
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Ski vacation
Ski vacation


 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990

 History
History

 International cities
International cities
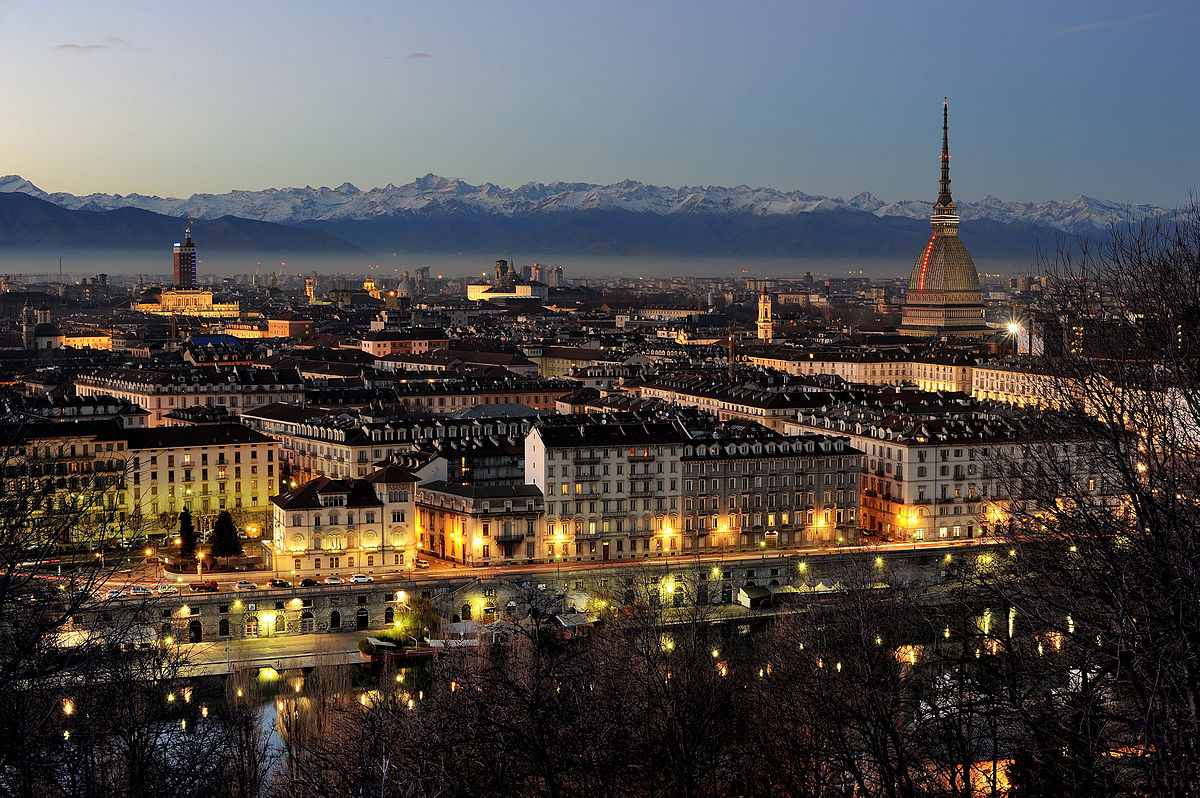
 Turin
Turin

 International cities
International cities
 *World Design Capital
*World Design Capital
 Italy
Italy
 Winter Olympics
Winter Olympics
 2006 Winter Olympics
2006 Winter Olympics

 Piemonte
Piemonte
 Turin
Turin

 Ski vacation
Ski vacation

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 World Heritage
World Heritage

