漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟
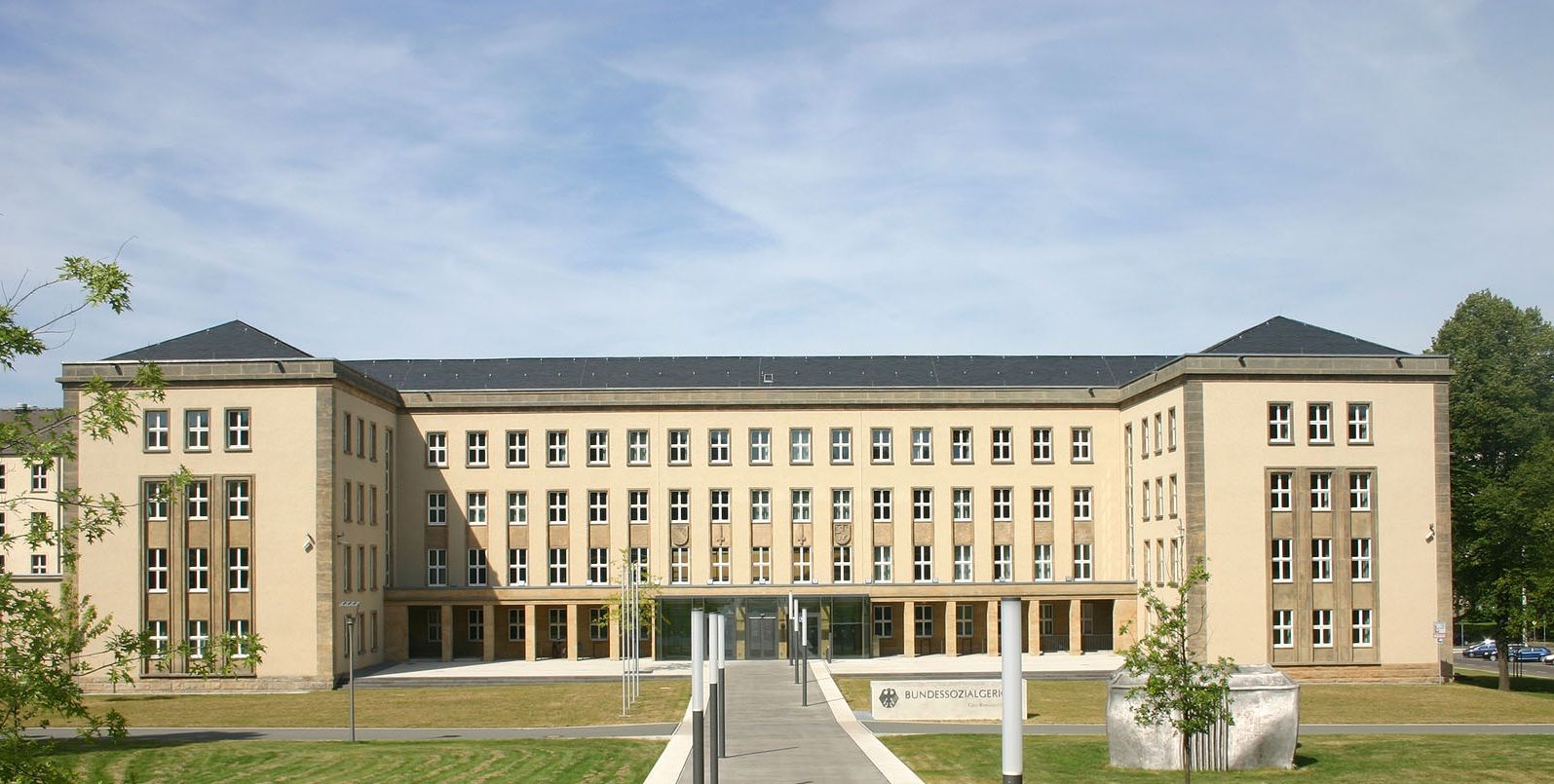



Das Bundessozialgericht (BSG) ist das oberste Gericht der Sozialgerichtsbarkeit in Deutschland und gehört mit Bundesarbeitsgericht, Bundesfinanzhof, Bundesgerichtshof und Bundesverwaltungsgericht zu den fünf obersten Gerichtshöfen des Bundes mit Sitz in Kassel (§ 38 Abs. 1 SGG).
Als Behörde ist das Bundessozialgericht – wie das Bundesarbeitsgericht – dem Ressort des Bundesministeriums für Arbeit und Soziales unterstellt und unterliegt dessen allgemeiner Dienstaufsicht.[1] In seiner Tätigkeit als Gericht ist es jedoch unabhängig.
德国联邦社会法院(德文:Bundessozialgericht)为德国五个联邦终审法院其中一者。其负责审理关于社会保障相关的上诉案件,其中最主要是关于公共卫生保险、长期护理保险、养老保险和职业灾害保险所产生的争讼。所有不服各邦高等社会法院的判决者都可以上诉至本法院。目前德国联邦社会法院位于黑森州的卡塞尔。

