ville. Elle est dominée par son château dont les fondations remontent au VIIe siècle mais c’est à partir du XIe siècle que fut construite cette résidence royale avant de devenir une forteresse redoutable au XVIe siècle. Édimbourg fut affranchie en 1329 et s’entoura de murailles au XVe siècle. Après la défaite de Flodden (1513) contre les Anglais, les bourgeois de la ville décidèrent de construire à titre préventif une seconde enceinte baptisée le mur de Flodden. Après l’unification des Parlements d’Écosse et d’Angleterre (1707), la ville perdit de son importance politique mais resta un important centre économique et culturel. En plus du Château, Édimbourg compte de nombreux lieux intéressants comme le Royal Botanic Garden, les cathédrales Saint-Gilles (presbytérienne), Sainte-Marie (épiscopalienne) et Sainte-Marie (catholique), la National Gallery, Charlotte Square, le Scott monument ou encore le National Museum of Scotland. Le palais de Holyrood (Holyrood Palace) est la résidence officielle de la reine lorsqu’elle séjourne dans la ville. Les districts de la vieille et de la nouvelle ville sont classés patrimoine mondial par l’UNESCO depuis 1995.
Édimbourg est célèbre pour son festival, le plus grand du monde, qui dure trois semaines en août et propose de nombreux spectacles de qualité dans toutes les disciplines.
La ville accueille l'une des plus prestigieuses universités d’Europe et du monde, l’université d’Édimbourg, pionnière dans l’informatique, la géologie, la chimie et la médecine. À Édimbourg se situe également la bibliothèque nationale d’Écosse (National Library of Scotland) qui est la plus importante bibliothèque d’Écosse (et l’une des plus grandes du Royaume-Uni).
Edimburgo (AFI: /edimˈburɡo/[3]; in inglese e scots Edinburgh, pron. [ˈɛdɪnbʌrə] oppure [ˈɛdɪnbrə], in gaelico scozzese Dùn Èideann) è una città del Regno Unito, capitale della Scozia dal 1437 e sede del suo nuovo parlamento dal 1999. È la seconda città della Scozia per popolazione dopo Glasgow e la settima del Regno Unito per popolazione. I dati ufficiali del 2014 stimano la popolazione in 464 990 abitanti per la città,[1] 492 680 per l'area dell'autorità locale[1] e 1 339 380 per l'area metropolitana[1] (Edinburgh è situata nel cuore della proposta "city region" di Edimburgo e Scozia sudorientale).
La città, situata sulla costa orientale della Scozia e sulla riva meridionale del Firth of Forth, a circa 70 km ad est di Glasgow, sorge su 7 colli. I punti più alti sono: Arthur's Seat, Castle Rock dove si trova il castello, Calton Hill, Corstorphine Hill, Braid Hills, Blackford Hill e Craiglockhard Hill, su di una serie di colline. Le parti storiche della città (Old e New Town), insieme al castello, nel 1995 sono state dichiarate patrimonio dell'umanità dall'UNESCO.
È una delle città più visitate della Gran Bretagna con circa 2 milioni di turisti l'anno[4] e a questo successo contribuisce anche il Festival di Edimburgo, che si tiene ogni anno ed è accompagnato da numerose manifestazioni collaterali.
Edimburgo ( /ˈɛdɪnb(ʌ)ɹə/ (?·i) en inglés y escocés: Edinburgh; en gaélico escocés: Dùn Èideann) es la capital y un concejo de Escocia (Reino Unido).23 Es la segunda ciudad más grande de Escocia tras Glasgow.
/ˈɛdɪnb(ʌ)ɹə/ (?·i) en inglés y escocés: Edinburgh; en gaélico escocés: Dùn Èideann) es la capital y un concejo de Escocia (Reino Unido).23 Es la segunda ciudad más grande de Escocia tras Glasgow.
Ubicada en la costa este de Escocia, a orillas del fiordo del río Forth y en la autoridad unitaria local de la Ciudad de Edimburgo, es la capital de Escocia desde 1437 y sede del gobierno escocés. Fue uno de los centros más importantes de educación y cultura durante la Ilustración gracias a la Universidad de Edimburgo. Sus distritos The Old Town (ciudad antigua) y The New Town (ciudad nueva) fueron designados Patrimonio de la Humanidad por la Unesco en 1995.4 Según el censo de 2011 tiene un población total de 459 366 habitantes.1
Edimburgo es famosa por su Festival Internacional, el festival de actuaciones en vivo más grande del mundo, y otros festivales desarrollados en verano de forma más o menos simultánea, la mayoría de los cuales se agrupan bajo la denominación Festival de Edimburgo. Durante el festival la población de la ciudad se duplica. Edimburgo es la segunda ciudad más visitada del Reino Unido, después de Londres, con aproximadamente 13 millones de turistas al año.
Эдинбу́рг (англ. и скотс. Edinburgh [ˈɛdɪnb(ʌ)rə], гэльск. Dùn Èideann [tuːn ˈeːtʃən]) — столица Шотландии (с 1437 года) и второй по величине её город. Административный центр округа Сити-оф-Эдинбург. Население Эдинбурга в 2016 году составляло 488,1 тыс. человек. Это седьмой по величине город Соединённого королевства. Расположен на восточном побережье Шотландии (территория Среднешотландской низменности), на южном берегу залива Ферт-оф-Форт.
Районы Эдинбурга — Старый город и Новый город — в 1995 году были занесены ЮНЕСКО в список объектов Всемирного наследия.
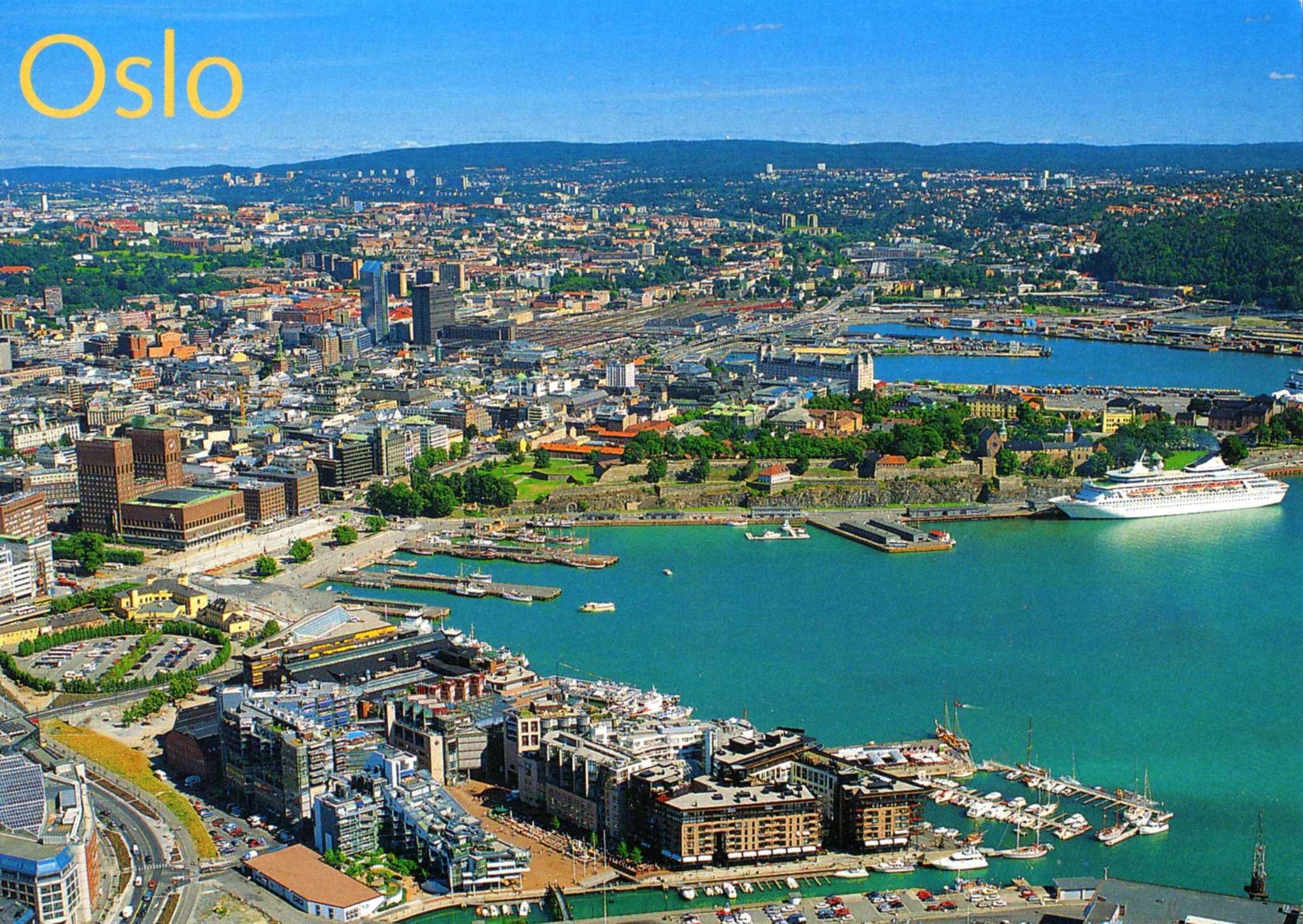

