
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY


 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA
 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Review
Review

 Saskatchewan-SK
Saskatchewan-SK

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY
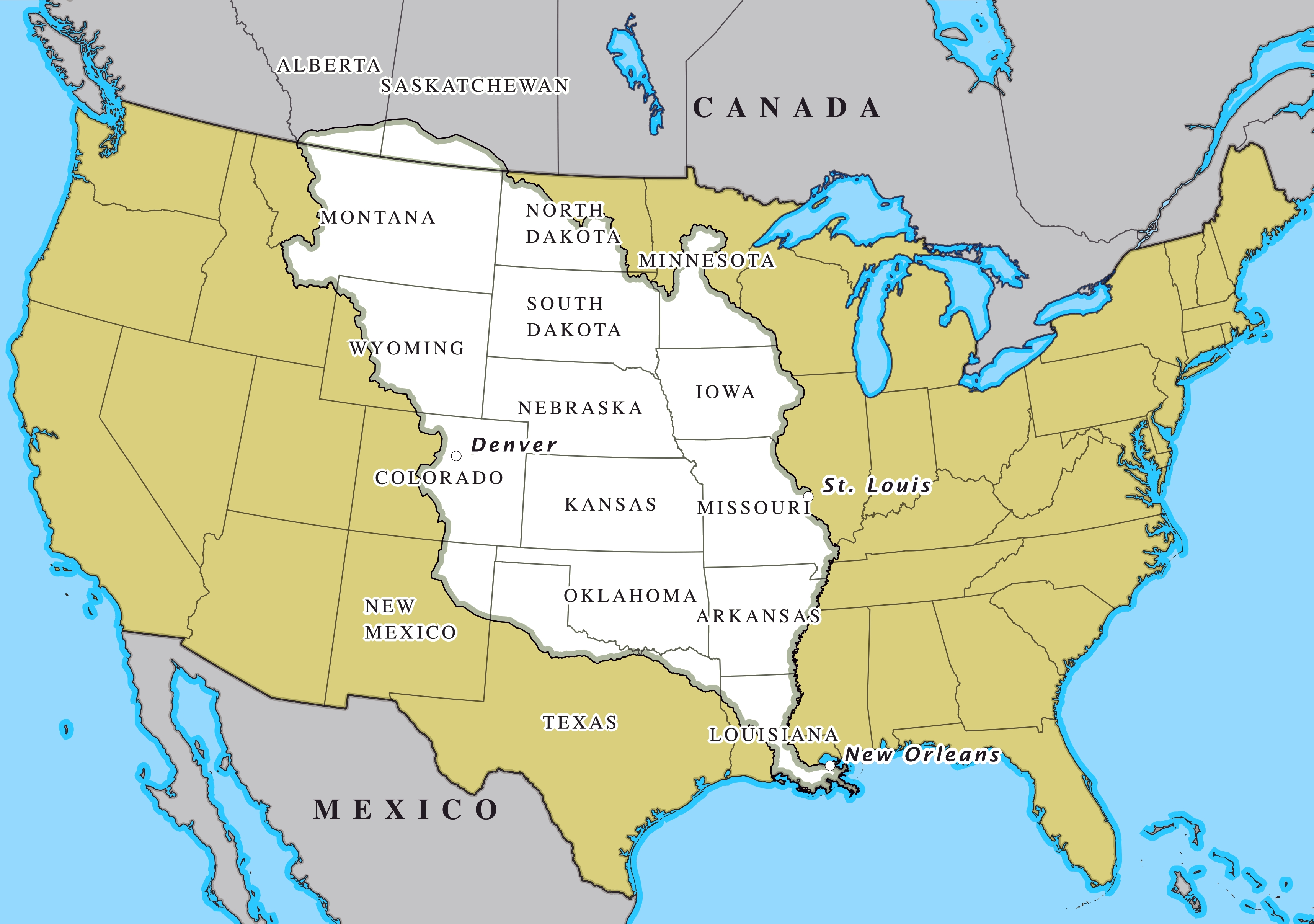
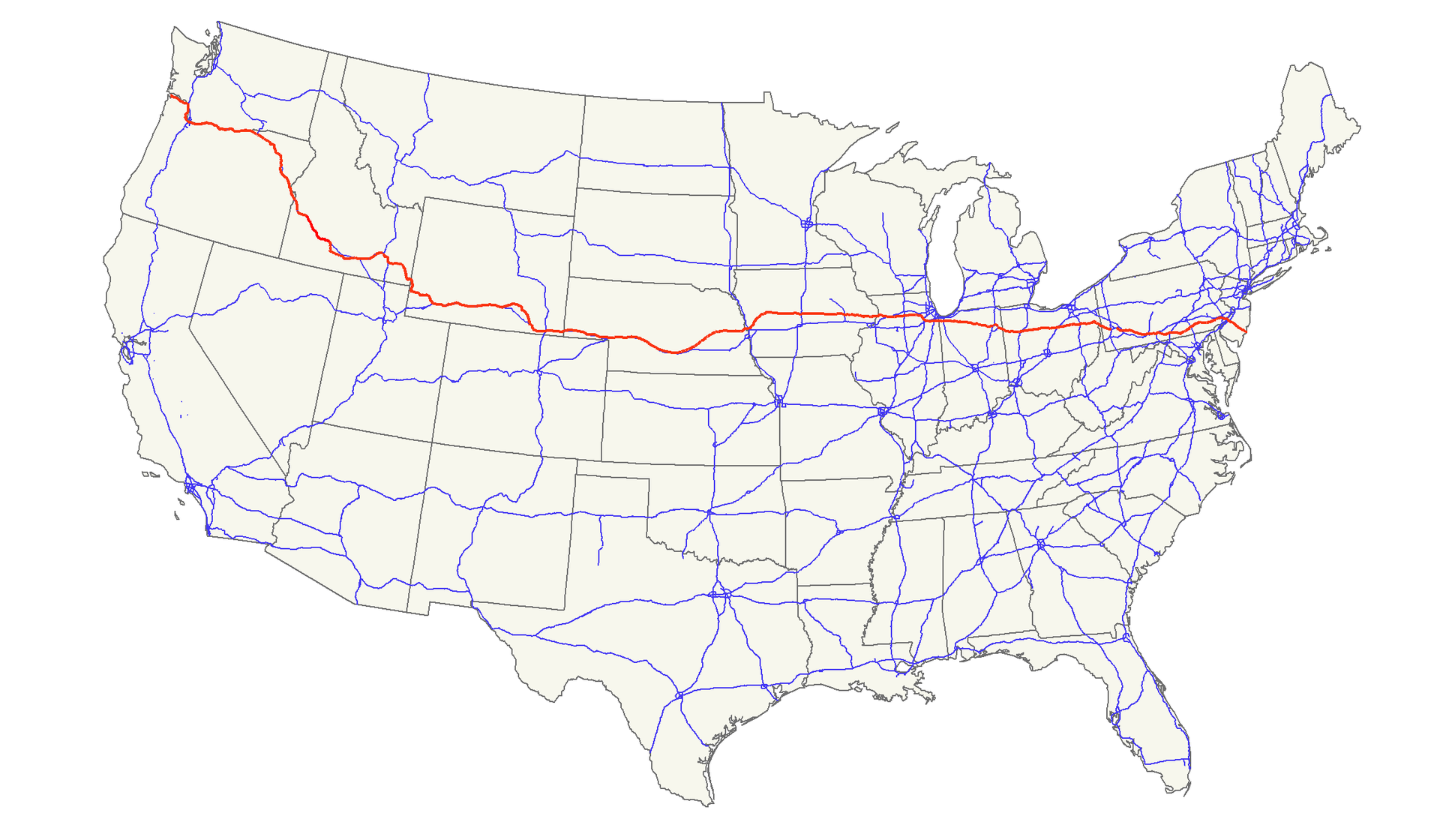
Der Louisiana Purchase (Louisiana-Kauf; im Französischen vente de la Louisiane, d. h. Verkauf von Louisiana) war der Kauf von 2.144.476 km² Land, das die USA 1803 von Frankreich erwarben. Der Kaufpreis betrug damals 15 Millionen US-Dollar oder 80 Millionen französische Francs (7 US-Dollar pro km²). Gemessen an der Kaufkraft entspricht das einem heutigen Wert von circa 251 Millionen US-Dollar oder knapp 117 Dollar pro km² (Stand 2018).[1]
Verkauft wurde das Gebiet der ehemaligen Kolonie Louisiana, das westlich des Mississippi River lag. Dieses Gebiet ist viel größer als der heutige Staat Louisiana: Es umfasst außer Teilen des heutigen Louisiana auch die heutigen Staaten Arkansas, Missouri, Iowa, Oklahoma, Kansas und Nebraska sowie Teile von Minnesota, North Dakota, South Dakota, Texas, New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, außerdem noch Randgebiete der kanadischen Provinzen Manitoba, Saskatchewan und Alberta.
Der Louisiana Purchase war das größte Grundstücksgeschäft der Geschichte. Das gekaufte Land verdoppelte damals das Territorium der Vereinigten Staaten und macht fast ein Viertel des heutigen Staatsgebiets aus.
路易斯安那购地(英语:Louisiana Purchase;法语:Vente de la Louisiane)是美国于1803年以每英亩三美分向法国购买超过529,911,680英亩(2,144,476平方公里)土地的交易案,该交易的总价为1500万美元或相当于8000万法郎;若计算通货膨胀等因素,此数额在今日相当于3亿100万美元。如以国内生产总值相对比例计算,此数额在2004年相当于4,178亿美元。而土地上所有后续条约和财务结算的总成本,估计约为26亿美元。[1]。
法属路易斯安那的版图远超今日美国的路易斯安那州。从南至北,该属地范围包括了现今美国路易斯安那州密西西比河两岸(包括新奥尔良市)、阿肯色州、奥克拉荷马州、德克萨斯州北部边界地带、新墨西哥州东北角、密苏里州、堪萨斯州、科罗拉多州洛基山脉以东、爱荷华州、内布拉斯加州、怀俄明州大部(落基山脉以东)、明尼苏达州密西西比河以西、南达科他州、北达科他州大部、蒙大拿州大部(除西端),以及现今加拿大马尼托巴、萨斯喀彻温、艾伯塔各省之密苏里河流域地区(也即南部边境地带)。购地所涉土地面积是今日美国国土的22.3%,与当时美国原有国土面积大致相当,因此使得当时美国的国土翻倍。

