
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 IT-Times
IT-Times




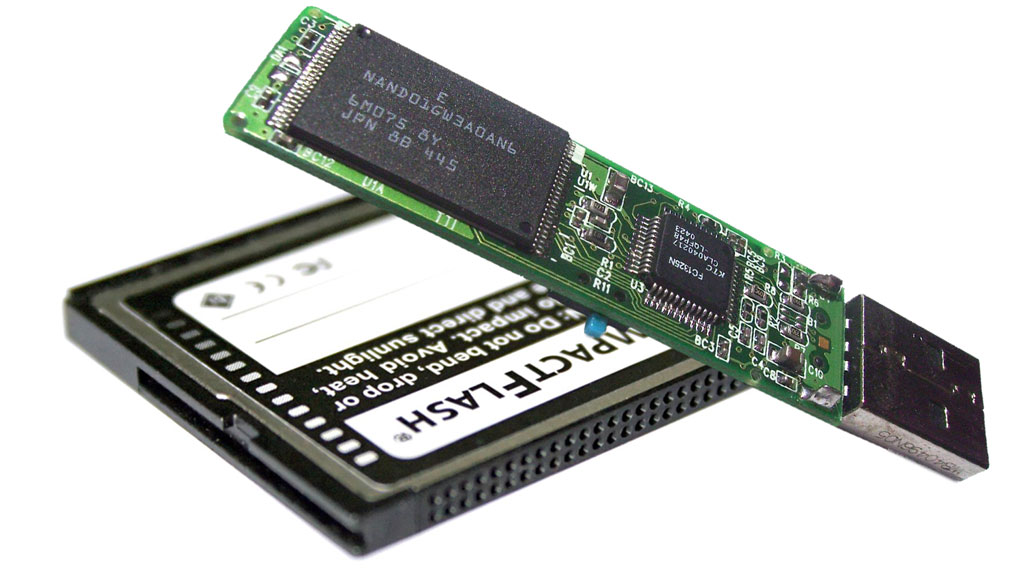
快闪存储器(英语:flash memory),是一种电子式可清除程序化只读存储器的形式,允许在操作中被多次擦或写的存储器。这种科技主要用于一般性数据存储,以及在计算机与其他数字产品间交换传输数据,如储存卡与U盘。闪存是一种特殊的、以宏块抹写的EEPROM。早期的闪存进行一次抹除,就会清除掉整颗芯片上的数据。
Flash-Speicher sind digitale Speicherbausteine; die genaue Bezeichnung lautet Flash-EEPROM. Sie gewährleisten eine nichtflüchtige Speicherung bei gleichzeitig niedrigem Energieverbrauch. Flash-Speicher sind portabel und miniaturisiert, es lassen sich jedoch bei Flash-EEPROM, im Gegensatz zu gewöhnlichem EEPROM-Speicher, Bytes, die kleinsten adressierbaren Speichereinheiten, nicht einzeln löschen oder überschreiben. Flash-Speicher sind auch langsamer als Festwertspeicher (ROM).
Flash memory is an electronic (solid-state) non-volatile computer storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed.
Toshiba developed flash memory from EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory) in the early 1980s and introduced it to the market in 1984.[citation needed] The two main types of flash memory are named after the NAND and NOR logic gates. The individual flash memory cells exhibit internal characteristics similar to those of the corresponding gates.
While EPROMs had to be completely erased before being rewritten, NAND-type flash memory may be written and read in blocks (or pages) which are generally much smaller than the entire device. NOR-type flash allows a single machine word (byte) to be written – to an erased location – or read independently.
The NAND type operates primarily in memory cards, USB flash drives, solid-state drives (those produced in 2009 or later), and similar products, for general storage and transfer of data. NAND or NOR flash memory is also often used to store configuration data in numerous digital products, a task previously made possible by EEPROM or battery-powered static RAM. One key disadvantage of flash memory is that it can only endure a relatively small number of write cycles in a specific block.[1]
Example applications of both types of flash memory include personal computers, PDAs, digital audio players, digital cameras, mobile phones, synthesizers, video games, scientific instrumentation, industrial robotics, and medical electronics. In addition to being non-volatile, flash memory offers fast read access times, although not as fast as static RAM or ROM.[2] Its mechanical shock resistance helps explain its popularity over hard disks in portable devices, as does its high durability, ability to withstand high pressure, temperature and immersion in water, etc.[3]
Although flash memory is technically a type of EEPROM, the term "EEPROM" is generally used to refer specifically to non-flash EEPROM which is erasable in small blocks, typically bytes.[citation needed] Because erase cycles are slow, the large block sizes used in flash memory erasing give it a significant speed advantage over non-flash EEPROM when writing large amounts of data. As of 2013, flash memory costs much less than byte-programmable EEPROM and had become the dominant memory type wherever a system required a significant amount of non-volatile solid-state storage.
La mémoire flash est une mémoire de masse à semi-conducteurs ré-inscriptible, c'est-à-dire une mémoire possédant les caractéristiques d'une mémoire vive mais dont les données ne disparaissent pas lors d'une mise hors tension. Ainsi, la mémoire flash stocke les bits de données dans des cellules de mémoire, mais les données sont conservées en mémoire lorsque l'alimentation électrique est coupée.
Sa vitesse élevée, sa durée de vie et sa faible consommation (qui est même nulle au repos) la rendent très utile pour de nombreuses applications : appareils photo numériques, téléphones cellulaires, imprimantes, assistants personnels (PDA), ordinateurs portables ou dispositifs de lecture et d'enregistrement sonore comme les baladeurs numériques, clés USB. De plus, ce type de mémoire ne possède pas d'éléments mécaniques, ce qui lui confère une grande résistance aux chocs.
La memoria flash, anche chiamata flash memory, è una tipologia di memoria a stato solido, di tipo non volatile, che per le sue prestazioni può anche essere usata come memoria a lettura-scrittura. Quando viene utilizzata come ROM viene anche chiamata flash ROM.
