
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Washington-WA
Washington-WA


 National Football Conference NFC
National Football Conference NFC
 West
West
 National Football League 2015
National Football League 2015
 National Football League 2016
National Football League 2016
 National Football League 2017
National Football League 2017
 National Football League 2018
National Football League 2018
 NFC West
NFC West
 National Football League 2018
National Football League 2018
 National Football Conference,NFC
National Football Conference,NFC
 Super Bowl
Super Bowl

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA



 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025
 United States
United States

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Important port
Important port
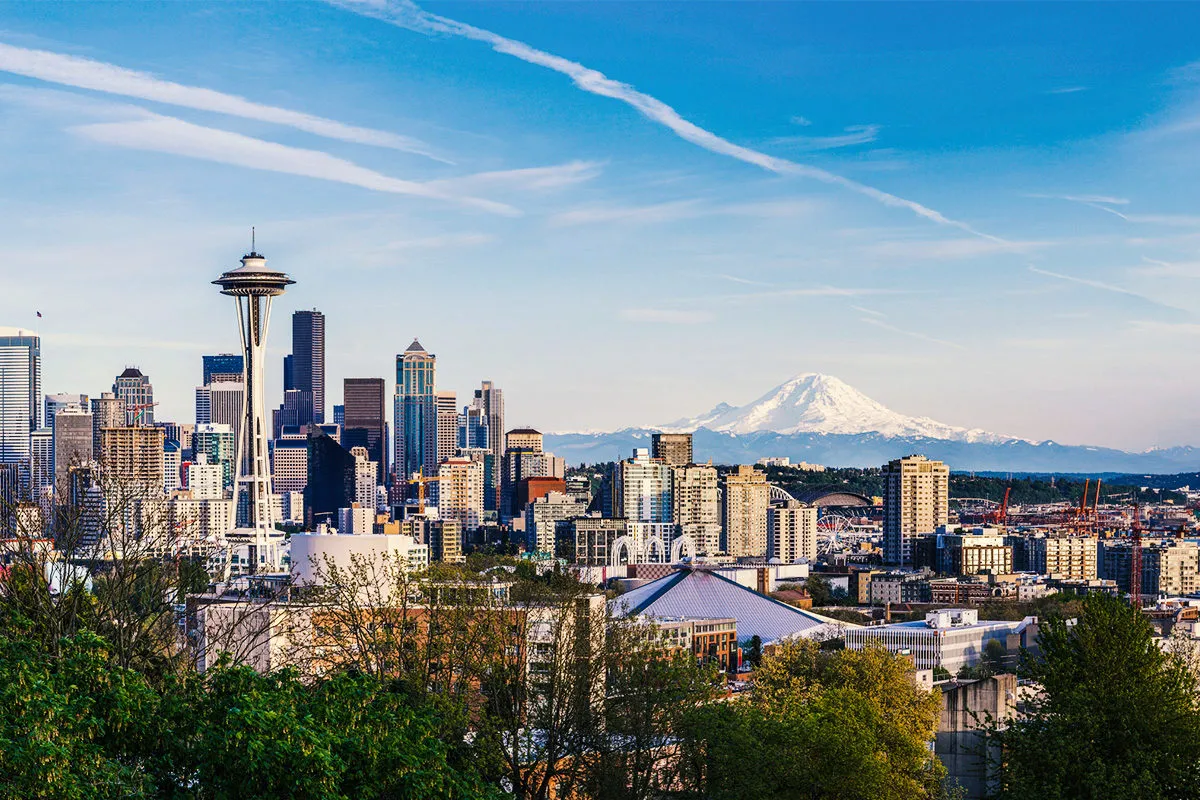