奥斯陆是挪威的首都,人口约85万,位于奥斯陆峡湾的最深处。奥斯陆南临奥斯陆湾,三面被群山环绕,整个城市与绿色的大自然和谐地融为一体。
从奥斯陆中央车站到王宫,再从卡尔约翰大街到国会议事堂周边为步行者天国。大街两侧是摩登的咖啡屋、餐馆和商店。每到夏季或周末这里可看到演艺人的各种演出。周围还有奥斯陆大教堂和国家美术馆。
奥 斯陆还是油画、雕刻、戏剧之都,充满了艺术气息。国家美术馆展出有蒙克的《呐喊》和《玛丽亚》。维格朗雕塑公园绿荫环绕,有200件雕塑艺术品,是人们休 闲娱乐的理想去处。奥斯陆的观光区域大致分为5个区域,卡尔约翰大街周边、阿肯修弗斯城堡周边、王宫周边、布里格周边以及维格朗公园周边等。
奥斯陆卡
还将享受汽车租赁、雪橇租赁以及其他部分设施,如餐厅和商店的折扣。
奥斯陆卡在游客信息中心、大酒店、奥斯陆中央车站售票处、报亭以及通过互联网都可以购买。有效期从第一次使用时的时间开始计算,请再开始使用前做好计划。(Quelle:http://www.visitscandinavia.org/)
奥斯陆(挪威语:Oslo ![]() 聆听 帮助·信息),1925年前旧称克里斯蒂安尼亚(Kristiania),是挪威首都和最大城市,全国政治、经济、文化中心,也是挪威的贸易、银行业、工业和航运枢纽,位于挪威东南部的奥斯陆峡湾内侧,人口666, 759人(截至2017年1月1日)。[8]包括邻近的10个自治市在内的城市区人口为975, 744人(截至2016年1月1日),[9]而整个大奥斯陆地区人口数为1, 546, 706。[8]
聆听 帮助·信息),1925年前旧称克里斯蒂安尼亚(Kristiania),是挪威首都和最大城市,全国政治、经济、文化中心,也是挪威的贸易、银行业、工业和航运枢纽,位于挪威东南部的奥斯陆峡湾内侧,人口666, 759人(截至2017年1月1日)。[8]包括邻近的10个自治市在内的城市区人口为975, 744人(截至2016年1月1日),[9]而整个大奥斯陆地区人口数为1, 546, 706。[8]
奥斯陆因其奇特的地理学和地质学特征而闻名。它被森林和田野所环绕,许多种类的动植物生活在其中。奥斯陆自治市内三分之二的面积是森林和水域,使得实际人口密度达到了5, 221.6人/平方公里。城市核心区的形状像是一个被植被茂密的丘陵所环绕的砂锅,许多河流从丘陵中流出,通过市区汇入奥斯陆峡湾。
根据考古学研究,奥斯陆于公元1000年前后建城。奥斯陆老城区是北欧除了维斯比以外最大的中世纪城市,而且至今保存完好。奥斯陆于1048年被确立为一个贸易点。1070年,奥斯陆被提升为主教辖区。在大约1300年,挪威国王哈康五世将奥斯陆定为挪威首都。在挪威从1397至1523年和1536至1814年与丹麦,以及1814至1905年与瑞典建立共主邦联期间,尽管哥本哈根和斯德哥尔摩先后成为了国家行政机构的所在地,奥斯陆仍然保有着一部分首都职能。
奥斯陆是14世纪挪威受到黑死病影响最严重的地区,在15和16世纪其人口和经济状况又经受了进一步的衰退。1624年,奥斯陆曾被一场大火摧毁,之后,在丹麦国王克里斯蒂安四世统治期间,城区被迁移到了更靠近阿克斯胡斯城堡的地方,并以国王的名字命名为克里斯蒂安尼亚(Christiania)。在1814年丹麦-挪威邦联解体之前,克里斯蒂安尼亚已被宣布成为挪威的首都。1838年1月1日,克里斯蒂安尼亚成为了一个自治市。尽管在19世纪以前,克里斯蒂安尼亚在欧洲范围内只是一座小城市,但从第二次工业革命之后,这座城市开始高速发展。在1900年前后,克里斯蒂安尼亚已经成为了一个发达的工业中心,有着近25万名居民。1925年,它的名字从克里斯蒂安尼亚改为了奥斯陆。
奥斯陆是欧洲重要的航海工业和航海贸易中心,是许多航运企业总部的所在地,其中包括一些世界级的航运公司、船舶经纪人和海上保险经纪人。奥斯陆也是欧洲委员会和欧洲联盟委员会的跨文化城市项目的试点城市。
奥斯陆被认为是一座全球城市,在2012年fDi杂志发表的欧洲大城市生活质量排名中名列第一位。[10] ECA国际2011年进行的一项调查显示,奥斯陆是全球生活成本第二高的城市,仅次于东京。[11] 根据经济学人智库(EIU)的统计,2013年奥斯陆也名列全球生活和学习成本最高的四座城市之一。[12]
1952年,奥斯陆曾举办过冬季奥运会。1993年5月,在美国的主导下,以色列和巴勒斯坦在这里签订了著名的奥斯陆协议。另外,奥斯陆也是诺贝尔和平奖的颁奖地,每年的颁奖仪式在奥斯陆市政厅举行。
21世纪初,奥斯陆的人口以创纪录的速度增长,使其成为了当时全欧洲人口增长速度最快的城市之一。[13] 这一高增长率主要和国际移民的流入和高生育率有关,但也离不开国内人口流动的影响。目前,奥斯陆的移民人口增长速度略高于本国人口增长速度,[14] 在市区部分,这一差异更为显著。2012年1月1日的数据显示,奥斯陆人口的23%是移民,[15]市内最大的少数族裔是挪威-瑞典人和挪威-巴基斯坦人。
(deutsch: [ˈʔɔslo], norwegisch: [ˈʊʂlʊ], [ˈʊʃlʊ] oder [ˈʊslʊ]) ist die Hauptstadt des Königreichs Norwegen. Ihr ehemaliger Name war Christiania (1624 bis 1924) bzw. Kristiania (alternative Schreibweise von 1877/1897 bis 1924).
Die Kommune Oslo hat 669.060 Einwohner(30. Jun. 2017)[2]. Sie bildet eine eigenständige Provinz (Fylke) und ist zudem Verwaltungssitz für die benachbarte Provinz Akershus.
Mit 975.744 Einwohnern ist Oslo der mit Abstand größte Ballungsraum des Landes[3]. In der Groß-Oslo-Region leben rund 1,5 Millionen Menschen, also fast ein Drittel der gesamten Bevölkerung Norwegens von rund 5,3 Millionen[4]. Der Hafen (UN/LOCODE NO OSL) eignet sich für Schiffe mit Längen unter 150 Meter.
オスロ(ノルウェー語: Oslo ノルウェー語発音: [²uʃlu] (![]() 音声ファイル)、旧称クリスチャニア、クリスティアーニアChristianiaもしくはKristiania)は、ノルウェー王国の首都にして最大の都市である。王宮、行政、立法、司法などの機関が集まる。オスロ市はオスロ県と同じ範囲である。世界でも物価の高い都市のひとつであり、北欧有数の世界都市でもある。
音声ファイル)、旧称クリスチャニア、クリスティアーニアChristianiaもしくはKristiania)は、ノルウェー王国の首都にして最大の都市である。王宮、行政、立法、司法などの機関が集まる。オスロ市はオスロ県と同じ範囲である。世界でも物価の高い都市のひとつであり、北欧有数の世界都市でもある。
Oslo (/ˈɒzloʊ/ OZ-loh;[9] Norwegian: [²uʂlu] (![]() listen), rarely [²uslu, ˈuʂlu]) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. Founded in the year 1040, and established as a kaupstad or trading place in 1048 by Harald Hardrada, the city was elevated to a bishopric in 1070 and a capital under Haakon V of Norway around 1300. Personal unions with Denmark from 1397 to 1523 and again from 1536 to 1814 and with Sweden from 1814 to 1905 reduced its influence. After being destroyed by a fire in 1624, during the reign of King Christian IV, a new city was built closer to Akershus Fortress and named Christiania in the king's honour. It was established as a municipality (formannskapsdistrikt) on 1 January 1838. The city's name was spelled Kristiania between 1877 and 1897 by state and municipal authorities, respectively. In 1925 it was renamed Oslo.
listen), rarely [²uslu, ˈuʂlu]) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. Founded in the year 1040, and established as a kaupstad or trading place in 1048 by Harald Hardrada, the city was elevated to a bishopric in 1070 and a capital under Haakon V of Norway around 1300. Personal unions with Denmark from 1397 to 1523 and again from 1536 to 1814 and with Sweden from 1814 to 1905 reduced its influence. After being destroyed by a fire in 1624, during the reign of King Christian IV, a new city was built closer to Akershus Fortress and named Christiania in the king's honour. It was established as a municipality (formannskapsdistrikt) on 1 January 1838. The city's name was spelled Kristiania between 1877 and 1897 by state and municipal authorities, respectively. In 1925 it was renamed Oslo.
Oslo is the economic and governmental centre of Norway. The city is also a hub of Norwegian trade, banking, industry and shipping. It is an important centre for maritime industries and maritime trade in Europe. The city is home to many companies within the maritime sector, some of which are among the world's largest shipping companies, shipbrokers and maritime insurance brokers. Oslo is a pilot city of the Council of Europe and the European Commission intercultural cities programme.
Oslo is considered a global city and was ranked "Beta World City" in studies carried out by the Globalization and World Cities Study Group and Network in 2008.[10] It was ranked number one in terms of quality of life among European large cities in the European Cities of the Future 2012 report by fDi magazine.[11] A survey conducted by ECA International in 2011 placed Oslo as the second most expensive city in the world for living expenses after Tokyo.[12] In 2013 Oslo tied with the Australian city of Melbourne as the fourth most expensive city in the world, according to the Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU)'s Worldwide Cost of Living study.[13]
As of 1 July 2017, the municipality of Oslo had a population of 672,061, while the population of the city's urban area was 942,084.[4] The metropolitan area had an estimated population of 1.71 million.[14] The population was increasing at record rates during the early 2000s, making it the fastest growing major city in Europe at the time.[15] This growth stems for the most part from international immigration and related high birth rates, but also from intra-national migration. The immigrant population in the city is growing somewhat faster than the Norwegian population,[16] and in the city proper this is now more than 25% of the total.[17]
OsloÉcouter est la capitale d'État de la Norvège. Le toponyme se prononce /↓ʊʂˈlʊ/ dans le dialecte osloïte. La ville s'est appelée Christiania de 1624 à 1924, selon l'ancienne graphie latine héritée du danois, ou communément Kristiania en dano-norvégien. Le 1er janvier 1925, elle a officiellement repris le nom d'un modeste faubourg, site historique de la première ville, fondée au fond de l'Oslofjord par Harald III et promue capitale royale sous Haakon V.
Alors que la ville d'Oslo compte une population de près de 600 000 habitants, dont 27 % d'immigrants2, la région d'Oslo compte 1 403 268 habitants en 2010. La ville, qui s'étend sur 450 km2, est restée en parfaite osmose avec la nature par ses prairies et parcs spacieux et ses pistes de ski de fond, bien que cet important nœud de communication ferroviaire et portuaire soit desservi par un réseau routier et autoroutier et de nombreux trains de banlieue. La capitale regroupe 11,5 % de la population norvégienne et constitue un fylkeskommune (district communal), regroupant quinze bydeler (subdivisions), s'étendant largement autour du fjord d'Oslo et vers le nord-est. Il n'y a pas de gentilé d'usage générique dans la langue norvégienne pour les habitants et originaires d'Oslo (sur le modèle de Tokyo, on parle parfois d'Osloïtes).
Oslo (AFI: /ˈɔzlo/[1]; pronuncia norvegese [²uʃlu]: , nel dialetto di Oslo [ùʂɭu][2] – conosciuta anche come Christiania dal 1624 al 1878 e come Kristiania dal 1878 al 1924) è una città del nord Europa ed è la capitale e la più grande città della Norvegia. Con una popolazione di circa 669 060 abitanti (2017), accoglie il 12% circa della popolazione norvegese. Tuttavia, considerando l'intera area metropolitana, comunemente chiamata "regione della grande Oslo" (Stor-Osloregionen), che si estende ben oltre i limiti del comune, si ha una popolazione complessiva di 1 546 706 abitanti (2015). I confini geografici della contea di Oslo e del comune sono coincidenti.
Oslo (![]() [ùʃlu] (?·i)), llamada Christiania o Cristianía en español de 1624 a 1897 y Kristiania de 1897 a 1924, es la capital y la ciudad más poblada de Noruega, además de ser su centro político, económico y cultural. Políticamente constituye un municipio y a la vez una de las diecinueve provincias del país. Según el censo del 1 de enero de 2015, su población era de 647 676 habitantes,1 un 12 % de la población total de Noruega; la estimación de enero de 2015 le asignó una población de 942 084. Es la tercera ciudad y área urbana escandinava más poblada, solo superada por Copenhague y Estocolmo.
[ùʃlu] (?·i)), llamada Christiania o Cristianía en español de 1624 a 1897 y Kristiania de 1897 a 1924, es la capital y la ciudad más poblada de Noruega, además de ser su centro político, económico y cultural. Políticamente constituye un municipio y a la vez una de las diecinueve provincias del país. Según el censo del 1 de enero de 2015, su población era de 647 676 habitantes,1 un 12 % de la población total de Noruega; la estimación de enero de 2015 le asignó una población de 942 084. Es la tercera ciudad y área urbana escandinava más poblada, solo superada por Copenhague y Estocolmo.
Su área metropolitana se extiende a los alrededores de la provincia de Akershus y tiene una población de 1 546 706 habitantes. La superficie total comprendida por Oslo es de 144 km², de los cuales 115 km² son urbanos y 7 km² son rurales. Los espacios abiertos dentro del área urbana suman un total de 22 km².
La ciudad de Oslo fue establecida como municipio el 3 de enero de 1838. Fue separada de la provincia de Akershus como una provincia independiente en 1842. El municipio rural de Aker fue absorbido por la expansión de Oslo en 1948 (y transferida de la provincia de Akershus al municipio de Oslo). La capital noruega aún comparte varias funciones importantes con Akershus y es oficialmente la capital de esta última.
О́сло (норв. Oslo , [↓ʊʂˈlʊ] или [↓ʊsˈlʊ]) — столица и самый крупный город Норвегии. До 1624 года, согласно карте А. Ортелиуса 1539 года, столица викингов называлась Викия (Vichia), с 1624 по 1877 годы называлась Христиания (норв. Christiania), с 1877 по 1925 годы — Кристиания (норв. Kristiania). Происхождение названия Осло было предметом многочисленных споров среди лингвистов. По одной из версий, название Oslo означает «устье Ло» (норв. os — «устье», Lo — название реки), по названию реки, некогда протекавшей здесь. Считается установленным, что ойконим имеет древнескандинавское происхождение и, по всей вероятности, первоначально был названием крупной фермы в Бьорвике[en], но значение этого названия оспаривается. Современные лингвисты обычно интерпретируют название Óslo или Áslo как «луг у подножия холма» или «луг, освященный богами», при этом оба варианта считаются одинаково вероятными[3].В своде саг «Круг Земной» исландского скальда Снорри Стурлусона упоминается, что Осло основал Харальд III в 1048 году. Во время археологических раскопок были найдены христианские захоронения, относящиеся примерно к 1000 году.
В Средние века город состоял из двух крепостей — королевского замка и епископского. В пределах городских стен находились 9 церквей, один госпиталь, около 400 деревянных домов торговцев и ремесленников. Король Хакон V Святой назвал Осло столицей Норвегии в 1299 году и построил здесь крепость Акерсхус. В годы Высокого Средневековья Осло стал важным торговым пунктом, в том числе были связи с Ганзейским союзом. Численность населения увеличилась вдвое до 3500 человек.
Из-за того, что постройки были выполнены по большей части из дерева, город часто горел, на месте сгоревших зданий сооружали новые, но опять же, из дерева. После трёхдневного пожара в 1624 году, уничтожившего город, датский король Кристиан IV (на то время Норвегия была провинцией Дании) перевёл жителей в новое место поблизости крепости Акерсхус, которое было названо Христиания в честь короля. Новый город строили в лучших традициях Ренессанса с широкими улицами и строго очерченными кварталами. Здания решили строить из камня, чтобы в будущем предотвратить разрушительные пожары. Несмотря на запрет короля, старый город был вновь заселён, в основном бедняками, которые не имели средств к проживанию в зажиточной Христиании. После Великой Северной войны в начале XVIII века экономика Христиании стала расти быстрыми темпами благодаря кораблестроению и торговле. Индустриализация пришла в город в 1840-х годах, когда возникло большое количество фабрик, в основном на берегах Акерсельвы.В результате англо-датской войны 1807—1814 годов Датско-норвежская уния объявила себя банкротом и по Кильскому договору 1814 года уступила Норвегию Швеции. В годы правления шведско-норвежского короля Оскара II прошла орфографическая реформа, в результате которой город был переименован в Кристианию в 1877 году. Лишь в 1924 году городу вернули его первоначальное название Осло.
В XX веке город заметно разросся, в 1948 году к нему присоединили Акер. В 1960-х Осло переделали в современный город с обширной сетью дорог, системой общественного транспорта и новыми офисными зданиями.
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 History
History
 Silk road
Silk road

