
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Mexiko
Mexiko
 Antigua und Barbuda
Antigua und Barbuda
 Bahamas
Bahamas
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belize
Belize
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Cuba
Cuba
 Dominica
Dominica
 Dominikanische Republik
Dominikanische Republik
 Grenada
Grenada
 Guatemala
Guatemala
 Guyana
Guyana
 Honduras
Honduras
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Mexiko
Mexiko
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua
 Panama
Panama
 Republik El Salvador
Republik El Salvador
 Republik Haiti
Republik Haiti
 St. Kitts und Nevis
St. Kitts und Nevis
 St. Lucia
St. Lucia
 St. Vincent und die Grenadinen
St. Vincent und die Grenadinen
 Suriname
Suriname
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Venezuela
Venezuela




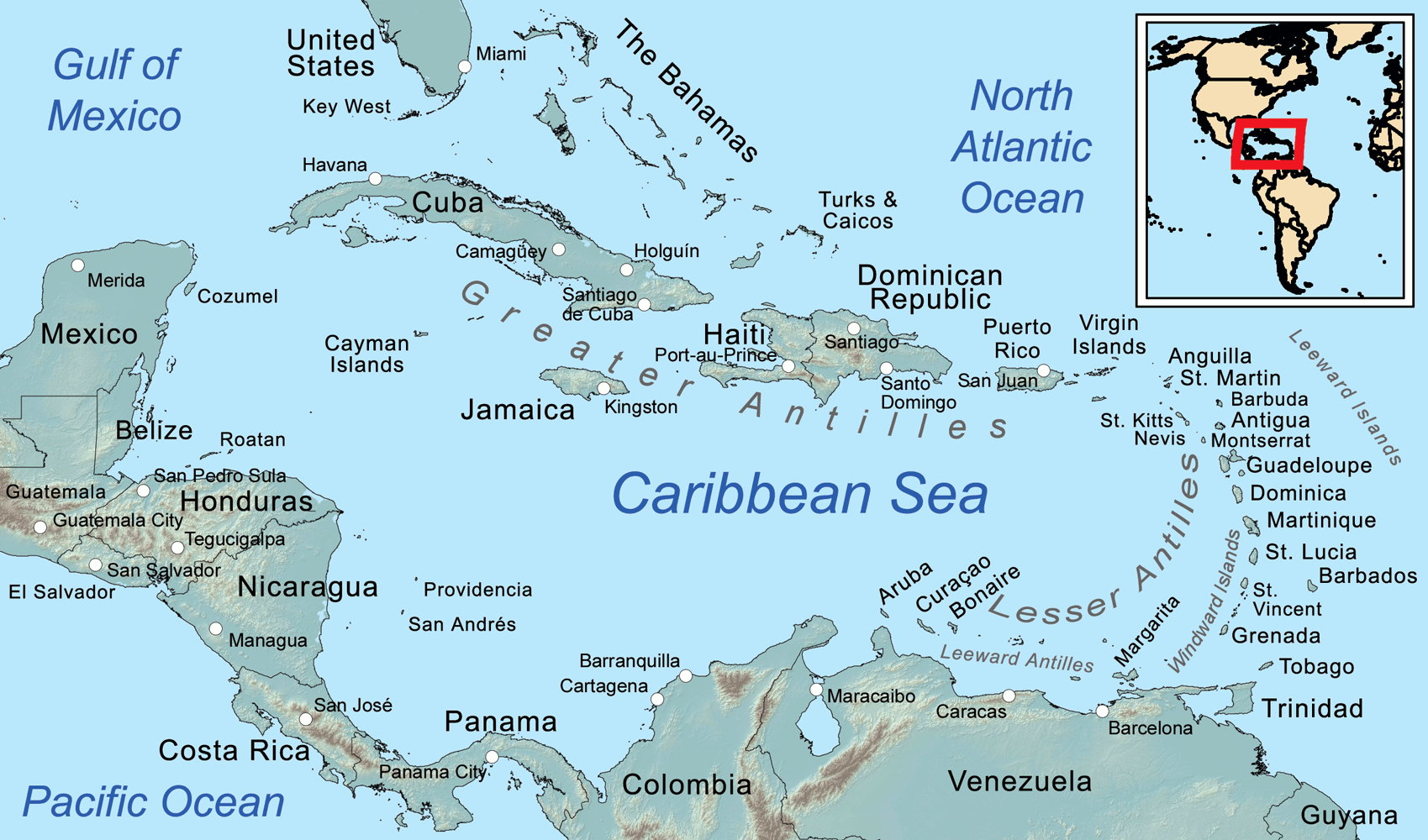
Die Karibik ist eine Region im westlichen, tropischen Teil des Atlantischen Ozeans nördlich des Äquators. Als Teil des mittelamerikanischen Subkontinents besteht sie aus den am und im Karibischen Meer gelegenen Inseln und Inselgruppen und dem Meeresgebiet zwischen ihnen. Am Westende reicht die Karibik in den Golf von Mexiko.
Die Karibik ist nach dem Volk der Kariben benannt, das die spanischen Eroberer auf den Kleinen Antillen (lat. ante ilium, „vorgelagerte Inseln“) vorgefunden haben. Sie wurde bzw. wird auch Westindien genannt, da man sich bei ihrer Entdeckung auf direktem Seeweg nach Indien glaubte.
若依照联合国地理分区里的地理亚区来判定,加勒比地区的范围为加勒比海上的诸岛—西印度群岛,国家与地区包含安圭拉、安提瓜和巴布达、阿鲁巴、巴哈马、巴巴多斯、博奈尔、圣尤斯特歇斯和萨巴、英属维尔京群岛、开曼群岛、古巴、库拉索、多米尼克、多米尼加、格林纳达、瓜德罗普、海地、牙买加、马提尼克、蒙特塞拉特、波多黎各、圣巴泰勒米、圣基茨和尼维斯、圣卢西亚、法属圣马丁、圣文森特和格林纳丁斯、荷属圣马丁、特立尼达和多巴哥、特克斯和凯科斯群岛、美属维尔京群岛。
カリブ海地域(カリブかいちいき、英語: The Caribbean、スペイン語: Caribe、オランダ語: ![]() Caraïben、カリブ・ヒンドゥスターニー語: कैरिबियन (Kairibiyana); フランス語: Caraïbe ないし Antilles)は、カリブ海と、その海域の島々(カリブ海域内の島々や、カリブ海と北大西洋の境界を成す島々)、周辺海域から構成されている。カリブ海地域はメキシコ湾と北アメリカ大陸の南東、中央アメリカの東、南アメリカ大陸の北に位置している。日本語ではカリブ地域、あるいはこの地域にある国を総称してカリブ諸国とも呼ばれる。
Caraïben、カリブ・ヒンドゥスターニー語: कैरिबियन (Kairibiyana); フランス語: Caraïbe ないし Antilles)は、カリブ海と、その海域の島々(カリブ海域内の島々や、カリブ海と北大西洋の境界を成す島々)、周辺海域から構成されている。カリブ海地域はメキシコ湾と北アメリカ大陸の南東、中央アメリカの東、南アメリカ大陸の北に位置している。日本語ではカリブ地域、あるいはこの地域にある国を総称してカリブ諸国とも呼ばれる。
この地方の大部分はカリブプレート上にあり、域内には700以上の島嶼、岩礁、キー(サンゴ礁上の低い島)などがある(カリブ海地域の島の一覧)。島々の多くは島弧を形成して、カリブ海のと東渕と北縁となっている[3]。カリブ海地域の島々は、北側の大アンティル諸島と、南および東側の小アンティル諸島(リーワード・アンティル諸島を含む) から成り、大アンティル諸島やカリブ海より北に位置するバハマ諸島(バハマからタークス・カイコス諸島に至る範囲)をも含んだ、より広い範囲を指す表現としての西インド諸島の一部となっている。広い意味では、大陸の一部であるベリーズ、ベネズエラ、ガイアナ、スリナム、フランス領ギアナもカリブ海地域に含める場合がある。
地政学的には、カリブ海地域の島々は北アメリカの下位区分 (subregion) と見なされることが多く[4][5][6][7][8]、合わせて30の主権国家、海外県、属領から成っている。1954年12月15日から2010年10月10日まで、5つの統治体から成るオランダ領アンティルと称されたオランダ属領があった[9]。また、1958年1月3日から1962年5月31日まで、イギリス属領であった英語圏の領域が構成した、西インド連邦と称された短命な自治国が存在していた。クリケット西インド諸島代表は、その後も、これら諸国の多くを代表して編成され続けている。
The Caribbean (/ˌkærɪˈbiːən, kəˈrɪbiən/, locally /ˈkærɪbiæn/;[4] Spanish: El Caribe; French: les Caraïbes; Haitian Creole: Karayib; Dutch: De Caraïben; Papiamento: Karibe) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea[5] and some bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean)[6] and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America.
Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has more than 700 islands, islets, reefs and cays (see the list of Caribbean islands). Island arcs delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea:[7] the Greater Antilles on the north and the Lesser Antilles on the south and east (which includes the Leeward Antilles). They form the West Indies with the nearby Lucayan Archipelago (The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands), which are sometimes considered to be a part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea. On the mainland, Belize, Nicaragua, the Caribbean region of Colombia, Cozumel, the Yucatán Peninsula, Margarita Island, and The Guianas (Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, Guayana Region in Venezuela, and Amapá in Brazil) are often included due to their political and cultural ties with the region.[8]
