
English Encyclopedia
 Financial
Financial



 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA


 Important port
Important port
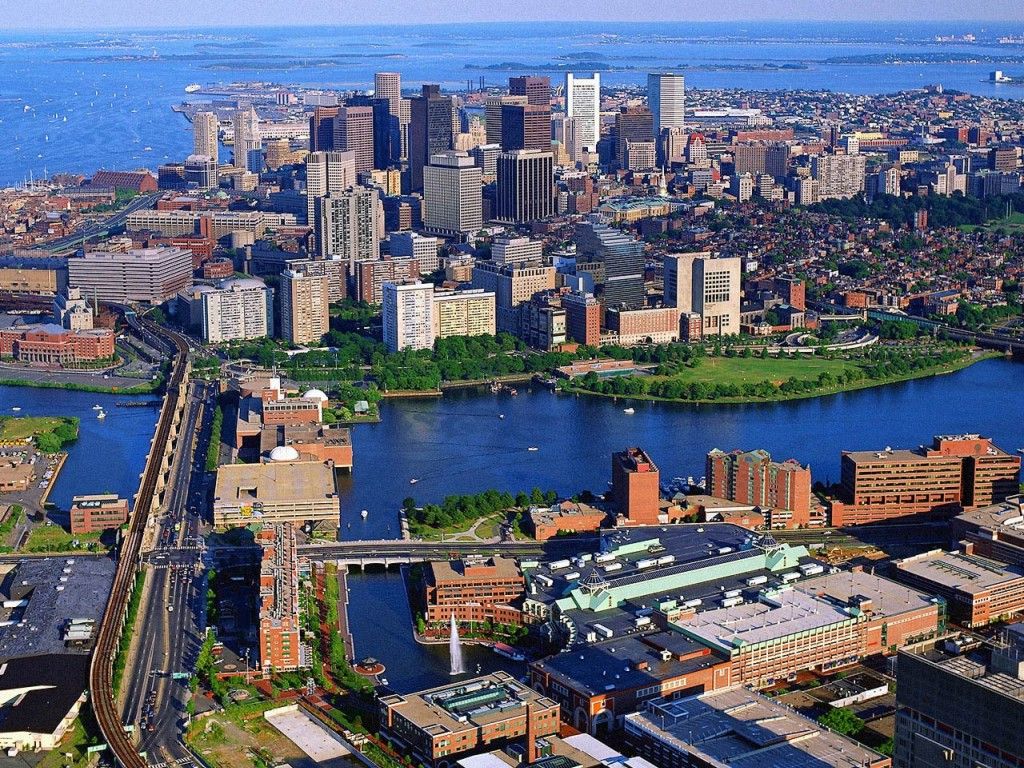

Boston (US: /ˈbɔːstən/, UK: /ˈbɒstən/),[5] officially the City of Boston, is the capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States and 24th-most populous city in the country.[6] The city proper covers 48.4 square miles (125 km2)[7] with a population of 675,647 in 2020,[2] also making it the most populous city in New England.[8] It is the seat of Suffolk County (although the county government was disbanded on July 1, 1999).[9] The city is the economic and cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Boston, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 4.8 million people in 2016 and ranking as the tenth-largest MSA in the country.[10] A broader combined statistical area (CSA), generally corresponding to the commuting area[11] and including Providence, Rhode Island, is home to some 8.2 million people, making it the sixth most populous in the United States.[12]
Boston is one of the oldest municipalities in the United States, founded on the Shawmut Peninsula in 1630 by Puritan settlers from the English town of the same name.[13][14] It was the scene of several key events of the American Revolution, such as the Boston Massacre, the Boston Tea Party, the Battle of Bunker Hill and the siege of Boston. Upon American independence from Great Britain, the city continued to be an important port and manufacturing hub as well as a center for education and culture.[15][16] The city has expanded beyond the original peninsula through land reclamation and municipal annexation. Its rich history attracts many tourists, with Faneuil Hall alone drawing more than 20 million visitors per year.[17] Boston's many firsts include the United States' first public park (Boston Common, 1634), first public or state school (Boston Latin School, 1635)[18] and first subway system (Tremont Street subway, 1897).[19]
Today, Boston is a thriving center of scientific research. The Boston area's many colleges and universities make it a world leader in higher education,[20] including law, medicine, engineering and business, and the city is considered to be a global pioneer in innovation and entrepreneurship, with nearly 5,000 startups.[21][22][23] Boston's economic base also includes finance,[24] professional and business services, biotechnology, information technology and government activities.[25] Households in the city claim the highest average rate of philanthropy in the United States;[26] businesses and institutions rank among the top in the country for environmental sustainability and investment.[27] The city has one of the highest costs of living in the United States[28][29] as it has undergone gentrification.[
 *American think tanks
*American think tanks
 *United States Political System
*United States Political System

