
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Lausanne
Lausanne
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans
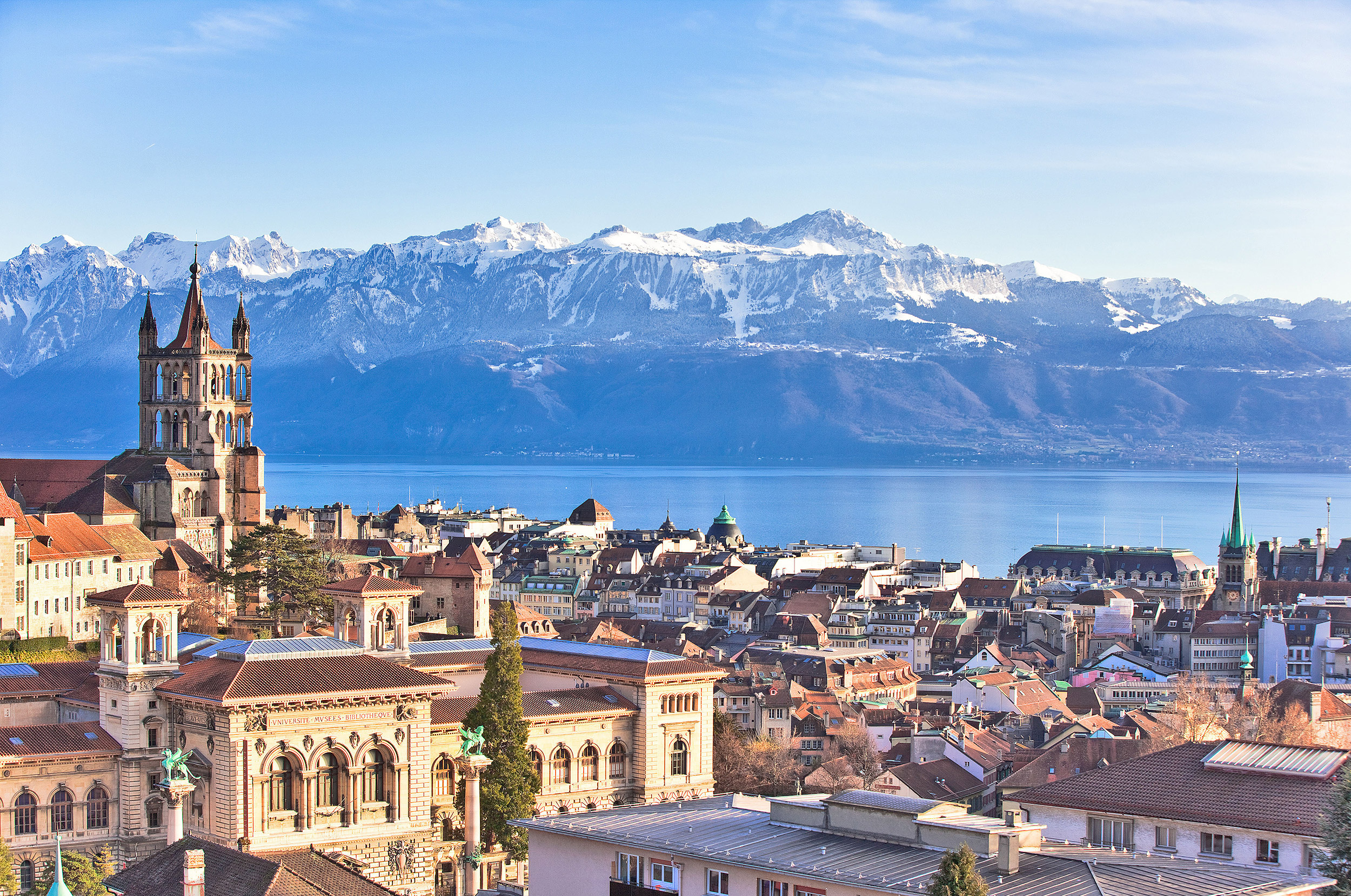

Lausanne [lɔˈzan] (deutsch veraltet auch Lausannen und Losanen,[4] frankoprovenzalisch Losena [lɔˈzəna],[5] italienisch und rätoromanisch Losanna) ist eine politische Gemeinde, der Hauptort des Schweizer Kantons Waadt und die Hauptstadt des Distrikts Lausanne. Die Stadt liegt in der französischsprachigen Schweiz (Romandie), am Genfersee und gehört mit ihren 144'000 Einwohnern[2] (Februar 2017) – neben Zürich, Genf, Basel, Bern und Winterthur – zu den grössten politischen Gemeinden der Schweiz.
Lausanne ist Teil der Metropolregion Genf-Lausanne mit 1,2 Millionen Einwohnern und ein bedeutendes Wirtschafts-, Kultur- und Bildungszentrum sowie eine wichtige Verkehrsdrehscheibe in der Westschweiz. Mit 43 Prozent Ausländern[2] (Einwohner ohne Bürgerrecht) zählt Lausanne, unter anderem neben Genf,[6] zu den Schweizer Städten mit hohem Ausländeranteil.
Das Bundesgericht (BGer) hat in Lausanne seinen Sitz, ebenso der Internationale Sportgerichtshof (TAS) und das Schweizer Filmarchiv. Zudem haben in Lausanne verschiedene Sportweltverbände, darunter das Internationale Olympische Komitee (IOC), ihren Hauptsitz. Seit 1994 trägt die Stadt den offiziellen Titel als «Olympische Hauptstadt».[7]
洛桑(法语:Lausanne,国际音标:[loˈzan])是瑞士法语区城市,位于莱芒湖(法语:Lac Léman)北岸,与法国城市埃维昂莱班隔湖相望,北面是侏罗纪山脉。洛桑位于日内瓦东北约50公里处,是瑞士联邦沃州和洛桑区首府,同时也是大洛桑都会区核心城市、瑞士第五大城市。洛桑与邻近的日内瓦一样,是许多著名的国际组织例如国际奥委会等的总部所在地,因此也称为“奥林匹克首都”。洛桑境内的洛桑管理学院亦是世界一流的著名学府与研究机构。洛桑也位于瑞士酿酒区的中心位置。另外,位于洛桑的洛桑联邦理工学院是瑞士两所联邦理工学院之一。
ローザンヌ(Lausanne)は、スイスのヴォー州に属する基礎自治体(コミューン) で、同州の州都。フランス語圏に属し、フランス語でのより正確な発音は「ロザン」[loˈzan][2]または「ロウザン」[loʊˈzan][3]、ドイツ語でのより正確な発音は「ロザン」[loˈzan][4]。イタリア語、ロマンシュ語ではLosannaと綴る。
レマン湖の北岸に位置する[5]。近隣の主要都市としては、約80km北東にベルン、レマン湖に沿って約50km南西にジュネーヴが位置する。
国際オリンピック委員会(IOC)の本部が置かれており、「オリンピックの首都(Olympic Capital)」とも言われる。2020年冬季ユースオリンピックの開催地となっている。
国際柔道連盟(IJF)、国際スケート連盟(ISU)、世界野球ソフトボール連盟(WBSC)の本部もここに置かれている。
スイス連邦の連邦最高裁判所が置かれ、同国の「司法首都」となっている。
1973年より、若手バレリーナの登竜門として知られるローザンヌ国際バレエコンクールが開催されていることでも知られる。
Lausanne (/loʊˈzæn/, French pronunciation: [lozan], German: Lausanne,[3] Italian: Losanna, Romansh: Losanna)[4] is a city in the French-speaking part of Switzerland, and the capital and biggest city of the canton of Vaud. The city is situated on the shores of Lake Geneva (French: Lac Léman, or simply Le Léman).[5] It faces the French town of Évian-les-Bains, with the Jura Mountains to its north-west. Lausanne is located 62 kilometres (38.5 miles) northeast of Geneva.
Lausanne has a population (as of November 2015) of 146,372,[6] making it the fourth largest city in Switzerland, with the entire agglomeration area having 420,000 inhabitants (as of March 2015).[7] The metropolitan area of Lausanne-Geneva (including Vevey-Montreux, Yverdon-les-Bains, and foreign parts) was over 1.2 million inhabitants in 2000.[8]
Lausanne is a focus of international sport, hosting the International Olympic Committee (which recognizes the city as the "Olympic Capital" since 1994),[9] the Court of Arbitration for Sport and some 55 international sport associations.[10] It lies in a noted wine-growing region. The city has a 28-station metro system, making it the smallest city in the world to have a rapid transit system.[citation needed] Lausanne will host the 2020 Winter Youth Olympics.[11]
Lausanne est une ville suisse située sur la rive nord du lac Léman. Elle est la capitale et ville principale du canton de Vaud3 et le chef-lieu du district de Lausanne. Elle constitue la quatrième ville du pays en termes de population4 après Zurich, Genève et Bâle. Fin 2014, l'agglomération lausannoise compte 402 900 habitants5 et la commune de Lausanne en compte, en incluant la population non-permanente, 145 000 en 2017 (près de 137 000 en comptant uniquement la population permanente, à fin 2016)6,1. En 2012, l'agglomération lausannoise compte 50 % de la population du canton de Vaud et concentre 60 % des emplois7. Elle héberge le vaste campus de l'Université de Lausanne (UNIL) et de l'École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), ainsi que l'EHL, l'ECAL et l'IMD.
Dans la ville se trouvent le Tribunal fédéral, le site principal de la Cinémathèque suisse ainsi que le siège du Comité international olympique (CIO) et de 55 fédérations sportives internationales. Elle porte le titre officiel de « Capitale olympique »8 depuis 1994. Elle sera l'hôte des Jeux olympiques de la jeunesse d'hiver de 2020.
Losanna (AFI: [loˈzanna][1]; in francese: Lausanne; in arpitano: Losena; in romancio: Losanna; in tedesco: Lausanne o anche, antiquati, Lausannen e Losanen) è una città della Svizzera, capitale del Canton Vaud e dell'omonimo distretto.
Conta 137.810 abitanti (424.000 nell'hinterland) ed è la quarta città più grande della Svizzera, preceduta in ordine decrescente da Zurigo, Ginevra e Basilea. È situata sulla sponda settentrionale del Lago Lemano (Lac Léman in Francese), chiamato anche Lago di Ginevra.
È un importante centro di attività commerciali bancarie e universitarie ed è sede della famosa scuola di danza Rudra-Béjart, fondata dal grande coreografo Maurice Béjart. Nel 1994, Losanna fu dichiarata Capitale Olimpica ed è quindi sede del Comitato Olimpico Internazionale.
La città di Losanna è collegata alla cittadina francese di Évian tramite battello.
Lausana2 (en francés y alemán, Lausanne [loˈzan], en italiano y romanche Losanna) es una ciudad y comuna de Suiza, capital del cantón de Vaud y del distrito de Lausana. Se sitúa a orillas del lago Lemán, frente a la ciudad francesa de Évian-les-Bains.
Lausana es la cuarta ciudad más poblada de Suiza tras Zúrich, Ginebra y Basilea. En Romandía es la segunda ciudad después de Ginebra. La ciudad es conocida como la Capital Olímpica, ya que es sede del Comité Olímpico Internacional, además del también deportivo Museo Olímpico. A finales de 2016, Lausana contaba con 139 624 habitantes,1 sumando un total de 420.067 habitantes en su área metropolitana.
Лоза́нна (фр. Lausanne [loˈzan], франкопров. Losena [lɔˈzəna]) — город на юго-западе Швейцарии, столица франкоязычного кантона Во и административный центр округа Лозанна.
Население — 138,6 тыс. человек (май 2013 года), четвёртый по величине город страны. Иммигранты составляют 40 % населения. В пределах агломерации проживает 336,4 тыс. человек (2010 год). Расположена в Романдии, на террасных холмах у северного берега Женевского озера, в 62 км от Женевы[4].
Лозанна носит звание «Олимпийской столицы» мира. Здесь располагаются штаб-квартиры Международного олимпийского комитета и многочисленных международных спортивных федераций. Местонахождение Спортивного арбитражного суда и Верховного суда Швейцарии. Имеются университет, политехническая школа и бизнес-школа IMD. Основной вид общественного транспорта — троллейбус; действует единственное в стране метро.
Исторический центр к северу от вокзала опутан сетью кривых и крутых улочек. На холме Ситэ средневековый замок Сен-Мер и готический собор Нотр-Дам; в Нижнем городе церковь святого Франциска; на площади Палю старинная ратуша. Реки убраны в подземные коллекторы, мосты сухопутны. К югу от вокзала набережная Уши́.
В древности на месте Лозанны существовало поселение, в I веке до н. э. получившее римское название Лузонна. С VI века была епископским городом под властью европейских государств. В XVI веке после завоевания Берном вошла в Швейцарский союз, введена Реформация. В 1803 году стала столицей кантона Во.
 England
England
 England
England
 Manchester
Manchester

 History
History
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 Important port
Important port
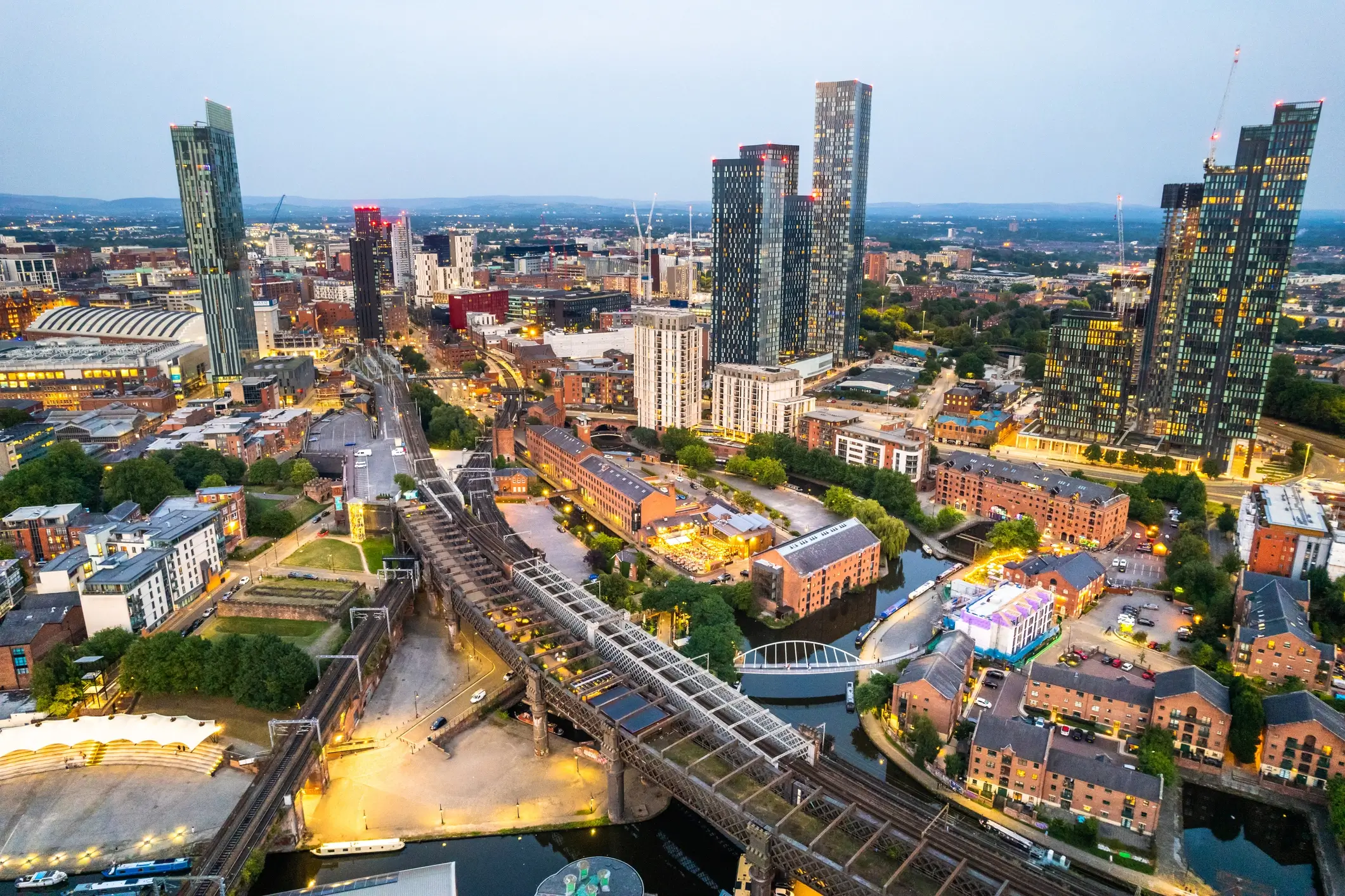