 *United States Political System
*United States Political System
 *United States presidential election
*United States presidential election
 *Republican Party
*Republican Party
 *U.S. foreign territories
*U.S. foreign territories
 Guam
Guam
 *U.S. foreign territories
*U.S. foreign territories
 Northern Mariana Islands
Northern Mariana Islands

 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Political parties with more than a hundred years of history
*Political parties with more than a hundred years of history
 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 Wisconsin-WI
Wisconsin-WI

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY

共和党(英语:Republican Party)是美国的一个政党,又称为大老党(英语:Grand Old Party,简称GOP),与民主党并列为美国当代的两大主要政党之一。目前为美国联邦执政党,且拥有美国国会参议院多数党地位,27个州的执政权,并控制绝大部分的州议会。
共和党成立于1854年,是由《堪萨斯内布拉斯加州法》的反对者创立的,《堪萨斯内布拉斯加州法》允许将奴隶制潜在地扩展到某些美国领土。共和党支持古典自由主义,反对扩大奴隶制,并支持经济改革。[14] [15]亚伯拉罕·林肯(Abraham Lincoln)是第一位共和党总统。在林肯和共和党国会的领导支持下,奴隶制于1865年在美国被禁止。在第三党系统和第四党系统中,共和党总体上处于统治地位。 1912年以后,该党在思想上向右转移。[16]继1964年的《民权法》和1965年的《投票权法》之后,共和党的核心基础发生了变化,南方各州在总统选举中变得更加可靠地成为共和党人。[17]农村地区的人们,男人,未受过大学教育的人,老年人和白人倾向于支持共和党。[18] [19] [20]。 21世纪的共和党意识形态是美国的保守主义。共和党支持降低税收,自由市场资本主义,限制移民,增加军事开支,持枪权,限制堕胎,放松管制和限制工会。共和党除了提倡保守的经济政策外,在社会上也是保守的。在最高法院于1973年在Roe v. Wade案中作出裁决之后,共和党在其政党平台上反对堕胎,并在福音派信徒中得到了更多的支持。[21]共和党在成立之初就坚定地致力于保护主义和关税,但在20世纪,尽管关税在21世纪重新崛起,但它对自由贸易的支持越来越强。 美国历史上共计有19位共和党总统(包括现任总统唐纳德·特朗普,他于2016年当选),其中最多的是任何一个政党。截至2019年,共和党控制总统职位,美国参议院的多数席位,多数州州长,多数(30)个州立法机关和21个州政府三重奏(州政府和两个立法会议厅)。美国最高法院的九名现任法官中有五名是由共和党总统提名的。
Die Republikanische Partei (englisch Republican Party), auch als Republikaner (englisch Republicans) oder als Grand Old Party („große alte Partei“) bzw. GOP bezeichnet, ist neben der Demokratischen Partei eine der beiden großen Parteien der USA. Sie war ursprünglich die liberale der beiden Großparteien, ist aber heute konservativer eingestellt als die Demokratische Partei. Ihr Wappentier ist der Elefant. Dessen Ursprung geht, ebenso wie der Esel der Demokraten, auf den Karikaturisten Thomas Nast zurück. Die inoffizielle Parteifarbe ist seit 2000 rot. In TV-Sendungen oder Medienberichten werden Senatoren und Parteimitglieder der Republikanischen Partei meistens mit einem "(R)" hinter ihrem Namen dargestellt.
Die Partei wurde 1854 insbesondere mit dem Ziel gegründet, die Sklaverei abzuschaffen, womit sie sich während des Sezessionskrieges unter ihrem ersten US-Präsidenten Abraham Lincoln gegen die Demokraten durchsetzte, die für die Beibehaltung der Sklaverei plädierten. Seit den 1960er Jahren wandte sie sich zunehmend rechtskonservativen und evangelikalen Wählern zu.
Seit 2017 stellt sie mit Donald Trump den amtierenden (45.) US-Präsidenten. Davor stellte sie den Präsidenten von 2001 bis 2009 mit George W. Bush. Vorsitzende des nationalen Organisationsgremiums der Partei, des Republican National Committee, ist seit Januar 2017 Ronna Romney McDaniel.
共和党(きょうわとう、英語: Republican Party)は、アメリカ合衆国の政党。国際民主同盟加盟。民主党と共に二大政党制を構成している政党である。一般的に保守主義及びキリスト教の立場を取る。別称はGOP[19][注 2]。
伝統的保守層とキリスト教主義勢力(300万人を擁する「クリスチャン・コアリション」を筆頭とする福音派)の集票に支えられた政党である。
外交面では、力(パワー)による秩序と強力な同盟関係による安全保障策が基本であり、米国の国益を優先し国際連合(UN)に対しては不信感を持っている。
一方で内政面では、人工妊娠中絶禁止(プロライフ)、死刑制度存続、伝統的家族制度重視(同性結婚反対)、性的少数者・LGBTの権利擁護反対、不法移民反対、銃規制反対などが特徴の伝統的保守思想の政党である。なお近年は、キリスト教原理主義的な宗教重視の党員が多い。
The Republican Party, also referred to as the GOP (Grand Old Party), is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States; the other is its historic rival, the Democratic Party.
The GOP was founded in 1854 by opponents of the Kansas–Nebraska Act, which allowed for the potential expansion of slavery into certain U.S. territories. The party supported classical liberalism, opposed the expansion of slavery, and supported economic reform.[14][15] Abraham Lincoln was the first Republican president. Under the leadership of Lincoln and a Republican Congress, slavery was banned in the United States in 1865. The Party was generally dominant during the Third Party System and the Fourth Party System. After 1912, the Party underwent an ideological shift to the right.[16] Following the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, the party's core base shifted, with Southern states becoming more reliably Republican in presidential politics.[17] People living in rural areas, men, people without a college degree, the elderly, and white Americans are generally more likely to support the GOP.[18][19][20]
The 21st century Republican Party ideology is American conservatism, which incorporates both economic policies and social values. The GOP supports lower taxes, free market capitalism, restrictions on immigration, increased military spending, gun rights, restrictions on abortion, deregulation and restrictions on labor unions. After the Supreme Court's 1973 decision in Roe v. Wade, the Republican Party opposed abortion in its party platform and grew its support among evangelicals.[21] The GOP was strongly committed to protectionism and tariffs at its founding, but grew more supportive of free trade in the 20th century, although tariffs experienced a resurgence in the 21st century.
There have been 19 Republican presidents (including incumbent president Donald Trump, who was elected in 2016), the most from any one political party. As of 2020, the GOP controls the presidency, a majority in the U.S. Senate, a majority of state governorships, a majority (30) of state legislatures, and 21 state government trifectas (governorship and both legislative chambers). Five of the nine sitting U.S. Supreme Court justices were nominated by Republican presidents.
Le Parti républicain (en anglais : Republican Party, également surnommé Grand Old Party et abrégé en GOP) est l'un des deux grands partis politiques américains contemporainsb. Il est fondé le 28 février 1854 par des dissidents nordistes du Parti whig et du Parti démocrate, hostiles au statu quo sur l'esclavage, aux revendications souverainistes des États fédérés et favorables au protectionnisme.
Supplantant le Parti whig moribond, il devint le principal parti politique du pays alternant au pouvoir avec le Parti démocrate. Depuis sa fondation, c'est le parti qui a le plus exercé le pouvoir exécutif aux États-Unis, y compris sur une durée continue (1861-1885)c. Dans le référentiel bipartite de l’échiquier politique contemporain, le Parti républicain est généralement classé à droite (right-wing). Donald Trump, qui investit ses fonctions de président des États-Unis le 20 janvier 2017, est le 20e et plus récent président issu du parti à ce jour16.
Il Partito Repubblicano (in inglese: Republican Party), popolarmente noto come «Grand Old Party» (GOP) e come il «partito di Lincoln», è uno dei due principali partiti del sistema politico degli Stati Uniti insieme al Partito Democratico. Nel Congresso in carica governato dal Repubblicano Donald Trump come presidente degli Stati Uniti detiene la maggioranza dei rappresentanti al Senato. Fondato col nome moderno nel 1854 da ex esponenti dei Whig e del Suolo Libero nonché militanti di preesistenti movimenti antischiavisti per opporre l'allora governo Democratico e contrastare la temuta espansione nell'Ovest del sistema schiavistico degli Stati meridionali, posizionandosi alla sinistra del Partito Democratico nelle questioni economiche e sociali, rimane uno dei partiti più antichi del mondo tra quelli ancora attivi. I Whig furono l'unione di diversi partiti minori, tra cui quello Anti-Massonico e Nazionale Repubblicano. Quest'ultimo fu a sua volta l'unione di ex esponenti Federalisti e Democratici-Repubblicani, i quali andarono a formare il Partito Democratico in sostegno di Andrew Jackson mentre i Nazionali Repubblicani sostennero l'ex Democratico-Repubblicano John Quincy Adams nelle elezioni presidenziali del 1828, facendo quindi risalire i Repubblicani a entrambi i primi due partiti nazionali.
Nel contesto politico statunitense odierno è ormai considerato come il partito della destra conservatrice (pur con le sue fazioni interne di centro-destra, della destra cristiana e di quella libertariana) in contrapposizione al Partito Democratico, che è invece diventato il partito liberale, considerato un'unione del liberalismo sociale e del progressismo. Perlomeno fino alla scissione del 1912, con il posizionamento contemporaneo dei Democratici sul fronte di sinistra e con l'avvento del New Deal del Democratico Franklin Delano Roosevelt negli anni 1930, il Partito Repubblicano era considerato un partito più liberal-progressista degli avversari (i conservatori-populisti Democratici del Sud appoggiarono la segregazione razziale), anche se a livello locale e statale ciò non si realizzò almeno sino angli anni 1980 e 1990 in quanto i sudisti preferivano le politiche economiche Democratiche, ma ciò venne meno quando entrambi i partiti appoggiarono il neoliberismo. Promotore dell'industria nell'Ottocento e delle imprese nel Novecento, il Partito Repubblicano si è spostato verso il liberismo nelle questioni economiche, ma rimase liberal-progressista in quelle sociali perlomeno fino agli anni 1960. Fu dagli anni 1950 e 1960, dominati dalla presidenza dell'eroe di guerra Dwight D. Eisenhower in un clima di guerra fredda caratterizzato dall'intensificarsi dell'anticomunismo e dalla presa di distanza dalla politica statalista del New Deal, oltre che per il movimento per i diritti civili degli anni 1960 (approvato dal Partito Democratico durante le presidenze di John Fitzgerald Kennedy e Lyndon B. Johnson) e della cosiddetta strategia del Sud che prevedeva una retorica razzista per attirarsi il consenso dei bianchi del Sud, che il partito assunse definitivamente la fisionomia conservatrice moderna.
Sulle questioni di politica estera entrambi i partiti Repubblicani e Democratici hanno cambiato diverse volte le rispettive politiche. Inizialmente scettici del destino manifesto e dell'espansione a ovest a causa del problema della schiavitù che voleva fermare e che alla fine abolì sotto la presidenza di Abraham Lincoln, seppur a costo di una cruenta guerra civile negli anni 1860 contro i secessionisti schiavisti sudisti che formarono gli Stati Confederati d'America per mantenere l'Unione, i Repubblicani sono diventati imperialisti e interventisti sotto la presidenza dei progressisti William McKinley e Theodore Roosevelt e poi isolazionisti in opposizione ai Democratici guidati da Thomas Woodrow Wilson, formando il blocco della cosiddetta vecchia destra. Durante la guerra fredda furono promotori dell'anticomunismo come i Democratici, ma con Eisenhower e i suoi sostenitori avversari dell'ultraconservatore Repubblicano Joseph McCarthy, censurato nel 1954. A partire dagli anni 1950 e 1960 c'è un'unione nota come fusionismo tra conservatori e libertariani che porta al moderno conservatorismo del partito con la candidatura alle elezioni presidenziali del 1964 di Barry Goldwater, che seppur sconfitto di misura dal Democratico Johnson portò all'elezione di Richard Nixon (1969–1974) e all'ascesa di Ronald Reagan (1981–1989), seppur lo stesso Goldwater criticò l'influsso della destra cristiana. Molti di questi libertariani sono sostenitori del vecchio isolazionismo in opposizione al neoconservatorismo che domina il partito sin dalla guerra fredda.
El Partido Republicano (GOP) (en inglés, Republican Party; también conocido como GOP, de Grand Old Party, El Gran Partido Viejo) es un partido político de los Estados Unidos. Al lado del Partido Demócrata, son los dos únicos partidos que han ejercido el poder en ese país desde mediados del siglo XIX. El partido se asocia comúnmente con el conservadurismo. En la actualidad es el partido de gobierno al que pertenece el presidente Donald Trump y el que posee la mayoría en el Senado de los Estados Unidos.20
Республиканская партия (англ. Republican Party) — наряду с Демократической, одна из двух основных политических партий США. Второе название — Великая Старая Партия (англ. Grand Old Party, GOP).
Неофициальный символ партии — слон (олицетворяет мощь), неофициальный цвет — красный.