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Think Tank
*Think Tank
 United States
United States
 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
The Brookings Institution, often simply called Brookings, is an American research group founded in 1916. Located on Think Tank Row in Washington, D.C.,[3] the organization conducts research and education in the social sciences, primarily in economics (and tax policy), metropolitan policy, governance, foreign policy, global economy, and economic development.[4][5] Its stated mission is to "provide innovative and practical recommendations that advance three broad goals: strengthen American democracy; foster the economic and social welfare, security and opportunity of all Americans; and secure a more open, safe, prosperous, and cooperative international system."[3]
Brookings has five research programs at its Washington campus: Economic Studies,[6] Foreign Policy,[7] Governance Studies,[8] Global Economy and Development,[9] and Metropolitan Policy.[10] It also established and operates three international centers which are based in Doha, Qatar (Brookings Doha Center, and since 2021, the Middle East Council on Global Affairs or MECGA);[11] Beijing, China (Brookings-Tsinghua Center for Public Policy, and since 2020, the Brookings-Tsinghua China Office at Tsinghua University);[12] and New Delhi, India (Brookings India, and since 2020, the Centre for Social and Economic Progress or CSEP).[13]
The University of Pennsylvania's Global Go To Think Tank Index Report has named Brookings "Think Tank of the Year" and "Top Think Tank in the World" every year since 2008.[14] The Economist describes Brookings as "perhaps America’s most prestigious think-tank."[15]
Brookings states that its staff "represent diverse points of view" and describes itself as nonpartisan,[16] and various media outlets have alternately described Brookings as centrist,[17] liberal,[18] or right-wing.[19] An academic analysis of congressional records from 1993 to 2002 found that Brookings was cited by conservative politicians almost as often as by liberal politicians, earning a score of 53 on a 1–100 scale, 100 representing the most liberal score.[20] The same study found Brookings to be the most frequently cited think tank by U.S. media and politicians.
 *American think tanks
*American think tanks

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Think Tank
*Think Tank
 United States
United States

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

The Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) is a think tank based in Washington, D.C., in the United States.[5] CSIS was founded as the Center for Strategic and International Studies of Georgetown University in 1962. The center conducts policy studies and strategic analyses of political, economic and security issues throughout the world, with a specific focus on issues concerning international relations, trade, technology, finance, energy and geostrategy.[6]
In the University of Pennsylvania's 2019 Global Go To Think Tanks Report, CSIS is ranked the number one think tank in the United States across all fields, the "Top Defense and National Security Think Tank" in the world, and the 4th best think tank in the world overall.[7][8] CSIS has been named the number one think tank for Defense and National Security for the past seven years, and has been declared the 'Center of Excellence'.[8]
Since its founding, CSIS "has been dedicated to finding ways to sustain American prominence and prosperity as a force for good in the world", according to its website.[9] CSIS is officially a bipartisan think tank with scholars that represent varying points of view across the political spectrum. The think tank is known for inviting well-known foreign policy and public service officials from the U.S. Congress and the executive branch, including those affiliated with either the Democratic or the Republican Party as well as foreign officials of varying political backgrounds. It has been labeled a "centrist" think tank by U.S. News & World Report.[10]
The center hosts the Statesmen's Forum, a bipartisan venue for international leaders to present their views. Past speakers have included UN Secretary General Ban Ki Moon and National Security Advisor Tom Donilon.[11] The center also conducts the CSIS-Schieffer School Dialogues, a series of discussions hosted by Bob Schieffer, of CBS News, in addition to the Global Security Forum, with keynote addresses by Defense Department officials including former Secretary of Defense Chuck Hagel.
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1999
Women's Soccer World Cup 1999

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
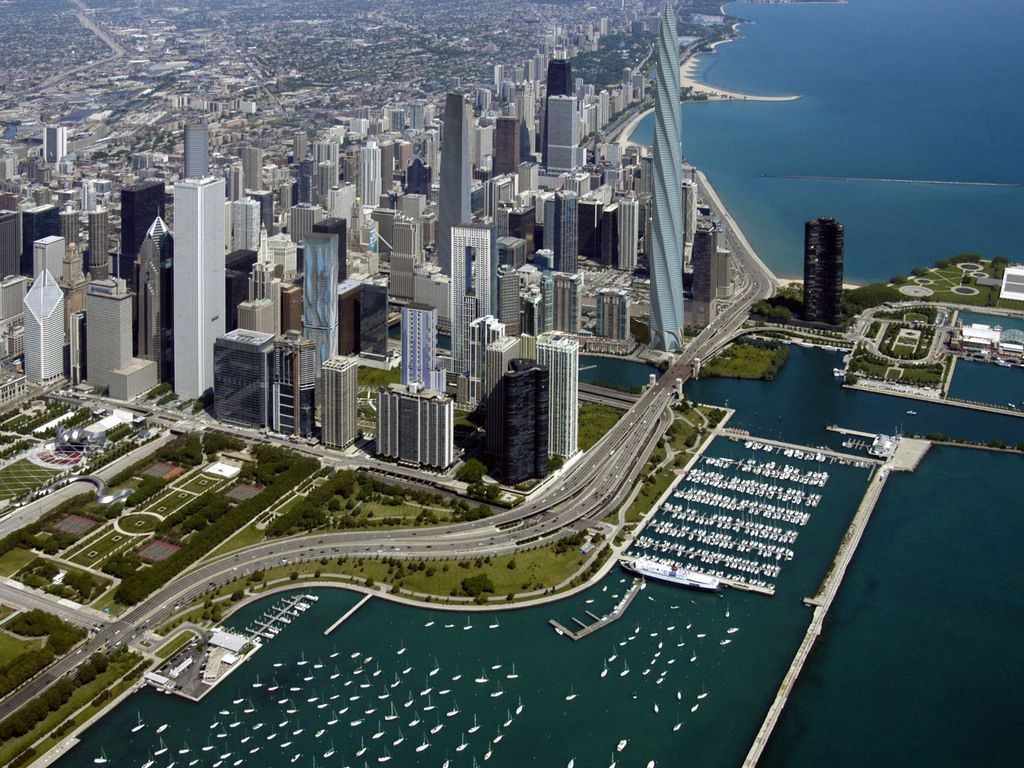