Manchester ([ˈmɛntʃɛstɐ], englisch [ˈmæntʃɪstə])[1] ist eine Stadt im Nordwesten von England im Vereinigten Königreich Großbritannien und Nordirland mit dem Status eines Metropolitan Borough sowie einer City. Sie hat etwa 570.000 Einwohner und liegt im Metropolitan County Greater Manchester, einer der größten Agglomerationen in England mit 2,9 Mio. Einwohnern (2022). Die Einwohner Manchesters werden „Mancunians“ oder verkürzt „Mancs“ genannt.
Die Ursprünge der Stadt Manchester gehen auf ein römisches Kastell am Zusammenfluss der Flüsse Irwell und Medlock zurück. Vor allem im Zeitalter der Industriellen Revolution wurde Manchester zu einem wichtigen Standort der Industrie. Einen besonderen Stellenwert nahm dabei die Textilindustrie ein, deren Anfänge in Manchester auf das Spätmittelalter zurückgehen. Im 20. Jahrhundert erfolgte der stetige Zerfall der Industrie. Heute ist Manchester dennoch eines der wichtigsten Wirtschaftszentren des Vereinigten Königreichs und beherbergt zahlreiche Museen, Hochschulen und Orte der Kunst und Kultur.
曼彻斯特市(英语:City of Manchester),即曼彻斯特(英语:Manchester),是英格兰的城市,都市自治市,位于西北英格兰区域,人口约为55万人,是曼彻斯特都市圈中人口最多的城市,且是英格兰西北第一多,英国第五多的城市。
曼彻斯特在工业革命史中有着重要位置。十八世纪,资本主义在这座城市萌芽,让本是农村地区的曼彻斯特经历急速发展并成为全世界第一座工业化的城市。全世界第一条城际通勤铁路在此诞生。因市内兴盛的纺织业,曼彻斯特在工业革命期间曾因仓库众多而闻名于世,使其获得了“仓库城市”的别称。曼彻斯特在科学技术史上也占有重要位置。成立于2002年的曼彻斯特大学及其前身见证了原子核物理学的诞生,世界上第一台存储程式电脑以及石墨烯的发现。
曼彻斯特被誉为“北方之都”[2][3],是英格兰北部一个极其重要的城市,尤其是在其经济、艺术、文化、交通运输、媒体和体育地位上。步入二十一世纪,曼彻斯特的发展愈发强势,为这座城市带来了与伯明翰竞争英国第二大城市的地位的资本[4]。
1974年,曼彻斯特与周围市镇联合组成大曼彻斯特郡,成为该郡的一个都会区。“曼彻斯特”此名常用来指整个都市区。整个大曼彻斯特的市区总人口在英国排名第二,仅次于伦敦。
マンチェスター (Manchester, IPA: [ˈmænˌtʃɪstə][ヘルプ/ファイル]) は、イングランドの北西部、グレーター・マンチェスターに位置する都市。北部イングランドを代表する都市であり、イギリスで9番目の都市である。1853年に市制(英語版)が布かれ、2011年の時点で、マンチェスター(都市と都市バラ)の人口は49万人である。2011年の近郊を含む都市圏人口は224万人であり、同国第3位である[2]。
[ˈmænˌtʃɪstə][ヘルプ/ファイル]) は、イングランドの北西部、グレーター・マンチェスターに位置する都市。北部イングランドを代表する都市であり、イギリスで9番目の都市である。1853年に市制(英語版)が布かれ、2011年の時点で、マンチェスター(都市と都市バラ)の人口は49万人である。2011年の近郊を含む都市圏人口は224万人であり、同国第3位である[2]。
Manchester (/ˈmæntʃɪstər, -tʃɛs-/)[5][6] is a city and metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England, with a population of 545,500 as of 2017.[7] It lies within the United Kingdom's third-most populous metropolitan area, with a population of 3.2 million.[8] Manchester is fringed by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and an arc of towns with which it forms a continuous conurbation. The local authority is Manchester City Council.
The recorded history of Manchester began with the civilian settlement associated with the Roman fort of Mamucium or Mancunium, which was established in about AD 79 on a sandstone bluff near the confluence of the rivers Medlock and Irwell. It was historically a part of Lancashire, although areas of Cheshire south of the River Mersey were incorporated in the 20th century.[9] Throughout the Middle Ages Manchester remained a manorial township but began to expand "at an astonishing rate" around the turn of the 19th century. Manchester's unplanned urbanisation was brought on by a boom in textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution,[10] and resulted in it becoming the world's first industrialised city.[11]
Manchester achieved city status in 1853. The Manchester Ship Canal opened in 1894, creating the Port of Manchester and directly linking the city to the Irish Sea, 36 miles (58 km) to the west. Its fortune declined after the Second World War, owing to deindustrialisation, but the IRA bombing in 1996 led to extensive investment and regeneration.[12]
In 2014, the Globalization and World Cities Research Network ranked Manchester as a beta world city, the highest-ranked British city apart from London.[13] Manchester is the third-most visited city in the UK, after London and Edinburgh.[14] It is notable for its architecture, culture, musical exports, media links, scientific and engineering output, social impact, sports clubs and transport connections. Manchester Liverpool Road railway station was the world's first inter-city passenger railway station; scientists first split the atom, developed the stored-program computer and produced graphene in the city. Manchester hosted the 2002 Commonwealth Games.
Manchester Ecoutez (ˈmanˌtʃɪstə) est une ville du Royaume-Uni située dans le comté métropolitain du Grand Manchester. Elle a le statut de cité depuis 1853 et compte 545 500 habitants en 2017. Elle est parfois considérée comme la « deuxième ville d’Angleterre » grâce à son importance économique, culturelle et sportive1, bien que sa superficie et sa population ne lui permettent pas de détrôner Birmingham. Manchester est catégorisée comme une ville « bêta » par Le GaWC (Réseau d’étude sur la mondialisation et les villes mondiales2). Ses habitants s'appellent les Mancunien(ne)s. La ville est au cœur d'une grande agglomération de plus de deux millions et demi d'habitants dont les villes principales sont : Bury, Bolton, Rochdale, Oldham, Ashton-under-Lyne, Stockport, Salford, Altrincham, Wigan. Le nom de « Manchester » est utilisé aussi bien pour désigner l'agglomération que la ville en tant que telle.
Manchester est située à 260 km au nord-ouest de Londres, sur la rive est de la rivière Irwell. La ville est bordée au Sud par la plaine du Cheshire et au Nord et à l'Est par la chaîne montagneuse des Pennines. Historiquement, la majeure partie de la ville faisait partie du Lancashire, mais des zones situées au sud de la rivière Mersey appartenaient au Cheshire. Le vicus créé par les Romains à proximité du fort de Mamucium, construit en 79 sur un monticule rocheux non loin de la confluence entre la Medlock et l'Irwell, est devenu au fil de son histoire une ville majeure du nord de l'Angleterre. Manchester est la première ville au monde à avoir été industrialisée, et elle a joué un rôle important durant la révolution industrielle. Durant le XIXe siècle, la ville acquiert d'ailleurs le surnom de « Cottonopolis » en raison de son importante industrie cotonnière. L'économie de la ville s'est depuis tournée vers le secteur tertiaire, et il s'agit aujourd'hui d'un pôle financier important.
Manchester est une ville importante culturellement, qui héberge de nombreux théâtres, musées et salles de concert. La ville a vu dans les années 1980 l'émergence de divers groupes de rock indépendant autour du club The Haçienda, qui deviendront très célèbres par la suite et que l'on regroupe sous l'appellation « Madchester ». Elle a une économie nocturne bien développée avec de nombreux bars et clubs. La ville est le siège de divers médias, dont de nombreuses stations de radios, des journaux et une importante base de la BBC. L'architecture de la ville est marquée par l'omniprésence des briques rouges. Elle mêle des bâtiments historiques, comme la cathédrale gothique, des édifices de l'époque victorienne et de la période industrielle, avec des bâtiments à l'architecture contemporaine, dont de hauts gratte-ciel. Manchester est la troisième ville la plus visitée par les étrangers au Royaume-Uni.
Manchester est également une importante ville étudiante avec ses deux universités, l'université de Manchester et l'université métropolitaine de Manchester qui, avec entre-autres le Royal Northern College of Music, regroupent plus de 70 000 étudiants.
La ville accueillit en 2002 les jeux du Commonwealth. Elle se démarque également dans le monde sportif par ses deux équipes de Premier League de football, Manchester United et Manchester City.
Manchester (AFI: /ˈmanʧester/[3]; in inglese [ˈmantʃɪstə][4]), in italiano antico Mancunia, è un borgo metropolitano di 503.127 abitanti del Regno Unito, che gode del titolo onorifico di città, ed è capoluogo della contea metropolitana inglese della Greater Manchester. Insediamento celtico poi rinominata dagli antichi romani magna castra, i suoi abitanti vengono chiamati Mancunians (Mancuniani).
Mánchester1 (pronunciado en inglés  /ˈmæntʃɛstə/ (?·i)) es una ciudad y un municipio metropolitano del condado de Gran Mánchester en Inglaterra. Mánchester obtuvo su estatus de ciudad en 1853 y tenía una población estimada de 530.300 habitantes en 2015.2 A su vez, forma parte de la segunda aglomeración urbana del Reino Unido y decimocuarta de la Unión Europea en términos de población.
/ˈmæntʃɛstə/ (?·i)) es una ciudad y un municipio metropolitano del condado de Gran Mánchester en Inglaterra. Mánchester obtuvo su estatus de ciudad en 1853 y tenía una población estimada de 530.300 habitantes en 2015.2 A su vez, forma parte de la segunda aglomeración urbana del Reino Unido y decimocuarta de la Unión Europea en términos de población.
Mánchester es un importante centro artístico, financiero, de medios de comunicación y de educación superior. En una encuesta de líderes empresariales británicos publicada en 2006, Mánchester era considerada como el mejor lugar en el Reino Unido para establecer un negocio. Un informe encargado por la Asociación de Mánchester, publicado en 2007, mostró a Mánchester como la "ciudad con más rápido crecimiento económico". Es la tercera ciudad más visitada en el Reino Unido por turistas extranjeros. Mánchester fue la anfitriona de los Juegos de la Mancomunidad de 2002, y es sede de dos equipos de fútbol de la Premier League, Manchester United y Manchester City.
Históricamente la mayor parte de la ciudad fue parte del condado de Lancashire, con las zonas ubicadas al sur del río Mersey en el condado de Cheshire. Mánchester fue la primera ciudad industrializada del mundo y desempeñó un papel central durante la Revolución industrial. Se convirtió en el principal centro internacional de la fabricación textil y de hilado de algodón. Durante el siglo XIX adquirió el apodo de "Cottonopolis", sugiriendo que era una metrópoli de las fábricas de algodón. El centro de la ciudad se encuentra en una lista provisional del Patrimonio de la Humanidad de la Unesco, debido principalmente a la red de canales y molinos construidos durante los siglos XVIII y XIX.
Манче́стер[2] (англ. Manchester ['mænʧɪstə]) — город и метрополитенский район в Северо-Западной Англии, графство Большой Манчестер. Менее чем полумиллионный город имеет крупнейшую в регионе 2,2-миллионную агломерацию Большой Манчестер. Девятый по величине город Великобритании (и восьмой — Англии).
Наряду с Бирмингемом, Лидсом, Шеффилдом, Ливерпулем и Лондоном Манчестер был одним из центров Промышленной революции. В настоящее время Манчестер — крупный культурный, промышленный, финансовый, коммерческий и транспортный центр страны. Развито машиностроение, текстильная, химическая, лёгкая, бумажная промышленность. Действует морской порт. Манчестерский университет является одним из самых престижных в Великобритании. Имеется городской музей и художественная галерея[3].
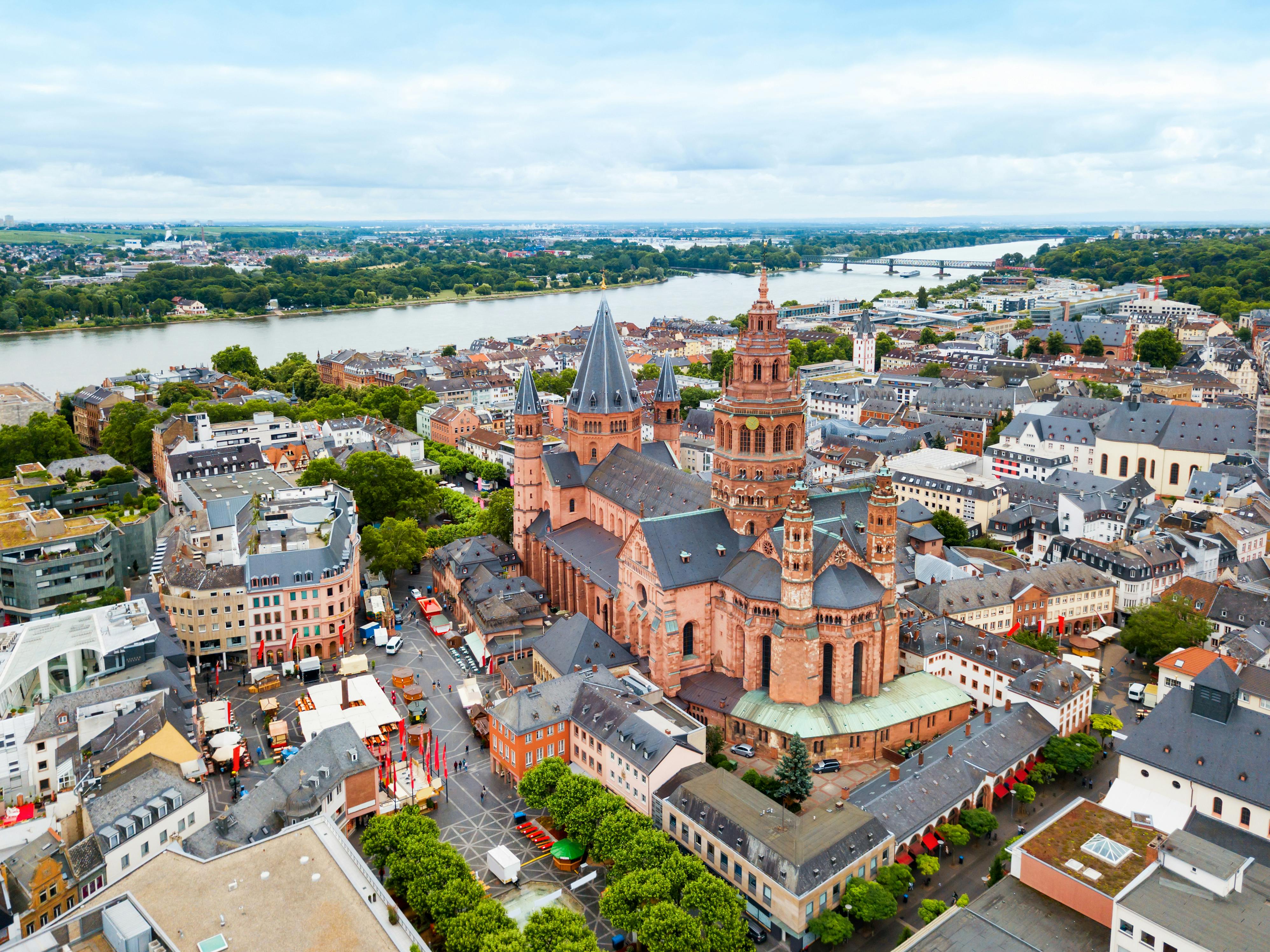
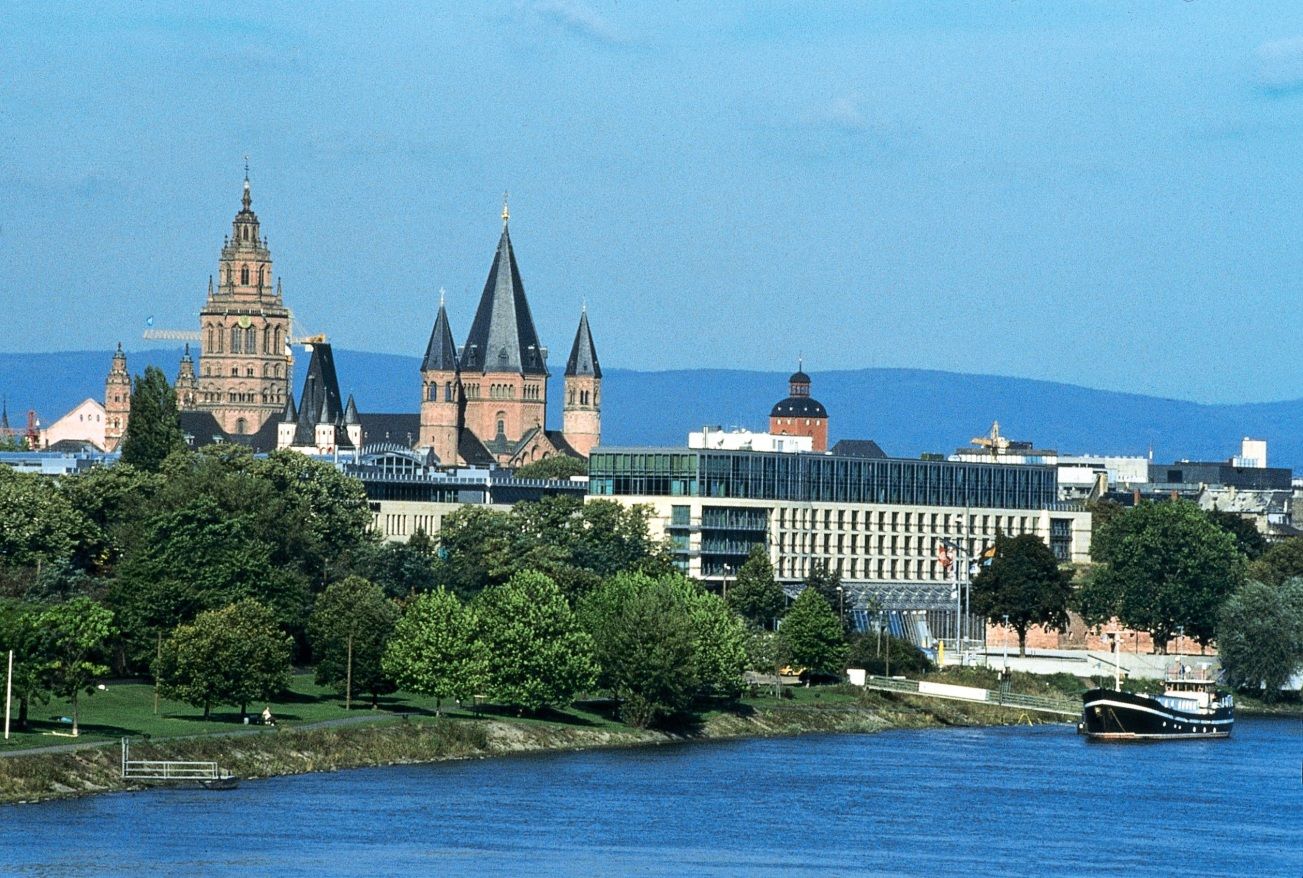




