
English Encyclopedia
 International cities
International cities
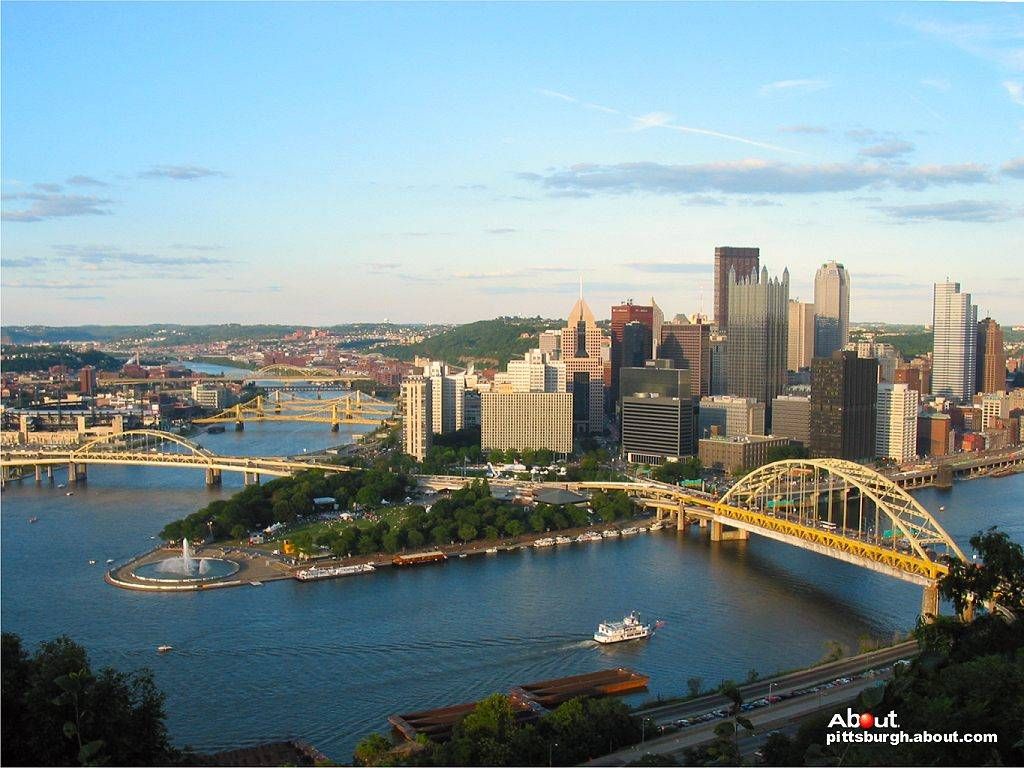


Pittsburgh (/ˈpɪtsbɜːrɡ/ PITS-burg) is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania in the United States and the county seat of Allegheny County. A population of 302,971 residents lives within the city limits as of the 2020 US Census, making it the 68th-largest city in the U.S. and the second-most populous city in Pennsylvania, behind Philadelphia. The Pittsburgh metropolitan area is the anchor of Western Pennsylvania; its population of 2.37 million is the largest in both the Ohio Valley and Appalachia, the second-largest in Pennsylvania, and the 27th-largest in the U.S.
Pittsburgh is located in the southwest of the state, at the confluence of the Allegheny River and the Monongahela River, forming the Ohio River.[5] Pittsburgh is known both as "the Steel City" for its more than 300 steel-related businesses and as the "City of Bridges" for its 446 bridges.[6] The city features 30 skyscrapers, two inclined railways, a pre-revolutionary fortification and the Point State Park at the confluence of the rivers. The city developed as a vital link of the Atlantic coast and Midwest, as the mineral-rich Allegheny Mountains led to the region being contested by the French and British empires, Virginians, Whiskey Rebels, and Civil War raiders.[7]
Aside from steel, Pittsburgh has led in the manufacturing of other important materials — aluminum and glass — and in the petroleum industry. Additionally, it is a leader in computing, electronics, and the automotive industry.[8] For part of the 20th century, Pittsburgh was behind only New York City and Chicago in corporate headquarters employment; it had the most U.S. stockholders per capita.[9] Deindustrialization in the 1970s and 1980s laid off area blue-collar workers as steel and other heavy industries declined, and thousands of downtown white-collar workers also lost jobs when several Pittsburgh-based companies moved out.[10] The population dropped from a peak of 675,000 in 1950 to 370,000 in 1990. However, this rich industrial history left the area with renowned museums, medical centers,[11] parks, research centers, and a diverse cultural district.[12]
After the deindustrialization of the mid-20th century, Pittsburgh has transformed into a hub for the health care, education, and technology industries.[13] Pittsburgh is a leader in the health care sector as the home to large medical providers such as University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC). The area is home to 68 colleges and universities, including research and development leaders Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Pittsburgh.[14] Google, Apple Inc., Bosch, Facebook, Uber, Nokia, Autodesk, Amazon, Microsoft and IBM are among 1,600 technology firms generating $20.7 billion in annual Pittsburgh payrolls. The area has served as the long-time federal agency headquarters for cyber defense, software engineering, robotics, energy research and the nuclear navy.[15] The nation's fifth-largest bank, eight Fortune 500 companies, and six of the top 300 U.S. law firms make their global headquarters in the area, while RAND Corporation (RAND), BNY Mellon, Nova, FedEx, Bayer, and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) have regional bases that helped Pittsburgh become the sixth-best area for U.S. job growth.[16]
In 2015, Pittsburgh was listed among the "eleven most livable cities in the world".[17][18] The Economist's Global Liveability Ranking placed Pittsburgh as the most or second-most livable city in the United States in 2005, 2009, 2011, 2012, 2014 and 2018.[19][20] The region is a hub for Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design and energy extraction.
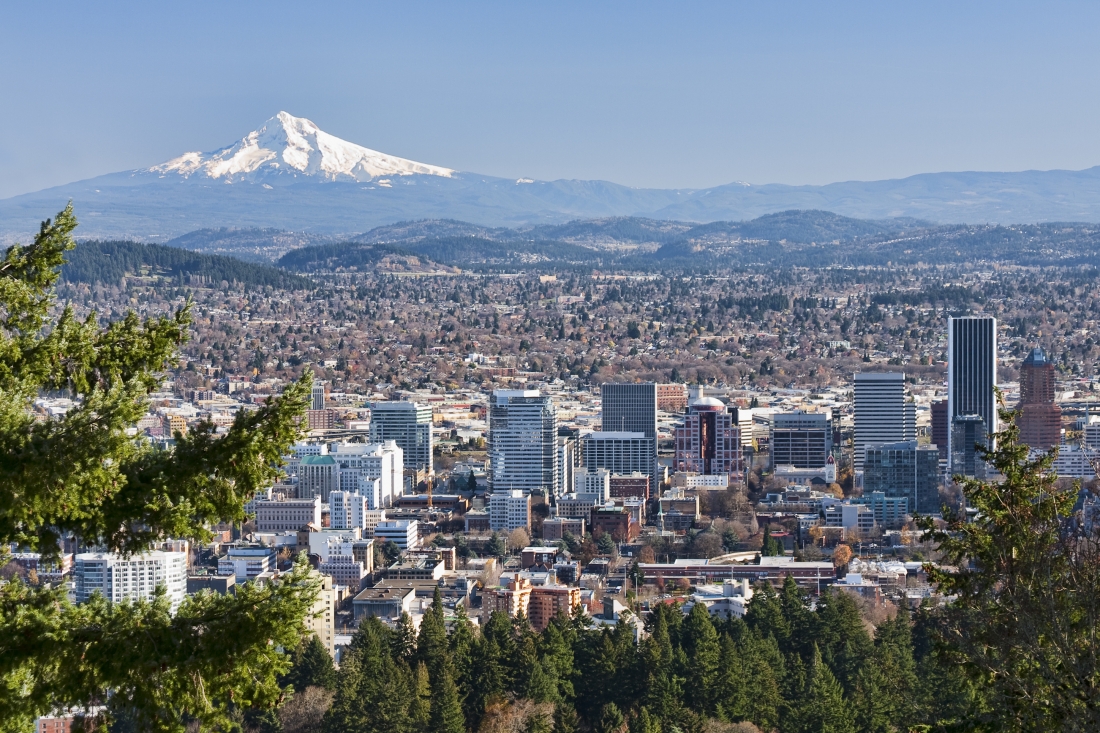