A mostly tropical geography, the climates are greatly shaped by sea temperatures and precipitation, with the hurricane season regularly leading to natural disasters. Because of its tropical climate and low-lying island geography, the Caribbean is vulnerable to a number of climate change effects, including increased storm intensity, saltwater intrusion, sea-level rise and coastal erosion, and precipitation variability.[9] These weather changes will greatly change the economies of the islands, and especially the major industries of agricultural and tourism.[9]
The Caribbean was occupied by indigenous people since at least 3600 BC. When European colonization followed the arrival of Columbus, the population was quickly decimated by brutal labor practices, enslavement and disease and on many islands, Europeans supplanted the native populations with enslaved Africans. Following the independence of Haiti from France in the early 19th century and the decline of slavery in the 19th century, island nations in the Caribbean gradually gained independence, with a wave of new states during the 1950s and 60s. Because of the proximity to the United States, there is also a long history of United States intervention in the region.
The islands of the Caribbean (the West Indies) are often regarded as a subregion of North America, though sometimes they are included in Middle America or then left as a subregion of their own[10][11] and are organized into 30 territories including sovereign states, overseas departments, and dependencies. From December 15, 1954, to October 10, 2010, there was a country known as the Netherlands Antilles composed of five states, all of which were Dutch dependencies.[12] From January 3, 1958, to May 31, 1962, there was also a short-lived political union called the West Indies Federation composed of ten English-speaking Caribbean territories, all of which were then British dependencies.
Les Caraïbes, (également nommées la Caraïbe, l'espace caraïbe, ou encore l'espace des Caraïbes) sont une région des Amériques qui comprend la mer des Caraïbes, ses îles (certaines entourées par la mer des Caraïbes et d'autres bordant à la fois la mer des Caraïbes et l'océan Atlantique Nord) et les côtes environnantes. La région est située au sud-est du golfe du Mexique et du continent nord-américain, à l'est de l'Amérique centrale et au nord de l'Amérique du Sud.
Située en grande partie sur la plaque des Caraïbes, la région compte plus de 700 îles, îlots, récifs et cayes. Les arcs insulaires délimitent les bords est et nord de la mer des Caraïbes : les Grandes Antilles au nord et les Petites Antilles au sud et à l'est (qui comprennent les îles sous le vent). Elles forment les Antilles avec l'archipel voisin de Lucayan (les Bahamas et les Îles Turques-et-Caïques), qui sont parfois considérées comme faisant partie des Caraïbes bien qu'elles ne bordent pas la mer des Caraïbes. Sur le continent, le Belize, le Nicaragua, la région caribéenne de Colombie, Cozumel, la péninsule du Yucatán, l'île de Margarita et les Guyanes (Guyane, Suriname, Guyane française, région de Guayana au Venezuela et Amapá au Brésil) sont souvent inclus en raison de leurs liens politiques et culturels avec la région.
La géographie est essentiellement tropicale et le climat est fortement influencé par la température de la mer et les précipitations, la saison des ouragans entraînant régulièrement des catastrophes naturelles. En raison de leur climat tropical et de leur géographie insulaire de basse altitude, les Caraïbes sont vulnérables à un certain nombre d'effets du changement climatique, notamment l'augmentation de l'intensité des tempêtes, l'intrusion d'eau salée, l'élévation du niveau de la mer et l'érosion côtière, ainsi que la variabilité des précipitations.