 World Heritage
World Heritage
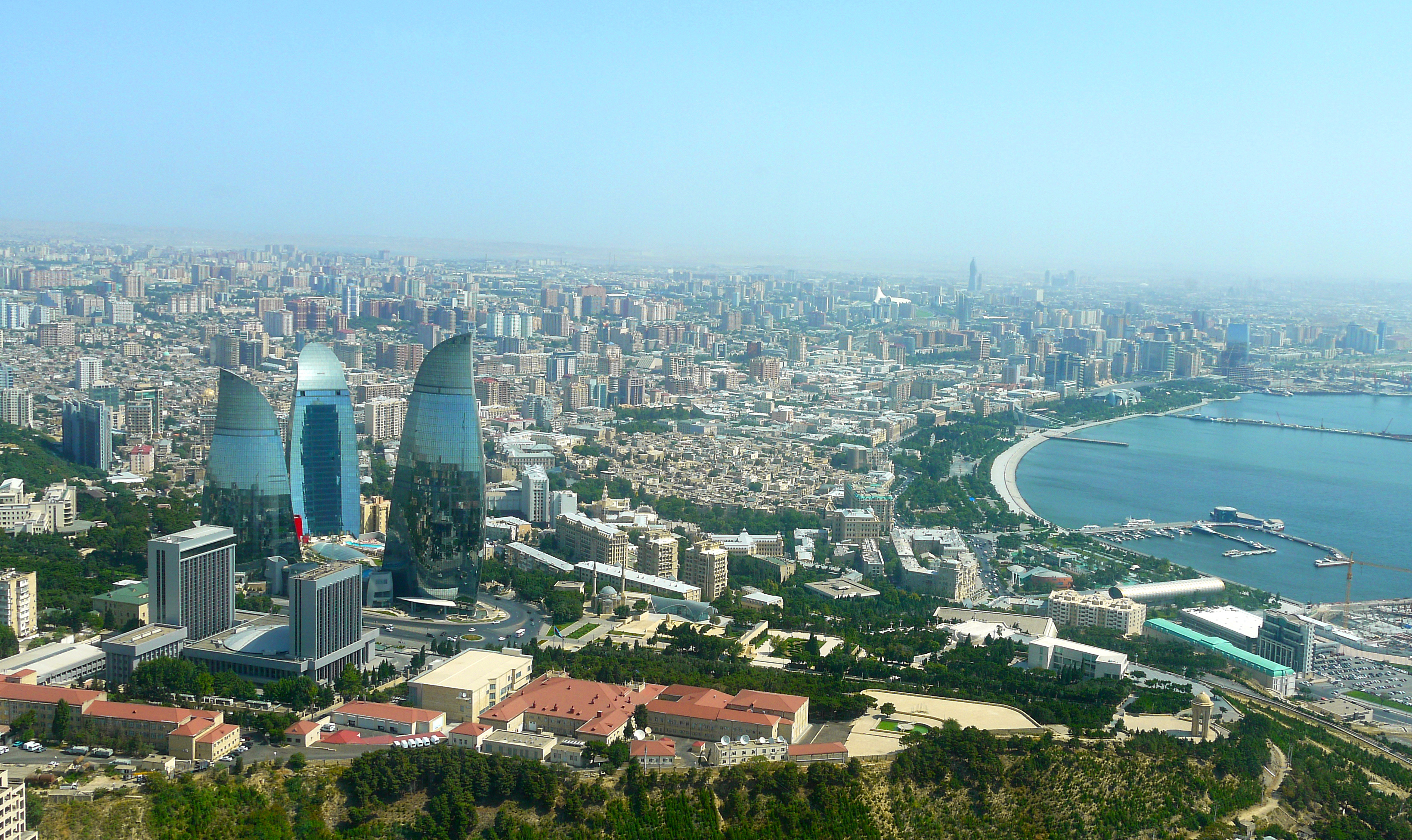

Baku (aserbaidschanisch Bakı / باکی; russisch Баку́ Baku) ist die Hauptstadt Aserbaidschans. Mit zwei Millionen Einwohnern in der Stadtprovinz ist Baku die bevölkerungsreichste und flächengrößte Stadt des Landes und des gesamten Kaukasus. Die Stadt an der Küste des Kaspischen Meeres ist Verkehrsknotenpunkt sowie Wirtschafts- und Kulturzentrum mit mehreren Universitäten, Hochschulen, Forschungsinstituten, Theatern und Museen. Durch die Lage innerhalb eines Erdölfördergebiets ist Baku der Knotenpunkt mehrerer Erdölleitungen und besitzt einen bedeutenden Erdölhafen. Baku kann aufgrund seiner günstigen Lage an mehreren historischen Handelswegen auf eine reiche Stadtgeschichte zurückblicken. In der Altstadt, die seit 2000 den Status eines UNESCO-Welterbes hat, sind zahlreiche Paläste, Moscheen und Festungsbauten erhalten geblieben.
巴库(Baku, Баку)是阿塞拜疆首都和全国经济、文化中心。里海最大港口。位于阿普歇伦米岛南部,是石油工业中心,有“石油城”之誉。也是前苏联外高加索最大城市。 巴库由10个行政区和46个城镇组成,面积2200平方公里。人口182.88万。1月平均气温为4℃,7月平均气温为27.3℃。 在18世纪,巴库为巴库汗国都城。19世纪70年代开始工业性采油,19世纪末成为外高加索工业中心和石油基地,有22大炼油基地,其他工业多与石油有 关。1991年8月成为独立后阿塞拜疆的首都。城市西部的比比埃巴特区为老采油区。东部的基什雷区和邵武勉区为重要工业区。石油是巴库的经济命脉。石油开 采正向深处和外围海域发展。以石油、天然气开采和石油加工为主要工业,还有石油机械、电力和轻工 、食品工业。外高加索主要铁路枢纽,铁路通罗斯托夫、第比利斯和埃里温。有输油管道通黑海港口巴统。巴库是里海航运中心,可泊中等吨位船舶。城市中部为行 政、文化和居住区。建有科学院,大学和博物馆。里海最大港口,有“石油城”之誉。市内建有地铁,有阿塞拜疆科学学院、阿塞拜疆大学、石油化工学院等多所高 等院校。城市的中部是行政、文化区域,有历史博物馆和艺术博物馆。老城区以旧要塞为中心。 巴库是一座有着悠久历史的古城,城内有众多名胜古迹,如11世纪建造的瑟纳克一卡尔清真寺塔,12世纪的克孜一卡拉瑟塔楼,13世纪的巴伊洛夫石堡,15 世纪的希尔凡王宫及17世纪的汗王宫殿至今保存完好。2000年联合国教科文组织将巴库墙城及城内的希尔梵国王宫殿和少女塔作为文化遗产,列入《世界遗产 名录》。(Quelle:http://you.kuxun.cn)
巴库(阿塞拜疆语:Bakı)是阿塞拜疆的首都、经济文化中心。巴库同时也是里海最大港口,外高加索最大城市[3]。面积2192平方千米,人口300万(2008年计算)[1]。巴库全市分为内城和新城两部分(亦有将苏联时期兴建区域分别划分的)。
在2007年,伊斯兰会议组织文化部长宣布巴库为2009年伊斯兰文化中心。为2015年第一届欧洲运动会主办国。巴库曾先后申办2016年夏季奥运会和2020年夏季奥运会,但皆因基础设施不完备没有入围。不过由于阿塞拜疆歌手艾尔与妮基在2011年欧洲歌唱大赛获得冠军,终使巴库获得举办2012年欧洲歌唱大赛的机会。
バクー(Baku)は、アゼルバイジャン共和国の首都。カスピ海西岸に突き出したアブシェロン半島南岸に位置し、市街はバクー湾に面するように広がった港町である。行政的には11の行政区、48の町区に分割されており、2005年時点の総人口は2,045,815人[1]。アゼルバイジャン最大の都市であると同時に、南カフカース地域でも有数の大都市である。大規模な油田(バクー油田)をもち、帝政ロシア時代から石油の生産地として発展してきた。
日本語名のバクーはキリル文字綴りによるロシア語綴り・アゼルバイジャン語(アゼリー語)旧綴り Баку (Baku) に基づくが、アゼルバイジャン語の発音では母音の前で子音 k が軟音化するためカタカナ表記するならば「バキュ」に近く、現在アゼルバイジャンで使われているアゼルバイジャン語のラテン文字正書法では Bakı と綴る。バクーという名前の由来には諸説あるが、最も一般的なものは、ペルシャ語で「風が吹きつけた」という意味の "bād-kūbe"(バード・クーベ)から来ているとする説が一般的である。
気候は晴天が多く、乾燥している。寒気と暖気がぶつかることで起きる強風が時折吹き付け、先述した語源の根拠となっている。海岸は美しく、市街近郊には温泉や鉱泉がある。
市街の中心はその南西部にあり、イチェリ・シェヘル (İçəri Şəhər) すなわち「内城」と呼ばれる城壁に囲まれた旧市街と、帝政ロシア時代にその周囲に築かれた新市街とに分かれる。その周囲、北から東にかけての平地から丘陵の斜面一帯にソビエト連邦時代につくられた市街が広がっている。近年は豊富なオイルマネーをもとに近未来的な巨大建築物が出現し、「第二のドバイ」「第二のシンガポール」とも呼ばれている[2]。
Baku (/bəˈkuː/ bə-KOO, /ˈbɑːkuː/ BAH-koo; Azerbaijani: Bakı, IPA: [bɑˈcɯ]) is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region, with a population of 2,262,600 (January 1, 2018). Baku is located 28 metres (92 ft) below sea level, which makes it the lowest lying national capital in the world and also the largest city in the world located below sea level. It is located on the southern shore of the Absheron Peninsula, alongside the Bay of Baku. At the beginning of 2009, Baku's urban population was estimated at just over two million people.[5] Officially, about 25 percent of all inhabitants of the country live in Baku's metropolitan area. Baku is the sole metropolis in Azerbaijan.
Baku is divided into twelve administrative districts (raions) and 48 townships. Among these are the townships on the islands of the Baku Archipelago, and the town of Oil Rocks built on stilts in the Caspian Sea, 60 kilometres (37 miles) away from Baku. The Inner City of Baku, along with the Shirvanshah's Palace and Maiden Tower, were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2000. According to the Lonely Planet's ranking, Baku is also among the world's top ten destinations for urban nightlife.[6]
The city is the scientific, cultural, and industrial center of Azerbaijan. Many sizeable Azerbaijani institutions have their headquarters there. The Baku International Sea Trade Port is capable of handling two million tons of general and dry bulk cargoes per year.[7] In recent years, Baku has become an important venue for international events. It hosted the 57th Eurovision Song Contest in 2012, the 2015 European Games, 4th Islamic Solidarity Games, the F1 Azerbaijan Grand Prix since 2016, and will host UEFA Euro 2020. The city is bidding for Expo 2025 against Yekaterinburg, Russia and Osaka, Japan.
La ville de Bakou (azéri : Bakı, IPA: [bɑˈcɯ]) est la capitale de l'Azerbaïdjan. Elle se trouve dans l'est du pays, sur la rive sud de la péninsule d'Abşeron, au bord de la mer Caspienne. Son histoire débute au Ier millénaire avant Jésus-Christ, mais les traces écrites les plus anciennes ne datent que du Ve siècle.
En 2011, sa population est estimée à 2 045 815 habitants1 et 3 millions de personnes environ vivent dans l'agglomération.
Baku (pron. bakù[2]; in azero: Bakı?; in russo: Баку?), conosciuta anche come Baqy, Baky o Baki, in italiano Bacù[2], è la capitale, la più grande città e il più grande porto dell'Azerbaigian e di tutto il Caucaso.
È considerata una delle più antiche e più grandi città dell'Oriente. Situata sulla costa meridionale della penisola di Abşeron, la città si compone di tre parti principali: il centro, la vecchia Città Murata estesa sul territorio di 21,5 ettari e la parte della città costruita nell'epoca sovietica. La sua popolazione nel 2014 era stimata in 2.122.300 di abitanti.
Bakú (en azerí, Bakı, [bɑˈkɯ]) es la capital y ciudad más poblada de Azerbaiyán, del mar Caspio y del Cáucaso. Está situada en la costa sur de la península de Absheron, que se proyecta en el Caspio. La ciudad se compone de dos partes principales: el centro y la ciudad vieja interior. En enero de 2018 Bakú tenía una población de 2.262.600 habitantes,3 de los cuales 153.400 eran desplazados internos y 143.400 refugiados de la guerra de Nagorno Karabaj.
Bakú se divide en once distritos administrativos (raiones) y 48 municipios. Entre estos se encuentran los municipios de las islas de la bahía de Bakú y Neft Daşları construidas sobre pilotes en el mar Caspio, a 60 km de Bakú. El centro urbano de la ciudad, con el Palacio de los Shirvanshah y la Torre de la Doncella, fue inscrito por la Unesco como Patrimonio de la Humanidad en 2000. De acuerdo con la clasificación de Lonely Planet, Bakú también se encuentra entre los diez mejores destinos de vida nocturna urbana del mundo.4
La ciudad fue uno de los mayores centros petrolíferos de la antigua Unión Soviética y actualmente es el centro científico, cultural e industrial de Azerbaiyán. Muchas instituciones importantes de Azerbaiyán tienen su sede allí, incluyendo SOCAR, una de las cien principales empresas del mundo, entre otras.5 El Puerto de Comercio Marítimo Internacional de Bakú, protegido por las islas del archipiélago Bakú hacia el este y la península de Absheron al norte, es capaz de transportar dos millones de toneladas de carga general y seca a granel por año.6 La ciudad acogió el 57.º Festival de Eurovisión en 2012 y fue la sede de los Juegos Europeos 2015, es la sede del Gran Premio de Azerbaiyán de Fórmula 1 desde 2016 y será la sede del Campeonato Mundial de Ciclismo BMX en 2018 y de la EURO 2020.7
Баку́ (азерб. Bakı, МФА (азерб.): [bɑˈcɯ]) — столица Азербайджанской Республики, крупнейший промышленный, экономический и научно-технический центр Закавказья, а также самый крупный порт на Каспийском море и самый большой город на Кавказе[9][10].
Площадь территории, которая административно управляется Баку, составляет 2150 км²[1]; население данной территории — 2 181,8 тыс. жителей (на 1 января 2014 года). Баку расположен на южном берегу Апшеронского полуострова. Город по своей древности, величине территории и численности населения является одним из старинных и крупнейших городов Востока. Население всего Апшеронского полуострова (Бакинской агломерации) составляет 2 673,7 тыс. жителей[7]. Баку удостоен в 2010 году Программой ООН по окружающей среде (UNEP) звания одного из главных городов по проведению Всемирного дня окружающей среды. Подобные города избираются ежегодно. В 2010 году, наряду с Баку, этих званий были удостоены также Генуя (Италия) и Женева (Швейцария)[11].

 Architecture
Architecture
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1998
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1998

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center
 France
France
 UEFA European Championship 2016
UEFA European Championship 2016
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2019
Women's Soccer World Cup 2019

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 Ile-de-France
Ile-de-France

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture

 Medieval cities in Europe
Medieval cities in Europe
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
 Silk road
Silk road
 Seine
Seine