Portland (/ˈpɔːrtlənd/, PORT-lənd) is a city of regional importance to the Pacific Northwest and the largest and most populous city in the U.S. state of Oregon. Within Oregon it is the sub-regional seat of power for Multnomah County, the largest county in Oregon by population. It is also an inland port city in the Willamette Valley region of the Pacific Northwest, at the confluence of the Willamette and Columbia rivers in Northwestern Oregon. As of 2020, Portland had a population of 652,503,[8] making it the 25th-most populated city in the United States, the sixth-most populous on the West Coast, and the second-most populous in the Pacific Northwest, after Seattle.[9] Approximately 2.5 million people live in the Portland metropolitan statistical area (MSA), making it the 25th most populous in the United States. Its combined statistical area (CSA) ranks 19th-largest with a population of around 3.2 million. Approximately 47% of Oregon's population resides within the Portland metropolitan area.[a]
Named after Portland, Maine,[10] the Oregon settlement began to be populated in the 1830s, near the end of the Oregon Trail. Its water access provided convenient transportation of goods, and the timber industry was a major force in the city's early economy. At the turn of the 20th century, the city had a reputation as one of the most dangerous port cities in the world, a hub for organized crime and racketeering. After the city's economy experienced an industrial boom during World War II, its hard-edged reputation began to dissipate. Beginning in the 1960s,[11] Portland became noted for its growing progressive political values, earning it a reputation as a bastion of counter-culture.[12]
The city operates with a commission-based government, guided by a mayor and four commissioners, as well as Metro, the only directly elected metropolitan planning organization in the United States.[13] Its climate is marked by warm, dry summers and cool, rainy winters. This climate is ideal for growing roses, and Portland has been called the "City of Roses" for over a century.
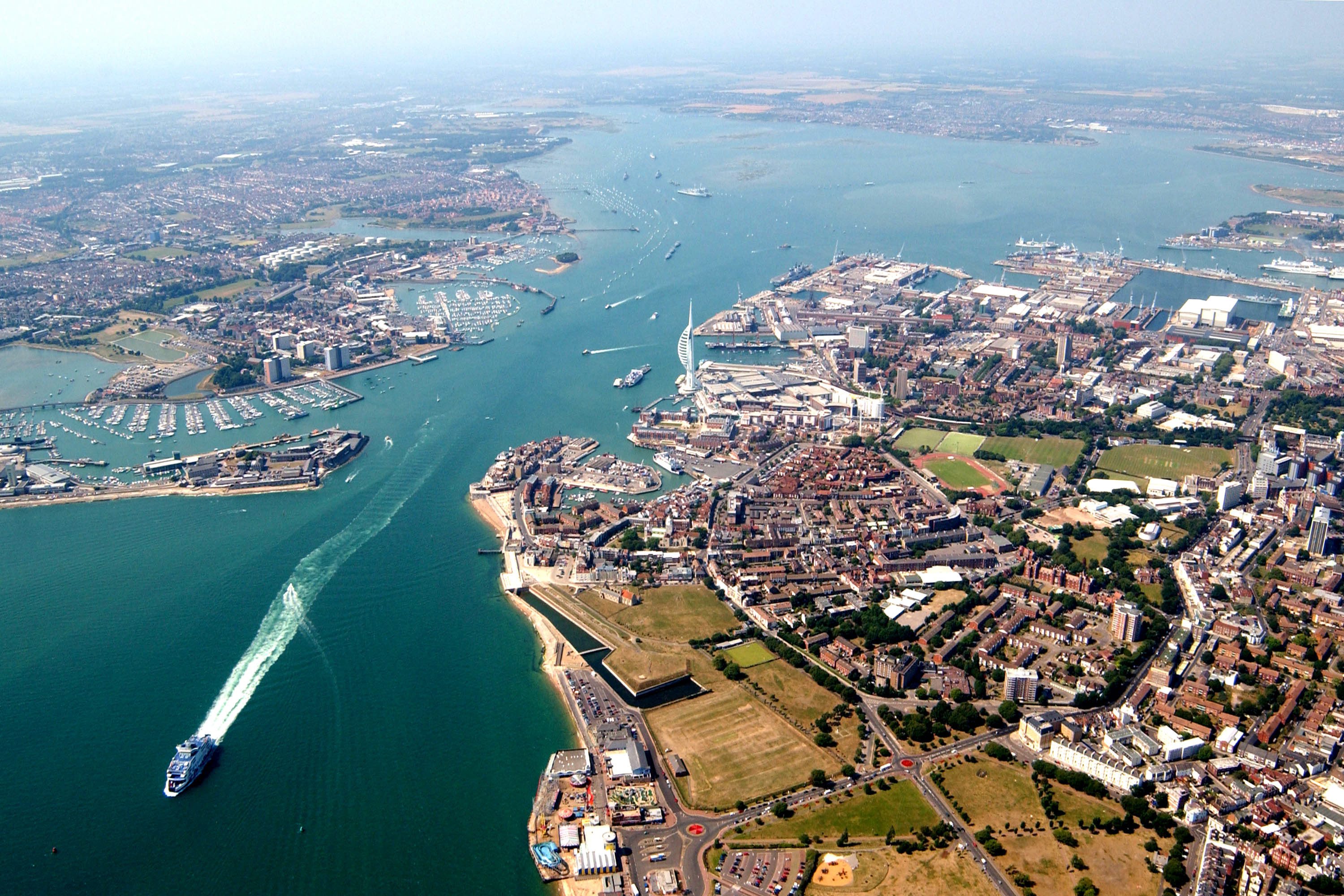

