
English Encyclopedia
 Sport
Sport


The 2022 World Athletics Championships, the eighteenth edition of the World Athletics Championships, are scheduled to be held in 2022 in Eugene, Oregon, United States.[1][2][3] It was originally scheduled for August 6–15, 2021. However, the postponement of the 2020 Summer Olympics prompted the need for postponement into 2022.[4] On April 8, 2020, World Athletics announced that the event would take place from July 15–24, 2022.
 America´s Cup 2017
America´s Cup 2017
 Australia
Australia

 California-CA
California-CA

 China
China

 Valencian Community
Valencian Community
 England
England
 France
France
 Greece
Greece

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Kyūshū
Kyūshū
 New Zealand
New Zealand

 New York-NY
New York-NY
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI
 Russia
Russia

 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 Sweden
Sweden
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport
 America´s Cup
America´s Cup

 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Western Australia-WA
Western Australia-WA

The America's Cup, affectionately known as the Auld Mug, is a trophy awarded to the winner of the America's Cup match races between two sailing yachts. One yacht, known as the defender, represents the yacht club that currently holds the America's Cup and the second yacht, known as the challenger, represents the yacht club that is challenging for the cup. The timing of each match is determined by an agreement between the defender and the challenger. The America's Cup is the oldest international sporting trophy.[1][2][3] It will next be raced for in the southern summer, in the early part of 2021.[4]
The cup was originally awarded in 1851 by the Royal Yacht Squadron for a race around the Isle of Wight in the United Kingdom, which was won by the schooner America. The trophy, originally named the '£100 Cup', was renamed the America's Cup after the yacht and was donated to the New York Yacht Club (NYYC) under the terms of the Deed of Gift, which made the cup available for perpetual international competition.
Any yacht club that meets the requirements specified in the deed of gift has the right to challenge the yacht club that holds the cup. If the challenging club wins the match, it gains stewardship of the cup.
The history and prestige associated with the America's Cup attracts not only the world's top sailors and yacht designers but also the involvement of wealthy entrepreneurs and sponsors. It is a test not only of sailing skill and boat and sail design, but also of fundraising and management skills.
The trophy was held by the NYYC from 1857 (when the syndicate that won the cup donated the trophy to the club) until 1983. The NYYC successfully defended the trophy twenty-four times in a row before being defeated by the Royal Perth Yacht Club, represented by the yacht Australia II. The NYYC's reign was the longest winning streak (in terms of date) in the history of all sports.[5]
From the first defence of the cup in 1870 through the twentieth defence in 1967, there was always only one challenger. In 1970, for the first time, there were multiple challengers, so the NYYC agreed that the challengers could run a selection series with the winner becoming the official challenger and competing against the defender in the America's Cup match. Since 1983, Louis Vuitton has sponsored the Louis Vuitton Cup as a prize for the winner of the challenger selection series.
Early matches for the cup were raced between yachts 65–90 ft (20–27 m) on the waterline owned by wealthy sportsmen. This culminated with the J-Class regattas of the 1930s. After World War II and almost twenty years without a challenge, the NYYC made changes to the deed of gift to allow smaller, less expensive 12-metre class yachts to compete; this class was used from 1958 until 1987. It was replaced in 1990 by the International America’s Cup Class which was used until 2007.
After a long legal battle, the 2010 America's Cup was raced in 90 ft (27 m) waterline multihull yachts in a best of three "deed of gift" match in Valencia, Spain. The victorious Golden Gate Yacht Club then elected to race the 2013 America's Cup in AC72 foiling, wing-sail catamarans. Golden Gate Yacht Club successfully defended the cup. The 35th America's Cup match was announced to be sailed in 50 ft foiling catamarans.[6]
The history of the America's Cup has included legal battles and disputes over rule changes including most recently over the rule changes for the 2017 America's Cup.[7]
The America's Cup is currently held by the Royal New Zealand Yacht Squadron,[8] who will stage the 36th defence of the Cup in 2021.
 American Football Conference AFC
American Football Conference AFC
 North
North
 American Football Conference AFC
American Football Conference AFC
 East
East
 American Football Conference AFC
American Football Conference AFC
 South
South
 American Football Conference AFC
American Football Conference AFC
 West
West
 National Football League 2015
National Football League 2015
 National Football League 2016
National Football League 2016
 National Football League 2017
National Football League 2017
 National Football League 2018
National Football League 2018
 American Football Conference,AFC
American Football Conference,AFC

The American Football Conference (AFC) is one of the two conferences of the National Football League (NFL), the highest professional level of American football in the United States. This conference currently contains 16 teams organized into 4 divisions, as does its counterpart, the National Football Conference (NFC). Both conferences were created as part of the 1970 merger between the National Football League, and the American Football League (AFL). All ten of the AFL teams, and three NFL teams, became members of the new AFC, with the remaining thirteen NFL teams forming the NFC. A series of league expansions and division realignments have occurred since the merger, thus making the current total of 16 teams in each conference. The current AFC champions are the Kansas City Chiefs, who defeated the Buffalo Bills in the 2020 AFC Championship Game for their second consecutive conference championship.