Les Caraïbes ont été occupées par des peuples indigènes depuis au moins 3600 avant J.-C. Lorsque la colonisation européenne a suivi l'arrivée de Christophe Colomb, la population a été rapidement décimée par des pratiques de travail brutales, l'esclavage et la maladie et sur de nombreuses îles, les Européens ont supplanté les populations indigènes par des Africains réduits en esclavage. Après l'indépendance d'Haïti par rapport à la France au début du XIXe siècle et le déclin de l'esclavage, les nations insulaires ont progressivement acquis leur indépendance, avec une vague de nouveaux États au cours des années 1950 et 1960. En raison de la proximité des États-Unis, il existe également une longue histoire d'intervention américaine dans la région.
Les Antilles sont souvent considérées comme une sous-région de l'Amérique du Nord, bien qu'elles soient parfois incluses dans l'Amérique centrale ou alors laissées comme une sous-région à part entière et sont organisées en 30 territoires comprenant des États souverains, des Département et région d'outre-mer et des dépendances. Du 15 décembre 1954 au 10 octobre 2010, il y avait un pays appelé Antilles néerlandaises composé de cinq États, tous dépendants des Pays-Bas. Du 3 janvier 1958 au 31 mai 1962, il y a également eu une union politique de courte durée, la Fédération des Indes occidentales, composée de dix territoires caribéens anglophones, tous dépendants des Britanniques à l'époque.
I Caraibi sono una vasta regione geografica delle Americhe che comprende tutti i paesi bagnati dal Mare Caraibico, cioè tutte le isole delle Antille e i litorali di alcuni paesi continentali del centro e sud America che si affacciano su di questo mare. L'area caraibica è costituita dalle numerose isole che separano il Golfo del Messico dal mar dei Caraibi e quest'ultimo dall'Oceano Atlantico.
El Caribe es una región conformada por el mar Caribe, sus islas y las costas que rodean a este mar. La región se localiza al sureste de América del Norte, al este de América Central, al oeste de América Insular y al norte de América del Sur.
Анти́льские острова́ (также Карибы или Карибские острова) — острова в Карибском море и Мексиканском заливе, расположенные между Северной Америкой и Южной Америкой. Вместе взятые, образуют площадь в 228 662 км² с населением примерно 42 млн чел. (на начало XXI века).
Впервые название «Антильские» встречается в 1493 году у Петра Мартира д’Ангиера, современника Христофора Колумба, придворного Фердинанда Арагонского и Изабеллы Кастильской. Предположительно, были названы по полумифическому острову или архипелагу Антилия, изображавшемуся на средневековых картах.
Подразделяются на две главные группы: Большие Антильские и Малые Антильские острова:
К первым относятся 4 острова: Куба, Гаити, Ямайка и Пуэрто-Рико; из них первые два и последний (самый малый) образуют почти прямую линию, направленную западным углом Кубы к полуострову Юкатан.[1]
Острова материкового и вулканического происхождения. Большая часть их поверхности гориста; равнинные участки главным образом на Кубе и на Юго-Восточном Гаити, а также на Виргинских и Подветренных островах. Горные сооружения Больших Антильских островов высотой до 3098 м (на острове Гаити) являются продолжением структур Центральной Америки. Климат тропический, пассатный, жаркий, преимущественно летне-влажный. Осадков 1200—2000 мм в год. Характерны сильные ураганы в конце лета. Естественная растительность — саванны, летне-зеленые и листопадно-вечнозелёные тропические леса и кустарники — сохранилась мало. На наветренных склонах гор уцелели вечнозелёные леса.[2]
 Mexiko
Mexiko