Portsmouth (/ˈpɔːrtsməθ/ ( listen) PORTS-məth) is a port and island city with unitary authority status in the ceremonial county of Hampshire, southern England. It is the most densely populated city in the United Kingdom, with a population last recorded at 238,800. Portsmouth is the only island-city in the United Kingdom. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also incorporates Southampton, Havant, Waterlooville, Eastleigh, Fareham, and Gosport. Located mainly on Portsea Island, Portsmouth is located 19 miles (31 km) south-east of Southampton and 70 miles (110 km) south-west of London.
listen) PORTS-məth) is a port and island city with unitary authority status in the ceremonial county of Hampshire, southern England. It is the most densely populated city in the United Kingdom, with a population last recorded at 238,800. Portsmouth is the only island-city in the United Kingdom. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also incorporates Southampton, Havant, Waterlooville, Eastleigh, Fareham, and Gosport. Located mainly on Portsea Island, Portsmouth is located 19 miles (31 km) south-east of Southampton and 70 miles (110 km) south-west of London.
The city's history can be traced to Roman times. A significant naval port for centuries, Portsmouth has the world's oldest dry dock and was England's first line of defence during the French invasion in 1545. Special Palmerston Forts were built in 1859 in anticipation of another invasion from continental Europe. By the early-19th century, Portsmouth was the most heavily fortified city in the world, and was considered "the world's greatest naval port" at the height of the British Empire throughout Pax Britannica. The world's first mass production line was set up in the city, making it the most industrialised site in the world. During the Second World War, the city was a pivotal embarkation point for the D-Day landings and was bombed extensively in the Portsmouth Blitz, which resulted in the deaths of 930 people. In 1982, the city was the main naval base for the task force in the Falklands War. Her Majesty's Yacht Britannia left the city to oversee the transfer of Hong Kong in 1997, which marked for many the end of the empire.
Portsmouth is one of the world's best known ports. HMNB Portsmouth is the largest dockyard for the Royal Navy and is home to two-thirds of the UK's surface fleet. The city is home to some famous ships, including HMS Warrior, the Tudor carrack Mary Rose and Horatio Nelson's flagship, HMS Victory (the world's oldest naval ship still in commission). The former HMS Vernon naval shore establishment has been redeveloped as a retail park known as Gunwharf Quays. Portsmouth is among the few British cities with two cathedrals: the Anglican Cathedral of St Thomas and the Roman Catholic Cathedral of St John the Evangelist. The waterfront and Portsmouth Harbour are dominated by the Spinnaker Tower, one of the United Kingdom's tallest structures at 560 feet (170 m). Nearby Southsea is a seaside resort with a pier amusement park and medieval castle.
Portsmouth F.C. is the city's professional association football club and play their home games at Fratton Park. The city has several mainline railway stations that connect to London Waterloo amongst other lines in southern England. Portsmouth International Port is a commercial cruise ship and ferry port for international destinations. The port is the second busiest in the United Kingdom after Dover, handling around three million passengers a year. The city formerly had its own airport, Portsmouth Airport, until its closure in 1973. The University of Portsmouth enrols 23,000 students and is ranked among the world's best modern universities. Portsmouth is also the birthplace of author Charles Dickens and engineer Isambard Kingdom Brunel.
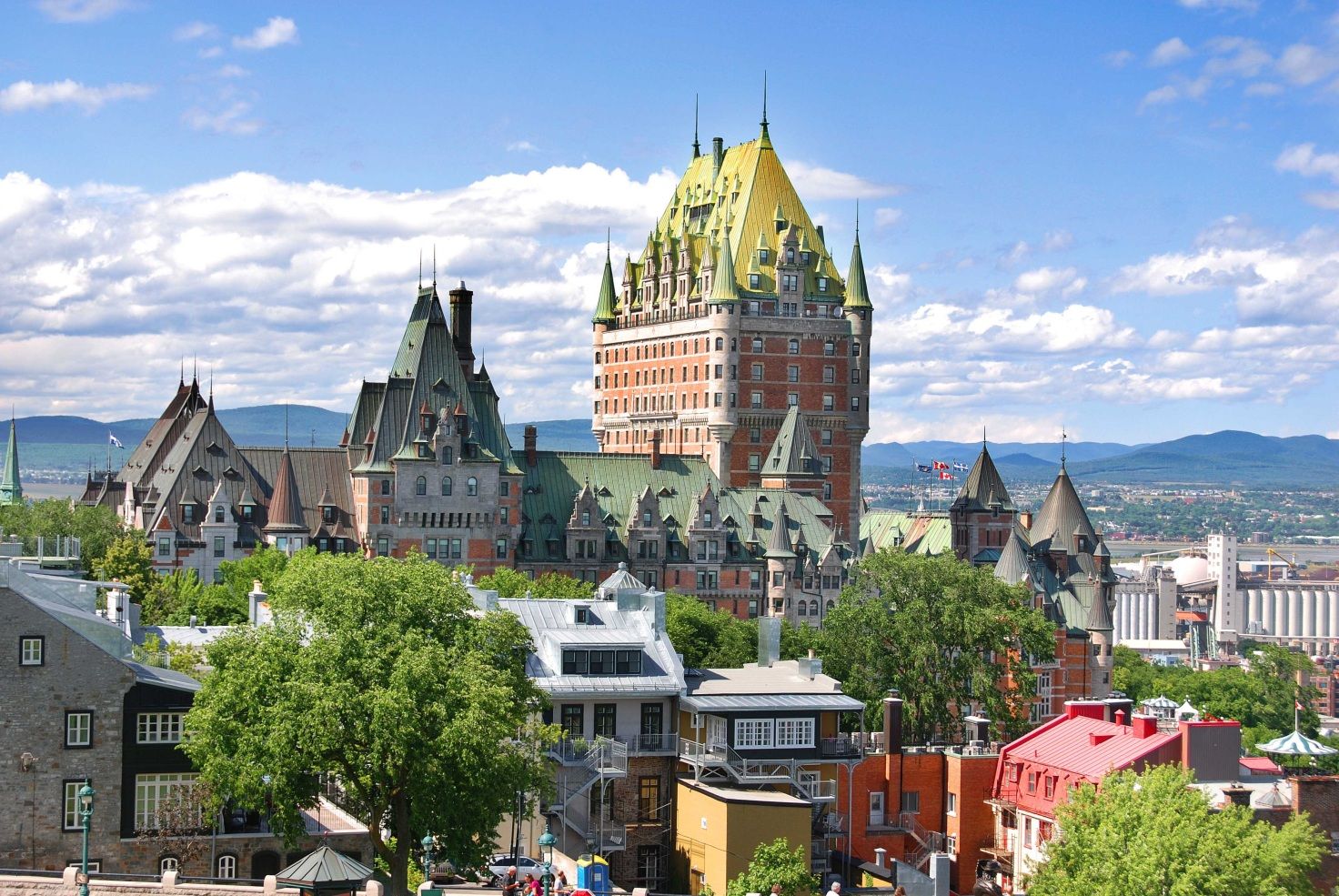

Quebec City (/kwɪˈbɛk/ (![]() listen) or /kəˈbɛk/;[12] French: Ville de Québec), officially Québec ([kebɛk] (
listen) or /kəˈbɛk/;[12] French: Ville de Québec), officially Québec ([kebɛk] (![]() listen)),[13] is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2016, the city had a population of 531,902,[14] and the metropolitan area had a population of 800,296.[15] It is the eleventh-largest city and the seventh-largest metropolitan area in Canada. It is also the second-largest city in the province after Montreal. It has a humid continental climate with warm summers coupled with cold and snowy winters.
listen)),[13] is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2016, the city had a population of 531,902,[14] and the metropolitan area had a population of 800,296.[15] It is the eleventh-largest city and the seventh-largest metropolitan area in Canada. It is also the second-largest city in the province after Montreal. It has a humid continental climate with warm summers coupled with cold and snowy winters.
The Algonquian people had originally named the area Kébec, an Algonquin[note 1] word meaning "where the river narrows", because the Saint Lawrence River narrows proximate to the promontory of Quebec and its Cape Diamant. Explorer Samuel de Champlain founded a French settlement here in 1608, and adopted the Algonquin name. Quebec City is one of the oldest European cities in North America. The ramparts surrounding Old Quebec (Vieux-Québec) are the only fortified city walls remaining in the Americas north of Mexico. This area was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1985 as the "Historic District of Old Québec".[16][17]
The city's landmarks include the Château Frontenac hotel that dominates the skyline and the Citadelle of Quebec, an intact fortress that forms the centrepiece of the ramparts surrounding the old city and includes a secondary royal residence. The National Assembly of Quebec (provincial legislature), the Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec (National Museum of Fine Arts of Quebec), and the Musée de la civilisation (Museum of Civilization) are found within or near Vieux-Québec.
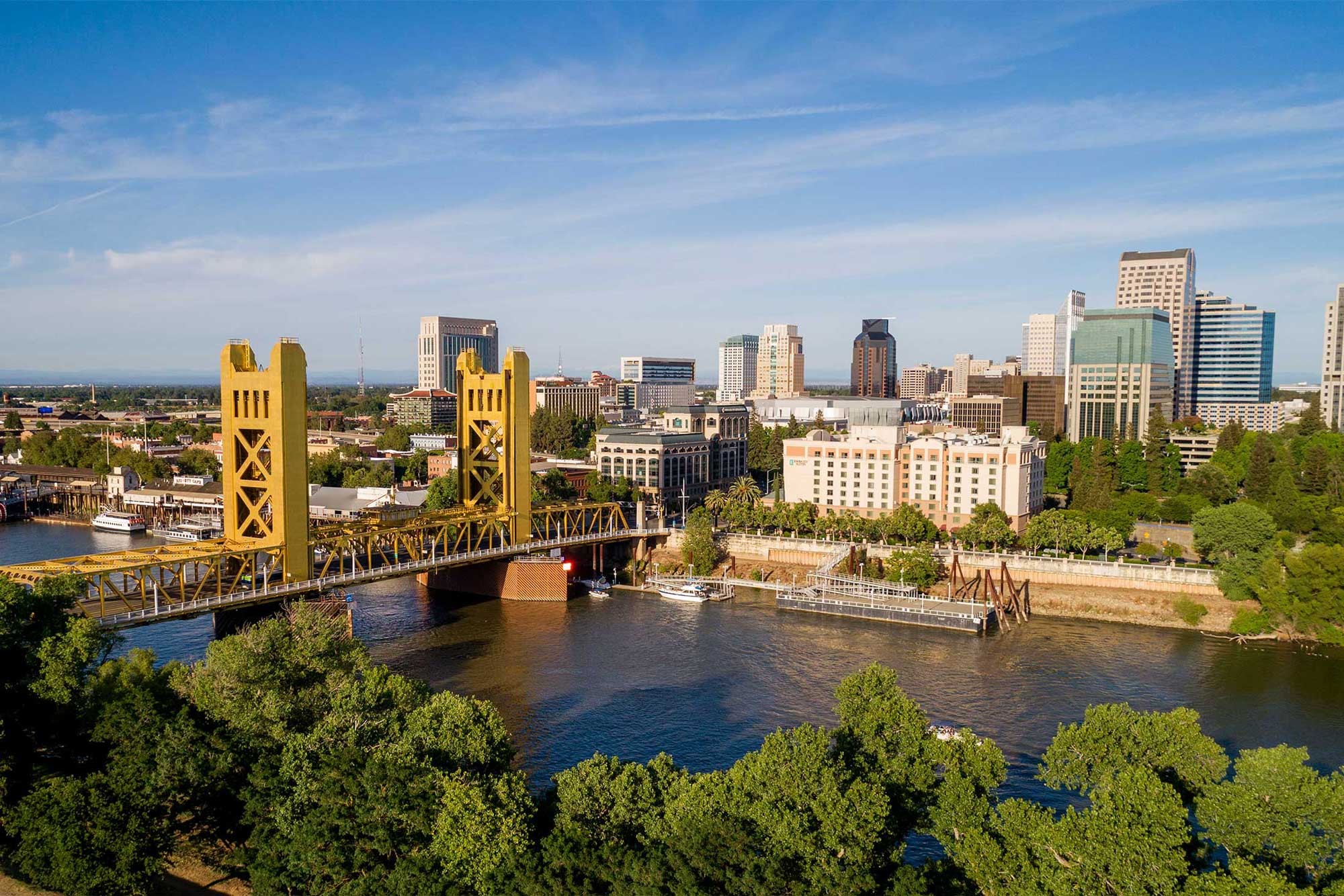