都灵(意大利语:Torino [toˈriːno] ![]() 聆听;皮埃蒙特语:Turin [tyˈɾiŋ];拉丁语:Augusta Taurinorum),中国大陆和港澳地区称为都灵,台湾称为杜林,是位于意大利北部的重要城市,皮埃蒙特大区和都灵广域市的首府。它坐落在波河的左岸,距离米兰大约140千米(87英里),阿尔卑斯山环绕在城市的西北。都灵中心区有面积130.17km²,人口911,534[2],是意大利人口第四多的城市;都灵城市区有面积1,126.6 km²,人口1,745,221[3];都灵都市圈有面积1,977 km²,人口2,200,000[4](占意大利总人口的3.4%[5])。
聆听;皮埃蒙特语:Turin [tyˈɾiŋ];拉丁语:Augusta Taurinorum),中国大陆和港澳地区称为都灵,台湾称为杜林,是位于意大利北部的重要城市,皮埃蒙特大区和都灵广域市的首府。它坐落在波河的左岸,距离米兰大约140千米(87英里),阿尔卑斯山环绕在城市的西北。都灵中心区有面积130.17km²,人口911,534[2],是意大利人口第四多的城市;都灵城市区有面积1,126.6 km²,人口1,745,221[3];都灵都市圈有面积1,977 km²,人口2,200,000[4](占意大利总人口的3.4%[5])。
都灵是一国际化的欧洲城市,[6][7] 都灵有时被称为“意大利自由的摇篮”、[8]、“阿尔卑斯之都”、“萨沃亚之都”。它拥有众多的文化设施和其他名胜。都灵因为它的巴洛克、洛可可和新古典主义法式建筑而举世闻名。它的很多广场、城堡、庭园和宫殿(如贵妇宫),都是由西西里建筑师菲利波·尤瓦拉建造的,他在设计时借鉴了法国经典建筑凡尔赛宫。[9] 这些法式建筑的典范包括:王宫、斯杜皮尼吉行宫和苏佩尔加大教堂。许多意大利高等教育机构位于此地,如都灵大学、都灵理工大学、都灵美术学院等。还有许多重要和著名的博物馆,如埃及博物馆[10] 和安托内利尖塔。
都灵曾经是欧洲重要的政治中心。1563年,它成为了萨伏依公国的首都,随后是萨伏依王室统治下的萨丁尼亚王国的首都,最后是意大利统一之后的第一个首都(1861年—1865年)。[11] 同时,它也是萨沃亚王室(意大利王室)的故乡。[12] 虽然因为第二次世界大战,它的大部分政治意义和重要性都丢失了,它还是在战后成为了欧洲重要的工业、商业和贸易的集散地。它现在是意大利的工业中心之一,和米兰、热那亚组成了“工业铁三角”。从经济上来说,都灵紧随罗马和米兰之后,是意大利第三大城市。[13] 它的GDP高达580亿美元,排名世界第78位。[14] 虽然不像罗马、米兰那样是“世界级城市”,GaWC评其为“适合发展”级别。[15]
都灵是意大利汽车制造业的摇篮,被称为“意大利汽车之都”或者“意大利的底特律”。是汽车品牌菲亚特、蓝旗亚和阿尔法·罗密欧的总部所在地。[16][17] 都灵还拥有足球俱乐部尤文图斯和都灵,举办过2006年冬季奥林匹克运动会。一些国际空间站设备,如和谐号节点舱和哥伦布实验舱,也是在都灵制造的。
トリノ(伊: Torino (![]() 音声ファイル))は、イタリア共和国ピエモンテ州にある都市で、その周辺地域を含む人口約87万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。ピエモンテ州の州都であり、トリノ県の県都。イタリア第4の人口規模を持つ。都市圏の人口は約170万人。一時は100万都市だったが昨今は人口減少が著しい。
音声ファイル))は、イタリア共和国ピエモンテ州にある都市で、その周辺地域を含む人口約87万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。ピエモンテ州の州都であり、トリノ県の県都。イタリア第4の人口規模を持つ。都市圏の人口は約170万人。一時は100万都市だったが昨今は人口減少が著しい。
ミラノに次ぐイタリア第2の工業都市であり、自動車工業の拠点である。近代にはサルデーニャ王国の首都が置かれた。サヴォイア王家の王宮群は世界遺産に登録されている。
Turin (/tjʊəˈrɪn, ˈtʊərɪn/;[2] Italian: Torino [toˈriːno] (![]() listen); Piemontese: Turin [tyˈriŋ])[3] is a city and an important business and cultural centre in northern Italy. It is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Turin (an administrative division of Italy) and of the Piedmont region, and was the first capital city of Italy from 1861 to 1865. The city is located mainly on the western bank of the Po River, in front of Susa Valley, and is surrounded by the western Alpine arch and Superga Hill. The population of the city proper is 883,281 (30 November 2017)[4] while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 1.7 million inhabitants. The Turin metropolitan area is estimated by the OECD to have a population of 2.2 million.[5]
listen); Piemontese: Turin [tyˈriŋ])[3] is a city and an important business and cultural centre in northern Italy. It is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Turin (an administrative division of Italy) and of the Piedmont region, and was the first capital city of Italy from 1861 to 1865. The city is located mainly on the western bank of the Po River, in front of Susa Valley, and is surrounded by the western Alpine arch and Superga Hill. The population of the city proper is 883,281 (30 November 2017)[4] while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 1.7 million inhabitants. The Turin metropolitan area is estimated by the OECD to have a population of 2.2 million.[5]
The city has a rich culture and history, being known for its numerous art galleries, restaurants, churches, palaces, opera houses, piazzas, parks, gardens, theatres, libraries, museums and other venues. Turin is well known for its Renaissance, Baroque, Rococo, Neo-classical, and Art Nouveau architecture. Many of Turin's public squares, castles, gardens and elegant palazzi such as the Palazzo Madama, were built between the 16th and 18th centuries. A part of the historical center of Turin was inscribed in the World Heritage List under the name Residences of the Royal House of Savoy.
The city used to be a major European political center. From 1563, it was the capital of the Duchy of Savoy, then of the Kingdom of Sardinia ruled by the Royal House of Savoy, and the first capital of the unified Italy (the Kingdom of Italy) from 1861 to 1865.[6][7] Turin is sometimes called "the cradle of Italian liberty" for having been the birthplace and home of notable individuals who contributed to the Risorgimento, such as Cavour.[8]
The city currently hosts some of Italy's best universities, colleges, academies, lycea and gymnasia, such as the University of Turin, founded in the 15th century, and the Turin Polytechnic. In addition, the city is home to museums such as the Museo Egizio[9] and the Mole Antonelliana. Turin's attractions make it one of the world's top 250 tourist destinations and the tenth most visited city in Italy in 2008.[10]
Even though much of its political significance and importance had been lost by World War II, Turin became a major European crossroad for industry, commerce and trade, and is part of the famous "industrial triangle" along with Milan and Genoa. Turin is ranked third in Italy, after Milan and Rome, for economic strength.[11] With a GDP of $58 billion, Turin is the world's 78th richest city by purchasing power.[12] As of 2010, the city has been ranked by GaWC as a Gamma World city.[13] Turin is also home to much of the Italian automotive industry.[14][15]
Turin is well known as the home of the Shroud of Turin, the football teams Juventus F.C. and Torino F.C., the headquarters of automobile manufacturers FIAT, Lancia and Alfa Romeo, and as host of the 2006 Winter Olympics.
Turin (Torino en italien, Turin en piémontais) est une ville italienne, chef-lieu de la ville métropolitaine de Turin et de la région du Piémont. Turin fut la capitale des États de Savoie de 1563 à 1713, du royaume de Sicile de 1713 à 1720, du royaume de Sardaigne de 1720 à 1861 et du royaume d'Italie de 1861 à 1865.
Torino (AFI: /toˈrino/[4], ; Turin in piemontese[5]) è un comune italiano di 879 808 abitanti[2], capoluogo dell'omonima città metropolitana e della regione Piemonte.
Cuore di un'area metropolitana che conta quasi 2 000 000 di abitanti su una superficie approssimativa di circa 2 300 km²,[6] la città di Torino è il quarto comune italiano per popolazione, il terzo complesso economico-produttivo del Paese e costituisce uno dei maggiori poli universitari, artistici, turistici, scientifici e culturali d'Italia. Nel suo territorio sono inoltre presenti aree ed edifici inclusi in due beni protetti dall'UNESCO: alcuni palazzi e zone facenti parte del circuito di residenze sabaude in Piemonte (patrimonio dell'umanità[7]) e l'area delle colline del Po (riserva della biosfera).
Città dalla storia bimillenaria, fu fondata probabilmente come Taurasia nei pressi della posizione attuale attorno al III secolo a.C. dai Taurini, popolazione ligure (o celto-ligure) dell'Italia settentrionale, e trasformata in colonia romana da Augusto col nome di Iulia Augusta Taurinorum nel I secolo a.C. Dopo il dominio ostrogoto fu capitale di un importante ducato longobardo, per poi passare, dopo essere divenuta capitale di marca carolingia, sotto la signoria nominale dei Savoia nell'XI secolo. Città dell'omonimo ducato, nel 1563 ne divenne capitale. Dal 1720 fu capitale del Regno di Sardegna (anche se solo de facto fino alla fusione perfetta del 1847, quando lo divenne anche formalmente),[8] stato che nel XIX secolo avrebbe portato all'unificazione italiana e che fece di Torino la prima capitale del Regno d'Italia (dal 1861 al 1865).
È stata la patria, natia o adottiva, di alcuni fra i più grandi scrittori e letterati italiani del XIX e XX secolo, tra i quali Edmondo De Amicis, Emilio Salgari, Italo Calvino, Natalia Ginzburg, Norberto Bobbio, Cesare Pavese e Primo Levi.
Sede nel 2006 dei XX Giochi olimpici invernali, città natale di alcuni fra i maggiori simboli del Made in Italy nel mondo, come il Martini, il cioccolato gianduja e il caffè espresso, è il fulcro dell'industria automobilistica italiana, nonché importante centro dell'editoria, del sistema bancario e assicurativo, delle tecnologie dell'informazione, del cinema, dell'enogastronomia, del settore aerospaziale, del disegno industriale e dello sport.
Turín (en italiano: Torino, en piamontés: Turin) es una ciudad, importante centro cultural y de negocios del norte de Italia, capital de la región de Piamonte, localizada principalmente en el margen izquierdo del río Po y rodeada por los Alpes. El área metropolitana de Turín, según la Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico, tiene una población de alrededor de 2.200.000 habitantes.2
La ciudad es rica en cultura e historia. Es conocida por sus numerosos museos de arte, sus restaurantes, sus iglesias, sus palacios, sus teatros de ópera, sus plazas, sus parques, sus jardines y sus bibliotecas, entre otros atractivos. Turín es ampliamente reconocida por su arquitectura barroca, rococo, neoclásica y Art Nouveau. Muchas de las plazas públicas de la ciudad, de los castillos, jardines y elegantes palacios (como el Palazzo Madama), fueron construidos por el arquitecto siciliano Filippo Juvarra, quien diseñó estos edificios en el estilo barroco y clásico del Palacio de Versalles, en Francia.3 Ejemplos de estos edificios de inspiración francesa incluyen el Palacio Real de Turín, el Pabellón de caza de Stupinigi y la Basílica de Superga.
Turín es frecuentemente llamada la «cuna de Italia» por ser el lugar de nacimiento de importantes políticos que contribuyeron con la unificación de Italia, como Cavour.4 La ciudad actualmente alberga algunas de las mejores universidades de Italia, como la Universidad de Turín, de seis siglos de antigüedad, y el Politécnico de Turín. También se encuentran en la ciudad museos prestigiosos e importantes, como el Museo Egipcio de Turín5 (el más antiguo en el mundo y considerado el segundo más importante en el mundo después de El Cairo por valor de los hallazgos) y la Mole Antonelliana. Los diversos monumentos y atracciones de Turín la convierten en una de los 250 principales destinos turísticos del mundo y en la décima ciudad más visitada de Italia para el año 2008.6
La ciudad solía ser un importante centro político europeo, siendo la primera capital de Italia en 1861 y la ciudad de residencia de la Casa de Saboya, la familia real de Italia.7 A pesar de que mucho de su significado e importancia política se había perdido cuando comenzó la Segunda Guerra Mundial, se convirtió en uno de los principales centros industriales y comerciales de Europa, y actualmente es una de las ciudades más industrializadas de Italia, formando junto con Milán y Génova el famoso "triángulo industrial". A pesar de tener muchos menos habitantes que Roma y Milán, Turín es la tercera ciudad más rica de Italia, después de estas.8 Con un Producto Interno Bruto de 58.000 millones de dólares, Turín es la ciudad número 78 en la lista de las más ricas del mundo por su poder adquisitivo.91011 Turín es también la sede de gran parte de la potente industria automovilística italiana.1213
La ciudad es también conocida por resguardar la «Sábana Santa», por ser la sede de los equipos de fútbol Juventus F.C. y Torino Football Club, el lugar donde se producen los coches FIAT, Lancia, Alfa Romeo, Maserati y la sede de los juegos olímpicos de invierno de 2006. Varios módulos de la Estación Espacial Internacional, como el Harmony y el Columbus, fueron fabricados en Turín.
Fue la capital del Ducado de Saboya desde 1563, luego del Reino de Cerdeña y finalmente la primera capital de Italia.14 Piero Fassino fue el alcalde de Turín, elegido en mayo de 2011 para un mandato de 5 años, representando a una coalición de centro-izquierda y fue a su vez el sucesor de Sergio Chiamparino. Desde junio de 2016, la alcaldesa es la economista Chiara Appendino, del partido Movimento 5 Estrellas.
Тури́н (итал. Torino [toˈriːno], пьем. Turin [tyˈɾiŋ]) — город в Италии, важный деловой и культурный центр северной Италии. Административный центр региона Пьемонт и одноимённой провинции Турин.
Расположен при впадении реки Дора-Рипария в реку По, на Паданской равнине у подножия Западных Альп, на подступах к Альпийским перевалам.
Четвёртый после Рима, Милана и Неаполя город Италии по количеству жителей, насчитывает около 880 тыс. чел. (2017), вместе с пригородами 1,7 миллион человек.
Город имеет богатую историю и культуру, и известен своими арт-галереями, дворцами, театрами, музеями, парками. Турин также знаменит своей архитектурой в стилях барокко, рококо, неоклассицизма и модерна.
Большая часть замков, дворцов (в частности Палаццо Мадама), садов и площадей были построены в XVI-XVIII вв. в процессе перевода столицы Савойского герцогства (позднее Сардинское королевство) из Шамбери (ныне Франция) в Турин.
Турин иногда называют «колыбелью итальянской свободы», за то, что он является родным городом заметных политиков и людей, внесших большой вклад в Рисорджименто, например Камилло Бенсо ди Кавур. В городе находятся множество университетов, колледжей, академий, лицеев и гимназий. Среди них основанный в XV веке Туринский университет. Самыми известными достопримечательностями Турина являются Египетский музей и символ города Моле Антонеллиана. Эти и многие другие достопримечательности делают город привлекательным для туристов со всего мира и позволяют Турину входить в десятку самых посещаемых городов Италии[3].
Город в XIX веке являлся важным политическим центром Европы. В 1861 году Турин стал первой столицей объединенной Италии и наряду с этим являлся столицей для Савойского дома, правящей династии Королевства Италии. Несмотря на то, что большая часть политической значимости Турина была растеряна после отмены монархии в Италии, город остается важным промышленным, экономическим и торговым центром Европы и Италии. Турин является третьим по экономическим показателям городом страны, после Милана и Рима. Также Турин является своего рода столицей автомобилестроения Италии. В городе располагаются штаб-квартиры компаний FIAT, Lancia, Iveco.
Город известен в мире благодаря христианской реликвии — Туринской плащанице, а также футбольным командам «Ювентус» и «Торино». Турин — столица зимних Олимпийских игр 2006 года.
Покровителем города считается Св. Иоанн Креститель (итал. San Giovanni Battista). Праздник города — 24 июня.




 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
Women's Soccer World Cup 2015

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 *World's Most Livable Cities
*World's Most Livable Cities
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Canada
Canada
 Winter Olympics
Winter Olympics

 Ski vacation
Ski vacation

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon

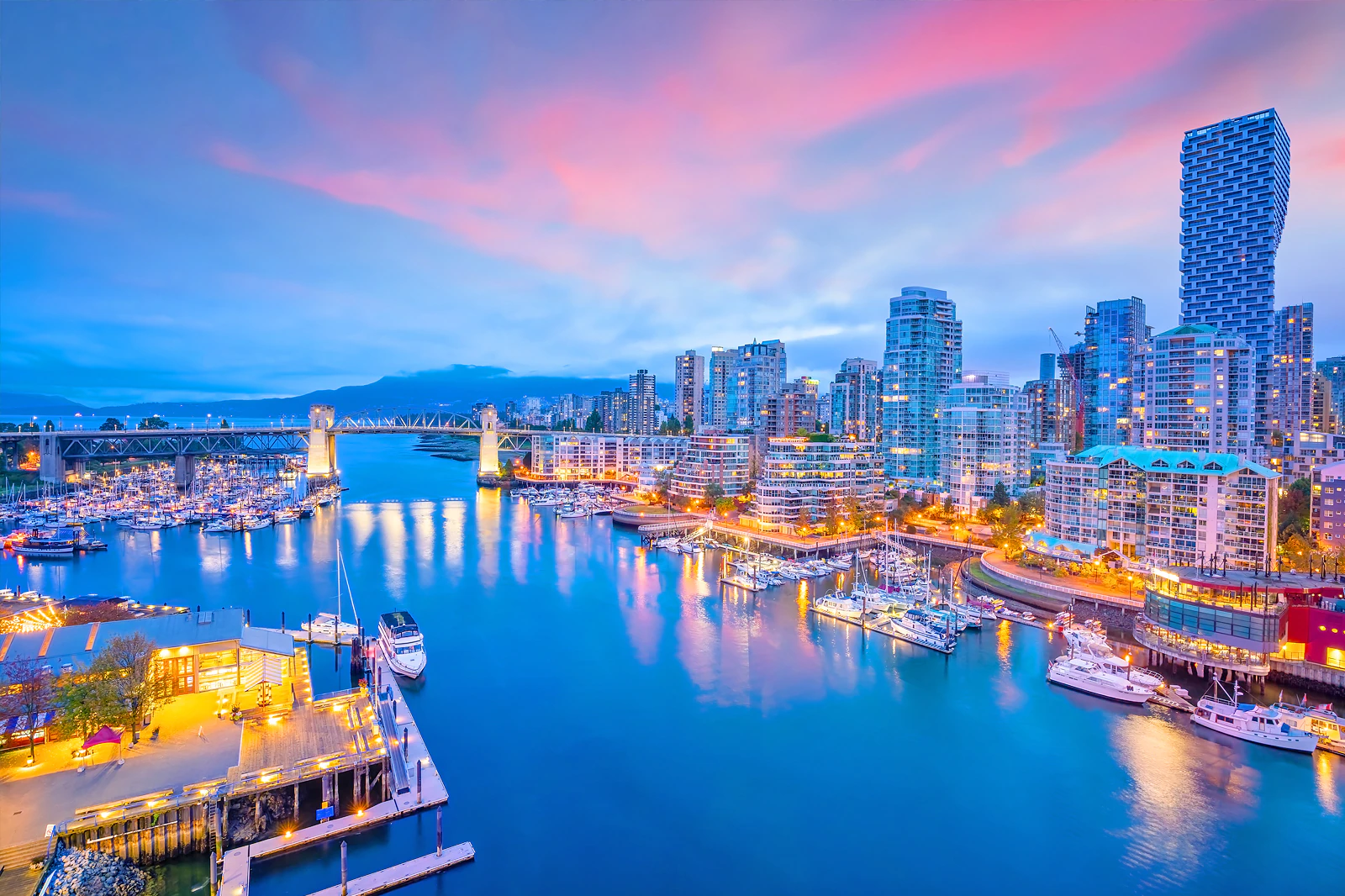
 Important port
Important port

一般所说的”温哥华”泛指”大温地区”(请参考温哥华概况介绍)。温哥华市中心位于一个半岛上,主要分成几块区域:西尾区与水滨(West End & Waterfront)、耶鲁镇(Yaletown)、盖士镇与华埠(Gastown & Chinatown)。市中心往南的温哥华市以Carrall街与Ontario街分成温西(West Side)与温东(East Side)。外地人常把温西与西温哥华(West Vancouver)搞混,后者是温哥华北岸的一个城市,从温哥华市中心向北跨越狮门大桥(Lions Gate Bridge)即可抵达。
西尾区(West End)在市中心西端,北与史丹利公园、南与市中心商业区紧邻,是由整片新兴的高级住宅大楼与罗布森街(Robson Street)购物区、各国风味餐厅、海滩、游艇码头等所组成的热闹区域。到温哥华旅游如果不自行开车,在西尾区住宿是明智选择。
耶鲁镇(Yaletown)是位于市中心东缘的新兴小区,这里有许多杂错的红砖仓库改建成精致典雅的新购物娱乐区与艺术家工作室。一栋栋平房红砖墙的建筑 及巷道上的石板路,将素有“Funky Town"之称的耶鲁镇特色表露无遗。耶鲁镇有电影制片公司、美发沙龙、室内设计工作室、小型设计师家具店、古董店、精品服饰店,加上各种特色美食与露天 咖啡座、小酒馆,让耶鲁镇的雅痞色彩十足,成为温哥华时尚一族抢着进驻的地区。
盖士镇(Gastown)是温哥华的发源地,是个以2条横街和3条直街组成的三角地带。卑诗省政府将盖士镇规划程成为独特的观光区与历史维护区。如今这里 保存完好的19世纪初维多利亚式建筑、铺满圆石的悠长街道、别致的露天咖啡屋,复古的路灯及一座座低矮的历史建筑,行走其间宛如时空错置。也是游客来温哥 华必至之处。(Quelle:http://www.usatrip.cn/jdjs/jdjs_Vancouver.asp)
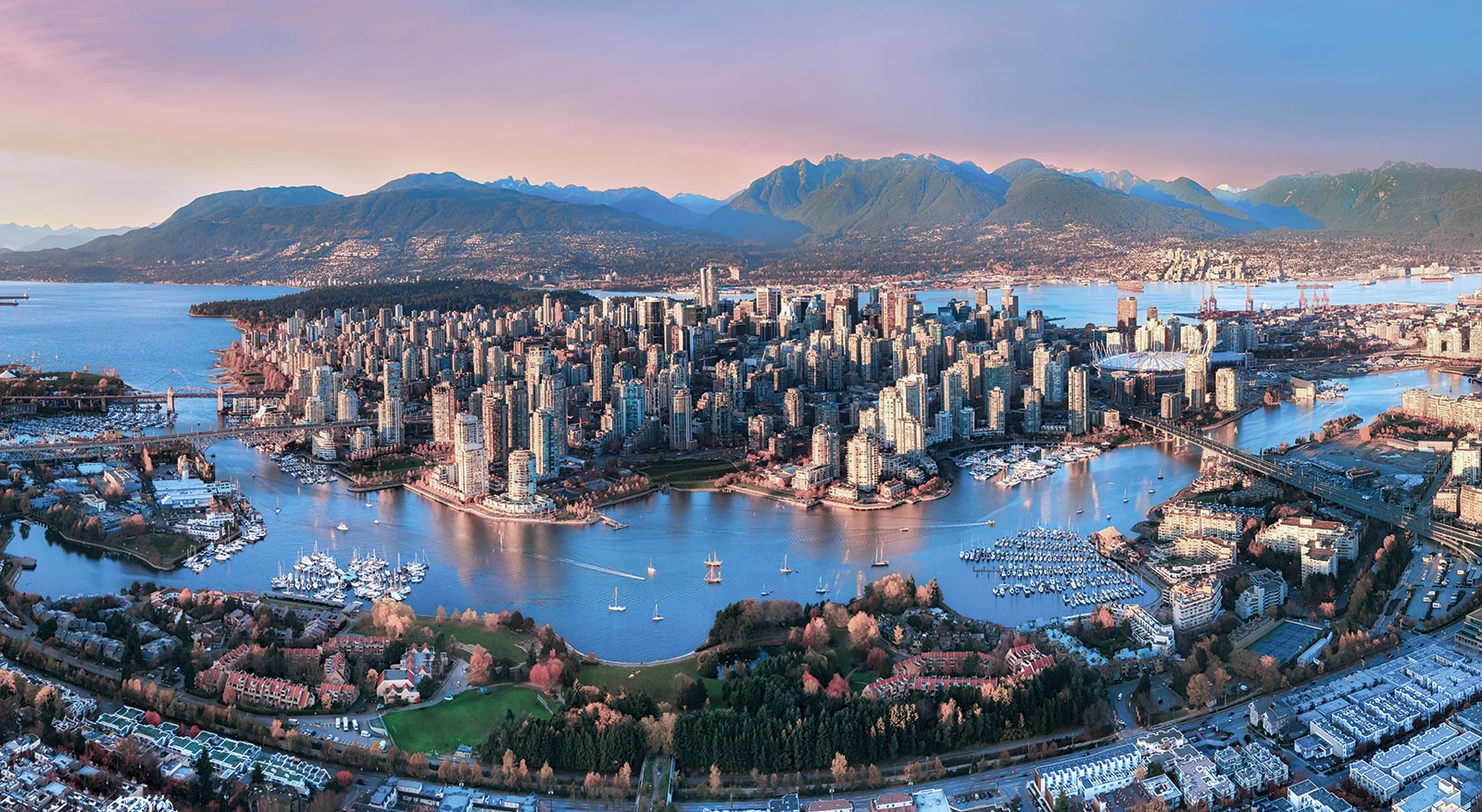
温哥华市(City of Vancouver)是加拿大不列颠哥伦比亚省低陆平原地区一沿岸城市。根据2016年加拿大统计局人口普查,温哥华市人口有631,486人,而大温哥华地区的人口为246万,[1]是不列颠哥伦比亚省以至加拿大西部最大的都会区,以及全国第三大都会区;市内人口则在全国排行第八。[2][3]
温哥华以英国航海家乔治·温哥华命名,欧洲人抵达温哥华一带后,区内经济早期主要依赖于林木业。加拿大太平洋铁路于1887年延至温哥华后,温哥华成为北美西岸水陆路交通的主要枢纽之一,更构成远东地区、加拿大东部和英国之间贸易往来的重要一环。[4][5]温哥华港现时是加拿大最大和最繁忙的港口,以货物总吨数计也是北美第四大港口。[6]此外,温哥华的自然环境深受游客欢迎,令旅游业成为市内第二大经济支柱。[7]温哥华也是北美第三大制片中心,有“北方好莱坞”之称。[8][9]也是20世纪后,与美国旧金山同为华人在北美最集中的地区。
温哥华近年经常在各项世界最佳居住城市的调查中名列前茅。[10][11]温哥华亦曾于2010年与125公里以外的惠斯勒联手举办冬季奥运会和冬季残奥会。[12]此外温哥华还曾举办2015年女子世界杯足球赛,决赛场地即设在不列颠哥伦比亚体育馆。
Vancouver (englische Aussprache [væŋˈkuːvɚ] oder [vænˈkuːvɚ]) ist eine Stadt im Südwesten von British Columbia an der Westküste Kanadas. Sie liegt zwischen der Straße von Georgia und den Coast Mountains, rund 45 Kilometer nordwestlich der Grenze zu den USA. Die Stadt gehört zum Regionaldistrikt Metro Vancouver, der mit 2.463.431 Einwohnern[1] die größte Metropolregion Westkanadas und nach Toronto und Montreal die drittgrößte des Landes bildet. Die Bevölkerungszahl der eigentlichen Stadt Vancouver beträgt 631.486.[2] Benannt ist die Stadt nach dem britischen Kapitän George Vancouver, der die Region Ende des 18. Jahrhunderts erforschte und vermaß. Der Name Vancouver selbst stammt vom niederländischen „van Coevorden“, abgeleitet von der Stadt Coevorden.
Die Stadt entstand in den 1860er Jahren als Folge der Einwanderungswelle während des Fraser-Canyon-Goldrauschs und entwickelte sich nach der Eröffnung der transkontinentalen Eisenbahn im Jahr 1887 innerhalb weniger Jahrzehnte von einer kleinen Sägewerkssiedlung zu einer Metropole. Die Wirtschaft basierte zu Beginn auf der Ausbeutung der natürlichen Ressourcen von British Columbia: Forstwirtschaft, Bergbau, Fischerei und Landwirtschaft. Der Hafen Vancouver erlangte nach der Eröffnung des Panamakanals internationale Bedeutung. Er ist heute der größte in Kanada und exportiert mehr Güter als jeder andere Hafen in Nordamerika.
Vancouver wandelte sich mit der Zeit zu einem Dienstleistungszentrum und (insbesondere nach der Weltausstellung Expo 86) zu einem Reiseziel für Touristen. Die Stadt ist darüber hinaus hinter Los Angeles und New York der drittwichtigste Standort der nordamerikanischen Filmindustrie und wird daher auch als „Hollywood North“ bezeichnet. Die Finanzwirtschaft spielt ebenfalls eine bedeutende Rolle. In einer Rangliste der wichtigsten Finanzzentren weltweit belegt Vancouver den 15. Platz (Stand: 2018).[3]
Vancouver veranstaltete vom 12. bis 28. Februar 2010 die XXI. Olympischen Winterspiele. Einige Wettbewerbe der Spiele fanden im 125 Kilometer von Vancouver entfernten Whistler statt. Nach Montreal im Jahr 1976 und Calgary im Jahr 1988 war Vancouver die dritte kanadische Stadt, die Olympische Spiele veranstaltet hat.
バンクーバー(英語: Vancouver)は、カナダ連邦ブリティッシュコロンビア州南西部にある都市。同州最大の都市である。ヴァンクーヴァーと表記されることもある[3]。
バンクーバーを中心とする都市圏人口は210万人とカナダ国内第3位の都市圏を形成している[4]。バンクーバー市のみの人口では同国内で第8位の約64万人[5]である。民族や言語が多様で、人口のおよそ52%は第一言語が同州の公用語にあたる英語ではない[6]。北米有数の世界都市であり、2016年に発表された「世界の都市総合力ランキング」では、世界28位と評価された[7]。
1867年に製材所ができ、これらを中心とする入植地であったギャスタウンは発展を続け、グランビルとして町は拡大した。東カナダから続く鉄道の終着駅が町まで敷かれることになった1886年に町はバンクーバーとして改名され市政となる。
林業が同市最大の産業で、都市部ながら自然に囲まれた都市として知られていることから、観光業が発達しており、同市第2の産業となっている[8]。同市にあるメトロバンクーバー港は同国最大の港であり、北米においても積載量で第4位の規模を持つ[9]。同市および隣のバーナビー市には、主要な各映画製作会社が拠点を置いており、ロサンゼルス、ニューヨークに続く北米第3位の規模となる映画製作拠点となっている。このため、通称ハリウッドノースとも呼ばれる[10][11]。国際会議や国際競技が数多く開催されており、2010年には第21回冬季オリンピック(バンクーバーオリンピック)が開催された。
Vancouver (/vænˈkuːvər/ ( listen)) is a coastal seaport city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2016 census recorded 631,486 people in the city, up from 603,502 in 2011. The Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2,463,431 in 2016, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada with over 5,400 people per square kilometre,[5][6] which makes it the fifth-most densely populated city with over 250,000 residents in North America behind New York City, Guadalajara, San Francisco,[7] and Mexico City according to the 2011 census. Vancouver is one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities in Canada according to that census; 52% of its residents have a first language other than English.[8][9] Roughly 30% of the city's inhabitants are of Chinese heritage.[10] Vancouver is classed as a Beta global city.
listen)) is a coastal seaport city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2016 census recorded 631,486 people in the city, up from 603,502 in 2011. The Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2,463,431 in 2016, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada with over 5,400 people per square kilometre,[5][6] which makes it the fifth-most densely populated city with over 250,000 residents in North America behind New York City, Guadalajara, San Francisco,[7] and Mexico City according to the 2011 census. Vancouver is one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities in Canada according to that census; 52% of its residents have a first language other than English.[8][9] Roughly 30% of the city's inhabitants are of Chinese heritage.[10] Vancouver is classed as a Beta global city.
Vancouver is consistently named as one of the top five worldwide cities for livability and quality of life,[11][12] and the Economist Intelligence Unit acknowledged it as the first city ranked among the top-ten of the world's most well-living cities[13] for five consecutive years.[14] Vancouver has hosted many international conferences and events, including the 1954 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, UN Habitat I, Expo 86, the World Police and Fire Games in 1989 and 2009; and the 2010 Winter Olympics and Paralympics which were held in Vancouver and Whistler, a resort community 125 km (78 mi) north of the city.[15] In 2014, following thirty years in California, the TED conference made Vancouver its indefinite home. Several matches of the 2015 FIFA Women's World Cup were played in Vancouver, including the final at BC Place.[16]
The original settlement, named Gastown, grew up on clearcuts on the west edge of the Hastings Mill logging sawmill's property, where a makeshift tavern had been set up on a plank between two stumps and the proprietor, Gassy Jack, persuaded the curious millworkers to build him a tavern, on July 1, 1867. From that first enterprise, other stores and some hotels quickly appeared along the waterfront to the west. Gastown became formally laid out as a registered townsite dubbed Granville, B.I. ("B.I" standing for "Burrard Inlet"). As part of the land and political deal whereby the area of the townsite was made the railhead of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), it was renamed "Vancouver" and incorporated shortly thereafter as a city, in 1886. By 1887, the Canadian Pacific transcontinental railway was extended westward to the city to take advantage of its large natural seaport to the Pacific Ocean, which soon became a vital link in a trade route between the Orient / East Asia, Eastern Canada, and Europe.[17][18] As of 2014, Port Metro Vancouver is the third-largest port by tonnage in the Americas (recently displacing New York City), 27th in the world,[19] the busiest and largest in Canada, and the most diversified port in North America.[20] While forestry remains its largest industry, Vancouver is well known as an urban centre surrounded by nature, making tourism its second-largest industry.[21]
Major film production studios in Vancouver and nearby Burnaby have turned Greater Vancouver and nearby areas into one of the largest film production centres in North America,[22][23] earning it the nickname "Hollywood North".[24][25][26]
Vancouver /vãkuvaɛ̯ʁ/a Écouter ou /vɑ̃kuvɛʁ/b (en anglais : /væŋˈkuvɚ/c Écouter) est une cité1 portuaire du pourtour du Pacifique située dans les basses-terres continentales de la province de Colombie-Britannique, au Canada. Avec 631 486 habitants selon le recensement du Canada de 2016, elle est la huitième plus grande municipalité canadienne3. Son agglomération de 2 463 431 est la troisième aire urbaine du pays, et la plus peuplée de l'Ouest canadien. Vancouver est une des villes les plus cosmopolites du Canada, 52 % des résidents ont une autre langue maternelle que l'anglais4. Vancouver est considérée comme une ville mondiale de classe beta. La superficie de Vancouver est de 114,97 km2, donnant une densité de population de 5 493 au kilomètre carré, faisant d'elle la municipalité canadienne la plus densément peuplée et la quatrième en Amérique du Nord, après New York, San Francisco et Mexico5. Elle est la vingt-troisième ville la plus peuplée d'Amérique du Nord6.
Le premier établissement, nommé Gastown, s'est développé autour d'une scierie appelé Hastings Mills, en 1867. Le site fut renommé Vancouver et incorporé comme cité en 1886. En 1887, le chemin de fer transcontinental a été étendu jusqu'à elle pour profiter de son grand port naturel, qui est rapidement devenu un maillon essentiel d'une route commerciale entre la côte est du Canada, l'Orient et l'Europe7,8. En 2009, Port Metro Vancouver est le port le plus grand et le plus achalandé du Canada, et le plus diversifié d'Amérique du Nord9. Même si l'exploitation forestière demeure sa plus grande industrie, Vancouver est réputée pour être un centre urbain entouré par la nature, faisant du tourisme sa deuxième industrie10. Les studios de production cinématographique de Vancouver et de Burnaby ont fait de la métropole l'un des plus grands centres cinématographiques en Amérique du Nord11,12, ce qui lui a valu le surnom de Hollywood North13,14,15.
Vancouver est régulièrement citée comme l'une des cinq meilleures villes au monde pour sa qualité de vie16,17, et l'Economist Intelligence Unit l'a classée parmi les dix villes les plus agréables durant cinq années consécutives18,19. Vancouver fut l'hôte de nombreux évènements internationaux, comme les Jeux de l'Empire britannique et du Commonwealth de 1954, la conférence Habitat I par l'Organisation des Nations unies en 1976, l'Exposition internationale de 1986 et les Jeux olympiques d'hiver de 201020. En 2015, elle a accueilli la finale de la Coupe du monde féminine de football21. La ville accueillera en 2018 le Congrès ornithologique international.
Vancouver (AFI: [vanˈkuver][1]) è una città canadese, sulla costa Pacifica della provincia canadese della Columbia Britannica (British Columbia). È situata nella parte meridionale della provincia e rappresenta uno dei maggiori porti dell'Oceano Pacifico. È delimitata dallo Stretto di Georgia (Georgia Strait), dal fiume Fraser, e dalla catena montuosa delle Montagne Costiere. Il nome è in onore del capitano George Vancouver, esploratore britannico.
La popolazione della città è di 603 502 abitanti, mentre l'area urbana ne conta 2 135 201. Vancouver fa parte della regione metropolitana, conosciuta come la "Greater Vancouver Regional District" (GVRD) o Metro Vancouver, nella quale vivono 2 463 700 (stima del 2012)[2]. Questo la rende la più grande area metropolitana nel Canada occidentale, e la terza più grande nel paese. Come in buona parte del Canada, anche Vancouver etnicamente è molto diversificata, basti pensare che il 52% dei residenti[3][4] della città e il 43% dell'area metropolitana hanno come prima lingua un idioma diverso dall'inglese[5].
La popolazione metropolitana è proiettata a raggiungere i 3 milioni di abitanti entro il 2021[6]. La densità di popolazione è tra le più alte del Nord America, e la pone al quarto posto dopo New York, San Francisco e Città del Messico. Il trend porta a stimare che possa raggiungere il secondo posto entro il 2021[7].
L'economia di Vancouver ha tradizionalmente fatto leva sulle risorse della Columbia Britannica: forestali, minerarie, pesca e agricoltura. Ma tuttavia è andata diversificandosi nel tempo, ed oggi Vancouver ha un'importante e vitale industria nel settore dei servizi e del turismo. La città è diventata il terzo più grande polo di produzione cinematografico del Nord America dopo Los Angeles e New York, tanto da guadagnarsi il soprannome di Hollywood del Nord[8][9][10]. Vancouver ha avuto un'espansione nell'industria dell'high-tech, in particolare nello sviluppo dei videogiochi.
Vancouver è costantemente classificata fra le prime tre città più vivibili del mondo[11][12][13]. Secondo il rapporto 2010 della Mercer Human Resource Consulting, ad esempio, Vancouver è considerata la prima città al mondo per qualità della vita. Nel 2007 Vancouver era la seconda città più cara del Canada dopo Toronto e la 89ª a livello globale.
Nel 2010 Vancouver, insieme a Whistler, situata 125 km a nord della città, ha ospitato i Giochi olimpici invernali e i Giochi Paralimpici invernali.
Vancouver (en inglés:  /væŋ'ku:vɚ/ (?·i), en español /baŋ'kuβ̞eɾ/) es una ciudad de la costa pacífica de Canadá, ubicada en el suroeste de la provincia de Columbia Británica, entre el estrecho de Georgia y las Montañas Costeras. La ciudad fue llamada así en honor del capitán George Vancouver, un explorador inglés.
/væŋ'ku:vɚ/ (?·i), en español /baŋ'kuβ̞eɾ/) es una ciudad de la costa pacífica de Canadá, ubicada en el suroeste de la provincia de Columbia Británica, entre el estrecho de Georgia y las Montañas Costeras. La ciudad fue llamada así en honor del capitán George Vancouver, un explorador inglés.
Es parte del área metropolitana del Distrito Regional del Gran Vancouver, el cual, con una población de 2 313 328 habitantes (2011),1 constituye el área metropolitana más grande del oeste canadiense y la tercera en el país después de Toronto y Montreal.2 Vancouver en sí mismo cuenta con 603 502 habitantes.1 El gentilicio utilizado para referirse a los residentes de Vancouver es vancuverita o vancouverense,3 (en inglés Vancouverite).
Vancouver, en los últimos años, siempre ha sido considerada como una de las cinco ciudades con mejor calidad de vida en el mundo.4567 En 2013, obtuvo el puesto 21º entre las ciudades en que es más caro vivir y resultó ser la más cara de Norteamérica. 8 También es una de las ciudades más seguras del mundo, debido a sus bajísimas tasas de criminalidad.
Los Juegos Olímpicos y Paralímpicos de invierno de 2010 se llevaron a cabo en Vancouver y en la cercana localidad de Whistler.91011
Ванку́вер (англ. Vancouver) — город на западе Канады, крупнейший населённый пункт провинции Британская Колумбия и третий по величине в Канаде. В 2010 году в Ванкувере проводились XXI зимние Олимпийские игры. Исследовательская группа Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) британского издания The Economist трижды — в 2005, 2007, 2009 годах — присваивала Ванкуверу звание «лучшего города Земли»[2][3][4].
Население самого города — 631 486 чел. (на 2016 год). В агломерации Большой Ванкувер (англ.)русск. проживает свыше 2 463 431 чел. (на 2016 год) — это третья по величине агломерация в Канаде. Ванкувер является наиболее этнически и лингвистически разнообразным городом страны — 52 % его жителей считают своим родным языком не английский[5].



惠 斯勒山滑雪场于1966年启用,占地3,657英亩,标高1,530公尺,共有超过100个滑雪道,是加拿大滑雪道最多的滑雪场。其中有25%的专业滑雪 道、55%为中级滑雪者设计的滑雪道,20%适合初学者所用的滑雪道,3种可供选择,变化很多,惠斯勒的滑雪期亦很长,每年十一月开始至翌年五月终结,有 时会延至八月还可以作夏季滑雪。1988年,惠斯勒山启用了10人高速缆车,运载逐年增加的滑雪人潮;1996年惠斯勒山另设了一条能供6人乘坐的高速缆 车载运上山路线。
惠斯勒除了是被选为全球最佳的“滑雪乐园”,也是世界闻名的理想渡假胜地,其受欢迎的程度完全没有受季节限制,春季滑雪一般开放到五月底左右,由于黑梳山山顶终年积雪,想要享受滑雪乐趣,不见得一定要等到冬季,夏季也到黑梳山顶享受在冰河上滑行的乐趣。
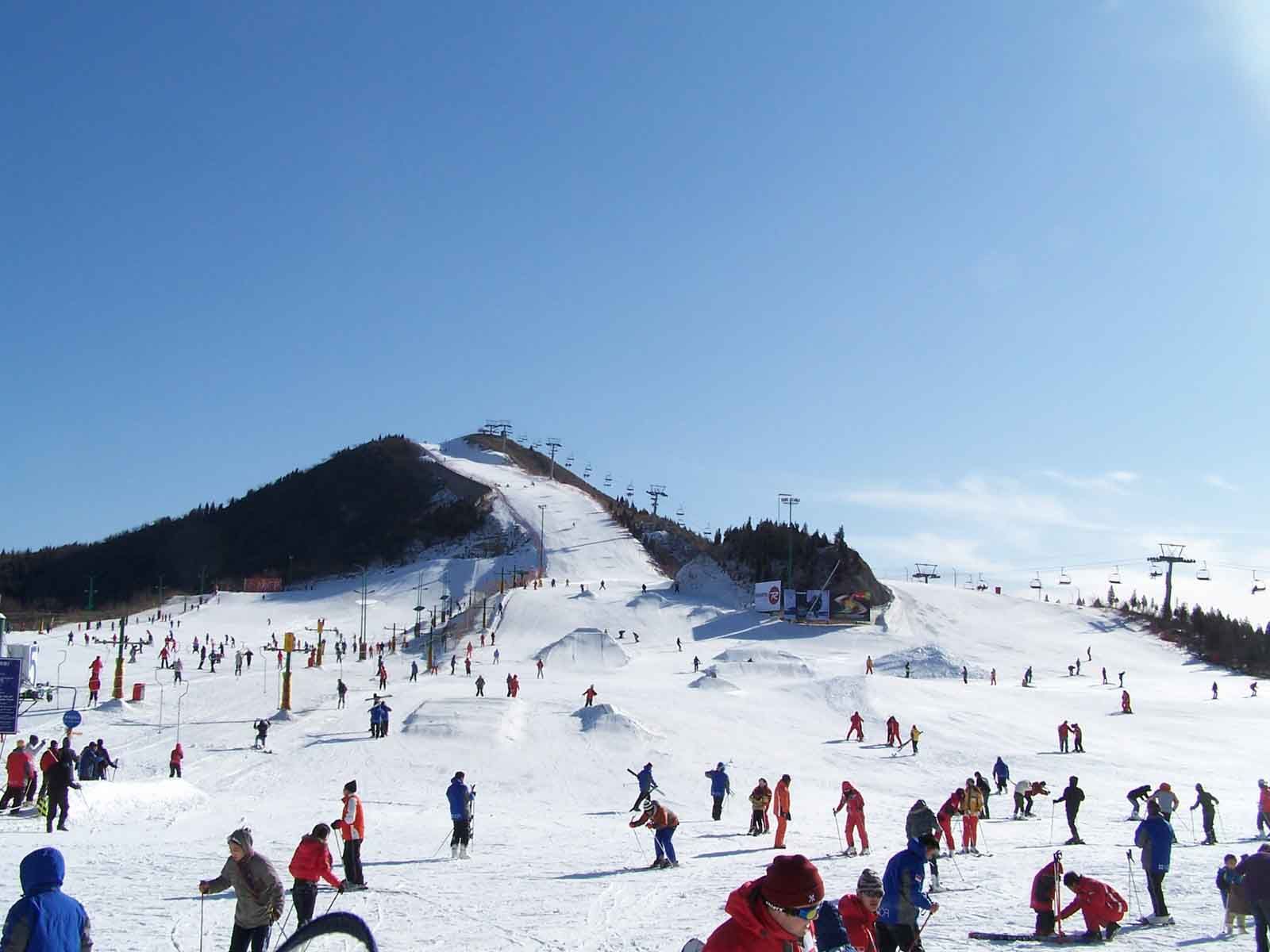




Ябули (亚布力 滑雪 旅游 度假区 yà-bù-lì huá-xuě lvˇ-yóu dù-jià-qū) — горнолыжный курорт в Китае. Расположен в провинции Хэйлунцзян в городском уезде Шанчжи, в 200 км к востоку от Харбина и в 120 км к западу от Муданьцзяна. Построен в 1996.
Находится на высоте 1374 м над уровнем моря. В среднем снег лежит здесь 170 дней в году. Действуют 4 фуникулера, 9 высокогорных лыжных трасс и 7 трасс лыжного кросса. В летний период кататься можно на «сухом лыжном склоне», длина которого 2,6 км.
Был местом проведения 3-х Азиатских зимних игр в феврале 1996. В 2009 году в Ябули прошли соревнования по лыжным видам спорта в рамках XXIV Зимней Универсиады.

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Bavaria
Bavaria
 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 New York-NY
New York-NY