Mainz () ist die Landeshauptstadt des Landes Rheinland-Pfalz und mit 218.578 Einwohnern[1] zugleich dessen größte Stadt. Mainz ist kreisfrei, eines der fünf rheinland-pfälzischen Oberzentren und Teil des Rhein-Main-Gebiets. Mit der angrenzenden hessischen Landeshauptstadt Wiesbaden bildet es ein länderübergreifendes Doppelzentrum mit rund 495.000 Einwohnern. Mainz und Wiesbaden sind die einzigen beiden Landeshauptstädte deutscher Flächenländer mit einer gemeinsamen Stadtgrenze.
Die zu römischer Zeit gegründete Stadt ist Sitz der Johannes Gutenberg-Universität, des römisch-katholischen Bistums Mainz sowie mehrerer Fernseh- und Rundfunkanstalten, wie des Südwestrundfunks (SWR) und des Zweiten Deutschen Fernsehens (ZDF). Mainz ist eine Hochburg der rheinischen Fastnacht.
美因茨[1](德语:Mainz)是德国莱茵兰-普法尔茨州的首府和最大城市,位于莱茵河左岸,正对美茵河注入莱茵河的入口处。美因茨是政教古都,在神圣罗马帝国时代,美因茨大主教身兼帝国七大选帝侯之一,驻跸在此,政治与宗教势力权倾一时。美因茨拥有一所古老的大学,以活字印刷术的发明人谷登堡为大学命名。目前有多个电视台和广播电台的总部设立在此。美因茨也是莱茵河流域的狂欢节重镇之一,每年二月,美因茨、科隆与杜塞尔多夫的狂欢节最为盛大。邻近美因茨的重要城市尚有威斯巴登、达姆施塔特和法兰克福等等。
マインツ(独: Mainz)は、ドイツ連邦共和国の都市。ラインラント=プファルツ州の州都。中世よりマインツ大司教の司教座聖堂の所在地であり、活版印刷の発明者ヨハネス・グーテンベルクの出身地でもある。一時フランス領であった時期には、フランス語のマイエンス(仏: Mayence)の名で呼ばれた。ラインガウ(Rheingau)とプファルツ(Pfalz)のワインの集散地であり、当地産のスパークリング・ワイン「クッパ―ベルク」(Kupferberg)は特に有名である。楽譜出版で著名なショット(de:Schott Music)もこの地にある。ローレライはじめ様々な伝説に彩られた風景や古城の景色を楽しめるライン下りの観光船はマインツを出港地としている。ビンゲンからコブレンツまでの「ライン渓谷中流上部」(Das Obere Mittelrheintal)は2002年ユネスコ文化遺産に登録された。赤地に白の車輪(Weiße Räder im roten Schild)を表わす市の紋章は、伝説によれば、1009年に司教に選任されたヴィレギス(Willegis)の故事に由来する[2]。
Mainz (/maɪnts/; German: [maɪ̯nt͡s] (![]() listen); Latin: Mogontiacum, French: Mayence) is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The city is located on the Rhine river at its confluence with the Main river, opposite Wiesbaden on the border with Hesse. Mainz is an independent city with a population of 217,118 (2018) and forms part of the Frankfurt Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region.[3]
listen); Latin: Mogontiacum, French: Mayence) is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The city is located on the Rhine river at its confluence with the Main river, opposite Wiesbaden on the border with Hesse. Mainz is an independent city with a population of 217,118 (2018) and forms part of the Frankfurt Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region.[3]
Mainz was founded by the Romans in the 1st century BC during the Classical antiquity era, serving as a military fortress on the northernmost frontier of the Roman Empire and as the provincial capital of Germania Superior. Mainz became an important city in the 8th century AD as part of the Holy Roman Empire, becoming the capital of the Electorate of Mainz and seat of the Archbishop-Elector of Mainz, the Primate of Germany. Mainz is famous as the home of Johannes Gutenberg, the inventor of the movable-type printing press, who in the early 1450s manufactured his first books in the city, including the Gutenberg Bible. Mainz was heavily damaged during World War II, with more than 30 air raids destroying about 80 percent of the city's center, including most of the historic buildings. Today, Mainz is a transport hub and a center of wine production.
Mayence (en allemand : Mainz, prononcé /maɪ̯nt͡s/, en latin classique Mogontiacum, devenu Magontia en latin tardif) est une ville allemande, capitale, arrondissement et plus grande ville du Land de Rhénanie-Palatinat (Rheinland-Pfalz). Entourée de vignobles (Mayence est la première ville d'Allemagne pour le commerce du vin), elle est située sur la rive gauche du Rhin, en face du confluent du Main.
Mayence est une ancienne cité romaine, une ville universitaire et un archevêché ; son archevêque était l'un des sept (huit à partir de la réforme des institutions du Reich en 1648, puis neuf en 1692, et à nouveau huit en 1777) princes-électeurs du Saint-Empire romain germanique.
C'est aussi le siège de nombreuses entreprises médiatiques. Elle est entourée de villes importantes comme Mannheim, Darmstadt, Wiesbaden et Francfort-sur-le-Main.
Ville natale de Johannes Gutenberg. Ancien chef-lieu du département du Mont-Tonnerre. Sa cathédrale a plus de 1 000 ans. Les habitants de Mayence sont les Mayençais (Mainzer en allemand).
La ville a mis au point un système de signalisation très simple : les rues inscrites en rouge et blanc mènent au Rhin tandis que les rues en bleu et blanc lui sont parallèles.
Magonza (AFI: /maˈɡonʦa/[2]; in tedesco: Mainz, in dialetto Määnz, in francese: Mayence) è una città della Germania occidentale situata alla confluenza dei fiumi Meno e Reno, capoluogo del Land della Renania-Palatinato. Sede dell'Università Johannes Gutenberg di Magonza, è molto nota per il suo carnevale.
Maguncia1 (en alemán: Mainz ![]() [maɪ̯nt͡s] (?·i); en francés: Mayence; en latín: Moguntiacum) es la capital del estado federado alemán de Renania-Palatinado. Es una ciudad situada en el suroeste de Alemania, a orillas del río Rin, en la margen opuesta a la desembocadura del Meno, por lo que es un importante puerto fluvial de Alemania. En la orilla contraria se encuentra la ciudad de Wiesbaden, en el estado de Hesse.
[maɪ̯nt͡s] (?·i); en francés: Mayence; en latín: Moguntiacum) es la capital del estado federado alemán de Renania-Palatinado. Es una ciudad situada en el suroeste de Alemania, a orillas del río Rin, en la margen opuesta a la desembocadura del Meno, por lo que es un importante puerto fluvial de Alemania. En la orilla contraria se encuentra la ciudad de Wiesbaden, en el estado de Hesse.
Destaca por ser el lugar donde Johannes Gutenberg inventó la imprenta de caracteres móviles. Actualmente Maguncia ha vuelto a ser centro de los medios de comunicación, ya que alberga la sede de la ZDF, el segundo canal más importante del medio televisivo alemán.
Aunque fue gravemente dañada durante la Segunda Guerra Mundial, la ciudad conserva gran parte de su casco antiguo, en el que destacan las construcciones realizadas en piedra de color rojo (arenisca, principalmente).
Maguncia tiene universidad propia desde 1477, denominada actualmente Universidad Johannes Gutenberg, ubicada cerca del centro de la ciudad. Su antiguo campus no solo comprende aulas y salas de conferencia, sino también viviendas, bares y restaurantes que constituyen un barrio independiente.
Con 215.110 habitantes (a 31 de diciembre de 2017), es la tercera ciudad más grande de la región Rin-Meno. Su equipo de fútbol FSV Maguncia 05 juega en la primera división de la Bundesliga.
Майнц (нем. Mainz, пфальц. Määnz / Meenz) — город в Германии, столица земли Рейнланд-Пфальц. Население — 213 528 человек (2016).

Southampton [saʊθˈæmptən] ist eine Hafenstadt im Vereinigten Königreich Großbritannien und Nordirland an der Südküste Englands im County Hampshire. Sie liegt am Southampton Water, der Flussmündung des Test und des Itchen, der in den Ärmelkanal mündet. Die Stadt hat 254.000 Einwohner. Sie ist als Metropolregion mit anderen Orten rund um den Solent locker zur Southampton Urban Area (856.000 Einwohner) zusammengeschlossen.
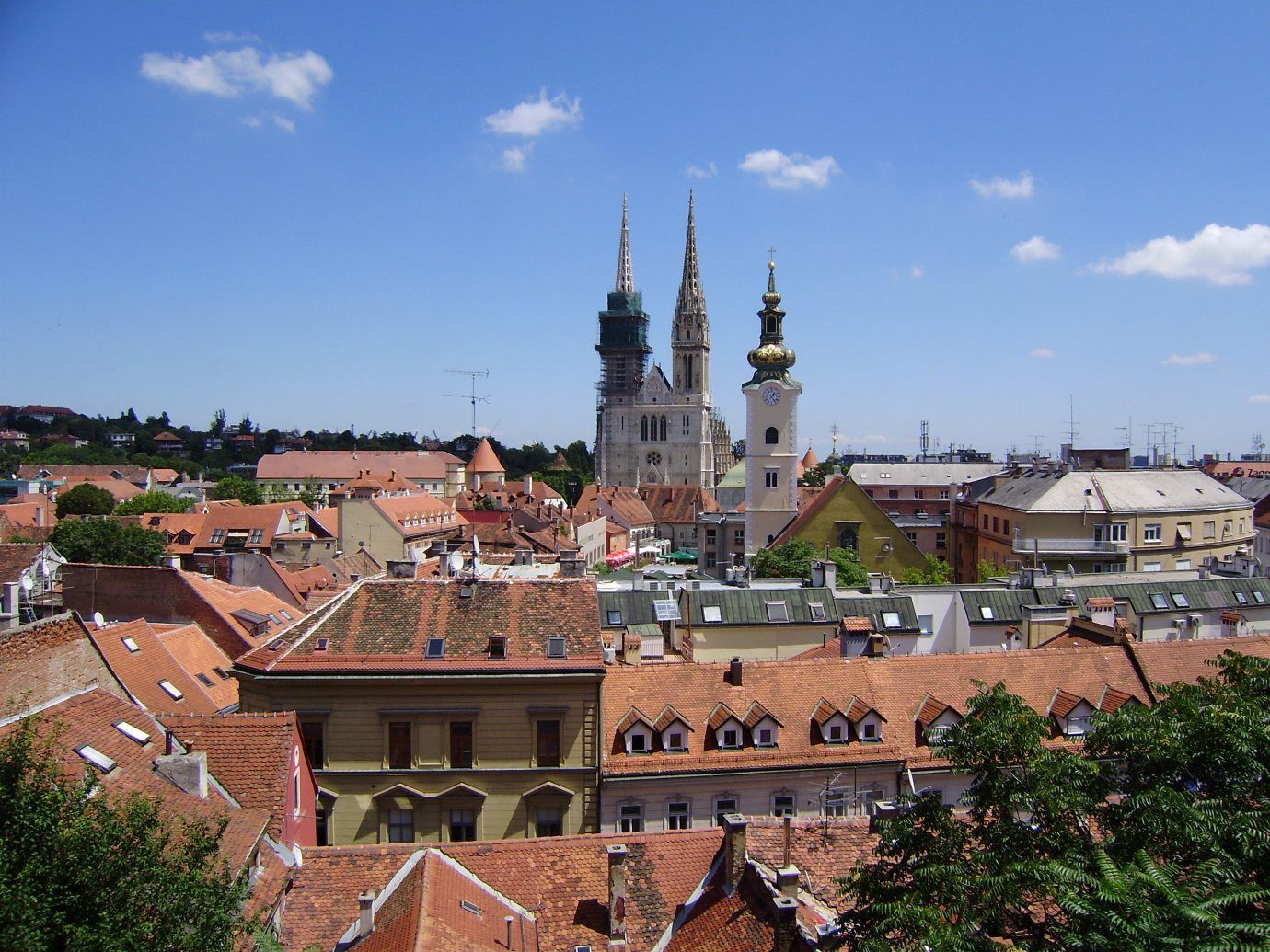