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

Paris (französisch [paˈʁi]) ist die Hauptstadt der Französischen Republik und Hauptort der Region Île-de-France. Der Fluss Seine teilt die Stadt in einen nördlichen (Rive Droite, „rechtes Ufer“) und einen südlichen Teil (Rive Gauche, „linkes Ufer“); administrativ ist sie in 20 Stadtbezirke (Arrondissements) unterteilt. Mit mehr als 2,2 Millionen Einwohnern ist Paris die fünftgrößte Stadt der Europäischen Union sowie mit über 12,5 Millionen Menschen nach London die zweitgrößte Metropolregion der EU.[1][2][3][4] Mit einer vergleichsweise kleinen Stadtfläche von nur 105 Quadratkilometern ist Paris mit rund 21.000 Einwohnern pro Quadratkilometer die am dichtesten besiedelte Großstadt Europas.
Paris ist das überragende politische, wirtschaftliche sowie kulturelle Zentrum des zentralistisch organisierten Frankreichs und mit drei Flughäfen und sechs Kopfbahnhöfen dessen größter Verkehrsknotenpunkt. Teile des Seine-Ufers zählen heute zum UNESCO-Welterbe. Die Stadt ist Sitz der UNESCO und darüber hinaus der OECD und der ICC. Sehenswürdigkeiten wie der Eiffelturm, die Kathedrale Notre-Dame oder der Louvre machen die Stadt zu einem beliebten Touristenziel. Mit rund 16 Millionen ausländischen Touristen pro Jahr ist die Stadt hinter London und Bangkok eine der meistbesuchten Städte weltweit.[5] Der Großraum Paris (Île-de-France) verzeichnet jährlich über 47 Millionen Gäste aus dem In- und Ausland und mehr als 184 Millionen Übernachtungen.[6]
Das heutige Paris entwickelte sich seit dem 3. Jahrhundert aus der keltischen Siedlung „Lutetia“ auf der Île de la Cité. Später errichteten die Römer an der Seine eine Stadt, die im 6. Jahrhundert zunächst eine Hauptresidenz des Fränkischen Reiches wurde. Eine Blütezeit der Kunst und Kultur erlebte Paris im 16. Jahrhundert unter Franz I. Durch den Absolutismus, insbesondere unter Ludwig XIV. im 17. Jahrhundert, wurde die Stadt um zahlreiche barocke Gebäude und Prachtstraßen bereichert und so zu einem beispielhaften Muster für barocken Städtebau. Obwohl die Königsresidenz 1682 nach Versailles verlegt wurde, blieb sie aufgrund ihrer politischen und wirtschaftlichen Bedeutung das Zentrum des Landes. In der Französischen Revolution kam ihr ab 1789 eine welthistorische Bedeutung zu. Die Industrialisierung führte im 19. Jahrhundert zu einem enormen Bevölkerungszuwachs, sodass 1846 erstmals die Grenze von einer Million Einwohnern überschritten wurde. In den folgenden Jahrzehnten bekam die Stadt durch die sogenannte Belle Époque und sechs Weltausstellungen weltweite Beachtung. Heute ist sie Hauptort der französischsprachigen und eine der wichtigsten Städte der westlichen Welt.
巴黎市(法语:Paris)是法国的首都和最大城市,也是法国的政治与文化中心。其隶属法兰西岛大区之下的巴黎省(编号第75省;仅辖有1个同名的省区与市镇),也是法兰西岛大区的核心。目前所谓的巴黎市辖区范围大至仅为旧巴黎城墙内(环城道路内侧),并未包含巴黎扩张发展的大巴黎实际都市区域,巴黎市辖区内依照发展历史共分成20个区,,自从1860年代开始就没有重大变化。截至2009年为止,巴黎市内人口超过223万[1] ,巴黎都会区的人口逾1,200万[2] ,是欧洲最大的都会区之一[3]。
巴黎在将近1,000年的时间中是西方世界最大的城市,也曾经是世界上最大的城市(16世纪至19世纪之间)[4][5][6]。目前是世界上最重要的政治与文化中心之一,对于教育、娱乐、时尚、科学、媒体、艺术与政治等方面皆有重大影响力,被认为是世界上最重要的全球城市之一[7][8][9][10] ,一般普世观念上与日本东京、美国纽约、英国伦敦并列世界四大国际级都市。许多国际组织都将总部设立在巴黎,例如联合国教育、科学及文化组织、经济合作与发展组织、国际商会或巴黎俱乐部等。巴黎也是欧洲绿化最深[11] 与最适合人类居住的城市之一[12] ,也是世界上生活费用最高的城市之一[13][14]。
巴黎与法兰西岛大区大约贡献法国4分之1的国内生产总值,在2009年为5,521亿欧元[15] 。根据估计,巴黎是欧洲第一[16] 或第二大城市经济体,也是世界上第六大城市经济体[17]〈按购买力平价PPP调整〉。总共有33间财富世界500强企业的总部设立在巴黎都会区[18],是欧洲最集中的地区。巴黎市辖区范围外的商业区拉德芳斯是欧洲最大的中央商务办公区[19]。巴黎的高等教育机构是欧盟最集中的地区[20],高等教育研究与发展支出也是欧洲最高的地区。巴黎也被认为是世界上最适合研发创新的城市之一[21]。每年有4,200万人造访巴黎与邻近都会区,也让巴黎成为世界上最多观光客造访的城市[20]。巴黎与与邻近都会区总共有3,800个法国国家遗产与4个世界遗产[20]。巴黎也是1989年的欧洲文化之城。
パリ(仏: Paris[1]、巴里)は、フランス北部、イル=ド=フランス地域圏にある都市。フランスの首都であり、イル=ド=フランス地域圏の首府である。
フランス最大の都市であり、同国の政治、経済、文化などの中心である。ロンドン、ニューヨーク、香港、東京などと並ぶ世界トップクラスの世界都市でもある。行政上では、1コミューン単独で県を構成する特別市であり、ルーヴル美術館を含む1区を中心に、時計回りに20の行政区が並ぶ(エスカルゴと形容される[2])。
市域はティエールの城壁跡に造られた環状高速道路の内側の市街地(面積は86.99km2。参考:東京都・山手線の内側は63km2、ニューヨーク市・マンハッタンは59km2)、および、その外側西部のブローニュの森と外側東部のヴァンセンヌの森を併せた形となっており、面積は105.40 km2。ケスタ地形を呈するパリ盆地のほぼ中央に位置し、市内をセーヌ川が貫く。この川の中州であるシテ島を中心に発達した。市内の地形は比較的平坦であるが、標高は最低でセーヌ川沿いの35メートル、最高でモンマルトルの丘の130メートルである[3]。北緯49度とやや高緯度に位置するが、温かい北大西洋海流と偏西風によって一年を通して比較的温暖となっており、西岸海洋性気候の代表的な都市である。
世界有数の大都市であり、アメリカのシンクタンクが2017年に発表した総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、ロンドン、ニューヨークに次ぐ世界3位の都市と評価された[4]。日本の民間シンクタンクによる2017年発表の「世界の都市総合力ランキング」(森記念財団都市戦略研究所、森ビル)では、ロンドン、ニューヨーク、東京に次ぐ世界4位の都市と評価された[5]。フランス経済の中心地で、世界屈指の経済都市であり、多国籍企業の本社数や資本市場の規模などビジネス分野を総合評価した都市ランキングでは、ロンドンと共にヨーロッパでトップクラスであり、世界500大企業の本社数では、ニューヨークやロンドンを凌ぎ、西洋の都市では最多である。2014年のアメリカのダウ・ジョーンズらの調査によると、世界7位の金融センターと評価されており、欧州ではロンドンに次ぐ2位である[6]。
パリは年間外国人観光客数が世界一の観光都市である。歴史的な建物を観ることができ、ルーヴル美術館、ポンピドゥーセンターなどを始めとした一流の美術館で厖大な数の一流の美術品を観賞できる。また世界最古のバレエ団や、世界で最も古くから存在している劇団などの公演を楽しむこともできる。
パリ出身者・居住者は男性がパリジャン(仏: Parisien、フランス語発音: [parizjɛ̃] パリズィヤン)、女性がパリジェンヌ(仏: Parisienne、フランス語発音: [parizjɛn] パリズィエンヌ)と呼ばれる。1960年代以降、旧植民地であったアフリカ中部・北部やインドシナ半島、更に近年は中近東や東欧、中国などからの移民も増え、パリジャン・パリジェンヌも多民族・多人種化している。
市域人口は1950年代の約290万人を絶頂に減少し続けたが、ここ数年は微増傾向に転じており、2011年現在で約225万人である(INSEEによる)。2011年の近郊を含む都市的地域の人口では1,200万人を超えており、ロンドンを凌ぐEU最大の都市部を形成している[7]。
Paris (French pronunciation: [paʁi] ( listen)) is the capital and most populous city of France, with an area of 105 square kilometres (41 square miles) and a population of 2,206,488.[5][6] Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of Europe's major centres of finance, commerce, fashion, science, music, and painting. The Paris Region had a GDP of €681 billion (US$850 billion) in 2016, accounting for 31 per cent of the GDP of France.[7] In 2013–2014, the Paris Region had the third-highest GDP in the world and the largest regional GDP in the EU. According to the Economist Intelligence Unit Worldwide Cost of Living Survey in 2018, Paris was the second-most expensive city in the world, behind Singapore and ahead of Zurich, Hong Kong, Oslo and Geneva.[8]
listen)) is the capital and most populous city of France, with an area of 105 square kilometres (41 square miles) and a population of 2,206,488.[5][6] Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of Europe's major centres of finance, commerce, fashion, science, music, and painting. The Paris Region had a GDP of €681 billion (US$850 billion) in 2016, accounting for 31 per cent of the GDP of France.[7] In 2013–2014, the Paris Region had the third-highest GDP in the world and the largest regional GDP in the EU. According to the Economist Intelligence Unit Worldwide Cost of Living Survey in 2018, Paris was the second-most expensive city in the world, behind Singapore and ahead of Zurich, Hong Kong, Oslo and Geneva.[8]
The City of Paris's administrative limits form an East-West oval centred on the island at its historical heart, the Île de la Cité; this island is near the top of an arc of the river Seine that divides the city into southern Rive Gauche (Left Bank) and northern Rive Droite regions. Paris is the core of a built-up area that extends well beyond its limits: commonly referred to as the agglomération Parisienne, and statistically as a unité urbaine (a measure of urban area), the Paris agglomeration's 2013 population of 10,601,122 made it the largest urban area in the European Union.[3][not in citation given] City-influenced commuter activity reaches well beyond even this in a statistical aire urbaine de Paris (a measure of metropolitan area), that had a 2013 population of 12,405,426,[9] a number one-fifth the population of France,[10] the largest metropolitan area in the Eurozone.
The city is a major rail, highway, and air-transport hub served by two international airports: Paris-Charles de Gaulle (the second busiest airport in Europe after London Heathrow Airport with 69.5 million passengers in 2017) and Paris-Orly.[11][12] Opened in 1900, the city's subway system, the Paris Métro, serves 5.23 million passengers daily,[13] and is the second busiest metro system in Europe after Moscow Metro. Paris's Gare du Nord is one of the ten busiest railway stations in the world, with 262 million passengers in 2015.[14]
Paris is especially known for its museums and architectural landmarks: the Louvre was the most visited art museum in the world in 2017, with 8.1 million visitors.[15][16] The Musée d'Orsay and Musée de l'Orangerie are noted for their collections of French Impressionist art, and the Pompidou Centre Musée National d'Art Moderne has the largest collection of modern and contemporary art in Europe. The historical district along the Seine in the city centre is classified as a UNESCO Heritage Site. Popular landmarks in the centre of the city include the Cathedral of Notre Dame de Paris and the Gothic royal chapel of Sainte-Chapelle, both on the Île de la Cité; the Eiffel Tower, constructed for the Paris Universal Exposition of 1889; the Grand Palais and Petit Palais, built for the Paris Universal Exposition of 1900; the Arc de Triomphe on the Champs-Élysées, and the Basilica of Sacré-Coeur on the hill of Montmartre. Paris received 23 million visitors in 2017, measured by hotel stays, with the largest numbers of foreign visitors coming from the United States, the UK, Germany and China.[17][18] It was ranked as the third most visited travel destination in the world in 2017, after Bangkok and London.[19]
The football club Paris Saint-Germain and the rugby union club Stade Français are based in Paris. The 80,000-seat Stade de France, built for the 1998 FIFA World Cup, is located just north of Paris in the neighbouring commune of Saint-Denis. Paris hosts the annual French Open Grand Slam tennis tournament on the red clay of Roland Garros. Paris hosted the Olympic Games in 1900, 1924 and will host the 2024 Summer Olympics. The 1938 and 1998 FIFA World Cups, the 2007 Rugby World Cup, and the 1960, 1984, and 2016 UEFA European Championships were also held in the city and, every July, the Tour de France bicycle race finishes there.
Paris (prononcé [pa.ʁi] Écouter) est la capitale de la France. Elle se situe au cœur d'un vaste bassin sédimentaire aux sols fertiles et au climat tempéré, le bassin parisien, sur une boucle de la Seine, entre les confluents de celle-ci avec la Marne et l'Oise. Ses habitants s’appellent les Parisiens. Paris est également le chef-lieu de la région Île-de-France et l'unique commune française qui est en même temps un département. Commune centrale de la métropole du Grand Paris, créée en 2016, elle est divisée en arrondissements, comme les villes de Lyon et de Marseille, au nombre de vingt. L’État y dispose de prérogatives particulières exercées par le préfet de police de Paris.
Ville la plus peuplée de France, elle est quatrième parmi les aires urbaines européennes derrière Moscou, Istanbul et Londres et la 29e plus peuplée du monde. Paris compte 2,21 millions d'habitants au 1er janvier 2015. L'agglomération parisienne s’est largement développée au cours du XXe siècle, rassemblant 10,71 millions d'habitants au 1er janvier 2015, et son aire urbaine (l'agglomération et la couronne périurbaine) comptait 12,53 millions d'habitants.
La position de Lutèce, sur une île permettant le franchissement du grand fleuve navigable qu'est la Seine par une voie reliant le Nord et le Sud des Gaules, en fait dès l'Antiquité une cité importante, capitale des Parisii, puis lieu de séjour d'un empereur romain. Sa position au centre du territoire contrôlé par les rois Francs la fait choisir comme capitale de la France à la place de Tournai. Située au cœur d'un territoire agricole fertile avec un climat humide et doux, Paris devient une des principales villes de France au cours du Xe siècle, avec des palais royaux, de riches abbayes et une cathédrale ; au cours du XIIe siècle, avec l'Université de Paris, la cité devient un des premiers foyers en Europe pour l’enseignement et les arts. Le pouvoir royal se fixant dans cette ville, son importance économique et politique ne cesse de croître. Ainsi, au début du XIVe siècle, Paris est l'une des villes les plus importantes du monde chrétien. Au XVIIe siècle, elle est la capitale de la principale puissance politique européenne, au XVIIIe siècle l'un des plus grands centres culturels de l’Europe et au XIXe siècle la capitale des arts et des plaisirs. Paris joue donc un rôle culturel, politique et économique majeur dans l’histoire de l'Europe et du monde occidental au cours du IIe millénaire.
Symbole de la culture française, abritant de nombreux monuments, la ville, surnommée la Ville Lumière, attire en 2017 près de 34 millions de visiteurs ce qui en fait une des capitales les plus visitées au monde. Paris occupe également une place prépondérante dans le monde dans le milieu de la mode, du luxe et de la haute gastronomie. La capitale française n'est jumelée qu'avec une seule autre ville, Rome, ce qui est valable dans l'autre sens, avec ce slogan : « Seul Paris est digne de Rome, seule Rome est digne de Paris ». Paris sera, par ailleurs, en 2024 la deuxième ville avec Londres à avoir accueilli trois fois les Jeux olympiques après ceux de 1900 et ceux de 1924.
La ville est, avec sa banlieue, la capitale économique et commerciale de la France, ainsi que sa première place financière et boursière. Elle accueillera en 2019 l'Autorité bancaire européenne. La région parisienne, avec un produit intérieur brut (PIB) de 649 milliards d'euros en 2014, est un acteur économique européen majeur et la première région européenne par le PIB régional, devant la Rhénanie du Nord-Westphalie (627 milliards d'euros) et le Grand Londres (509 milliards d'euros). Elle est également l'une des régions les plus riches d'Europe avec un PIB par habitant de 52 900 euros en 2014. Paris est le siège de plusieurs organisations internationales comme l'UNESCO ou l'OCDE.
La densité de ses réseaux ferroviaire, autoroutier et de ses structures aéroportuaires en font un point de convergence pour les transports nationaux et internationaux. Cette situation résulte d’une longue évolution, en particulier des conceptions centralisatrices des monarchies et des républiques, qui donnent un rôle considérable à la capitale dans le pays et tendent à y concentrer les institutions. Depuis les années 1960, les politiques gouvernementales oscillent toutefois entre déconcentration et décentralisation. La macrocéphalie dont est atteinte la ville se concrétise par la convergence de la plupart des réseaux routiers et ferroviaires du pays en son centre et des écarts démographiques et économiques disproportionnés entre la capitale et la province : près de 19 % de la population française vit dans l'aire urbaine de Paris.
París (en francés Paris, pronunciado  [paʁi] (?·i)) es la capital de Francia y su ciudad más poblada. Capital de la región de Isla de Francia (o "Región Parisina"), es constituida en la única comuna unidepartamental del país. Está situada a ambos márgenes de un largo meandro del río Sena, en el centro de la cuenca parisina, entre la confluencia del río Marne y el Sena, aguas arriba, y el Oise y el Sena, aguas abajo.
[paʁi] (?·i)) es la capital de Francia y su ciudad más poblada. Capital de la región de Isla de Francia (o "Región Parisina"), es constituida en la única comuna unidepartamental del país. Está situada a ambos márgenes de un largo meandro del río Sena, en el centro de la cuenca parisina, entre la confluencia del río Marne y el Sena, aguas arriba, y el Oise y el Sena, aguas abajo.
La ciudad de París, dentro de sus estrechos límites administrativos, tiene una población de 2 273 305 habitantes en 2015.2 Sin embargo, en el siglo XX, el área metropolitana de París se expandió más allá de los límites del municipio de París, y es hoy en día, con una población de 12 405 426 habitantes en 2013, la segunda área metropolitana del continente europeo (después de Londres) y la 28ª del mundo.4
La región de París es junto con la de Londres, uno de los núcleos económicos más importantes de Europa.6 Con 607 000 millones de euros (845 000 millones de dólares), produjo más de una cuarta parte del producto interior bruto (PIB) de Francia en 2011.7 La Défense es el principal barrio de negocios de Europa,8 alberga la sede social de casi la mitad de las grandes empresas francesas, así como la sede de veinte de las 100 más grandes del mundo.
Durante el siglo XIX y XX junto con la ciudad de Londres, 9 París fue el centro de desarrollo de proyectos arquitectónicos dentro del marco de la Revolución Industrial y sus famosas exposiciones. Ejemplos de ello son: el Mercado de la Madeleine, en 1824; las Grandes Halles iniciadas en 1853 , las Galerie des Machines y la Torre Eiffel ambas realizadas en la exposición de París de 1889.
Es conocida también como la «Ciudad Luz» (la Ville lumière), es el destino turístico más popular del mundo, con más de 42 millones de visitantes extranjeros por año.10 Cuenta con muchos de los monumentos más famosos y admirados del orbe: la Torre Eiffel, la Catedral de Notre Dame, la avenida de los Campos Elíseos, el Arco de Triunfo, la Basílica del Sacré Cœur, el Palacio de Los Inválidos, el Pante&
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture
 Norwegen
Norwegen