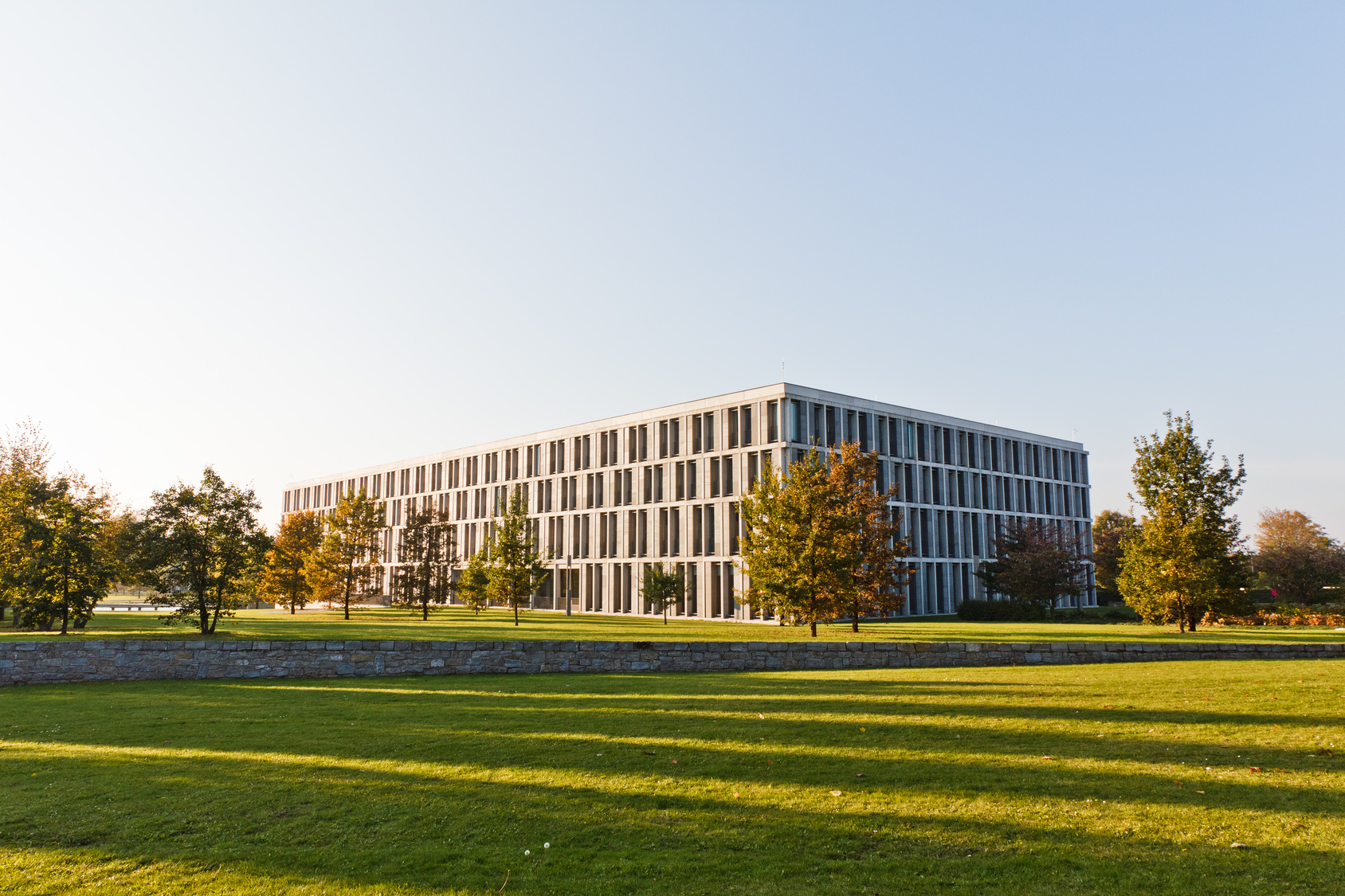
Der Bundesgerichtshof (BGH)[2] ist das oberste Gericht der Bundesrepublik Deutschland auf dem Gebiet der ordentlichen Gerichtsbarkeit und damit letzte Instanz in Zivil- und Strafverfahren. Ferner ist er für verwandte Spezialrechtsgebiete zuständig wie etwa das Berufsrecht in der Rechtspflege. Der BGH soll die Rechtseinheit wahren und das Recht fortbilden, vor allem aber die Entscheidungen der ihm untergeordneten Gerichte überprüfen. Er ist neben dem Bundesarbeitsgericht, Bundesfinanzhof, Bundessozialgericht und Bundesverwaltungsgericht einer der fünf obersten Gerichtshöfe des Bundes (Art. 95 Abs. 1 GG) und neben dem Bundesverfassungsgericht eines von zwei Bundesgerichten mit Sitz in Karlsruhe (§ 123 GVG), wobei zwei Senate des BGH in Leipzig angesiedelt sind.
联邦最高法院(德语:Bundesgerichtshof,简称BGH)是德国普通法院系统的最高法院,是德国民事和刑事案件的终审法院。为德国5个联邦终审法院之一,另外四个是联邦最高劳工法院、联邦最高财政法院、联邦最高社会法院、联邦最高行政法院。
这几个最高级别法院做出的裁决是不可上诉的,只有两个例外,一是案件涉及人权问题而由德国联邦宪法法院做出最终裁决,另一个是案件涉及欧盟法上的问题,联邦最高法院做出裁决后可以上诉至欧洲法院。
Das Bundesarbeitsgericht (BAG) ist das letztinstanzliche Gericht der deutschen Arbeitsgerichtsbarkeit und damit einer der fünf obersten Gerichtshöfe der Bundesrepublik Deutschland mit Sitz in Erfurt (§ 40 Abs. 1 ArbGG).
Als Behörde ist das Bundesarbeitsgericht dem Bundesministerium für Arbeit und Soziales unterstellt und unterliegt dessen Dienstaufsicht.[1] In seiner Tätigkeit als Gericht ist es jedoch unabhängig.
In den anderen Staaten des deutschen Sprachraums existiert kein eigenständiges oberstes Arbeitsgericht; die letztinstanzlichen Entscheidungen in Arbeitssachen sind dort Teil der Zuständigkeit des obersten Zivilgerichts. Dieses heißt in Liechtenstein Fürstlicher Oberster Gerichtshof, in Luxemburg Oberster Gerichtshof, in Österreich Oberster Gerichtshof und in der Schweiz Bundesgericht.
德国联邦最高劳工法院(德语:Bundesarbeitsgericht)为德国境内关于劳工法案件的终审法院。包含了个别的劳工法律问题(大部分是与雇主间的契约问题)以及集体的劳工法律问题(像是罢工和集体谈判这类的问题)。本法院主要是接受来自于各邦劳工最高法院(Landesarbeitsgerichte)的上诉。而目前德国联邦最高劳工法院位于图林根州的爱尔福特。

 *田径
*田径
 女子4×100米接力
女子4×100米接力
 *田径
*田径
 女子4x400米接力
女子4x400米接力
 联邦德国
联邦德国

 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟
 欧盟的历史
欧盟的历史

 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟
 *创始国
*创始国

 地理
地理

 地理
地理
 ***IMF发达国家
***IMF发达国家
 IMF发达国家
IMF发达国家
 IMF发达国家
IMF发达国家
 第二级
第二级
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2001 Edmonton
2001 Edmonton
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1997 Athens
1997 Athens

 北约会员国
北约会员国

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团
二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 七国集团
七国集团