Zagreb [ˈzaːgrɛb] (deutsch Agram, heute selten genutzt; ungarisch Zágráb) ist die Hauptstadt und zugleich größte Stadt Kroatiens. Die Stadt Zagreb selbst hat auch die Funktionen einer Gespanschaft. Die nähere Umgebung der Stadt bildet getrennt von dieser die Gespanschaft Zagreb, deren Verwaltungssitz auch die Stadt Zagreb ist. In Zagreb residieren ein katholischer Erzbischof, die Kroatische Akademie der Wissenschaften und Künste sowie wichtige Verwaltungs- und Militärbehörden. Als Handels- und Finanzzentrum hat die Stadt nationale und regionale Bedeutung.
Die Zagreber Kathedrale ist Sitz der katholischen Erzdiözese Zagreb.
萨格勒布(克罗地亚语:Zagreb;德语旧称:Agram,阿格拉姆;匈牙利语:Zágráb),是克罗地亚的首都和札格雷布县的首府同时也是全国最大城市、一个直辖市。萨格勒布克罗地亚国内足球强队萨格勒布迪纳摩主场位于这里。萨格勒布位于海平面122m(400英尺),它位于克罗地亚的西北部的梅德韦德尼察山南坡,境内有萨瓦河流过。在2011年的正式人口普查中,萨格勒布市人口是792,875人[1]。连同萨格勒布县总人口达到了1,110,517。是克罗地亚唯一一个超过百万人口的大都市区。[2]
萨格勒布是一个有着悠久历史的城市(从古罗马时代到现在)。1094年在东部的卡普托尔主教教区内“萨格勒布”这个名称始见于史籍。在1845年扬科·卡毛夫成为萨格勒布的第一位市长。在1945年,随着人口快速的膨胀和城市的扩张,萨格勒布成为了克罗地亚的首都,从此萨格勒布开始闻名于世界。
萨格勒布在克罗地亚行政区划中有着十分特殊的地位(直辖市)。被管理细分为17个区域,它们大多是都位处低于海平面的萨瓦河山谷。
萨格勒布是克罗地亚全国、西欧和地中海和东南部欧洲的的最重要的交通枢纽。萨格勒布还有通往其他国家的国际列车。市内还有有轨电车。
ザグレブ(クロアチア語: Zagreb)は、クロアチアの首都。同国最大の都市である。クロアチアの北西部サヴァ川河畔に位置しメドヴェドニツァ山の南斜面にあり海抜は122mである。2011年の国勢調査による人口はザグレブ市街が686,568人、ザグレブ市域では792,875人であった。ザグレブ市と周辺の行政的に分かれているザグレブ郡の人口317,642人を合わせたザグレブ都市圏の人口は1,110,517人である。ザグレブはクロアチアでは唯一、100万人を超える都市圏を形成している。[5]
アルプスやディナルアルプス、アドリア海方向へ広がるパンノニア平原南西部の有利な地理的な条件により、中央ヨーロッパとアドリア海を結ぶ良く整備された交通回廊によって周辺地域と結ばれている。ザグレブは交通の要衝である他、産業の集積や科学研究機関、伝統的な産業などでクロアチアで先導する地位にある。また、首都としてクロアチアの中央政府や行政機関、省庁のほとんどがザグレブに拠点を置いている。
Zagreb (/ˈzɑːɡrɛb/ ZAH-greb, Croatian pronunciation: [zǎːɡreb] (![]() listen))[8] is the capital and the largest city of Croatia.[9] It is located in the northwest of the country, along the Sava river, at the southern slopes of the Medvednica mountain. Zagreb lies at an elevation of approximately 122 m (400 ft) above sea level.[10][11] The estimated population of the city in 2018 is 810,003. The population of the Zagreb urban agglomeration is about 1.1 million, approximately a quarter of the total population of Croatia.
listen))[8] is the capital and the largest city of Croatia.[9] It is located in the northwest of the country, along the Sava river, at the southern slopes of the Medvednica mountain. Zagreb lies at an elevation of approximately 122 m (400 ft) above sea level.[10][11] The estimated population of the city in 2018 is 810,003. The population of the Zagreb urban agglomeration is about 1.1 million, approximately a quarter of the total population of Croatia.
Zagreb is a city with a rich history dating from the Roman times to the present day. The oldest settlement located in the vicinity of the city was the Roman Andautonia, in today's Ščitarjevo.[12][13][14][15] The name "Zagreb" is recorded in 1134, in reference to the foundation of the settlement at Kaptol in 1094. Zagreb became a free royal town in 1242.[16][17][18][19][20] In 1851 Zagreb had its first mayor,[21][22][23][24] Janko Kamauf.
Zagreb has a special status in the Croatia's administrative division and is a consolidated city-county (but separated from Zagreb County),[25][26][27][28] and is administratively subdivided into 17 city districts.[29][30][31] Most of them are at a low elevation along the river Sava valley, whereas northern and northeastern city districts, such as Podsljeme[32][33][34] and Sesvete[35][36][37] districts are situated in the foothills of the Medvednica mountain,[38] making the city's geographical image rather diverse. The city extends over 30 kilometres (19 miles) east-west and around 20 kilometres (12 miles) north-south.[39][40]
The transport connections, concentration of industry, scientific, and research institutions and industrial tradition underlie its leading economic position in Croatia.[41][42][43] Zagreb is the seat of the central government, administrative bodies, and almost all government ministries.[44][45][46] Almost all of the largest Croatian companies, media, and scientific institutions have their headquarters in the city. Zagreb is the most important transport hub in Croatia where Central Europe, the Mediterranean and Southeast Europe meet, making the Zagreb area the centre of the road, rail and air networks of Croatia. It is a city known for its diverse economy, high quality of living, museums, sporting, and entertainment events. Its main branches of economy are high-tech industries and the service sector.
Zagreb (prononcé en croate : /ˈzɑːgrɛb/ ; hongrois : Zágráb ; italien : Zagabria ; anciennement nommée en allemand : Agram) est une ville et un comitat (« ville de Zagreb »), capitale de la Croatie. Au recensement de 2011, la ville comptait 688 163 habitants, le comitat 790 017 habitants, dont 93,14 % de Croates5 et la région de Zagreb (le comitat « ville de Zagreb » plus le comitat de Zagreb) comptait 1 107 623 habitants.
Zagreb est située au nord du pays sur les flancs de la Medvednica à côté de la Save à une altitude d'environ 122 m au-dessus du niveau de la mer. Sa situation géographique favorable dans le Sud-Ouest de la plaine de Pannonie qui s'étend des Alpes aux Alpes dinariques et à la mer Adriatique la place sur les axes de communication entre l'Europe centrale et la mer Adriatique.
Les interconnexions de transports, la concentration des industries, de la recherche scientifique et industrielle font de Zagreb le centre économique de la Croatie. Zagreb est également le siège du gouvernement, des corps administratifs et de presque tous les ministères.
Zagabria (in croato Zagreb, pronuncia [ˈzɑːgrɛb]; in tedesco, ai tempi dell'Impero austro-ungarico, Agram; in ungherese Zágráb) è la capitale e la maggiore città della Croazia, con i suoi 809 832 abitanti. Il centro cittadino costituisce una delle regioni della Croazia, mentre l'area geografica intorno alla città fa parte di un'altra unità amministrativa, la Regione di Zagabria.
Zagabria è sede degli organi centrali dello Stato (il Parlamento, il Presidente della Repubblica, il Governo ed il Primo ministro, la Corte Costituzionale, la Corte Suprema) e praticamente di tutti i ministeri. È anche sede universitaria (Università di Zagabria, Università Cattolica Croata, Università Internazionale Libertas, alte scuole, politecnici) e arcivescovile metropolitana (l'arcidiocesi di Zagabria con diocesi suffraganee a Varasdino, Sisak, Bjelovar-Križevci e l'eparchia greco-cattolica a Križevci di rito bizantino).
Zagreb (![]() [ˈzǎːɡreb] (?·i)) es la capital y ciudad más poblada de Croacia. Está localizada al noroeste del país, entre el río Sava y la ladera sur del monte Medvednica, a unos 122 metros sobre el nivel del mar. Dentro de su término municipal residen más de 890 000 habitantes en 2018, lo que la convierte en la cuarta ciudad más grande de Europa Sudoriental y en la segunda por extensión. Si se tienen en cuenta las poblaciones limítrofes, la cifra del área metropolitana asciende a 1 100 000 personas empadronadas.
[ˈzǎːɡreb] (?·i)) es la capital y ciudad más poblada de Croacia. Está localizada al noroeste del país, entre el río Sava y la ladera sur del monte Medvednica, a unos 122 metros sobre el nivel del mar. Dentro de su término municipal residen más de 890 000 habitantes en 2018, lo que la convierte en la cuarta ciudad más grande de Europa Sudoriental y en la segunda por extensión. Si se tienen en cuenta las poblaciones limítrofes, la cifra del área metropolitana asciende a 1 100 000 personas empadronadas.
La zona sobre la que se asienta Zagreb está habitada desde el Imperio romano. El yacimiento más antiguo que se ha localizado es la ciudad romana de Andautonia, situada a 10 km de la actual capital. El término «Zagreb» fue registrado por primera vez en 1134 para referirse a la archidiócesis de Zagreb, fundada en 1094,5 si bien durante siglos hubo dos pueblos distintos: Gradec —con bula de oro desde 1242— y Kaptol, donde se hallaba la catedral. Ambas localidades se fusionaron en 1851 por orden del ban Josip Jelačić para formar la ciudad actual.5
A diferencia de otras localidades del país, Zagreb tiene un estatus especial como «ciudad-condado», independiente del condado de Zagreb. A nivel administrativo está dividida en 17 distritos; la mayoría se encuentran en las zonas bajas cercanas al río Sava, mientras que los barrios del noroeste se sitúan a los pies del monte Medvednica. Su extensión total es de 30 km de este a oeste, y de 20 km de norte a sur.
En calidad de capital de Croacia, Zagreb alberga la sede del gobierno central, de las administraciones públicas y de casi todos los ministerios. La actividad económica concentra la mayoría de la industria, las sedes empresariales y los centros de investigación, con un sistema especializado en tecnologías de la información y en el sector servicios. Es asimismo el principal centro de comunicaciones de Croacia por tierra y aire, siendo un punto clave en la encrucijada entre Europa Central, el Adriático y el resto de la península balcánica. Dispone de una amplia oferta de eventos culturales y deportivos.
За́греб (хорв. Zagreb [ˈzâːɡrɛb]), Аграм (нем. Agram) — столица и крупнейший город Хорватии. Население — 790 017 человек (2011), площадь — 641,29 км². Город расположен на реке Саве, притоке Дуная, на 45,815° северной широты и 15,98306° восточной долготы, на высоте 104 метров над уровнем моря (низшая точка) рядом с горным массивом Медведница. Загреб основан более 900 лет назад.
Город Загреб с пригородами имеет статус отдельной жупании в составе Хорватии, руководство городом осуществляет мэр, избираемый городской ассамблеей. 31 мая 2009 года мэром города на четвёртый срок (третий подряд) был избран Милан Бандич[1].
Загреб находится в зоне континентального климата. Средняя летняя температура составляет +21 градус по Цельсию, средняя зимняя температура +2 градуса по Цельсию. Время — среднеевропейское, GMT+1.