The American Hockey League (AHL) is a professional ice hockey league based in the United States and Canada that serves as the primary developmental league for the National Hockey League (NHL).[2] Since the 2010–11 season, every team in the league has an affiliation agreement with one NHL team. When NHL teams do not have an AHL affiliate, players are assigned to AHL teams affiliated with other NHL teams. Twenty-six AHL teams are located in the United States and the remaining five are in Canada. The league offices are located in Springfield, Massachusetts, and its current president is Scott Howson.[3]
In general, a player must be at least 18 years of age to play in the AHL or not currently be beholden to a junior ice hockey team. The league limits the number of experienced professional players on a team's active roster during any given game; only five skaters can have accumulated four full seasons of play or more at the professional level (goaltenders are exempt from this rule and can stay in the AHL indefinitely without being subject to this cap).[4] The AHL allows for practice squad contracts.[5]
The annual playoff champion is awarded the Calder Cup, named for Frank Calder, the first President (1917–1943) of the NHL. The most recent champions are the Charlotte Checkers in 2019 as the Calder Cup playoffs were not held in 2020 or 2021.
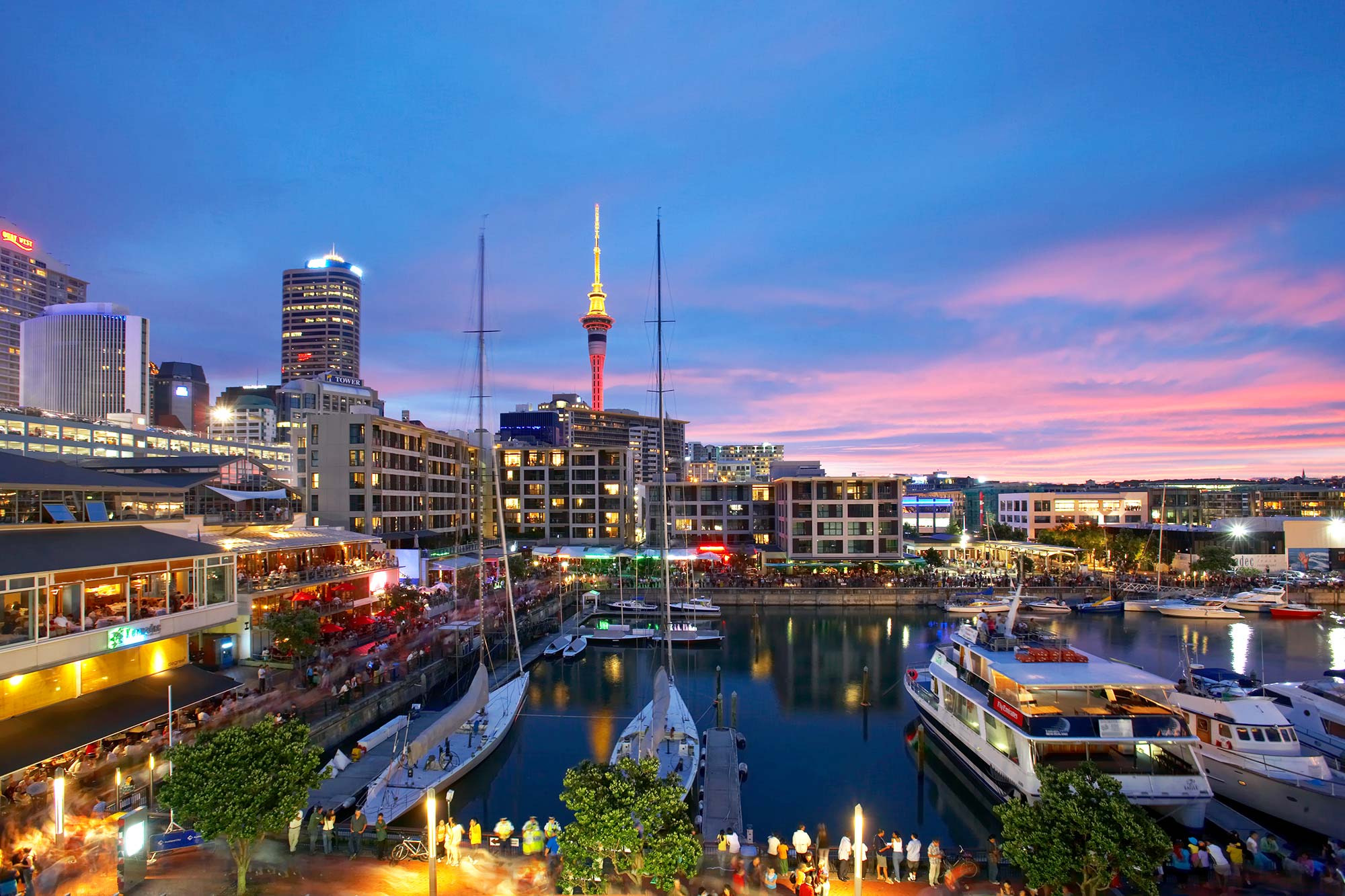

Auckland (Māori: Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country, Auckland has an urban population of about 1,463,000 (June 2021).[4] It is located in the Auckland Region—the area governed by Auckland Council—which includes outlying rural areas and the islands of the Hauraki Gulf, and which has a total population of 1,715,600.[4] While Europeans continue to make up the plurality of Auckland's population, the city became multicultural and cosmopolitan in the late-20th century, with Asians accounting for 31% of the city's population in 2018.[6] Auckland is also home to the largest Polynesian population in the world.[7] The Māori-language name for Auckland is Tāmaki Makaurau, meaning "Tāmaki desired by many", in reference to the desirability of its natural resources and geography.[8]
Auckland lies between the Hauraki Gulf to the east, the Hunua Ranges to the south-east, the Manukau Harbour to the south-west, and the Waitākere Ranges and smaller ranges to the west and north-west. The surrounding hills are covered in rainforest and the landscape is dotted with 53 volcanic centres that make up the Auckland Volcanic Field. The central part of the urban area occupies a narrow isthmus between the Manukau Harbour on the Tasman Sea and the Waitematā Harbour on the Pacific Ocean. Auckland is one of the few cities in the world to have a harbour on each of two separate major bodies of water.
The isthmus on which Auckland sits was first settled c. 1350 and was valued for its rich and fertile land. The Māori population in the area is estimated to have peaked at 20,000 before the arrival of Europeans.[9] After a British colony was established in New Zealand in 1840, William Hobson, then Lieutenant-Governor of New Zealand, chose Auckland as its new capital. He named the area for George Eden, Earl of Auckland, British First Lord of the Admiralty. Māori–European conflict over land in the region led to war in the mid-19th century. In 1865, Auckland was replaced by Wellington as the capital, but continued to grow, initially because of its port and the logging and gold-mining activities in its hinterland, and later because of pastoral farming (especially dairy farming) in the surrounding area, and manufacturing in the city itself.[10] It has been the nation's largest city throughout most of its history. Today, Auckland's central business district is New Zealand's leading economic hub.
The University of Auckland, founded in 1883, is the largest university in New Zealand. The city's significant tourist attractions include national historic sites, festivals, performing arts, sports activities, and a variety of cultural institutions, such as the Auckland War Memorial Museum, the Museum of Transport and Technology, and the Auckland Art Gallery Toi o Tāmaki. Its architectural landmarks include the Harbour Bridge, the Town Hall, the Ferry Building and the Sky Tower. The city is served by Auckland Airport, which handles around 2 million international passengers a month. Despite being one of the most expensive cities in the world,[11] Auckland is recognised as one of the world's most liveable cities, ranking third in the 2019 Mercer Quality of Living Survey and at first place in a 2021 ranking of the global liveability index by The Economist.
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2010
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2010

 International cities
International cities
 *World Design Capital
*World Design Capital
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport
 The Ocean Race
The Ocean Race
 South Africa
South Africa

 Important port
Important port
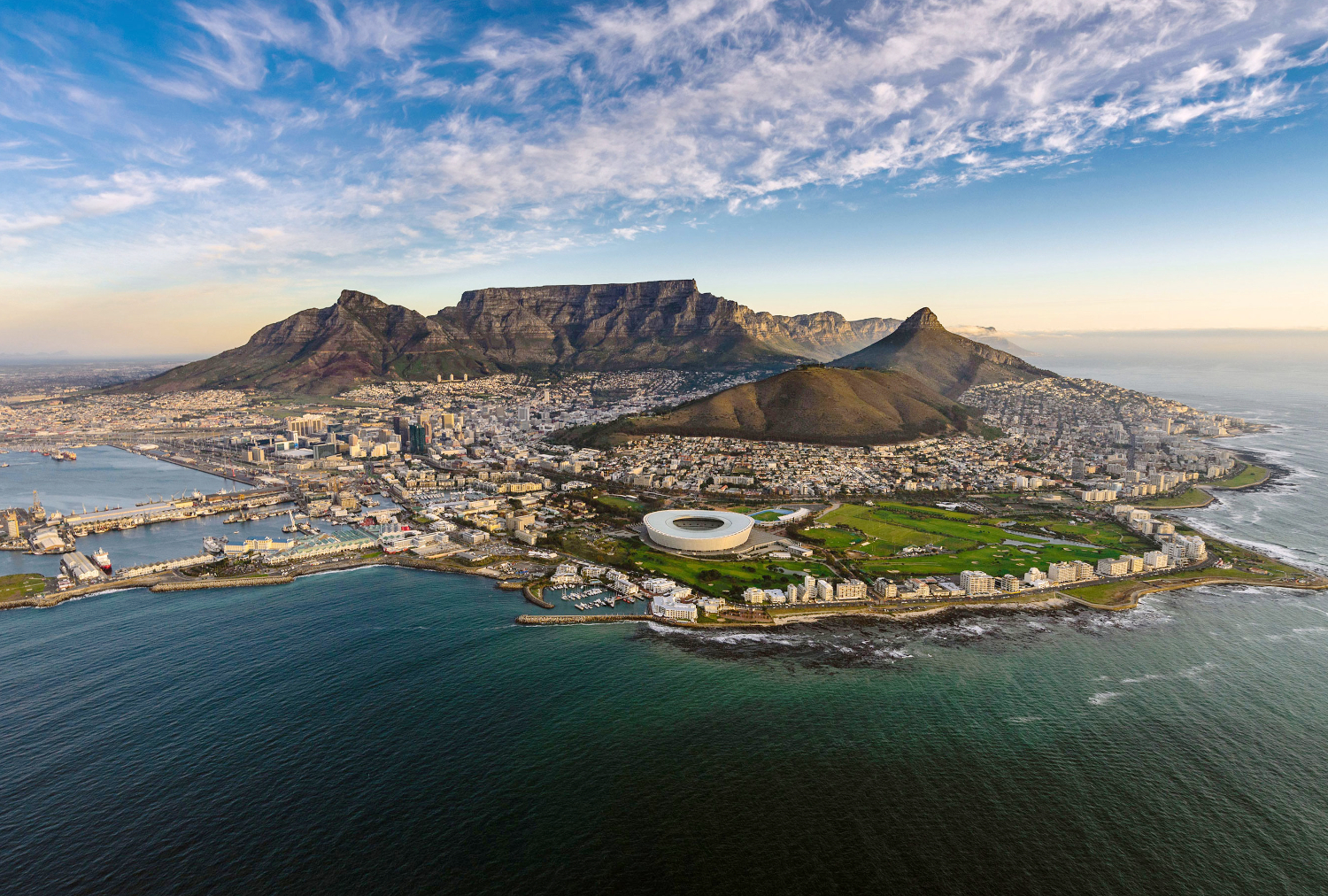

Cape Town (Afrikaans: Kaapstad [ˈkɑːpstat]; Xhosa: iKapa; Dutch: Kaapstad; South Sotho: Motse Kapa) is the oldest city in South Africa, colloquially named the Mother City. It is the legislative capital of South Africa and primate city of the Western Cape province.[7] It forms part of the City of Cape Town metropolitan municipality.
The Parliament of South Africa sits in Cape Town.[8] The other two capitals are located in Pretoria (the administrative capital where the Presidency is based) and Bloemfontein (the judicial capital where the Supreme Court of Appeal is located).[9] The city is known for its harbour, for its natural setting in the Cape Floristic Region, and for landmarks such as Table Mountain and Cape Point. Cape Town is home to 64% of the Western Cape's population.[10] It is one of the most multicultural cities in the world, reflecting its role as a major destination for immigrants and expatriates to South Africa.[11] The city was named the World Design Capital for 2014 by the International Council of Societies of Industrial Design.[12] In 2014, Cape Town was named the best place in the world to visit by both The New York Times[13] and The Daily Telegraph.[14]
Located on the shore of Table Bay, Cape Town, as the oldest urban area in South Africa, was developed by the Dutch East India Company (VOC) as a supply station for Dutch ships sailing to East Africa, India, and the Far East. Jan van Riebeeck's arrival on 6 April 1652 established Dutch Cape Colony, the first permanent European settlement in South Africa. Cape Town outgrew its original purpose as the first European outpost at the Castle of Good Hope, becoming the economic and cultural hub of the Cape Colony. Until the Witwatersrand Gold Rush and the development of Johannesburg, Cape Town was the largest city in South Africa.
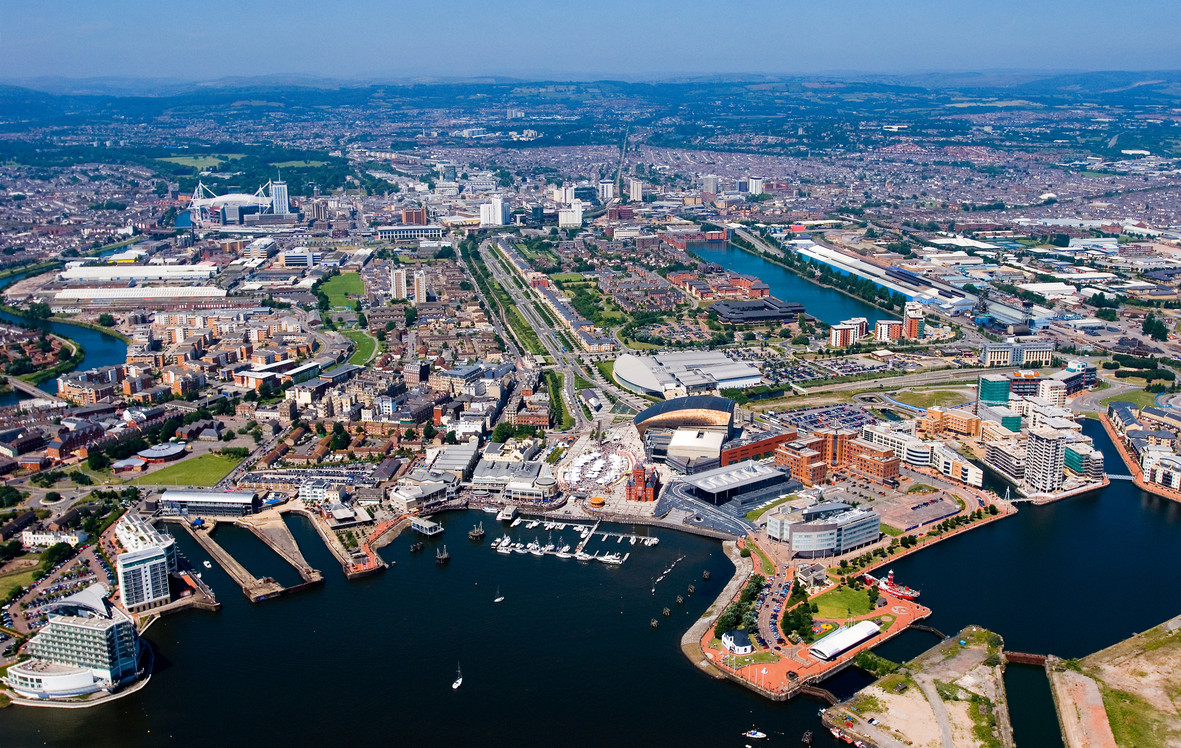

Cardiff (/ˈkɑːrdɪf/ ( listen); Welsh: Caerdydd [kairˈdiːð, kɑːɨrˈdɨːð] (
listen); Welsh: Caerdydd [kairˈdiːð, kɑːɨrˈdɨːð] ( listen)) is the capital of, and largest city in, Wales, and the eleventh-largest city in the United Kingdom. It is Wales's chief commercial centre, the base for most national cultural and sporting institutions, the Welsh national media, and the seat of the National Assembly for Wales. The unitary authority area's 2017 population was estimated to be 362,756.[1] Cardiff is a significant tourist centre and the most popular visitor destination in Wales with 21.3 million visitors in 2017.[5] In 2011, Cardiff was ranked sixth in the world in National Geographic's alternative tourist destinations.[6]
listen)) is the capital of, and largest city in, Wales, and the eleventh-largest city in the United Kingdom. It is Wales's chief commercial centre, the base for most national cultural and sporting institutions, the Welsh national media, and the seat of the National Assembly for Wales. The unitary authority area's 2017 population was estimated to be 362,756.[1] Cardiff is a significant tourist centre and the most popular visitor destination in Wales with 21.3 million visitors in 2017.[5] In 2011, Cardiff was ranked sixth in the world in National Geographic's alternative tourist destinations.[6]
Cardiff is the county town of the historic county of Glamorgan (and later South Glamorgan). Cardiff is part of the Eurocities network of the largest European cities.[7] A small town until the early 19th century, its prominence as a major port for the transport of coal following the arrival of industry in the region contributed to its rise as a major city. The Cardiff Built-up Area covers a slightly larger area outside the county boundary and includes the towns of Dinas Powys and Penarth. In 1905, Cardiff was made a city and proclaimed the capital of Wales in 1955.
Since the 1980s, Cardiff has seen significant development. A new waterfront area at Cardiff Bay contains the Senedd building, home to the Welsh Assembly and the Wales Millennium Centre arts complex. Current developments include the continuation of the redevelopment of the Cardiff Bay and city centre areas with projects such as the Cardiff International Sports Village, a BBC drama village,[8] and a new business district in the city centre.[9] Sporting venues in the city include the Principality Stadium—the national stadium and the home of the Wales national rugby union team—Sophia Gardens (the home of Glamorgan County Cricket Club), Cardiff City Stadium (the home of Cardiff City football team and the Wales football team), Cardiff International Sports Stadium (the home of Cardiff Amateur Athletic Club), Cardiff Arms Park (the home of Cardiff Blues and Cardiff RFC rugby union teams) and Ice Arena Wales (the home of Cardiff Devils ice hockey team). The city hosted the 1958 British Empire and Commonwealth Games. The city was awarded the title of European City of Sport twice, due to its role in hosting major international sporting events: first in 2009 and again in 2014.[10] The Principality Stadium hosted 11 football matches as part of the 2012 Summer Olympics, including the games' opening event and the men's bronze medal match.
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1999
Women's Soccer World Cup 1999

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
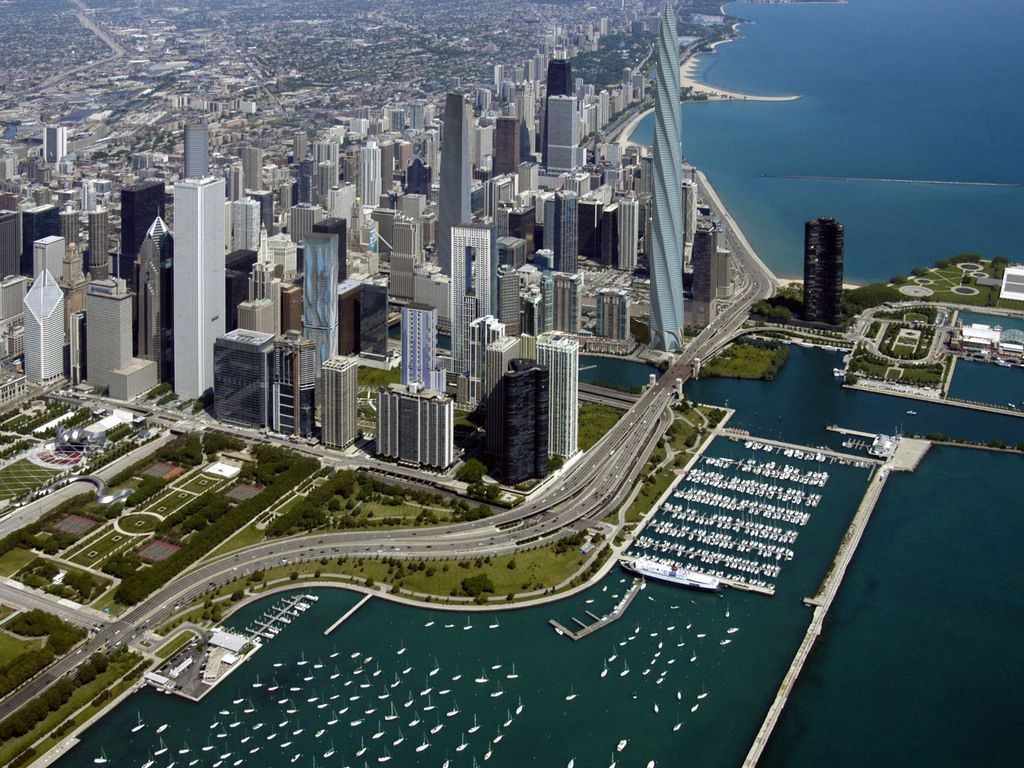


Chicago (/ʃɪˈkɑːɡoʊ/ ( listen), locally also /-ˈkɔː-/), officially the City of Chicago, located on the shores of freshwater Lake Michigan, is the third most populous city in America after New York and Los Angeles. As of the 2017 census-estimate, Chicago has a population of 2,716,450, which makes it the most populous city in both the state of Illinois and the Midwestern United States. It is the county seat of Cook County, the second most populous county in the U.S. Chicago is the principal city of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is often referred to as "Chicagoland." The Chicago metropolitan area has nearly 10 million people, is the third-largest in the United States, the fourth largest in North America, and the third largest metropolitan area in the world by land area. Chicago is the birthplace of the skyscraper, and considered the most influential architectural city of the 20th century.[6] In finance, the city saw the creation of the first standardized futures contracts at the Chicago Board of Trade; which today is the largest and most diverse derivatives market in the world, generating 20% of all volume in commodities and financial futures.[7]
listen), locally also /-ˈkɔː-/), officially the City of Chicago, located on the shores of freshwater Lake Michigan, is the third most populous city in America after New York and Los Angeles. As of the 2017 census-estimate, Chicago has a population of 2,716,450, which makes it the most populous city in both the state of Illinois and the Midwestern United States. It is the county seat of Cook County, the second most populous county in the U.S. Chicago is the principal city of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is often referred to as "Chicagoland." The Chicago metropolitan area has nearly 10 million people, is the third-largest in the United States, the fourth largest in North America, and the third largest metropolitan area in the world by land area. Chicago is the birthplace of the skyscraper, and considered the most influential architectural city of the 20th century.[6] In finance, the city saw the creation of the first standardized futures contracts at the Chicago Board of Trade; which today is the largest and most diverse derivatives market in the world, generating 20% of all volume in commodities and financial futures.[7]
Chicago was incorporated as a city in 1837 near a portage between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River watershed and grew rapidly in the mid-nineteenth century.[8] After the Great Chicago Fire of 1871, which destroyed several square miles and left more than 100,000 homeless, the city made a concerted effort to rebuild.[9] The construction boom accelerated population growth throughout the following decades, and by 1900 Chicago was one of the five largest cities in the world.[10] During this period, Chicago made noted contributions to urban planning and zoning standards, which included creating new construction styles (including the Chicago School of architecture), the development of the City Beautiful Movement, and the steel-framed skyscraper.[11]
Positioned along Lake Michigan, the city is an international hub for finance, commerce, industry, technology, telecommunications, and transportation. O'Hare International Airport is the one of the busiest airports in the world, and the region also has the largest number of U.S. highways and railroad freight.[12] In 2012, Chicago was listed as an alpha global city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network,[13] and it ranked seventh in the entire world in the 2017 Global Cities Index.[14] Chicago has the fourth-largest gross metropolitan product in the world — generating about $670.5 billion according to September 2017 estimates — ranking it after the metropolitan areas of Tokyo, New York City, and Los Angeles, and ranking ahead of number five London and number six Paris.[15] Chicago has one of the world's largest and most diversified and balanced economies, not being dependent on any one industry, with no single industry employing more than 14% of the workforce.[16]
Chicago was the second most visited city in the United States with 55 million domestic and international visitors,[17][18] not far behind the 62 million visitors to New York City in 2017.[19] The city ranked first place in the 2018 Time Out City Life Index, a global quality of life survey of 15,000 people in 32 cities.[20][21][22][23][24] Landmarks in the city include Millennium Park, Navy Pier, the Magnificent Mile, the Art Institute of Chicago, Museum Campus, the Willis (Sears) Tower, the Museum of Science and Industry, and Lincoln Park Zoo. Chicago's culture includes the visual arts, literature, film, theater, comedy (especially improvisational comedy), food, and music, particularly jazz, blues, soul, hip-hop, gospel,[25] and electronic dance music including house music. There are many colleges and universities in the Chicago area, of which the University of Chicago, Northwestern University, and the University of Illinois at Chicago are classified as "highest research" doctoral universities.
Chicago has professional sports teams in each of the major professional leagues, including two Major League Baseball teams. The city has had several nicknames throughout its history such as the Windy City, Chi-Town, Second City, and the City of the Big Shoulders, referring to its numerous towers and skyscrapers.[26]
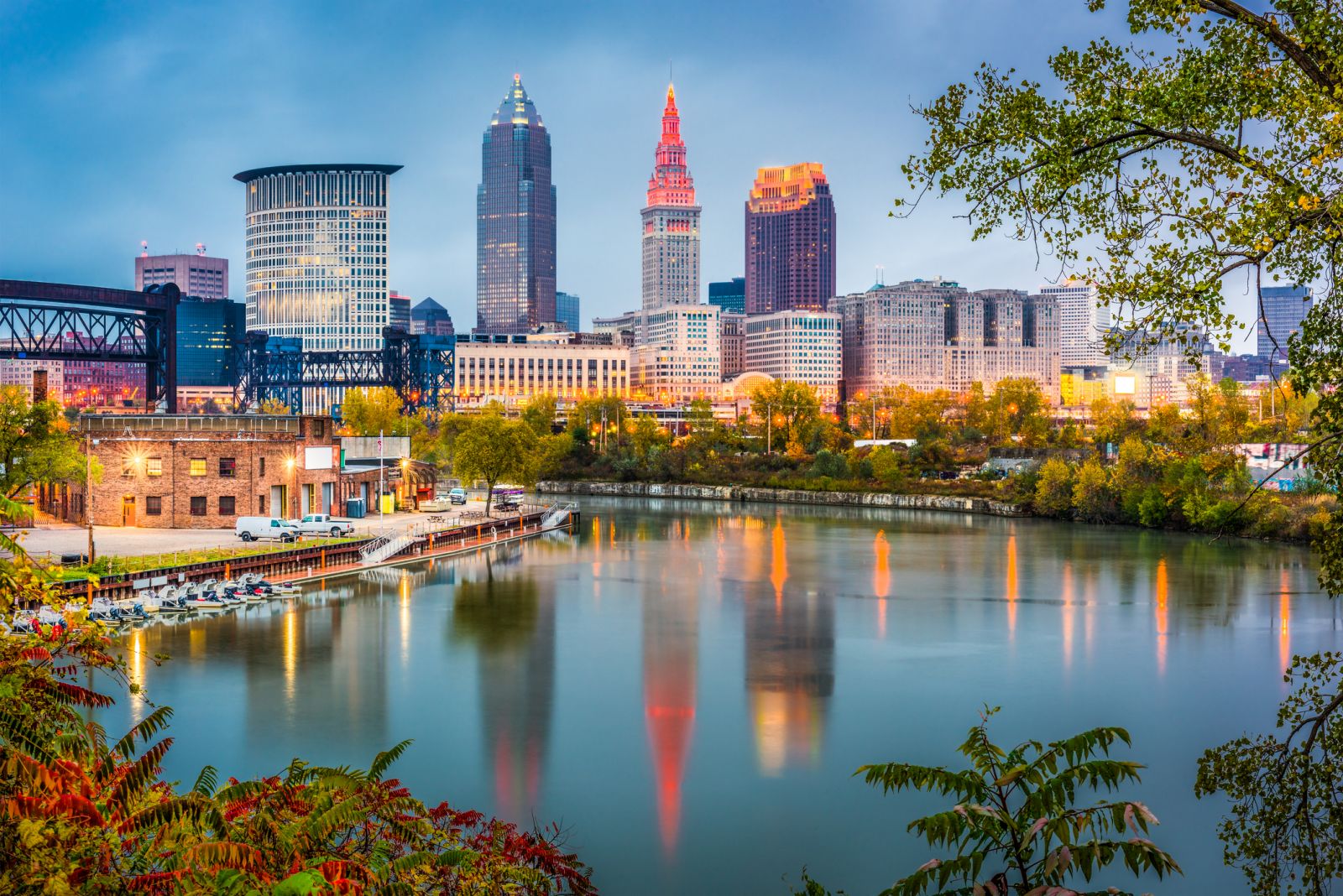

Cleveland (/ˈkliːvlənd/ KLEEV-lənd), officially the City of Cleveland, is a major city in the U.S. state of Ohio, and the county seat of Cuyahoga County.[7] It is located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U.S. maritime border with Canada and approximately 60 miles (100 kilometers) west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania state border.
The largest city on Lake Erie and one of the most populous urban areas in the country,[8] Cleveland anchors the Greater Cleveland Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) and the Cleveland–Akron–Canton Combined Statistical Area (CSA). The CSA is the most populous combined statistical area in Ohio and the 17th largest in the United States, with a population of 3,633,962 in 2020.[9][10] The city proper, with a 2020 population of 372,624, ranks as the 54th-largest city in the U.S.,[11] as a larger portion of the metropolitan population lives outside the central city. The seven-county metropolitan Cleveland economy, which includes Akron, is the largest in the state.
Cleveland was founded in 1796 near the mouth of the Cuyahoga River by General Moses Cleaveland, after whom the city was named. It grew into a major manufacturing center due to its location on both the river and the lake shore, as well as numerous canals and railroad lines. A port city, Cleveland is connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence Seaway. The city's economy relies on diversified sectors such as manufacturing, financial services, healthcare, biomedicals, and higher education.[12] The gross domestic product (GDP) for the Greater Cleveland MSA was $135 billion in 2019.[13] Combined with the Akron MSA, the seven-county Cleveland–Akron metropolitan economy was $175 billion in 2019, the largest in Ohio, accounting for 25% of the state's GDP.[13]
Designated as a "Gamma -" global city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network,[14] the city's major cultural institutions include the Cleveland Museum of Art, the Cleveland Museum of Natural History, the Cleveland Orchestra, Playhouse Square, and the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame. Known as "The Forest City" among many other nicknames, Cleveland serves as the center of the Cleveland Metroparks nature reserve system.[15] The city's major league professional sports teams include the Cleveland Browns, the Cleveland Cavaliers, and the Cleveland Guardians.

 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Canada
Canada

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
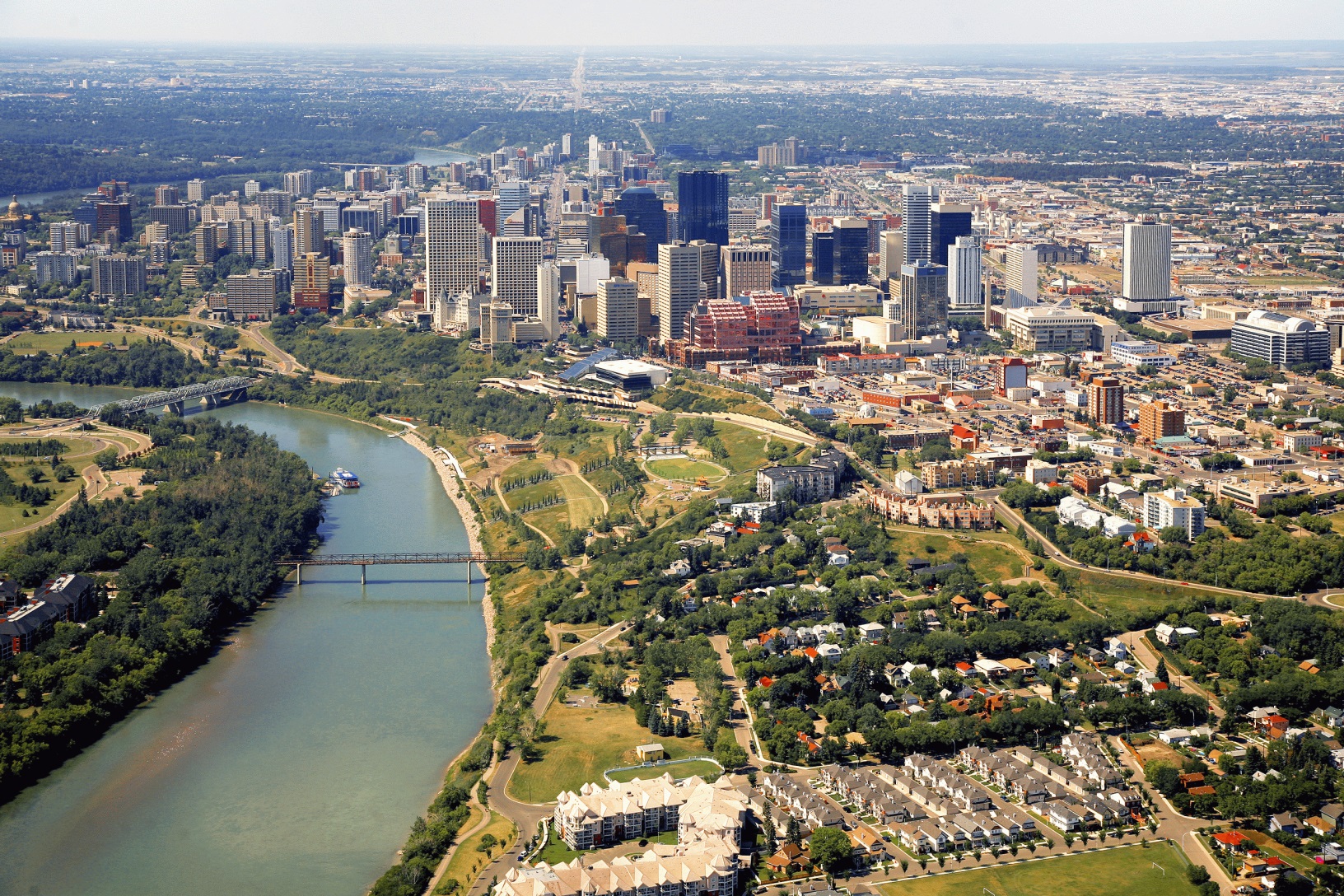

Edmonton (/ˈɛdməntən/ ( listen) ED-mən-tən) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the north end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor".[14]
listen) ED-mən-tən) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the north end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor".[14]
As of 2021, Edmonton had a city population of 1,010,899 and a metropolitan population of 1,418,118, making it the fifth-largest city[15][16] and sixth-largest metropolitan area (CMA) in Canada.[17][18] Edmonton is North America's northernmost city and metropolitan area with a population over one million. A resident of Edmonton is known as an Edmontonian.[19]
Edmonton's historic growth has been facilitated through the absorption of five adjacent urban municipalities (Strathcona, North Edmonton, West Edmonton, Beverly and Jasper Place)[20] in addition to a series of annexations through 1982,[21] and the annexation of 8,260 ha (82.6 km2; 31.9 sq mi) of land from Leduc County and the City of Beaumont on January 1, 2019.[22] Known as the "Gateway to the North",[23] the city is a staging point for large-scale oil sands projects occurring in northern Alberta and large-scale diamond mining operations in the Northwest Territories.[24]
Edmonton is a cultural, governmental and educational centre. It hosts a year-round slate of festivals, reflected in the nickname "Canada's Festival City".[1] It is home to North America's second largest mall, West Edmonton Mall (the world's largest mall from 1981 until 2004),[25][26][27] and Fort Edmonton Park, Canada's largest living history museum.
 England
England
 Fabio Capello
Fabio Capello
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2014
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2014
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2018
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2018
 Group G
Group G
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2022
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2022
 FIFA Weltmeister Favoriten Teams *
FIFA Weltmeister Favoriten Teams *
 UEFA European Championship 2016
UEFA European Championship 2016
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020
 Group A
Group A

 Sport
Sport
 Group G
Group G

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Nations League
(F)UEFA Nations League
 Sven-Göran Eriksson
Sven-Göran Eriksson
 UEFA Nations League
UEFA Nations League
 UEFA Nations League A - Group 4
UEFA Nations League A - Group 4
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom





The England national football team has represented England in international football since the first international match in 1872. It is controlled by The Football Association (FA), the governing body for football in England, which is affiliated with UEFA and comes under the global jurisdiction of world football's governing body FIFA.[3][4] England competes in the three major international tournaments contested by European nations: the FIFA World Cup, the UEFA European Championship, and the UEFA Nations League.
England is the joint oldest national team in football. It played in the world's first international football match in 1872, against Scotland. England's home ground is Wembley Stadium, London, and its training headquarters is St George's Park, Burton upon Trent. The team's manager is Gareth Southgate.
England is one of eight nations to have won the World Cup.[5] England has qualified for the World Cup 15 times. It won the 1966 World Cup Final, a tournament it also hosted, and finished fourth in both 1990 and 2018. England has never won the European Championship, with its best performance to date being runners-up in 2020. As a constituent country of the United Kingdom, England is not a member of the International Olympic Committee and so does not compete at the Olympic Games. England is currently the only team to have won the World Cup but not won any major continental title at senior level, and the only non-sovereign entity to have won the World Cup.
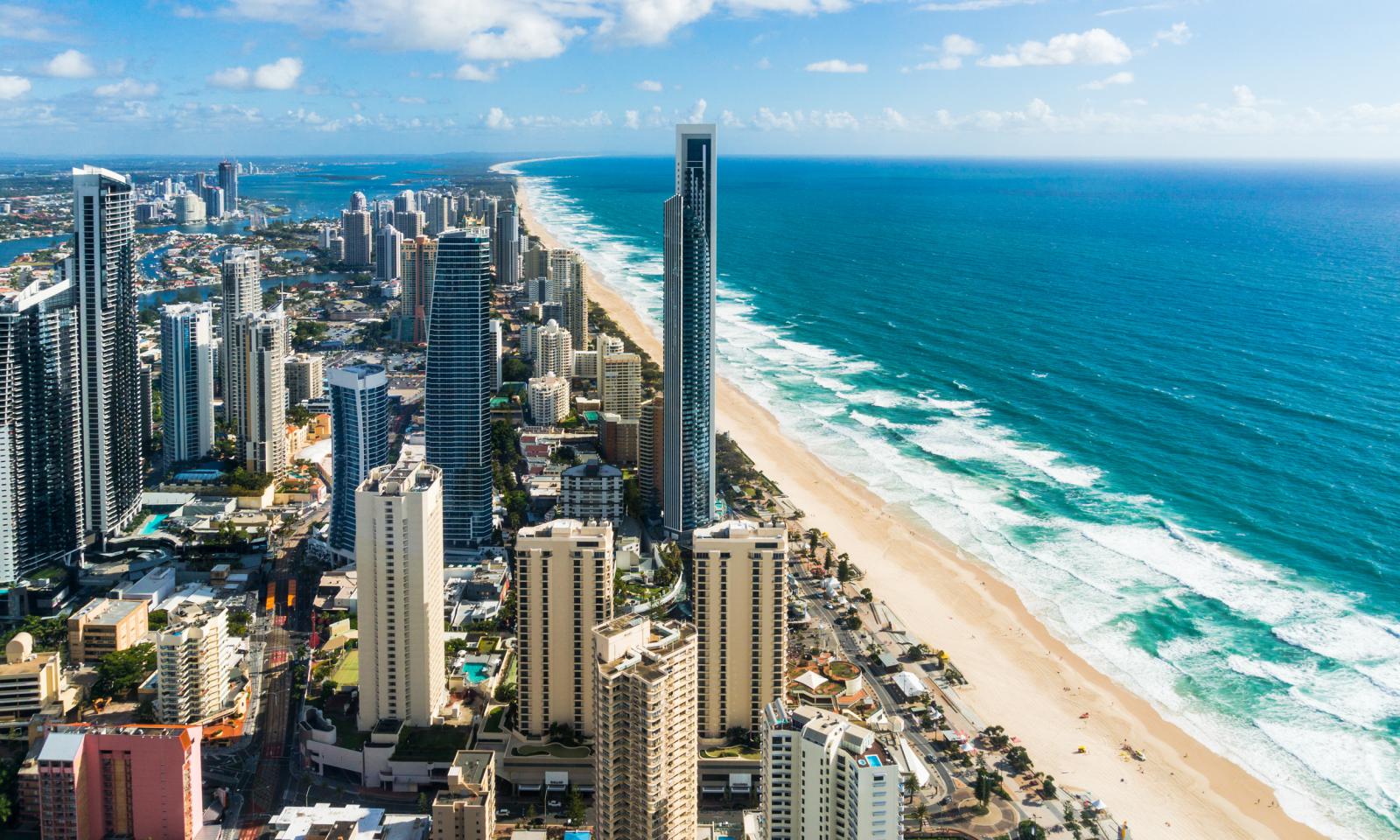

The Gold Coast is a coastal city in the state of Queensland, Australia, approximately 66 kilometres (41 mi) south-southeast of the centre of the state capital Brisbane and immediately north of the border with New South Wales. The area was previously occupied prior to European settlement by the Yugambeh language people. The demonym for the Gold Coast is Gold Coaster. With an estimated population of 679,127[1] in June 2018 (including 79,001 in the adjacent Tweed Valley of New South Wales), the Gold Coast is the sixth-largest city in Australia, Australia's largest non-capital city, and Queensland's second-largest city.[3]
The Gold Coast is a major tourist destination with a sunny, subtropical climate and has become widely known for its world-class surfing beaches, high-rise dominated skyline, theme parks, nightlife, and rainforest hinterland. The city is part of the nation's entertainment industry with television productions and a major film industry.
 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR
 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH
 Queensland-QLD
Queensland-QLD