 Musik
Musik

 Musik
Musik
 *Wertschätzung berühmter Musik
*Wertschätzung berühmter Musik

 Tänze
Tänze

 Tänze
Tänze
 Amerikanische Tänze
Amerikanische Tänze

 Tänze
Tänze
 Volkstänze
Volkstänze

 Tänze
Tänze
 *Tanzmusik/Dance music
*Tanzmusik/Dance music

 Australien
Australien
 Belgien
Belgien
 Chile
Chile
 Dänemark
Dänemark
 Deutschland
Deutschland
 Estland
Estland
 Finnland
Finnland
 Frankreich
Frankreich
 Griechenland
Griechenland
 Irland
Irland
 Island
Island
 Israel
Israel
 Italien
Italien
 Japan
Japan
 Kanada
Kanada
 Luxemburg
Luxemburg
 Mexiko
Mexiko
 Neuseeland
Neuseeland
 Niederlande
Niederlande
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 OECD
OECD
 Emiel van Lennep
Emiel van Lennep
 OECD
OECD
 Don Johnston
Don Johnston
 OECD
OECD
 Jean-Claude Paye
Jean-Claude Paye
 OECD
OECD
 José Ángel Gurría
José Ángel Gurría
 OECD
OECD
 Staffan Sohlman
Staffan Sohlman
 OECD
OECD
 Thorkil Kristensen
Thorkil Kristensen
 Österreich
Österreich
 Polen
Polen
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republik Korea
Republik Korea
 Schweden
Schweden
 Schweiz
Schweiz
 Slowakei
Slowakei
 Slowenien
Slowenien
 Spanien
Spanien
 Tschechien
Tschechien
 Türkei
Türkei
 Ungarn
Ungarn
 Vereinigte Staaten
Vereinigte Staaten
 Vereinigtes Königreich
Vereinigtes Königreich