Chicago (/ʃɪˈkɑːɡoʊ/ ( listen), locally also /-ˈkɔː-/), officially the City of Chicago, located on the shores of freshwater Lake Michigan, is the third most populous city in America after New York and Los Angeles. As of the 2017 census-estimate, Chicago has a population of 2,716,450, which makes it the most populous city in both the state of Illinois and the Midwestern United States. It is the county seat of Cook County, the second most populous county in the U.S. Chicago is the principal city of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is often referred to as "Chicagoland." The Chicago metropolitan area has nearly 10 million people, is the third-largest in the United States, the fourth largest in North America, and the third largest metropolitan area in the world by land area. Chicago is the birthplace of the skyscraper, and considered the most influential architectural city of the 20th century.[6] In finance, the city saw the creation of the first standardized futures contracts at the Chicago Board of Trade; which today is the largest and most diverse derivatives market in the world, generating 20% of all volume in commodities and financial futures.[7]
listen), locally also /-ˈkɔː-/), officially the City of Chicago, located on the shores of freshwater Lake Michigan, is the third most populous city in America after New York and Los Angeles. As of the 2017 census-estimate, Chicago has a population of 2,716,450, which makes it the most populous city in both the state of Illinois and the Midwestern United States. It is the county seat of Cook County, the second most populous county in the U.S. Chicago is the principal city of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is often referred to as "Chicagoland." The Chicago metropolitan area has nearly 10 million people, is the third-largest in the United States, the fourth largest in North America, and the third largest metropolitan area in the world by land area. Chicago is the birthplace of the skyscraper, and considered the most influential architectural city of the 20th century.[6] In finance, the city saw the creation of the first standardized futures contracts at the Chicago Board of Trade; which today is the largest and most diverse derivatives market in the world, generating 20% of all volume in commodities and financial futures.[7]
Chicago was incorporated as a city in 1837 near a portage between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River watershed and grew rapidly in the mid-nineteenth century.[8] After the Great Chicago Fire of 1871, which destroyed several square miles and left more than 100,000 homeless, the city made a concerted effort to rebuild.[9] The construction boom accelerated population growth throughout the following decades, and by 1900 Chicago was one of the five largest cities in the world.[10] During this period, Chicago made noted contributions to urban planning and zoning standards, which included creating new construction styles (including the Chicago School of architecture), the development of the City Beautiful Movement, and the steel-framed skyscraper.[11]
Positioned along Lake Michigan, the city is an international hub for finance, commerce, industry, technology, telecommunications, and transportation. O'Hare International Airport is the one of the busiest airports in the world, and the region also has the largest number of U.S. highways and railroad freight.[12] In 2012, Chicago was listed as an alpha global city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network,[13] and it ranked seventh in the entire world in the 2017 Global Cities Index.[14] Chicago has the fourth-largest gross metropolitan product in the world — generating about $670.5 billion according to September 2017 estimates — ranking it after the metropolitan areas of Tokyo, New York City, and Los Angeles, and ranking ahead of number five London and number six Paris.[15] Chicago has one of the world's largest and most diversified and balanced economies, not being dependent on any one industry, with no single industry employing more than 14% of the workforce.[16]
Chicago was the second most visited city in the United States with 55 million domestic and international visitors,[17][18] not far behind the 62 million visitors to New York City in 2017.[19] The city ranked first place in the 2018 Time Out City Life Index, a global quality of life survey of 15,000 people in 32 cities.[20][21][22][23][24] Landmarks in the city include Millennium Park, Navy Pier, the Magnificent Mile, the Art Institute of Chicago, Museum Campus, the Willis (Sears) Tower, the Museum of Science and Industry, and Lincoln Park Zoo. Chicago's culture includes the visual arts, literature, film, theater, comedy (especially improvisational comedy), food, and music, particularly jazz, blues, soul, hip-hop, gospel,[25] and electronic dance music including house music. There are many colleges and universities in the Chicago area, of which the University of Chicago, Northwestern University, and the University of Illinois at Chicago are classified as "highest research" doctoral universities.
Chicago has professional sports teams in each of the major professional leagues, including two Major League Baseball teams. The city has had several nicknames throughout its history such as the Windy City, Chi-Town, Second City, and the City of the Big Shoulders, referring to its numerous towers and skyscrapers.[26]
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD
 Medieval cities in Europe
Medieval cities in Europe
 Schottland
Schottland
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 World Heritage
World Heritage
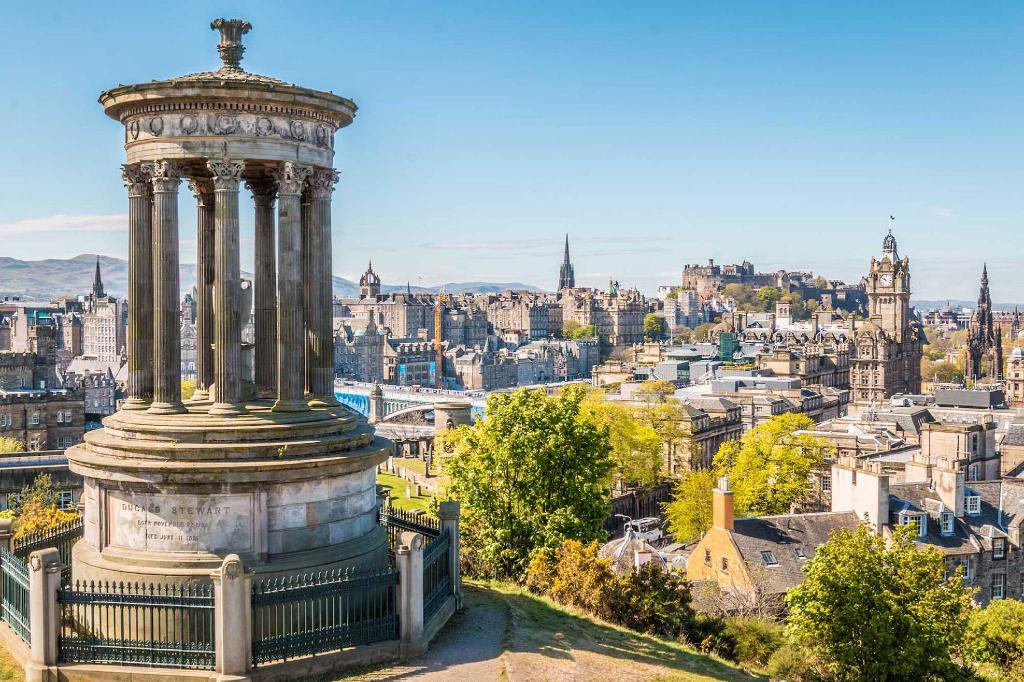

