漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 2026年世界杯足球赛
2026年世界杯足球赛
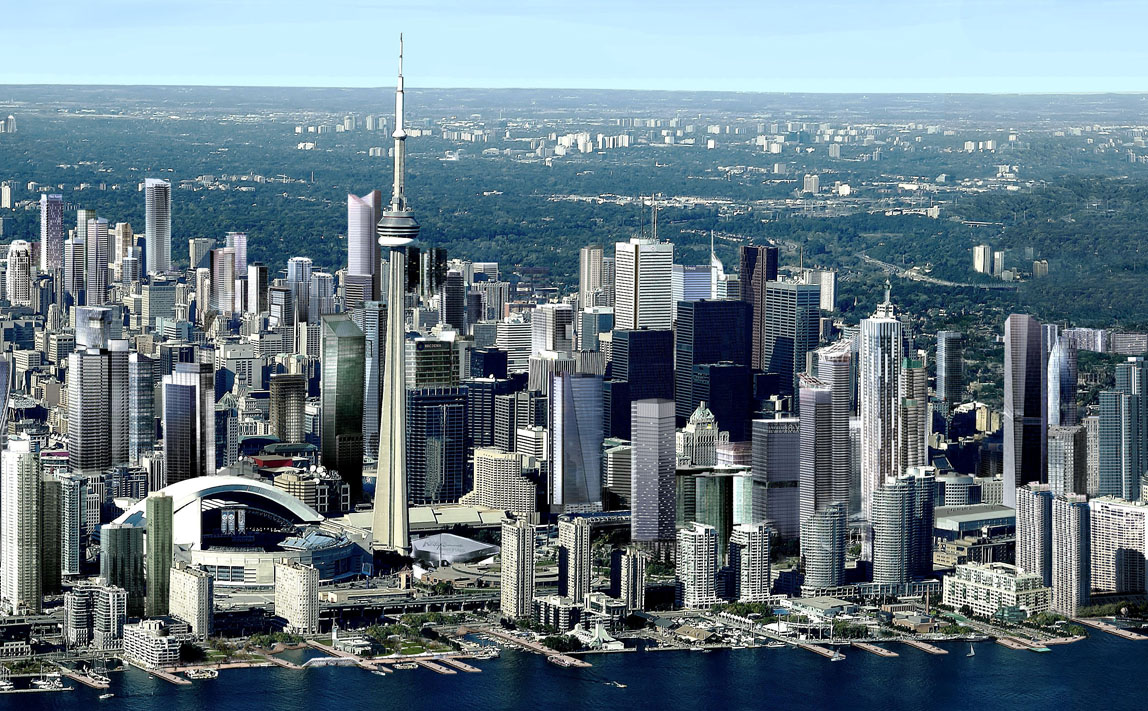