 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID
 Canada
Canada

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM
 United States
United States

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY

落基山脉(英语:Rocky Mountains),又译作落矶山脉,是美洲西部的主要山脉,从加拿大西部不列颠哥伦比亚横越美国西部,直到美国西南部的新墨西哥州,绵延超过4800公里。和其平行的有太平洋海岸山脉、喀斯喀特山脉及内华达山脉。
此山脉的最高峰是埃尔伯特峰[1],位于科罗拉多州境内,高度有4401米。罗布森山则是加拿大境内的最高峰,高度为3954米。整个落基山脉系统是美国地文区的一大部分。
当时有许多板块在北美洲板块下移动。隐没带的角度很浅,因此造成北美西部广阔的山脉带。进一步的板块构造活动及冰河的侵蚀,使落基山脉出现显著的山峰及峡谷,在第四纪冰河时期结束时,人类开始在落基山脉居住。在欧洲人(例如亚历山大麦肯齐)及美洲人(如刘易斯与克拉克)发现此地区后,开始在此地采矿及打猎制作毛皮,不过落基山脉的人口还是不多。
现在的落基山脉中有很多地方是国家公园保护区及森林地,也是受欢迎的旅游景点,可以进行像露营、远足、爬山、钓鱼、打猎、山地自行车、滑雪及单板滑雪等休闲活动。
Die Rocky Mountains [ˌɹɒkiˈmaʊntənz] (deutsch, aber veraltet auch Felsengebirge, umgangssprachlich auch Rockies genannt) sind ein ausgedehntes Faltengebirge im westlichen Nordamerika. Die Berge erstrecken sich, je nach Definition, über 4500–5000 km von New Mexico durch die kontinentalen Vereinigten Staaten bis nach Kanada und bilden eine der wesentlichen geografischen Provinzen der USA.
Nicht zu den Rocky Mountains zählen die Coast Mountains, die Kaskadenkette und die Sierra Nevada. Der Mount Elbert in Colorado ist mit 4401 m der höchste Berg der Rocky Mountains.
Die Rocky Mountains sind Teil der von Feuerland bis Alaska reichenden Kordilleren. Sie beheimaten bedeutende Nationalparks wie den Yellowstone-Nationalpark und diverse Wintersportzentren. Außerdem sind sie reich an Bodenschätzen. Die Region der in den Rocky Mountains gelegenen US-Bundesstaaten wird Mountain States genannt.
ロッキー山脈(ロッキーさんみゃく、英: Rocky Mountains、Rockies、仏: Montagnes Rocheuses [mɔ̃ntaɲ ʁɔʃøz]、Rocheuses)は、北アメリカ大陸西部を北西から南東に走る山脈である。ロッキー山脈は北へ行くほど険しい岩山となり、広大な針葉樹の森にはエメラルド色の湖が数多く存在する。
一口に「ロッキー山脈」と言っても実際は複数の山地を連ねた山系で、北は北緯60度に近いカナダ・ブリティッシュコロンビア州最北部から、南は東京23区とほぼ同緯度に位置するアメリカ合衆国ニューメキシコ州の州都サンタフェの近くまで、その長さは4,800kmを超える。
地質学的には、この山脈は褶曲運動により形成された褶曲山脈である。同山脈はアンデス山脈や日本列島などと共に環太平洋火山帯に属している。
山脈の最高峰はアメリカ合衆国コロラド州のエルバート山(4,401m)である。「カナディアン・ロッキー」(Canadian Rockies、Rocheuses canadiennes)と呼ばれるカナダ領内では、ブリティッシュコロンビア州とアルバータ州の州境にそびえるロブソン山(3,954m)が最も高い。
全域にわたって植生や生態系が豊かで、手つかずの自然が残されている地帯も多く、国立公園や世界遺産に登録されている自然遺産も多い。 世界遺産に登録されているのは、バンフ、ジャスパー、クートニィ、ヨーホーの4つの国立公園と、ハンバー、マウント・ロブソン、マウント・アシニボインの3つの州立公園を含めた7つの自然公園である。
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch 3,000 mi (4,800 km)[1] in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico in the Southwestern United States. The northern terminus is located in the Liard River area east of the Pacific Coast Ranges, while the southernmost point is near the Albuquerque area adjacent the Rio Grande Basin and north of the Sandia–Manzano Mountain Range. Located within the North American Cordillera, the Rockies are distinct from the Cascade Range and the Sierra Nevada, which all lie farther to the west.
The Rocky Mountains formed 80 million to 55 million years ago during the Laramide orogeny, in which a number of plates began sliding underneath the North American plate. The angle of subduction was shallow, resulting in a broad belt of mountains running down western North America. Since then, further tectonic activity and erosion by glaciers have sculpted the Rockies into dramatic peaks and valleys. At the end of the last ice age, humans began inhabiting the mountain range. After Europeans, such as Sir Alexander Mackenzie, and Americans, such as the Lewis and Clark expedition, began exploring the range, minerals and furs drove the initial economic exploitation of the mountains, although the range itself never experienced a dense population.
Of the 100 highest peaks in the Rocky Mountains, 78 (including the 30 highest) are located in Colorado, ten in Wyoming, six in New Mexico, three in Montana, and one in Utah. Public parks and forest lands protect much of the mountain range, and they are popular tourist destinations, especially for hiking, camping, mountaineering, fishing, hunting, mountain biking, skiing, and snowboarding.
Les montagnes Rocheuses, ou simplement les Rocheuses, en anglais Rocky Mountains ou Rockies, sont une grande chaîne de montagnes dans l'Ouest de l'Amérique du Nord, sur les territoires des États-Unis et du Canada.
Elles ont représenté un obstacle pour les immigrants américains et canadiens blancs dans l'extension de leur emprise sur le territoire nord-américain à l'occasion de la conquête de l'Ouest.
Le Montagne Rocciose (in inglese Rocky Mountains, spesso denominate semplicemente Rockies) sono una delle più vaste catene montuose della Terra, localizzata nella parte occidentale del Nord America, tra Stati Uniti d'America e Canada.
Si snodano su una lunghezza che supera i 4.800 km, dal nord della Columbia Britannica, in Canada, al Nuovo Messico, negli Stati Uniti. La vetta più alta della catena è il Monte Elbert in Colorado che tocca i 4.401 m sul livello del mare. Anche se fanno parte della Cordigliera del Pacifico del Nord America, le Montagne Rocciose sono distinte invece dalla Catena Costiera del Pacifico che corre immediatamente adiacente sopra la costa dell'Oceano Pacifico.
Il bordo orientale delle Montagne Rocciose s'innalza sopra le Grandi Pianure del Nord America, e su questo versante come sottocatene troviamo il Front Range che va dal nord del Nuovo Messico al nord del Colorado, il Wind River Range e i Monti Big Horn del Wyoming, i Monti Crazy e il Rocky Mountain Front nel Montana, e i Monti Clark in Alberta, insieme ad una serie di catene in Canada chiamate Continental Range. Il Monte Robson nella Columbia Britannica, con i suoi 3954 metri sul livello del mare, è la vetta più elevata delle Montagne Rocciose Canadesi.
Il bordo occidentale delle Montagne Rocciose, come ad esempio i Monti Wasatch a Est di Salt Lake City nello Utah divide il Gran Bacino da altre catene montuose più occidentali. Non si estendono nelle regioni nord-occidentali della Columbia Britannica e pertanto non raggiungono il territorio canadese dello Yukon e l'Alaska. Sono comunemente comprese nell'ampia regione che va dal fiume Liard in Columbia Britannica a nord, fino al Rio Grande nel Nuovo Messico a sud.Una lunga serie di altre catene montuose continuano al di là di questi due fiumi, tra cui i Monti Selwyn nello Yukon, i Monti Mackenzie al confine con i Territori del Nord-Ovest, la Catena dei Monti Brooks nel nord dell'Alaska e la Sierra Madre in Messico, ma non fanno parte delle Montagne Rocciose, anche se sono parte della più ampia Cordigliera americana. Nella definizione statunitense di Montagne Rocciose, tuttavia, vengono incluse anche i monti Cabinet e Salish in Idaho e Montana, mentre le loro controparti a nord del fiume Kootenai, i Monti Columbia che si snodano nelle regioni centro meridionali della Columbia Britannica, sono considerati un sistema separato in Canada.
Las Montañas Rocosas o Rocallosas (Rocky Mountains o Rockies en inglés) es un sistema de cordilleras montañosas situado en el sector occidental de Norteamérica y que corre paralelo a la costa occidental, desde Columbia Británica en el noroeste, pasando por la frontera entre Alberta y Columbia Británica y llegando hasta el suroeste de Estados Unidos, en Nuevo México. El pico más alto es el monte Elbert en Colorado, con 4401 m s. n. m..
Las Montañas Rocosas se formaron durante la orogénesis cenozoica y están constituidas por un núcleo central de rocas cristalinas rodeado de formaciones laterales de rocas sedimentarias; el sistema ha sido marcado profundamente por la glaciación cuaternaria y la erosión atmosférica, y presenta ejemplos de fenómenos volcánicos. Tienen importantes reservas de minerales, como oro, plata, plomo, cinc, cobre y en las regiones marginales petróleo y carbón.
En sus zonas altas se extienden prados de alta montaña; en los valles se dan cultivos agrícolas cereales y patatas; y la ganadería ovina en las regiones septentrionales del sector estadounidense. Atravesadas por muchos ferrocarriles y autopistas que dan valor a sus bellezas naturales (tuteladas por muchos parques nacionales), las Montañas Rocosas constituyen también un notable elemento de atracción turística con muchas localidades de vacaciones y de deportes de invierno.
Скали́стые го́ры (англ. Rocky Mountains) — основной горный хребет в системе Кордильер Северной Америки, на западе США и Канады, между 60 и 32° с. ш.
Скалистые горы тянутся на 4830 километров с севера на юг от самой северной точки в провинции Британская Колумбия (Канада) до штата Нью-Мексико на юго-западе США. Ширина гор достигает 700 километров. Скалистые горы являются естественным водоразделом между бассейнами Тихого и Атлантического океанов. В Скалистых горах берут начало реки Миссури, Колорадо, Рио-Гранде, Снейк, Арканзас и множество других. Скалистые горы образовались от 80 до 55 миллионов лет назад в эру ларамийского орогенеза. С тех пор под воздействием воды и ледников в горной гряде сформировались эффектные долины и пики. В конце последнего ледникового периода люди начали заселять территорию Скалистых гор. После нескольких экспедиций, таких как путешествие Александра Маккензи или экспедиции Льюиса и Кларка, Скалистые горы начали осваиваться; минералы и меха дали начало первоначальному экономическому освоению гор, несмотря на то, что Скалистые горы оставались малонаселённым районом. В настоящее время большая часть территории Скалистых гор защищена национальными парками и лесными угодьями. Скалистые горы — популярное место для туристов, особенно для пешеходного туризма, альпинизма, рыбалки, охоты, лыжного спорта, сноуборда и других.