 Wichtige internationale Organisationen
Wichtige internationale Organisationen

経済協力開発機構(けいざいきょうりょくかいはつきこう)は、国際経済全般について協議することを目的とした国際機関。公用語の正式名称は、英語では"Organisation[1] for Economic Co-operation and Development"(イギリス英語表記)、フランス語では"Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Economiques"。略称は英語ではOECD、フランス語ではOCDE。
本部事務局はパリ16区の旧ラ・ミュエット宮殿に置かれている。事務総長はアンヘル・グリア。
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; French: Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques, OCDE) is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 37 member countries,[1] founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum of countries describing themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. Generally, OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries. As of 2017, the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trillion)[3] and 42.8% of global GDP (Int$54.2 trillion) at purchasing power parity.[4] The OECD is an official United Nations observer.[5]
In 1948, the OECD originated as the Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC),[6] led by Robert Marjolin of France, to help administer the Marshall Plan (which was rejected by the Soviet Union and its satellite states).[7] This would be achieved by allocating United States financial aid and implementing economic programs for the reconstruction of Europe after World War II. (Similar reconstruction aid was sent to the war-torn Republic of China and post-war Korea, but not under the name "Marshall Plan".)[8]
In 1961, the OEEC was reformed into the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development by the Convention on the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and membership was extended to non-European states.[9][10] The OECD's headquarters are at the Château de la Muette in Paris, France.[11] The OECD is funded by contributions from member countries at varying rates and had a total budget of €386 million in 2019.[2]
Although OECD does not have a power to enforce its decisions, which further require unanimous vote from its members, it is recognized as highly influential publisher of mostly economic data through publications as well as annual evaluations and rankings of members countries.[12]
L'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) est une organisation internationale d'études économiques, dont les pays membres — des pays développés pour la plupart — ont en commun un système de gouvernement démocratique et une économie de marché. Elle joue essentiellement un rôle d'assemblée consultative1.
L'OCDE a succédé à l'Organisation européenne de coopération économique (OECE) issue du plan Marshall et de la Conférence des Seize (Conférence de coopération économique européenne) qui a existé de 1948 à 1960. Son but était l'établissement d'une organisation permanente chargée en premier lieu d'assurer la mise en œuvre du programme de relèvement commun (le plan Marshall), et, en particulier, d'en superviser la répartition2.
En 2020, l'OCDE compte 37 pays membres et regroupe plusieurs centaines d'experts. Elle publie fréquemment des études économiques et sociales — analyses, prévisions et recommandations de politique économique — et des statistiques, principalement concernant ses pays membres.
Le siège de l'OCDE se situe à Paris (16e), au château de la Muette. L'organisation possède également des bureaux dans plusieurs autres métropoles, notamment à Berlin, Mexico, Tokyo et Washington.
L'Organizzazione per la cooperazione e lo sviluppo economico (OCSE) – in inglese Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), e in francese Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) – è un'organizzazione internazionale di studi economici per i paesi membri, paesi sviluppati aventi in comune un'economia di mercato.
L'organizzazione svolge prevalentemente un ruolo di assemblea consultiva che consente un'occasione di confronto delle esperienze politiche, per la risoluzione dei problemi comuni, l'identificazione di pratiche commerciali e il coordinamento delle politiche locali e internazionali dei paesi membri[1]. Ha sede a Parigi nello Château de la Muette[2].
Gli ultimi paesi ad aver aderito all'OCSE sono la Colombia (28 aprile 2020),la Lettonia (1º luglio 2016) e la Lituania (5 luglio 2018), per un totale di 36 paesi membri.
La Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico1 (OCDE) es un organismo de cooperación internacional, compuesto por 37 estados,34 cuyo objetivo es coordinar sus políticas económicas y sociales. La OCDE fue fundada en 1961 y su sede central se encuentra en el Château de la Muette en París (Francia). Los idiomas oficiales de la entidad son el francés y el inglés.2
En la OCDE, los representantes de los países miembros se reúnen para intercambiar información y armonizar políticas con el objetivo de maximizar su crecimiento económico y colaborar a su desarrollo y al de los países no miembros.
Conocida como «club de los países ricos»,56 a partir de 2017, sus países miembros comprendieron colectivamente el 62,2 % del PIB nominal global (US$49,6 billones) y el 42,8 % del PIB global (Int US$54,2 billones).7
Организа́ция экономи́ческого сотру́дничества и разви́тия (сокр. ОЭСР, англ. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD) — международная экономическая организация развитых стран, признающих принципы представительной демократии и свободной рыночной экономики.
Создана в 1948 году под названием Организа́ция европе́йского экономи́ческого сотру́дничества (англ. Organisation for European Economic Co-operation, OEEC) для координации проектов экономической реконструкции Европы в рамках плана Маршалла.
Штаб-квартира организации располагается в Шато де ла Мюетт, в Париже. Генеральный секретарь (с 2006 года) — Хосе Анхель Гурриа Тревиньо (Мексика). Руководящим органом ОЭСР является совет представителей стран — членов организации. Все решения в нём принимаются на основе консенсуса.
По данным на 2011 год, в странах ОЭСР проживало 18 % населения мира[2].
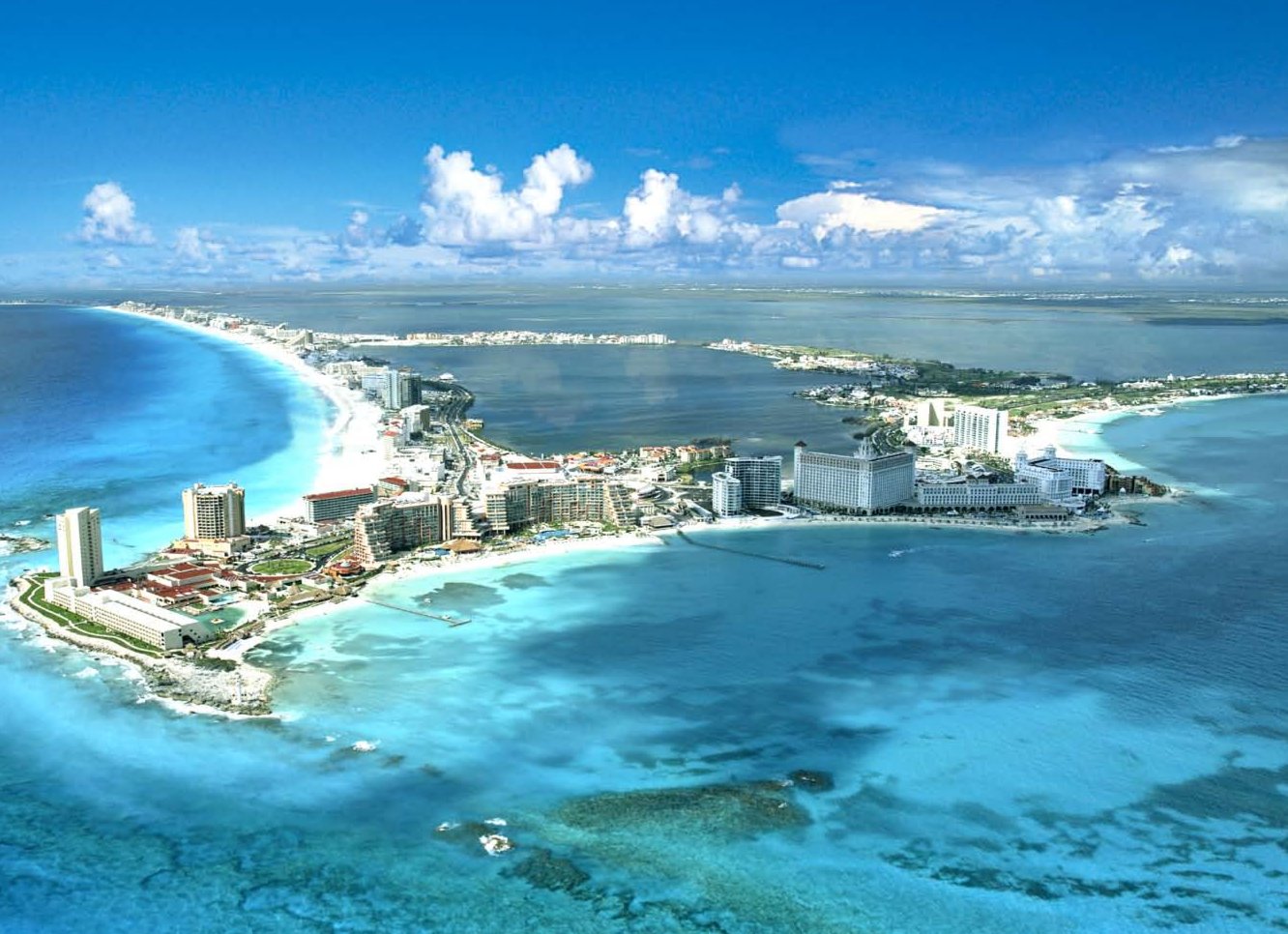