 欧洲国家
欧洲国家
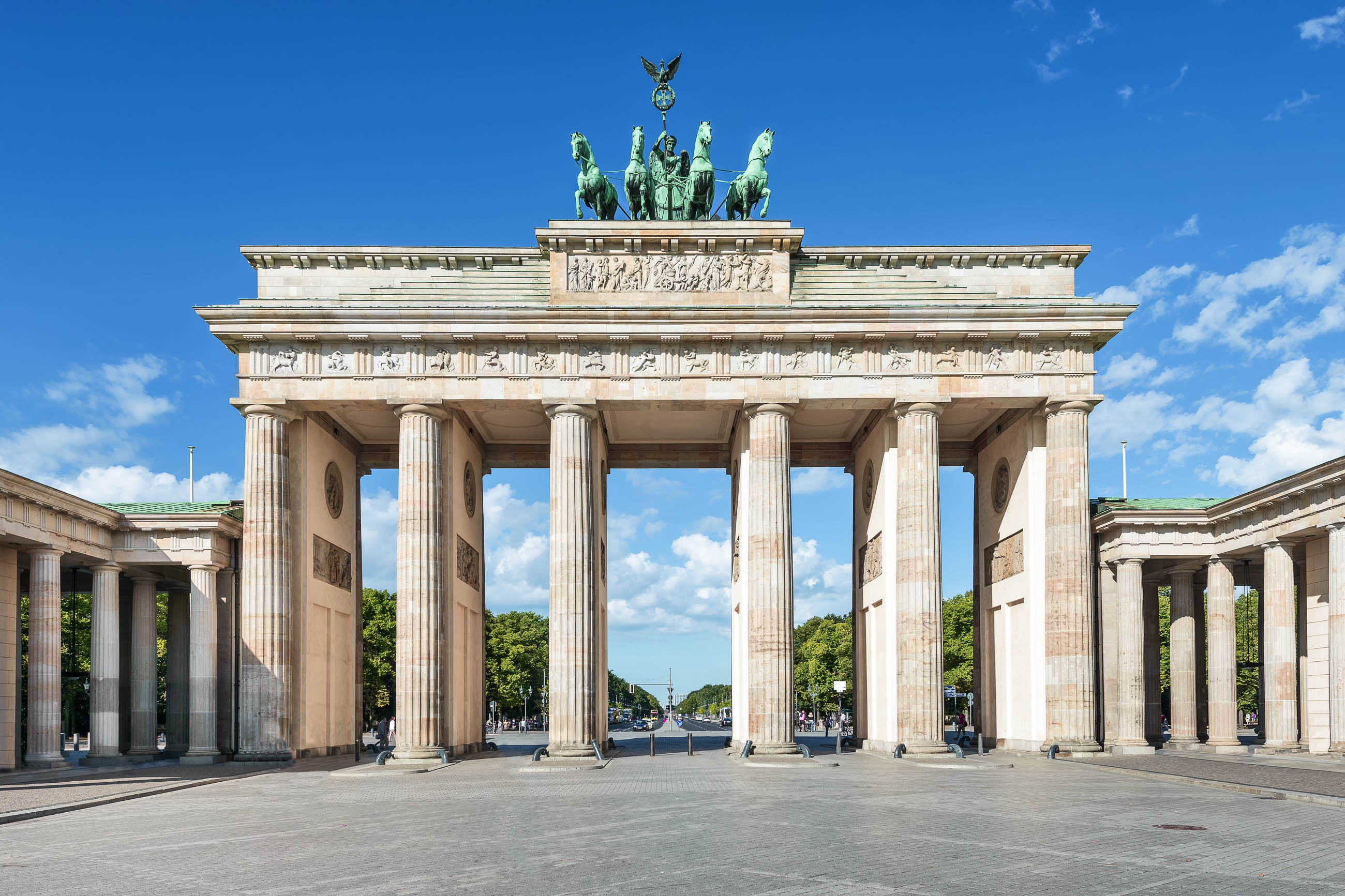

(Vollform: Bundesrepublik Deutschland) ist ein föderal verfasster Staat in Mitteleuropa, der aus den 16 deutschen Ländern besteht. Die Bundesrepublik ist ein freiheitlich-demokratischer Rechtsstaat[8] und stellt die jüngste Ausprägung des deutschen Nationalstaates dar.[9] Mit rund 82,8 Millionen Einwohnern (31. Dezember 2016) zählt Deutschland zu den dicht besiedelten Flächenstaaten.
An Deutschland grenzen neun Staaten, im Norden die Gewässer der Nord- und Ostsee und im Süden das Bergland der Alpen. Es liegt in der gemäßigten Klimazone. Bundeshauptstadt sowie bevölkerungsreichste deutsche Stadt ist Berlin. Weitere bedeutende Metropolen sind Hamburg, München, Köln, Frankfurt, Stuttgart und Düsseldorf; größter Ballungsraum ist das Ruhrgebiet. Deutschland gilt international als das Land mit der zweithöchsten Zahl von Einwanderern nach den Vereinigten Staaten (Stand 2015).[10][11] Seine Bevölkerung ist die zweitälteste und hat mit 1,47 Kindern pro Frau (2014) eine der niedrigsten Geburtenraten der Welt.[12]
Auf dem Territorium des heutigen Deutschlands wurden frühe Siedlungsformen von vor etwa 500.000 Jahren nachgewiesen, wie Funde vom Heidelbergmenschen, vom Neandertaler sowie von einigen der ältesten Kunstwerke der Menschheit aus der Altsteinzeit belegen. Seit der Antike ist die lateinische Bezeichnung Germania für das Siedlungsgebiet der Germanen bekannt, seit dem 4. Jahrhundert ist die Verwendung des Begriffes deutsch in althochdeutscher Form belegt. Das seit dem 10. Jahrhundert bestehende Heilige Römische Reich bestand aus vielen Herrschaftsgebieten und war mit dem 1815 nachfolgenden Deutschen Bund der Ursprung des föderalen deutschen Staates. Dieser entstand erstmals mit der Gründung des Deutschen Reichs im Jahr 1871, woraus eine rasche Wirtschaftsentwicklung vom Agrar- zum Industrieland folgte.
Nach dem Ersten Weltkrieg kam es infolge der Novemberrevolution 1918 zur Bildung der demokratischen Weimarer Republik und zum Friedensvertrag von Versailles. Der nationalsozialistischen Diktatur von 1933 bis 1945 samt verheerendem Zweitem Weltkrieg folgte eine Zeit der Veränderung und Teilung des Staates. Der Gründung der Bundesrepublik als demokratischer westdeutscher Teilstaat mit Inkrafttreten des Grundgesetzes am 24. Mai 1949 folgte wiederum die Gründung der sozialistischen DDR am 7. Oktober 1949 als ostdeutscher Teilstaat.[13] Nach der friedlichen Revolution 1989 folgte die Wiedervereinigung beider Landesteile am 3. Oktober 1990; seitdem wird der Tag der Deutschen Einheit als nationaler Feiertag begangen.
Deutschland ist Gründungsmitglied des Europarates und der Europäischen Union sowie deren bevölkerungsreichstes Land. Mit 18 anderen EU-Mitgliedstaaten bildet es eine Währungsunion, die Eurozone. Es ist Mitglied der UN, der OECD, der OSZE, der NATO, der G7 und der G20. Die Bundesrepublik Deutschland gilt als einer der politisch einflussreichsten Staaten Europas und ist ein gesuchtes Partnerland auf globaler Ebene.[14]
Gemessen am Bruttoinlandsprodukt ist Deutschland die größte Volkswirtschaft Europas und die viertgrößte der Welt.[5] Im Jahr 2015 war es die drittgrößte Export- und Importnation.[15] Es ist marktwirtschaftlich geprägt. Aufgrund der Rohstoffarmut und der Automatisierung der Industrie entwickelt sich das Land, das stark von der Qualität seines Bildungssystems abhängt, zunehmend zur Informations- und Wissensgesellschaft.[16] Gemäß dem Index der menschlichen Entwicklung zählt Deutschland zu den sehr hoch entwickelten Ländern.[17]
Die deutsche Sprache ist die meistgesprochene Muttersprache und nach Englisch die zweithäufigste Fremdsprache in der Europäischen Union; die Zahl ihrer Sprecher rangiert weltweit auf dem zehnten Platz. Die Kultur Deutschlands hat vielschichtige und weltbekannte Ausdrucksformen hervorgebracht, etwa in der Kunst und Architektur, der Musik, der Philosophie, der Filmkultur, der Küche, der Traditionspflege, im Design, im Sport, in der Wissenschaft und der Wirtschaft. Das UNESCO-Welterbe in Deutschland sowie die Vielfalt der Kulturdenkmale und Altstädte ist umfangreich. Eine Vielzahl von National- und Naturparks sind im Land ausgewiesen.