Edinburgh (/ˈɛdɪnbərə/ ( listen);[6][7][8] Scottish Gaelic: Dùn Èideann [ˈt̪uːn ˈeːtʲən̪ˠ]; Scots: Edinburgh) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (or Edinburghshire), it is located in Lothian on the Firth of Forth's southern shore.
listen);[6][7][8] Scottish Gaelic: Dùn Èideann [ˈt̪uːn ˈeːtʲən̪ˠ]; Scots: Edinburgh) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (or Edinburghshire), it is located in Lothian on the Firth of Forth's southern shore.
Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the supreme courts of Scotland. The city's Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scots law, literature, the sciences and engineering. It is the second largest financial centre in the United Kingdom (after London)[9] and the city's historical and cultural attractions have made it the United Kingdom's second most popular tourist destination, attracting over one million overseas visitors each year.[10]
Edinburgh is Scotland's second most populous city and the seventh most populous in the United Kingdom. The official population estimates are 464,990 (2012) for the Locality of Edinburgh (Edinburgh pre 1975 regionalisation plus Currie and Balerno),[1] 513,210 (2017) for the City of Edinburgh,[2] and 1,339,380 (2014) for the city region.[2][3] Edinburgh lies at the heart of the Edinburgh and South East Scotland city region comprising East Lothian, Edinburgh, Fife, Midlothian, Scottish Borders and West Lothian.[11]
The city is the annual venue of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland. It is home to national institutions such as the National Museum of Scotland, the National Library of Scotland and the Scottish National Gallery. The University of Edinburgh, founded in 1582 and now one of four in the city, was placed 23rd in the QS World University Rankings in 2018.[12] The city is also famous for the Edinburgh International Festival and the Fringe, the latter being the world's largest annual international arts festival. Historic sites in Edinburgh include Edinburgh Castle, the Palace of Holyroodhouse, the churches of St. Giles, Greyfriars and the Canongate, and the extensive Georgian New Town, built in the 18th/19th centuries. Edinburgh's Old Town and New Town together are listed as a UNESCO World Heritage site,[13] which has been managed by Edinburgh World Heritage since 1999.
 *American think tanks
*American think tanks

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Think Tank
*Think Tank

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research

The Heritage Foundation (abbreviated to Heritage)[1][2] is an American conservative think tank based in Washington, D.C., primarily geared towards public policy. The foundation took a leading role in the conservative movement during the presidency of Ronald Reagan, whose policies were taken from Heritage's policy study Mandate for Leadership.[4]
Historically, the Heritage Foundation has had significant influence in U.S. public policy making. It is among the most influential conservative public policy organizations in the United States.
 *American think tanks
*American think tanks

 California-CA
California-CA

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research

The Hoover Institution on War, Revolution, and Peace is a conservative American public policy institution and research institution that promotes personal and economic liberty, free enterprise, and limited government.[2][3][4] Located in Stanford, California, on the campus of Stanford University, it began as a library founded in 1919 by Stanford alumnus Herbert Hoover, before he became President of the United States. The library, known as the Hoover Institution Library and Archives, houses multiple archives related to Hoover, World War I, World War II, and other world-historical events.
The Hoover Institution has been a place of scholarship for individuals who previously held high-profile positions in government, such as George Shultz, Condoleezza Rice, Michael Boskin, Edward Lazear, John B. Taylor, Edwin Meese, and Amy Zegart—all Hoover Institution fellows. In 2007, retired U.S. Army General John P. Abizaid, former commander of the U.S. Central Command, was named the Institution's first annual Annenberg Distinguished Visiting Fellow.[5] Former Secretary of Defense General James Mattis served as a research fellow at Hoover before being appointed by the Trump administration.[6]
Hoover was ranked as the tenth most influential think tank in the world in 2020 by Academic Influence, and the 22nd of the "Top Think Tanks in the United States" by the Global Go To Think Tank Index Report in 2019 (Think Tanks and Civil Societies Program, University of Pennsylvania).[7][8]
While the Hoover Institution is formally a unit of Stanford University,[9] it has its own board of overseers[10] and less than 2% of its funding come from the university; instead it relies on its own endowment income and gifts.
 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil

 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 France
France
 Holland
Holland
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Camille Gutt
Camille Gutt
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Christine Lagarde
Christine Lagarde
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Dominique Strauss-Kahn
Dominique Strauss-Kahn
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Horst Köhler
Horst Köhler
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Ivar Rooth
Ivar Rooth
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Jacques de Larosière
Jacques de Larosière
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Johan Witteveen
Johan Witteveen
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Michel Camdessus
Michel Camdessus
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Per Jacobsson
Per Jacobsson
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Pierre-Paul Schweitzer
Pierre-Paul Schweitzer
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Rodrigo Rato
Rodrigo Rato
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa

 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research

The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 189 countries working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world while periodically depending on the World Bank for its resources.[1] Formed in 1944 at the Bretton Woods Conference primarily by the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes,[6] it came into formal existence in 1945 with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international payment system. It now plays a central role in the management of balance of payments difficulties and international financial crises.[7] Countries contribute funds to a pool through a quota system from which countries experiencing balance of payments problems can borrow money. As of 2016, the fund had XDR 477 billion (about US$ 667 billion).[8]
Through the fund and other activities such as the gathering of statistics and analysis, surveillance of its members' economies, and the demand for particular policies,[9] the IMF works to improve the economies of its member countries.[10] The organization's objectives stated in the Articles of Agreement are:[11] to promote international monetary co-operation, international trade, high employment, exchange-rate stability, sustainable economic growth, and making resources available to member countries in financial difficulty.[12] IMF funds come from two major sources: quotas and loans. Quotas, which are pooled funds of member nations, generate most IMF funds. The size of a member's quota depends on its economic and financial importance in the world. Nations with larger economic importance have larger quotas. The quotas are increased periodically as a means of boosting the IMF's resources in the form of special drawing rights.[13]
The current Managing Director (MD) and Chairwoman of the IMF is Bulgarian Economist Kristalina Georgieva, who has held the post since October 1, 2019.[14]
Gita Gopinath was appointed as Chief Economist of IMF from 1 October 2018. She received her PhD in economics from Princeton University. Prior to her IMF appointment she was economic adviser to the Chief Minister of Kerala, India.[15]

 Architecture
Architecture
 England
England
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History
 J 0 - 500 AD
J 0 - 500 AD

 History
History
 K 500 - 1000 AD
K 500 - 1000 AD

 History
History
 L 1000 - 1500 AD
L 1000 - 1500 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series

 Medieval cities in Europe
Medieval cities in Europe
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
 1908 Summer Olympics
1908 Summer Olympics
 1944 Summer Olympics
1944 Summer Olympics
 1948 Summer Olympics
1948 Summer Olympics
 2012 Summer Olympics
2012 Summer Olympics
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Important port
Important port
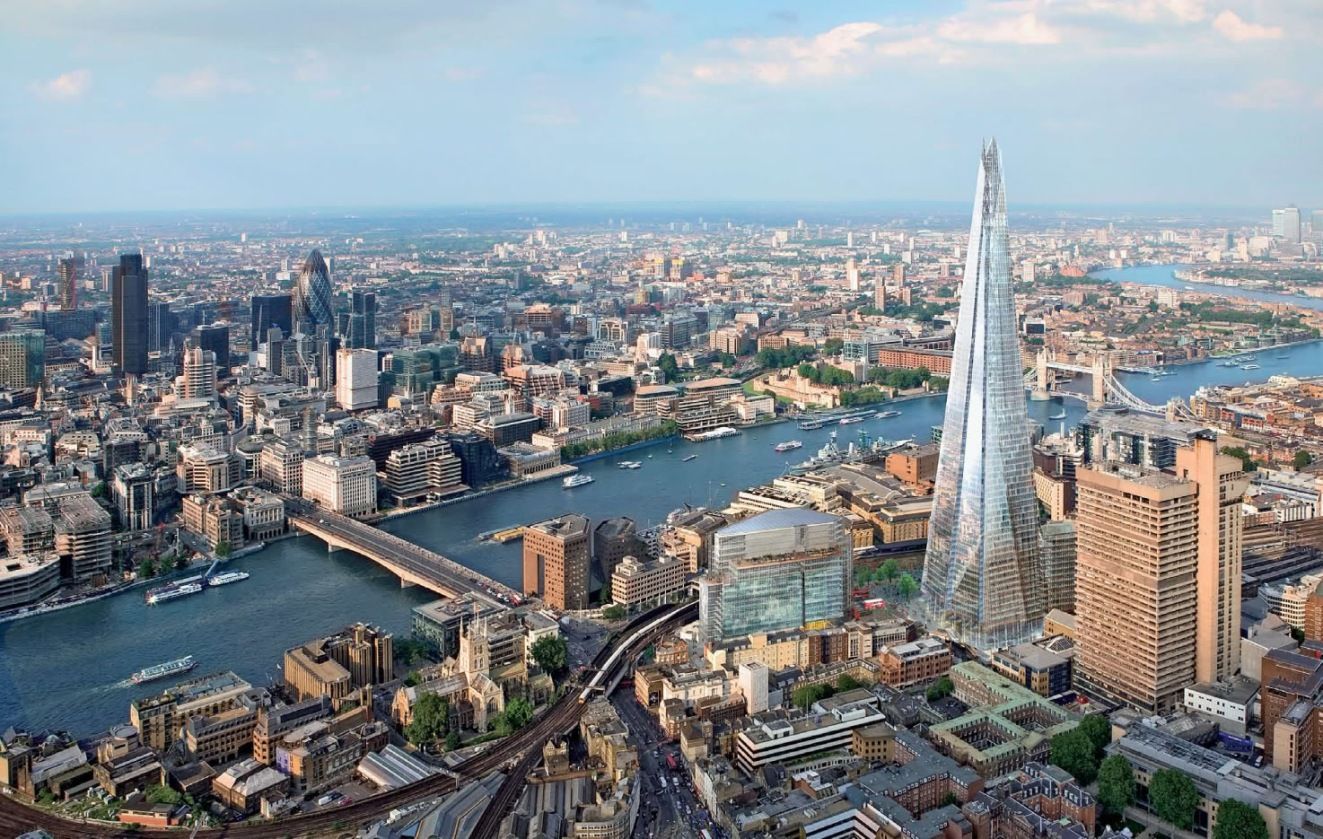