Seattle (englisch: 
![]() [sɪˈætəl]; deutsch: [siˈɛtl̩]) ist die größte Stadt im Nordwesten der Vereinigten Staaten. Sie ist der Verwaltungssitz des King County im US-Bundesstaat Washington und liegt zwischen dem Puget Sound und dem Lake Washington, etwa 155 Kilometer südlich der Grenze zu Kanada. Neben Vancouver und Portland ist Seattle der Verkehrsknotenpunkt und das wirtschaftliche, wissenschaftliche und kulturelle Zentrum in der Region des Pazifischen Nordwestens.
[sɪˈætəl]; deutsch: [siˈɛtl̩]) ist die größte Stadt im Nordwesten der Vereinigten Staaten. Sie ist der Verwaltungssitz des King County im US-Bundesstaat Washington und liegt zwischen dem Puget Sound und dem Lake Washington, etwa 155 Kilometer südlich der Grenze zu Kanada. Neben Vancouver und Portland ist Seattle der Verkehrsknotenpunkt und das wirtschaftliche, wissenschaftliche und kulturelle Zentrum in der Region des Pazifischen Nordwestens.
Die Stadt trägt die Beinamen The Emerald City („Die Smaragdstadt“), was eine Anspielung auf das viele Grün im Stadtgebiet und die großen Wälder ist (sie wird von den Einheimischen allerdings fast nie so bezeichnet), und Rain City – obwohl der Niederschlag geringer ist als in vielen anderen amerikanischen Städten. Der Spitzname kommt von den vielen wolkenreichen und regnerischen Tagen im Jahr. Von den Einheimischen wird sie auch als Jet City bezeichnet, was eine Anspielung auf die nahe gelegenen Boeingwerke ist.
Der Hafen von Seattle ist ein bedeutender Handelsknotenpunkt für den Handel mit Asien, Alaska und Hawaii. Die wichtigsten ansässigen Industrien sind die Luft- und Raumfahrt (Boeing), Eisen- und Stahlindustrie sowie die Holzverarbeitung. Als bauliches Wahrzeichen von Seattle gilt der für die Weltausstellung 1962 errichtete Turm Space Needle. Die Stadt ist Sitz der University of Washington.
Die Stadt wurde benannt nach Noah Sealth, Häuptling der Duwamish und Suquamish, besser bekannt unter dem Namen Häuptling Seattle.
西雅图(英语:Seattle),华文早期译作舍路,是美国华盛顿州的一座港口城市。西雅图是华盛顿州金郡首府,位于普吉特海湾和华盛顿湖之间,距离美加边境约174千米,是该州最大的城市,也是美国太平洋西北区最大的城市。据2020年人口普查数据,全市人口737,015人[5],都会区人口400万左右,为美国第15大都会区[6]。2010至2020年间,西雅图的人口增长率为21.1%,是全美人口增长最快的大城市之一。[7]
距今约4000年前,就已经有美洲原住民在今天的西雅图地区居住[8]。1851年11月13日,阿瑟·阿姆斯特朗·丹尼及其探险队从伊利诺伊州出发,在俄勒冈州的波特兰乘坐帆船出海,抵达现今西雅图地区的阿尔凯角并建立了第一个定居点[9],这个定居点于1853年被迁移到现在的位置并被命名为“西雅图”(得名于西雅图酋长)。
伐木业是西雅图第一个主要产业,但在19世纪后期的克朗代克淘金热中,该市成为位于通往阿拉斯加途中的一个商业和造船业中心。到1910年,西雅图已成为美国25大城市之一[10]。但在大萧条时期,其经济发展受到严重影响,于第二次世界大战期间及以后逐渐恢复,这部分得益于当地的波音公司将其制造中心定于此地。上世纪80年代起,西雅图发展为一个科技中心,不少像微软这样的公司在西雅图地区创立。杰夫·贝索斯也于1994年在西雅图创立了网络零售商亚马逊。软件,生物技术和互联网公司的发展使该市经济得以复兴,人口也在1990至2000间增加了超过5万人。2010年起,西雅图又成为了一个绿色工业和可持续发展模式的中心,并被认为是2010至2020年间美国发展速度最快的主要城市之一[11][12]。
西雅图的官方别名为“翡翠之城(the Emerald City)”,其他别名还有“雨城(the Rainy City)”、“常绿之城(Evergreen City)”、“阿拉斯加门户(the Gateway to Alaska)”、“女王之城(Queen City)”和“喷气机之城(Jet City)”。西雅图是摇滚音乐家吉米·亨德里克斯的出生地,也被认为是另类摇滚风格垃圾音乐的诞生之地[13]。涅槃乐队,珍珠果酱乐队,爱丽丝囚徒,喷火战机乐队都在西雅图出道。西雅图的咖啡消费量极大,是品牌星巴克诞生之地,第一家门市就在此。




 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Self-driving car
*Self-driving car


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Internet of Things
Internet of Things


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 ***Metaverse
***Metaverse


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence

 Life and Style
Life and Style

 Life and Style
Life and Style
 *E-Commerce
*E-Commerce

 Companies
Companies
 *Big retail companies
*Big retail companies
 United States
United States

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Global Innovators
Global Innovators

 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC

 Australian Capital Territory-ACT
Australian Capital Territory-ACT
 Australia
Australia
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Chile
Chile
 China
China
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kantō
Kantō
 Kinki
Kinki
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand

 New South Wales-NSW
New South Wales-NSW
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Singapore
Singapore
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Thailand
Thailand
 United States
United States
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

Die Asiatisch-Pazifische Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft (für englisch Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, kurz APEC, auch übersetzt als Asiatisch-Pazifische Wirtschaftskooperation oder Asien-Pazifik-Forum) ist eine internationale Organisation, die es sich zum Ziel gesetzt hat, im pazifischen Raum eine Freihandelszone einzurichten.
In den 21 APEC-Staaten lebt knapp die Hälfte der Weltbevölkerung. Der Wirtschaftsraum erbringt mehr als die Hälfte der Weltwirtschaftsleistung und ist eine der am schnellsten wachsenden Wirtschaftsregionen der Welt.
亚太经济合作组织(简称亚太经合组织;英语:Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,缩写:APEC),是亚太区内各地区之间促进经济成长、合作、贸易、投资的论坛。此组织的创办在历史上取代了该区域的冷战结构,但由于日本在该区域会因过去历史记忆引发负面评价,所以由澳大利亚主导创始事项[1]。
始设于1989年,现有21个经济体成员。亚太经合组织是经济合作的论坛平台,其运作是通过非约束性的承诺与成员的自愿,强调开放对话及平等尊重各成员意见,不同于其他经由条约确立的政府间组织。“APEC”与“Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation”均是亚太经济合作组织的注册商标。[2]
アジア太平洋経済協力会議(アジアたいへいようけいざいきょうりょくかいぎ、英: Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation)は、環太平洋地域における多国間経済協力を進めるための非公式なフォーラム[2]である。略称、APEC(エイペック[3][4])。
「アジア太平洋」という概念が最初に打ち出されたのは、永野重雄が1967年に発足させた太平洋経済委員会(PBEC)という経済団体の設立時であるとされるが[5][6][7]、具体的にこうした地域概念が政府レベルの協力枠組みに発展する萌芽は、1978年、日本の大平正芳首相が就任演説で「環太平洋連帯構想」を呼びかけたことにある。これを具体化した大平政権の政策研究会「環太平洋連帯研究グループ」(議長:大来佐武郎、幹事佐藤誠三郎)の報告を受け、大平がオーストラリアのマルコム・フレイザー首相に提案して強い賛同を得たことが、1980年9月の太平洋経済協力会議(PECC)の設立につながった。PECCは地域における様々な課題を議論し研究するセミナーといった趣のものであったが、これを土台にして、各国政府が正式に参加する会合として設立されたのが、APECである[8][9]。
APECは、1989年にオーストラリアのホーク首相の提唱で、日本・アメリカ合衆国・カナダ・韓国・オーストラリア・ニュージーランド及び当時の東南アジア諸国連合(ASEAN)加盟6か国の計12か国で発足し、同国のキャンベラで閣僚会議(Ministerial Meeting)を開催した。また、1993年には米国のシアトルで初の首脳会議(Economic Leaders' Meeting)がもたれた。現在は、首脳会議、及び、外相、経済担当相による閣僚会議をそれぞれ年1回開いている。シンガポールに常設事務局を置き、開催国から任期1年で事務局長が選任されている[10]。 参加しているメンバーは、21カ国・地域で、2012年現在、人口では世界の41.4%、GDP(国内総生産)では57.8%、貿易額では47%を占めている。
APECは、開かれた地域協力によって経済のブロック化を抑え、域内の貿易・投資の自由化を通じて、世界貿易機関(WTO)のもとでの多角的自由貿易体制を維持・発展することを目的としてきたが、近年のWTOの新ラウンドの停滞や自由貿易協定締結の動きの活発化などによって、その存在意義が問われている。
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is an inter-governmental forum for 21 Pacific Rim member economies[2] that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Inspired from the success of Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)’s series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s, the APEC was established in 1989 in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; and to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe.[3][4][5] Headquartered in Singapore, the APEC is recognised as one of the oldest forums and highest-level multilateral blocs in the Asia-Pacific region, and exerts a significant global influence.[6][7][8][9][10][11]