德意志联邦共和国(德语:Bundesrepublik Deutschland、![]() 发音(帮助·信息))简称德国(德语:Deutschland)[参 7],是一个位于欧洲的联邦议会共和制国家,国家元首为联邦总统,政府首脑为联邦总理。它由16个联邦州组成,首都与最大城市为柏林。其国土面积约35.7万平方公里,南北距离为876公里,东西相距640公里,从北部的北海与波罗的海延伸至南部的阿尔卑斯山[参 8]。气候温和,季节分明。德国人口约8,180万,为欧洲联盟中人口最多的国家,也是世界第二大移民目的地,仅次于美国[参 9]。
发音(帮助·信息))简称德国(德语:Deutschland)[参 7],是一个位于欧洲的联邦议会共和制国家,国家元首为联邦总统,政府首脑为联邦总理。它由16个联邦州组成,首都与最大城市为柏林。其国土面积约35.7万平方公里,南北距离为876公里,东西相距640公里,从北部的北海与波罗的海延伸至南部的阿尔卑斯山[参 8]。气候温和,季节分明。德国人口约8,180万,为欧洲联盟中人口最多的国家,也是世界第二大移民目的地,仅次于美国[参 9]。
在50万年前的旧石器时代晚期,海德堡人及其后代尼安德特人生活在今德国中部。自古典时代以来各日耳曼部族开始定居于今日德国的北部地区。公元1世纪时,有罗马人著作的关于“日耳曼尼亚”的历史记载。在公元4到7世纪的民族迁徙期,日耳曼部族逐渐向欧洲南部扩张。自公元10世纪起,德意志领土组成神圣罗马帝国的核心部分[参 10]。16世纪时,德意志北部地区成为宗教改革中心。1871年,在普鲁士主导之下,多数德意志邦国统一并加入德意志帝国。在第一次世界大战和1918-1919年德国革命后,德意志帝国解体,议会制的魏玛共和国取而代之。1933年国家社会主义党获取政权并建立独裁统治,最终导致第二次世界大战及系统性种族灭绝的发生。在战败并经历同盟国军事占领后,两个德国分别建立:德意志民主共和国和德意志联邦共和国。在1990年10月3日重新统一成为现在的德国。
德国是世界大国之一,其国内生产总值以国际汇率计居世界第四,以购买力平价计居世界第五。其诸多工业和科技部门位居世界前列,例如全球驰名的德国车厂、精密部件等,为世界第三大出口国。德国为发达国家,生活水平居世界前列。德国人也以热爱大自然闻名,都市绿化率极高,也是欧洲再生能源大国,是可持续发展经济的样板,除了强调环境保护与自然生态保育,在人为饲养活体的态度十分严谨,不但获得大量外汇和资讯优势,其动物保护法律管束、生命教育水准也是首屈一指的,在高等教育方面并提供免费大学教育[参 11],并具备完善的社会保障制度和医疗体系,催生出拜尔等大药厂。
德国为1993年欧洲联盟建立时的创始国之一,为申根区一部分,并于1999年推动欧元区的建立。德国亦为联合国、北大西洋公约组织、八国集团、20国集团及经济合作与发展组织成员。其军事开支总额居世界第九。
德语是欧盟境内使用人数最多的母语。德国文化的丰富层次和对世界的影响表现在其美术和建筑、音乐、哲学以及电影等等。德国的文化遗产主要以老城为代表。另外国家公园和自然公园共计有上百处。
ドイツ連邦共和国(ドイツれんぽうきょうわこく、独: Bundesrepublik Deutschland)、通称ドイツ(独: Deutschland)は、中央ヨーロッパ西部に位置する連邦共和制国家。首都および最大の都市はベルリン州。南がスイスとオーストリア、北にデンマーク、西をオランダとベルギーとルクセンブルク、東はポーランドとチェコとそれぞれ国境を接する。
欧州大陸における政治的・経済的な主要国であり、歴史上、多くの文化・科学・技術分野における重要な指導国でもある。人口は8300万人で、これは欧州連合において最大である。同国は限定的主権を有する16の州によって構成される。国土の総面積は35万7386平方キロメートルであり、主に温暖な気候に属する。かつて「西ドイツ」と呼ばれていた時代は「西欧」に分類されていたが、東ドイツ(ドイツ民主共和国)の民主化と東西ドイツの統一により「中欧」または「中西欧」に分類されるようになっている。
ドイツ経済の規模は、対米ドル名目為替レートによって計算される米ドル建て名目GDP(MERベースGDP)で世界第4位であり、対米ドル購買力平価によって計算される米ドル建て実質GDP(PPPベースGDP)で世界第5位である。技術及び産業分野における世界的なリーダーとして、世界第3位の輸出国かつ世界第3位の輸入国である。世界最古のユニバーサルヘルスケア制度を含む、包括的な社会保障を特色とする非常に高い生活水準が実現されている先進国である。豊かな政治及び文化の歴史で知られ、影響力ある多数の芸術家、音楽家、映画人、哲学者、科学者及び技術者、起業家の故国である。
1993年に欧州連合へ発展した1957年の欧州諸共同体の原加盟国であるほか、1995年以来シェンゲン圏の一員で、1999年以降はユーロ圏の一員でもある。また、国際連合、欧州評議会、NATO、G7、G20、OECDの主要なメンバーであり、欧州の大国「ビッグ4」や列強の一国に数えられる。アメリカ合衆国に次ぎ、ドイツは世界第2位の移住地である[1]。
Germany (German: Deutschland, pronounced [ˈdɔʏtʃlant] (![]() listen)), officially the Federal Republic of Germany,[e] is a country in Central Europe. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of 357,022 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi), with a population of over 83 million within its 16 constituent states. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and largest city is Berlin, and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr.
listen)), officially the Federal Republic of Germany,[e] is a country in Central Europe. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of 357,022 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi), with a population of over 83 million within its 16 constituent states. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and largest city is Berlin, and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr.
Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In the 10th century, German territories formed a central part of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th century, northern German regions became the centre of the Protestant Reformation. Following the Napoleonic Wars and the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the German Confederation was formed in 1815. In 1871, Germany became a nation-state when most of the German states unified into the Prussian-dominated German Empire. After World War I and the German Revolution of 1918–1919, the Empire was replaced by the semi-presidential Weimar Republic. The