 World Heritage
World Heritage
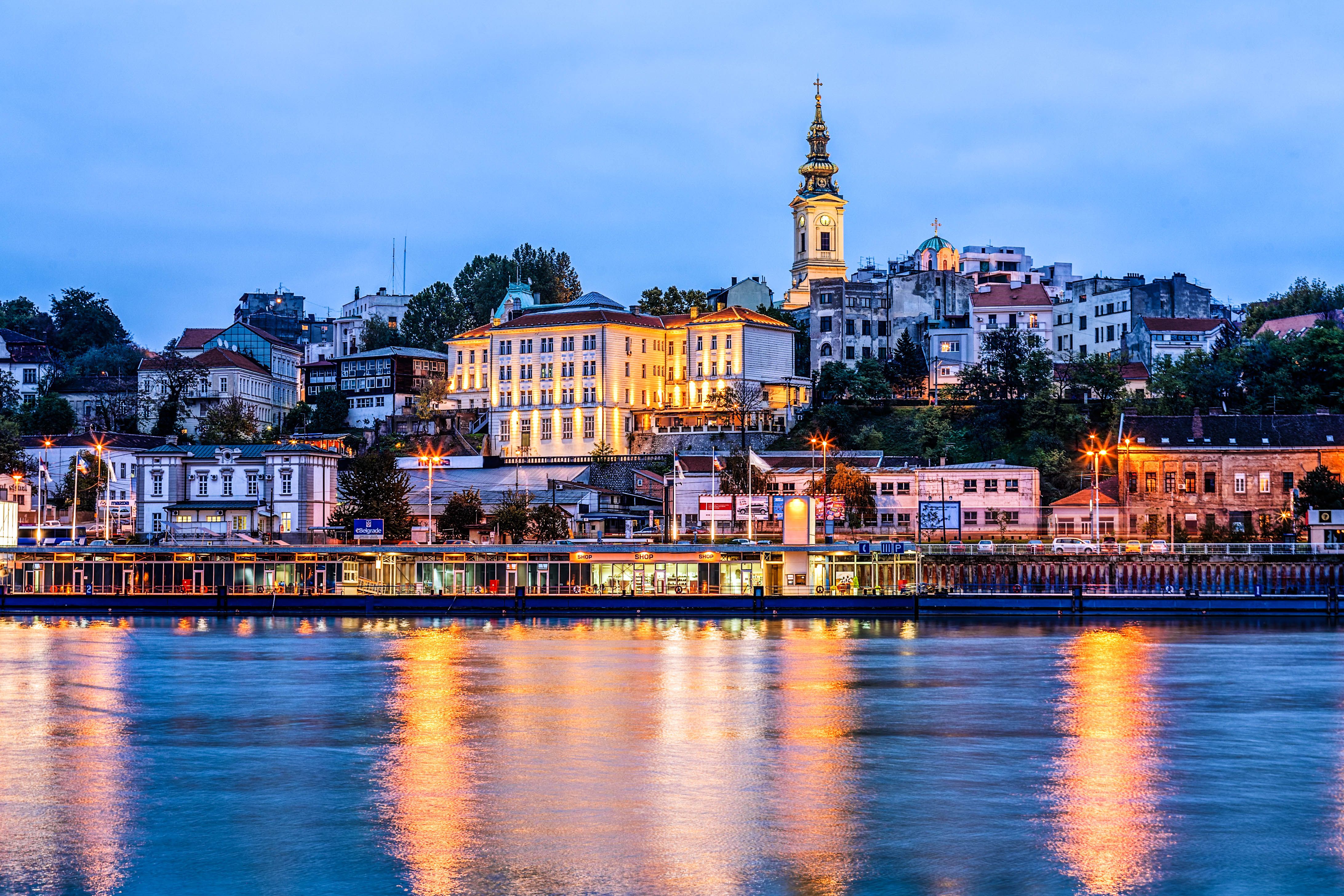


Belgrad (serbisch Београд/Beograd [ anhören?/i], übersetzt „weiße Stadt“, daher der altertümliche Name Griechisch Weißenburg), ist die Hauptstadt der Republik Serbien. Die Stadt gliedert sich in zehn Stadtgemeinden und sieben Vorstadtgemeinden. Die Kernstadt besitzt eine Fläche von 359,96 km², die umgebenden Vorstadtgebiete 2862,72 km², wobei die Fläche einiger Gemeinden teilweise zur Kernstadt und teilweise zur Vorstadt gehört. Zusammen bilden sie den Okrug Beograd mit 1,71 Millionen Einwohnern (Zensus 2011) und gehört somit zu den größten Metropolregionen in Südosteuropa. Mit 1.233.796 Einwohnern[1] ist sie außerdem die serbische Primatstadt.
anhören?/i], übersetzt „weiße Stadt“, daher der altertümliche Name Griechisch Weißenburg), ist die Hauptstadt der Republik Serbien. Die Stadt gliedert sich in zehn Stadtgemeinden und sieben Vorstadtgemeinden. Die Kernstadt besitzt eine Fläche von 359,96 km², die umgebenden Vorstadtgebiete 2862,72 km², wobei die Fläche einiger Gemeinden teilweise zur Kernstadt und teilweise zur Vorstadt gehört. Zusammen bilden sie den Okrug Beograd mit 1,71 Millionen Einwohnern (Zensus 2011) und gehört somit zu den größten Metropolregionen in Südosteuropa. Mit 1.233.796 Einwohnern[1] ist sie außerdem die serbische Primatstadt.
Mit seinen Universitäten, Hochschulen und wissenschaftlichen Einrichtungen stellt Belgrad das überragende Bildungszentrum und mit zahlreichen Verlagen, Rundfunk- und Fernsehanstalten sowie Tages- und Monatszeitungen auch das dominierende Medienzentrum des Landes. Belgrad ist Sitz der Serbisch-Orthodoxen Kirche und Residenz des Serbischen Patriarchen. Das größte christliche Gotteshaus der Balkanhalbinsel, die Kathedrale Hl. Sava, steht in Belgrad.
Dank der Lage an der Mündung der Save in die Donau am südöstlichen Rand der Pannonischen Tiefebene und an der Nordgrenze der Balkanhalbinsel ist die Stadt Dreh- und Angelpunkt für den Verkehr zwischen Mittel- und Südosteuropa. In der regionalen Vernetzung der Verkehrswege ist es Sitz des Sekretariats für Transport der Länder im Westbalkan.[2][3] Daher wird Belgrad oft auch als Tor zum Balkan bezeichnet. Wahrzeichen Belgrads ist die in der Geschichte häufig umkämpfte, über der Save-Mündung in die Donau thronende Festung von Belgrad. In der Nähe befindet sich die historische Universitäts-Sternwarte und jenseits des Flusses (Novi Beograd) das 1977–1979 erbaute Sava Centar, das größte Kongresszentrum aller Balkanländer.
Belgrad war erstmals zu Anfang des 15. Jahrhunderts Hauptstadt der mittelalterlichen Serbischen Herrscherdynastien und ist seit dem 19. Jahrhundert Residenzstadt Serbiens. Im 20. Jahrhundert war es die Hauptstadt des Königreichs Jugoslawien und des sozialistischen Jugoslawien. Durch die jugoslawische Ablehnung sowjetischer Hegemonie und Stalinismus und als Versammlungsort der Blockfreien war Belgrad in der Zeit des Kalten Krieges ein bedeutendes politisches Zentrum.
贝尔格莱德(塞尔维亚语:Београд,意为“白城”),欧洲国家塞尔维亚首都和最大城市,以及当年南斯拉夫联邦时期的总首都。贝尔格莱德市位于塞尔维亚北部萨瓦河和多瑙河汇合处,此处也是潘诺尼亚平原和巴尔干半岛的相遇处。贝尔格莱德市内共有人口123万,整个行政区范围内的人口达到近170万,是原南斯拉夫地区最大的城市。
贝尔格莱德地区最早的人类居住出现在公元前4800年温查文明时期。凯尔特人于公元前3世纪征服了这一地区,并将其命名为Singidunum,[5] 后被罗马帝国占领[6] [7]。
公元520年,斯拉夫人占领了这一地区。此后它在拜占庭帝国、法兰克王国、保加利亚王国和奥匈帝国之间几次易手。城市的斯拉夫语名字Beligrad(字面意思为“白城”)第一次被提及是在878年。1284年,贝尔格莱德第一次成为塞尔维亚斯雷姆王国的首都。此后,它还先后成为塞尔维亚(1404年-1918年、2006年-)、南斯拉夫(1918年-2003年)首都以及塞尔维亚和黑山的行政、立法首都(2003年-2006年)[8]。
贝尔格莱德是塞尔维亚唯一的直辖市[9],被分为17个自治市,每一个都拥有自己的地方委员会[10]。贝尔格莱德占塞尔维亚总面积的3.6%,约21%(不包括科索沃自治省)的塞尔维亚人居住在该市[11]。贝尔格莱德是塞尔维亚的经济、文化、教育和科技中心。
Belgrade (/ˈbɛlɡreɪd/ BEL-grayd; Serbian: Beograd / Београд, meaning "white city", Serbian pronunciation: [beǒɡrad] ( listen); names in other languages) is the capital and largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers, where the Pannonian Plain meets the Balkans.[7] The urban area of the City of Belgrade has a population of 1.23 million, while nearly 1.7 million people live within its administrative limits.[5]
listen); names in other languages) is the capital and largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers, where the Pannonian Plain meets the Balkans.[7] The urban area of the City of Belgrade has a population of 1.23 million, while nearly 1.7 million people live within its administrative limits.[5]
One of the most important prehistoric cultures of Europe, the Vinča culture, evolved within the Belgrade area in the 6th millennium BC. In antiquity, Thraco-Dacians inhabited the region and after 279 BC Celts conquered the city, naming it Singidūn.[8] It was conquered by the Romans during the reign of Augustus, and awarded city rights in the mid-2nd century.[9] It was settled by the Slavs in the 520s, and changed hands several times between the Byzantine Empire, Frankish Empire, Bulgarian Empire and Kingdom of Hungary before it became the capital of Serbian king Stephen Dragutin (1282–1316). In 1521, Belgrade was conquered by the Ottoman Empire and became the seat of the Sanjak of Smederevo.[10] It frequently passed from Ottoman to Habsburg rule, which saw the destruction of most of the city during the Austro-Ottoman wars. Belgrade was again named the capital of Serbia in 1841. Northern Belgrade remained the southernmost Habsburg post until 1918, when the city was reunited. As a strategic location, the city was battled over in 115 wars and razed 44 times.[11] Belgrade was the capital of Yugoslavia from its creation in 1918.
Belgrade has a special administrative status within Serbia[12] and it is one of five statistical regions of Serbia. Its metropolitan territory is divided into 17 municipalities, each with its own local council.[13] The city of Belgrade covers 3.6% of Serbia's territory, and around 24% of the country's population lives within its administrative limits.[5] It is classified as a Beta-Global City.[14]
Belgrade (en serbe cyrillique : Београд ; en serbe latin : Beograd) est la capitale et la plus grande ville de Serbie. Au recensement de 2011, la ville intra muros comptait 1 233 796 habitants et, avec le district dont elle est le centre, appelé Ville de Belgrade (Град Београд/Grad Beograd), 1 659 440 habitants3.
Belgrade est l'une des plus anciennes cités d'Europe, avec une histoire qui s’étend sur plus de 7 000 ans. Selon les historiens, on évalue la destruction de la ville entre 28 et 33 fois, sa position stratégique en Europe étant son bonheur et son malheur, d'où les vers du XVe siècle de Constantin le philosophe, « Pleure ville blanche, le noir de tes deuils »4. Les premières traces de présence humaine dans la région remontent à la Préhistoire et à la culture de Vinča. Historiquement, Belgrade est l’antique cité de Singidunum, colonie romaine située dans la province de Mésie. Le nom slave Beograd apparaît pour la première fois le 16 avril 878, dans une épître envoyée par le pape Jean VIII au prince Boris Ier de Bulgarie. Il a pour signification la « ville blanche ». Au fil de son histoire mouvementée, Belgrade a été conquise par 40 armées : elle a été romaine qui l'a surnommé « La colline aux méditations »5, byzantine, hongroise, serbe, ottomane puis capitale de la Serbie officiellement indépendante de la Sublime Porte en 1878.
Aujourd'hui, Belgrade dispose d'un statut qui la dote d'une assemblée et d'un gouvernement particuliers, à l'instar des districts de Serbie6. Sa zone métropolitaine, appelée « district de Belgrade » ou « ville de Belgrade », est divisée en 17 municipalités qui possèdent toutes leur propre conseil local7. Le district de Belgrade couvre ainsi 3,6 % du territoire de la Serbie et abrite 21 % de la population du pays (hors Kosovo). Belgrade est le centre économique de la Serbie, mais aussi la capitale de la culture serbe et celui de l'éducation et des sciences du pays.
Belgrado (AFI: /belˈɡrado/[2][3]; in serbo Бeoгpaд, Beograd?) è la capitale della Serbia e, fino al 1992, della Jugoslavia.
Si trova nell'ex provincia della Serbia centrale, nel punto di confluenza tra i fiumi Sava e Danubio, dove il territorio della Penisola Balcanica incontra la Pannonia. È una delle città più antiche d'Europa.
Con una popolazione di 1.233.796 abitanti, quella di Belgrado è l'area metropolitana più popolata dell'ex Jugoslavia, nonché la terza nell'Europa sudorientale, dopo quelle di Atene e di Bucarest; l'estensione superficiale dell'area urbana occupa il 3,6% del territorio della Serbia e vi risiede il 21% della popolazione serba (escludendo quella della provincia del Kosovo[4]).
La città possiede uno status che le conferisce una maggiore autonomia rispetto agli altri centri urbani della Serbia. È divisa in 17 comuni[5], dotati anch'essi di una propria autonomia organizzativa[6]. Belgrado non solo è la capitale economica e finanziaria della Serbia, ma anche culturale e scientifica, ed è uno dei principali luoghi turistici della nazione.
Nel 4800 a.C. circa, nell'area dell'attuale città di Belgrado si sviluppò la cultura Starčevo. Il medesimo territorio fu occupato alcuni secoli dopo dal popolo dei Vinča. Nel III secolo a.C. i Celti fondarono un villaggio nella zona che oggi è il centro storico di Belgrado, che fu, successivamente, conquistato dai Romani, che gli diedero il nome di Singidunum. Dal IX al XVI secolo Singidunum fu, alternativamente, sotto il potere dei Bizantini, dei Bulgari, dei Magiari e dei Serbi. Nel 1521 gli Ottomani la conquistarono. Tra il XVII secolo e il XVIII secolo Belgrado fu più volte espugnata e perduta della Casa d'Asburgo. Dopo la definitiva liberazione, nel 1841, dal dominio turco, divenne la capitale del Principato di Serbia, che, nel 1882 fu rinominato Regno di Serbia. La città fu capitale della Jugoslavia dal 1918 al 1991.
Belgrado (en serbio: Beograd; la Ciudad Blanca; escrito en alfabeto cirílico: Беoград) es la capital de la República de Serbia, además de la ciudad más grande y poblada del territorio de la antigua Yugoslavia.
Situada en la confluencia del río Sava con el Danubio y en el límite de la Llanura Panónica con la Península Balcánica, Belgrado se extiende sobre una superficie de 3222,68 km², que ocupan el 3,6 % del territorio de la República. El área metropolitana alberga a una población de 1 756 534 habitantes3 que representa el 21 % de la población serbia,45 siendo por ello también la cuarta ciudad más poblada del sureste de Europa, después de Estambul, Atenas y Bucarest.
Belgrado dispone, de acuerdo a la Constitución serbia, de un estatus especial dentro de la organización territorial del país, por el que se articula la representación ciudadana mediante un sistema de gobierno autónomo dividido en varios cuerpos6 que son la Asamblea de la Ciudad, la Alcaldía y el Consejo, siendo cada uno de los 17 municipios en los que se divide administrado por un consejo propio.7
Como capital de Serbia, Belgrado es sede de los principales organismos e instituciones de su Estado, así como de las universidades y establecimientos de investigación más importantes. Es asimismo el motor económico del país, con un sector agrario singular, y principal centro para la difusión de la cultura de Serbia. Es una de las ciudades más antiguas de Europa, con una historia que se remonta a casi 7000 años, con frecuencia convulsionada al ser escenario de enfrentamientos entre las potencias que dominaron sucesivamente la región.
Los primeros asentamientos aparecieron con la cultura prehistórica de Vinča hacia el 4800 a. C. En el siglo III a. C. se asentaron los celtas, y más tarde, los romanos fundaron la ciudad de Singidunum.89 Los primeros documentos donde consta el nombre eslavo Beligrad datan del año 878. En 1284 pasa a manos de los serbios de Sirmia, y a partir de 1403, del Despotado de Serbia. Más tarde también fue capital del Principado de Serbia, convertido en Reino de Serbia en 1882, así como de las diferentes variaciones estatales de Yugoslavia entre 1918 y 2003, lo mismo que de la Confederación de Serbia y Montenegro hasta su disolución en 2006.10
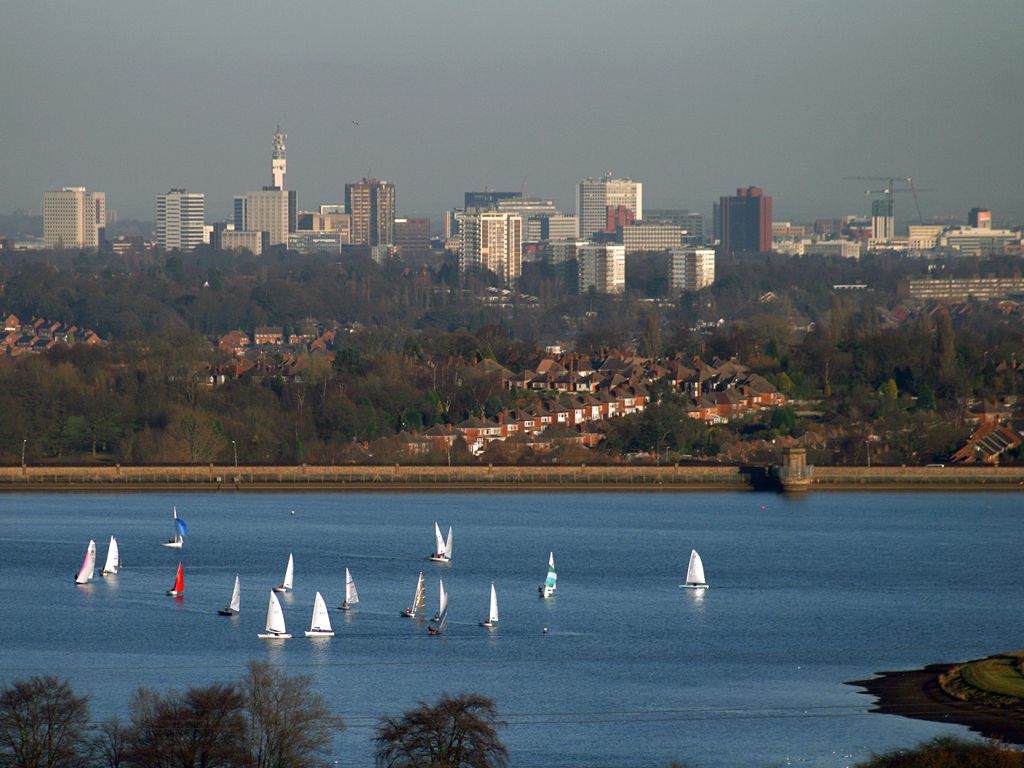