Speyer (bis 1825 auch Speier[2]) ist eine kreisfreie Universitätsstadt in Rheinland-Pfalz und Teil der Metropolregion Rhein-Neckar. Als römische Gründung, damals Noviomagus oder Civitas Nemetum (Hauptstadt des Stammes der Nemeter) genannt, ist sie eine der ältesten Städte Deutschlands und wurde als Spira um 600 Zentrum des Speyergaues. Im Mittelalter war Speyer als freie Reichsstadt eine der bedeutendsten Städte des Heiligen Römischen Reiches Deutscher Nation. Von 1816 bis 1945 war sie Sitz der bayerischen Verwaltung der Pfalz. Heute gehört Speyer zu Rheinland-Pfalz und hat 51.368 Einwohner (Stand 2022).
Weithin bekannt ist die heutige Mittelstadt durch ihren Kaiser- und Mariendom, der zugleich Kathedrale des römisch-katholischen Bistums Speyer ist. Er ist die weltweit größte noch erhaltene romanische Kirche und zählt seit 1981 zum UNESCO-Welterbe. Die jüdischen Stätten Speyers, zusammen mit denen der anderen beiden SchUM-Städte Mainz und Worms, sind 2021 ebenfalls UNESCO-Weltkulturerbe geworden.
施派尔[2](德语:Speyer,德语发音:[ˈʃpaɪ̯ɐ] (ⓘ))是位于德国莱茵兰-普法尔茨州莱茵河畔的一座非县辖城市,总面积42.71平方千米,截至2022年12月31日总人口为51,368人。
施派尔拥有许多保存良好的古老建筑,例如被联合国教育科学文化组织(UNESCO)评定为世界文化遗产的施派尔主教座堂(Der Dom Zu Speyer)、纪念抗议宗在议会中争取改革的纪念教堂(Gedächtniskirche)、莱茵流域唯一后洛可可风格的三位一体教堂(Dreifaltigkeitkirche)、以及德国境内最高耸和最重要的护城门。
施派尔(Speyer)是位于德国莱茵兰-普法尔茨州莱茵河畔的一座城市。
1529年4月19日神圣罗马帝国在此召开帝国会议,讨论解冻迫害新教徒的《沃木斯议会》议案,遭到部分与会的诸侯和自由城市代表的反对,史称“抗议者”(德语:Protestanten),即新教徒的代名词。
约在五千年前,施派尔即拥有着第一批原始住民在这块土地上活动。接着自从凯撒争夺下高卢地区以后,莱因河成了迅速扩展的罗马帝国一道保护疆界,而刚好位于莱因河东方的施派尔,也成了罗马士兵驻军的一大据点。在主后一百五十年,施派尔以“NOVIOMAGUS”的名称出现在希腊人托勒密(Ptolemaios)的世界地图中。直到主后346年以后,才以施派尔这个名称纳入主教区中。
十六世纪中期,施派尔成为德国历史的转捩点,自从路德于主后1521年站上沃木斯帝国会议,和皇帝卡尔五世以及教廷答辩以降,就在欧洲大陆掀起了一股宗教改革的风潮,而主后1526年,帝国会议举办在施派尔主教座堂,也使施派尔瞬间涌进了大批的皇亲贵族。历经了1526年的帝国会议,在1529年帝国会议再一次于施派尔举行,并且至此时奠定了抗议宗教会(Protestation)的基础。
施派尔拥有许多保存良好的古老建筑,例如被联合国教育科学文化组织(ENESCO)评定为世界文化遗产的施派尔主教座堂(Der Dom Zu Speyer)、纪念抗议宗在议会中争取改革的纪念教堂(Gedächtniskirche)、莱因流域唯一后洛可可风格的三位一体教堂(Dreifaltigkeitkirche)、以及德国境内最高耸和最重要的护城门。
シュパイアー(標準ドイツ語: Speyer、アレマン語: Spayre(シュパイレ))は、ドイツ中南部の都市。ラインラント=プファルツ州南東部に属する。街の人口は約5万人(2003年)である。ローマ帝国時代に建設された。かつては舞台ドイツ語の発音に基づいてシュパイエルと呼ばれた。シュパイヤーの表記も用いられる。
Speyer (German pronunciation: [ˈʃpaɪ̯ɐ], older spelling Speier, known as Spire in French and formerly as Spires in English) is a town in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, with approximately 50,000 inhabitants. Located beside the river Rhine, Speyer is 25 km (16 miles) south of Ludwigshafen and Mannheim. Founded by the Romans, it is one of Germany's oldest cities. Speyer is dominated by the Speyer Cathedral, a number of churches and the Altpörtel (old gate). In the cathedral, beneath the high altar, are the tombs of eight Holy Roman emperors and German kings.
The city is famous for the 1529 Protestation at Speyer.
Spire (Speyer en allemand) est une ville portuaire et un arrondissement du Sud du Land de Rhénanie-Palatinat. Elle compte 50 513 habitants au 30 juin 2006.
Le Conseil de l'Europe lui décerne le prix de l'Europe de 19991.
Spira[1] (in tedesco Speyer, in tedesco palatino Schbaija, in francese Spire) è una città extracircondariale (targa SP) di 49.811 abitanti della Renania-Palatinato, in Germania. Situata lungo il corso del Reno, si trova a circa 25 km a sud di Ludwigshafen e Mannheim.
Centro di grande importanza storica e culturale, la città è nota per l'imponente cattedrale, inserita dal 1981 nella lista dei patrimoni dell'umanità dell'UNESCO.
Espira (en alemán: Speyer) es una ciudad del estado federado alemán de Renania-Palatinado. Espira tiene aproximadamente 50 000 habitantes y está localizada a orillas del río Rin, 25 km al sur de Mannheim y 25 km al norte de Karlsruhe. Fue fundada por los romanos, lo que convierte a Espira en una de las ciudades más antiguas de Alemania. En la antigüedad, la zona se conocía como Noviomagus y Civitas Nemetum, de la tribu teutónica de los németes, que estaban asentados en la zona.
La ciudad está dominada por la Catedral de Espira, numerosas iglesias y la Puerta Vieja (Altportal). En la Catedral, detrás del altar mayor se sitúan las tumbas de ocho emperadores del Sacro Imperio Romano Germánico.
En 1999, la ciudad fue laureada con el Premio de Europa, una distinción otorgada anualmente por el Consejo de Europa, desde 1955, a aquellos municipios que hayan hecho notables esfuerzos para promover el ideal de la unidad europea.
Шпа́йер[2] (также Шпе́йер; нем. Speyer, пфальц. Schbaija) — город земельного подчинения в Германии, в земле Рейнланд-Пфальц.
Расположен на Рейне (регион Рейн-Неккар). Население — около 50 тысяч человек. Археологические данные позволяют предполагать, что город был населён кельтами 500 лет до н. э., сначала носил название Новиомаг (Noviomagus), позднее, в эпоху римлян, город был известен под именем Аугуста Неметум и Цивитас Неметум (город племени Неметер), по имени германского племени, населявшего эту область. В VI веке город получил имя Спира (Spira) от названия реки Шпайербах (Speyerbach), протекающей через город.
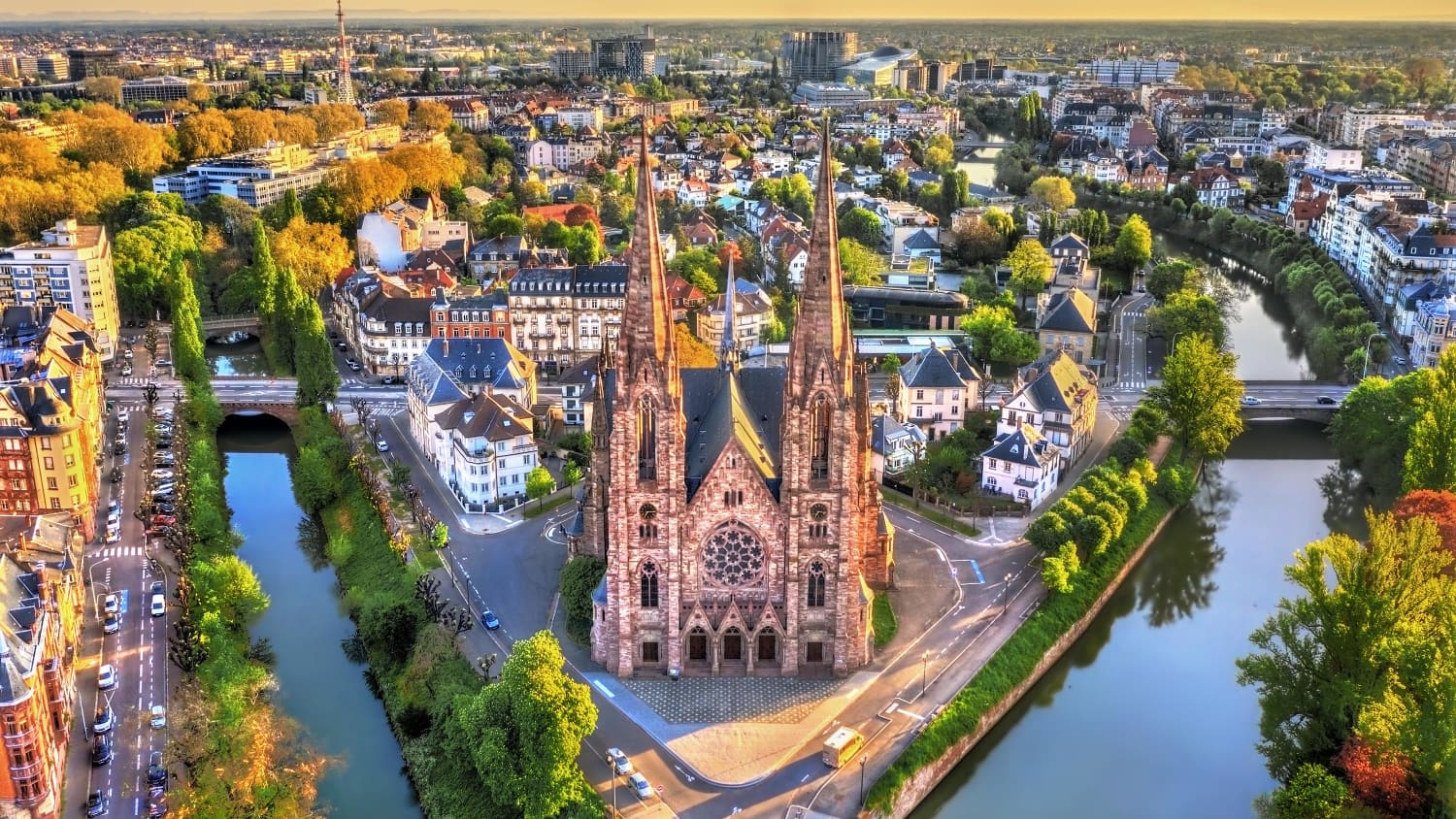
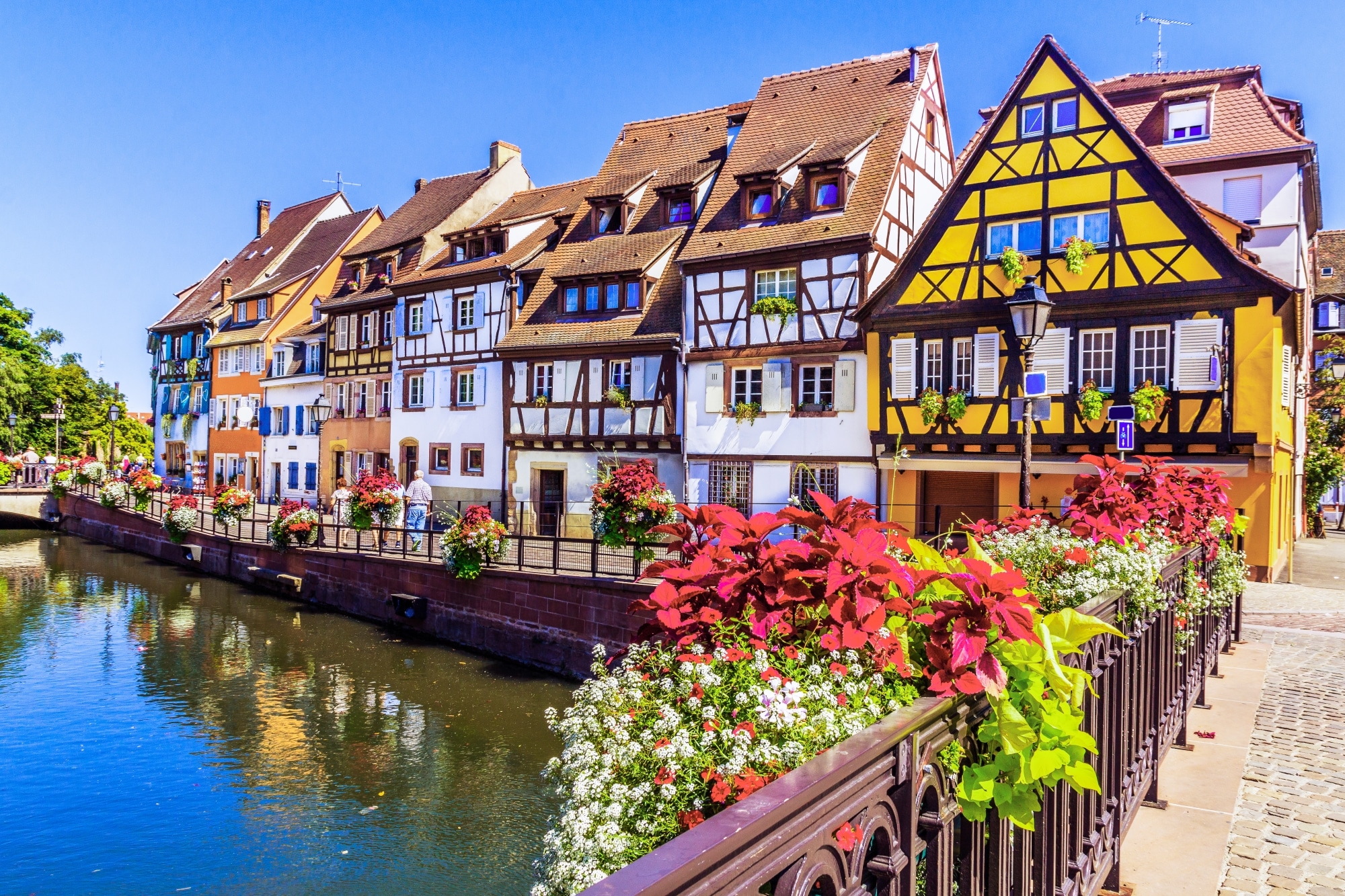
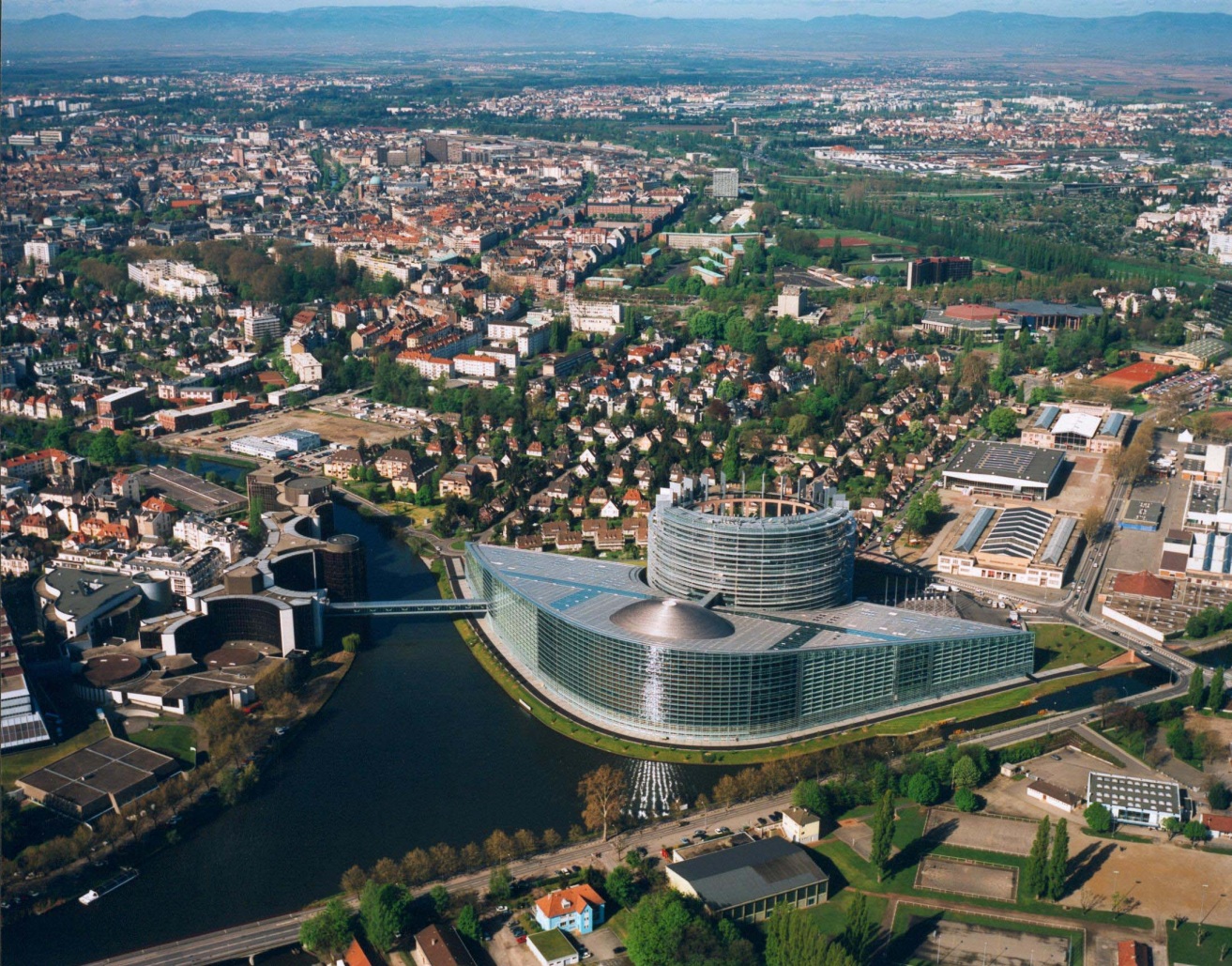



Straßburg (französisch Strasbourg [stʁazbuʁ], im Straßburger Dialekt Schdroosburi [ˈʃdɾoːsburi][1]) ist eine Stadt im Elsass, einer Landschaft im Osten Frankreichs an der Grenze zu Deutschland.
Die Stadt ist Hauptstadt und damit Sitz des Regionalrats und des Regionspräfekten der Region Grand Est sowie Sitz der Präfektur des Départements Bas-Rhin. Die Präfektur verwaltet auch das Arrondissement Strasbourg, das aus 33 Gemeinden besteht. Mit 277.270 Einwohnern (Stand 1. Januar 2015) im Stadtgebiet und etwa 640.000 Einwohnern in der Agglomeration ist Straßburg die größte Stadt im Elsass.[2]
Straßburg ist Sitz zahlreicher europäischer Einrichtungen, unter anderem Europarat, Europaparlament, Europäischer Gerichtshof für Menschenrechte, Europäischer Bürgerbeauftragter und Eurokorps. Aufgrund dessen versteht sich Straßburg als „Hauptstadt Europas“.[3][4][5]
Teile der Innenstadt, die mittelalterliche Altstadt auf der Grande-île und die Neustadt, sind unter dem Titel Straßburg: von der Grande-Île zur Neustadt, eine europäische Stadtszenerie UNESCO-Weltkulturerbe.
斯特拉斯堡 (Strasbourg),法国东北部城市,大东部大区(Région Grand Est)的首府和下莱茵省(Bas-Rhin,67省)的省会,也是法国第七大城市和最大的边境城市 ,又称白堡。市区位于莱茵河西岸,东侧与德国巴登-符腾堡州隔河相望,西侧则为孚日山区。斯特拉斯堡远离海岸线,但仍然受到北大西洋暖流的影响,属于非典型性的温带海洋性气候。历史上,斯特拉斯堡处于多个民族活动范围的重合地带。从最初的凯尔特,再到高卢、日耳曼以及后来的法兰克、查理曼,这些民族都在斯特拉斯堡留下了足迹。十九时期中期开始则逐渐成为了德法长期争夺的焦点。二战后,凭借得天独厚的地理优势,欧洲委员会、欧洲人权法院、欧洲反贪局及欧洲议会等多个欧盟合作组织均在斯特拉斯堡设立总部 。
斯特拉斯堡(法语:Strasbourg;德语:Straßburg[4],意为“街道城堡”)是法国大东部大区与下莱茵省的首府,位于法国国土的东端,与德国的巴登-符腾堡州隔莱茵河相望。全市人口约27万,城市圈人口则超过64万[5],是法国东北部人口最多的城市,按2010年人口也是法国人口第九多的城市。
斯特拉斯堡属于法国,但是在历史上,此地的主权曾多次交替由德国和法国拥有,因而在语言和文化上兼有法国和德国的特点,是这两种不同文化的交汇之地。谷登堡、加尔文、歌德、莫扎特、巴斯德等德意志法兰西文化名人都曾在斯特拉斯堡居留。
斯特拉斯堡也是众多国际组织总部所在地的城市。斯特拉斯堡与比利时的首都布鲁塞尔一样,驻有欧盟的许多重要机构,包括欧洲委员会、欧洲人权法院、欧盟反贪局、欧洲军团、欧洲视听观察,以及欧洲议会的所在地,因此被誉为欧盟的“第二首都”。斯特拉斯堡是欧洲议会的所在地,尽管每个月只在斯特拉斯堡举行四天会议,其他主要事务则在布鲁塞尔处理。议会大厦建于1998年,是世界上最大的议会建筑。
斯特拉斯堡是法国乃至西欧公路、铁路和内河航运的重要中心。斯特拉斯堡港是莱茵河沿线的第二大港口,仅次于德国的杜伊斯堡[6]。该市也是莱茵河航运中央委员会的驻地。
斯特拉斯堡的历史中心位于伊尔河两条支流环绕的大岛,这一区域拥有中世纪以来的大量精美建筑,包括斯特拉斯堡大教堂与小法兰西,1988年被联合国教科文组织列为世界文化遗产,这也是首次有一个城市的整个市中心区域获此荣誉。
ストラスブール(仏・英: Strasbourg[注釈 1]、アルザス語: Schdroosburi[注釈 2]、アレマン語: Strossburi[注釈 3]、独: Straßburg[注釈 4])は、グラン・テスト地域圏の首府である。バ=ラン県の県庁所在地でもある。
フランス北東部の、ライン川左岸に位置する。河川港を抱える交通の要衝である。対岸にはドイツの都市ケールが存在するが、シェンゲン協定によってパスポートチェック無しで自由に行き来できる。2007年6月10日にはTGV東ヨーロッパ線が開業し、パリ東駅と2時間20分で結ばれた。
ストラスブール(シュトラースブルク)の語源はドイツ語で「街道の街」であり、交通の要衝として栄える。ライン川にフランス最大の河川港をもち、交通の便の良さから商工業が盛んである。1998年から当地のクレディ・ミュチュエル(フランス語版、英語版)が商工信用銀行(フランス語版、英語版)を支配している[注釈 5]。
かつてはドイツの神聖ローマ帝国に属したが、近世初頭にドイツの混乱に乗じてフランス王国が侵略して併合する。以降、ドイツとフランスが領有権を争った土地として有名である。言語や文化の上ではドイツ系であるといえるが、下記のように1944年以降、政治的にはフランスに属する。
現在は欧州評議会や欧州人権裁判所、またEUの欧州議会の本会議場を擁し、ベルギーのブリュッセルと共にEUの象徴的な都市の一つとなっている。フランス国立行政学院(ENA, エナ)の校舎もあり、欧州のエリートが当地で養成される。また、近郊の村エンツハイムにはスポーツウェア等で知られるルコックスポルティフの、同様に近郊のモルスアイムにはブガッティ・オトモビルの各本社機能がそれぞれ置かれている。
グーテンベルクやカルヴァン、ゲーテ、モーツァルト、パストゥールなども人生の一時期をこの地で過ごした。その中には現代史に欠かせないユダヤ銀行家がおり、マーク・ユージン・マイヤー(Marc Eugene Meyer 1842-1925)といった。その祖父はユダヤ教会役員会のラビ書記だった。自身は1859年17歳のときにカリフォルニアへ移住し、ロサンゼルスのデパート所有者となった。それからニューヨークでラザードの共同経営者となった[2]。その息子もラザードでキャリアを積み、連邦準備制度議長と初代世銀総裁を務めた。このようなマークの息子が授かった娘はキャサリン・グラハム女史である。
もっと永く過ごしたマークの同時代人で、ストラスブールの立場を理解するのに知っておくべき女性がいる。メラニー・ド・プルタレスは政治も担った。シュテファニー・フォン・ヴェデル(Stéphanie von Wedels, 1852-1937)はスウェーデンのヤーコプ・ハミルトンが父である。ストックホルム駐在ドイツ帝国大使のカール・フォン・ヴェデルと結婚した。1907年夫がラインラント総督へ就任したのを機に、ストラスブールへ定住した。身体障害児の養護施設シュテファニー・ホスピスをつくらせるなどの社会貢献をなした。
Strasbourg (/ˈstræzbɜːrɡ/, French: [stʁazbuʁ, stʁas-]; Alsatian: Strossburi [ˈʃd̥ʁɔːsb̥uʁi]; German: Straßburg [ˈʃtʁaːsbʊɐ̯k]) is the capital and largest city of the Grand Est region of France and is the official seat of the European Parliament. Located close to the border with Germany in the historic region of Alsace, it is the capital of the Bas-Rhin département. In 2014, the city proper had 276,170 inhabitants and both the Eurométropole de Strasbourg (Greater Strasbourg) and the Arrondissement of Strasbourg had 484,157 inhabitants.[2] Strasbourg's metropolitan area had a population of 773,347 in 2013 (not counting the section across the border in Germany), making it the ninth largest metro area in France and home to 13% of the Grand Est region's inhabitants. The transnational Eurodistrict Strasbourg-Ortenau had a population of 915,000 inhabitants in 2014.[5]
Strasbourg is one of the de facto capitals of the European Union (alongside Brussels and Luxembourg), as it is the seat of several European institutions, such as the Council of Europe (with its European Court of Human Rights, its European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and its European Audiovisual Observatory) and the Eurocorps, as well as the European Parliament and the European Ombudsman of the European Union. The city is also the seat of the Central Commission for Navigation on the Rhine and the International Institute of Human Rights.[6]
Strasbourg's historic city centre, the Grande Île (Grand Island), was classified a World Heritage site by UNESCO in 1988, the first time such an honour was placed on an entire city centre. Strasbourg is immersed in Franco-German culture and although violently disputed throughout history, has been a cultural bridge between France and Germany for centuries, especially through the University of Strasbourg, currently the second largest in France, and the coexistence of Catholic and Protestant culture. It is also home to the largest Islamic place of worship in France, the Strasbourg Grand Mosque.[7]
Economically, Strasbourg is an important centre of manufacturing and engineering, as well as a hub of road, rail, and river transportation. The port of Strasbourg is the second largest on the Rhine after Duisburg, Germany.[8]
Strasbourg (prononcé [stʁas.buʁ] Écouter) est une commune française située dans le département du Bas-Rhin. Préfecture du département, elle est également, depuis le 1er janvier 2016, le chef-lieu de la région Grand Est. Strasbourg se trouve dans la région historique d'Alsace, dont elle est considérée comme la capitale, et était le chef-lieu de la région administrative du même nom de 1982 à 2015.
La ville accueille de multiples institutions européennes et internationales, notamment le Conseil de l'Europe dont dépendent la Cour européenne des droits de l'homme et la Pharmacopée européenne, le Parlement européen ou encore le Médiateur européen. Elle revendique ainsi le titre de « capitale européenne ».
Par sa population, Strasbourg intra-muros est la première commune du Grand Est français et, à la date du 1er janvier 2018, la huitième de France. Son aire urbaine est la neuvième de France, comptant 768 868 habitants en 2012 dans sa partie françaiseNote 1 et 1 189 086 habitants avec la partie allemande. Ses habitants sont appelés les Strasbourgeois. Elle est l'un des principaux pôles économiques du Nord-Est et se distingue par un secteur secondaire très diversifié et un secteur tertiaire essentiellement tourné vers les activités financières, la recherche et le conseil aux entreprises1.
Ville frontière avec l'Allemagne, Strasbourg a été marquée par les différentes administrations germaniques et françaises. Son histoire, riche et tourmentée, a laissé un patrimoine architectural remarquable. Son centre-ville, situé sur la Grande Île, est entièrement inscrit au patrimoine mondial de l'humanité par l’UNESCO depuis 1988 et comprend notamment la cathédrale Notre-Dame de Strasbourg et le quartier de la Petite France. En 2017, le périmètre classé est étendu à une partie de la Neustadt, quartier construit par les autorités allemandes à partir de 18802.
Strasbourg est également devenue le symbole de la réconciliation franco-allemande et plus généralement de la construction européenne. La ville s’est progressivement spécialisée dans les fonctions politiques, culturelles, et institutionnelles. Elle est ainsi l’une des seules villes au monde à être le siège d'organisations internationales sans être capitale d’un pays3. Strasbourg est une ville de congrès internationaux, la deuxième de France après Paris4.
La présence de plusieurs établissements nationaux renommés, comme le théâtre national, la bibliothèque nationale et universitaire et l’Opéra national du Rhin en fait un centre culturel important.
Strasbourg est aussi une grande ville étudiante, son université, ses grandes écoles et son hôpital universitaire forment un pôle universitaire majeur tourné vers l’international avec plus de 20 % d'étudiants étrangers et plus de cent nationalités représentées5. L'université qui a accueilli 18 prix Nobel dans ses murs, a été lauréate de nombreux appels d'offres dans le cadre des investissements d'avenir, visant à en faire un pôle d'excellence dans l'enseignement supérieur et la recherche au niveau mondial6,7.
Strasburgo (AFI: /straˈzburɡo/[2][3]; in francese Strasbourg, [stʁas.buʁ]; in alsaziano Strossburi, [ˈʃtɾʊːsburi]; in tedesco Straßburg; dal latino Strateburgus, letteralmente "la città delle strade", nome alternativo dell'antica Argentoratum) è una città della Francia orientale, capoluogo della regione Grande Est e del dipartimento del Basso Reno, al confine con la Germania sulla riva sinistra del Reno.
Il suo nome è tedesco perché, in passato, il territorio dell'Alsazia è stato sotto il dominio sia della Francia che della Germania. L'Alsazia fu presa alla Francia dalla Germania (che allora era comandata da Bismarck) durante la battaglia di Sedan del 1870, e da allora fra i francesi nacque il sentimento del revanscismo.
I suoi abitanti sono chiamati strasburghesi (in tedesco Straßburger, in francese strasbourgeois). La città fa parte di un agglomerato urbano transfrontaliero di 1 145 000 abitanti che comprende anche la città tedesca di Kehl.
Strasburgo è sede, con Bruxelles, del Parlamento europeo e ospita, inoltre, il Consiglio d'Europa.
In essa operano l'Università di Strasburgo, la seconda più importante Università francese, e la prestigiosa Scuola Nazionale della Pubblica Amministrazione (ENA) fondata dal Presidente De Gaulle.
Estrasburgo3 (en francés: Strasbourg [stʁazbuʁ]; en alsaciano: Strossburi [ˈʃdɾoːsburi]; en alemán: Straßburg [ˈʃtʁaːsbʊɐ̯k]) es una ciudad de Francia, situada en la región histórica y cultural de Alsacia. Estrasburgo es capital del departamento del Bajo Rin, y desde el 1 de enero de 2016 de la región administrativa del Gran Este.
El área urbana de Estrasburgo alcanzó en 2009 una población de 1.175.393 habitantes, extendiendo su influencia a localidades próximas de Alemania y situándose en la novena posición de los núcleos de población más grandes de Francia. Por su situación, Estrasburgo es desde la antigüedad un importante centro de comunicaciones, especialmente fluvial, albergando el segundo puerto en importancia sobre el río Rin, siendo éste el río más transitado del mundo. Ciudad universitaria con más 58 000 estudiantes, tiene numerosas escuelas nacionales, siendo el mayor polo de estudios de tercer grado del país. La estructura comercial de Estraburgo es muy importante y su rango cultural, muy elevado con la presencia de un teatro, biblioteca, orquesta y ópera todos ellos de ámbito nacional. La ciudad es, con la capital del país, la única en tener ese nivel de instituciones culturales. Estrasburgo es la segunda plaza bancaria de Francia con una bolsa y 8 sedes bancarias. El sector industrial es especialmente activo, siendo la región de Estrasburgo la más dinámica del país en cuanto al PIB per cápita.
Su centro histórico está declarado Patrimonio Unesco de la Humanidad desde 1988 y su actividad turística es muy intensa. Es la octava ciudad de la lista mundial de ciudades organizadoras de congresos, por detrás de París y por delante de Barcelona.
Стра́сбу́рг[1], или Страсбу́р[2][3][4][5] (фр. Strasbourg [stʁas.buʁ]  слушать, эльз. Strossburi [ʃtrosburi], нем. Straßburg [ˈʃtʁaːsbʊɐ̯k]) — город и коммуна на востоке Франции, историческая столица Эльзаса и префектура департамента Нижний Рейн. Расположен в регионе Гранд-Эст[6] (бывший Эльзас — Шампань — Арденны — Лотарингия), департамент Нижний Рейн, округ Страсбур, кантоны: Страсбур-1, Страсбур-2, Страсбур-3, Страсбур-4, Страсбур-5, Страсбур-6[7] на реке Иль, близ левого (западного) берега реки Рейн, по которой проходит граница Франции и Германии, напротив немецкого города Кель. Население — 272 800 чел. (2004 год).
слушать, эльз. Strossburi [ʃtrosburi], нем. Straßburg [ˈʃtʁaːsbʊɐ̯k]) — город и коммуна на востоке Франции, историческая столица Эльзаса и префектура департамента Нижний Рейн. Расположен в регионе Гранд-Эст[6] (бывший Эльзас — Шампань — Арденны — Лотарингия), департамент Нижний Рейн, округ Страсбур, кантоны: Страсбур-1, Страсбур-2, Страсбур-3, Страсбур-4, Страсбур-5, Страсбур-6[7] на реке Иль, близ левого (западного) берега реки Рейн, по которой проходит граница Франции и Германии, напротив немецкого города Кель. Население — 272 800 чел. (2004 год).