 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL
 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK

 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Sport
Sport

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

 Wisconsin-WI
Wisconsin-WI

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY
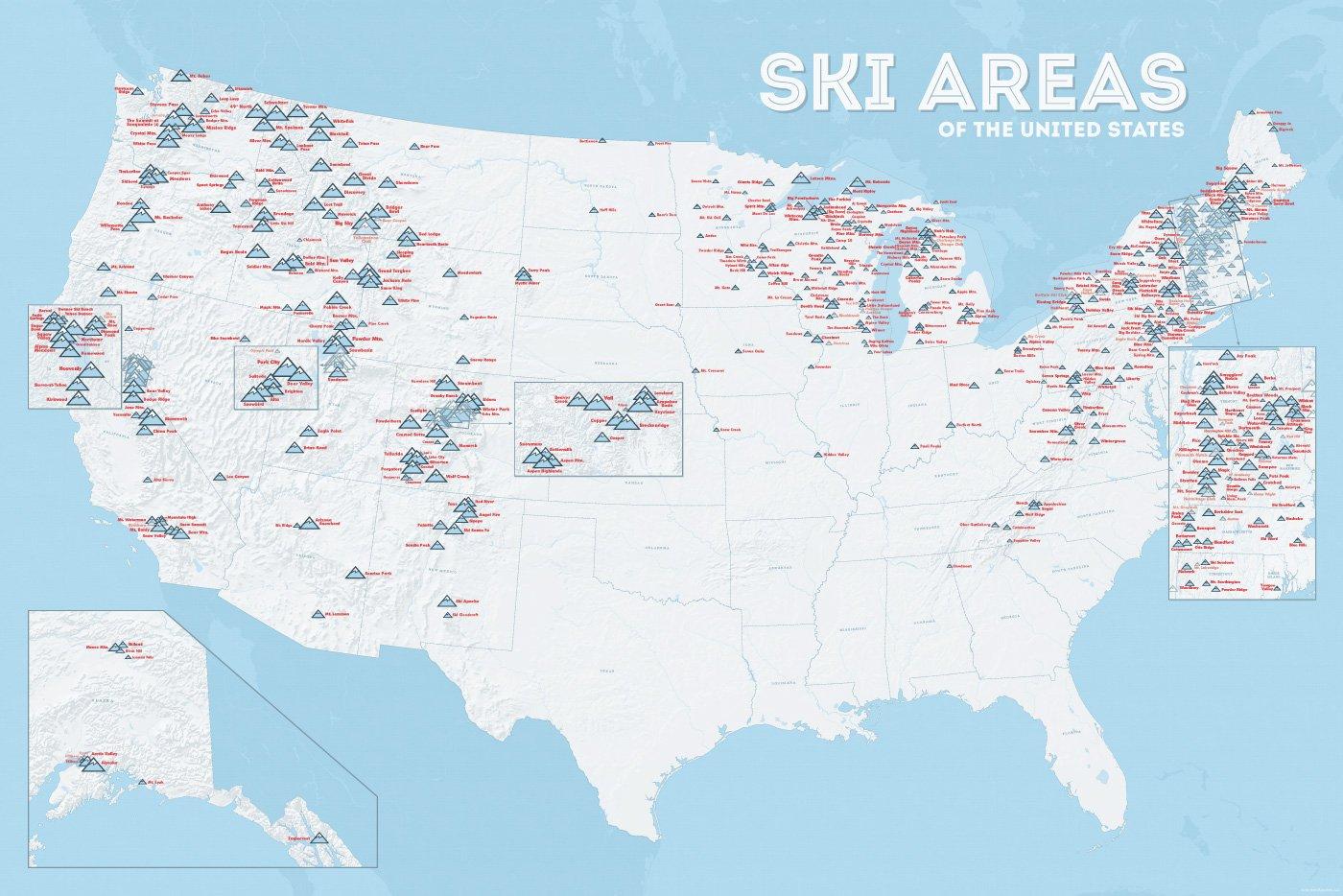
| Name | Orte im Gebiet | Staat | Seehöhe in m |
Liftanlagen1 | Pisten in km |
Weblink | |
| von | bis | ||||||
| Alta Snowbird | Snowbird | Utah | 2365 | 3350 | 1/18/0 | 150 | www.snowbird.com |
| Arapaho Basin | Colorado | 3292 | 3978 | 0/4/0 | 34 | www.arapahoebasin.com | |
| Aspen Highlands | Aspen | Colorado | 2460 | 3536 | 0/5/0 | 58 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Aspen Mountain | Aspen | Colorado | 2422 | 3417 | 1/7/0 | 50 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Aspen Butermilk | Aspen | Colorado | 2398 | 3013 | 0/5/1 | 34 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Aspen Snowmass | Aspen | Colorado | 2473 | 3813 | 2/13/5 | 137 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Beaver Creek Resort | Vail/Beaver Creek | Colorado | 2268 | 3478 | 0/15/8 | 152 | www.beavercreek.com |
| Big Sky Resort | Big Sky Village | Montana | 2072 | 3403 | 2/18/2 | 186 | www.bigskyresort.com |
| Breckenridge | Breckenridge | Colorado | 2926 | 3962 | 1/25/25 | 146 | www.snow.com |
| Deer Valley | Deer Valley | Utah | 2003 | 2918 | 1/20/0 | 105 | www.deervalley.com |
| Grand Targhee | Wyoming | 2438 | 3048 | 0/4/0 | 40 | www.grandtarghee.com | |
| Heavenly | Nevada | 1914 | 3039 | 2/17/6 | 89 | www.heavenly.com | |
| Jackson Hole Mountain | Teton Village | Wyoming | 1924 | 3185 | 3/9/0 | 150 | www.jacksonhole.com |
| Keystone | Keystone | Colorado | 2829 | 3782 | 2/16/16 | 116 | www.snow.com |
| Klamath Falls | Oregon | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | www.oregon.com | |
| Mammoth Mountain | Kalifornien | 2456 | 3362 | 3/23/4 | 112 | www.mammothmountain.com | |
| Park City Mountain | Park City | Utah | 2103 | 3039 | 0/15/0 | 87 | www.parkcitymountain.com |
| Squaw Valley | Squaw Valley | Kalifornien | 1886 | 2664 | 3/26/3 | 88 | www.squaw.com |
| Steamboat | Steamboat Springs | Colorado | 2097 | 3207 | 1/18/0 | 110 | www.steamboat.com |
| Telluride Skiresort | Telluride | Colorado | 2661 | 3735 | 3/11/0 | 98 | www.tellurideskiresort.com |
| The Canyons | Utah | 2061 | 3038 | 2/12/2 | 106 | www.thecanyons.com | |
| Vail | Vail | Colorado | 2450 | 3527 | 1/23/9 | 215 | www.vail.com |