Toronto (englische Aussprache [təˈɹɒn(t)oʊ̯]; regional auch  [təˈɹɒnə] oder [ˈtɹɒnoʊ̯]) ist mit 2,6 Millionen Einwohnern[2] die größte Stadt Kanadas und die Hauptstadt der Provinz Ontario. Sie liegt im Golden Horseshoe (Goldenes Hufeisen), einer Region mit über 8,1 Millionen Einwohnern, die sich halbkreisförmig um das westliche Ende des Ontariosees bis zu den Niagarafällen erstreckt. Rund ein Drittel der Bevölkerungszunahme des ganzen Landes lebte in den letzten Jahren in diesem Großraum. Die Einwohnerzahl der Metropolregion (Census Metropolitan Area) stieg von 4,1 Millionen im Jahr 1992 auf 5,6 Millionen im Jahr 2011.[3] Die Greater Toronto Area hatte 2010 über 6,2 Millionen Einwohner.[4]
[təˈɹɒnə] oder [ˈtɹɒnoʊ̯]) ist mit 2,6 Millionen Einwohnern[2] die größte Stadt Kanadas und die Hauptstadt der Provinz Ontario. Sie liegt im Golden Horseshoe (Goldenes Hufeisen), einer Region mit über 8,1 Millionen Einwohnern, die sich halbkreisförmig um das westliche Ende des Ontariosees bis zu den Niagarafällen erstreckt. Rund ein Drittel der Bevölkerungszunahme des ganzen Landes lebte in den letzten Jahren in diesem Großraum. Die Einwohnerzahl der Metropolregion (Census Metropolitan Area) stieg von 4,1 Millionen im Jahr 1992 auf 5,6 Millionen im Jahr 2011.[3] Die Greater Toronto Area hatte 2010 über 6,2 Millionen Einwohner.[4]
Die Stadt liegt am nordwestlichen Ufer des Ontariosees, dem mit 18.960 km² Fläche[5] kleinsten der fünf Großen Seen. Durch die Eingemeindung einer Reihe von Vorstädten, die bereits mit Toronto verschmolzen waren (Etobicoke, Scarborough, York, East York und North York), wurde Toronto Ende der 1990er Jahre mehrfach vergrößert. Das Zentrum mit dem Einkaufs- und Bankendistrikt befindet sich in der Nähe des Sees. Die Haupteinkaufsstraße ist die Yonge Street. Toronto ist seit ungefähr den 1970er Jahren, nachdem Montreal über Jahrzehnte hinweg diese Rolle zugefallen war, Kanadas Wirtschaftszentrum und weltweit einer der führenden Finanzplätze.
多伦多(英语/法语:Toronto),是北美洲国家加拿大安大略省首府,加拿大的最大城市。
多伦多坐落在安大略湖西北岸的南安大略地区。根据2012年七月的加拿大人口普查,多伦市人口达2,790,060,为加拿大最大城市。多伦多市是大多伦多地区的心脏地区,也是安大略省南部人口稠密区(称作“金马蹄地区”)的一部分。[1][2][3]城市区有5,132,794名居民。[4]在2011年人口普查中,多伦多人口普查区有5,583,064名居民,而覆盖范围较广的大多伦多地区则有6,054,191名居民。[2]
作为加拿大的经济中心,多伦多是一个世界级城市,[5]也是世界上最大的金融中心之一。[6][7] 多伦多在经济上的领先地位在于金融、商业服务、电信、航太、交通运输、媒体、艺术、电影、电视制作、出版、软件、医药研究、教育、旅游、体育等产业。[8][9]多伦多证券交易所是世界第七大交易所,总部设于市内,有多数加拿大公司在这里上市。
多伦多的国际性人口[10] 体现出它是前往加拿大移民的重要落脚点。[11]而市内49%的人口是在加拿大以外诞生[12],也造就多伦多成为世上种族最多样化的城市之一。目前多伦多的低犯罪率、洁净的环境、高生活水准、以及对多样文化的包容性,令该市被多个经济学智囊团列为世界上最宜居的城市之一。[13][14]另一方面,多伦多于2006年被列为加拿大生活成本最高的城市。[15]
大约1/3的加拿大人居住在距多伦多两小时车程的郊区。加拿大大约1/6的就业机会在该市。
多伦多当地的华侨及华裔人口多达四十万,相当于加拿大全国约百分之一的人口,该城市也是加拿大华人最多的城市。除此之外也有大量世界各地的移民,加拿大安大略省多伦多市的人口统计资料使多伦多成为世界上最多元文化和多种族的城市之一。2016年,该市居民的51.5%属于明显的少数族裔,而2011年这一比例为49.1%,和1981年为13.6%。多伦多还建立了多个社区,例如唐人街,意大利的Corso,小意大利,小印度,希腊城,韩国城,小牙买加,小葡萄牙和朗塞瓦勒,以庆祝该市的多元文化主义的成功。
多伦多[注 1](英语:Toronto)是加拿大安大略省首府,也是加拿大最大的城市,坐落在安大略湖西北岸的南安大略地区。根据2021年的加拿大人口普查,多伦多市人口达2,794,356人,为加拿大最大城市。多伦多市是大多伦多地区的核心地区,也是安大略省南部人口稠密区(称作“金马蹄地区”)的一部分。[9][10][11]都会区有6,202,225名居民,[12]而覆盖范围较广的大多伦多地区则有9,765,188名居民。[10]作为加拿大的经济中心,多伦多是一个世界级城市,[13]也是世界上最大的金融中心之一。[14][15]多伦多在经济上的领先地位在于金融、商业服务、电信、航太、交通运输、媒体、艺术、电影、电视制作、出版、软件、医药研究、教育、旅游、体育等产业。[16][17]多伦多证券交易所是世界第七大交易所,总部设于市内,有多数加拿大公司在这里上市。
多伦多的国际性人口[18]体现出它是前往加拿大移民的重要落脚点。[19]而市内49%的人口是在加拿大以外诞生[20],也造就多伦多成为世上种族最多样化的城市之一。目前多伦多的低犯罪率、洁净的环境、高生活水准、以及对多样文化的包容性,令该市被多个经济学智囊团列为世界上最宜居的城市之一。[21][22]另一方面,多伦多于2006年被列为加拿大生活成本最高的城市。
トロント(英語: Toronto、標準音:[təˈɹɒntoʊ]、現地音:[ˈtɹɒnoʊ, təˈɹɒnoʊ])は、カナダのオンタリオ州の州都であり、同国最大の都市である。オンタリオ湖岸の北西に位置し、2016年の統計で人口273万人[1]。
国際影響力の強い世界都市であり、2016年の都市圏人口は624万人[2]。またヒューロン語で「集まる場所」という意味がある。
オンタリオ湖西岸を囲むゴールデン・ホースシュー(Golden Horseshoe)と呼ばれる都市化された地域の人口はおよそ924万人とされ、カナダ随一の金融センターとしてその中心を成している。1834年までの旧名はヨーク(Town of York)。
Toronto is the provincial capital of Ontario and the most populous city in Canada, with an estimated population of 2,956,024 (2018) and an estimated population of 6,341,935 in the Toronto Region (2018.)[14] Located on the shores of the western end of Lake Ontario, Toronto is also the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,245,438 (2016)[15] that accounts for a significant portion of Canada's economic activity and more than 20% of Canada's population. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, and culture. Its large population of immigrants from around the globe has also made Toronto one of the most multicultural and cosmopolitan cities in the world.[16][17][18]
People have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, located on a broad sloping plateau interspersed with rivers, deep ravines, and urban forest, for more than 10,000 years.[19] After the broadly disputed Toronto Purchase, when the Mississauga surrendered the area to the British Crown,[20] the British established the town of York in 1793 and later designated it as the capital of Upper Canada.[21] During the War of 1812, the town was the site of the Battle of York and suffered heavy damage by American troops.[22] York was renamed and incorporated in 1834 as the city of Toronto. It was designated as the capital of the province of Ontario in 1867 during Canadian Confederation.[23] The city proper has since expanded past its original borders through both annexation and amalgamation to its current area of 630.2 km2 (243.3 sq mi).
The diverse population of Toronto reflects its current and historical role as an important destination for immigrants to Canada.[24][25] More than 50 percent of residents belong to a visible minority population group,[26] and over 200 distinct ethnic origins are represented among its inhabitants.[27] While the majority of Torontonians speak English as their primary language, over 160 languages are spoken in the city.[28]
Toronto is a prominent centre for music,[29] theatre,[30] motion picture production,[31] and television production,[32] and is home to the headquarters of Canada's major national broadcast networks and media outlets.[33] Its varied cultural institutions,[34] which include numerous museums and galleries, festivals and public events, entertainment districts, national historic sites, and sports activities,[35] attract over 43 million tourists each year.[36][37] Toronto is known for its many skyscrapers and high-rise buildings,[38] in particular the tallest free-standing structure in the Western Hemisphere, the CN Tower.[39]
The city is home to the Toronto Stock Exchange, the headquarters of Canada's five largest banks,[40] and the headquarters of many large Canadian and multinational corporations.[41] Its economy is highly diversified with strengths in technology, design, financial services, life sciences, education, arts, fashion, aerospace, environmental innovation, food services, and tourism.[42][43][44]
Toronto (/tɔ.ʁɔ̃.to/1 ; en anglais : /təˈɹɒntoʊ̯/2 Écouter voire localement /təˈɹɒnə/ ou /ˈtɹɒnoʊ̯/ Écouter) est la plus peuplée des villes du Canada et la capitale de la province de l'Ontario. Elle se situe dans le Sud-Est du Canada, sur la rive nord-ouest du lac Ontario. Selon le recensement de 2016, Toronto compte plus de 2,7 millions d'habitants, faisant d'elle la quatrième ville la plus peuplée en Amérique du Nord. Son aire métropolitaine compte 5,9 millions d'habitants, et la mégalopole du Golden Horseshoe, dont elle est le cœur, plus de 8,7 millions d'habitants en 2011, soit le quart de la population canadienne. Ville mondiale, Toronto est le centre bancaire, financier, commercial et artistique du Canada anglophone, et l'une des villes les plus multiculturelles et cosmopolites au monde.
La région de Toronto, située sur un vaste plateau en pente jalonné de rivières, de ravins et de forêts, est habitée depuis plus de 10 000 ans. Après la brève installation d'un fort par les Français puis l’achat contesté de la région au peuple Mississauga par la Couronne britannique, les colons anglais fondent en 1793 la ville d'York, qui devient la capitale du Haut-Canada. Pendant la guerre de 1812, la ville est le théâtre de la bataille d'York et subit de lourds dégâts par les troupes américaines. York est renommée Toronto en 1834. Elle est désignée capitale de la province de l'Ontario en 1867 par la Confédération canadienne. La ville s'est depuis étendue au-delà de ses frontières d'origine, à la suite de plusieurs fusions, jusqu'à atteindre la superficie actuelle de 630,2 km2.
La population particulièrement cosmopolite de Toronto reflète son rôle historique de destination des immigrants au Canada. Plus de 50 % des résidents appartiennent à un groupe de minorités visibles et plus de 200 origines ethniques distinctes sont représentées parmi ses habitants. Bien que la majorité des Torontois parlent l'anglais principalement, plus de 160 langues sont parlées dans la ville.
Toronto est devenu un important centre de musique, théâtre, de production cinématographique et télévisuelle. Elle abrite le siège des principaux réseaux de diffusion et des médias nationaux du Canada. Ses institutions culturelles variées, qui comprennent de nombreux musées et galeries d'art, des festivals et événements publics, des quartiers de divertissement, des lieux historiques nationaux et des activités sportives, attirent plus de 25 millions de touristes chaque année. Toronto est connue pour ses nombreux gratte-ciel, en particulier la plus haute structure autoportante de l' hémisphère occidental, la tour CN.
La ville abrite la Bourse de Toronto, le siège des cinq plus grandes banques du Canada et de nombreuses autres grandes sociétés canadiennes et multinationales, de tous les secteurs économiques. Elle abrite aussi de nombreux établissements d'enseignement supérieur réputés, dont l'université de Toronto qui figure parmi les plus réputées au monde.
Toronto apparaît régulièrement dans les classements des meilleures villes en termes de qualité de vie, malgré un coût de la vie important. Ses habitants s'appellent les Torontois.
Toronto (IPA: [təˈɹɒntoʊ̯]; pronuncia locale: [ˈtrɒnoʊ] oppure [təˈɹɒnə], ascolta[?·info]) è una città dell'estremo Sud-Est del Canada, capoluogo della provincia dell'Ontario e centro più popoloso del Canada con i suoi 3 120 668 abitanti[1] (5 928 040 nell'area metropolitana[2]).
Motore economico del Canada, Toronto è, assieme a Montréal, la città del paese nordamericano più conosciuta nel mondo, seguita da Ottawa. Caratteristica della città è quella di essere una delle più multiculturali nel mondo, con circa il 36% degli abitanti di origine non canadese. Per dare un'idea di ciò basti pensare che il 911 (numero telefonico di emergenza) di Toronto è attrezzato per rispondere in oltre 150 lingue[3]. La seconda più grande comunità, superata da qualche anno da quella cinese, è costituita dagli italiani che hanno dato un enorme contributo allo sviluppo di questo paese. Si stima che le persone di origine italiana residenti a Toronto siano superiori a 500 000. Il primo quartiere dove si insediarono gli italiani fu quello di College, successivamente si spostarono a Saint Clair denominata col nome aggiuntivo di Corso Italia[4] dal 1988.
Toronto è suddivisa in 240 quartieri all'interno dei suoi confini, raggruppati in sei distretti (Old Toronto, East York, Etobicoke, Scarborough, North York e York (dove si trova anche il quartiere di Weston). Nella parte centrale di Toronto (Downtown Toronto) c'è una città sotterranea, chiamata PATH (in inglese: il sentiero o il percorso), costituita da una rete di collegamenti che mettono in collegamento i grattacieli della città. Il percorso è lungo più di 30 km. Secondo il Guinness dei primati, con i suoi 371600 m² di estensione, il PATH è più esteso centro commerciale sotterraneo del mondo.[5]