Cancún (spanisch [kaŋˈkun], englisch [kænˈkuːn/kaːn-], oft auch nur Cancun) ist eine Stadt an der Nordostküste der Halbinsel Yucatán und liegt im Municipio Benito Juárez im Nordosten des Bundesstaats Quintana Roo im südöstlichsten Teil Mexikos.
Cancún ist das Zentrum des Urlaubsgebiets Riviera Maya und hat etwa 745.000 Einwohner (Stand: Zensus 2015). Die Stadt ist besonders als Touristenziel wegen seines 23 Kilometer langen Strandes weltbekannt und empfing 2016 über 6 Millionen Besucher.[1] Der Name can cún bedeutet in der Sprache der Maya „Schlangennest“ oder „Schlangentopf“ (der Name wird aber auch oft von „Ort der goldenen Schlange“ hergeleitet).
坎昆(西班牙语:Cancún,西班牙语发音:[kaŋˈkũn] 发音ⓘ[1]),又名康昆,是墨西哥东南部城市,位于加勒比海沿岸,是世界著名度假胜地[2]。坎昆的气候宜人,平均气温介乎26-36°C之间。1970年代,墨西哥政府主力把坎昆发展成度假胜地,现在每年有超过300万人到坎昆旅游,更包括一些名人明星等。坎昆有超过140家酒店,提供24000房间。23公里长的坎昆岛是度假区的中心,部分度假酒店十分豪华,临近加勒比海,海水清澈,在海里游泳的鱼亦清晰可见,不少旅客在这里潜水或乘游艇出海。坎昆附近有一些历史遗迹。
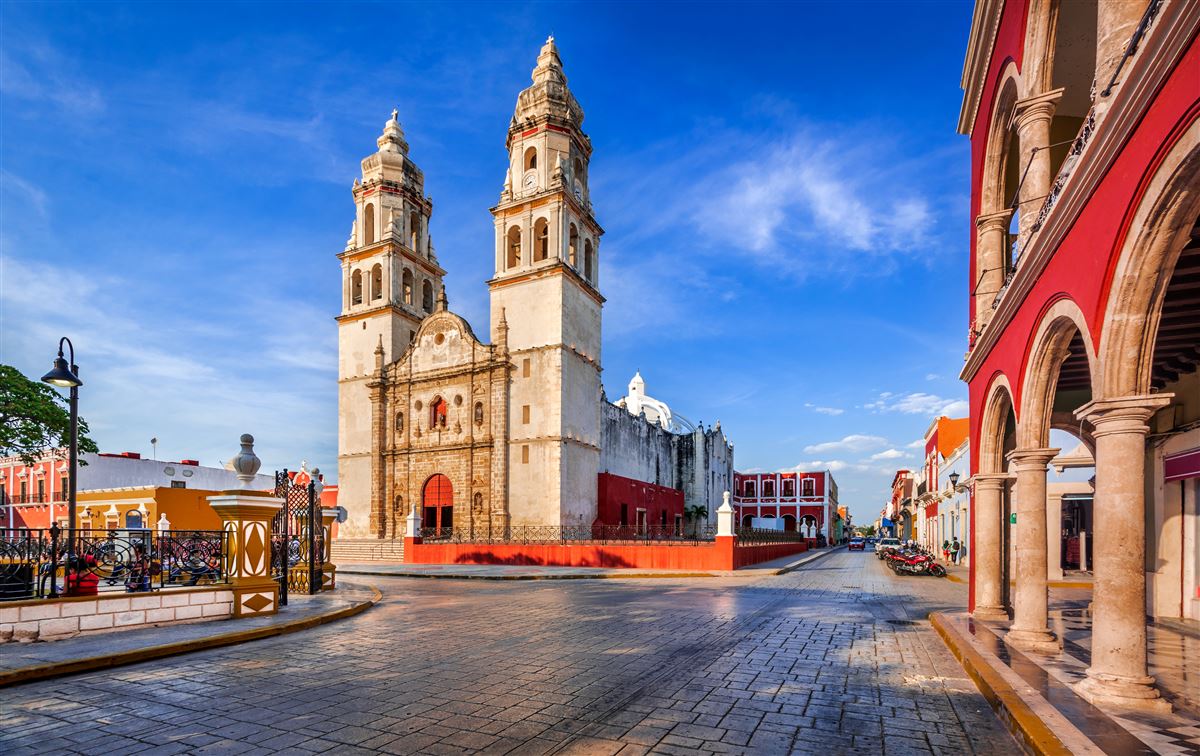

Die Großstadt Campeche, offiziell San Francisco de Campeche, ist die Hauptstadt des gleichnamigen Bundesstaates im Südosten Mexikos. Seit dem Jahr 1999 gehört die Stadt zum Weltkulturerbe der UNESCO.[1] Das im Jahr 1895 von Papst Leo XIII. eingerichtete Bistum Campeche (lat.: Dioecesis Campecorensis, span.: Diócesis de Campeche) ist eine römisch-katholische Diözese mit Sitz in Campeche.
坎佩切 (西班牙语:San Francisco de Campeche)是墨西哥坎佩切州的州府,位于墨西哥湾南部的坎佩切湾。坎佩切是一座海滨城市,截止2005年全市总人口211671人。
坎佩切由西班牙征服者在1540年建立。不过,这里早在玛雅文明时期就是一个名为阿·金·佩奇的部落,当时有3000多个建筑物和一些纪念碑,其中的一部分遗址至今依然可见。此外,这个城市还保留了许多西班牙殖民时期修建的城墙,这些保存较为完好、质量较高的建筑使得坎佩切在1999年时被联合国教科文组织列入世界遗产,登录名称为坎佩切历史要塞城。
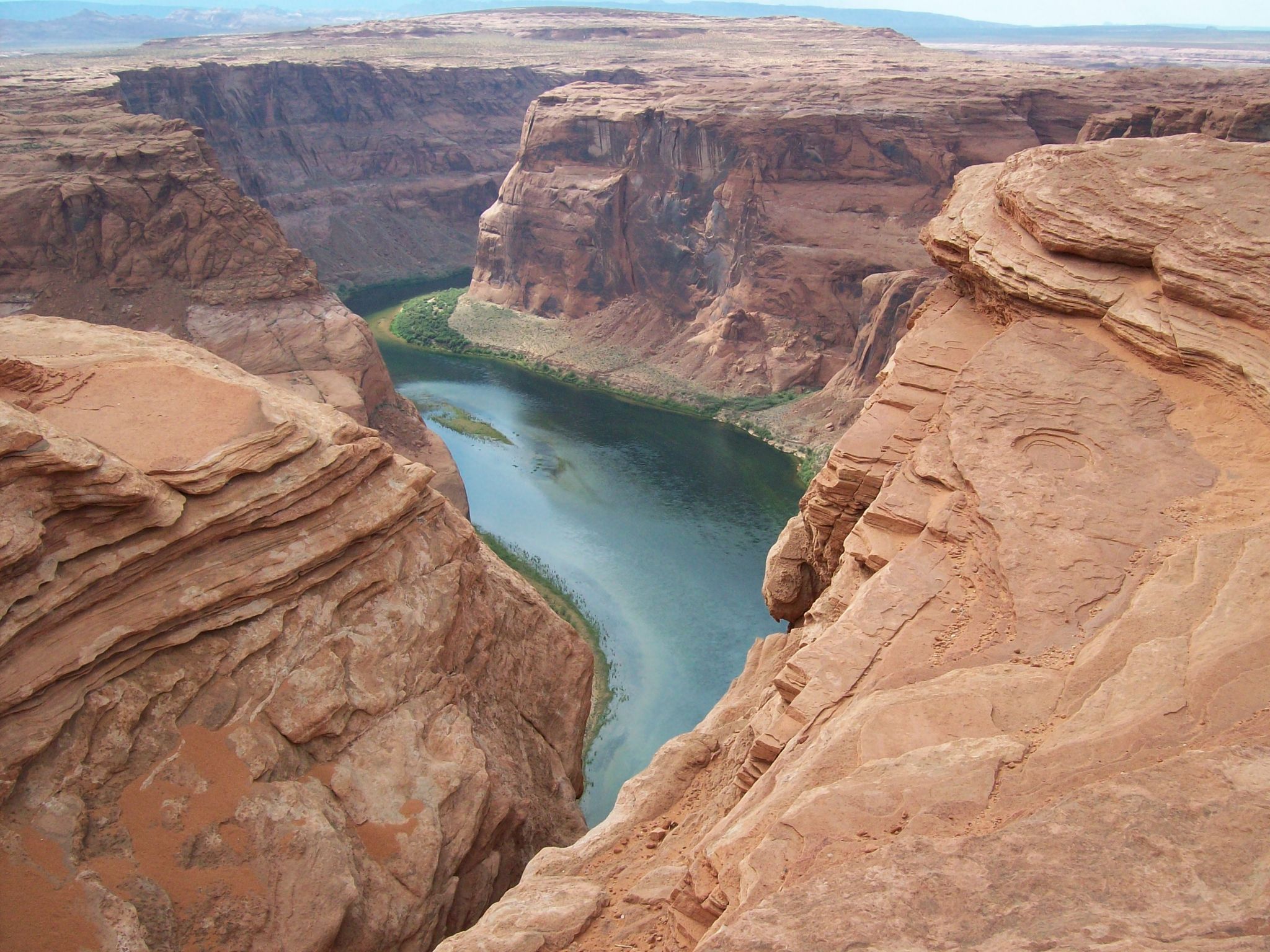