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY

 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK

 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Geography
Geography

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY

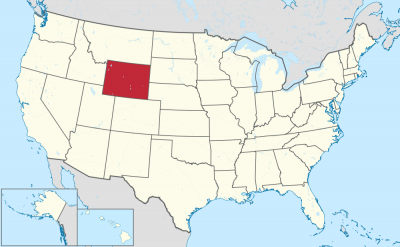


Wyoming (engl. Aussprache [wai̯ˈoʊ̯mɪŋ]) ist mit 579.315 Einwohnern[1][2] (2017) der bevölkerungsärmste Bundesstaat der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika und, nach Alaska, der Bundesstaat mit der zweitgeringsten Bevölkerungsdichte.[3][4] Er liegt im Westen der Vereinigten Staaten und steigt von den Great Plains Ost-Wyomings zu den Rocky Mountains hin an.
Der Name stammt aus der Sprache der Algonkin-Indianer und bedeutet „Große Ebenen“. Er wurde der poetischen Erzählung Gertrude of Wyoming entnommen, die Thomas Campbell 1809 geschrieben hatte.
Der größte Ort ist die Hauptstadt Cheyenne. Der Spitzname ist Equality State nach dem Motto des Staates: „Equal Rights“ (deutsch: gleiche Rechte).
Mit seinen 253.336 km² ist Wyoming flächenmäßig der zehntgrößte Bundesstaat der USA. Nach Colorado ist er mit 2044 m auch der durchschnittlich am zweithöchsten gelegene Staat des Landes. Er befindet sich im westlichen Zentrum des US-Staatsgebiets und zählt somit durch seine Lage (wie auch seine Kultur) zum legendären sogenannten (Wilden) Westen (daher auch der Kosename Cowboy State).
Wyoming erstreckt sich auf einer Breite von 450 km zwischen etwa 41° N und 45° N und einer Länge von 550 bis 580 km zwischen etwa 104° W und 111° W und gehört gemeinsam mit seinen südlichen und westlichen Nachbarstaaten Colorado und Utah zu den Bundesstaaten, deren Grenzen fast ausschließlich nach geographischen Längen- und Breitengraden definiert wurden. Die Grenzziehung entspricht (auf einem entsprechenden Kartennetzentwurf, etwa der Mercator-Projektion) mit geringfügigen Abweichungen einem Rechteck.
Im Prinzip ist das Gebiet von Wyoming ein weites, gebrochenes Plateau, aus dem verschiedene Bergkämme der Rocky Mountains aufragen. Aus einer Querschnittsperspektive gesehen, befindet sich dieses Plateau in einer Schräglage, die von einem höher gelegenen Westen in einen tieferen Osten übergeht. Diese Neigung beschreibt auch den Übergang von den weiten östlichen Ebenen der Prärien über zentrale Beckenlandschaften zum westlich gelegenen Felsengebirge. Wyoming ist ein Staat, der die großen Kulturlandschaften der Great Plains und der Rocky Mountains verbindet – eine Position, die er nur mit drei der 50 weiteren Bundesstaaten teilt: Montana im Norden sowie Colorado und New Mexico im Süden.
Eine weitere geographische Bedeutsamkeit ist Wyomings Lage an der Great Continental Divide, der großen kontinentalen Wasserscheide des nordamerikanischen Kontinents, die die Bundesstaatsfläche in nordwestlich-südöstlicher Richtung durchzieht. Sie verläuft entlang der Absaroka Range und Wind River Ranges und setzt sich im Great Divide Basin, und später der Park Range (großteils in Colorado), fort. Alle Flüsse, die östlich dieser Linie entspringen, entwässern Richtung Osten und münden irgendwann alle in den Missouri River, der in den Mississippi River und schließlich in den Atlantischen Ozean (Golf von Mexiko) fließt. Jene Flüsse, die westlich der Wasserscheide ihren Lauf beginnen, enden im Pazifik (entweder im offenen Ozean, wenn sie dem Columbia River westwärts folgen, oder im Golf von Kalifornien, wenn sie nach Süden in den Green River und später den Colorado River entwässern).
Wyoming kann in drei große geographische Räume gegliedert werden, die alle grob ein Drittel des Staatsgebiets umfassen: die Great Plains, die Intermountain Basins (Gebirgsbecken) und die Rocky Mountains.
ワイオミング州(英: State of Wyoming [waɪˈoʊmɪŋ] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国西部の山岳地域にある州である。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国西部の山岳地域にある州である。
州都はシャイアン市。陸地面積は全米50州の中で第10位だが、人口は563,626人(2010年国勢調査)[1]と全米50州の中で最も少なく[2]、州都シャイアンからわずか160km南にあるコロラド州の州都デンバーを含む、全米の31都市よりも少ない。人口密度は2人/km2で、全米50州の中では、アラスカ州に次いで2番目に低い。ワイオミングとはアルゴンキン語族インディアンの言葉で「大平原」を意味し、州の東側3分の1はハイプレーンズと呼ばれ、広大なグレートプレーンズの西部にあたる標高の高い平原地帯が広がっている。西側3分の2はロッキー山脈東部の山岳地帯と丘陵の牧草地帯である。州の愛称は「平等の州 (Equality State)」、「カウボーイ州 (Cowboy State)」である。
Wyoming (/waɪˈoʊmɪŋ/ (![]() listen)) is a doubly landlocked state in the western United States. The 10th largest state by area, it is also the least populous and second most sparsely populated state in the country. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Colorado to the south, Utah to the southwest, and Idaho to the west. The state population was estimated at 578,759 in 2019, which is less than 31 of the most populous U.S. cities.[6] The state capital and the most populous city is Cheyenne, which had an estimated population of 63,957 in 2018.[7]
listen)) is a doubly landlocked state in the western United States. The 10th largest state by area, it is also the least populous and second most sparsely populated state in the country. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Colorado to the south, Utah to the southwest, and Idaho to the west. The state population was estimated at 578,759 in 2019, which is less than 31 of the most populous U.S. cities.[6] The state capital and the most populous city is Cheyenne, which had an estimated population of 63,957 in 2018.[7]
Wyoming's western half is mostly covered by the ranges and rangelands of the Rocky Mountains, while the eastern half of the state is high-elevation prairie called the High Plains. Almost half of the land in Wyoming is owned by the U.S. government, leading Wyoming to rank sixth by area and fifth by proportion of a state's land owned by the federal government.[8] Federal lands include two national parks—Grand Teton and Yellowstone—two national recreation areas, two national monuments, several national forests, historic sites, fish hatcheries, and wildlife refuges.
Original inhabitants of the region include the Arapaho, Crow, Lakota, and Shoshone. Southwest Wyoming was claimed by the Spanish Empire and then as Mexican territory until it was ceded to the U.S. in 1848 at the end of the Mexican–American War. The region acquired the name "Wyoming" when a bill was introduced to Congress in 1865 to provide a temporary government for the territory of Wyoming. The name had been used earlier for the Wyoming Valley in Pennsylvania, and is derived from the Munsee word xwé:wamənk, meaning "at the big river flat".[9][10]
The main drivers of Wyoming's economy are tourism and extraction of minerals such as coal, oil, natural gas, and trona. Agricultural commodities include livestock, hay, sugar beets, grain (wheat and barley), and wool. The climate is semi-arid and continental, drier and windier than the rest of the country with greater temperature extremes. Wyoming has been a politically conservative state since the 1950s, with the Republican nominee carrying the state in every presidential election since 1968.[11] Donald Trump won it by 46 points in 2016, which was the best performance in the 21st century in the state and Trump's best performance in any state.
Le Wyoming /wi.o.miŋ/ (prononciation en anglais : /waɪ.ˈoʊ.mɪŋ/) est un État de l'Ouest des États-Unis, bordé à l'ouest par l'Idaho, au nord par le Montana, à l'est par le Nebraska et le Dakota du Sud et au sud par le Colorado et l'Utah. Le tiers de l’État est situé dans les Grandes Plaines, mais le Wyoming est montagneux sur tout le reste de son territoire. C'est aussi l'État le moins peuplé des États-Unis avec ses 563 626 habitants. Sa capitale et plus grande ville est Cheyenne.
Il Wyoming è uno Stato degli Stati Uniti, quello con minore popolazione. Confina a nord con il Montana, a est con il Dakota del Sud e il Nebraska, a sud con il Colorado e a ovest con lo Utah e l'Idaho. La capitale dello Stato è Cheyenne. Il nome Wyoming deriva dalla parola in lingua munsee xwé:wamənk che significa presso il grande fiume calmo usata in origine per denominare la Wyoming Valley in Pennsylvania.
Wyoming (pronunciación en inglés: /waɪˈoʊmɪŋ/ (![]() escuchar)) es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Cheyenne (63 335 habs. en 2015). Está ubicado en la región Oeste del país, división Montañas Rocosas, limitando al norte con Montana, al este con Dakota del Sur y Nebraska, al sur con Colorado, al suroeste con Utah y al oeste con Idaho.
escuchar)) es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Cheyenne (63 335 habs. en 2015). Está ubicado en la región Oeste del país, división Montañas Rocosas, limitando al norte con Montana, al este con Dakota del Sur y Nebraska, al sur con Colorado, al suroeste con Utah y al oeste con Idaho.
Con 586 107 habitantes en 2015 es el estado menos poblado, con 253 336 km², el décimo más extenso —por detrás de Alaska, Texas, California, Montana, Nuevo México, Arizona, Nevada, Colorado y Oregón— y con 2,2 hab/km², el segundo menos densamente poblado, por detrás de Alaska. Fue admitido en la Unión el 10 de julio de 1890, como el estado número 44.2 Con una tasa de 449 empleados cada 10 000 habs., es el estado con mayor proporción de empleo público no federal del país.3
Dos tercios del territorio oeste están cubiertos, mayormente, por las sierras y montañas de las Montañas Rocosas, mientras que el resto este del estado son praderas de grandes alturas sobre el nivel del mar conocidas como High Plains. Casi la mitad de la tierra de Wyoming es propiedad del gobierno estadounidense, haciendo de Wyoming el sexto estado con mayor número de acres en manos del gobierno federal. Estas tierras federales incluyen dos parques nacionales —Grand Teton y Yellowstone— dos áreas recreativas nacionales, dos monumentos nacionales, así como varios bosques nacionales, sitios históricos, zonas de pescas y áreas protegidas para la vida silvestre.
Las naciones indias Crow, Arapajó, Lakota y Shoshón son algunos de los pobladores originales de la región. La región suroeste del estado fue incluida en el Imperio Español y, consecuentemente, en territorio mexicano, hasta que fue cedido a los Estados Unidos en 1848 como resultado de la intervención estadounidense en México. La región adquirió el nombre de Wyoming cuando un proyecto de ley fue introducido al Congreso en 1865 para proveer "un gobierno temporal al territorio de Wyoming". El territorio fue nombrado por el Valle de Wyoming en Pensilvania, siendo el nombre derivado de la palabra xwé:wamənk, en idioma munsee, que significa "en el gran río plano".45
La industria de extracción de minerales—especialmente carbón, petróleo, gas natural y trona—junto con el turismo son los principales motores de la economía de Wyoming. La agricultura ha sido históricamente un importante componente de la economía del estado. El clima es generalmente semiárido y continental, siendo más seco y con más vientos que el resto de los Estados Unidos, con temperaturas extremas comunes.
Exceptuando las elecciones de 1964, Wyoming ha sido un estado políticamente conservador desde la década de 1950, con el Partido Republicano ganando todas las elecciones presidenciales en el estado desde entonces.
Вайо́минг[1][2] (англ. Wyoming, американское произношение: [waɪˈoʊmɪŋ] (![]() слушать)) — штат[3] на западе США, входящий в группу так называемых Горных штатов. Столица и крупнейший город — Шайенн. Официальное прозвище — «Штат равноправия» (англ. Equality State). Официальный девиз — «Равные права» (англ. Equal Rights). Занимает в государстве последнее место по численности населения.
слушать)) — штат[3] на западе США, входящий в группу так называемых Горных штатов. Столица и крупнейший город — Шайенн. Официальное прозвище — «Штат равноправия» (англ. Equality State). Официальный девиз — «Равные права» (англ. Equal Rights). Занимает в государстве последнее место по численности населения.
 *Capitols in the United States
*Capitols in the United States
 *United States Political System
*United States Political System

 Architecture
Architecture
 Neo-Renaissance architecture
Neo-Renaissance architecture
 United States
United States