An annual APEC Economic Leaders' Meeting is attended by the heads of government of all APEC members except Republic of China (Taiwan) (which is represented by a ministerial-level official under the name Republic of China as economic leader).[12] The location of the meeting rotates annually among the member economies, and a famous tradition, followed for most (but not all) summits, involves the attending leaders dressing in a national costume of the host country. APEC has three official observers: the Association of Southeast Asian Nations Secretariat, the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council and the Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat.[13] APEC's Host Economy of the Year is considered to be invited in the first place for geographical representation to attend G20 meetings following G20 guidelines.[14][15][16][17]
La Coopération économique pour l'Asie-Pacifique (en anglais : Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, APEC) est un forum économique intergouvernemental visant à faciliter la croissance économique, la coopération, les échanges et l'investissement de la région Asie Pacifique. Elle se réunit chaque année1.
L'Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), ossia Cooperazione Economica Asiatico-Pacifica, è un organismo nato nel 1989 allo scopo di favorire la cooperazione (o, più in generale, la crescita) economica, il libero scambio e gli investimenti nell'area asiatico-pacifica. Tale area (come suggerisce il logo stesso dell'APEC) coincide non solo con l'Asia Pacifica, ma potenzialmente con l'intero Pacific Rim.
L'APEC ha sede a Singapore, Paese considerato una delle tigri dell'Asia.
Dal punto di vista del diritto internazionale l'APEC si definisce organismo e non organizzazione internazionale perché, essendo composto da economie e non da Stati, è privo di una piena personalità giuridica. Ciò spiega, fra l'altro, come mai possano farne parte contemporaneamente la Cina continentale, Hong Kong e Taiwan, ossia tre realtà che, territorialmente (secondo Pechino e secondo tutti i governi che intrattengono relazioni diplomatiche con Pechino), appartengono a un unico Stato: la Repubblica Popolare di Cina.
APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, en español Foro de Cooperación Económica Asia-Pacífico) es un foro multilateral creado en 1989, con el fin de consolidar el crecimiento y la prosperidad de los países del Pacífico, que trata temas relacionados con el intercambio comercial, coordinación económica y cooperación entre sus integrantes.1
Como mecanismo de cooperación y concertación económica, está orientado a la promoción y facilitación del comercio, las inversiones, la cooperación económica y técnica y al desarrollo económico regional de los países y territorios de la cuenca del océano Pacífico. Fomentando un crecimiento económico inclusivo, equitativo, sustentable e innovador.2
La suma del Producto Nacional Bruto de las veintiuna economías que conforman el APEC equivale al 56 % de la producción mundial, en tanto que en su conjunto representan el 46 % del comercio global.
La APEC no tiene un tratado formal. Sus decisiones se toman por consenso y funciona con base en declaraciones no vinculantes. Tiene una Secretaría General, con sede en Singapur, que es la encargada de coordinar el apoyo técnico y de consultoría. Cada año uno de los países miembros es huésped de la reunión anual de la APEC. La vigésimo novena cumbre se realizó en noviembre de 2017 en Da Nang, Vietnam; y la próxima será en Santiago, Chile.
Азиатско-Тихоокеанское экономическое сотрудничество (АТЭС) (англ. Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, APEC) — форум 21 экономики Азиатско-Тихоокеанского региона для сотрудничества в области региональной торговли и облегчения и либерализации капиталовложений.
Целью АТЭС является повышение экономического роста, процветания в регионе и укрепление азиатско-тихоокеанского сообщества. В экономиках-участницах проживает около 40 % мирового населения, на них приходится приблизительно 54 % ВВП и 44 % мировой торговли[1].

 Music
Music
 Architecture
Architecture
 Sport
Sport
 International cities
International cities
 Universities in the USA
Universities in the USA
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade