
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Architecture
Architecture
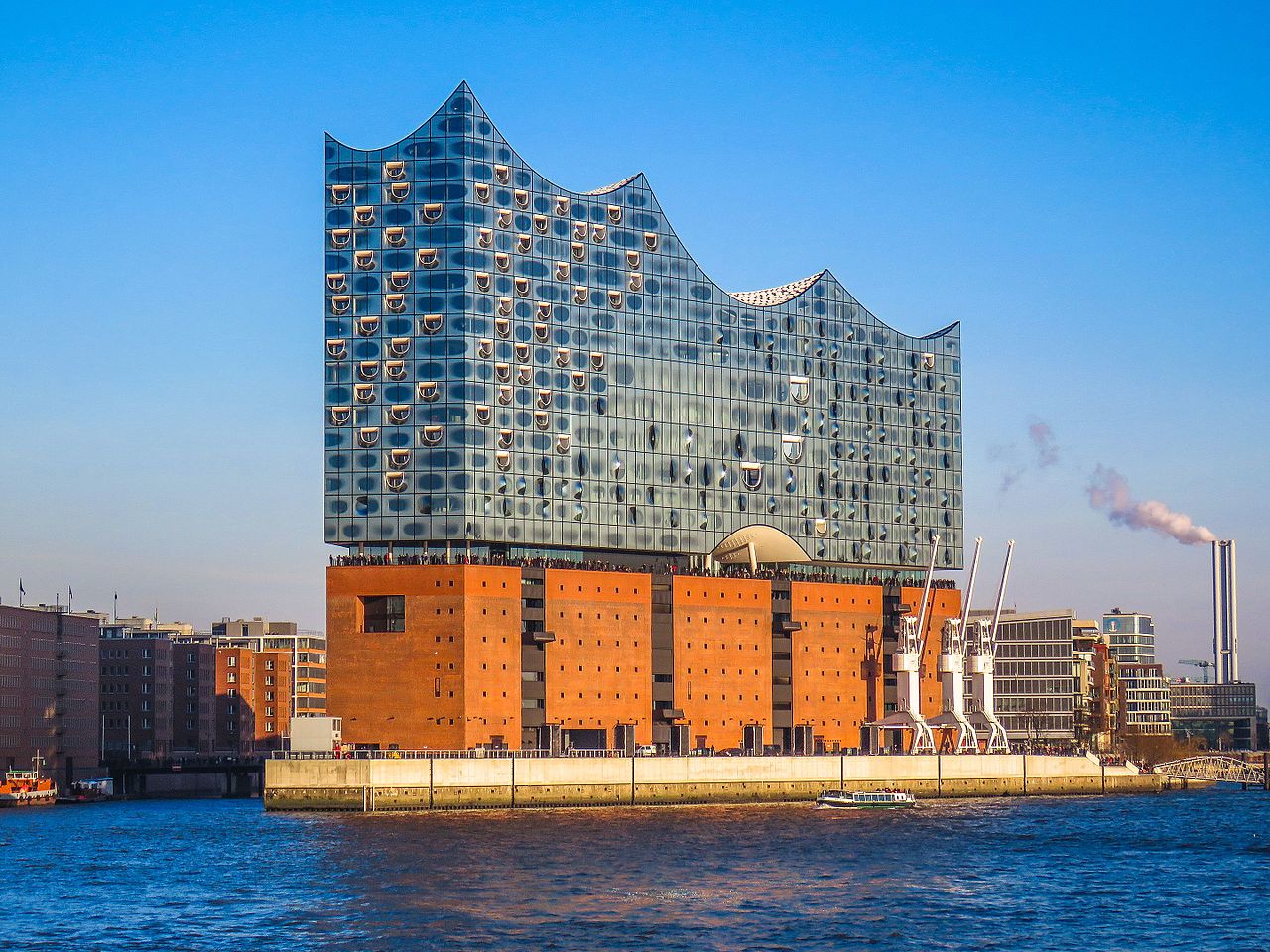


