
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Belgien
Belgien
 Australien
Australien
 Belgien
Belgien
 Chile
Chile
 Dänemark
Dänemark
 Deutschland
Deutschland
 Estland
Estland
 Finnland
Finnland
 Frankreich
Frankreich
 Griechenland
Griechenland
 Irland
Irland
 Island
Island
 Israel
Israel
 Italien
Italien
 Japan
Japan
 Kanada
Kanada
 Luxemburg
Luxemburg
 Mexiko
Mexiko
 Neuseeland
Neuseeland
 Niederlande
Niederlande
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 OECD
OECD
 Emiel van Lennep
Emiel van Lennep
 OECD
OECD
 Don Johnston
Don Johnston
 OECD
OECD
 Jean-Claude Paye
Jean-Claude Paye
 OECD
OECD
 José Ángel Gurría
José Ángel Gurría
 OECD
OECD
 Staffan Sohlman
Staffan Sohlman
 OECD
OECD
 Thorkil Kristensen
Thorkil Kristensen
 Österreich
Österreich
 Polen
Polen
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republik Korea
Republik Korea
 Schweden
Schweden
 Schweiz
Schweiz
 Slowakei
Slowakei
 Slowenien
Slowenien
 Spanien
Spanien
 Tschechien
Tschechien
 Türkei
Türkei
 Ungarn
Ungarn
 Vereinigte Staaten
Vereinigte Staaten
 Vereinigtes Königreich
Vereinigtes Königreich

 Wichtige internationale Organisationen
Wichtige internationale Organisationen

経済協力開発機構(けいざいきょうりょくかいはつきこう)は、国際経済全般について協議することを目的とした国際機関。公用語の正式名称は、英語では"Organisation[1] for Economic Co-operation and Development"(イギリス英語表記)、フランス語では"Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Economiques"。略称は英語ではOECD、フランス語ではOCDE。
本部事務局はパリ16区の旧ラ・ミュエット宮殿に置かれている。事務総長はアンヘル・グリア。
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; French: Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques, OCDE) is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 37 member countries,[1] founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum of countries describing themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. Generally, OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries. As of 2017, the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trillion)[3] and 42.8% of global GDP (Int$54.2 trillion) at purchasing power parity.[4] The OECD is an official United Nations observer.[5]
In 1948, the OECD originated as the Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC),[6] led by Robert Marjolin of France, to help administer the Marshall Plan (which was rejected by the Soviet Union and its satellite states).[7] This would be achieved by allocating United States financial aid and implementing economic programs for the reconstruction of Europe after World War II. (Similar reconstruction aid was sent to the war-torn Republic of China and post-war Korea, but not under the name "Marshall Plan".)[8]
In 1961, the OEEC was reformed into the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development by the Convention on the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and membership was extended to non-European states.[9][10] The OECD's headquarters are at the Château de la Muette in Paris, France.[11] The OECD is funded by contributions from member countries at varying rates and had a total budget of €386 million in 2019.[2]
Although OECD does not have a power to enforce its decisions, which further require unanimous vote from its members, it is recognized as highly influential publisher of mostly economic data through publications as well as annual evaluations and rankings of members countries.[12]
L'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) est une organisation internationale d'études économiques, dont les pays membres — des pays développés pour la plupart — ont en commun un système de gouvernement démocratique et une économie de marché. Elle joue essentiellement un rôle d'assemblée consultative1.
L'OCDE a succédé à l'Organisation européenne de coopération économique (OECE) issue du plan Marshall et de la Conférence des Seize (Conférence de coopération économique européenne) qui a existé de 1948 à 1960. Son but était l'établissement d'une organisation permanente chargée en premier lieu d'assurer la mise en œuvre du programme de relèvement commun (le plan Marshall), et, en particulier, d'en superviser la répartition2.
En 2020, l'OCDE compte 37 pays membres et regroupe plusieurs centaines d'experts. Elle publie fréquemment des études économiques et sociales — analyses, prévisions et recommandations de politique économique — et des statistiques, principalement concernant ses pays membres.
Le siège de l'OCDE se situe à Paris (16e), au château de la Muette. L'organisation possède également des bureaux dans plusieurs autres métropoles, notamment à Berlin, Mexico, Tokyo et Washington.
L'Organizzazione per la cooperazione e lo sviluppo economico (OCSE) – in inglese Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), e in francese Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) – è un'organizzazione internazionale di studi economici per i paesi membri, paesi sviluppati aventi in comune un'economia di mercato.
L'organizzazione svolge prevalentemente un ruolo di assemblea consultiva che consente un'occasione di confronto delle esperienze politiche, per la risoluzione dei problemi comuni, l'identificazione di pratiche commerciali e il coordinamento delle politiche locali e internazionali dei paesi membri[1]. Ha sede a Parigi nello Château de la Muette[2].
Gli ultimi paesi ad aver aderito all'OCSE sono la Colombia (28 aprile 2020),la Lettonia (1º luglio 2016) e la Lituania (5 luglio 2018), per un totale di 36 paesi membri.
La Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico1 (OCDE) es un organismo de cooperación internacional, compuesto por 37 estados,34 cuyo objetivo es coordinar sus políticas económicas y sociales. La OCDE fue fundada en 1961 y su sede central se encuentra en el Château de la Muette en París (Francia). Los idiomas oficiales de la entidad son el francés y el inglés.2
En la OCDE, los representantes de los países miembros se reúnen para intercambiar información y armonizar políticas con el objetivo de maximizar su crecimiento económico y colaborar a su desarrollo y al de los países no miembros.
Conocida como «club de los países ricos»,56 a partir de 2017, sus países miembros comprendieron colectivamente el 62,2 % del PIB nominal global (US$49,6 billones) y el 42,8 % del PIB global (Int US$54,2 billones).7
Организа́ция экономи́ческого сотру́дничества и разви́тия (сокр. ОЭСР, англ. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD) — международная экономическая организация развитых стран, признающих принципы представительной демократии и свободной рыночной экономики.
Создана в 1948 году под названием Организа́ция европе́йского экономи́ческого сотру́дничества (англ. Organisation for European Economic Co-operation, OEEC) для координации проектов экономической реконструкции Европы в рамках плана Маршалла.
Штаб-квартира организации располагается в Шато де ла Мюетт, в Париже. Генеральный секретарь (с 2006 года) — Хосе Анхель Гурриа Тревиньо (Мексика). Руководящим органом ОЭСР является совет представителей стран — членов организации. Все решения в нём принимаются на основе консенсуса.
По данным на 2011 год, в странах ОЭСР проживало 18 % населения мира[2].
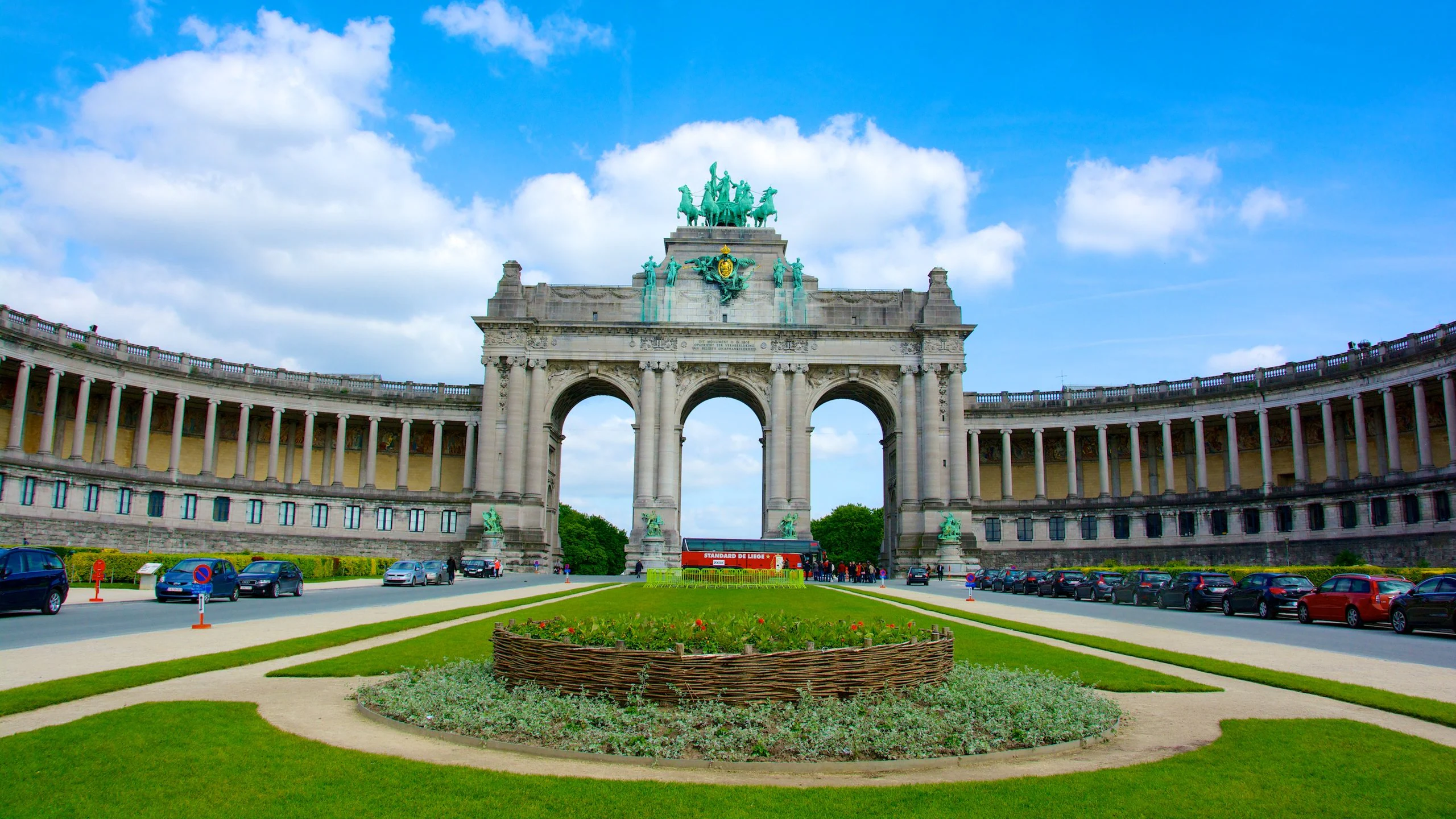




五十周年纪念拱廊(法语:Arcade(s) du Cinquantenaire;荷兰语:Arcade(s) van het Jubelpark)是位于比利时布鲁塞尔五十周年纪念公园/朱贝尔公园中心的一座纪念拱廊。其中心是一座巨大的三重拱门,被称为五十周年纪念拱门(法语:Arc du Cinquantenaire;荷兰语:Triomfboog van het Jubelpark)。它的顶部是一组青铜四码战车雕塑,其中有一位女性车夫,象征着布拉班特省升起国旗。
Die Cinquantenaire-Arkaden (französisch: Arcade(s) du Cinquantenaire; niederländisch: Arcade(s) van het Jubelpark) sind eine Gedenkarkade im Zentrum des Parc du Cinquantenaire/Jubelparks in Brüssel, Belgien. Das Herzstück ist ein monumentaler Dreifachbogen, bekannt als Cinquantenaire-Bogen (französisch: Arc du Cinquantenaire; niederländisch: Triomfboog van het Jubelpark). Er wird von einer bronzenen Quadriga-Skulpturengruppe mit einer weiblichen Wagenlenkerin gekrönt, die die personifizierte Provinz Brabant darstellt, die die Nationalflagge hisst.





Die Zentralkommission für die Rheinschifffahrt (ZKR) (französisch: Commission Centrale pour la Navigation du Rhin (CCNR); niederländisch: Centrale Commissie voor de Rijnvaart (CCR)) ist eine Internationale Organisation mit Sitz in Straßburg (Frankreich). Ihre Aufgabe ist in erster Linie die Erarbeitung und Fortentwicklung der von den Mitgliedstaaten der revidierten Rheinschifffahrtsakte zu erlassenden Verordnungen zu allen Fragen der Schifffahrt auf dem Rhein, sie prüft daneben alle Beschwerden, die ihr wegen der Anwendung der revidierten Rheinschifffahrtsakte sowie der Durchführung der gemeinsam von den Vertragsstaaten erlassenen Verordnungen vorgelegt werden. Ihre Berufungskammer kann bei Berufungen gegen Urteile der nationalen Rheinschifffahrtsgerichte angerufen werden. Darüber hinaus wirkt die Kommission auf die Weiterentwicklung des Binnenschifffahrtsrechts hin und initiiert hierzu weitere internationale Übereinkommen.
莱茵河航运中央委员会(法語:Commission Centrale pour la Navigation du Rhin;英語:Central Commission for Navigation on the Rhine;缩写:CCNR)是世界上历史最长的国际组织,其目的是保障莱茵河的环境和航运安全,以促进欧洲的繁荣。



 Wirtschaft und Handel
Wirtschaft und Handel
 Parteien und Regierung
Parteien und Regierung
 Architektur
Architektur
 Kunst
Kunst
 Religion
Religion
 Bildung und Forschung
Bildung und Forschung
 Sport
Sport
 Schiffe und Nautik
Schiffe und Nautik
 Grand Est
Grand Est

 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Unternehmen
Unternehmen
 Europäische Union
Europäische Union