 Belgium
Belgium
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 History
History

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
Mit Brüssel (französisch Bruxelles [bryˈsɛl], niederländisch Brussel [brɵsəɫ]) kann entweder eine Stadt in Belgien gemeint sein oder die größere Hauptstadtregion mit 19 Gemeinden beziehungsweise das gesamte städtische Gebiet der Hauptstadtregion.
Die zweisprachige Region Brüssel-Hauptstadt (französisch Région de Bruxelles-Capitale, niederländisch Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest) ist neben Flandern und der Wallonischen Region eine von drei Regionen im föderalen belgischen Staatsaufbau. Die Region hat über eine Million Einwohner und besitzt eine höhere Bevölkerungsdichte als irgendeine deutsche Großstadt.[1] Sie ist daher nicht mit den weit ins Umland reichenden Metropolregionen vergleichbar, die in den letzten Jahren rund um viele europäische, unter anderem auch deutsche Großstädte definiert wurden. Der Ballungsraum Brüssel ist noch einmal wesentlich größer als die Region Brüssel.
Die Stadt Brüssel ist die Haupt- und Residenzstadt des Königreichs Belgien. Sie bildet das Zentrum der Region Brüssel-Hauptstadt, ist eine ihrer 19 Gemeinden und hat etwa 180.000 Einwohner. Dort haben mehrere föderale Institutionen ihren Sitz: Die Stadt Brüssel ist Verwaltungssitz der Region Brüssel-Hauptstadt. Hier befindet sich darüber hinaus der Verwaltungssitz der Französischen Gemeinschaft Belgiens, während die Wallonische Region ihren Sitz in Namur hat. Die Organe der Region Flandern und der Flämischen (niederländischsprachigen) Gemeinschaft sind fusioniert und haben ihren Sitz ebenfalls in der Stadt Brüssel. Zudem stellt die Stadt den Hauptsitz der Europäischen Union sowie den Sitz der NATO, ferner den des ständigen Sekretariats der Benelux-Länder und von EUROCONTROL dar.
Im Jahre 996 erstmals urkundlich erwähnt und im Mittelalter zur Hauptstadt des Herzogtums Brabant aufgestiegen, wurde Brüssel mit der Unabhängigkeit Belgiens 1830 zu dessen Hauptstadt erhoben. Zusammen mit seinen umliegenden Gemeinden ist Brüssel heute als Industrie- und Handelsstadt mit zwei Universitäten, mehreren Hochschulen, Akademien, Bibliotheken, Museen und Bühnen ein bedeutendes Wirtschafts-, Wissenschafts- und Kulturzentrum sowie ein wichtiger Verkehrsknotenpunkt im Zentrum des Landes.
Der Artikel Region Brüssel-Hauptstadt behandelt vor allem die Themen Politik, Verwaltung und Sprachensituation. Weitere und übergreifende Themen werden nachfolgend behandelt.
布鲁塞尔(法语:Bruxelles;荷兰语:Brussel)是比利时的首都和最大的城市,也是欧洲联盟的主要行政机构所在地。位于布鲁塞尔首都区的布鲁塞尔市,[1]。 在不同的语境中,布鲁塞尔有着不同的外延。她可能代表布鲁塞尔市(比利时的布鲁塞尔首都区中最大的地方自治体及首府,常住人口140,000),也可能代表布鲁塞尔首都区(据2008年2月1日统计,常住人口为1,067,162),或者也可能用于表示布鲁塞尔城市圈(常住人口1,350,000[2])。
欧洲联盟三个主要的机构当中,欧盟委员会和欧盟部长理事会位于布鲁塞尔,另一个重要机构欧洲议会在布鲁塞尔也有分处(全体议会在法国斯特拉斯堡),所以它有欧洲首都的美誉。另外,北大西洋公约组织的总部也设在布鲁塞尔。
布鲁塞尔是一个双语城市,通用法语和荷兰语,法语的使用者占较多数。另外,土耳其语、阿拉伯语等语言被布鲁塞尔的穆斯林广泛使用。
布鲁塞尔(Brussels)是比利时的首都和最大的城市,也是欧洲联盟(欧盟,EU)的主要行政机构所在地,北大西洋公约组织(北约,NATO)总部驻地,有欧洲的首都之称。另外也是200多个国际行政中心及超过1000个官方团体的日常会议举办城市。
布鲁塞尔位于塞纳河畔,北部是低平的弗兰德平原,南部是略有起伏的布拉邦特台地,平均海拔58米。上城依坡而建,为行政区,主要名胜有路易十六式建筑风格的王宫、皇家广场、埃格蒙宫、国家宫、皇家图书馆、现代古代艺术博物馆。下城为繁华的商业中心。市中心的“大广场”周围屹立着许多中世纪的哥特式建筑,其中以市政厅较为壮观。
布鲁塞尔拥有全欧洲最精美的建筑和博物馆、摩天大楼跟中世纪古建筑相得益彰。整座城市以皇宫为中心,沿“小环”而建,游览以步行为佳。
布鲁塞尔是一个双语城市,通用法语和荷兰语,法语使用者占较多数。另外土耳其语、阿拉伯语等语言也被布鲁塞尔的穆斯林广泛使用。
在欧洲联盟的四个主要机构中,欧洲理事会、欧盟委员会和欧盟理事会位于布鲁塞尔,另一个机构欧洲议会在布鲁塞尔也有分处(全体议会在法国斯特拉斯堡),所以它有“欧洲首都”的美誉。
ブリュッセル市(ブリュッセルし、フランス語: Ville de Bruxelles [ˈvil də bʀyˈsɛl] または Bruxelles-Ville、オランダ語: Stad Brussel [s̪t̪ɑt̪ ˈbrʏ.s̪əl̪] または Brussel-Stad)は、ブリュッセル首都圏地域を構成する最大の基礎自治体である。ベルギーの憲法上の首都である[2]が、実際にはブリュッセル首都圏地域全体で首都としての機能を果たしている。主としてブリュッセルの歴史的中心部から成り、ロンドンにおけるシティにたとえることができる。
ブリュッセル市は、ブリュッセルの歴史的な中心市街地に加えて、ブリュッセル首都圏地域内のいくつかの地区、すなわち北部のアレン(英語版)、ラーケンおよびネデル=オヴェル=エンベーク(英語版)、ならびに南部のルイーズ大通り(英語版)およびカンブルの森(英語版)から構成される。
ブリュッセル市の総面積は32.61 km2、2014年9月1日現在の総人口は173,540人で、人口密度は5,321.68人/km2である[1]。また2014年時点で、ブリュッセル市の人口約17万人のうち、約6万人が外国人(うち3万6千人がEU市民、2万4千人が非EU市民)となっている[3]。
The City of Brussels (French: Ville de Bruxelles [vil də bʁysɛl] or alternatively Bruxelles-Ville [bʁysɛl vil], Dutch: Stad Brussel [stɑd ˈbrɵsəl][2] or Brussel-Stad) is the largest municipality and historical centre of the Brussels-Capital Region, and the de jure capital of Belgium.[3] Besides the strict centre, it also covers the immediate northern outskirts where it borders municipalities in Flanders. It is the administrative centre of the European Union, thus often dubbed, along with the region, the EU's capital city.
The City of Brussels is a municipality consisting of the central historic town and certain additional areas within the greater Brussels-Capital Region, namely Haren, Laeken and Neder-Over-Heembeek to the north, and Avenue Louise/Louizalaan and the Bois de la Cambre/Ter Kamerenbos park to the south.
On 1 January 2017, the City of Brussels had a total population of 176,545. The total area is 32.61 km2 (12.59 sq mi) which gives a population density of 5,475 inhabitants per square kilometre (14,180/sq mi). As of 2007, there were approximately 50,000 registered non-Belgians in the City of Brussels.[4] In common with all the Brussels municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch).
Bruxelles (prononcé [bʁy.sɛl]1 Écouter ; Brussel [ˈbrʏ.səl] Écouter en néerlandais ; Brüssel en allemand ; parfois aussi appelé aire urbaine de Bruxelles, Stedelijk gebied van Brussel en néerlandais, ou Grand Bruxelles2) est une agglomération de Belgique qui s'étend au-delà des limites administratives de la Région de Bruxelles-Capitale pour englober des parties du Brabant wallon et l'arrondissement de Hal-Vilvorde, et au centre de laquelle se trouve la ville de Bruxelles proprement dite.
La plupart des institutions de l’Union européenne, ainsi que de nombreuses organisations internationales entre autres lobbyistes, dont l’OTAN, ont leur siège en Région de Bruxelles-Capitale. Par extension, on dit donc « Bruxelles » pour désigner, en général et par métonymie, les institutions européennes (le plus souvent, la Commission européenne).
L'initiative Brussels Metropolitan, lancée en 2008, vise à mieux coordonner la ville et son arrière-pays pour valoriser le Grand Bruxelles en tant que métropole économique attrayante au cœur de l'Europe3, lui donner plus de poids sur le plan mondial et y stimuler la croissance et la création d'emplois4. Cette plateforme de coopération implique la participation de quatre organisations patronales - la FEB, BECI, le Voka et l'UWE4.
Bruxelles (nome francese; pronuncia /bʀy'sɛl/ o, meno correttamente, /bʀyk'sɛl/, italianizzata in /brukˈsɛl/[1]; in olandese Brussel, in tedesco Brüssel; in italiano storico Brusselle[2] o Borsella[3]) è un'area metropolitana del Belgio che ospita all'incirca 2,6 milioni di abitanti.[4]
Il comune di Bruxelles è uno dei 19 comuni della regione amministrativa di "Bruxelles-capitale", con cui non dovrebbe essere confuso. Questa regione è una delle tre regioni amministrative del Belgio, con la Regione vallone e la Regione fiamminga. L'area metropolitana di Bruxelles si estende oltre i confini amministrativi della Regione di Bruxelles in quanto comprende molti comuni situati nella regione fiamminga. Questa situazione è all'origine del conflitto linguistico in Belgio poiché molti residenti di Bruxelles, per lo più francofoni, sono stabiliti nella regione fiamminga di lingua olandese.
Bruxelles è considerata la capitale de facto dell'Unione europea in quanto sede di varie istituzioni, tra cui la Commissione europea, il Consiglio dell'Unione europea e parzialmente il Parlamento europeo (ufficialmente con sede a Strasburgo). Ad Evere ha inoltre sede il quartier generale della NATO. Bruxelles ospita anche il Comitato delle Regioni e il Comitato economico e sociale.
Gran parte dell'area metropolitana di Bruxelles è amministrata dalla regione di Bruxelles-Capitale, suddivisa in 19 comuni, tra cui quello del centro storico, il Comune di Bruxelles (Ville de Bruxelles/Brussel-stad). La città si estende però anche al di là dei confini della regione: vari comuni della periferia brussellese, amministrativamente parte della regione delle Fiandre, sono parte integrante del tessuto urbano di Bruxelles.[5] Tra questi Zaventem (sede dell'aeroporto internazionale), Kraainem (capolinea della metropolitana) e Tervuren (quartiere residenziale).
Bruselas (en francés: Bruxelles  [bʁysɛl] (?·i), en neerlandés: Brussel
[bʁysɛl] (?·i), en neerlandés: Brussel  [ˈbrɵsəl] (?·i) y en alemán: Brüssel) es la capital de Bélgica,1 y la principal sede administrativa de la Unión Europea (UE).
[ˈbrɵsəl] (?·i) y en alemán: Brüssel) es la capital de Bélgica,1 y la principal sede administrativa de la Unión Europea (UE).
Bruselas es un municipio situado en la región administrativa "Bruselas-Capital" que es una de las tres regiones de Bélgica, con la Región Valona y la Región flamenca.
Como capital del Estado, Bruselas es la sede del gobierno y el Parlamento. Alberga también, el Castillo de Laeken la residencia de Su Majestad el rey Felipe de Bélgica y la familia real belga.
Брюссе́льский столи́чный регио́н (фр. Région de Bruxelles-Capitale, ʁe'ʒjɔ̃ də bʁy'sɛlkapi'tal  слушать, нидерл. Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest, ˈbrʏsəɫs ɦoːft'steːdələk xəʋɛst
слушать, нидерл. Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest, ˈbrʏsəɫs ɦoːft'steːdələk xəʋɛst  слушать, а также просто фр. Bruxelles, bʁysɛl
слушать, а также просто фр. Bruxelles, bʁysɛl  слушать; нидерл. Brussel, ˈbrʏsəɫ
слушать; нидерл. Brussel, ˈbrʏsəɫ  слушать) — один из трёх регионов Бельгии, субъект федерации наравне с Фламандским и Валлонским регионами. Крупнейшая городская зона-агломерация в Бельгии[1], состоящая из 19 муниципалитетов, каждый со своим бургомистром, ратушей и т. д. Фактически они являются районами одного города (часто граница проходит посередине улицы). Формально название Брюссель относится только к одному из вышеуказанных муниципалитетов, но на практике его употребляют ко всей агломерации. Одним из муниципалитетов является Брюссель, который де-юре является столицей Бельгии, и в котором находятся Французское и Фламандское сообщества[2]. Де-факто, в силу того что столичные учреждения распределены по различным муниципалитететам Брюссельского столичного региона, регион считается столицей Бельгии, столицей Европейского союза[3].
слушать) — один из трёх регионов Бельгии, субъект федерации наравне с Фламандским и Валлонским регионами. Крупнейшая городская зона-агломерация в Бельгии[1], состоящая из 19 муниципалитетов, каждый со своим бургомистром, ратушей и т. д. Фактически они являются районами одного города (часто граница проходит посередине улицы). Формально название Брюссель относится только к одному из вышеуказанных муниципалитетов, но на практике его употребляют ко всей агломерации. Одним из муниципалитетов является Брюссель, который де-юре является столицей Бельгии, и в котором находятся Французское и Фламандское сообщества[2]. Де-факто, в силу того что столичные учреждения распределены по различным муниципалитететам Брюссельского столичного региона, регион считается столицей Бельгии, столицей Европейского союза[3].
Брюссель начинался как город-крепость в 10 веке, основанный Карлом I[4]. Население региона составляет 1,1 миллион человек, а всё население метрополии — более 1,8 миллионов, занимая таким образом первое место по этому показателю в Бельгии[5][6]. Со времён окончания Второй мировой войны Брюссель является одним из главных центров мировой политики. Будучи местом расположения институтов Европейского союза[7] и штаб-квартиры НАТО, Брюссель стал многоязыковым домом для многочисленных международных организаций, политиков и дипломатов[8].
Исторически нидерландоязычный, Брюссель со времён обретения Бельгией независимости в 1830 году, превратился почти полностью во франкоязычный регион. На сегодняшний день официальными считаются оба языка. Все дорожные знаки, названия улиц и большая часть рекламы и названий услуг приводятся на двух языках[9]. Языковой вопрос остаётся острым в Брюсселе, законы, затрагивающие его, являются предметом неутихающих обсуждений в Бельгии.
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture
 Ireland
Ireland