I residenti considerano questi 27 km di strade sotterranee come parte della città stessa, come se la città iniziasse non dal suolo, ma dal piano -3. Venne creata agli inizi degli anni sessanta perché in inverno, spazzata da venti nordici, Toronto è molto fredda in rapporto alla latitudine, mentre sotto ci si può muovere in abiti primaverili, sulle strade superiori, durante straordinarie irruzioni gelide ci possono essere temperature di −25/−30 °C al primo mattino o di sera. Di notte si può scendere un po' più in basso ed in tali casi le massime rimangono spesso a -20 sotto lo zero. Ovviamente il traffico automobilistico convenzionale è bandito nella città sotterranea, gli spostamenti sono previsti a piedi o con mezzi per disabili, ma il path ha numerosi punti di contatto con la viabilità esterna (parcheggi) o, molto più frequentemente, con una fitta rete di stazioni del trasporto pubblico di superficie o sotterraneo (subway).
Per muoversi nella parte sotterranea è molto importante fare riferimento a elementi di identificazione degli incroci (come elementi architettonici, facciate di banche, negozi tipici, ecc.), dato che non sempre il percorso sotterraneo (pedonale) corrisponde a quello (stradale) di superficie; o meglio, se non si è pratici, bisogna usare la mappa. La città sotterranea è completamente attrezzata come una città comune: ci sono banche, uffici postali, locali pubblici, ristoranti, uffici e supermercati. Le maggiori istituzioni (stazioni ferroviarie, aziende pubbliche, aziende commerciali, ecc.) hanno accesso multiplo: di superficie e sotterraneo.
Toronto (pronunciación en inglés: /tʲəˈɹɑntʲoʊ/ (![]() escuchar), localmente /tʲəˈɹɑnoʊ/, /ˈtʲɹɑnoʊ/) es la capital de la provincia de Ontario3 y, con una población de 2 615 060 habs.4 es la ciudad más grande de Canadá,5 además del centro financiero de dicho país.
escuchar), localmente /tʲəˈɹɑnoʊ/, /ˈtʲɹɑnoʊ/) es la capital de la provincia de Ontario3 y, con una población de 2 615 060 habs.4 es la ciudad más grande de Canadá,5 además del centro financiero de dicho país.
Localizada en la orilla noroeste del lago Ontario,6 es la quinta ciudad más grande de Norteamérica.7 Toronto se encuentra en el corazón del Área Metropolitana de Toronto (Greater Toronto Area en inglés y abreviado como GTA), la mayor área metropolitana de Canadá, y es parte de una región densamente poblada en el centro-sur de Ontario conocida como Golden Horseshoe (Herradura Dorada), donde residen ocho millones de habitantes.8910
Al ser la capital económica de Canadá, Toronto es considerada una ciudad global y una de las principales ciudades financieras del mundo.11 Lidera los sectores económicos de finanzas, servicios empresariales, telecomunicaciones, transporte, medios de comunicación, arte, cine, investigación médica, educación, y turismo de Canadá.1213 El Toronto Stock Exchange es la mayor bolsa de valores del país y la séptima del mundo.12
Toronto es famosa por la Torre CN, con 553 metros de altura. La ciudad se considera el centro de la cultura canadiense anglófona y es la anfitriona de muchas celebraciones nacionales.
La población de Toronto es cosmopolita,1415 y es un importante destino para muchos inmigrantes a Canadá.16 Toronto es la mayor ciudad del mundo en porcentaje de residentes no nacidos en el propio país; sobre un 49 % de los habitantes de la ciudad no ha nacido en Canadá.141516 Debido al bajo índice de criminalidad,17 el cuidado medio ambiente y el alto nivel de vida, Toronto, es considerada con asiduidad una de las ciudades mejor habitables del mundo.1819 Además, en 2006 fue clasificada como la ciudad más cara de Canadá.20 Los nacidos en Toronto reciben el gentilicio de torontonianos.21
En enero de 2005, Toronto fue escogida por el gobierno canadiense como una de las capitales culturales de Canadá. Toronto posee una de las mejores calidades de vida de América del Norte, y es considerada por muchos como una de las mejores metrópolis del mundo para vivir.22 Es una de las ciudades más seguras de América —su tasa de criminalidad es menor que la de cualquier gran ciudad del continente, y una de las menores de Canadá.23
En la ciudad vecina de Mississauga está el Aeropuerto Internacional Toronto Pearson. Además, en 'las islas de Toronto' dentro de la ciudad está el Billy Bishop Toronto City Airport, que es más pequeño.
Торо́нто (англ. Toronto [təˈrɒntoʊ], местн. [təˈrɒnoʊ], [ˈtrɒnoʊ], [-nə]) — крупнейший город Канады, административный центр провинции Онтарио. Население — 2 731 571 чел. (2016); вместе с городами Миссиссога, Брамптон, Маркем и другими образует агломерацию Большой Торонто с населением 5928 тыс. жителей.
Торонто является частью «золотой подковы» — густонаселённого региона вокруг западной части озера Онтарио с населением около 7 млн человек. Приблизительно одна треть всего населения Канады живёт в радиусе 500 км от Торонто. Около шестой части всех рабочих мест Канады находятся в пределах городской черты.
Город Торонто известен также как «экономический двигатель» Канады, считается одним из ведущих мегаполисов мира и имеет большой вес как в регионе, так и на государственном и международном уровне. В ежегодном рейтинге Global Liveability Ranking журнала The Economist, оценивающем совокупное качество жизни, Торонто занимает четвёртое место в мире среди 140 городов — участников рейтинга[1].
В Торонто располагается главный офис Всемирного конгресса украинцев. В июне 2010 года в Торонто прошла встреча глав государств и правительств «Большой двадцатки».
К северо-востоку от Торонто в городе Пикеринг находится атомная электростанция АЭС Пикеринг с восемью ядерными реакторами.
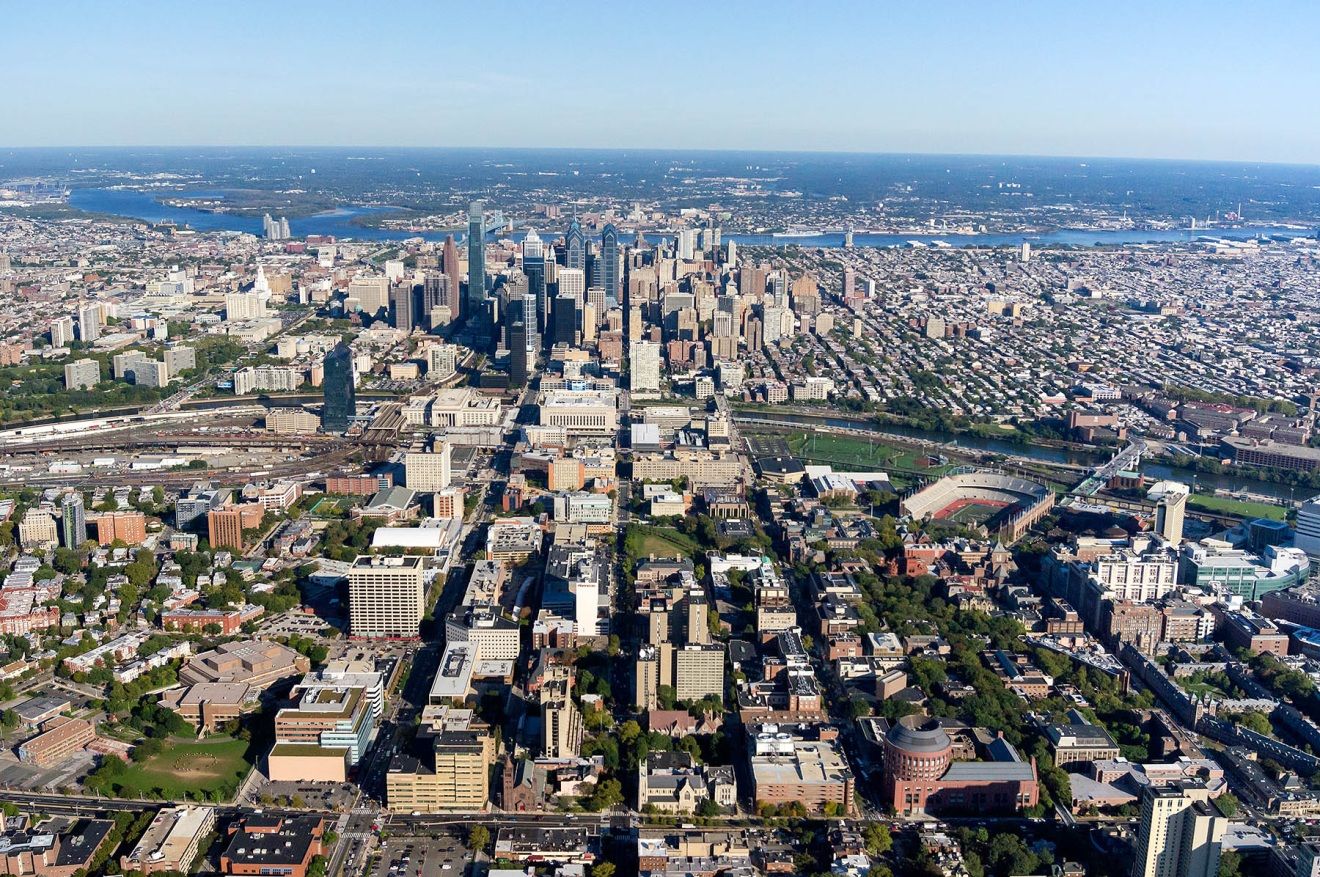