Sacramento (/ˌsækrəˈmɛntoʊ/ SAK-rə-MEN-toh; Spanish: [sakɾaˈmento], Spanish for ''sacrament'') is the capital city of the U.S. state of California and the seat and largest city of Sacramento County. Located at the confluence of the Sacramento and American Rivers in Northern California's Sacramento Valley, Sacramento's 2020 population of 524,943[7] makes it the sixth-largest city in California and the ninth-largest capital in the United States.[9][10] Sacramento is the seat of the California Legislature and the Governor of California, making it the state's political center and a hub for lobbying and think tanks. It features the California State Capitol Museum.
Sacramento is also the cultural and economic core of the Greater Sacramento area, which at the 2020 census had a population of 2,397,382,[8] the fifth-largest metropolitan area in California.[11]
Before the arrival of the Spanish, the area was inhabited by the historic Nisenan, Maidu, and other indigenous peoples of California. Spanish cavalryman Gabriel Moraga surveyed and named the Río del Santísimo Sacramento (Sacramento River) in 1808, after the Blessed Sacrament, referring to the Eucharist in the Catholic Church. In 1839, Juan Bautista Alvarado, Mexican governor of Alta California, granted the responsibility of colonizing the Sacramento Valley to Swiss-born Mexican citizen John Augustus Sutter, who subsequently established Sutter's Fort and the settlement at the Rancho Nueva Helvetia. Following the American Conquest of California and the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo, the waterfront developed by Sutter began to be developed, and incorporated in 1850 as the City of Sacramento.
Sacramento is the fastest-growing major city in California,[12] owing to its status as a notable political center on the West Coast and as a major educational hub, home of California State University, Sacramento and University of California, Davis. Similarly, Sacramento is a major center for the California healthcare industry, as the seat of Sutter Health, the world-renowned UC Davis Medical Center, and the UC Davis School of Medicine. It is a tourist destination, featuring the California Museum, Crocker Art Museum, California State Railroad Museum, California Hall of Fame, and Old Sacramento State Historic Park. Sacramento International Airport, located northwest of the city, is the city's major airport.
Sacramento is known for its evolving contemporary culture, and is dubbed the most "hipster city" in California.[13][14] In 2002, the Harvard University Civil Rights Project conducted for Time magazine ranked Sacramento as "America's Most Diverse City".
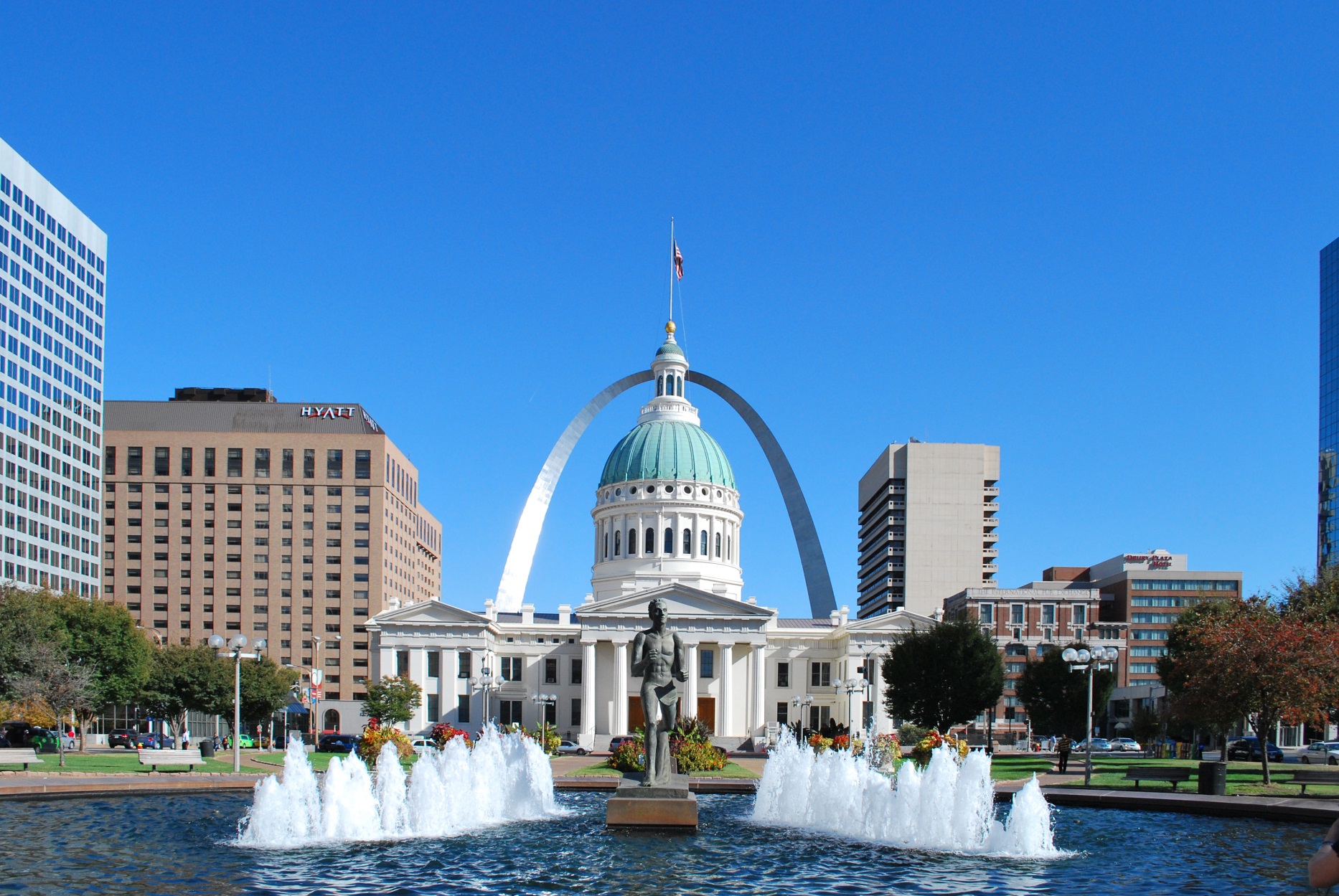