Nazi seizure of power in 1933 led to the establishment of a dictatorship, World War II, and the Holocaust. After the end of World War II in Europe and a period of Allied occupation, Germany was divided into the Federal Republic of Germany, generally known as West Germany, and the German Democratic Republic, East Germany. The Federal Republic of Germany was a founding member of the European Economic Community and the European Union, while the German Democratic Republic was a communist Eastern Bloc state and member of the Warsaw Pact. After the fall of communism, German reunification saw the former East German states join the Federal Republic of Germany on 3 October 1990—becoming a federal parliamentary republic.
Germany is a great power with a strong economy; it has the largest economy in Europe, the world's fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the fifth-largest by PPP. As a global leader in several industrial, scientific and technological sectors, it is both the world's third-largest exporter and importer of goods. As a developed country, which ranks very high on the Human Development Index, it offers social security and a universal health care system, environmental protections, and a tuition-free university education. Germany is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the G7, the G20, and the OECD. It has the third-greatest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
L'Allemagne (/almaɲ/ ; en allemand : Deutschland /ˈdɔʏtʃlant/ Écouter), en forme longue la République fédérale d'Allemagneb, abrégée en RFA (en allemand : Bundesrepublik Deutschland /ˈbʊn.dəs.ʁe.puˌblik ˈdɔʏtʃ.lant/ Écouter, abrégée en BRD), est un État d'Europe centrale, et selon certaines définitions d'Europe de l'Ouest, entouré par la mer du Nord, le Danemark et la mer Baltique au nord, par la Pologne à l'est-nord-est, par la Tchéquie à l'est-sud-est, par l'Autriche au sud-sud-est, par la Suisse au sud-sud-ouest, par la France au sud-ouest, par la Belgique et le Luxembourg à l'ouest, enfin par les Pays-Bas à l'ouest-nord-ouest. Décentralisée et fédérale, l'Allemagne compte quatre métropoles de plus d'un million d'habitants : la capitale Berlin, ainsi que Hambourg, Munich et Cologne. Le siège du gouvernement est situé dans la ville de Berlin et dans la ville fédérale de Bonn. Francfort-sur-le-Main est considérée comme la capitale financière de l'Allemagnec : dans cette ville se trouve le siège de la Banque centrale européenne.
Beaucoup de peuples germaniques occupent le Nord du territoire actuel depuis l'Antiquité classique. Durant ce que l'on nomme les invasions barbares, les tribus germaniques se rapprochent du Sud de ce territoire. À partir du Xe siècle, les territoires forment la partie centrale du Saint-Empire romain germanique. Au XVIe siècle, le Nord de l'Allemagne est au cœur de la réforme protestante. Le pangermanisme entraîne l'unification des États allemands en 1871 pour former l'Empire allemand. Après la Première Guerre mondiale, et la révolution allemande de 1918-1919, l'Empire est remplacé par la république parlementaire de Weimar. L'accès au pouvoir des nazis en 1933 mène à la Seconde Guerre mondiale, au cours de laquelle le régime totalitaire connu sous le nom de Troisième Reich, fondé sur un racisme et un antisémitisme singulier, et dirigé par le dictateur Adolf Hitler, perpètre des crimes de masse en Europe, dont la Shoah, et laisse le pays en ruines. Après sa défaite militaire en 1945, l'Allemagne perd des territoires et — par la volonté des vainqueurs alliés qui entrent dans la « guerre froide » — est contrainte de se scinder en deux nations : à l'ouest un État démocratique, la République fédérale d'Allemagne (en abrégé RFA) et, à l'est, la République démocratique allemande (en abrégé RDA) sous emprise de l'Union soviétique. Le mur de Berlin — qui symbolise cette division dans l'ancienne capitale — tombe le 9 novembre 1989 et l'Allemagne est à nouveau réunifiée le 3