Philadelphia ist eine Stadt im US-Bundesstaat Pennsylvania. Mit rund 1,6 Millionen Einwohnern (Stand: 2016, Schätzung des U.S. Census Bureau) ist sie die sechstgrößte Stadt der Vereinigten Staaten[1] und die größte des Bundesstaates Pennsylvania. An der Ostküste ist Philadelphia nach New York City die zweitgrößte Stadt. Die Stadt liegt am Delaware River im Zentrum der Metropolregion Delaware Valley.
In der Geschichte der USA ist Philadelphia eine der bedeutendsten Städte. Nach New York und vor Washington war sie 1790 bis 1800 Nationalhauptstadt und damals die größte Stadt der USA sowie nach London die zweitgrößte englischsprachige Stadt der Welt. In Philadelphia tagte der erste und teilweise auch der zweite Kontinentalkongress sowie der Verfassungskonvent von 1787, die Amerikanische Unabhängigkeitserklärung wurde hier verkündet und die Verfassung beschlossen.
Philadelphia wird umgangssprachlich Philly oder City of Brotherly Love genannt, was von einer Übersetzung des griechischen Namens Philadelphia herrührt (φιλíα philía ‚Liebe‘ und ἀδελφός adelphós ‚Bruder‘ → φιλαδελφία philadelphía ‚Bruderliebe‘).
费城(英语:Philadelphia),即费利德菲亚,也常被简称为费利(或菲利,英语:Philly) ,中文又音译为非拉铁非和菲拉德尔斐亚,是美国宾夕法尼亚州人口最多、面积最大的都市,同时是美国第五大城。根据2010年人口普查数据,费城人口为1,526,006人。费城市中心的人口在全美国排名第五,仅次于纽约、洛杉矶、芝加哥和休斯顿。以现在美国官方的定义而言,费城都会区的面积大小排名全美第四,共约620万人居住其中,但若以其他定义来衡量,费城排名第六,次于旧金山湾区与华盛顿-巴尔的摩都会区。费城是德拉瓦河谷都会区的中心城市。
费利德菲亚即希腊文“友爱”的意思,是传教士命名的,费城是美国最老、最具历史意义的城市,它在美国史上有非常重要的地位。在18世纪时,费城是美国第二大城与人口最多的城市,在当时,它的政治与社会重要性超过纽约与波士顿。本杰明·富兰克林对费城的兴起贡献良多。从1854年起,费城市和费城县为两个并行的地方政府,而从1952年起,市与县共有一个政府组织,但费城县仍属宾州州政府下的一个独立的县。
自从1854年通过“合并法案”(Act of Consolidation)后,费城市的边界就与费城县相同。在此之前,费城市只在南街(South Street)、葡萄街(Vine Street)与德拉瓦河与斯库基尔河(Schuylkill River)之间的区域。费城后来扩张至周围的西费城(West Philadelphia)、北费城(North Philadelphia)与东北费城(Northeast Philadelphia),同时也包括了几个小型的聚落如罗布鲁(Roxborough)、马拉扬克(Manayunk)、艾利山(Mount Airy)与栗树丘(Chestnut)。费城同时是全美最大的大学城(college town)之一,拥有许多高等学府,其中包括常春藤盟校的宾夕法尼亚大学,国家第一所医学院和法学院兼缘于此校。有超过120,000名大学生就读市区的学院与大学,周遭的都会区也有接近300,000名的大学与学院学生。
フィラデルフィア(英語: Philadelphia)は、アメリカ合衆国ペンシルベニア州南東部にある都市。同州の最大都市かつ北米有数の世界都市である。市内の人口は156万7442人(2015年推計[1])で全米第5位。
名門のペンシルベニア大学や工学系に強いドレクセル大学、日本にもキャンパスを置く州立大学のテンプル大学を抱える学術都市である。市内に約12万人、都市圏全体で約30万人と、全米で最も多くの学生を持つ都市のひとつである。
漢字の当て字和名は費拉特費、また短縮して費府。
なお、フィラデルフィア都市圏の治安は概ね良好であるが、デラウェア川の対岸にあるニュージャージー州カムデンは、デトロイトやセントルイスなどと並んで、全米で最も危険な都市のひとつとされる。
独立記念館や自由の鐘があり、近郊にはバレーフォージがある合衆国建国ゆかりの地である。
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the U.S. state and Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, and the sixth-most populous U.S. city, with a 2017 census-estimated population of 1,580,863.[6] Since 1854, the city has been coterminous with Philadelphia County, the most populous county in Pennsylvania and the urban core of the eighth-largest U.S. metropolitan statistical area, with over 6 million residents as of 2017.[4] Philadelphia is also the economic and cultural anchor of the greater Delaware Valley, located along the lower Delaware and Schuylkill Rivers, within the Northeast megalopolis. The Delaware Valley's population of 7.2 million ranks it as the eighth-largest combined statistical area in the United States.[5]
William Penn, an English Quaker, founded the city in 1682 to serve as capital of the Pennsylvania Colony.[8] Philadelphia played an instrumental role in the American Revolution as a meeting place for the Founding Fathers of the United States, who signed the Declaration of Independence in 1776 at the Second Continental Congress, and the Constitution at the Philadelphia Convention of 1787. Several other key events occurred in Philadelphia during the Revolutionary War including the First Continental Congress, the preservation of the Liberty Bell, the Battle of Germantown, and the Siege of Fort Mifflin. Philadelphia was one of the nation's capitals during the revolution, and served as temporary U.S. capital while Washington, D.C., was under construction. In the 19th century, Philadelphia became a major industrial center and a railroad hub. The city grew from an influx of European immigrants, most of whom came from Ireland, Italy and Germany—the three largest reported ancestry groups in the city as of 2015.[9] In the early 20th century, Philadelphia became a prime destination for African Americans during the Great Migration after the Civil War,[10] as well as Puerto Ricans.[11] The city's population doubled from one million to two million people between 1890 and 1950.
The Philadelphia area's many universities and colleges make it a top study destination, as the city has evolved into an educational and economic hub.[12][13] According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis, the Philadelphia area had a gross domestic product of US$431 billion in 2016, the eighth-largest metropolitan economy in the United States.[14] Philadelphia is the center of economic activity in Pennsylvania and is home to five Fortune 1000 companies. The Philadelphia skyline is expanding, with a market of almost 81,900 commercial properties in 2016,[15] including several nationally prominent skyscrapers.[16] Philadelphia has more outdoor sculptures and murals than any other American city.[17][18] Fairmount Park, when combined with the adjacent Wissahickon Valley Park in the same watershed, is one of the largest contiguous urban park areas in the United States.[19] The city is known for its arts, culture, cuisine, and colonial history, attracting 42 million domestic tourists in 2016 who spent US$6.8 billion, generating an estimated $11 billion in total economic impact in the city and surrounding four counties of Pennsylvania.[20] Philadelphia has also emerged as a biotechnology hub.[21]
Philadelphia is the birthplace of the United States Marine Corps,[22][23] and is also the home of many U.S. firsts, including the first library (1731),[24] hospital (1751),[24] medical school (1765),[25] national capital (1774),[26] stock exchange (1790),[24] zoo (1874),[27] and business school (1881).[28] Philadelphia contains 67 National Historic Landmarks and the World Heritage Site of Independence Hall.[29] The city became a member of the Organization of World Heritage Cities in 2015,[30] as the first World Heritage City in the United States.[13] Although Philadelphia is rapidly undergoing gentrification, the city actively maintains mitigation strategies to minimize displacement of homeowners in gentrifying neighborhoods.[31]
Philadelphie (en anglais Philadelphia, prononcé [ˌfɪləˈdɛlfiə]), surnommée Philly, est une ville du Commonwealth de Pennsylvanie, située dans le Nord-Est des États-Unis, entre New York et Washington DC. Le nom de la ville, choisi par William Penn, signifie « amitié fraternelle2 » en grec, car elle devait être un îlot de tolérance religieuse.
Cinquième ville du pays selon le recensement fédéral de 2010 (après New York, Los Angeles, Chicago et Houston) et sixième agglomération3, Philadelphie compte 1 526 006 habitants dans la municipalité (Philadelphia City) et 5 965 343 habitants dans son aire métropolitaine (PMSA de Philadelphie–Camden–Wilmington)4.
Centre historique, culturel et artistique majeur aux États-Unis, Philadelphie est également un grand port industriel sur le fleuve Delaware qui se jette dans l’océan Atlantique. Fondée en 1682, elle fut jusqu'à 1790 la ville la plus peuplée d'Amérique du Nord. Entre 1774 et 1800, le Congrès des États-Unis s'est réuni en plusieurs endroits, le plus souvent à Philadelphie, faisant de celle-ci la capitale temporaire du pays, jusqu'à ce que Washington devienne la capitale définitive. Par ailleurs, Philadelphie entretient pendant quelques décennies une rivalité financière et politique avec New York, avant d'être éclipsée par sa rivale.
À présent, Philadelphie est la principale métropole de l'État de Pennsylvanie, dont la capitale est Harrisburg, et le siège du comté de Philadelphie.
Filadelfia[1][2] (in inglese: Philadelphia, informalmente anche Philly[3]) è la sesta città per popolazione degli Stati Uniti d'America e la più importante dello stato della Pennsylvania. Nel 2014 contava 1 560 297 abitanti; mentre la sua area metropolitana, estesa anche su parti dei vicini stati del Delaware e del New Jersey, raggiungeva i 5,8 milioni di abitanti.
Fondata nel 1682 dal quacchero William Penn, Filadelfia è una delle più antiche città degli Stati Uniti d'America, e fra la fine del XVIII secolo e l'inizio del XIX fu la città più grande del Paese. In quell'epoca vi furono redatte la dichiarazione di Indipendenza (1776) e la costituzione statunitense.
Filadelfia sorge sulla riva occidentale del fiume Delaware, ed è attraversata da un suo affluente, lo Schuylkill; il centro storico della città è compreso fra questi due fiumi.
Filadelfia3 (en inglés, Philadelphia, también apodada coloquialmente Philly) es la mayor ciudad del estado de Pensilvania, Estados Unidos. Está ubicada sobre la orilla derecha del río Delaware —poco antes de su desembocadura en la bahía de Delaware—, que la separa del estado de Nueva Jersey, y en un punto intermedio entre las importantes ciudades de Nueva York y Washington D. C. Es la quinta ciudad del país por población y la 51.ª del mundo. El condado de Filadelfia, del que es sede, tiene 1 526 000 habs. (Philadelphia City) y su área metropolitana (Valle de Delaware) alcanza los 6 millones de habs. (censo de 2014).
Es un gran centro histórico, cultural y artístico en los Estados Unidos, y de la misma forma un importante puerto industrial sobre el río Delaware, que se extiende hasta el océano Atlántico. Fundada en 1682, fue durante el siglo XVIII la ciudad más poblada de las Trece Colonias y la tercera ciudad más poblada del Imperio británico (tras Londres y Dublín), antes de convertirse provisionalmente en la ciudad capital de los Estados Unidos. Fue velozmente superada por Nueva York y le cedió su estatus de capital a la flamante ciudad de Washington D.C. Hoy, Filadelfia es la principal metrópolis del estado de Pensilvania, aunque la capital y sede del gobierno es Harrisburg.
El nombre de la ciudad, elegido por William Penn, significa "la ciudad del amor fraternal" (compuesta de philos (φίλος) "amor", y adelphos (ἀδελφός) "hermano"), pues se deseaba que fuese un refugio de tolerancia religiosa.
Establecida en 1682, es una de las ciudades más antiguas del país, y, como capital original y ciudad más grande de la época colonial, gozaba de una importancia política y social mayor que Boston o Nueva York. En 1776, el Congreso Continental de las Trece Colonias se reunió en Filadelfia y en el 4 de julio de ese año, declaró la independencia de Gran Bretaña. Quizás el ciudadano más famoso de Filadelfia fue Benjamin Franklin, escritor, científico y político.
Filadelfia es fundamental para la historia afroamericana, su gran población negra es anterior a la Gran Migración.
Филаде́льфия (англ. Philadelphia [ˌfɪləˈdɛlfiə], общеупотр. сокр. «Фи́л(л)и», англ. Philly [ˈfɪli])[1][2] — один из старейших городов США, пятый по величине населения город страны и самый населённый город штата Пенсильвания, с населением 1 526 006 жителей (согласно переписи 2010 года). Население агломерации вместе с пригородами составляет 6 034 678 жителей. Расположен на реке Делавэр у побережья Атлантического океана[3].
Филадельфия богата историей и культурой. В исторической части города до сих пор царит атмосфера маленького и тихого городка, каким была и Филадельфия, и другие колониальные города во время образования государства Соединённые Штаты Америки.
Основан в 1682 году Уильямом Пенном. Имеет прозвище «Город братской любви» (Φιλαδέλφεια на греческом языке означает 'братолюбие'), это связано с тем, что город основан переселенцами, принадлежавшими к протестантской общине квакеров (в США и сейчас его неофициально называют Квакертаун - 'город квакеров'). В 1776 году в Филадельфии Второй континентальный конгресс тринадцати североамериканских штатов принял Декларацию независимости. В 1776, 1777, 1778—1783 и 1790—1800 Филадельфия была временной столицей США.
Одним из известных жителей города был Бенджамин Франклин.

Guadalajara spanisch [gwaðalaˈxaɾa] ist die Hauptstadt des Bundesstaates Jalisco und mit ca. 1,9 Mio. Einwohnern (Stadt) und ca. 5 Mio. (Metropolitanregion) die zweitgrößte Stadt in Mexiko. Die Stadt ist Sitz eines Erzbischofs und ist auch bekannt unter dem Namen Perla del Occidente (spanisch für „Perle des Westens“). Die Einwohner der Stadt werden als tapatíos bezeichnet. Die Stadt ist Ausgangspunkt vieler mexikanischer Traditionen wie der Musik der Mariachi und des Tanzes Jarabe Tapatío. Guadalajara liegt im Westen des zentralmexikanischen Hochlandes, etwa 550 km (Fahrtstrecke) nordwestlich der Hauptstadt Mexiko-Stadt in einer Höhe von ca. 1590 m. Das Klima ist gemäßigt bis warm; Regen (ca. 940 mm/Jahr) fällt überwiegend im Sommerhalbjahr.
瓜达拉哈拉市(西班牙语:Guadalajara、纳瓦特尔语:Atemaxac)是墨西哥哈利斯科州的首府,也是瓜达拉哈拉大都市区的首府、墨西哥第二大城市。瓜达拉哈拉市地处墨西哥西太平洋区,在哈里斯科州的中心,建立于1542年,面积187.91平方公里,海拔高度1560米。
瓜达拉哈拉是墨西哥的文化、工业和经济重镇,市内设有轻轨系统。因其传统、文化休闲的魅力和烹饪而闻名于世,有西方之珠(Pearl of the Occident )的称号[1]。大街上富有殖民时期传统特色的建筑也显现出城市四个半世纪的文化底蕴。墨西哥是世界上唯一酿造龙舌兰酒(tequila,因出产该酒的小镇而得名)的国家,而龙舌兰酒原产地即为哈里斯科州,目前该酒原产地权由墨西哥政府持有。
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019
 亚洲足球联合会
亚洲足球联合会
 中北美洲及加勒比海足球协会
中北美洲及加勒比海足球协会
 南美洲足球协会
南美洲足球协会
 非洲足球协会
非洲足球协会
 国际足球联合会
国际足球联合会
 1990年世界杯足球赛
1990年世界杯足球赛
 1994年世界杯足球赛
1994年世界杯足球赛
 1998年世界杯足球赛
1998年世界杯足球赛
 2002年世界杯足球赛
2002年世界杯足球赛
 2006年世界杯足球赛
2006年世界杯足球赛
 2010年世界杯足球赛
2010年世界杯足球赛
 世界杯决赛队
世界杯决赛队
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 2022年世界杯足球赛
2022年世界杯足球赛

 2026年世界杯足球赛
2026年世界杯足球赛
 2013年国际足联联合会杯
2013年国际足联联合会杯
 2017年国际足联联合会杯
2017年国际足联联合会杯
 1991年女子世界杯足球
1991年女子世界杯足球
 1995年女子世界杯足球
1995年女子世界杯足球
 1999年女子世界杯足球
1999年女子世界杯足球
 2003年女子世界杯足球
2003年女子世界杯足球
 2007年女子世界杯足球
2007年女子世界杯足球
 2011年女子世界杯足球
2011年女子世界杯足球
 2015年女子世界杯足球赛
2015年女子世界杯足球赛
 2019年女子世界杯足球赛
2019年女子世界杯足球赛
 大洋洲足球联合会
大洋洲足球联合会
 瑞士
瑞士
 苏黎世
苏黎世

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足联女子世界杯
(F)国际足联女子世界杯

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足球联赛
(F)国际足球联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)非洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)非洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)中北美洲及加勒比海地区足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)中北美洲及加勒比海地区足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)美洲解放杯
(F)美洲解放杯

 体育
体育
 (F)欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)欧洲足球锦标赛
(F)欧洲足球锦标赛

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足联U-20世界杯
(F)国际足联U-20世界杯

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足联联合会杯
(F)国际足联联合会杯

 体育
体育
 (F)亚洲杯足球赛
(F)亚洲杯足球赛

 体育
体育
 (F)非洲国家杯
(F)非洲国家杯
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015/16
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015/16
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2016/17
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2016/17
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017/18
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017/18
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018/19
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018/19
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019/20
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019/20
 欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2017/18
欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2017/18
 欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2018/19
欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2018/19
 欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2019/20
欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2019/20
 欧洲足联国家联赛
欧洲足联国家联赛
 欧洲足球协会联盟
欧洲足球协会联盟

 重要的国际组织
重要的国际组织

Die Fédération Internationale de Football Association (deutsch Internationaler Verband des Association Football), kurz FIFA oder Fifa, ist ein privater Verband, der „die Kontrolle des Association Football in all seinen Formen“ zum Zweck hat.[3] Der Weltfußballverband ist ein gemeinnütziger Verein im Sinne der Artikel 60 ff. des Schweizerischen Zivilgesetzbuches mit Sitz in Zürich und im Handelsregister eingetragen.[4][5][6] Die FIFA muss als nicht steuerbefreiter Verein im Kanton Zürich eine reduzierte Gewinnsteuer von 4 % entrichten.[1][2]
Die FIFA erwirtschaftet in ihrer aktuellen Vierjahresertragsperiode 5,66 Milliarden Dollar, die zu 89 % aus der Vermarktung der von ihr organisierten Männer-Fußball-WM stammen. Darüber hinaus organisiert sie auch die Frauen-Fußball-WM und zahlreiche weitere Turniere. Ihr Präsident ist Gianni Infantino.
国际足球联合会(法语:Fédération Internationale de Football Association;英语:International Federation of Association Football[注 1]),简称国际足联(FIFA),是管理英式足球、室内五人足球和沙滩足球的国际体育组织,下辖211个会员协会。总部设于瑞士苏黎世。现任主席为吉安尼·因凡蒂诺。国际足联负责组织世界重大足球赛事,当中最著名的是4年举行一次的世界杯。[3]
国際サッカー連盟(こくさいサッカーれんめい、仏: Fédération Internationale de Football Association)は、サッカー(アソシエーション式フットボール)の国際競技連盟であり、スイスの法律に基づいた自立法人である。略称はFIFA(フランス語発音: [fifa] フィファ、英語発音: [ˈfiːfə] フィーファ)。本部はスイスのチューリッヒに置かれている。
2018年時点で全211の国内競技連盟が加盟し[1]、国際競技連盟としては世界最大である[3]。FIFAワールドカップ・FIFA女子ワールドカップの主催が、もっとも大きな任務となっている。
The Fédération Internationale de Football Association[a] (FIFA /ˈfiːfə/ FEE-fə; French for International Federation of Association Football; Spanish: Federación Internacional de Fútbol Asociación; German: Internationaler Verband des Association Football) is a non-profit organization which describes itself as an international governing body of association football, fútsal, beach soccer, and efootball. It is the highest governing body of football.
FIFA was founded in 1904[3] to oversee international competition among the national associations of Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland. Headquartered in Zürich, its membership now comprises 211 national associations. Member countries must each also be members of one of the six regional confederations into which the world is divided: Africa, Asia, Europe, North & Central America and the Caribbean, Oceania, and South America.
Today, FIFA outlines a number of objectives in the organizational Statues, including growing football internationally, providing efforts to ensure football is accessible to everyone, and advocating for integrity and fair play.[4] FIFA is responsible for the organization and promotion of football's major international tournaments, notably the World Cup which commenced in 1930 and the Women's World Cup which commenced in 1991. Although FIFA does not solely set the rules of football, that being the responsibility of the International Football Association Board of which FIFA is a member, it applies and enforces the rules across all FIFA competitions.[5] All FIFA tournaments generate revenue from sponsorship; in 2018, FIFA had revenues of over US $4.6 billion, ending the 2015–2018 cycle with a net positive of US$1.2 billion, and had cash reserves of over US$2.7 billion.[6]
Reports by investigative journalists have linked FIFA leadership with corruption, bribery, and vote-rigging related to the election of FIFA president Sepp Blatter and the organization's decision to award the 2018 and 2022 World Cups to Russia and Qatar, respectively. These allegations led to the indictments of nine high-ranking FIFA officials and five corporate executives by the U.S. Department of Justice on charges including racketeering, wire fraud, and money laundering. On 27 May 2015, several of these officials were arrested by Swiss authorities, who were launching a simultaneous but separate criminal investigation into how the organization awarded the 2018 and 2022 World Cups. Those among these officials who were also indicted in the U.S. are expected to be extradited to face charges there as well.[7][8][9] Many officials were suspended by FIFA's ethics committee including Sepp Blatter[10] and Michel Platini.[11] In early 2017 reports became public about FIFA president Gianni Infantino attempting to prevent the re-elections[12] of both chairmen of the ethics committee, Cornel Borbély and Hans-Joachim Eckert, during the FIFA congress in May 2017.[13][14] On 9 May 2017, following Infantino's proposal,[15] FIFA Council decided not to renew the mandates of Borbély and Eckert.[15] Together with the chairmen, 11 of 13 committee members were removed.[16]
La Fédération internationale de football association2 (souvent désignée par l'acronyme FIFA) est la fédération sportive internationale du football, du futsal et du football de plage. Association des fédérations nationales fondée le 21 mai 1904 à Paris, elle a pour vocation de gérer et de développer le football dans le monde. La Coupe du monde de football est créée en 1924 par Jules Rimet3, président de la fédération internationale de 1920 à 1954. Le terme Football Association est le nom originel du football, utilisé pour le distinguer des autres sports de ballon.
Fondée par les fédérations d'Allemagne, de Belgique, du Danemark, d'Espagne, de France, des Pays-Bas, de Suède et de Suisse, elle compte au 13 mai 2016 211 associations nationales affiliées à travers le monde, qui doivent être reconnues par l'une des six confédérations continentales. Son siège est situé depuis 1932 à Zurich, en Suisse.
Bien qu'étant officiellement une association à but non lucratif, la FIFA brasse un chiffre d'affaires très important du fait de l'organisation des compétitions et de leur sponsoring. En 2013, la FIFA génère 1,3 milliard de dollars de chiffre d'affaires, et dispose de réserves évaluées à 1,4 milliard de dollars4. La FIFA est chargée de l'organisation des grands tournois mondiaux, et notamment des Coupes du monde masculines, depuis le 13 juillet 1930, et féminines, depuis le 30 novembre 1991.
Après plusieurs années de rumeurs et d'enquêtes de journalistes sur les affaires financières au sein de la FIFA, notamment autour de l'attribution de l'organisation des Coupes du monde de 2018 et 2022 à la Russie et au Qatar, une enquête lancée par le département de la Justice des États-Unis pour des faits de corruption aboutit à un grand scandale en 2015, à la suite duquel le président Sepp Blatter, le 2 juin 2015, trois jours après sa réélection pour un cinquième mandat, annonce qu'il convoque un congrès extraordinaire, prévu en février 2016, afin de remettre son mandat de président à disposition. Le 8 octobre 2015, la commission d'éthique de la FIFA suspend Sepp Blatter de manière provisoire, pendant 90 jours5. Le 21 décembre 2015, la commission suspend Sepp Blatter pour 8 ans6. Cette suspension est ramenée à six ans le 24 février 2016, peu avant l'élection de son successeur, Gianni Infantino, le 26 février 2016.
La Fédération Internationale de Football Association (in italiano "Federazione internazionale di calcio"[Nota 1]), più nota con l'acronimo FIFA, è la federazione internazionale che governa gli sport del calcio, del calcio a 5 e del beach soccer. La sua sede si trova a Zurigo, in Svizzera, e il presidente è Gianni Infantino, eletto nel 2016.
La federazione fu fondata a Parigi il 21 maggio 1904 e si occupa dell'organizzazione di tutte le manifestazioni intercontinentali degli sport sopraccitati, tra le quali la più importante è sicuramente il Campionato mondiale di calcio, che premia il vincitore con il trofeo della Coppa del Mondo. Tale torneo viene disputato ogni quattro anni dal 1930, eccetto che per il 1942 e il 1946 a causa della Seconda guerra mondiale, e la federazione ha il compito di scegliere il paese organizzatore che ospita la fase finale della manifestazione.
La Fédération Internationale de Football Association2 (en español: Federación Internacional de Fútbol Asociación),3 universalmente conocida por sus siglas FIFA, es la institución que gobierna las federaciones de fútbol en todo el planeta. Se fundó el 21 de mayo de 1904 y tiene su sede en Zúrich, Suiza. Forma parte del IFAB, organismo encargado de modificar las reglas del juego. Además, la FIFA organiza la Copa Mundial de Fútbol, los otros campeonatos del mundo en sus distintas categorías, ramas y variaciones de la disciplina, y los Torneos Olímpicos a la par del COI.
La FIFA agrupa 211 asociaciones o federaciones de fútbol de distintos países, contando con 17 países afiliados más que la Organización de las Naciones Unidas, tres menos que la Asociación Internacional de Federaciones de Atletismo y dos menos que la Federación Internacional de Baloncesto.45
Междунаро́дная федера́ция футбо́ла[1] (фр. Fédération Internationale de Football Association, сокращённо FIFA, в русской транслитерации — ФИФА́) — главная футбольная организация, являющаяся крупнейшим международным руководящим органом в футболе, мини-футболе и пляжном футболе. Штаб-квартира ФИФА находится в швейцарском городе Цюрихе.
Под эгидой ФИФА проходят все футбольные турниры всемирного масштаба, в числе которых чемпионат мира ФИФА, аналогичный турнир среди женщин, молодёжные и юношеские турниры, Кубок конфедераций и клубный чемпионат мира.
 阿根廷
阿根廷
 巴西
巴西
 联邦德国
联邦德国
 迭戈·弗兰
迭戈·弗兰
 世界杯决赛队
世界杯决赛队
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 2022年世界杯足球赛
2022年世界杯足球赛

 2026年世界杯足球赛
2026年世界杯足球赛
 金球奖
金球奖
 法国
法国
 意大利
意大利
 克罗地亚
克罗地亚
 利昂内尔·梅西
利昂内尔·梅西
 卢卡·莫德里奇
卢卡·莫德里奇
 马拉多纳
马拉多纳
 奥利弗·卡恩
奥利弗·卡恩
 保罗·罗西
保罗·罗西
 罗马里奥
罗马里奥
 罗纳尔多
罗纳尔多
 萨尔瓦托雷·斯基拉奇
萨尔瓦托雷·斯基拉奇
 乌拉圭
乌拉圭
 齐内丁·齐达内
齐内丁·齐达内

 阿根廷
阿根廷
 巴西
巴西
 保加利亚
保加利亚
 智利
智利
 哥伦比亚
哥伦比亚
 联邦德国
联邦德国
 世界杯决赛队
世界杯决赛队
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 2022年世界杯足球赛
2022年世界杯足球赛

 2026年世界杯足球赛
2026年世界杯足球赛
 金鞋奖
金鞋奖
 法国
法国
 意大利
意大利
 克罗地亚
克罗地亚
 波兰
波兰
 葡萄牙
葡萄牙
 俄罗斯
俄罗斯
 捷克
捷克
 匈牙利
匈牙利
 英国
英国

| Top goalscorer[45][46] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World Cup | Top goalscorer | Goals | Runners-up | Goals | Third place | Goals |
| 1930 Uruguay | 8 | 5 | 4 | |||
| 1934 Italy | 5[a] | 4 | None |
— |
||
| 1938 France | 7[b] | 5 | None |
— |
||
| 1950 Brazil | 9[c] | 5 | 4 | |||
| 1954 Switzerland | 11 | 6 | None |
— |
||
| 1958 Sweden | 13 | 6 | None |
— |
||
| 1962 Chile | 4 | None |
— |
None |
— |
|
| 1966 England | 9 | 6 | 4 | |||
| 1970 Mexico | 10 | 7 | 5 | |||
| 1974 West Germany | 7 | 5 | None |
— |
||
| 1978 Argentina[50] | 6 | 5 | 5 | |||
| Golden Shoe[44] | ||||||
| World Cup | Golden Shoe | Goals | Silver Shoe | Goals | Bronze Shoe | Goals |
| 1982 Spain | 6 | 5 | 4 | |||
| 1986 Mexico | 6 | 5 | None[51] | |||
| 1990 Italy | 6 | 5 | 4 | |||
| 1994 United States | 6 | None |
— |
5[f] | ||
| 1998 France[54] | 6 | 5 | None[g] | |||
| 2002 South Korea/Japan[55] | 8[h] | 5 | ||||
| 2006 Germany[57] | 5 | 3[i] | 3[i] | |||
| Golden Boot[44] | ||||||
| World Cup | Golden Boot | Goals | Silver Boot | Goals | Bronze Boot | Goals |
| 2010 South Africa | 5[j] | 5[j] | 5[j] | |||
| 2014 Brazil | 6 | 5 | 4[k] | |||
| 2018 Russia | 6 | 4[l] | 4[l] | |||
| 2022 Qatar | 8 | 7 | 4[m] | |||
| Notes | ||||||
|
||||||
 建筑艺术
建筑艺术
 新泽西州
新泽西州


 国际城市
国际城市
 安大略
安大略
 重要港口
重要港口

 宾夕法尼亚州
宾夕法尼亚州


 马萨诸塞州
马萨诸塞州