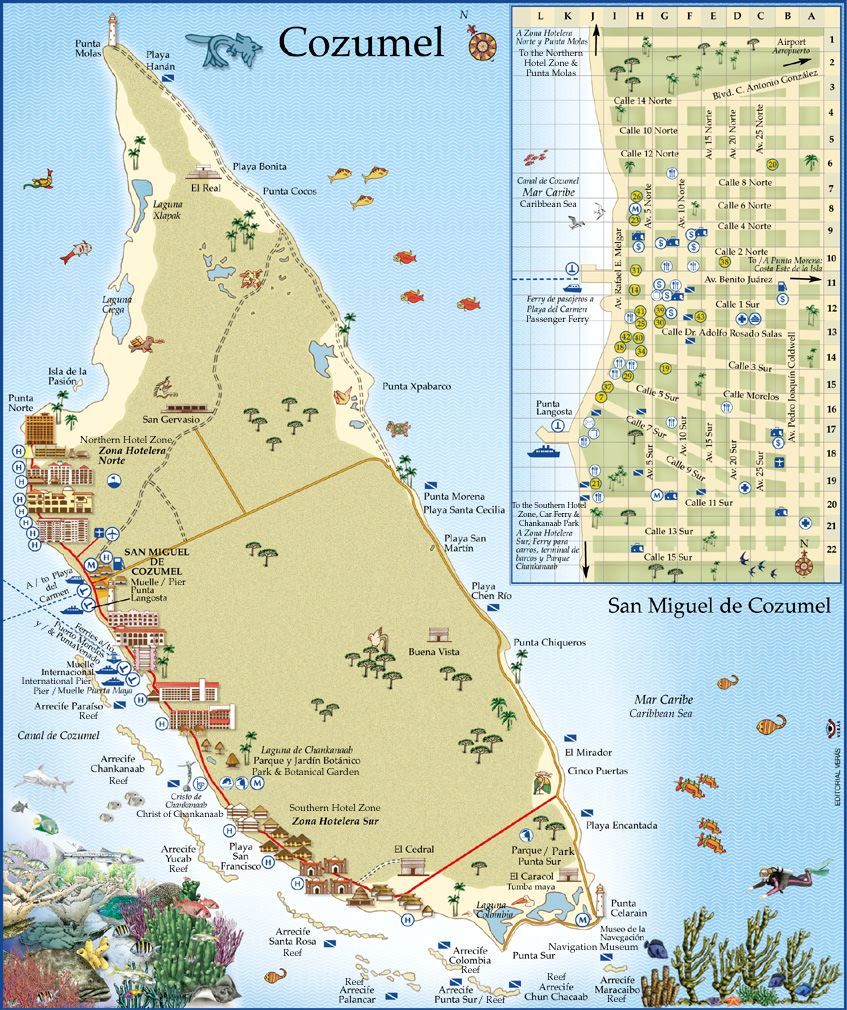
Cozumel (Mayathan: Kusamil „Schwalbenort“[1], von kusam „Schwalbe“ und il „Ort“)[2] ist eine der östlichen Küste der mexikanischen Halbinsel Yucatán vorgelagerte Insel. Sie gehört zum mexikanischen Bundesstaat Quintana Roo und bildet den Hauptteil des Municipio Cozumel.
Die flache und eine dichte Vegetation aufweisende Insel hat eine maximale Nord-Süd-Ausdehnung von 45,3 km und eine maximale Ost-West-Ausdehnung von 16,6 km. Mit einer Fläche von 477,85 km² ist Cozumel die drittgrößte Insel Mexikos nach Isla Tiburón und Isla Ángel de la Guarda. Bevölkerungsmäßig wird sie nur von der Isla del Carmen übertroffen (siehe die Liste mexikanischer Inseln). Sie liegt 15,8 km vom Festland entfernt und befindet sich etwa 60 km südlich von Cancún. Inselhauptstadt ist San Miguel de Cozumel (amtlich Cozumel, 77.236 Einwohner im Jahr 2010[3]), wo nahezu die ganze Bevölkerung von Cozumel lebt.
科苏梅尔岛(尤卡坦玛雅语: Kùutsmil,意为“燕子岛”),墨西哥尤卡坦半岛附近加勒比海中的一个岛屿。科苏梅尔岛隶属金塔纳罗奥州,为该州的一个市镇。行政中心位于圣米格尔德科苏梅尔(San Miguel de Cozumel),该地也是岛上的主要城镇。


 Australien
Australien
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Chile
Chile
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Japan
Japan
 Kanada
Kanada
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexiko
Mexiko
 Neuseeland
Neuseeland
 Peru
Peru
 Singapur
Singapur


 Geographie
Geographie
 Wirtschaft und Handel
Wirtschaft und Handel
 Internationale Städte
Internationale Städte
 Sport
Sport
 Weltkulturerbe
Weltkulturerbe
 Essen und Trinken
Essen und Trinken
 Unternehmen
Unternehmen
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ
 California-CA
California-CA
 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO
 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV
 Tierwelt
Tierwelt
 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 Schiffe und Nautik
Schiffe und Nautik
 Energieressource
Energieressource