 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟
 欧盟的历史
欧盟的历史

 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟
 *创始国
*创始国
 欧洲流行歌曲大赛
欧洲流行歌曲大赛

 财政金融
财政金融
 ***全球金融中心
***全球金融中心

 地理
地理

 地理
地理
 ***IMF发达国家
***IMF发达国家

 历史
历史
 公元 1500 - 2000
公元 1500 - 2000

 历史
历史
 公元 2000 - 2100
公元 2000 - 2100

 国际城市
国际城市
 *欧洲文化之都
*欧洲文化之都

 国际城市
国际城市
 欧洲城市
欧洲城市
 IMF发达国家
IMF发达国家
 IMF发达国家
IMF发达国家
 第六级
第六级
 卢森堡
卢森堡

 北约会员国
北约会员国

 欧洲国家
欧洲国家
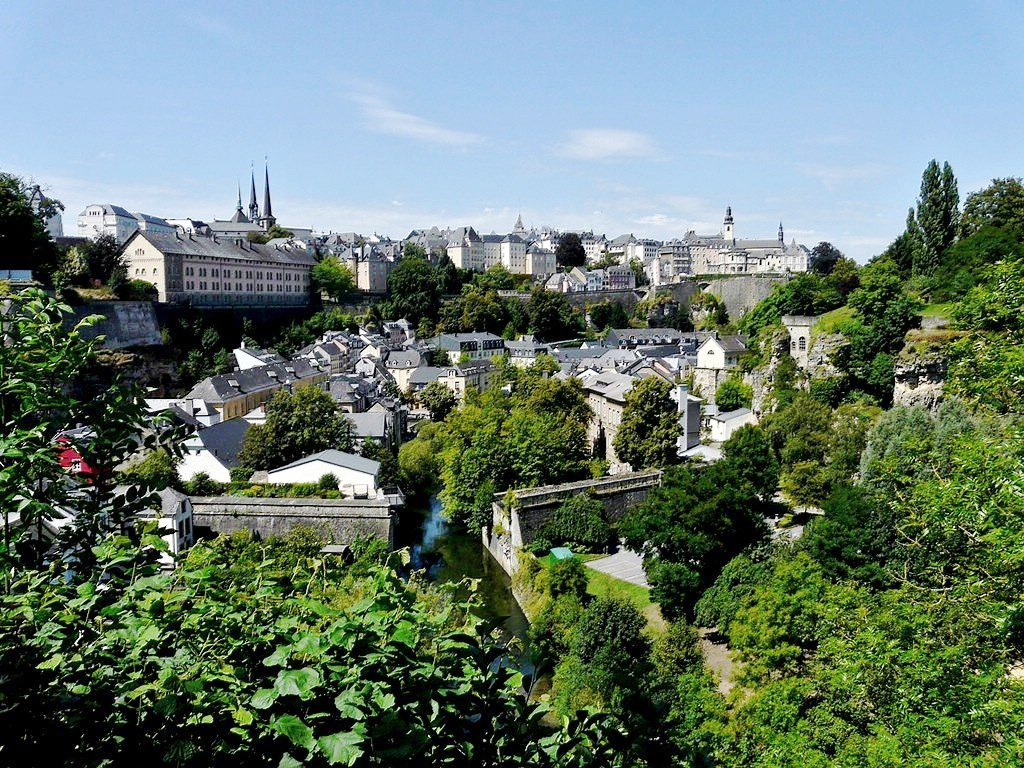


Das Großherzogtum Luxemburg (luxemburgisch Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg [ˈgʀəʊsˌhɛχtsoːktuːm ˈlətsəbuəɕ], französisch Grand-Duché de Luxembourg [ɡʁɑ̃ dyʃe də lyksɑ̃buʁ]) ist ein demokratischer Staat in Form einer parlamentarischen Monarchie[1] im Westen Mitteleuropas. Es ist das letzte Großherzog- bzw. Großfürstentum (von einst zwölf) in Europa. Das Land gehört zum mitteldeutschen Sprachraum. Landessprache ist Luxemburgisch, Verwaltungs- und Amtssprachen sind Französisch, Deutsch und Luxemburgisch. Gemeinsam mit seinem Nachbarn Belgien und mit den Niederlanden bildet Luxemburg die Beneluxstaaten.
卢森堡大公国(卢森堡语:Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg,法语:Grand-Duché de Luxembourg,德语:Großherzogtum Luxemburg),简称“卢森堡”,位于欧洲西北部,被邻国法国、德国和比利时包围,是一个内陆小国,也是现今欧洲大陆仅存的大公国,首都卢森堡市。因国土小、古堡多,又有“袖珍王国”、“千堡之国”的称呼 。
卢森堡地形富于变化,在历史上又处于德法要道,地势险要,一直是西欧重要的军事要塞,有北方直布罗陀的称号 。
卢森堡是一个高度发达的资本主义国家,也是欧盟和北约创始成员国之一,拥有欧盟多个下设机构,如欧洲法院、欧洲审计院以及欧洲投资银行,被称为继布鲁塞尔和斯特拉斯堡之后的欧盟“第三首都”。同时是高度发达的工业国家,还是欧元区内最重要的私人银行中心,及全球第二大仅次于美国的投资信托中心。金融、广播电视、钢铁是其三大经济支柱产业,该国失业率极低,人均寿命80岁。
卢森堡大公国(卢森堡语:Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg[注 1];法语:Grand-Duché de Luxembourg; 德语:Großherzogtum Luxemburg[注 2]),通称卢森堡(卢森堡语:Lëtzebuerg;法语:Luxembourg;德语:Luxemburg),被邻国法国、德国和比利时包围,是一个位于欧洲的内陆国家,也是现今欧洲大陆仅存的大公国,首都卢森堡市。卢森堡是欧盟成员国,因境内有欧洲法院、欧洲审计院、欧洲投资银行等多个欧盟机构被称为继布鲁塞尔和斯特拉斯堡之后的欧盟“第三首都”。
ルクセンブルク大公国(ルクセンブルクたいこうこく)、通称ルクセンブルクは、西ヨーロッパに位置する立憲君主制国家。首都は国名と同名のルクセンブルク市。隣接国は、南のフランス、西と北のベルギー、東のドイツである。ベルギー、オランダと併せてベネルクスと呼ばれる。
Luxembourg (/ˈlʌksəmbɜːrɡ/ ( listen)) (Luxembourgish: Lëtzebuerg [ˈlətsəbuə̯ɕ] (
listen)) (Luxembourgish: Lëtzebuerg [ˈlətsəbuə̯ɕ] ( listen); French: Luxembourg ; German: Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg,[note 2] is a small landlocked country in western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital, Luxembourg City, together with Brussels and Strasbourg, is one of the three official capitals of the European Union[6] and the seat of the European Court of Justice, the highest judicial authority in the EU. Its culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its neighbours, making it essentially a mixture of French and German cultures, as evident by the nation's three official languages: French, German, and the national language, Luxembourgish (sometimes considered a dialect of German). The repeated invasions by Germany, especially in World War II, resulted in the country's strong will for mediation between France and Germany and, among other things, led to the foundation of the European Union.[7]
listen); French: Luxembourg ; German: Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg,[note 2] is a small landlocked country in western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital, Luxembourg City, together with Brussels and Strasbourg, is one of the three official capitals of the European Union[6] and the seat of the European Court of Justice, the highest judicial authority in the EU. Its culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its neighbours, making it essentially a mixture of French and German cultures, as evident by the nation's three official languages: French, German, and the national language, Luxembourgish (sometimes considered a dialect of German). The repeated invasions by Germany, especially in World War II, resulted in the country's strong will for mediation between France and Germany and, among other things, led to the foundation of the European Union.[7]
With an area of 2,586 square kilometres (998 sq mi), it is one of the smallest sovereign states in Europe.[8] In 2016, Luxembourg had a population of 576,249, which makes it one of the least-populous countries in Europe,[9] but by far the one with the highest population growth rate.[10] Foreigners account for nearly half of Luxembourg's population.[11] As a representative democracy with a constitutional monarch, it is headed by Grand Duke Henri and is the world's only remaining grand duchy. Luxembourg is a developed country, with an advanced economy and one of the world's highest GDP (PPP) per capita. The City of Luxembourg with its old quarters and fortifications was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994 due to the exceptional preservation of the vast fortifications and the old city.[12]
The history of Luxembourg is considered to begin in 963, when count Siegfried I acquired a rocky promontory and its Roman-era fortifications known as Lucilinburhuc, ′little castle′, and the surrounding area from the Imperial Abbey of St. Maximin in nearby Trier.[13][14] Siegfried's descendants increased their territory through marriage, war and vassal relations. At the end of the 13th century, the Counts of Luxembourg reigned over a considerable territory. [15] In 1308, Henry VII, Count of Luxembourg became King of the Germans and Holy Roman Emperor. The House of Luxembourg produced four Holy Roman Emperors at the high time of the Middle Ages. In 1354, Charles IV elevated the County to the Duchy of Luxembourg. Since Sigismund had no male heir, the Duchy became part of the Burgundian Circle and then one of the Seventeen Provinces of the Habsburg Netherlands.[16] Over the centuries, the City and Fortress of Luxembourg, of great strategic importance situated between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg territories, was gradually built up to be one of the most reputed fortifications in Europe. After belonging to both the France of Louis XIV and the Austria of Maria Theresia, Luxembourg became part of the First French Republic and Empire under Napoleon.[17]
The present-day state of Luxembourg first emerged at the Congress of Vienna in 1815. The Grand-Duchy, with its powerful fortress, became an independent state under the personal possession of William I of the Netherlands with a Prussian garrison to guard the city against another invasion from France. [18] In 1839, following the turmoil of the Belgian Revolution, the purely Oil-speaking part of Luxembourg was ceded to Belgium and the Luxembourgish-speaking part (except the Arelerland, the area around Arlon) became what is the present state of Luxembourg. [19]