London (/ˈlʌndən/ ( listen) LUN-dən) is the capital and most populous city of England and the United Kingdom.[8][9] Standing on the River Thames in the south east of the island of Great Britain, London has been a major settlement for two millennia. It was founded by the Romans, who named it Londinium.[10] London's ancient core, the City of London, largely retains its 1.12-square-mile (2.9 km2) medieval boundaries. Since at least the 19th century, "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent and Hertfordshire,[11][12][13] which today largely makes up Greater London,[14][15][note 1] a region governed by the Mayor of London and the London Assembly.[16][note 2][17]
listen) LUN-dən) is the capital and most populous city of England and the United Kingdom.[8][9] Standing on the River Thames in the south east of the island of Great Britain, London has been a major settlement for two millennia. It was founded by the Romans, who named it Londinium.[10] London's ancient core, the City of London, largely retains its 1.12-square-mile (2.9 km2) medieval boundaries. Since at least the 19th century, "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent and Hertfordshire,[11][12][13] which today largely makes up Greater London,[14][15][note 1] a region governed by the Mayor of London and the London Assembly.[16][note 2][17]
London is one of the leading global cities[18][19] in the arts, commerce, education, entertainment, fashion, finance, healthcare, media, professional services, research and development, tourism and transportation.[20][21][22] It is the world's largest financial centre[23][24][25][26] and has the fifth or sixth largest metropolitan area GDP in the world.[note 3][27][28] London is often regarded as a world cultural capital.[29][30][31] It is the world's most-visited city as measured by international arrivals[32] and has the world's largest city airport system measured by passenger traffic.[33] It is the world's leading investment destination,[34][35][36][37] hosting more international retailers[38][39] and ultra high-net-worth individuals[40][41] than any other city. London's universities form the largest concentration of higher education institutes in Europe.[42] In 2012, London became the first city to have hosted the modern Summer Olympic Games three times.[43]
London has a diverse range of people and cultures, and more than 300 languages are spoken in the region.[44] Its estimated mid-2016 municipal population (corresponding to Greater London) was 8,787,892,[4] the largest of any city in the European Union[45] and accounting for 13.4% of the UK population.[46] London's urban area is the second most populous in the EU, after Paris, with 9,787,426 inhabitants at the 2011 census.[47] The city's metropolitan area is the most populous in the EU with 14,040,163 inhabitants in 2016,[note 4][3] while the Greater London Authority states the population of the city-region (covering a large part of the south east) as 22.7 million.[48][49] London was the world's most populous city from around 1831 to 1925.[50]
London contains four World Heritage Sites: the Tower of London; Kew Gardens; the site comprising the Palace of Westminster, Westminster Abbey, and St Margaret's Church; and the historic settlement of Greenwich (in which the Royal Observatory, Greenwich defines the Prime Meridian, 0° longitude, and GMT).[51] Other landmarks include Buckingham Palace, the London Eye, Piccadilly Circus, St Paul's Cathedral, Tower Bridge, Trafalgar Square and The Shard. London is home to numerous museums, galleries, libraries, sporting events and other cultural institutions, including the British Museum, National Gallery, Natural History Museum, Tate Modern, British Library and West End theatres.[52] The London Underground is the oldest underground railway network in the world.
 California State Route 1
California State Route 1

 California-CA
California-CA

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 League of Legends
League of Legends
 League of Legends World Championship
League of Legends World Championship
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games


 Important port
Important port
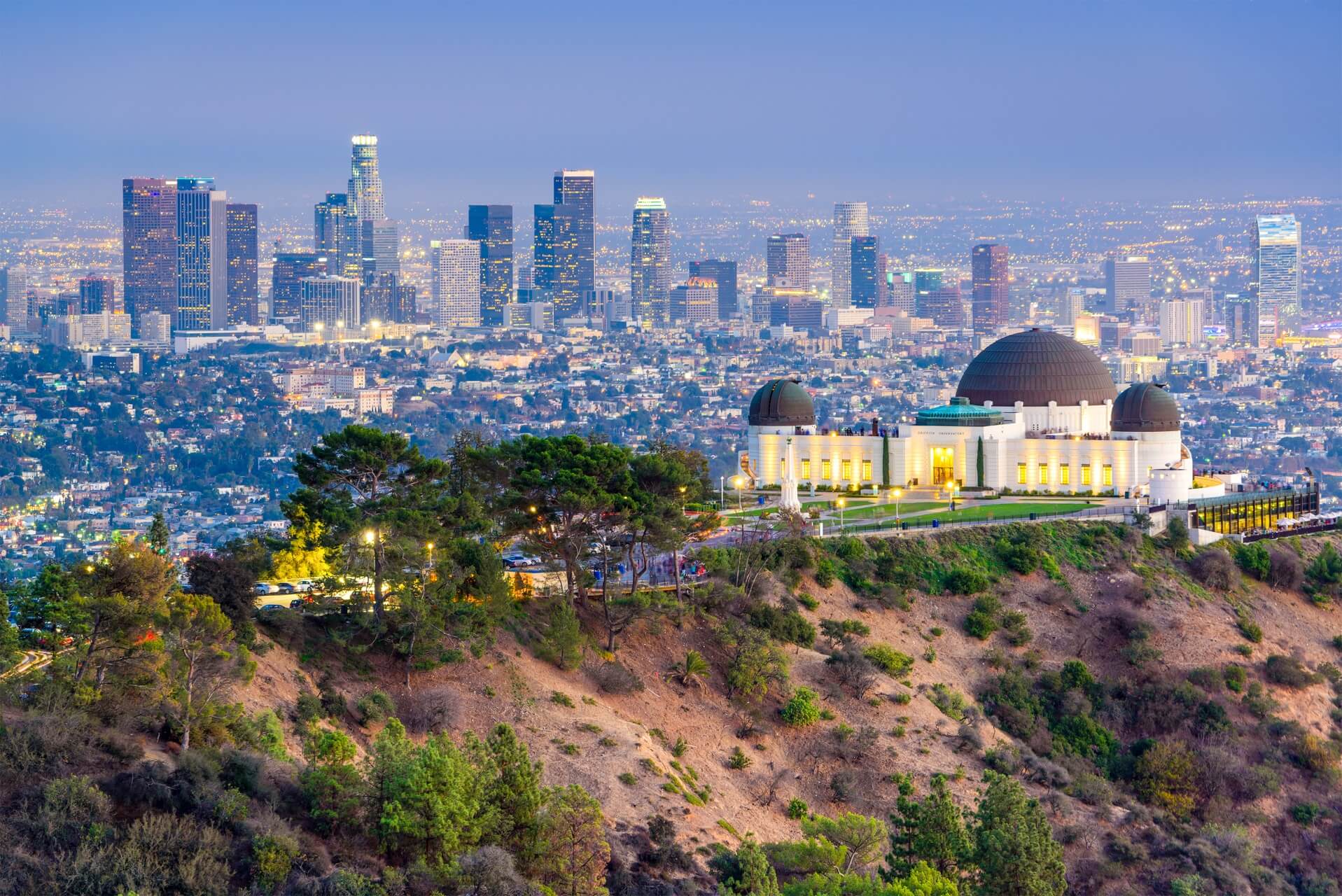

Los Angeles (US: /lɔːs ˈændʒələs/ ( listen);[16][a] Spanish for "The Angels"; Spanish: Los Ángeles; Spanish: [los ˈaŋxeles]; officially the City of Los Angeles, known colloquially by its initials L.A.) is the second-most populous city in the United States, after New York City, and the most populous city in the Western United States. With an estimated population of four million,[17] Los Angeles is the largest and most populous city in the state of California and the cultural, financial, and commercial center of Southern California. Nicknamed the "City of Angels" partly because of its name's Spanish meaning, Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic diversity, and sprawling metropolis.
listen);[16][a] Spanish for "The Angels"; Spanish: Los Ángeles; Spanish: [los ˈaŋxeles]; officially the City of Los Angeles, known colloquially by its initials L.A.) is the second-most populous city in the United States, after New York City, and the most populous city in the Western United States. With an estimated population of four million,[17] Los Angeles is the largest and most populous city in the state of California and the cultural, financial, and commercial center of Southern California. Nicknamed the "City of Angels" partly because of its name's Spanish meaning, Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic diversity, and sprawling metropolis.
Los Angeles is located in a large basin bounded by the Pacific Ocean on one side and by mountains as high as 10,000 feet (3,000 m) on the others. The city proper, which covers about 469 square miles (1,210 km2),[18] is the seat of Los Angeles County, the most populated county in the country. Los Angeles is the principal city of the Los Angeles metropolitan area; with a population of 13.1 million residents it is the second largest in the United States after that of New York City.[19] It is part of the Los Angeles-Long Beach combined statistical area, also the second most populous in the nation with a 2015 estimated population of 18.7 million.[20]
Los Angeles is one of the most substantial economic engines within the United States, with a diverse economy in a broad range of professional and cultural fields. Los Angeles is also famous as the home of Hollywood, a major center of the world entertainment industry. A global city, it has been ranked 6th in the Global Cities Index and 9th in the Global Economic Power Index. The Los Angeles combined statistical area also has a gross metropolitan product of $831 billion (as of 2008), making it the third-largest in the world, after the Tokyo and New York metropolitan areas. Los Angeles hosted the 1932 and 1984 Summer Olympics and will host the event for a third time in 2028. The city also hosted the Miss Universe pageant twice, in 1990 and 2006.
Historically home to the Chumash and Tongva, Los Angeles was claimed by Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo for Spain in 1542 along with the rest of what would become Alta California. The city was officially founded on September 4, 1781, by Spanish governor Felipe de Neve. It became a part of Mexico in 1821 following the Mexican War of Independence. In 1848, at the end of the Mexican–American War, Los Angeles and the rest of California were purchased as part of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, becoming part of the United States. Los Angeles was incorporated as a municipality on April 4, 1850, five months before California achieved statehood. The discovery of oil in the 1890s brought rapid growth to the city.[21] The completion of the Los Angeles Aqueduct in 1913, delivering water from Eastern California, later assured the city's continued rapid growth.
 *British think tank
*British think tank

 Financial
Financial
 *United Kingdom economic data
*United Kingdom economic data

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Think Tank
*Think Tank

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research

LSE IDEAS is a foreign policy think tank at the London School of Economics and Political Science. IDEAS was founded as a think tank for Diplomacy and Strategy in February 2008, succeeding the Cold War Studies Centre founded in 2004. The Chair is Professor Michael Cox and its Directors are Professor Christopher Coker and Professor Christopher Alden. The 2018 and 2017 Global Go To Think Tank Index run by the University of Pennsylvania's Think Tank and Civil Societies Program ranked LSE IDEAS as the number one European university-affiliated think tank, and the number two university-affiliated think tank in the world.[1][2]
IDEAS runs seven research projects, hosts public and private events (43 in 2017-2018), and publishes analysis of international affairs. From 2017 to 2018, it released 75 publications and held 43 fellowships and scholarships. In addition, IDEAS houses the LSE Executive MSc International Strategy and Diplomacy, a programme designed to enhance the strategic vision of mid-career professionals.
 United Nations
United Nations