Dublin ([ˈdʌblɪn], lokal auch [dʊbᵊlən]) ist die Hauptstadt und größte Stadt der Republik Irland. Der irische Name ist Baile Átha Cliath ([ˈbalʲɑːˈkʲlʲiə] oder [ˈbʲlʲɑːˈkʲlʲiə]). Die deutsche Übersetzung lautet „Stadt an der Hürdenfurt“. Der englische Name stammt vom irischen Duibhlinn ([ˈdivʲ.lʲiːnʲ]), „Schwarzer Teich“.[1]
Dublin liegt an der Ostküste der Insel Irland, an der Mündung des Flusses Liffey in die Dublin Bay. Dublin liegt durchschnittlich 20 Meter über dem Meeresspiegel.
Die Liffey teilt Dublin in den Nordteil (Northside) und den eher vornehmen Süden (Southside), wobei diese Unterteilung heute weniger scharf ist als in früheren Jahrzehnten. Die Innenstadt erhält ihre Struktur durch das Kreuz aus dem Fluss Liffey mit seinen zahlreichen Brücken und der Hauptachse O’Connell Street–Grafton Street–Harcourt Street. Hier liegen die meisten Kaufhäuser, aber auch das Trinity College mit seiner berühmten Bibliothek und der städtische Park St. Stephen’s Green. Die Straßenzüge im typischen Georgianischen Stil findet man vor allem im Gebiet um den Merrion Square, in der Nähe der Nationalgalerie und beim Sitz der Landesregierung (Leinster House), um St. Stephen’s Green, aber auch auf der Nordseite am Mountjoy Square. Umschlossen wird dieses Gebiet von der North Circular Road und der South Circular Road. Außerhalb der Innenstadt liegen die Wohnquartiere, von denen manche noch einen sehr einheitlichen Stil aufweisen; das klassische Arbeiterviertel Cabra besteht aus langen Reihen winziger Häuser aus Backsteinen, Marino ist ein Beispiel für eine am Reißbrett konzipierte Mittelschicht-Siedlung, in Beaumont überwiegen die semi-detached, die Doppelhaushälften.
Die Geschichte Dublins ist eng mit der Geschichte Irlands im Allgemeinen verknüpft.
Die erste bekannte Erwähnung findet Dublin in den Schriften des Ptolemäus aus dem Jahr 140 unter dem Namen Eblana. Ursprünglich bestand die Stadt aus einer keltischen Siedlung mit dem Namen „Áth Cliath“, was so viel wie „Hürden-Furt“ bedeutet. 842 gründeten Wikinger daneben ein eigenes Dorf, das sie „Duibhlinn“, in etwa „schwarzer Teich“, nannten nach einem von ihnen als Hafenbecken genutzten Gewässer. Die Machtstellung des von ihnen gegründeten Königreich Dublin ging nach der Schlacht von Clontarf 1014 verloren.
Die Stadt wurde 1170 von den Anglonormannen unter der Führung von Richard de Clare und seinem irischen Verbündeten Diarmuid Mac Murchadha Caomhánach eingenommen. Ab 1172 wurde Dublin das Verwaltungszentrum der Anglonormannen. Die Stadt hatte zu der Zeit weitverzweigte internationale Handelsbeziehungen zu Skandinavien, Island, Großbritannien und in zunehmendem Maße zu Frankreich.[2]
Der Bereich der gerichtlichen Zuständigkeit der Stadt wurde 1192 in einer Urkunde niedergelegt. Insgesamt wurde ein sechs Quadratmeilen großes Gebiet durch Erlass des Königs Heinrich II. übereignet. Die Stadt blieb im Prinzip innerhalb dieser Abgrenzungen selbstverwaltet.[3]
Im Jahre 1204 befahl König Johann von England die Errichtung einer Festung in Dublin (Dublin Castle), um seine Machtposition im Land zu stärken.[4] In den folgenden Jahrhunderten entwickelte sich diese Burg zum britischen Verwaltungszentrum in Irland. Der britische Vizekönig wohnte bis 1782 in diesem Schloss.
1229 wurde den freien Bürgern und Ehrenbürgern der Stadt das Recht zuerkannt, jedes Jahr einen Bürgermeister zu wählen. Der Stadtrat setzte sich aus 24 prominenten Bürgern, meist Kaufleuten, zusammen.
Die Pest kam 1348 nach Dublin und verursachte eine beachtliche Schrumpfung der (jetzt überwiegenden englischen) Bevölkerung.
Zwischen 1541 und 1800 war Dublin Hauptstadt des Königreiches Irland.
都柏林(英语:Dublin;爱尔兰语:Baile Átha Cliath)是爱尔兰共和国的首都以及最大的城市,[3][4]靠近爱尔兰岛东岸的中心点,位处都柏林郡的利菲河(River Liffey)河口、都柏林地区的中心。都柏林自中世纪以来一直是爱尔兰首都城市,也是爱尔兰岛上最大的城市。由于很多高技术企业聚集,所以有欧洲的硅谷之称。
Dublin这个字起源于爱尔兰语的Dubh Linn(意为“黑色池塘”)。都柏林的现代爱尔兰名Baile Átha Cliath(意为“芦苇障碍做成的浅滩之城”)则是指在黑色池塘旁边的定居地。
最早关于都柏林的文献是托勒密的手稿,大约写于140年,他称之为埃布拉纳(Eblana)。
都柏林在官方城市边界内的人口是大约495,000人(爱尔兰中央统计处2002年人口调查),然而这种统计已经没有什么太大的意义,因为都柏林的市郊地区和卫星城镇已经大幅地发展与扩张。都柏林市和都柏林郡的人口加起来已经超过了1,100,000人(爱尔兰中央统计处2002年人口调查)。虽然对于“大都柏林都会区”的定义没有一个确切的共识,但是普遍而言大家可以接受这个地区包括了都柏林市和郡,以及部分的威克娄郡、基尔代尔郡和米斯郡,因为通勤带可以延伸到很远的地方。
ダブリン(英: Dublin [ˈdʌblᵻn]、アイルランド語:Baile Átha Cliath [ˈbˠalʲə aːhə ˈclʲiə]、Bleá Cliath [blʲaˈklʲiə] または Dubh linn)は、アイルランド島東部の都市で、アイルランドの首都である。リフィー川河口に位置し、その南北に町が広がる。
アイルランドの政治・経済・交通・文化の中心地であり、アイルランドの全人口の3分の1がダブリン首都圏に集中するアイルランド国内最大の都市である。欧州有数の世界都市であり、重要な金融センターの一つになっている。
市内にはアイルランド人の権利の拡大に尽力した人々やイギリスからの独立運動のために命を落とした活動家の名前が記念日や通りの名前に多く見られる。ダニエル・オコンネルに因む町の目抜き通りのオコンネル通り[3]やパトリック・ピアースにちなむピアース通り、コノリー駅などが例に挙げられる。これらは本来は別の名前がつけられていたが、1921年の独立[4]後に改名されたものである(オコンネル通りはかつてはサックビル通りと呼ばれていた)。
Dublin (/ˈdʌblɪn/, locally /ˈdʊb-/; Irish: Baile Átha Cliath[11] [ˈbˠalʲə aːhə ˈklʲiə; ˌbʲlʲaː ˈklʲiə]) is the capital and largest city of Ireland.[12][13] Situated on a bay on the east coast, at the mouth of the River Liffey, it lies within the province of Leinster. It is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. It has an urban area population of 1,173,179,[7] while the population of the Dublin Region (formerly County Dublin) as of 2016 was 1,347,359.[14] The population of the Greater Dublin Area was 1,904,806 per the 2016 census.[15]
There is archaeological debate regarding precisely where Dublin was established by the Gaels in or before the 7th century AD.[16] Later expanded as a Viking settlement, the Kingdom of Dublin, the city became Ireland's principal settlement following the Norman invasion.[16] The city expanded rapidly from the 17th century and was briefly the second largest city in the British Empire before the Acts of Union in 1800. Following the partition of Ireland in 1922, Dublin became the capital of the Irish Free State, later renamed Ireland.
Dublin is a historical and contemporary centre for education, the arts, administration and industry. As of 2018 the city was listed by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) as a global city, with a ranking of "Alpha −", which places it amongst the top thirty cities in the world.
Dublin /dyblɛ̃/a Écouter (en anglais : /ˈdʊbᵊlən/b ; en gaélique : Baile Átha Cliathc /ˈbˠalʲə aːhə ˈclʲiə/d ou Bleá Cliathe /ˌbʲlʲaː ˈclʲiə/d) est la plus grande ville de l'île d'Irlande et de l'État d'Irlande, dont elle est la capitale (Belfast étant la capitale de l'Irlande du Nord). La ville est située à proximité du point central de la côte orientale de l'île et au centre du comté de Dublin. Dublin est la plus grande ville d'Irlande en importance et en nombre d’habitants depuis le haut Moyen Âge. Elle est aujourd’hui classée à la soixante-sixième place dans l’index des places financières mondiales1, et a un des plus forts taux de développement parmi les capitales européennes2,3. Dublin est le centre historique, politique, artistique, culturel, économique et industriel de l’Irlande.
La population de la commune de Dublin est de 553 165 habitants au recensement de 2016. Au même recensement, le comté de Dublin — divisé en quatre zones administratives : ville de Dublin, Dublin Sud, Fingal et Dún Laoghaire-Rathdown — compte 1 270 603 habitants tandis que la région du Grand Dublin abrite 1 804 156 habitants.
Dublino (AFI: /duˈblino/[2]; in inglese Dublin, /ˈdʌblɪn/; in irlandese Baile Átha Cliath,[3] "città del guado della staccionata", o semplicemente Áth Cliath, o meno correttamente Dubh Linn, "stagno nero") è la capitale della Repubblica d'Irlanda, oltre che la città più grande e popolata, non solo del paese, ma di tutta l'isola. Gli abitanti sono complessivamente 554 554 ma se si considera l'area metropolitana, superano il milione.[1] La città è in continua espansione urbanistica ed economica da qualche decennio, e contribuisce al PIL della Repubblica con 60 miliardi di euro.
Fondata dai Vichinghi come centro per il commercio di schiavi, la città è situata sulla foce del fiume Liffey, al centro della costa orientale dell'isola e di quella che oggi viene chiamata Dublin Region, affacciata sul Mar d'Irlanda (in inglese Irish Sea). È stata la capitale irlandese sin dai tempi medievali.
La Città consiste nella zona amministrata dal Dublin City Council assieme ai contigui sobborghi un tempo appartenenti alla Contea di Dublino e ora divisi tra le contee di Dún Laoghaire-Rathdown, Fingal e South Dublin. La Greater Dublin Area si compone di quanto sopra assieme alle contee di Kildare, Meath e Wicklow.
Molly Malone è il titolo dell'inno non ufficiale della città.
Dublín (en irlandés: Baile Átha Cliath, AFI: [ˌbʲlʲɑː ˈclʲiə] o población del vado de cañizo;1 en inglés: Dublin, AFI: [ˈdʌblɪn]) es la capital de la República de Irlanda y ciudad más poblada de la isla. Está ubicada cerca del centro de la costa este sobre el mar de Irlanda, en la desembocadura del río Liffey y en el centro del condado de Dublín. Fue fundada por los vikingos alrededor de 841 como base militar y centro de comercio de esclavos, y ha sido capital del país desde la Edad Media.23 Está constituida por diferentes áreas; el Consejo de la Ciudad de Dublín junto con suburbios contiguos en el condado de Dublín, y que a su vez se subdivide en los condados administrativos de Dún Laoghaire-Rathdown, Fine Gall-Fingal y el Consejo del Condado de Dublín Sur. La Gran Área abarca la Ciudad de Dublín y el Consejo junto con los condados contiguos de Kildare, Meath y Wicklow.
La población del área urbana de Dublín era de 1 110 614 habitantes en el censo de 2010, pero ampliada al condado de Dublín ascendía a 1 122 821 en 2011 y en 2019 la cantidad de habitantes es 199 personas.
En la Gran Área o región metropolitana de Dublín había 1 804 156 habitantes. La ciudad contribuye con 60 000 millones de euros al PIB irlandés y es el centro político, administrativo, económico, industrial y cultural de la República de Irlanda. Dublín ha sido declarada ciudad global por el GaWC (Grupo de Estudios sobre Globalización y Ciudades Mundiales) y Capital Europea de la Ciencia 2012 debido a la celebración del día del duende.
Ду́блин[3] (англ. Dublin [ˈdʌblɨn], местн. [ˈdʊblən], [ˈdʊbələn]; ирл. Baile Átha Cliath — Балэ-Аха-Клиэх[4] [bˠalʲə aːha klʲiəh] или Duibhlinn (Дувьлинь)) — город-графство в Ирландии, столица страны[5][6]. Находится в административном графстве Дублин (провинция Ленстер). Расположен на месте впадения реки Лиффи в Дублинский залив Ирландского моря. Самый большой город на острове Ирландия и в республике, занимающий почти 115 км². Главный порт страны, расположенный у побережья Ирландского моря. Основной центр политической, экономической и культурной жизни страны.
 Germany
Germany
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC

 UEFA European Championship 2024
UEFA European Championship 2024

 North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
 Silk road
Silk road

杜塞尔多夫(德语:Düsseldorf),是德国北莱茵-威斯特法伦州首府,位于莱茵河畔。杜塞尔多夫市区人口约58万人,是德国广告、服装和通讯业的重要城市[1][2][3]。杜塞尔多夫也是德国最大的海外日本人聚居地,市内有许多日资公司设立。杜塞尔多夫也是19世纪德国诗人海因里希·海涅的出生地。杜塞尔多夫位于莱茵-鲁尔都会区(Metropolregion Rhein-Ruhr)核心地带,该都会区人口超过1,100万人[4]。杜塞尔多夫位于蓝香蕉范围内,是5家财富世界500强公司与几间德国DAX指数公司总部的所在地。
著名的美术学院杜塞尔多夫艺术学院(Kunstakademie Düsseldorf)设立在此,其电子及实验音乐影响广泛。因莱茵河流经杜塞尔多夫,所以杜塞尔多夫是莱茵河狂欢节活动据点。每年7月有超过450万人参观莱茵河狂欢节[5]。
杜塞尔多夫 (德语:Düsseldorf或,英语:Duesseldorf),人口57万,位于莱茵河畔。杜塞紧邻世界著名的鲁尔区,是欧洲人口最稠密、经济最发达地区北莱茵-威斯特法伦州的首府,是德国广告,服装,展览业和通讯业的重要城市,欧洲物流中心城市。
市内有十三至十八世纪古迹、艺术学院、著名陶器博物馆等。杜塞尔多夫还是19世纪德国著名诗人海因里希·海涅的出生地。杜塞尔多夫最早的文字记载可回溯于1135年。1186年,杜塞尔多夫于被纳入伯格(Berg)的管辖地(伯格是中世纪时代在北莱茵-威斯特法伦州的一个领地)。在1280年,伯格的行政署被迁到此处。过后,杜塞尔多夫在1288年8月14日被赐城市地位。1380年,杜塞尔多夫成为伯格领地的区域首府。
 Düsseldorf?/i ist die Landeshauptstadt Nordrhein-Westfalens und der Behördensitz des Regierungsbezirks Düsseldorf. Die kreisfreie Stadt am Rhein ist mit 617.280 Einwohnern nach Köln die zweitgrößte Stadt des Landes.[3] In Deutschland ist Düsseldorf nach Einwohnern die siebtgrößte Stadt. Düsseldorf ist Teil der Metropolregion Rhein-Ruhr mit rund zehn Millionen Einwohnern und der Metropolregion Rheinland mit 8,6 Millionen Einwohnern. Die Stadt liegt im Kern des zentralen europäischen Wirtschaftsraumes.
Düsseldorf?/i ist die Landeshauptstadt Nordrhein-Westfalens und der Behördensitz des Regierungsbezirks Düsseldorf. Die kreisfreie Stadt am Rhein ist mit 617.280 Einwohnern nach Köln die zweitgrößte Stadt des Landes.[3] In Deutschland ist Düsseldorf nach Einwohnern die siebtgrößte Stadt. Düsseldorf ist Teil der Metropolregion Rhein-Ruhr mit rund zehn Millionen Einwohnern und der Metropolregion Rheinland mit 8,6 Millionen Einwohnern. Die Stadt liegt im Kern des zentralen europäischen Wirtschaftsraumes.
Im Jahr 1288 erhielt der Ort an der Mündung des Flüsschens Düssel in den Rhein das Stadtrecht. Vom Ende des 14. Jahrhunderts bis zum Beginn des 19. Jahrhunderts war die Stadt Regierungssitz von Ländern des Heiligen Römischen Reichs und des Rheinbundes: des Herzogtums Berg, der Herzogtümer Jülich-Berg und Jülich-Kleve-Berg sowie des Großherzogtums Berg, von 1690 bis 1716 auch Residenz des Pfalzgrafen und Kurfürsten Johann Wilhelm von der Pfalz. Vom 19. bis ins 20. Jahrhundert war sie Parlamentssitz der Rheinprovinz des Königreichs Preußen. Im Kaiserreich entwickelte sich Düsseldorf im Zuge der Hochindustrialisierung in Deutschland zum „Schreibtisch des Ruhrgebiets“ und wurde mit dem Überschreiten der Marke von 100.000 Einwohnern im Jahr 1882 zur Großstadt.
Die Rheinmetropole gehört zu den fünf wichtigsten, international stark verflochtenen Wirtschaftszentren Deutschlands.[4][5][6][7] Düsseldorf ist eine Messestadt und Sitz vieler börsennotierter Unternehmen, darunter der im DAX notierte Konzern Henkel. Zudem ist sie der umsatzstärkste deutsche Standort für Wirtschaftsprüfung, Unternehmens- und Rechtsberatung,[8][9] Werbung[10] und Kleidermode[11] sowie ein wichtiger Banken- und Börsenplatz.[12][13] Auch im Kunsthandel Deutschlands ist sie führend.[14]
Düsseldorf besitzt mehrere Rheinhäfen. Sein Flughafen Düsseldorf Airport ist das interkontinentale Drehkreuz Nordrhein-Westfalens. Die Stadt ist des Weiteren Sitz von 22 Hochschulen, darunter die renommierte Kunstakademie Düsseldorf und die Heinrich-Heine-Universität.[15] Überregionale Bekanntheit genießt Düsseldorf außerdem durch seine Altstadt („längste Theke der Welt“), seinen Einkaufsboulevard Königsallee („Kö“), seinen Düsseldorfer Karneval, den Fußballverein Fortuna Düsseldorf und den Eishockeyverein Düsseldorfer EG. Weitere Anziehungspunkte sind zahlreiche Museen und Galerien sowie die Rheinuferpromenade und der moderne Medienhafen. Das Stadtbild wird auch durch zahlreiche Hochhäuser und Kirchtürme, den 240 Meter hohen Rheinturm, viele Baudenkmäler und sieben Rheinbrücken geprägt. Bemerkenswert ist die große Anzahl ostasiatischer Einwohner, darunter die japanische Gemeinde, welche die größte japanische Gemeinde Deutschlands bildet.[16] In einem Vergleich der Lebensqualität von 231 Großstädten in der Welt nimmt Düsseldorf den sechsten Platz ein.[17][18][19][20]
デュッセルドルフ(Düsseldorf, ドイツ語発音: [ˈdʏsl̩ˌdɔɐ̯f] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、ドイツ連邦共和国の都市でノルトライン=ヴェストファーレン州の州都[2]。ライン川河畔に位置し、ライン・ルール大都市圏地域の中心でルール工業地帯のすぐ南西部にある。人口は約62万人。金融やファッション、世界的な見本市の中心都市の一つである[3][4][5]。また西ヨーロッパの中でもブルーバナナと呼ばれる、経済的にも人口的にもとくに発展した地域内に位置し、市内にはフォーチュン・グローバル500に含まれる5社や、いくつかのDAXに含まれている企業が本社を置いている。日本企業の進出も盛んで、デュッセルドルフ市内には約5,000人の日本人の駐在員やその家族などが居住し、日本総領事館などのあるインマーマン通りは日本人街の様相を呈している[6]。1971年にはデュッセルドルフ日本人学校も開校し、1990年前後には生徒数1000名近くにまで達した。2011年に行われたマーサー・ヒューマン・リソース・コンサルティングによる世界で最も居住に適した都市の調査では世界では5位、ドイツ国内では2位につけている[7][8]。
音声ファイル))は、ドイツ連邦共和国の都市でノルトライン=ヴェストファーレン州の州都[2]。ライン川河畔に位置し、ライン・ルール大都市圏地域の中心でルール工業地帯のすぐ南西部にある。人口は約62万人。金融やファッション、世界的な見本市の中心都市の一つである[3][4][5]。また西ヨーロッパの中でもブルーバナナと呼ばれる、経済的にも人口的にもとくに発展した地域内に位置し、市内にはフォーチュン・グローバル500に含まれる5社や、いくつかのDAXに含まれている企業が本社を置いている。日本企業の進出も盛んで、デュッセルドルフ市内には約5,000人の日本人の駐在員やその家族などが居住し、日本総領事館などのあるインマーマン通りは日本人街の様相を呈している[6]。1971年にはデュッセルドルフ日本人学校も開校し、1990年前後には生徒数1000名近くにまで達した。2011年に行われたマーサー・ヒューマン・リソース・コンサルティングによる世界で最も居住に適した都市の調査では世界では5位、ドイツ国内では2位につけている[7][8]。
デュッセルドルフは経済的な中心としてだけではなく、芸術的な分野でも知られた都市で、デュッセルドルフ芸術アカデミー(英語版)からはヨーゼフ・ボイスやアウグスト・マッケ、ゲルハルト・リヒター、ジグマー・ポルケ、アンドレアス・グルスキーといった画家や写真家などの芸術家を輩出している。電子音楽の先駆者で影響を与えたクラフトワークも、デュッセルドルフを起点としている。デュッセルドルフはカーニバルの開催都市としても知られている。また、毎年7月にはGrößte Kirmes am Rhein (en) が開催され、450万人以上の人々が市内を訪れる[9]。
Düsseldorf (/ˈdʊsəldɔːrf/, German: [ˈdʏsl̩dɔɐ̯f] ( listen); Low Franconian and Ripuarian: Düsseldörp [ˈdʏsl̩dœɐ̯p]), often Dusseldorf in English sources, is the capital and, after Cologne, second most populous city of the most populous German federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, as well as the seventh most populous city in Germany.[2] At the confluence of the Rhine and its tributary Düssel, the city lies in the centre of both the Rhine-Ruhr and the Rhineland Metropolitan Regions with the Cologne/Bonn urban area to its south and the Ruhr to its north. The city is the largest in the German Low Franconian (closely related to Dutch) dialect area. Most of the city lies on the right bank of the Rhine (as opposed to Cologne, whose city centre lies on the river's left bank). "Dorf" meaning "village", Düsseldorf is the largest settlement with that suffix in the German-speaking area.
listen); Low Franconian and Ripuarian: Düsseldörp [ˈdʏsl̩dœɐ̯p]), often Dusseldorf in English sources, is the capital and, after Cologne, second most populous city of the most populous German federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, as well as the seventh most populous city in Germany.[2] At the confluence of the Rhine and its tributary Düssel, the city lies in the centre of both the Rhine-Ruhr and the Rhineland Metropolitan Regions with the Cologne/Bonn urban area to its south and the Ruhr to its north. The city is the largest in the German Low Franconian (closely related to Dutch) dialect area. Most of the city lies on the right bank of the Rhine (as opposed to Cologne, whose city centre lies on the river's left bank). "Dorf" meaning "village", Düsseldorf is the largest settlement with that suffix in the German-speaking area.
Mercer's 2012 Quality of Living survey ranked Düsseldorf the sixth most livable city in the world.[3][4] Düsseldorf Airport is Germany's third-busiest airport after those of Frankfurt and Munich, serving as the most important international airport for the inhabitants of the densely populated Ruhr, Germany's largest urban area. Düsseldorf is an international business and financial centre, renowned for its fashion and trade fairs,[5][6][7] and is headquarters to one Fortune Global 500 and two DAX companies. Messe Düsseldorf organises nearly one fifth of premier trade shows.[8] As second largest city of the Rhineland, Düsseldorf holds Rhenish Carnival celebrations every year in February/March, the Düsseldorf carnival celebrations being the third most popular in Germany after those held in Cologne and Mainz.[9]
There are 22 institutions of higher education in the city including the Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, the university of applied sciences (Hochschule Düsseldorf), the academy of arts (Kunstakademie Düsseldorf) (Joseph Beuys, Emanuel Leutze, August Macke, Gerhard Richter, Sigmar Polke, and Andreas Gursky), and the university of music (Robert-Schumann-Musikhochschule Düsseldorf). The city is also known for its pioneering influence on electronic/experimental music (Kraftwerk) and its Japanese community.
Düsseldorf ou Duesseldorf2 (aussi anciennement en français et en néerlandais : Dusseldorp3) est une ville de l'ouest de l'Allemagne. Capitale et deuxième plus grande ville (après Cologne) du Land de Rhénanie-du-Nord-Westphalie, située principalement sur la rive droite du Rhin, elle se trouve aux limites occidentales de la vaste agglomération de Rhin-Ruhr qui regroupe environ 11 300 000 habitants4. Septième plus grande ville d'Allemagne, Düsseldorf a une population de 601 074 habitants (recensement de juin 2014)5. En 2018, la qualité de vie à Düsseldorf est l'une des plus agréables au monde selon le classement Mercer6.
Düsseldorf (IPA: [ˈdʏsl̩dɔɐ̯f], pronuncia[?·info]; in basso tedesco Düsseldörp, IPA: [ˈdʏsl̩dœɐ̯p]) è una città extracircondariale della Germania, capitale del Land della Renania Settentrionale-Vestfalia. Situata sulle rive del Reno (Rhein in tedesco) è a circa 40 km a nord di Colonia e a circa 20 km a sud della Regione della Ruhr con le città Duisburg, Essen e Dortmund. La città, dopo Colonia, è la seconda del Land e la settima dell'intera Germania e conta 613 230 abitanti. Situata al centro della regione metropolitana Reno-Ruhr e al centro dell'area economica europea, Düsseldorf fa parte, dopo Francoforte sul Meno, Berlino, Amburgo e Monaco, dei cinque centri più intrecciati e più importanti per quanto riguarda l'economia, il traffico, la cultura e la politica tedesca.
La città è nota per essere un polo fieristico ed è sede di parecchie aziende quotate in borsa, fra cui la Uniper e la Henkel che appartengono anche al DAX 30, il più importante indice della Borsa di Francoforte. Il volume d'affari di Düsseldorf è il più alto della Germania negli ambiti della moda, pubblicità, revisione contabile, consulenza giurisprudenza e consulenza aziendale, e anche una sede importante per banche e la borsa. L'aeroporto di Düsseldorf è il punto nodale internazionale del Land Renania Settentrionale-Vestfalia.
La metropoli possiede due porti interni ed è la sede di alcune università, tra cui la famosa accademia d'arte e l'Università Heinrich-Heine. È nota in tutta la regione per l'elegante boulevard Königsallee, il centro storico, il carnevale e la squadra di calcio Fortuna Düsseldorf. Una moltitudine di musei, gallerie e il lungofiume attirano tanto abitanti quanto turisti. La quantità di abitanti dell'Asia orientale è notevole, tra questi c'è la grande comunità giapponese. Nelle indagini sulla qualità di vita nazionali ed internazionali continua ad avere un ottimo risultato.
Düsseldorf1 ( /ˈdʏsl̩dɔɐ̯f/ (?·i)) es una ciudad de Alemania, capital del estado federado de Renania del Norte-Westfalia. Tiene una población de 593 393 habitantes.
/ˈdʏsl̩dɔɐ̯f/ (?·i)) es una ciudad de Alemania, capital del estado federado de Renania del Norte-Westfalia. Tiene una población de 593 393 habitantes.
Limita al norte con la ciudad de Duisburgo, al este y al sur con el distrito de Mettmann, y al oeste con el distrito de Rhein-Kreis Neuss. La ciudad está atravesada por el Rin, es el núcleo de un área metropolitana y es el centro económico de Alemania Occidental. Es también conocida por se Academia de Bellas Artes de Düsseldorf, con figuras de la talla de Joseph Beuys, Emanuel Leutze, August Macke, Gerhard Richter, Sigmar Polke y Andreas Gursky. En 2012 la consultora Mercer la situó como la sexta ciudad con más calidad de vida del mundo.
Дю́ссельдорф (нем. Düsseldorf [ˈdʏsl̩ˌdɔɐ̯f]  слушать, н.-нем. Düsseldörp) — город на западе Германии, в Рейнско-Рурском регионе, административный центр федеральной земли Северный Рейн-Вестфалия и резиденция земельного правительства округа Дюссельдорф. Население — 592,4 тыс. человек (2011)[6]. Первое упоминание Дюссельдорфа относится к 1135 году, статус города — с 1288 года.
слушать, н.-нем. Düsseldörp) — город на западе Германии, в Рейнско-Рурском регионе, административный центр федеральной земли Северный Рейн-Вестфалия и резиденция земельного правительства округа Дюссельдорф. Население — 592,4 тыс. человек (2011)[6]. Первое упоминание Дюссельдорфа относится к 1135 году, статус города — с 1288 года.
Расположенный в центре Рейнско-Рурского и европейского экономического регионов, Дюссельдорф — наряду с Берлином, Франкфуртом-на-Майне, Мюнхеном и Гамбургом — входит в пятёрку крупнейших экономических, транспортных, культурных и политических центров Германии[7][8]. В нём находятся штаб-квартиры множества крупных компаний, в том числе E.ON и Henkel Group. Городской аэропорт является международным хабом. В Дюссельдорфе расположены две гавани, а также многочисленные высшие учебные заведения, в частности Дюссельдорфская академия художеств и Университет Генриха Гейне.