Die Elbphilharmonie (kurz auch „Elphi“ genannt)[1][2] ist ein im November 2016 fertiggestelltes Konzerthaus in Hamburg. Sie wurde mit dem Ziel geplant, ein neues Wahrzeichen der Stadt und ein „Kulturdenkmal für alle“ zu schaffen.[3][4][5] Das 110 Meter hohe Gebäude im Stadtteil HafenCity liegt am rechten Ufer der Norderelbe an der Spitze des Großen Grasbrooks zwischen den Mündungen der Hafenbecken Sandtorhafen und Grasbrookhafen. Es wurde unter Einbeziehung der Hülle des früheren Kaispeichers A (Baujahr 1963) errichtet. Auf diesen Sockel wurde ein moderner Aufbau mit einer Glasfassade gesetzt, die an Segel, Wasserwellen, Eisberge oder einen Quarzkristall erinnert. Die Lage am Kaiserhöft ist von der einstigen industriellen Hafennutzung und der neugotischen Backsteinarchitektur der Speicherstadt geprägt.
Das Konzept des Konzerthauses geht auf eine 2001 vorgestellte Idee des Hamburger Projektentwicklers Alexander Gérard zurück. Der Bau wurde dann 2007 durch die Bürgerschaft unter Bürgermeister Ole von Beust beschlossen. Entwurf und Planung der Philharmonie stammen im Wesentlichen vom Architekturbüro Herzog & de Meuron. Bauherr war die Elbphilharmonie Bau KG, deren Teilgesellschafter und Hauptfinanzier die Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg mit Steuermitteln ist. Das Gebäude wurde in ihrem Auftrag vom Baudienstleister Hochtief errichtet.
Die Fertigstellung des Gebäudes war nach einem mehrjährigen Vorlauf für das Jahr 2010 vorgesehen, verzögerte sich jedoch mehrfach, u. a. auch bedingt durch einen anderthalbjährigen Baustopp im öffentlichen Bereich. Erst nach einer umfangreichen Projektneuordnung zwischen den Architekten, dem Bauherren und der Baufirma kurz nach der Wahl des Bürgermeisters Olaf Scholz wurde nach dem Baustopp weitergebaut. Durch die Verzögerungen am Bau und die Überschreitung der ursprünglich veranschlagten Baukosten wurde die Elbphilharmonie bereits lange vor der Fertigstellung bundesweit bekannt: Die Baukosten betrugen am Ende mit rund 866 Millionen Euro etwas mehr als das 11,24-fache bzw. mehr als plus 1.124 % der mit ursprünglich 77 Millionen Euro geplanten Summe.[6] Der im neuen Vertrag vereinbarte Termin für die Bau- und Schlüsselübergabe am 31. Oktober 2016 wurde eingehalten.[7] Die Einweihung des Konzertbereichs wurde am 11. und 12. Januar 2017 mit dem Konzert „Zum Raum wird hier die Zeit“ des NDR Elbphilharmonie Orchesters gefeiert (Konzertprogramm).[8][9] Der Kleine Saal wurde am 12. Januar 2017 vom Ensemble Resonanz eingeweiht. Im ersten Jahr nach der Eröffnung besuchten rund 850.000 Menschen die über 600 Konzerte in der Elbphilharmonie, über 4,5 Millionen Besucher pilgerten auf die Plaza, mehr als 70.000 Menschen nahmen an Konzerthausführungen und über 60.000 am Musikvermittlungsprogramm des Hauses teil.[10]
汉堡易北爱乐音乐厅是德国北部音乐之都的新心脏,凭借其别具一格的建筑风格和精彩纷呈的各类活动,这座宏伟的音乐厅将卓越艺术和开放包容融为一体。易北爱乐音乐厅由赫尔佐格和德梅隆建筑事务所(Herzog & de Meuron)设计,矗立于城市与港口之间,并将从前的码头仓库与新颖的玻璃结构和弧形屋顶合为一体。建筑内除了设有三座音乐厅外,还拥有豪华酒店和公共观景平台,平台的开放式设计突显出汉堡这座德国新地标建筑作为“一个面向所有人的音乐厅”的特点。(Quelle:www.Baidu.com)
易北爱乐厅(Elbphilharmonie)是一座位于德国汉堡的音乐厅,是建设中的汉堡港城的一部分,位于仓库城的最西端,高达110米,是汉堡最高的居住建筑。音乐厅的一至七层使用了港口仓库A(Kaispeicher A)的37米高的基座[1]。港口仓库A曾经用于存贮可可、茶及烟草[2]。音乐厅除了面向音乐厅听众和酒店住户外,也向其他所有人开放[1]。
エルプフィルハーモニー・ハンブルク (独: Elbphilharmonie Hamburg、愛称: Elphi) は、2017年1月にオープンしたドイツ・ハンブルクのハーフェンシティ地区にあるコンサートホール。「エルプ」はハーフェンシティが面するエルベ川を意味する。
当該ホールの竣工により、NDRエルプフィルハーモニー管弦楽団(NDR Elbphilharmonie Orchestra, 旧称:北ドイツ放送交響楽団)の新たな本拠地となった。
古い倉庫「埠頭倉庫A(Kaispeicher A)」の上部にコンサートホールを新設する計画で、建築設計を担当するのはスイス・バーゼルのヘルツォーク&ド・ムーロン[2][3]、建設業者はホッホティーフ。また、日本からも永田音響設計が音響設計に携わっている[4]。完成すると高さが110mになり、人が居住する建物としてはハンブルクで最も高い建築物となる予定である。