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 *World's Most Livable Cities
*World's Most Livable Cities

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Zurich
Zurich
 Silk road
Silk road

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans
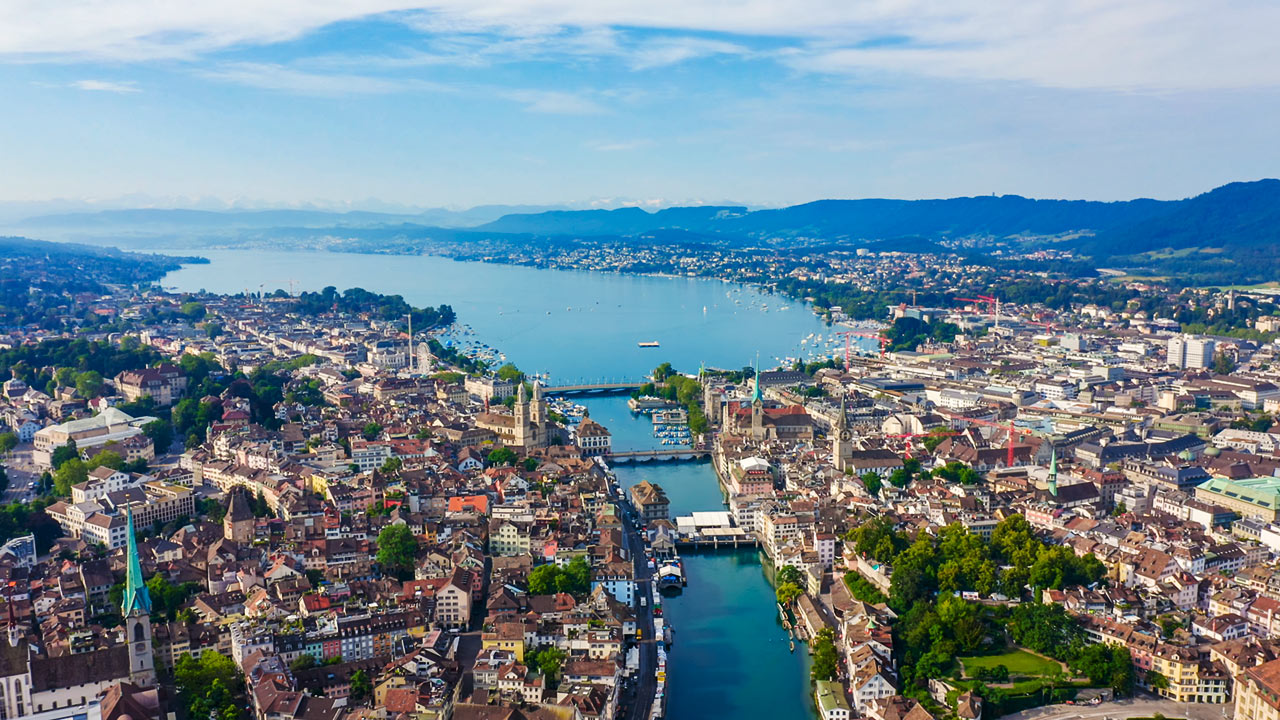

Zürich (zürichdeutsch Züri [ˈt͡sʏrɪ],[4] französisch Zurich [zyʁik], italienisch Zurigo [dzuˈriːɡo], rätoromanisch  Turitg?/i [tuˈritɕ]) ist eine Stadt, politische Gemeinde sowie Hauptort des gleichnamigen Kantons Zürich.
Turitg?/i [tuˈritɕ]) ist eine Stadt, politische Gemeinde sowie Hauptort des gleichnamigen Kantons Zürich.
Die Stadt Zürich ist mit 402'762 Einwohnern (Stand 31. Dezember 2016)[5] die grösste Stadt der Schweiz und weist eine Bevölkerungsdichte von 4384 Einwohnern pro Quadratkilometer auf. Die Stadt Zürich gibt die Wohnbevölkerung nach dem wirtschaftlichen Wohnsitzbegriff (umfasst unter anderem auch Wochenaufenthalter, Asylsuchende, Flüchtlinge mit vorläufiger Aufnahme) mit 425'795 Personen per Mai 2018 an.[6] Mit 32,1 Prozent (31. Dezember 2016)[7] weist Zürich einen überdurchschnittlich hohen Ausländeranteil (registrierte Bevölkerung ohne Schweizer Bürgerrecht) auf. Das Umland ist dicht besiedelt, so dass in der Agglomeration Zürich etwa 1,3 Millionen[8] und in der Metropolitanregion Zürich etwa 1,83 Millionen Menschen leben.[9] Der Bezirk Zürich ist mit dem Stadtgebiet identisch.
Die Stadt liegt im östlichen Schweizer Mittelland, an der Limmat am Ausfluss des Zürichsees. Ihre Einwohner werden Zürcher genannt (bzw. Stadtzürcher zur Differenzierung von den übrigen Einwohnern des Kantons).
Das aus dem römischen Stützpunkt Turicum entstandene Zürich wurde 1262 freie Reichsstadt und 1351 Mitglied der Eidgenossenschaft. Die Stadt des Reformators Huldrych Zwingli erlebte im Industriezeitalter ihren Aufstieg zur heutigen Wirtschaftsmetropole der Schweiz. 2014 wurde Zürich der Ehrentitel „Reformationsstadt Europas“ durch die Gemeinschaft Evangelischer Kirchen in Europa verliehen.[10]
Mit ihrem Hauptbahnhof, dem grössten Bahnhof der Schweiz, und dem Flughafen ist die Stadt Zürich ein kontinentaler Verkehrsknotenpunkt. Dank der ansässigen Grossbanken (u. a. UBS und Credit Suisse) und Versicherungen (Zurich Insurance Group und Swiss Re) ist sie ein internationaler Finanzplatz und der grösste Finanzplatz der Schweiz, gefolgt von Genf und Lugano. Daneben beherbergt die Stadt mit der Eidgenössischen Technischen Hochschule Zürich und der Universität Zürich die zwei grössten universitären Hochschulen der Schweiz. Trotz der vergleichsweise geringen Einwohnerzahl wird Zürich zu den Weltstädten gezählt. Zürich ist das wichtigste Zentrum der Schweizer Medien- und Kreativbranche.[11] Mit seiner Lage am Zürichsee, seiner gut erhaltenen mittelalterlichen Altstadt und einem vielseitigen Kulturangebot und Nachtleben ist es zudem ein Zentrum des Tourismus.
Seit Jahren wird Zürich neben Genf als eine der Städte mit der weltweit höchsten Lebensqualität[12][13] und zugleich mit den höchsten Lebenshaltungskosten[14][15][16] weltweit gelistet.
瑞士第一大城市,是工商、金融业和文化中心。拥有苏黎世国际机场(Unique Airport),是中国到瑞士的门户城市。乘坐火车或巴士10分钟即可从机场到达市中心。也可从其它城市轻松抵达,交通十分方便,是旅游的好选择。苏黎 世不但是经济文化中心城市,同时也具有旧街区和美丽的建筑,虽为大城市,兼具小城镇的独特魅力。苏黎世湖畔和利马特河沿岸绿树成荫,是人们休闲的好场所。 该城历史悠久,曾经是罗马帝国时期重要的关卡,至今仍保留了很多历史遗产。以圣母教堂(Fraumunster)为标志性建筑的旧城区,保留着浓郁的中世 纪风情。列宁和爱因斯坦等众多名人都在这里居住过。另一方面,名牌专卖店、高档餐厅、酒吧、俱乐部等时尚设施一应俱全,是美食、购物的天堂。另外,苏黎世 美术馆、苏黎世歌剧院、国际会议中心、音乐厅及剧场等文化设施应有尽有,各类文化活动也非常丰富。
*苏黎世州拥有120万人口,几乎是 瑞 士全国人口的六分之一。苏黎世市居民人口则为36万左右。当地人口的大多数除德语外,都至少会讲另一种外语。瑞士约有370万人(占瑞士总人口的一半)在 距离苏黎世中心一小时车程的范围内生活和工作。100家瑞士最大的企业中,有85家总部设在苏黎世地区。全球最大的美世人力资源咨询公司的“最适宜居住城 市”调查显示,苏黎世被认为是世界上生活质量整体指标最高的城市。
(Quelle:http://www.myswitzerland.com.cn)
苏黎世(德语:Zürich [ˈt͡syːrɪç];瑞士德语:Züri [ˈt͡syɾi]),又译苏黎士,是瑞士联邦的最大城市(2012年城市人口约38万,市区人口近110万,包括郊区在内的苏黎世都会区人口达190万。),苏黎世州的首府。苏黎世是瑞士主要的商业和文化中心(瑞士的政治中心和首都在伯尔尼)。苏黎世是瑞士银行业的代表城市,世界金融中心之一,瑞士联合银行、瑞士信贷银行和许多私人银行都将总部设在苏黎世。苏黎世国际机场是瑞士全国最大的机场。国际足球联合会总部也设在苏黎世。根据2006年[3]和2007年[4]的部分调查显示,苏黎世在这两年的世界最佳居住城市评选中高居全球首位。
“苏黎世”的名称可能来源于凯尔特语中的“Turus”,一项有力的证据就是在出土的公元2世纪罗马帝国占领时期的墓志铭上发现了古代该城名称的罗马化形式——“Turicum”。
チューリッヒ(ドイツ語: Zürich, ドイツ語発音: [ˈtsyːrɪç]; スイスドイツ語: Züri )は、スイス最大の都市でチューリッヒ州の州都である。スイス中央部にあり[1] 、チューリッヒ湖の北西端に位置している。チューリッヒ市の人口は約390,000人で[2]、チューリッヒ都市圏地域(英語版)には200万人近くが居住している[3]。チューリッヒは鉄道、道路、航空など交通の要衝で、チューリッヒ国際空港やチューリッヒ中央駅共にスイスでは最大規模で交通量が多い。7,000年間継続的に人が居住しているが、チューリッヒはローマ人により創建された紀元前15年のトゥリクムTuricumと呼ばれていた時代に遡る。中世、チューリッヒは独立性と帝国直接身分(英語版)を得ており、1519年にはフルドリッヒ・ツヴィングリが導くスイスのドイツ語圏でのプロテスタント宗教改革の発祥とその中心であった[4]。
チューリッヒは欧州有数の世界都市であり、2016年に発表された「世界の都市総合力ランキング」では、世界16位と評価された[5]。また、世界の巨大な金融センターの一つに含まれる[6]。2017年の調査によると、世界11位の金融センターであり、ヨーロッパの都市ではロンドンに次ぐ2位である[7]。街には多くの金融機関や大手銀行、研究開発センターが立地している。これは、法人税率の低さが海外の企業が本社を設置する際に魅力的であるためである。ライフスタイルマガジン (Monocle) の2012年の生活の質の調査 "Quality of Life Survey" でチューリッヒはリストされた25都市中1位であった[8]。いくつかの調査によれば、2006年から2008年にチューリッヒは世界で最も居住に適した都市 との評価があり、同様にヨーロッパでは最も裕福な都市とされた[9][10][11]。2014年、アメリカのシンクタンクが公表したビジネス・人材・文化・政治などを対象とした総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界第31位の都市と評価されており、同国では第1位である[12]。治安・教育水準・各種インフラ等バランスよく整っている。なかでも金融においてはひときわ有名であり、数多くの金融機関・投資ファンド・投資家が存在している。特にチューリッヒに拠点を置く投機筋は「チューリッヒの小鬼(英語版)」[13]と呼ばれ国際市場に大きな影響力を持っている。国際サッカー連盟(FIFA)をはじめとして、多くの国際機関・国際団体の本部も存在する。多くの博物館や美術館がチューリッヒ市内には立地しており、その中にはスイス国立博物館(英語版)やチューリッヒ美術館が含まれる[14]。チューリッヒはまたドイツ語圏では最も重要な劇場の一つがある[15]。
Zürich or Zurich (/ˈzjʊərɪk/ ZEWR-ik; see below for other names) is the largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zürich. It is located in north-central Switzerland[3] at the northwestern tip of Lake Zürich. The municipality has approximately 400,028[4] inhabitants, the urban agglomeration 1.315 million[5] and the Zürich metropolitan area 1.83 million.[6] Zürich is a hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Both Zürich Airport and railway station are the largest and busiest in the country.
Permanently settled for over 2,000 years, Zürich was founded by the Romans, who, in 15 BC, called it Turicum. However, early settlements have been found dating back more than 6,400 years ago.[7] During the Middle Ages, Zürich gained the independent and privileged status of imperial immediacy and, in 1519, became a primary centre of the Protestant Reformation in Europe under the leadership of Huldrych Zwingli.[8]
The official language of Zürich is German,[a] but the main spoken language is the local variant of the Alemannic Swiss German dialect, Zürich German.
Many museums and art galleries can be found in the city, including the Swiss National Museum and the Kunsthaus.[9] Schauspielhaus Zürich is one of the most important theatres in the German-speaking world.[10]
Zürich is a leading global city and among the world's largest financial centres despite having a relatively small population.[11] The city is home to a large number of financial institutions and banking companies. Most of Switzerland's research and development centres are concentrated in Zürich and the low tax rates attract overseas companies to set up their headquarters there.
Monocle's 2012 "Quality of Life Survey" ranked Zürich first on a list of the top 25 cities in the world "to make a base within".[12] According to several surveys from 2006 to 2008, Zürich was named the city with the best quality of life in the world as well as the wealthiest city in Europe in terms of GDP per capita.[13][14][15] The Economist Intelligence Unit's Global Liveability Ranking[16] sees Zürich rank among the top ten most liveable cities in the world.
Zurich (/zy.ʁik/) (allemand : Zürich /ˈtsyːʁɪç/, en Suisse /ˈtsyːrɪx/ Zürich, suisse allemand : Züri /ˈtsyɾi/, italien : Zurigo /dzuˈriːɡo/, romanche : Turitg /tuˈritɕ/) est une cité alémanique de Suisse, capitale du canton de Zurich. Même si l'allemand est la langue officielle, les Zurichois parlent le Züritüütsch, un dialecte de l'alémanique qui emprunte d'ailleurs certains termes à d'autres langues en plus de l'allemand dont le français, l'italien, ou encore l'anglais3. C'est une cité très cosmopolite, comptant 30 % d'étrangers. Dans son article intitulé « World's most expensive place to live is... » du 15 février 2012, The Economist classe Zurich comme étant la ville la plus chère au monde. Depuis, la ville occupe régulièrement la deuxième place dans le classement du journal britannique, juste derrière Hong Kong. Le cabinet Mercer la classe en deuxième position de 221 villes dans le monde en 2012 pour sa qualité de vie, juste derrière Amsterdam et devant Vienne 4.
Alors que Berne est la capitale de la Confédération suisse et un centre politique, Zurich est le centre économique, financier, scientifique et artistique international majeur du pays. Elle est la ville concentrant le plus d'établissements bancaires et financiers du pays, et fait d'ailleurs partie des « villes mondiales » de catégorie Alpha- selon la GaWC. Zurich est ainsi le sixième centre bancaire et financier mondial, derrière Londres, New York, Hong Kong, Singapour et Tokyo.
Zurich est la ville la plus peuplée de Suisse avec une population de près de 402 800 habitants en décembre 2016. L'agglomération, quant à elle, compte environ 1,3 million d'habitants, ce qui fait de Zurich une « petite » métropole en comparaison d'autres cités ayant une importance similaire5.
Située au bord du lac de Zurich (Zurichsee), le quatrième plus grand lac de Suisse en termes de superficie, Zurich est un lieu de villégiature apprécié par la bourgeoisie suisse, allemande et autrichienne, notamment en raison de la beauté de sa vue et de son centre historique, ainsi que de la douceur exceptionnelle de son climat. La rivière la traversant, la Limmat, a été classée rivière urbaine la plus propre d'Europe selon le Département de l'Agriculture des États-Unis en 2015. Les Zurichois ont l'habitude de s'y baigner, en plein cœur de la ville, en été.
Zurigo (/ʣuˈrigo/; in tedesco Zürich, pronunciato [ˈʦyːʀɪç]; in alemanno Züri; in francese Zurich, [zyˈʁik]; in romancio Turitg; in latino Turicum) è, con 402.762 abitanti, la maggiore città della Svizzera, nonché il capoluogo del cantone omonimo. È divisa in 12 quartieri. L'agglomerato urbano raggiunge 1,3 milioni di abitanti[1] e la sua regione metropolitana 1,83 milioni.
Zúrich4 (en alemán Zürich [ˈtsyːʁɪç] o [ˈtsʏrɪç], en francés Zurich [zyʁik], en italiano Zurigo [dzuˈriːɡo],5 en romanche Turitg [tuˈritɕ]) es la principal ciudad de la Confederación Suiza, con una población de 404 783 habitantes en 2014 y un área metropolitana de 1 392 396 de habitantes. Es la capital del cantón de Zúrich y se encuentra ubicada en el distrito de Zúrich, en la llanura central de Suiza y próxima a los Alpes. Es el motor financiero (en Zúrich se encuentra la banca internacional) y centro cultural del país, siendo además una ciudad galardonada con el título de ciudad con mayor calidad de vida en el mundo por dos ocasiones consecutivas (2006-2008).67
Los primeros asentamientos en la ciudad se remontan hasta el año 15 a. C., con la fundación de la aduana romana Turicum, y en el siglo X adquirió el estatus de ciudad. Rodeando al pequeño casco antiguo se disponen los Kreise (distritos) de Zúrich, ordenados según el sentido de las agujas del reloj. La ciudad moderna sirve de contraste con la histórica, gracias a los numerosos y vanguardistas bancos, tiendas de lujo y modernos bares y cafés. Uno de los símbolos de la ciudad es el lago de Zúrich.
Цю́рих (нем. Zürich [ˈtsyːrɪç]; швейц. Züri [tsy:ri], фр. Zurich, итал. Zurigo) — город на северо-востоке Швейцарии. Столица немецкоязычного кантона Цюрих и административный центр одноимённого округа.
С населением в 397 тыс. человек (2015 год), Цюрих является крупнейшим городом страны. В пределах агломерации проживает более 1 млн человек.
Расположен на берегу Цюрихского озера при выходе из него реки Лиммат, в долине между горными вершинами Утлиберг и Цюрихберг.
Относится к глобальным городам. Крупнейший финансовый центр Швейцарии: местонахождение штаб-квартир страховых компаний и банков, в том числе международных UBS и Credit Suisse, швейцарской фондовой биржи и одной из штаб-квартир центрального банка Швейцарии. Крупный научный центр: университет и высшая техническая школа. В 2011 году Цюрих занял второе место в мире по качеству жизни[3], в 2012 году признан самым дорогим городом мира[4].
Над историческим центром возвышаются романо-готические соборы Гросмюнстер, Фраумюнстер и церковь святого Петра. На острове расположена ратуша в стиле ренессанса.
В древности на месте Цюриха существовало кельтско-германское поселение, в I веке до н. э. получившее римское название Турикум. Как город впервые упоминается в 929 году. В XIII—XVII веках был имперским городом. В XIV веке вошёл в Швейцарский союз. В XVI веке один из центров Реформации во главе с Цвингли. Во 2-й половине XIX века превратился в финансовый центр страны.
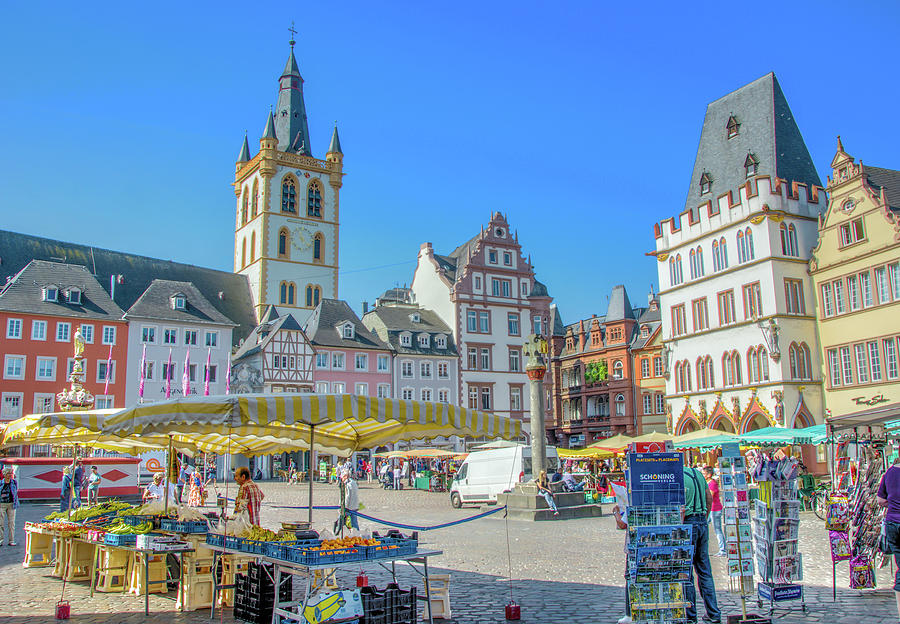


Trier (französisch Trèves, luxemburgisch Tréier) ist eine kreisfreie Stadt im Westen des Landes Rheinland-Pfalz. Mit etwa 110.000 Einwohnern ist sie nach Mainz, Ludwigshafen am Rhein und Koblenz dessen viertgrößte Stadt.
Die Stadt wurde vor mehr als 2000 Jahren unter dem Namen Augusta Treverorum (ab der zweiten Hälfte des 3. Jahrhunderts Treveris) gegründet und beansprucht den Titel der ältesten Stadt Deutschlands für sich. Trier beruft sich hierbei auf die längste Geschichte als bereits von den Römern anerkannte Stadt, im Gegensatz zu einer Siedlung oder einem Heerlager.
Die Römischen Baudenkmäler in Trier zählen seit 1986 zum UNESCO-Welterbe. Hierzu gehören Amphitheater, Barbarathermen, Kaiserthermen, Konstantinbasilika, Porta Nigra, Römerbrücke sowie die Igeler Säule in Igel. Ebenfalls zum Trierer Weltkulturerbe zählt der im Kern romanische Dom und die frühgotische Liebfrauenkirche. Darüber hinaus gibt es in Trier Kulturdenkmäler aus nahezu allen Epochen von der Frühgeschichte bis zum 21. Jahrhundert.
Trier ist Sitz der Universität Trier und der Hochschule Trier, der Verwaltung des Landkreises Trier-Saarburg, der Verwaltung der Verbandsgemeinde Trier-Land, der Aufsichts- und Dienstleistungsdirektion (ADD, bis 1999 Bezirksregierung Trier), mehrerer Dienststellen des Landesuntersuchungsamtes (LUA), einer Dienststelle des Landesamtes für Soziales, Jugend und Versorgung Rheinland-Pfalz und einer römisch-katholischen Diözese (Bistum Trier, das älteste nördlich der Alpen) und des evangelischen Kirchenkreises Trier.
特里尔,依粤语又译堤雅(德语:Trier,法语:Trèves),德国最古老的城市,位于莱茵兰-普法尔茨州西南部,摩泽尔河岸,靠近卢森堡边境。开埠于公元前16年,曾为罗马帝国四帝共治制时期西部恺撒(副皇帝)的驻节地。特里尔不是唯一声称最古老的德国城市,但它作为“城市”有超过两千年的历史,而不是作为殖民地或者军队驻扎地,这在德国确实是最古老的。
特里尔位于莱茵兰-普法尔茨州西南部的摩泽尔河谷中,两岸是低缓的红砂岩山丘,布满葡萄田,属于著名的摩泽尔-萨尔-乌沃(Mosel-Saar-Ruwer)葡萄酒产区。
特里尔是最早的基督教在阿尔卑斯山北侧的主教教区。中世纪,特里尔大主教是一个重要的教会诸侯;他管辖的主教辖区控制了从法国边界到莱茵河的大片地区。特里尔大主教也是神圣罗马帝国的7个选帝侯之一。
特里尔也以马克思诞生地而闻名。
トリーア(ドイツ語: Trier [tʁiːɐ̯] (![]() 音声ファイル), フランス語: Trèves [tʁɛv])は、ドイツ連邦共和国ラインラント=プファルツ州の都市。人口は約10万人(2005年)。トリアーとも表記される。
音声ファイル), フランス語: Trèves [tʁɛv])は、ドイツ連邦共和国ラインラント=プファルツ州の都市。人口は約10万人(2005年)。トリアーとも表記される。
かつては舞台ドイツ語式発音に基づいてトリール、トリエルと呼ばれたが、近年では現在の標準ドイツ語の発音に近い「トリーア」が主に用いられる。
Trier (German pronunciation: [tʁiːɐ̯] ( listen); Luxembourgish: Tréier [ˈtʀɜɪ̯ɐ]), formerly known in English as Treves (French: Trèves, IPA: [tʁɛv]) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city in Germany on the banks of the Moselle. Trier lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the west of the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, near the border with Luxembourg and within the important Moselle wine region. The German philosopher and one of the founders of Marxism, Karl Marx was born in the city in 1818.
listen); Luxembourgish: Tréier [ˈtʀɜɪ̯ɐ]), formerly known in English as Treves (French: Trèves, IPA: [tʁɛv]) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city in Germany on the banks of the Moselle. Trier lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the west of the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, near the border with Luxembourg and within the important Moselle wine region. The German philosopher and one of the founders of Marxism, Karl Marx was born in the city in 1818.
Founded by the Celts in the late-4th century BC as Treuorum, it was later conquered by the Romans in the late-1st century BC and renamed Trevorum or Augusta Treverorum (Latin for "The City of Augustus among the Treveri"). Trier may be the oldest city in Germany.[2][3] It is also the oldest seat of a bishop north of the Alps. In the Middle Ages, the Archbishop-Elector of Trier was an important prince of the church, as the archbishop-electorate controlled land from the French border to the Rhine. The Archbishop-Elector also had great significance as one of the seven electors of the Holy Roman Empire.
With an approximate population of 105,000, Trier is the fourth-largest city in its state, after Mainz, Ludwigshafen, and Koblenz.[4] The nearest major cities are Luxembourg (50 km or 31 mi to the southwest), Saarbrücken (80 kilometres or 50 miles southeast), and Koblenz (100 km or 62 mi northeast).
The University of Trier, the administration of the Trier-Saarburg district and the seat of the ADD (Aufsichts- und Dienstleistungsdirektion), which until 1999 was the borough authority of Trier, and the Academy of European Law (ERA) are all based in Trier. It is one of the five "central places" of the state of Rhineland-Palatinate. Along with Luxembourg, Metz and Saarbrücken, fellow constituent members of the QuattroPole union of cities, it is central to the greater region encompassing Saar-Lor-Lux (Saarland, Lorraine and Luxembourg), Rhineland-Palatinate, and Wallonia.
Trèves (en allemand : Trier /ˈtʁiːɐ̯/ Écouter, en luxembourgeois : Tréier) est une ville et un arrondissement d'Allemagne, dans le Land de Rhénanie-Palatinat. La ville est située sur la Moselle. En 2008, la ville comptait 104 640 habitants.
Treviri (AFI: [ˈtrɛviri][1]; in tedesco: Trier, in francese: Trèves, in lussemburghese: Tréier) è una città extracircondariale nella parte occidentale del Land tedesco della Renania-Palatinato; è sede di una prestigiosa università.
Pur essendo una città extracircondariale, ospita la sede amministrativa del circondario (Landkreis) di Treviri-Saarburg.
La città è nota per aver dato i natali a Karl Marx.
Tréveris (en alemán, Trier; en francés, Trèves; véanse los nombres en otros idiomas) es una ciudad de Renania-Palatinado, Alemania, ubicada en la ribera derecha del río Mosela. Dista unos 9 km de Luxemburgo, 35 km de Francia y 50 km de Bélgica. Tiene 100 000 habitantes aproximadamente. Se considera la ciudad más antigua de Alemania y en 1986, la Unesco declaró el conjunto de «monumentos romanos, la catedral de San Pedro y la iglesia de Nuestra Señora en Tréveris» Patrimonio de la Humanidad.1. En Tréveris nació Karl Marx el 5 de mayo de 1818.

 Valencian Community
Valencian Community

 International cities
International cities
 *World Design Capital
*World Design Capital
 Spain
Spain

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 Important port
Important port

 Grand Est
Grand Est
 Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate
 Balearic Islands
Balearic Islands
 World Heritage
World Heritage