St. Louis (/seɪnt ˈluːɪs, sənt ˈluːɪs/)[9] is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. As of 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578,[8] while the bi-state metropolitan area, which extends into Illinois, had an estimated population of over 2.8 million, making it the largest metropolitan area in Missouri, the second-largest in Illinois, and the 20th-largest in the United States.
Before European settlement, the area was a regional center of Native American Mississippian culture. St. Louis was founded on February 14, 1764, by French fur traders Gilbert Antoine de St. Maxent,[10] Pierre Laclède and Auguste Chouteau, who named it for Louis IX of France. In 1764, following France's defeat in the Seven Years' War, the area was ceded to Spain. In 1800, it was retroceded to France, which sold it three years later to the United States as part of the Louisiana Purchase;[11] the city was then the point of embarkation for the Corps of Discovery on the Lewis and Clark Expedition. In the 19th century, St. Louis became a major port on the Mississippi River; from 1870 until the 1920 census, it was the fourth-largest city in the country. It separated from St. Louis County in 1877, becoming an independent city and limiting its own political boundaries. In 1904, it hosted the Louisiana Purchase Exposition and the Summer Olympics.
A "Gamma" global city with a metropolitan GDP of more than $160 billion in 2017,[12] metropolitan St. Louis has a diverse economy with strengths in the service, manufacturing, trade, transportation, and tourism industries. It is home to eight Fortune 500 companies. Major companies headquartered or with significant operations in the city include Ameren Corporation, Peabody Energy, Nestlé Purina PetCare, Anheuser-Busch, Wells Fargo Advisors, Stifel Financial, Spire, Inc., MilliporeSigma, FleishmanHillard, Square, Inc., U.S. Bank, Anthem BlueCross and Blue Shield, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, U.S. Department of Agriculture, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, Centene Corporation, and Express Scripts.
Major research universities include Saint Louis University and Washington University in St. Louis. The Washington University Medical Center in the Central West End neighborhood hosts an agglomeration of medical and pharmaceutical institutions, including Barnes-Jewish Hospital.
St. Louis has four professional sports teams: the St. Louis Cardinals of Major League Baseball, the St. Louis Blues of the National Hockey League, St. Louis City SC of Major League Soccer, anticipated to begin play in 2023, and the St. Louis BattleHawks of the XFL. Among the city's notable sights is the 630-foot (192 m) Gateway Arch in Downtown St. Louis, the St. Louis Zoo, the Missouri Botanical Garden, the Saint Louis Art Museum, and Bellefontaine Cemetery and Arboretum.
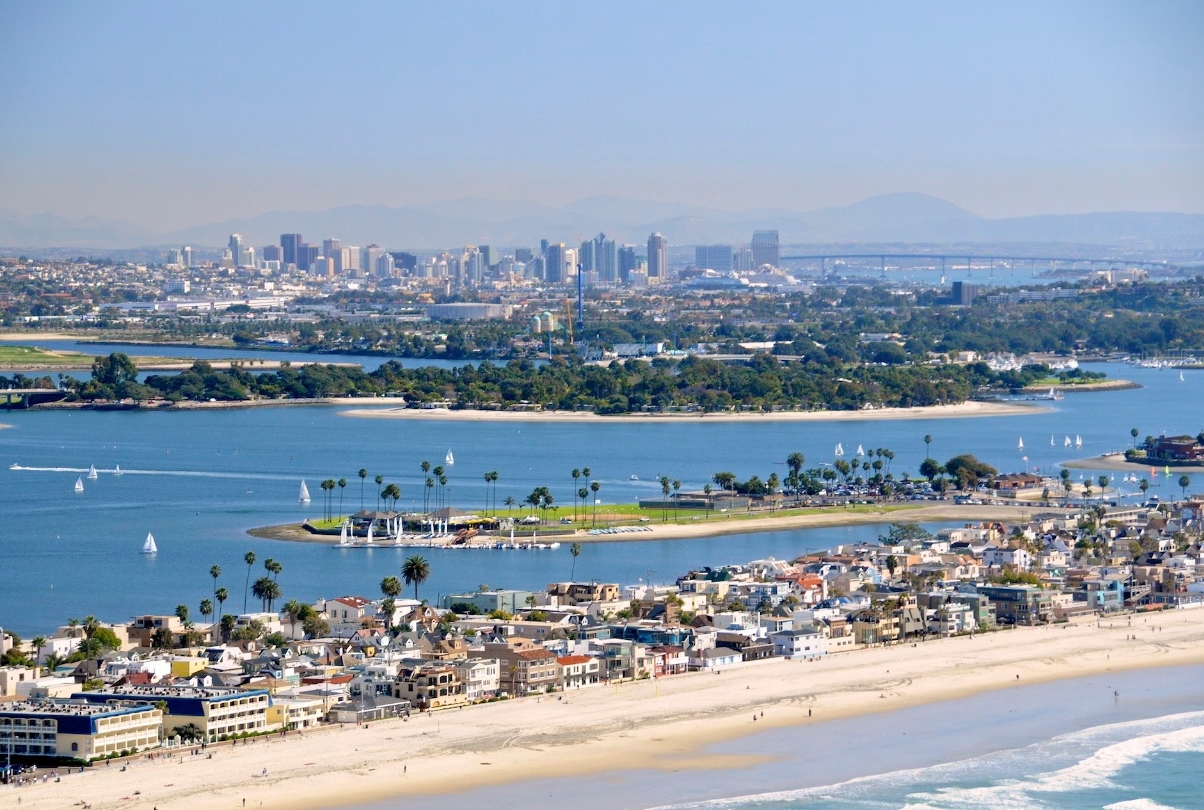

San Diego (/ˌsæn diˈeɪɡoʊ/ SAN dee-AY-goh, Spanish: [san ˈdjeɣo]; Spanish for 'Saint Didacus') is a city in the U.S. state of California on the coast of the Pacific Ocean and immediately adjacent to the Mexican border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932,[11] San Diego is the eighth most populous city in the United States and second most populous in California (after Los Angeles). The city is the county seat of San Diego County, the fifth most populous county in the United States, with 3,338,330 estimated residents as of 2019. The city is known for its mild year-round climate, natural deep-water harbor, extensive beaches and parks, long association with the United States Navy and Marine Corps, and recent emergence as a healthcare and biotechnology development center.
Historically home to the Kumeyaay people, San Diego is frequently referred to as the "Birthplace of California", as it was the first site visited and settled by Europeans on what is now the West Coast of the United States.[12] Upon landing in San Diego Bay in 1542, Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo claimed the area for Spain, forming the basis for the settlement of Alta California 200 years later. The Presidio and Mission San Diego de Alcalá, founded in 1769, formed the first European settlement in what is now California. In 1821, San Diego became part of the newly declared Mexican Empire, which reformed as the First Mexican Republic two years later. California became part of the United States in 1848 following the Mexican–American War and was admitted to the union as a state in 1850.
San Diego's main economic engines are military and defense-related activities, tourism, international trade, research, and manufacturing. The city is the economic center of the San Diego–Tijuana conurbation, the second most populous transborder metropolitan area in the western hemisphere (after Detroit–Windsor), home to an estimated 4,922,723 people as of 2012.[13] The primary border crossing between San Diego and Tijuana, the San Ysidro Port of Entry, is the busiest international land border crossing in the world outside of Asia (fourth-busiest overall). The city's primary airport, San Diego International Airport, is the busiest single-runway airport in the world.
 California State Route 1
California State Route 1

 California-CA
California-CA

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 Silk road
Silk road
 United States
United States