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY
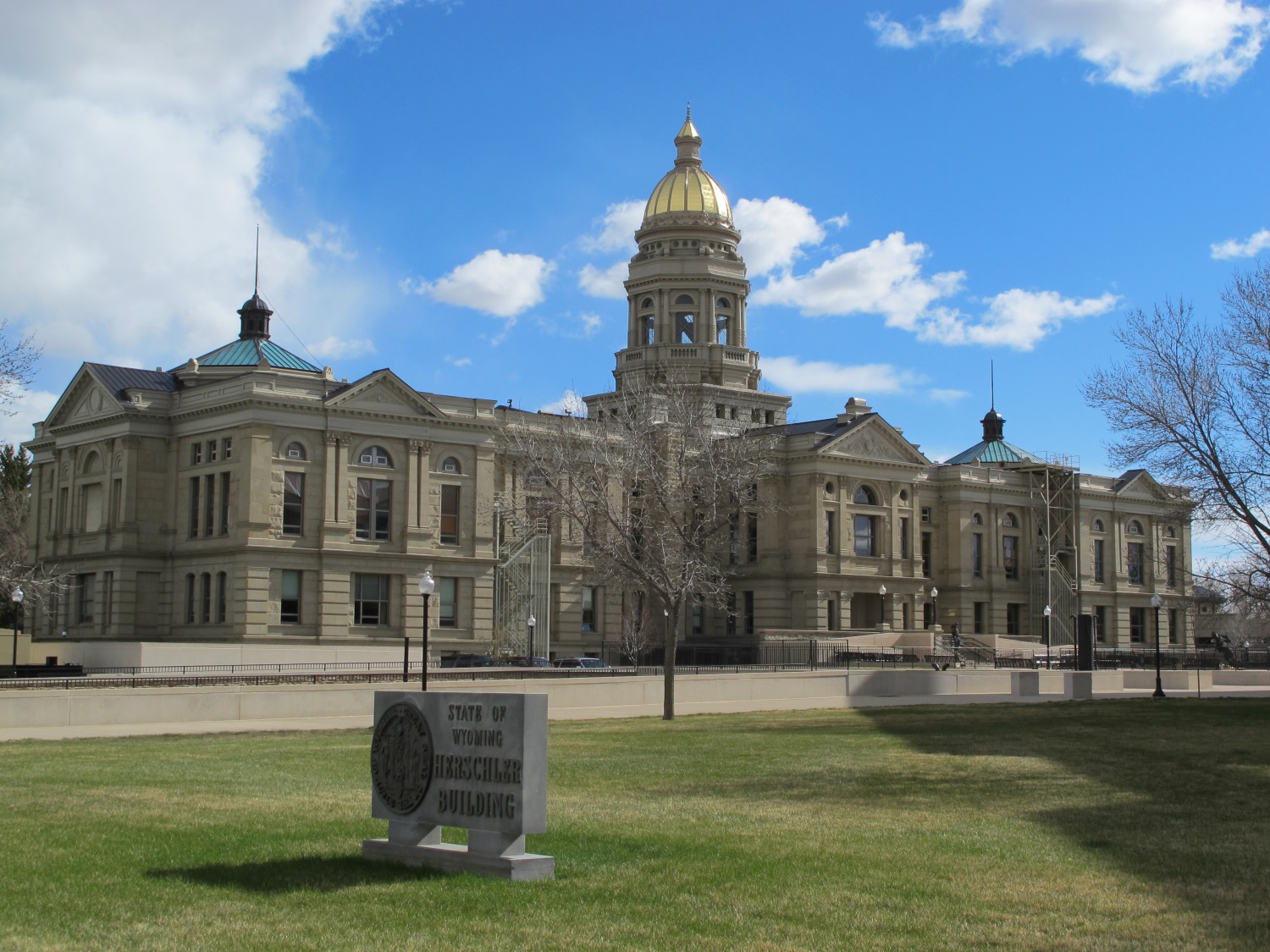

黄石国家公园(简称黄石公园,英语:Yellowstone National Park)是美国第一个国家公园。主要位于怀俄明州,部分位于蒙大拿州和爱达荷州,于1872年3月1日美国总统尤利西斯·辛普森·格兰特签署国会通过的法案后建立[4][5],是世界上第一个国家公园[6]。黄石公园以其丰富的野生动物种类和地热资源闻名,老忠实间歇泉更是其中最富盛名的景点之一[7]。公园中有着多种类型的生态系统,其中以亚高山带森林为主。
美洲原住民已经在黄石公园地区生活了至少1万1千年[8],19世纪早期的刘易斯与克拉克远征也绕过了这一区域。对该地区的有组织的勘探活动直到1860年代末才开始出现,此前只有一些选择在野外捕猎和居住的山地人在19世纪早期到中叶曾偶尔进入。美国陆军在公园刚刚建立后就受委托对其进行监管。1917年后,公园的管理工作移交给了之前一年刚刚成立的美国国家公园管理局。园中有数以百计因其建筑学和历史学意义而保护起来的建筑物,研究人员已经发现了超过1000个考古遗迹。
黄石国家公园占地面积约为8983平方千米[1],其中包括湖泊、峡谷、河流和山脉[7]。公园内最大的湖泊是位于黄石火山中心的黄石湖,是整个北美地区最大的高海拔湖泊之一。黄石火山是北美最大且仍处于活跃状态的超级火山,在过去两百万年中它曾数次以巨大的力量爆发[9]。喷出的熔岩和火山灰也覆盖了公园内的绝大部分地区。得益于其持续的活跃状态,世界上的地热资源有半数位于黄石公园地区[10]。黄石公园也是大黄石生态系统的核心所在,这是北温带地区现存最大且仍然近乎完好的自然生态系统[11]。
公园内有记录的哺乳动物、 鸟类、鱼类和爬行动物有数百种之多,其中包括多种濒危或受威胁物种[7],广袤的森林和草原中同样存有多种独特的植物。黄石公园是美国本土最大和最著名的巨型动物居住地。公园中有灰熊、狼、美洲野牛和加拿大马鹿的栖息地。黄石公园野牛群是美国最古老也最大的野牛群。公园内每年都会发生山火,其中最大的一次是1988年黄石公园大火,公园内近三分之一的面积被烧毁。黄石公园也是休闲娱乐的好去处,园内可进行远足、露营、划船、钓鱼、度假和观光等活动。沿着园内铺设的道路可以就近接触到主要的地热区域以及一些湖泊和瀑布。冬天,游客们则往往会在导游指引下乘坐雪上摩托车等冰上交通工具来造访公园。
イエローストーン国立公園(イエローストーンこくりつこうえん、Yellowstone National Park)はアイダホ州、モンタナ州、及びワイオミング州に位置するアメリカ合衆国の国立公園である。1872年に世界初の国立公園に指定されており [1]、ワイオミング州北西部を中心として3,470平方マイル(8,980㎢)にわたる。この国立公園には様々な間欠泉や温泉、地熱による観光スポットが散在していることで有名であるが、グリズリーやオオカミ、アメリカバイソン(バッファロー)やワピチ(エルク)の群れが生息していることでも知られる。ここは地上に残された数少ない手付かずの巨大温帯生態系の一つであるイエローストーン圏生態系 (Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem) の中心になっている。アメリカで最も人気のある国立公園で、2015年には410万人の観光客が訪れた。
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in Wyoming, Montana, and Idaho. It was established by the U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Ulysses S. Grant on March 1, 1872.[5][6] Yellowstone was the first national park in the U.S. and is also widely held to be the first national park in the world.[7] The park is known for its wildlife and its many geothermal features, especially Old Faithful geyser, one of its most popular features.[8] It has many types of ecosystems, but the subalpine forest is the most abundant. It is part of the South Central Rockies forests ecoregion.
Native Americans have lived in the Yellowstone region for at least 11,000 years.[9] Aside from visits by mountain men during the early-to-mid-19th century, organized exploration did not begin until the late 1860s. Management and control of the park originally fell under the jurisdiction of the Secretary of the Interior, the first being Columbus Delano. However, the U.S. Army was subsequently commissioned to oversee management of Yellowstone for a 30-year period between 1886 and 1916.[10] In 1917, administration of the park was transferred to the National Park Service, which had been created the previous year. Hundreds of structures have been built and are protected for their architectural and historical significance, and researchers have examined more than a thousand archaeological sites.
Yellowstone National Park spans an area of 3,468.4 square miles (8,983 km2),[2] comprising lakes, canyons, rivers and mountain ranges.[8] Yellowstone Lake is one of the largest high-elevation lakes in North America and is centered over the Yellowstone Caldera, the largest supervolcano on the continent. The caldera is considered an active volcano. It has erupted with tremendous force several times in the last two million years.[11] Half of the world's geysers[12][13] and hydrothermal features[14] are in Yellowstone, fueled by this ongoing volcanism. Lava flows and rocks from volcanic eruptions cover most of the land area of Yellowstone. The park is the centerpiece of the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, the largest remaining nearly-intact ecosystem in the Earth's northern temperate zone.[15] In 1978, Yellowstone was named a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Hundreds of species of mammals, birds, fish, and reptiles have been documented, including several that are either endangered or threatened.[8] The vast forests and grasslands also include unique species of plants. Yellowstone Park is the largest and most famous megafauna location in the contiguous United States. Grizzly bears, wolves, and free-ranging herds of bison and elk live in this park. The Yellowstone Park bison herd is the oldest and largest public bison herd in the United States. Forest fires occur in the park each year; in the large forest fires of 1988, nearly one third of the park was burnt. Yellowstone has numerous recreational opportunities, including hiking, camping, boating, fishing and sightseeing. Paved roads provide close access to the major geothermal areas as well as some of the lakes and waterfalls. During the winter, visitors often access the park by way of guided tours that use either snow coaches or snowmobiles.
Le parc national de Yellowstone (en anglais : Yellowstone National Park) est un parc national des États-Unis, ainsi qu'un site du patrimoine mondial protégé par l'UNESCO, couvrant trois États au nord-ouest du Wyoming, au sud-est de l'Idaho (en bordure de la forêt nationale de Caribou-Targhee) et au sud-ouest du Montana (adjacent à la forêt nationale de Gallatin). Créé le 1er mars 1872 par le président Ulysses S. Grant, Yellowstone est le plus ancien parc national du monde2. Il s'étend sur 8 983 km2 (898 300 hectares), soit une superficie plus importante que celle de la Corse.
Il constitue le deuxième plus grand parc naturel des États-Unis hormis ceux localisés en Alaska. La caldeira de Yellowstone est célèbre pour ses phénomènes géothermiques ; il contient deux tiers des geysers de la planète et de nombreuses sources chaudes3. L'une des figures emblématiques du parc est le geyser « Old Faithful ». Le parc abrite aussi de nombreux grands mammifères comme des ours noirs, des grizzlys, des coyotes, des loups, des orignaux, des cerfs ou encore des troupeaux sauvages de bisons et de wapitis. Il constitue le cœur d'un vaste habitat naturel préservé, l'un des derniers écosystèmes relativement intacts des zones tempérées. Parmi les différents écosystèmes du parc, la forêt subalpine domine. Il est inscrit sur la liste des réserves de biosphère de l'UNESCO en 19764 et au Patrimoine mondial depuis 19785. Il reçoit chaque année la visite d'environ trois millions de personnes6, ce qui en fait l'un des parcs nationaux américains les plus fréquentés.
Il Parco nazionale di Yellowstone (Yellowstone National Park) si trova negli Stati Uniti d'America e più precisamente nell'estremo settore nord-occidentale dello Stato del Wyoming e sconfina, per un piccolo tratto, negli Stati del Montana (a Nord) e dell'Idaho (a Ovest)[1], occupando un'ampia zona delle Montagne Rocciose[2].
Il nome Yellowstone (pietra gialla) deriva dai fenomeni vulcanici attivi e la pietra gialla probabilmente deriva dallo zolfo presente in zona.
È il nucleo centrale del Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, uno dei più grandi ecosistemi intatti della zona temperata rimasto sulla Terra, oltre ad essere il più antico Parco nazionale del mondo (fondato nel 1872 durante la presidenza di Ulysses S. Grant) e la più grande area protetta statunitense e, dal 1978, dichiarato Patrimonio dell'umanità dall'Unesco.
Nel 2015, il Parco è stato visitato da più di 4.000.000 di persone[3].
El parque nacional de Yellowstone (en inglés: Yellowstone National Park) fue creado por el Congreso de los Estados Unidos y convertido en ley por el entonces presidente Ulysses S. Grant el 1 de marzo de 1872,23 es un parque nacional ubicado en los Estados Unidos, principalmente en el estado de Wyoming, aunque se extiende por Montana e Idaho. Yellowstone, el primer parque nacional de los Estados Unidos, también se considera ampliamente el parque nacional más antiguo del mundo.4 Se encuentra encima de la caldera del mayor volcán de América, muy vivo pero sin erupción desde hace 640 000 años. Consecuencia son sus numerosos fenómenos geotérmicos, especialmente el géiser Old Faithful, una de sus atracciones más populares.5 Es famoso también por su diversidad en fauna, beneficiada por la prohibición de caza durante los últimos 150 años. A pesar de que posee múltiples ecosistemas, domina el bosque subalpino.
Los nativos americanos vivieron en la región de Yellowstone al menos durante 11 000 años.6 La expedición de Lewis y Clark, a principios del siglo XIX, circunvaló la región. Aparte de las visitas de los mountain men a mediados del siglo XIX, las exploraciones organizadas no comenzaron hasta la década de 1860. La armada de los Estados Unidos fue comisionada para supervisar el parque desde su establecimiento. En 1917, la administración del parque se transfirió al Servicio de Parques Nacionales, creado el año anterior. Desde entonces, se han construido y protegido cientos de estructuras, tanto por su importancia arquitectónica como histórica. Los investigadores estiman que hay más de 1000 sitios arqueológicos.
El parque nacional de Yellowstone se extiende en un área de 8983 km².7 Comprende lagos, cañones, ríos y cadenas montañosas.5 El lago Yellowstone es el lago de montaña más grande de América del Norte y su mitad meridional se encuentra la Caldera Yellowstone, el supervolcán más grande del continente, considerado un volcán activo. Se tienen datos de que al menos en los últimos millones de años ha entrado en erupción con una fuerza tremenda en varias ocasiones.8 Al menos la mitad de las atracciones geotermales del mundo se localizan en Yellowstone, provocadas por su fuerte y consistente actividad volcánica.9 Los flujos de lava y rocas emanados por las erupciones volcánicas cubren la mayor parte del área de Yellowstone. El parque es el centro del Gran Ecosistema de Yellowstone, el más grande ecosistema restante y casi intacto en la zona norte de la Tierra.10
Se han documentado cientos de especies de mamíferos, aves, peces y reptiles, incluyendo muchos en peligro o amenaza de extinción.5 Los vastos bosques y pastizales también incluyen especies únicas de plantas. El parque Yellowstone es el lugar más extenso con la megafauna más famosa en los Estados Unidos continentales. Osos grizzly, lobos, manadas de bisontes y alces pastan libremente y viven en el parque. El rebaño de bisontes del Yellowstone Park es el rebaño de bisontes más grande y antiguo abierto al público en los Estados Unidos.
A pesar de medidas de protección, los incendios forestales ocurren en el parque casi todos los años, tal y como el incendio de Yellowstone de 1988, donde casi un tercio del parque se quemó. Yellowstone tiene numerosas actividades recreacionales, que incluyen alpinismo, acampadas, paseos en bote, pesca y avistamientos de su fauna. Los caminos pavimentados proveen acceso cercano a las áreas de mayor actividad geotérmica, así como a algunos de los lagos y cataratas. Durante el invierno, a menudo los visitantes acceden al parque con paseos guiados en los que se usan vehículos para la nieve o motonieve.
Йе́ллоустонский национа́льный парк[3][4][5][6], Йе́ллоустон (англ. Yellowstone National Park) — международный биосферный заповедник, объект Всемирного Наследия ЮНЕСКО, первый в мире национальный парк (основан 1 марта 1872 года). Находится в США, на территории штатов Вайоминг, Монтана и Айдахо. Парк знаменит многочисленными гейзерами и другими геотермическими объектами, богатой живой природой, живописными ландшафтами. Площадь парка — 898,3 тыс. га.
Согласно археологическим данным люди начали жить на территории, занимаемой парком, 11 000 лет назад. Современные исследователи впервые появились в регионе в 1805 году (участники экспедиции Льюиса и Кларка), но до 1860-х годов здесь не проводилось никакой хозяйственной или научной деятельности. В первые годы после возникновения парка он находился под управлением армии США, а в 1917 году управление было передано созданной за два года до этого Службе национальных парков.
На огромной территории парка находятся озёра, реки, каньоны и пещеры. Озеро Йеллоустон, одно из самых больших высокогорных озёр в Северной Америке, расположено в центре Йеллоустоунской кальдеры, самого большого супервулкана на континенте. Кальдера считается дремлющим супервулканом; он извергался с огромной силой несколько раз за последние два миллиона лет. Большая часть территории парка покрыта застывшей лавой; в парке находится одно из пяти существующих в мире гейзерных полей.
В парке растёт около двух тысяч видов растений, встречаются несколько сотен видов млекопитающих, птиц, пресмыкающихся и рыб, в том числе находящихся под угрозой уничтожения. Большая часть территории покрыта лесом, меньшая — степью. Каждый год случаются лесные пожары; около трети всех лесов выгорело в результате катастрофических пожаров 1988 года. В парке проложено несколько сот километров асфальтовых дорог, по которым осуществляется доступ посетителей. Имеются многочисленные возможности для активного отдыха.
 History
History
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Ski vacation
Ski vacation
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Animal world
Animal world