The steel industry exploiting the Red Lands' rich iron-ore grounds in the beginning of the 20th century drove the country's industrialisation. ArcelorMittal, the world's largest steel producer with headquarters in Luxembourg City, is still a reminder of these times. After the decline of the steel industry in the 1970s, the country focused on establishing itself as a global financial centre and developed into the banking hub it is reputed for. Since the beginning of the 21st century, its governments have focused on developing the country into a knowledge economy, with the founding of the University of Luxembourg and a national space programme, projecting the first involvement in a robotic lunar expedition by 2020.[20]
Luxembourg is a founding member of the European Union, OECD, United Nations, NATO, and Benelux. The city of Luxembourg, which is the country's capital and largest city, is the seat of several institutions and agencies of the EU. Luxembourg served on the United Nations Security Council for the years 2013 and 2014, which was a first in the country's history.[21] In 2016 Luxembourgish citizens had visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to 172 countries and territories, ranking the Luxembourgish passport 15th in the world, tied with countries such as Canada and Switzerland.[22]
Le Luxembourg, en forme longue le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg2,b,c ou le grand-duché de Luxembourgd, en luxembourgeois Lëtzebuerg et Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg, en allemand Luxemburg et Großherzogtum Luxemburg, est un pays d'Europe de l'Ouest sans accès à la mere Il est bordé par la Belgique à l'ouest et au nord, l'Allemagne à l'est, et la France au sud. Il comprend deux régions principales : l'Oesling au nord, qui est une partie du massif des Ardennes, et le Gutland au sud, prolongement de la Lorraine au sens géologique du terme. Le Luxembourg compte 602 005 habitants au 1er janvier 20181, et s'étend sur une superficie de 2 586 km2, faisant de lui l'une des plus petites nations souveraines d'Europe.
Le Luxembourg est une démocratie représentative et une monarchie constitutionnelle avec un grand-duc pour chef d'État, faisant du pays le seul grand-duché encore existant. Son économie dynamique en fait un des pays les plus riches et des plus prospères du monde, avec le PIB par habitant le plus élevé du monde selon le FMI en 2014. L'économie est principalement centrée sur les activités financières (environ la moitié du produit intérieur brut), favorisée par une fiscalité attractive voire dérisoire dans certains domaines (quasi-exonération d'impôts pour les bénéfices issus de l'exploitation de brevets ou de logiciels). La localisation centrale du territoire luxembourgeois en Europe a historiquement fait de lui un lieu d'une grande importance stratégique pour de nombreuses puissances, depuis sa fondation en tant que fortin romain7, son accueil d'un château franc durant le Haut Moyen Âge, et son rôle de bastion pour le chemin des Espagnols entre les XVIe et XVIIe siècles.
Le Luxembourg est le plus petit membre fondateur de l'Union européenne, de la zone euro, de l'OTAN, de l'OCDE, de l'ONU, de l'OSCE, du Conseil de l'Europe8,9,10,11 et du Benelux, reflétant son consensus politique en faveur de l'intégration économique, politique et militaire. La ville de Luxembourg, sa capitale et sa plus grande ville, est le siège de plusieurs établissements et institutions de l'UE. En 2012, le Luxembourg a été élu pour la première fois de son histoire à un siège temporaire au Conseil de sécurité des Nations unies. En raison de sa position géographique, la culture luxembourgeoise est une fusion de l'Europe germanique et romane, intégrant chacune des deux. De ce fait, le Luxembourg est un pays trilingue : le luxembourgeois, le français et l'allemand sont les trois langues officielles et, depuis 1984, le luxembourgeois a légalement le statut de « langue nationale »12.
Il Granducato di Lussemburgo (in francese: le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg; in lussemburghese: Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg; in tedesco: Großherzogtum Luxemburg) è un paese membro dell'Unione europea situato tra Germania, Francia e Belgio. È uno stato senza sbocco sul mare.
Membro fondatore dell'Unione europea, della NATO, del Benelux e delle Nazioni Unite, la sua capitale, l'omonima città di Lussemburgo, è sede di numerose istituzioni e agenzie europee oltre ad essere uno snodo finanziario di primaria importanza.
È l'unico granducato rimasto al mondo.
Luxemburgo, oficialmente denominado Gran Ducado de Luxemburgo (luxemburgués: Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg, francés: Grand-Duché de Luxembourg, alemán: Großherzogtum Luxemburg), es un pequeño país de Europa Central que forma parte de la Unión Europea. Se trata de un Estado sin litoral, rodeado por Francia, Alemania y Bélgica. Luxemburgo cuenta con una población de medio millón de habitantes sobre un área de 2586 kilómetros cuadrados.1
El gobierno de Luxemburgo es una monarquía constitucional y parlamentaria, siendo el único gran ducado soberano en la actualidad. El Estado tiene una economía altamente desarrollada, con el mayor producto interior bruto por cápita del mundo de acuerdo al Banco Mundial, y el segundo de acuerdo al Fondo Monetario Internacional.
Luxemburgo es miembro de la Unión Europea, la Organización del Tratado del Atlántico Norte, la Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico, las Naciones Unidas y el Benelux, reflejando la orientación política a favor de la integración económica, política y militar. Su capital, Luxemburgo, es sede de numerosas instituciones y agencias de la Unión Europea.
Luxemburgo posee culturas y tradiciones diversas por encontrarse entre la Europa romana y la Europa germánica. El país tiene tres lenguas oficiales: alemán, francés y luxemburgués. La localidad Schengen, que dio su nombre al espacio de Schengen, está ubicada en Luxemburgo.
Люксембу́рг (люксемб. Lëtzebuerg), официально Вели́кое Ге́рцогство Люксембу́рг (люксемб. Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg, фр. Grand-Duché de Luxembourg, нем. Großherzogtum Luxemburg) — государство (великое герцогство) в Западной Европе. Граничит с Бельгией на севере, на западе и на юге с Францией, на востоке с Германией, не имеет выхода к морю. Название происходит от древневерхненемецкого «lucilinburch» — «малый город». Общая площадь Люксембурга составляет 2586,4 км², что делает его одним из самых маленьких суверенных государств в Европе[5]. Население на 1 января 2018 года составляет 602 005 человек[2].
Член Европейского союза с 1957 года, также является членом НАТО, ОЭСР и ООН. Вместе с Бельгией и Нидерландами входит в состав Бенилюкса.


Rumen Georgiew Radew (bulgarisch Румен Георгиев Радев; * 18. Juni 1963 in Dimitrowgrad, Bulgarien) ist der amtierende Staatspräsident Bulgariens. Er ist Generalmajor der Reserve und gewann die Stichwahl zum Präsidenten Bulgariens 2016. Radew ist seit dem 22. Januar 2017 im Amt.[1] Am 21. November 2021 wurde er für eine zweite Amtszeit wiedergewählt.
鲁梅尼-格奥尔基耶夫-拉德夫(保加利亚语:Румен Георгиев Радев;* 1963 年 6 月 18 日生于保加利亚季米特洛夫格勒)是保加利亚现任总统。拉德夫自 2017 年 1 月 22 日起开始任职,并于 2021 年 11 月 21 日再次当选连任。
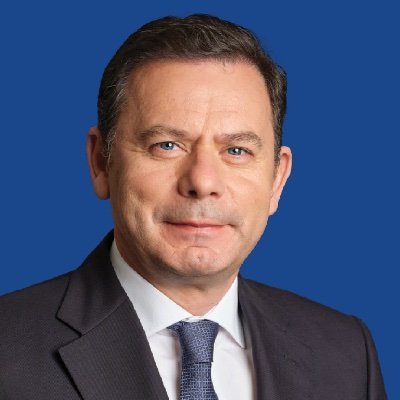


路易斯·菲利佩·蒙特内格罗·卡多索·德莫赖斯·埃斯特维斯(葡萄牙语:Luís Filipe Montenegro Cardoso de Morais Esteves,1973年2月16日—) [1]是一位葡萄牙政治家,现任葡萄牙总理兼社会民主党(PSD)主席。
蒙特内格罗于2002年至2018年期间担任阿威罗共和国议会议员,并于2011年至2017年期间领导该党的议会小组。在该党2020年领导人选举中被鲁伊·里奥击败后,他于2022年击败豪尔赫·莫雷拉·达席尔瓦,成为社会民主党主席。
在蒙特内格罗领导下,社会民主党与右翼政党CDS-PP达成协议,在2024年葡萄牙立法选举前组成民主联盟。[2]民主联盟在选举中获得最多席位,获得80个席位,比社会党多两个。[3]2024年3月21日,葡萄牙总统马塞洛·雷贝洛·德索萨任命他为总理。他于2024年4月2日就职。
Luís Filipe Montenegro Cardoso de Morais Esteves (* 16. Februar 1973 in Porto), genannt Luís Montenegro, ist ein portugiesischer Jurist und Politiker.[1] Seit dem 2. April 2024 ist er Premierminister von Portugal.[2] Seit Mai 2022 ist er Vorsitzender der Partido Social Democrata. Von Mai 2022 bis März 2024 war er Oppositionsführer im Parlament.
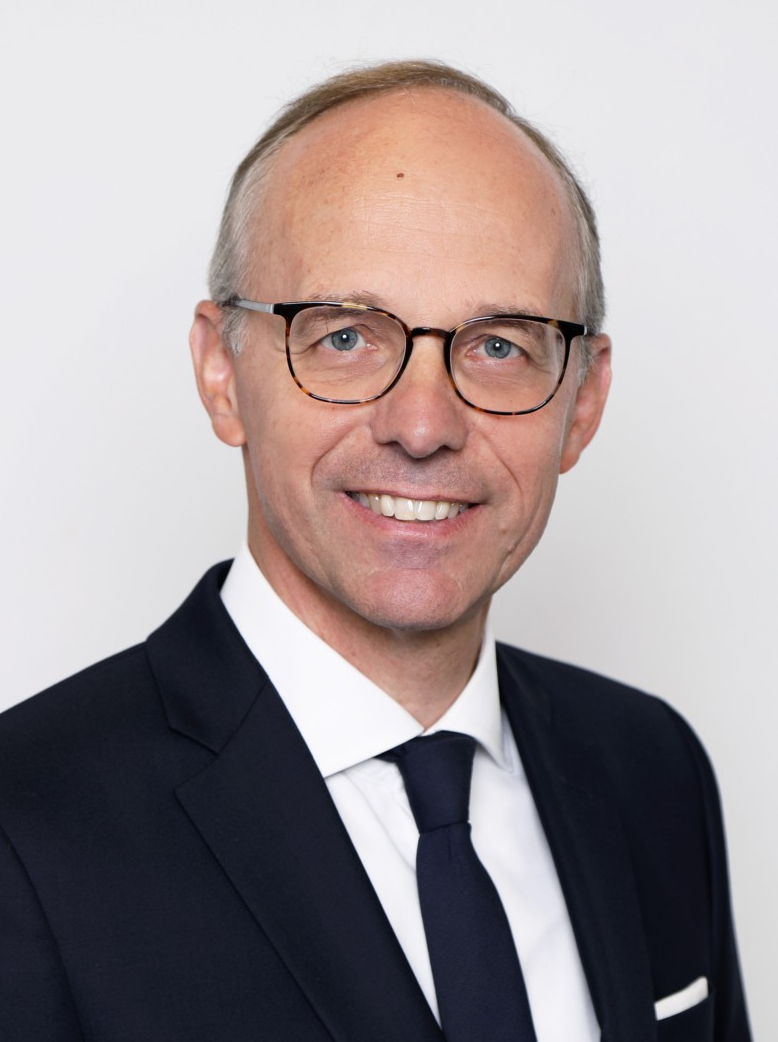


Luc Frieden (* 16. September 1963 in Esch an der Alzette) ist ein luxemburgischer Politiker (CSV) und ehemaliger Kammerfunktionär. Er ist seit dem 17. November 2023 Premierminister des Großherzogtums Luxemburg.
吕克·弗里登(卢森堡语:Luc Frieden,卢森堡语发音:[luk ˈfʀi.dən],1963年9月16日—),卢森堡政治人物、律师,自2023年11月起出任第25任卢森堡首相,基督教社会人民党,1998年至2013年在卢森堡政府担任多个内阁职务,当中又以财政与预算部长任内将卢森堡法郎过渡到欧元,以及财政部长任内率领卢森堡渡过欧洲主权债务危机而知名。另外,他也是卢森堡商会及欧洲商会主席。
2023年初,他当选基督教社会人民党首席候选人,代表社民党参加10月份举行的大选,最终帮助社民党取得大胜,得票率上涨同时,也保住了21个议。2023年10月9日,他受卢森堡大公亨利委托组建政府,11月17日正式接任格扎维埃·贝泰尔出任卢森堡首相[1]。
 法律
法律
 黑森州
黑森州
 巴登-符藤堡州
巴登-符藤堡州
 图林根州
图林根州