 Important port
Important port
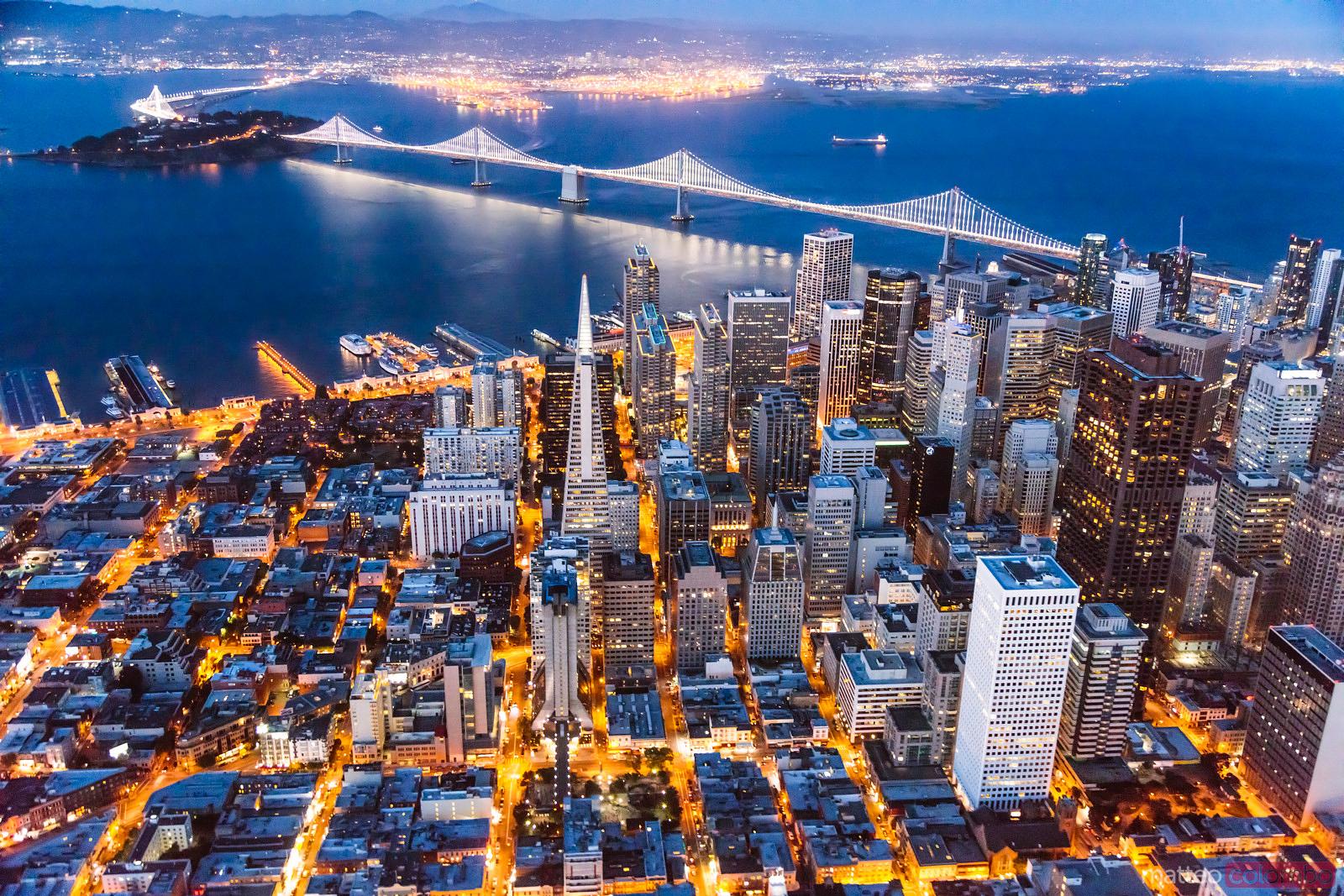

San Francisco (/ˌsæn frənˈsɪskoʊ/; Spanish for "Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a cultural, commercial, and financial center in the U.S. state of California. Located in Northern California, San Francisco is the 17th most populous city proper in the United States, and the fourth most populous in California, with 873,965 residents as of 2020.[15] It covers an area of about 46.9 square miles (121 square kilometers),[20] mostly at the north end of the San Francisco Peninsula in the San Francisco Bay Area, making it the second most densely populated large U.S. city, and the fifth most densely populated U.S. county, behind only four of the five New York City boroughs. San Francisco is the 12th-largest metropolitan statistical area in the United States with 4.7 million residents, and the fourth-largest by economic output, with a GDP of $592 billion in 2019.[21] With San Jose, California, it forms the San Jose–San Francisco–Oakland, CA Combined Statistical Area, the fifth most populous combined statistical area in the United States, with 9.6 million residents as of 2019. Colloquial nicknames for San Francisco include SF, San Fran, The City, and Frisco.[22][23]
In 2019, San Francisco was the county with the seventh-highest income in the United States, with a per capita income of $139,405.[24] In the same year, San Francisco proper had a GDP of $203.5 billion, and a GDP per capita of $230,829.[21][25] The San Jose–San Francisco–Oakland, CA Combined Statistical Area, with a GDP of $1.09 trillion as of 2019, is the country's third-largest economy.[26] Of the 105 primary statistical areas in the U.S. with over 500,000 residents, this CSA had the highest GDP per capita in 2019, at $112,348.[26] San Francisco was ranked 5th in the world and second in the United States on the Global Financial Centres Index as of September 2021.[27]
San Francisco was founded on June 29, 1776, when colonists from Spain established the Presidio of San Francisco at the Golden Gate and Mission San Francisco de Asís a few miles away, both named for Francis of Assisi.[3] The California Gold Rush of 1849 brought rapid growth, making it the largest city on the West Coast at the time; between 1870 and 1900, approximately one quarter of California's population resided in the city proper.[28] In 1856, San Francisco became a consolidated city-county.[29] After three-quarters of the city was destroyed by the 1906 earthquake and fire,[30] it was quickly rebuilt, hosting the Panama-Pacific International Exposition nine years later. In World War II, it was a major port of embarkation for service members shipping out to the Pacific Theater.[31] It then became the birthplace of the United Nations in 1945.[32][33][34] After the war, the confluence of returning servicemen, significant immigration, liberalizing attitudes, the rise of the "beatnik" and "hippie" countercultures, the Sexual Revolution, the Peace Movement growing from opposition to United States involvement in the Vietnam War, and other factors led to the Summer of Love and the gay rights movement, cementing San Francisco as a center of liberal activism in the United States. Politically, the city votes strongly along liberal Democratic Party lines.
A popular tourist destination,[35] San Francisco is known for its cool summers, fog, steep rolling hills, eclectic mix of architecture, and landmarks, including the Golden Gate Bridge, cable cars, the former Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary, Fisherman's Wharf, and its Chinatown district. San Francisco is also the headquarters of companies such as Wells Fargo, Twitter, Block, Airbnb, Levi Strauss & Co., Gap Inc., Salesforce, Dropbox, Pacific Gas and Electric Company, Uber, and Lyft. The city, and the surrounding Bay Area, is a global center of the sciences and arts[36][37] and is home to a number of educational and cultural institutions, such as the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), the University of San Francisco (USF), San Francisco State University (SFSU), the de Young Museum, the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art, the SFJAZZ Center, the San Francisco Symphony and the California Academy of Sciences. More recently, statewide droughts in California have strained the city's water security.
Seattle (/siˈætəl/ ( listen) see-AT-əl) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015,[2] it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The Seattle metropolitan area's population is 4.02 million, making it the 15th-largest in the United States.[9] Its growth rate of 21.1% between 2010 and 2020 makes it one of the nation's fastest-growing large cities.[10]
listen) see-AT-əl) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015,[2] it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The Seattle metropolitan area's population is 4.02 million, making it the 15th-largest in the United States.[9] Its growth rate of 21.1% between 2010 and 2020 makes it one of the nation's fastest-growing large cities.[10]
Seattle is situated on an isthmus between Puget Sound (an inlet of the Pacific Ocean) and Lake Washington. It is the northernmost major city in the United States, located about 100 miles (160 km) south of the Canadian border. A major gateway for trade with East Asia, Seattle is the fourth-largest port in North America in terms of container handling as of 2015.[11]
The Seattle area was inhabited by Native Americans for at least 4,000 years before the first permanent European settlers.[12] Arthur A. Denny and his group of travelers, subsequently known as the Denny Party, arrived from Illinois via Portland, Oregon, on the schooner Exact at Alki Point on November 13, 1851.[13] The settlement was moved to the eastern shore of Elliott Bay and named "Seattle" in 1852, in honor of Chief Si'ahl of the local Duwamish and Suquamish tribes. Today, Seattle has high populations of Native, Scandinavian, Asian American and African American people, as well as a thriving LGBT community that ranks sixth in the United States by population.[14]
Logging was Seattle's first major industry, but by the late 19th century, the city had become a commercial and shipbuilding center as a gateway to Alaska during the Klondike Gold Rush. Growth after World War II was partially due to the local Boeing company, which established Seattle as a center for aircraft manufacturing. The Seattle area developed into a technology center from the 1980s onwards with companies like Microsoft becoming established in the region; Microsoft founder Bill Gates is a Seattleite by birth. Internet retailer Amazon was founded in Seattle in 1994, and major airline Alaska Airlines is based in SeaTac, Washington, serving Seattle's international airport, Seattle–Tacoma International Airport. The stream of new software, biotechnology, and Internet companies led to an economic revival, which increased the city's population by almost 50,000 between 1990 and 2000. Seattle also has a significant musical history. Between 1918 and 1951, nearly two dozen jazz nightclubs existed along Jackson Street, from the current Chinatown/International District to the Central District. The jazz scene nurtured the early careers of Ray Charles, Quincy Jones, Ernestine Anderson, and others. Seattle is also the birthplace of rock musician Jimi Hendrix, as well as the origin of the bands Nirvana, Pearl Jam, Soundgarden, Alice in Chains, Foo Fighters, and the alternative rock movement grunge.