巨額なコストの増加と建設の大幅な遅れから、スキャンダラスな事業であるとみられている。当事業の当初の推定予算は7700万ユーロで、ハンブルク市が負担するはずであったが、2007年には、市は建設コストを支えるために、1.14億ユーロとすることで決着した。その後も幾度かの交渉を経て、2012年12月にはゼネコンのホッホティーフに対して市側が(計画コストを含めて)最終的な建設コストの総計を手取りで5.75億ユーロとすることで合意した。2013年4月23日、ハンブルク市長のオーラフ・ショルツは、当事業にかかる費用の合計が7.89億ユーロになることを納税者(市民)に公表した[5]。建物の完成は、当初は2010年に計画されていたが、度々延期された。上棟式は、3年間の建設期間の後に、2010年5月に挙行された。建設作業は2016年10月に完了し、古い建物と新しい建物の間にある公共広場は2016年11月から一般公開された。
The Elbphilharmonie (![]() German pronunciation (help·info)) (Elbe Philharmonic) is a concert hall in the HafenCity quarter of Hamburg, Germany, on the Grasbrook peninsula of the Elbe River. It is one of the largest and acoustically most advanced concert halls in the world.[3] It is popularly nicknamed Elphi.[4][5]
German pronunciation (help·info)) (Elbe Philharmonic) is a concert hall in the HafenCity quarter of Hamburg, Germany, on the Grasbrook peninsula of the Elbe River. It is one of the largest and acoustically most advanced concert halls in the world.[3] It is popularly nicknamed Elphi.[4][5]
The new glassy construction resembles a hoisted sail, water wave, iceberg or quartz crystal; it sits on top of an old warehouse building (Kaispeicher A, built 1963) near the historical Speicherstadt and is designed by architecture firm Herzog & de Meuron.[6][7] It is the tallest inhabited building in Hamburg, with a final height of 108 metres (354 ft).[2]
The Elbphilharmonie was officially inaugurated with concerts of the NDR Elbphilharmonie Orchestra and a light show on 11 January 2017.[8][9][10]
La Philharmonie de l’Elbe (Elbphilharmonie, surnommée Elphi) est une salle de concert symphonique de Hambourg construite par les architectes Herzog & de Meuron.
La Elbphilharmonie (letteralmente "Filarmonica dell'Elba") è una sala da concerto della città di Amburgo, in Germania, situata nel quartiere di HafenCity (distretto di Hamburg-Mitte).
È una delle sale di concerto più grandi ed acusticamente avanzate a livello mondiale. È anche nota con il soprannome Elphi.
La costruzione in vetro assomiglia ad una vela issata, ad una onda o ad un cristallo di quarzo, ed è appoggiata sopra un vecchio magazzino (Kaispeicher A, costruito nel 1963), nelle vicinanze dello storico Speicherstadt. Costruita su progetto dello studio Herzog & de Meuron[1][2], include due sale da concerto, una da 2 000 posti e una da 550 circa, un hotel e 44 appartamenti.[3] È l'edificio abitabile più alto di Amburgo, con una altezza finale di 108 metri.[4]
È stata inaugurata l'11 gennaio 2017, con un concerto della NDR Elbphilharmonie Orchester diretto da Thomas Hengelbrock.[3]
La Filarmónica del Elba (en alemán, Elbphilharmonie), conocida también por su sobrenombre Elphi,12 es una sala de conciertos en la HafenCity de Hamburgo, Alemania.
Proyectada por el estudio de arquitectura suizo Herzog & de Meuron, esta construcción junto al río Elba incluye apartamentos en sus pisos superiores. La construcción fue finalizada el 31 de octubre 2016; no obstante, debido a los múltiples retrasos e incalculables incrementos de costo de obra, en torno al 1000%,3 la prensa estuvo castigando a este proyecto.4
La inauguración de la nueva sala de conciertos se produjo el 11 de enero de 2017, con un concierto de la NDR Elbphilharmonie Orchester5 (anteriormente conocida como Orquesta Sinfónica de la NDR), que se convertirá en la orquesta residente del auditorio.6
Эльбская филармония (нем. Elbphilharmonie) — концертный зал Гамбурга, расположенный на острове Грасброок на Эльбе.

 Architecture
Architecture

 Astronomy
Astronomy
 China
China

 Horoscope
Horoscope
 I Ging
I Ging


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Literature
Literature

 Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine

 Science and technology
Science and technology
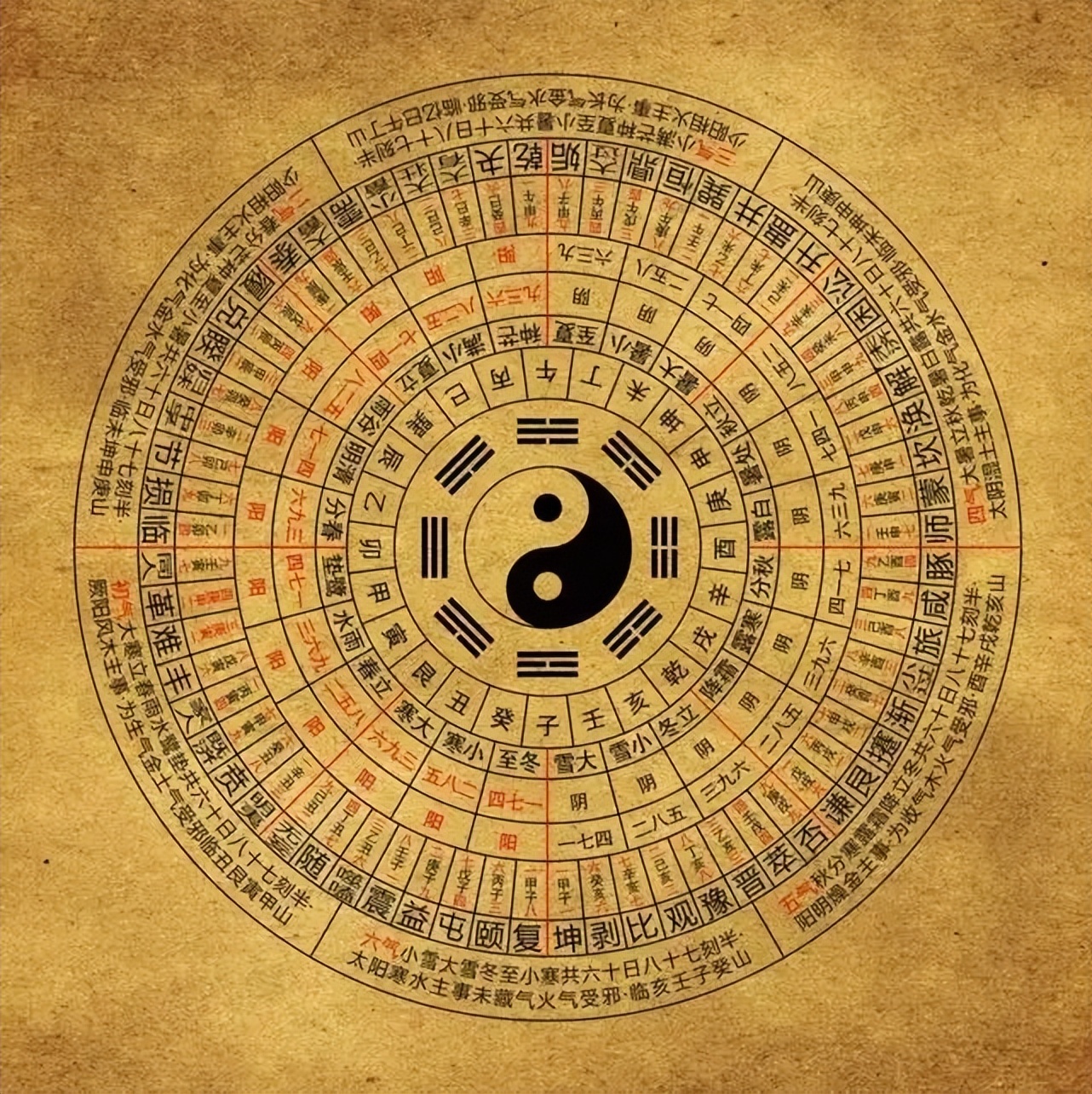


Das I Ging, hist. Romanisierung, heute: Yijing (chinesisch 易經 / 易经, Pinyin Yìjīng, W.-G. I-Ching ‚Buch der Wandlungen od. Klassiker der Wandlungen‘) ist eine Sammlung von Strichzeichen und zugeordneten Sprüchen. Es ist der älteste der klassischen chinesischen Texte. Seine legendäre Entstehungsgeschichte wird traditionell bis in das 3. Jahrtausend v. Chr. zurückgeführt. Das Werk ist im Chinesischen allgemein auch als Zhouyi (周易, Zhōuyì ‚Wandlungen der Zhou‘) bekannt.
《易经》是中国汉族最古老的文献之一[1],并被儒家尊为“五经”之始;一般说上古三大奇书包括《黄帝内经》、《易经》、《山海经》,但它们成书都较晚。《易经》以一套符号系统来描述状态的简易、变易、不易,表现了中国古典文化的哲学和宇宙观。它的中心思想,是以阴阳的交替变化描述世间万物。《易经》最初用于占卜和预报天气,但它的影响遍及中国的哲学、宗教、医学、天文、算术、文学、音乐、艺术、军事和武术等各方面,是一部无所不包的巨著。自从17世纪开始,《易经》也被介绍到西方。在四库全书中为经部,十三经中未经秦始皇焚书之害,它是最早哲学书。自从十七世纪开始,《易经》也被介绍到西方。
《易》原有三种版本:《连山》、《归藏》和《周易》[2],《连山》和《归藏》已经失传,一般所称《易经》即源于《周易》发展而来。
《易经》包括狭义的《周易》与《易传》。《周易》相传是依循周文王主编《易》的著述而来,成书大约在西周时期。由于随时代演变,《周易》文字含义到了春秋战国时代已经不便读懂,因此孔子撰写了“十翼”,后世又称为《易传》并列入《易经》。
『易経』(えききょう、正字体:易經、拼音: )は、古代中国の書物。『卜』が動物である亀の甲羅や牛や鹿の肩甲骨に入ったヒビの形から占うものであるのに対して、『筮』は植物である『蓍[1]』の茎の本数を用いた占いである。商の時代から蓄積された卜辞を集大成したものとして易経は成立した。易経は儒家である荀子の学派によって儒家の経典として取り込まれた。現代では、哲学書としての易経と占術のテキストとしての易経が、一部重なりながらも別のものとなっている。中心思想は、陰陽二つの元素の対立と統合により、森羅万象の変化法則を説く。著者は伏羲とされている[2]。
中国では『黄帝内經』・『山海經』と合わせて「上古三大奇書」とも呼ぶ。
The I Ching (/ˈiː ˈdʒɪŋ/),[2] also known as Classic of Changes or Book of Changes, is an ancient Chinese divination text and the oldest of the Chinese classics. Possessing a history of more than two and a half millennia of commentary and interpretation, the I Ching is an influential text read throughout the world, providing inspiration to the worlds of religion, psychoanalysis, literature, and art. Originally a divination manual in the Western Zhou period (1000–750 BC), over the course of the Warring States period and early imperial period (500–200 BC) it was transformed into a cosmological text with a series of philosophical commentaries known as the "Ten Wings".[3] After becoming part of the Five Classics in the 2nd century BC, the I Ching was the subject of scholarly commentary and the basis for divination practice for centuries across the Far East, and eventually took on an influential role in Western understanding of Eastern thought.
The I Ching uses a type of divination called cleromancy, which produces apparently random numbers. Six numbers between 6 and 9 are turned into a hexagram, which can then be looked up in the I Ching book, arranged in an order known as the King Wen sequence. The interpretation of the readings found in the I Ching is a matter of centuries of debate, and many commentators have used the book symbolically, often to provide guidance for moral decision making as informed by Taoism and Confucianism. The hexagrams themselves have often acquired cosmological significance and paralleled with many other traditional names for the processes of change such as yin and yang and Wu Xing.
Le Yi Jing (sinogrammes 易经simpl./易經trad., pinyin yì jīng, Wade-Giles i4 ching1, également orthographié Yi King ou Yi-King), prononcé en français i ting est un manuel chinois dont le titre peut se traduire par « Classique des changements » ou « Traité canonique des mutations ». Il s'agit d'un système de signes binaires qui peut être utilisé pour faire des divinations. Le Yi Jing s'appelle aussi Zhou Yi (周易, pinyin : Zhōu Yì, Wade-Giles : Chou1 I4) c'est-à-dire « changements de Zhou » pour la raison que son élaboration date du Ier millénaire avant l'ère chrétienne, époque des Zhou (1027, 256 av. J.-C.).
Il occupe une place fondamentale dans l'histoire de la pensée chinoise et peut être considéré comme un traité unique en son genre dont la finalité est de décrire les états du monde et leurs évolutions. Premier des cinq classiques, il est donc considéré comme le plus ancien texte chinois.
Le Yi Jing est le fruit d'une recherche spéculative et cosmogonique élaborée, dont les articulations ont influencé durablement la pensée chinoise. Sa structure mathématique a impressionné Leibniz qui y aurait vu la première formulation de l'arithmétique binaire. De fait, partant d'une opposition/complémentarité entre les principes d'engendrement Yin et Yang (yin // réceptif // lune // femelle // passif alors que yang // créatif // soleil // mâle // actif) et subdivisant cette dualité de façon systématique (adret = côté au Soleil alors qu'ubac = côté à l'ombre ; vents favorables opposés aux nuages contraires), le Yi Jing arrive à la série des 64 figures qui peuvent interpréter toutes les transformations possibles.
« Le Yi-King ou Livre des transformations de l'archaïque magie chinoise apporte l'image la plus exemplaire de l'identité du Génésique et du Génétique. La boucle circulaire est un cercle cosmogonique symboliquement tourbillonnaire par le S intérieur qui à la fois sépare et unit le Yin et le Yang. La figure se forme non à partir du centre mais de la périphérie et naît de la rencontre de mouvements de directions opposés. Le Yin et le Yang sont intimement épousés l'un dans l'autre, mais distincts, ils sont à la fois complémentaires, concurrents, antagonistes. La figure primordiale du Yi-King est donc une figure d'ordre, d'harmonie, mais portant en elle l'idée tourbillonnaire et le principe d'antagonisme. C'est une figure de complexité. »
— Edgar Morin, La Méthode 1. La Nature de la Nature, p. 228, Seuil, Paris, 1977.
Il Libro dei Mutamenti[2] (易經T, 易经S, YìjīngP, I ChingW[3]), conosciuto anche come Zhou Yi 周易 o I Mutamenti (della dinastia) Zhou, è ritenuto il primo dei testi classici cinesi sin da prima della nascita dell'impero cinese. È sopravvissuto alla distruzione delle biblioteche operata dal Primo imperatore, Qin Shi Huang Di.
L'Yi Jing è diviso in due porzioni, jing 經 o 'classico' e zhuan 傳 o 'commentario', composti in momenti differenti ma tramandati come testo unico da due millenni circa. La porzione jing è composta da sessantaquattro unità, ognuna basata su un esagramma (gua 卦) composto di sei linee che sono o continue (⚊) rappresentanti il principio yang o interrotte (⚋) rappresentanti il principio yin. Per ogni esagramma vi è una spiegazione chiamata 卦辞 guaci, accompagnata dalla spiegazione delle singole linee costituenti il trigramma chiamate 爻辞 yaoci. I primi due esagrammi del testo 乾 qian e 坤 kun sono accompagnati da due ulteriori testi chiamati 用六 yongliu e 用九 yongjiu.
Considerato da Confucio libro di saggezza, è utilizzato a livello popolare a scopo divinatorio, e dagli studiosi per approfondire aspetti matematici, filosofici e fisici. I metodi per ottenere i responsi sono vari e si passa dai gusci di tartaruga al lancio di 3 monete. Quando si utilizzano gli steli di achillea per estrarre i responsi, l'arte divinatoria è chiamata achilleomanzia.
El I Ching, Yijing o I King (en chino tradicional: 易經; en chino simplificado: 易经; en pinyin: yì jīng) es un libro oracular chino cuyos primeros textos se suponen escritos hacia el 1200 a. C. Es uno de los Cinco Clásicos confucianos.
El término i ching significa ‘libro de las mutaciones’. El texto fue aumentado durante la dinastía Zhou y posteriormente por comentaristas de la escuela de Confucio, pero su contenido original es de procedencia taoísta, y no confucianista. Se cree que describe la situación presente de quien lo consulta y predice el modo en que se resolverá en el futuro si se adopta ante ella la posición correcta. Es un libro adivinatorio y también un libro moral, a la vez que por su estructura y simbología es un libro filosófico y cosmogónico.
«И цзин» (кит. трад. 易經, упр. 易经, пиньинь: Yì Jīng), или «Чжоу И»[1] (周易) — наиболее ранний из китайских философских текстов. Наиболее ранний слой, традиционно датируемый ок. 700 г. до. н. э.[2] и предназначавшийся для гадания, состоит из 64 гексаграмм. Во II веке до н. э. был принят конфуцианской традицией как один из канонов конфуцианского Пятикнижия.
«Кни́га Переме́н» — название, закрепившееся за «И цзин» на Западе. Более правильный, хоть и не столь благозвучный вариант — «Кано́н Переме́н».


Die Langobarden in Italien, Orte der Macht (568 bis 774 n. Chr.) lautet der offizielle deutsche Name[1] der UNESCO für sieben Gruppen von wichtigen Gebäuden (einschließlich Festungen, Kirchen und Klöster) auf der italienischen Halbinsel, die im Juni 2011 auf die Liste des UNESCO-Welterbes gesetzt wurden.
In der Begründung heißt es, dass die Stätten von der hohen Leistung des germanischen Volks der Langobarden zeugten, die aus dem Norden Europas nach Italien eingewandert waren und wo sie vom 6. bis 8. Jahrhundert ihre eigene spezifische Kultur entwickelten. Weiter heißt es, die lombardische Synthese von Baustilen markiere den Übergang von der Antike bis zum europäischen Mittelalter, anknüpfend an das Erbe des antiken Rom, an christliche Spiritualität, an die byzantinische Kunst und die des germanischen Nordeuropas. Die sieben Gruppen zeugten von der wichtigen Rolle der Langobarden in der geistigen und kulturellen Entwicklung des mittelalterlichen europäischen Christentums, insbesondere durch die Stärkung der monastischen Bewegung.[2]
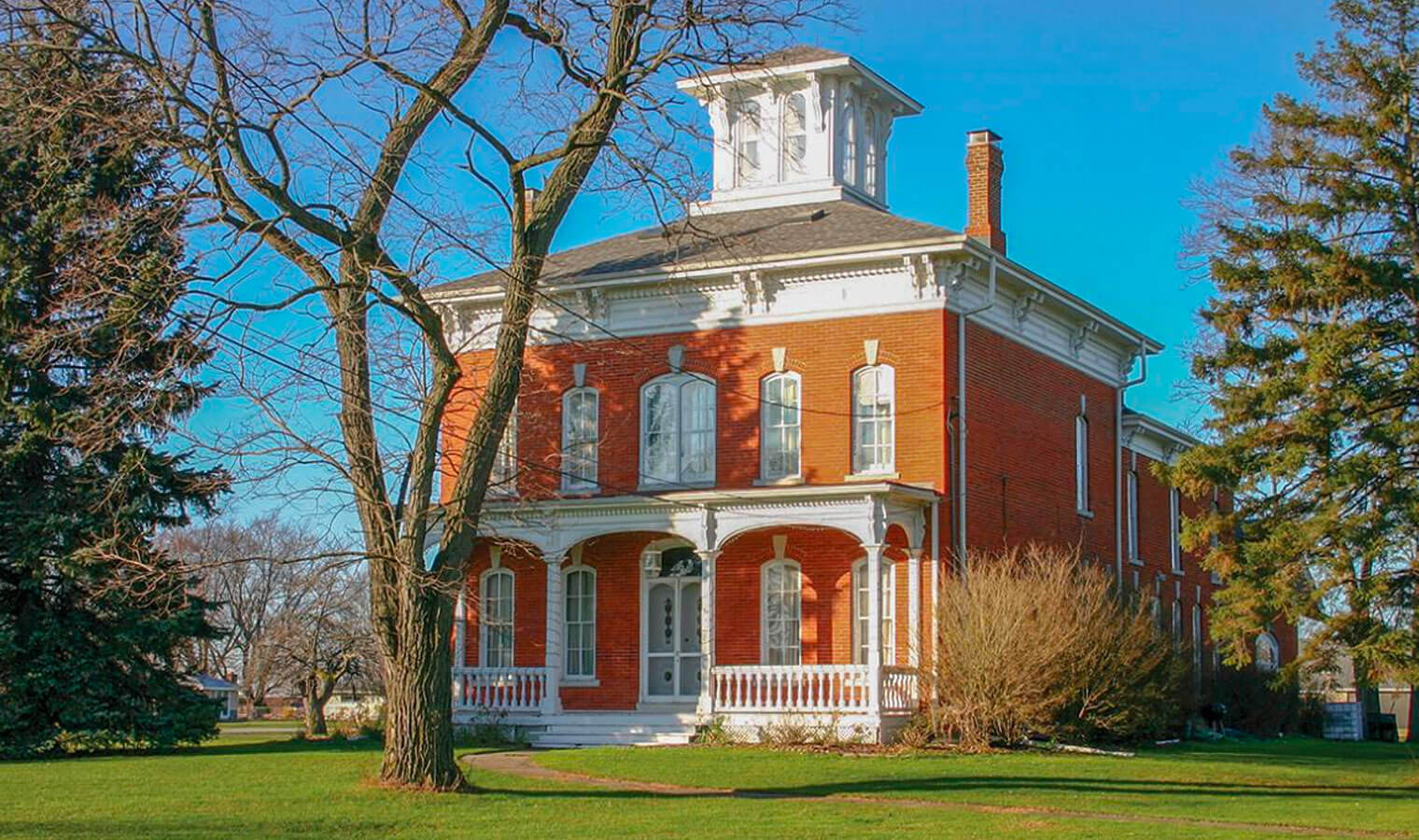

Italianate architecture continues the trend of asymmetrical design, romanticism, and Medieval influence — this time borrowing features from Medieval Italy. Italianate style is common up and down the East Coast and peaked in popularity between 1850 and 1880.
Italianate architecture features:
- Belvederes for natural light and airflow
- Overhanging eaves with decorative support brackets
- Tall and narrow or pedimented windows with rounded crowns
- Cast iron detailing and decor
Pattern books were becoming a popular way for craftsmen to build homes in different styles. This flexibility meant Italianate features were accessible for a variety of homes including large estates and urban townhouses.
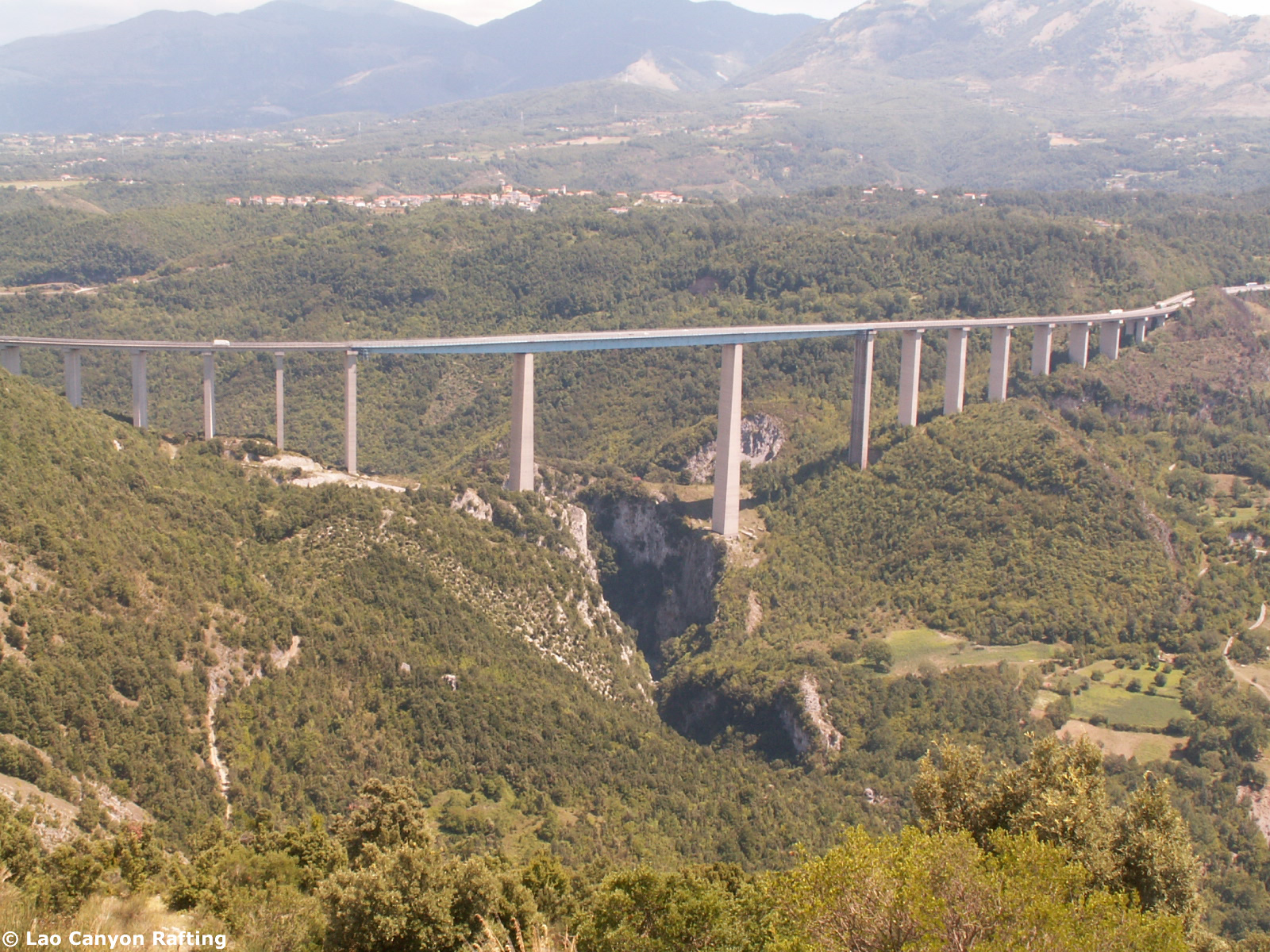

Das Viadotto Italia ist eine Autobahnbrücke im Zuge der Autostrada del Sole, genauer der Autostrada A2, bei den Orten Laino Borgo und Laino Castello im Norden der Provinz Cosenza in der italienischen Region Kalabrien.
Sie überquert den tief eingeschnittenen Fluss Lao in einer Höhe von 259 m und war damit die höchste Brücke Europas, bis sie 2004 von dem Viaduc de Millau abgelöst wurde. Seitdem ist sie die höchste Brücke Italiens und die zweithöchste in Europa.


 *Italian political system
*Italian political system

 Architecture
Architecture
 Baroque / Rococo architecture
Baroque / Rococo architecture

 Architecture
Architecture
 Neoclassic architecture *
Neoclassic architecture *

 European Union
European Union
 Supreme Court of the Member States of the EU
Supreme Court of the Member States of the EU

 Law
Law
 §Supreme Court
§Supreme Court
 Italy
Italy

 Lazio
Lazio

 Party and government
Party and government




 Music
Music
 Performing Arts
Performing Arts
 Hamburg
Hamburg
 History
History
 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 Lombardia
Lombardia
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Calabria
Calabria
 Life and Style
Life and Style