In una memoria flash le informazioni vengono registrate in un vettore di floating gate MOSFET, una tipologia di transistor ad effetto di campo in grado di mantenere carica elettrica per un tempo lungo. Ogni transistor costituisce una "cella di memoria" che conserva il valore di un bit. Le nuove flash utilizzano delle celle multilivello che permettono di registrare il valore di più bit attraverso un solo transistor.
Diversamente dalle tecnologie precedenti, la tecnologia Flash ha reso possibile il salvataggio o la cancellazione di dati in un unico passo, introducendo quindi un incredibile guadagno in velocità, e grazie alla non-volatilità è usata frequentemente nelle fotocamere digitali, nei lettori di musica portatili, nei cellulari, nelle pendrive (chiavette), nei palmari, nei moderni computer portatili e in molti altri dispositivi che richiedono un'elevata portabilità e una buona capacità di memoria per il salvataggio dei dati.
Esistono principalmente due tipologie di memorie flash, dette NOR flash e NAND flash, che differiscono per l'architettura ed il procedimento di programmazione. Vi è anche una tipologia ibrida, la AND flash, che sfrutta le caratteristiche di entrambe, NOR e NAND.
La memoria flash derivada de las siglas EEPROM permite la lectura y escritura de múltiples posiciones de memoria en la misma operación. Gracias a ello, la tecnología flash, mediante impulsos eléctricos, permite velocidades de funcionamiento muy superiores frente a la tecnología EEPROM primigenia, que sólo permitía actuar sobre una única celda de memoria en cada operación de programación. Se trata de la tecnología empleada en los dispositivos denominados memoria USB.
Extended Remote Copy or XRC is an IBM zSeries and System z9 mainframe computer technology for data replication. It combines supported hardware and z/OS software to provide asynchronous replication over long distances. It is complementary to IBM's Peer to Peer Remote Copy (PPRC) service, which is designed to operate either synchronously or asynchronously over shorter distances.
XRC as a z/OS copy services solution can be compared to Global Mirror for ESS, which is a controller-based solution for either the open systems or z/Series environments. Both Global Mirror for ESS (Asynchronous PPRC) and XRC (Global Mirror for z/Series) are asynchronous replication technologies, although their implementations are somewhat different.
Extended Remote Copy or XRC is now known as Global Mirror for z/Series (XRC).
XRC is a z/Series asynchronous disk mirroring technique which is effective over any distance. It keeps the data time consistent across multiple ESS (Enterprise Storage Server) or HDS (Hitachi Data Systems) disk subsystems at the recovery site.
XRC functions as a combination of disk (IBM ESS or HDS licensed) Microcode and application code running on a z/Series host and provides a recovery point that is time consistent across multiple disk subsystems.
The host component of the software is called the System Data Mover or SDM. The SDM ensures that no dependent writes are made out of sequence and data residing on the secondary volumes will always provide a time consistent copy of the primary volumes being mirrored.
Dabbala Rajagopal „Raj“ Reddy (* 13. Juni 1937 in Katur, Andhra Pradesh, Indien) ist ein indisch-amerikanischer Informatiker, der bedeutende Leistungen auf dem Gebiet der Robotik erbracht hat und 1994 zusammen mit Edward Feigenbaum den Turing Award für deren Arbeit im Bereich der künstlichen Intelligenz verliehen bekommen hat.

Lawrence „Larry“ Edward Page (* 26. März 1973 in East Lansing, Michigan)[1] ist ein US-amerikanischer Informatiker und Unternehmer.
Er entwickelte zusammen mit Sergey Brin die Suchmaschine Google. Der Prototyp wurde am 7. September 1998 gestartet. Zudem ist er CMO und CEO des kalifornischen Unternehmens Google Inc. Laut Forbes-Liste 2013 beträgt das Vermögen von Larry Page 23 Milliarden US-Dollar. Damit belegt er Platz 20 der reichsten Menschen der Welt.
An der University of Michigan erwarb er den Bachelor in Ingenieurwissenschaften, dem an der Stanford University der Master-Abschluss in Informatik folgte.[2]

 Unternehmen
Unternehmen

 Bayern
Bayern
 Wissenschaft und Technik
Wissenschaft und Technik
 California-CA
California-CA