Sydney (/ˈsɪdni/ (
 listen))[7] is the state capital of New South Wales and the most populous city in Australia and Oceania.[8] Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Port Jackson and extends about 70 km (43.5 mi) on its periphery towards the Blue Mountains to the west, Hawkesbury to the north, and Macarthur to the south.[9] Sydney is made up of 658 suburbs, 40 local government areas and 15 contiguous regions. Residents of the city are known as "Sydneysiders".[10] As of June 2017, Sydney's estimated metropolitan population was 5,131,326.[11]
listen))[7] is the state capital of New South Wales and the most populous city in Australia and Oceania.[8] Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Port Jackson and extends about 70 km (43.5 mi) on its periphery towards the Blue Mountains to the west, Hawkesbury to the north, and Macarthur to the south.[9] Sydney is made up of 658 suburbs, 40 local government areas and 15 contiguous regions. Residents of the city are known as "Sydneysiders".[10] As of June 2017, Sydney's estimated metropolitan population was 5,131,326.[11]
Indigenous Australians have inhabited the Sydney area for at least 30,000 years, and it remains one of the richest in Australia in terms of Aboriginal archaeological sites, with thousands of engravings located throughout the region. In 1770, during his first Pacific voyage in the Endeavour, Lieutenant James Cook, after leaving Botany Bay, saw the entrance to Port Jackson, but sailed past and did not enter the inlet. In 1788, the First Fleet of convicts, led by Arthur Phillip, were the first recorded Europeans to sail into Port Jackson. Here they founded Sydney as a British penal colony, the first European settlement in Australia. Phillip named the city "Sydney" in recognition of Thomas Townshend, 1st Viscount Sydney.[12] Penal transportation to New South Wales ended soon after Sydney was incorporated as a city in 1842. A gold rush occurred in the colony in 1851, and over the next century, Sydney transformed from a colonial outpost into a major global cultural and economic centre. After World War II, it experienced mass migration and became one of the most multicultural cities in the world.[3] At the time of the 2011 census, more than 250 different languages were spoken in Sydney and about 40 percent of residents spoke a language other than English at home.[13] Furthermore, 36% of the population reported having been born overseas.[14][15]
Despite being one of the most expensive cities in the world,[16] the 2018 Mercer Quality of Living Survey ranks Sydney tenth in the world in terms of quality of living,[17] making it one of the most livable cities.[18] It is classified as an Alpha World City by Globalization and World Cities Research Network, indicating its influence in the region and throughout the world.[19][20] Ranked eleventh in the world for economic opportunity,[21] Sydney has an advanced market economy with strengths in finance, manufacturing and tourism.[22][23] There is a significant concentration of foreign banks and multinational corporations in Sydney and the city is promoted as one of Asia Pacific's leading financial hubs.[24][25] Established in 1850, the University of Sydney is Australia's first university and is regarded as one of the world's leading universities.[26] Sydney is also home to the oldest library in Australia, State Library of New South Wales, opened in 1826.[27]
Sydney has hosted major international sporting events such as the 2000 Summer Olympics. The city is among the top fifteen most-visited cities in the world,[28] with millions of tourists coming each year to see the city's landmarks.[29] Boasting over 1,000,000 ha (2,500,000 acres) of nature reserves and parks,[30] its notable natural features include Sydney Harbour, the Royal National Park, Royal Botanic Garden and Hyde Park, the oldest parkland in the country.[31] Built attractions such as the Sydney Harbour Bridge and the World Heritage-listed Sydney Opera House are also well known to international visitors. The main passenger airport serving the metropolitan area is Kingsford-Smith Airport, one of the world's oldest continually operating airports.[32] Established in 1906, Central station, the largest and busiest railway station in the state, is the main hub of the city's rail network.[33]
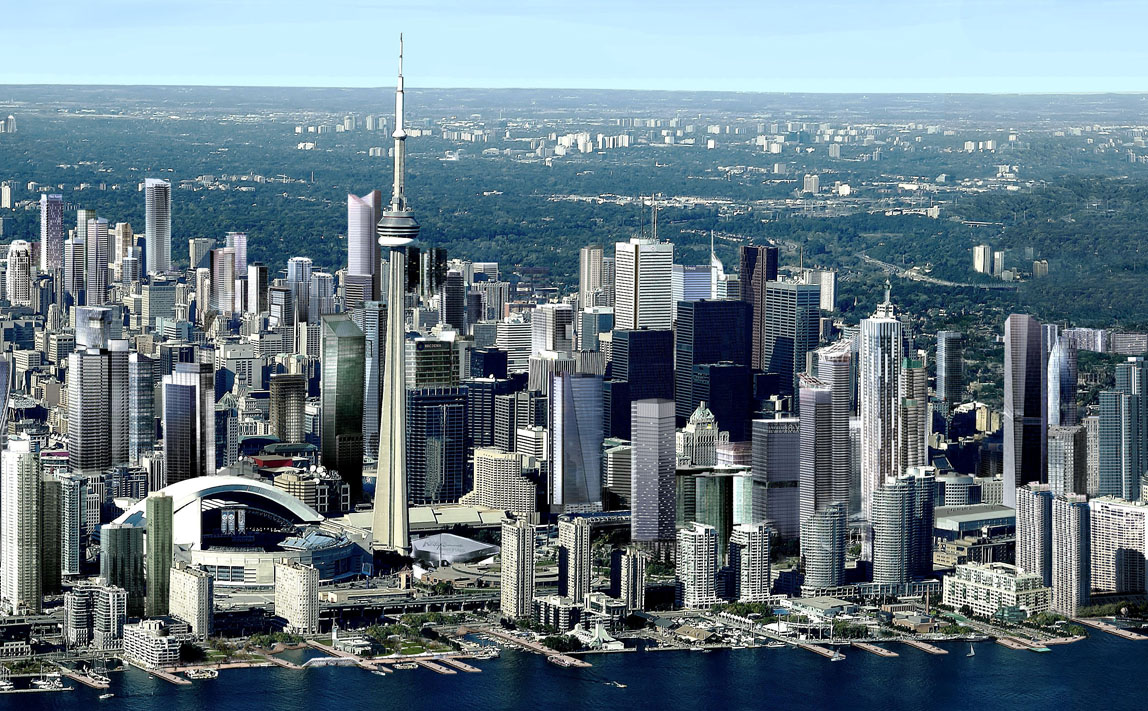

Toronto is the provincial capital of Ontario and the most populous city in Canada, with an estimated population of 2,956,024 (2018) and an estimated population of 6,341,935 in the Toronto Region (2018.)[14] Located on the shores of the western end of Lake Ontario, Toronto is also the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,245,438 (2016)[15] that accounts for a significant portion of Canada's economic activity and more than 20% of Canada's population. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, and culture. Its large population of immigrants from around the globe has also made Toronto one of the most multicultural and cosmopolitan cities in the world.[16][17][18]
People have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, located on a broad sloping plateau interspersed with rivers, deep ravines, and urban forest, for more than 10,000 years.[19] After the broadly disputed Toronto Purchase, when the Mississauga surrendered the area to the British Crown,[20] the British established the town of York in 1793 and later designated it as the capital of Upper Canada.[21] During the War of 1812, the town was the site of the Battle of York and suffered heavy damage by American troops.[22] York was renamed and incorporated in 1834 as the city of Toronto. It was designated as the capital of the province of Ontario in 1867 during Canadian Confederation.[23] The city proper has since expanded past its original borders through both annexation and amalgamation to its current area of 630.2 km2 (243.3 sq mi).
The diverse population of Toronto reflects its current and historical role as an important destination for immigrants to Canada.[24][25] More than 50 percent of residents belong to a visible minority population group,[26] and over 200 distinct ethnic origins are represented among its inhabitants.[27] While the majority of Torontonians speak English as their primary language, over 160 languages are spoken in the city.[28]
Toronto is a prominent centre for music,[29] theatre,[30] motion picture production,[31] and television production,[32] and is home to the headquarters of Canada's major national broadcast networks and media outlets.[33] Its varied cultural institutions,[34] which include numerous museums and galleries, festivals and public events, entertainment districts, national historic sites, and sports activities,[35] attract over 43 million tourists each year.[36][37] Toronto is known for its many skyscrapers and high-rise buildings,[38] in particular the tallest free-standing structure in the Western Hemisphere, the CN Tower.[39]
The city is home to the Toronto Stock Exchange, the headquarters of Canada's five largest banks,[40] and the headquarters of many large Canadian and multinational corporations.[41] Its economy is highly diversified with strengths in technology, design, financial services, life sciences, education, arts, fashion, aerospace, environmental innovation, food services, and tourism.[42][43][44]

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC

 Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Winter Olympics
Winter Olympics
 Ski vacation
Ski vacation

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon

 Important port
Important port
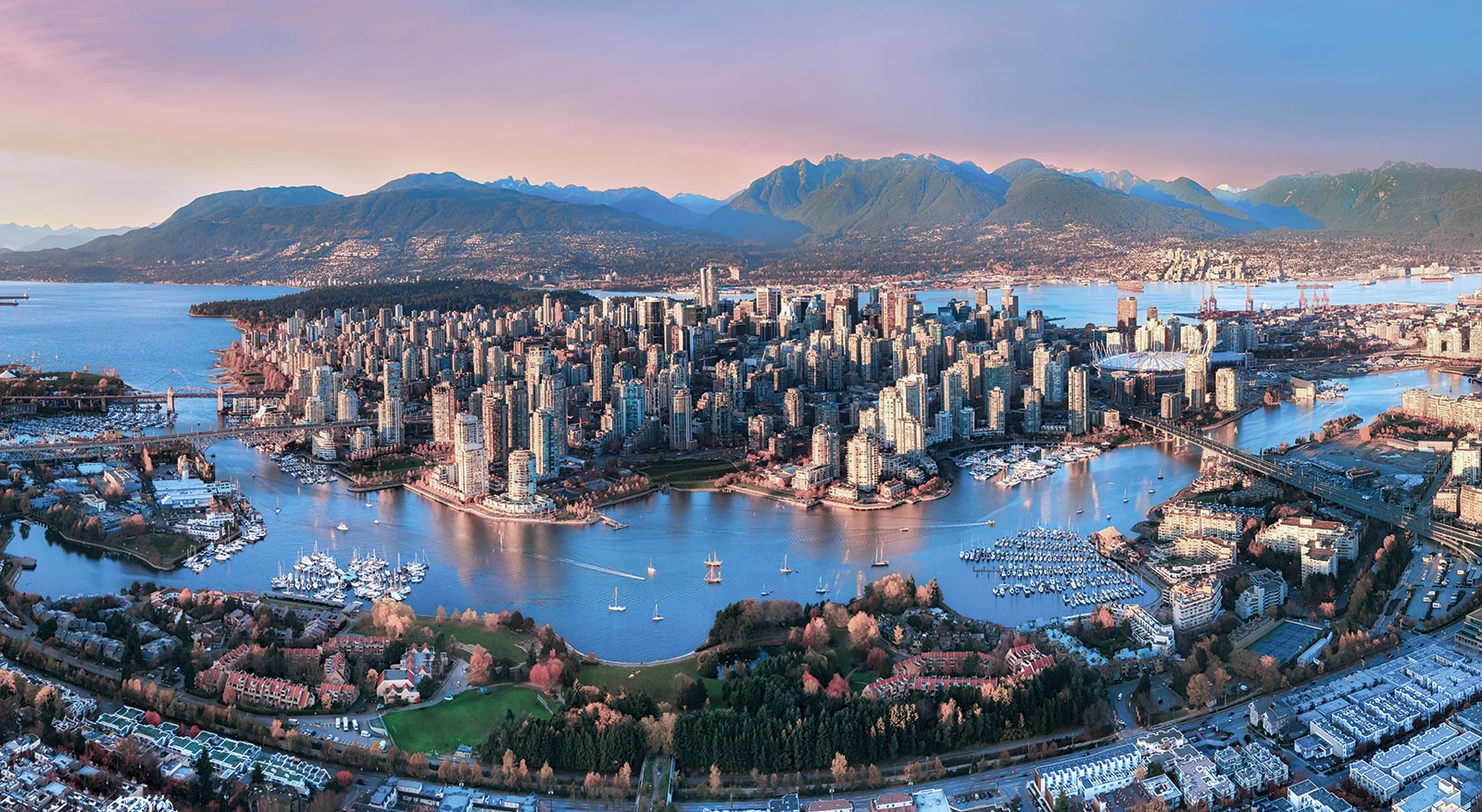 Vancouver (/vænˈkuːvər/ (
Vancouver (/vænˈkuːvər/ ( listen)) is a coastal seaport city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2016 census recorded 631,486 people in the city, up from 603,502 in 2011. The Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2,463,431 in 2016, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada with over 5,400 people per square kilometre,[5][6] which makes it the fifth-most densely populated city with over 250,000 residents in North America behind New York City, Guadalajara, San Francisco,[7] and Mexico City according to the 2011 census. Vancouver is one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities in Canada according to that census; 52% of its residents have a first language other than English.[8][9] Roughly 30% of the city's inhabitants are of Chinese heritage.[10] Vancouver is classed as a Beta global city.
listen)) is a coastal seaport city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2016 census recorded 631,486 people in the city, up from 603,502 in 2011. The Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2,463,431 in 2016, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada with over 5,400 people per square kilometre,[5][6] which makes it the fifth-most densely populated city with over 250,000 residents in North America behind New York City, Guadalajara, San Francisco,[7] and Mexico City according to the 2011 census. Vancouver is one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities in Canada according to that census; 52% of its residents have a first language other than English.[8][9] Roughly 30% of the city's inhabitants are of Chinese heritage.[10] Vancouver is classed as a Beta global city.
Vancouver is consistently named as one of the top five worldwide cities for livability and quality of life,[11][12] and the Economist Intelligence Unit acknowledged it as the first city ranked among the top-ten of the world's most well-living cities[13] for five consecutive years.[14] Vancouver has hosted many international conferences and events, including the 1954 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, UN Habitat I, Expo 86, the World Police and Fire Games in 1989 and 2009; and the 2010 Winter Olympics and Paralympics which were held in Vancouver and Whistler, a resort community 125 km (78 mi) north of the city.[15] In 2014, following thirty years in California, the TED conference made Vancouver its indefinite home. Several matches of the 2015 FIFA Women's World Cup were played in Vancouver, including the final at BC Place.[16]
The original settlement, named Gastown, grew up on clearcuts on the west edge of the Hastings Mill logging sawmill's property, where a makeshift tavern had been set up on a plank between two stumps and the proprietor, Gassy Jack, persuaded the curious millworkers to build him a tavern, on July 1, 1867. From that first enterprise, other stores and some hotels quickly appeared along the waterfront to the west. Gastown became formally laid out as a registered townsite dubbed Granville, B.I. ("B.I" standing for "Burrard Inlet"). As part of the land and political deal whereby the area of the townsite was made the railhead of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), it was renamed "Vancouver" and incorporated shortly thereafter as a city, in 1886. By 1887, the Canadian Pacific transcontinental railway was extended westward to the city to take advantage of its large natural seaport to the Pacific Ocean, which soon became a vital link in a trade route between the Orient / East Asia, Eastern Canada, and Europe.[17][18] As of 2014, Port Metro Vancouver is the third-largest port by tonnage in the Americas (recently displacing New York City), 27th in the world,[19] the busiest and largest in Canada, and the most diversified port in North America.[20] While forestry remains its largest industry, Vancouver is well known as an urban centre surrounded by nature, making tourism its second-largest industry.[21]
Major film production studios in Vancouver and nearby Burnaby have turned Greater Vancouver and nearby areas into one of the largest film production centres in North America,[22][23] earning it the nickname "Hollywood North".[24][25][26]
 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA
 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR
 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC
 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO
 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 New South Wales-NSW
New South Wales-NSW
 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON