
English Encyclopedia
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
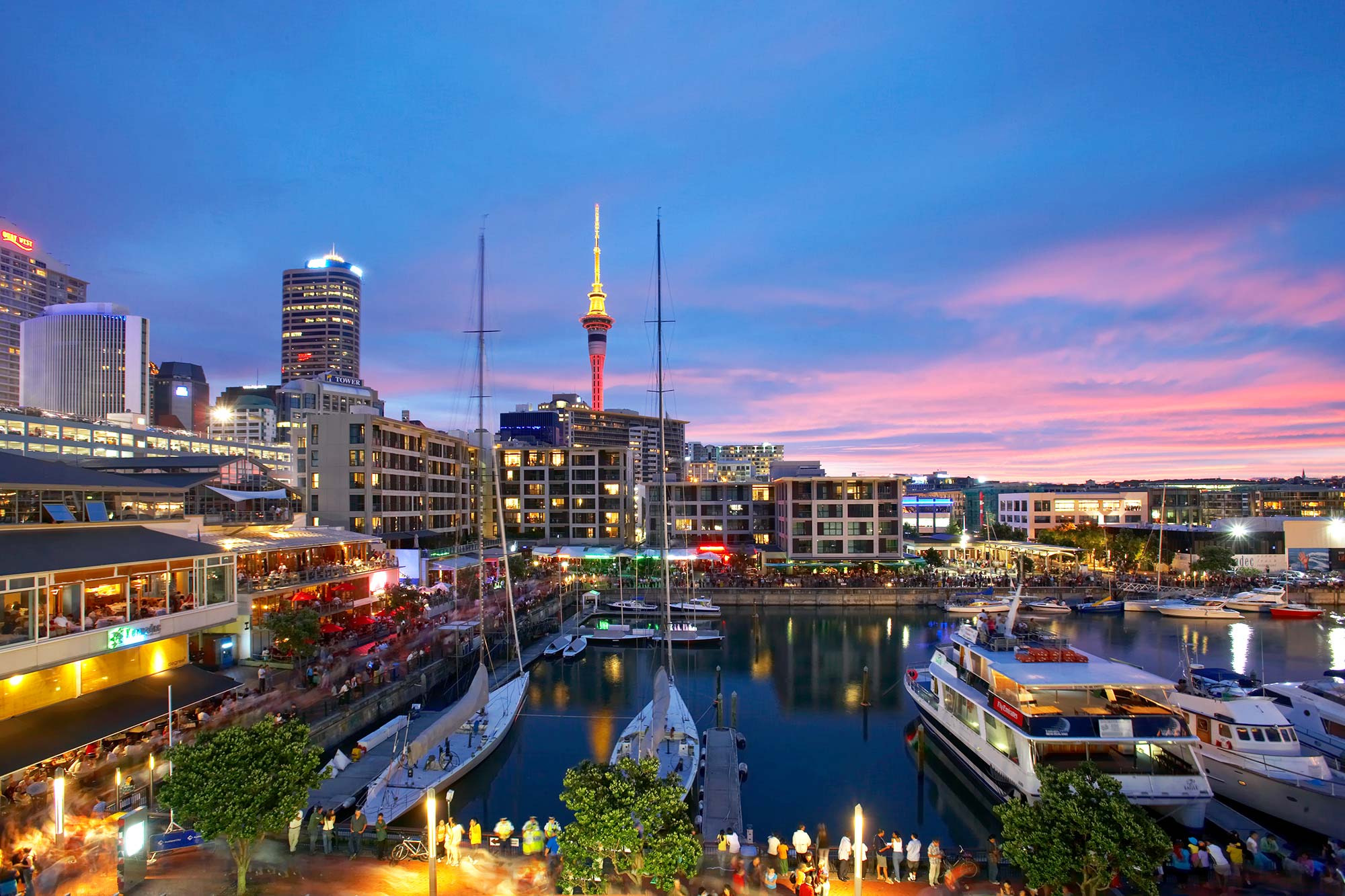

Auckland (Māori: Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country, Auckland has an urban population of about 1,463,000 (June 2021).[4] It is located in the Auckland Region—the area governed by Auckland Council—which includes outlying rural areas and the islands of the Hauraki Gulf, and which has a total population of 1,715,600.[4] While Europeans continue to make up the plurality of Auckland's population, the city became multicultural and cosmopolitan in the late-20th century, with Asians accounting for 31% of the city's population in 2018.[6] Auckland is also home to the largest Polynesian population in the world.[7] The Māori-language name for Auckland is Tāmaki Makaurau, meaning "Tāmaki desired by many", in reference to the desirability of its natural resources and geography.[8]
Auckland lies between the Hauraki Gulf to the east, the Hunua Ranges to the south-east, the Manukau Harbour to the south-west, and the Waitākere Ranges and smaller ranges to the west and north-west. The surrounding hills are covered in rainforest and the landscape is dotted with 53 volcanic centres that make up the Auckland Volcanic Field. The central part of the urban area occupies a narrow isthmus between the Manukau Harbour on the Tasman Sea and the Waitematā Harbour on the Pacific Ocean. Auckland is one of the few cities in the world to have a harbour on each of two separate major bodies of water.
The isthmus on which Auckland sits was first settled c. 1350 and was valued for its rich and fertile land. The Māori population in the area is estimated to have peaked at 20,000 before the arrival of Europeans.[9] After a British colony was established in New Zealand in 1840, William Hobson, then Lieutenant-Governor of New Zealand, chose Auckland as its new capital. He named the area for George Eden, Earl of Auckland, British First Lord of the Admiralty. Māori–European conflict over land in the region led to war in the mid-19th century. In 1865, Auckland was replaced by Wellington as the capital, but continued to grow, initially because of its port and the logging and gold-mining activities in its hinterland, and later because of pastoral farming (especially dairy farming) in the surrounding area, and manufacturing in the city itself.[10] It has been the nation's largest city throughout most of its history. Today, Auckland's central business district is New Zealand's leading economic hub.
The University of Auckland, founded in 1883, is the largest university in New Zealand. The city's significant tourist attractions include national historic sites, festivals, performing arts, sports activities, and a variety of cultural institutions, such as the Auckland War Memorial Museum, the Museum of Transport and Technology, and the Auckland Art Gallery Toi o Tāmaki. Its architectural landmarks include the Harbour Bridge, the Town Hall, the Ferry Building and the Sky Tower. The city is served by Auckland Airport, which handles around 2 million international passengers a month. Despite being one of the most expensive cities in the world,[11] Auckland is recognised as one of the world's most liveable cities, ranking third in the 2019 Mercer Quality of Living Survey and at first place in a 2021 ranking of the global liveability index by The Economist.
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1999
Women's Soccer World Cup 1999

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
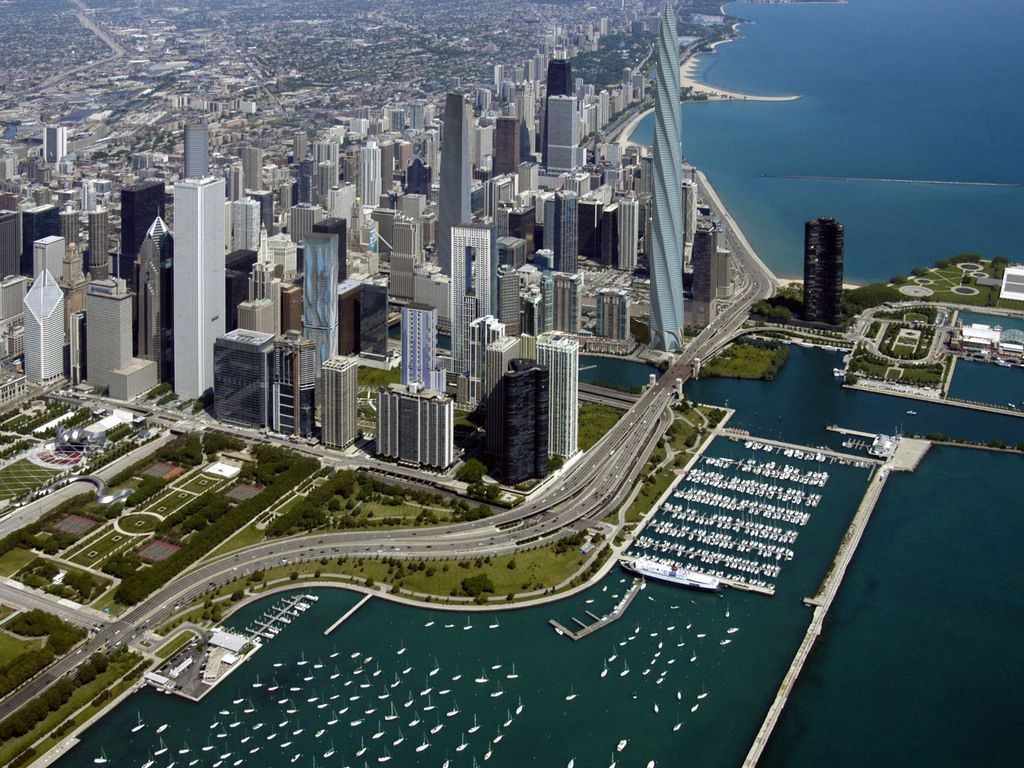


Chicago (/ʃɪˈkɑːɡoʊ/ ( listen), locally also /-ˈkɔː-/), officially the City of Chicago, located on the shores of freshwater Lake Michigan, is the third most populous city in America after New York and Los Angeles. As of the 2017 census-estimate, Chicago has a population of 2,716,450, which makes it the most populous city in both the state of Illinois and the Midwestern United States. It is the county seat of Cook County, the second most populous county in the U.S. Chicago is the principal city of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is often referred to as "Chicagoland." The Chicago metropolitan area has nearly 10 million people, is the third-largest in the United States, the fourth largest in North America, and the third largest metropolitan area in the world by land area. Chicago is the birthplace of the skyscraper, and considered the most influential architectural city of the 20th century.[6] In finance, the city saw the creation of the first standardized futures contracts at the Chicago Board of Trade; which today is the largest and most diverse derivatives market in the world, generating 20% of all volume in commodities and financial futures.[7]
listen), locally also /-ˈkɔː-/), officially the City of Chicago, located on the shores of freshwater Lake Michigan, is the third most populous city in America after New York and Los Angeles. As of the 2017 census-estimate, Chicago has a population of 2,716,450, which makes it the most populous city in both the state of Illinois and the Midwestern United States. It is the county seat of Cook County, the second most populous county in the U.S. Chicago is the principal city of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is often referred to as "Chicagoland." The Chicago metropolitan area has nearly 10 million people, is the third-largest in the United States, the fourth largest in North America, and the third largest metropolitan area in the world by land area. Chicago is the birthplace of the skyscraper, and considered the most influential architectural city of the 20th century.[6] In finance, the city saw the creation of the first standardized futures contracts at the Chicago Board of Trade; which today is the largest and most diverse derivatives market in the world, generating 20% of all volume in commodities and financial futures.[7]
Chicago was incorporated as a city in 1837 near a portage between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River watershed and grew rapidly in the mid-nineteenth century.[8] After the Great Chicago Fire of 1871, which destroyed several square miles and left more than 100,000 homeless, the city made a concerted effort to rebuild.[9] The construction boom accelerated population growth throughout the following decades, and by 1900 Chicago was one of the five largest cities in the world.[10] During this period, Chicago made noted contributions to urban planning and zoning standards, which included creating new construction styles (including the Chicago School of architecture), the development of the City Beautiful Movement, and the steel-framed skyscraper.[11]
Positioned along Lake Michigan, the city is an international hub for finance, commerce, industry, technology, telecommunications, and transportation. O'Hare International Airport is the one of the busiest airports in the world, and the region also has the largest number of U.S. highways and railroad freight.[12] In 2012, Chicago was listed as an alpha global city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network,[13] and it ranked seventh in the entire world in the 2017 Global Cities Index.[14] Chicago has the fourth-largest gross metropolitan product in the world — generating about $670.5 billion according to September 2017 estimates — ranking it after the metropolitan areas of Tokyo, New York City, and Los Angeles, and ranking ahead of number five London and number six Paris.[15] Chicago has one of the world's largest and most diversified and balanced economies, not being dependent on any one industry, with no single industry employing more than 14% of the workforce.[16]
Chicago was the second most visited city in the United States with 55 million domestic and international visitors,[17][18] not far behind the 62 million visitors to New York City in 2017.[19] The city ranked first place in the 2018 Time Out City Life Index, a global quality of life survey of 15,000 people in 32 cities.[20][21][22][23][24] Landmarks in the city include Millennium Park, Navy Pier, the Magnificent Mile, the Art Institute of Chicago, Museum Campus, the Willis (Sears) Tower, the Museum of Science and Industry, and Lincoln Park Zoo. Chicago's culture includes the visual arts, literature, film, theater, comedy (especially improvisational comedy), food, and music, particularly jazz, blues, soul, hip-hop, gospel,[25] and electronic dance music including house music. There are many colleges and universities in the Chicago area, of which the University of Chicago, Northwestern University, and the University of Illinois at Chicago are classified as "highest research" doctoral universities.
Chicago has professional sports teams in each of the major professional leagues, including two Major League Baseball teams. The city has had several nicknames throughout its history such as the Windy City, Chi-Town, Second City, and the City of the Big Shoulders, referring to its numerous towers and skyscrapers.[26]
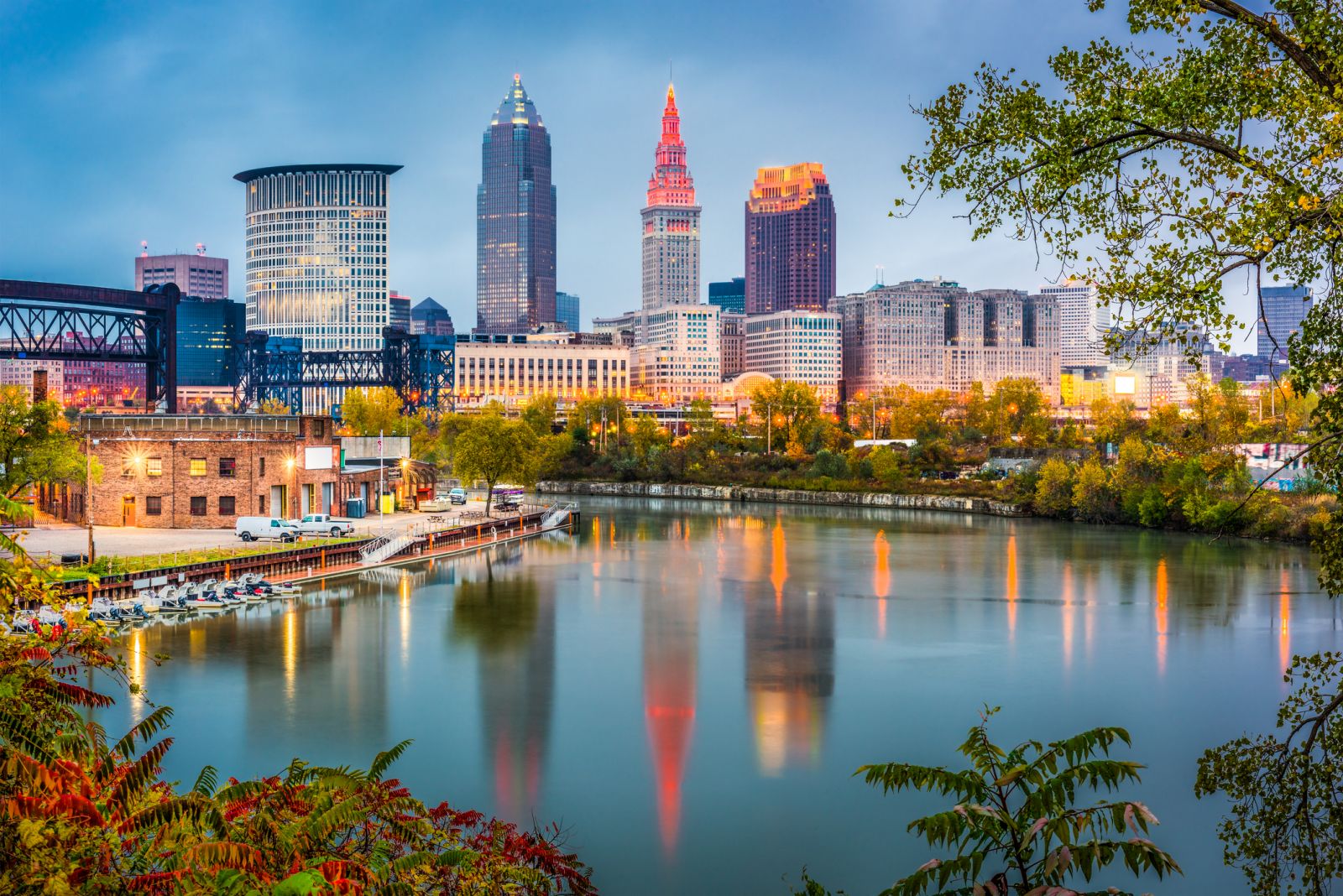

Cleveland (/ˈkliːvlənd/ KLEEV-lənd), officially the City of Cleveland, is a major city in the U.S. state of Ohio, and the county seat of Cuyahoga County.[7] It is located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U.S. maritime border with Canada and approximately 60 miles (100 kilometers) west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania state border.
The largest city on Lake Erie and one of the most populous urban areas in the country,[8] Cleveland anchors the Greater Cleveland Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) and the Cleveland–Akron–Canton Combined Statistical Area (CSA). The CSA is the most populous combined statistical area in Ohio and the 17th largest in the United States, with a population of 3,633,962 in 2020.[9][10] The city proper, with a 2020 population of 372,624, ranks as the 54th-largest city in the U.S.,[11] as a larger portion of the metropolitan population lives outside the central city. The seven-county metropolitan Cleveland economy, which includes Akron, is the largest in the state.
Cleveland was founded in 1796 near the mouth of the Cuyahoga River by General Moses Cleaveland, after whom the city was named. It grew into a major manufacturing center due to its location on both the river and the lake shore, as well as numerous canals and railroad lines. A port city, Cleveland is connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence Seaway. The city's economy relies on diversified sectors such as manufacturing, financial services, healthcare, biomedicals, and higher education.[12] The gross domestic product (GDP) for the Greater Cleveland MSA was $135 billion in 2019.[13] Combined with the Akron MSA, the seven-county Cleveland–Akron metropolitan economy was $175 billion in 2019, the largest in Ohio, accounting for 25% of the state's GDP.[13]
Designated as a "Gamma -" global city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network,[14] the city's major cultural institutions include the Cleveland Museum of Art, the Cleveland Museum of Natural History, the Cleveland Orchestra, Playhouse Square, and the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame. Known as "The Forest City" among many other nicknames, Cleveland serves as the center of the Cleveland Metroparks nature reserve system.[15] The city's major league professional sports teams include the Cleveland Browns, the Cleveland Cavaliers, and the Cleveland Guardians.

 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Canada
Canada

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
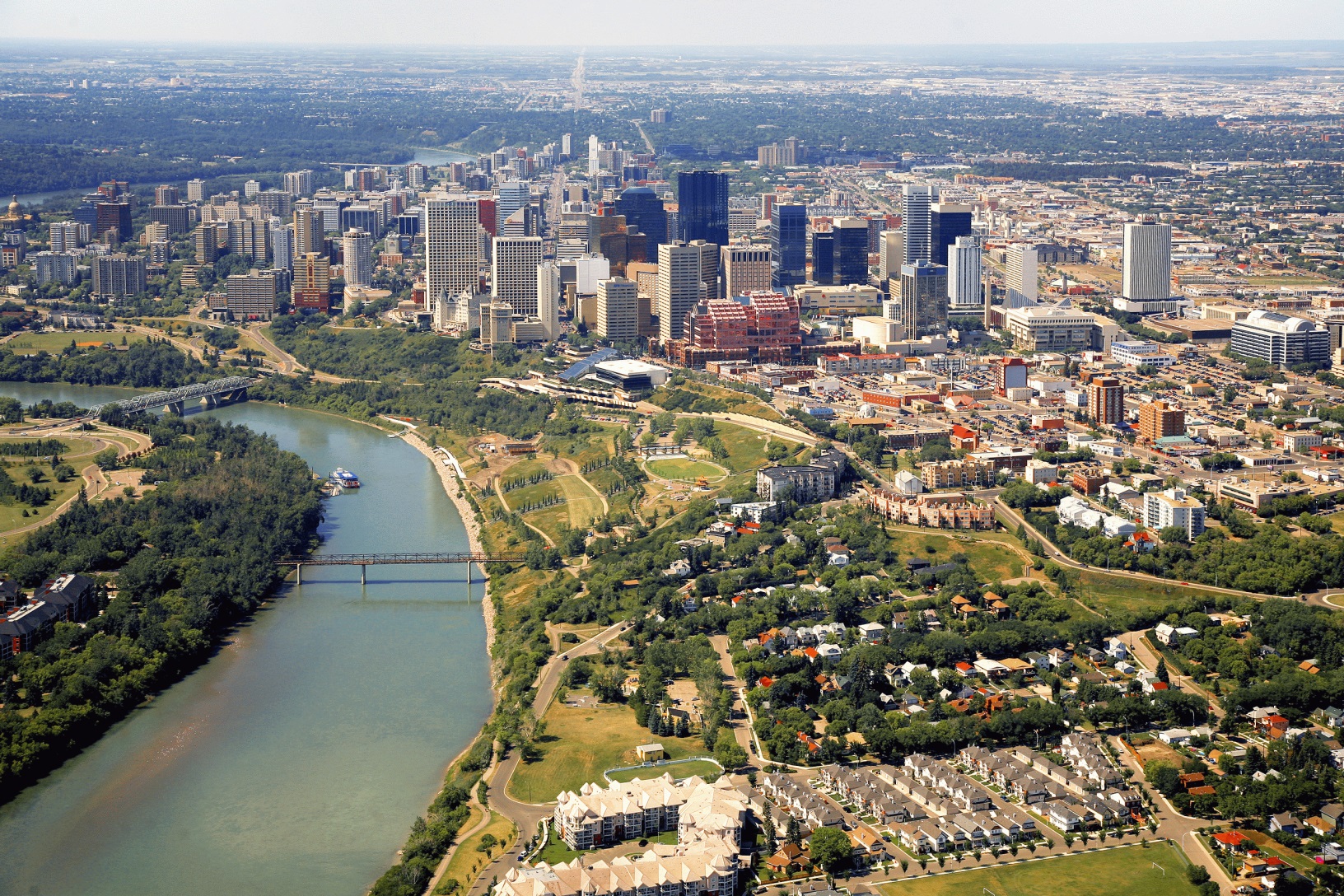

Edmonton (/ˈɛdməntən/ ( listen) ED-mən-tən) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the north end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor".[14]
listen) ED-mən-tən) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the north end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor".[14]
As of 2021, Edmonton had a city population of 1,010,899 and a metropolitan population of 1,418,118, making it the fifth-largest city[15][16] and sixth-largest metropolitan area (CMA) in Canada.[17][18] Edmonton is North America's northernmost city and metropolitan area with a population over one million. A resident of Edmonton is known as an Edmontonian.[19]
Edmonton's historic growth has been facilitated through the absorption of five adjacent urban municipalities (Strathcona, North Edmonton, West Edmonton, Beverly and Jasper Place)[20] in addition to a series of annexations through 1982,[21] and the annexation of 8,260 ha (82.6 km2; 31.9 sq mi) of land from Leduc County and the City of Beaumont on January 1, 2019.[22] Known as the "Gateway to the North",[23] the city is a staging point for large-scale oil sands projects occurring in northern Alberta and large-scale diamond mining operations in the Northwest Territories.[24]
Edmonton is a cultural, governmental and educational centre. It hosts a year-round slate of festivals, reflected in the nickname "Canada's Festival City".[1] It is home to North America's second largest mall, West Edmonton Mall (the world's largest mall from 1981 until 2004),[25][26][27] and Fort Edmonton Park, Canada's largest living history museum.
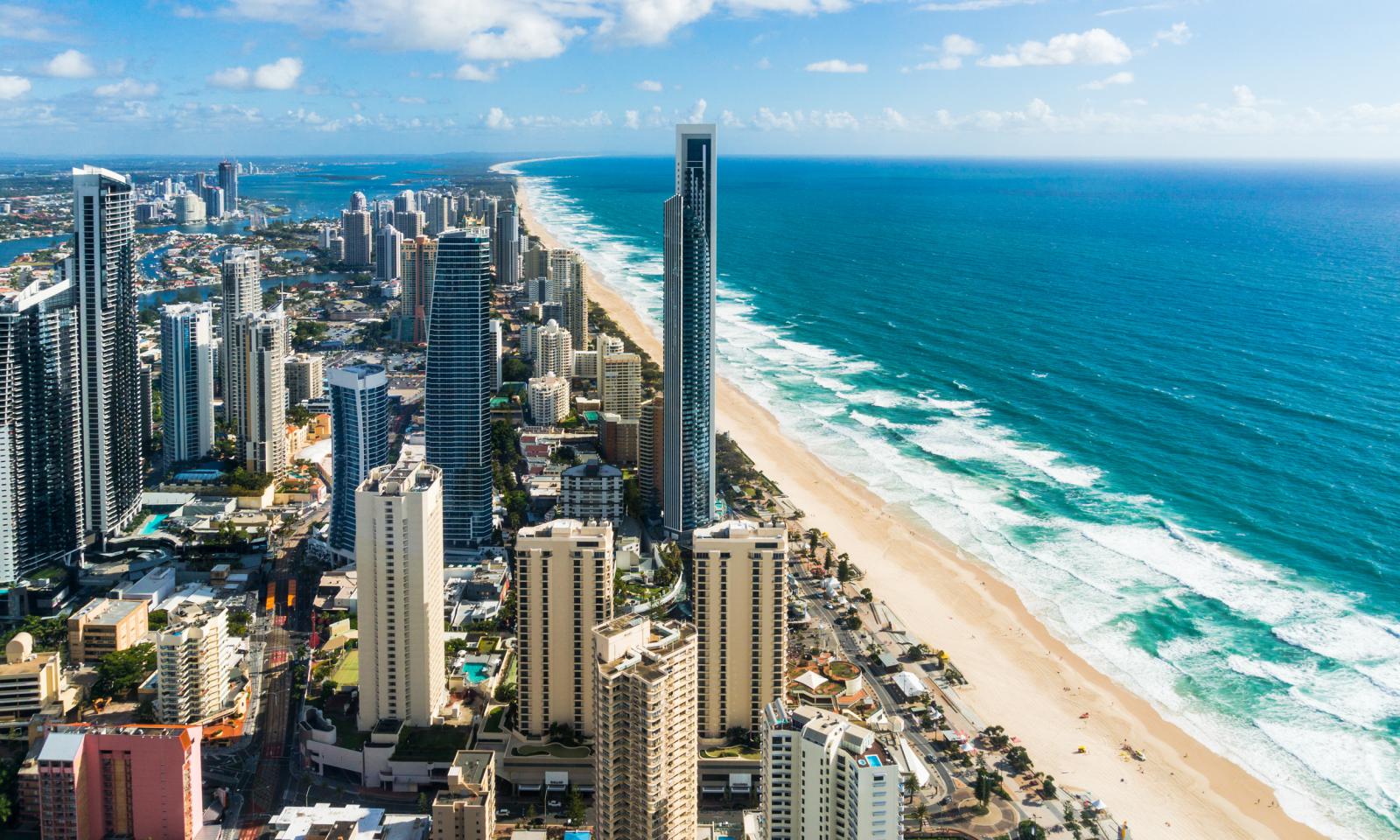

The Gold Coast is a coastal city in the state of Queensland, Australia, approximately 66 kilometres (41 mi) south-southeast of the centre of the state capital Brisbane and immediately north of the border with New South Wales. The area was previously occupied prior to European settlement by the Yugambeh language people. The demonym for the Gold Coast is Gold Coaster. With an estimated population of 679,127[1] in June 2018 (including 79,001 in the adjacent Tweed Valley of New South Wales), the Gold Coast is the sixth-largest city in Australia, Australia's largest non-capital city, and Queensland's second-largest city.[3]
The Gold Coast is a major tourist destination with a sunny, subtropical climate and has become widely known for its world-class surfing beaches, high-rise dominated skyline, theme parks, nightlife, and rainforest hinterland. The city is part of the nation's entertainment industry with television productions and a major film industry.

 Architecture
Architecture
 England
England
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History
 J 0 - 500 AD
J 0 - 500 AD

 History
History
 K 500 - 1000 AD
K 500 - 1000 AD

 History
History
 L 1000 - 1500 AD
L 1000 - 1500 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Medieval cities in Europe
Medieval cities in Europe
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
 1908 Summer Olympics
1908 Summer Olympics
 1944 Summer Olympics
1944 Summer Olympics
 1948 Summer Olympics
1948 Summer Olympics
 2012 Summer Olympics
2012 Summer Olympics
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Important port
Important port
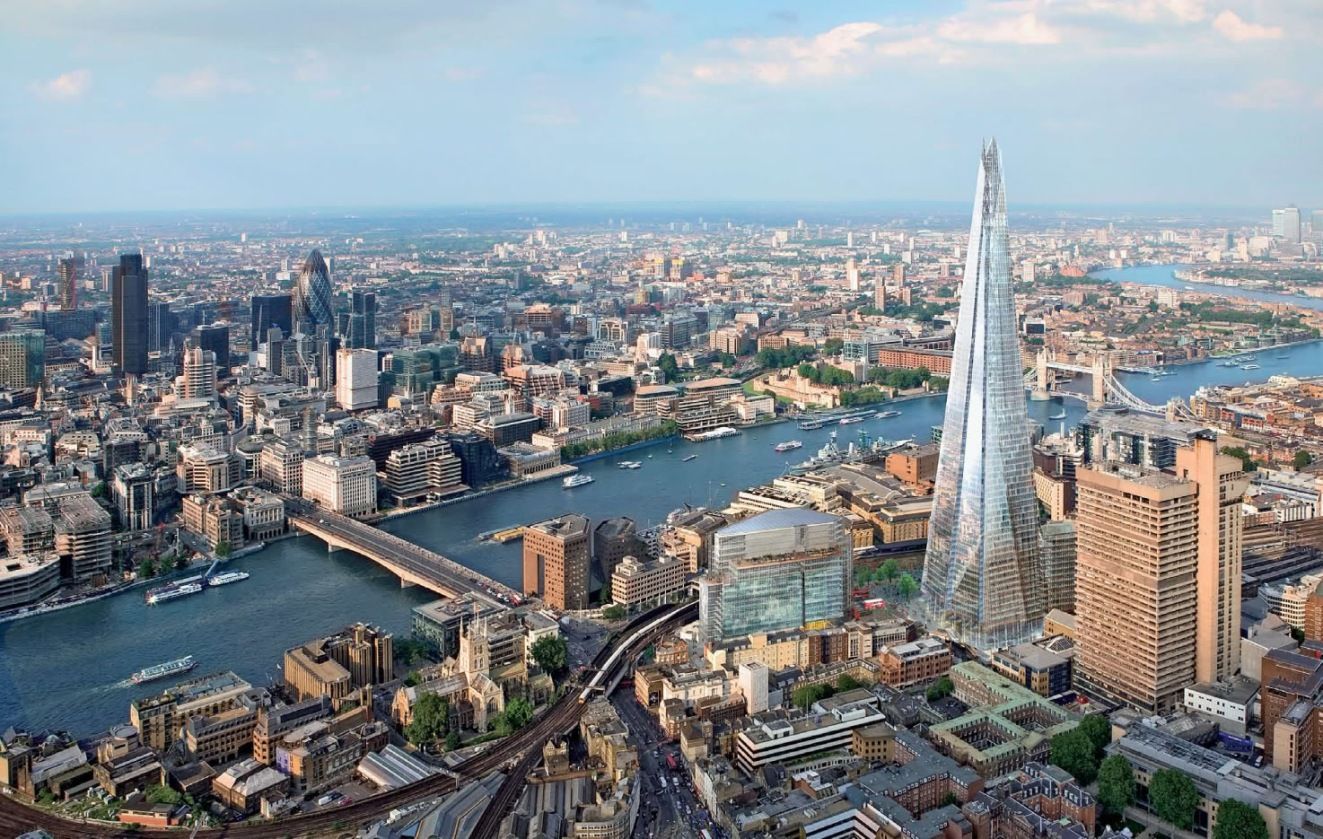

London (/ˈlʌndən/ ( listen) LUN-dən) is the capital and most populous city of England and the United Kingdom.[8][9] Standing on the River Thames in the south east of the island of Great Britain, London has been a major settlement for two millennia. It was founded by the Romans, who named it Londinium.[10] London's ancient core, the City of London, largely retains its 1.12-square-mile (2.9 km2) medieval boundaries. Since at least the 19th century, "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent and Hertfordshire,[11][12][13] which today largely makes up Greater London,[14][15][note 1] a region governed by the Mayor of London and the London Assembly.[16][note 2][17]
listen) LUN-dən) is the capital and most populous city of England and the United Kingdom.[8][9] Standing on the River Thames in the south east of the island of Great Britain, London has been a major settlement for two millennia. It was founded by the Romans, who named it Londinium.[10] London's ancient core, the City of London, largely retains its 1.12-square-mile (2.9 km2) medieval boundaries. Since at least the 19th century, "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent and Hertfordshire,[11][12][13] which today largely makes up Greater London,[14][15][note 1] a region governed by the Mayor of London and the London Assembly.[16][note 2][17]
London is one of the leading global cities[18][19] in the arts, commerce, education, entertainment, fashion, finance, healthcare, media, professional services, research and development, tourism and transportation.[20][21][22] It is the world's largest financial centre[23][24][25][26] and has the fifth or sixth largest metropolitan area GDP in the world.[note 3][27][28] London is often regarded as a world cultural capital.[29][30][31] It is the world's most-visited city as measured by international arrivals[32] and has the world's largest city airport system measured by passenger traffic.[33] It is the world's leading investment destination,[34][35][36][37] hosting more international retailers[38][39] and ultra high-net-worth individuals[40][41] than any other city. London's universities form the largest concentration of higher education institutes in Europe.[42] In 2012, London became the first city to have hosted the modern Summer Olympic Games three times.[43]
London has a diverse range of people and cultures, and more than 300 languages are spoken in the region.[44] Its estimated mid-2016 municipal population (corresponding to Greater London) was 8,787,892,[4] the largest of any city in the European Union[45] and accounting for 13.4% of the UK population.[46] London's urban area is the second most populous in the EU, after Paris, with 9,787,426 inhabitants at the 2011 census.[47] The city's metropolitan area is the most populous in the EU with 14,040,163 inhabitants in 2016,[note 4][3] while the Greater London Authority states the population of the city-region (covering a large part of the south east) as 22.7 million.[48][49] London was the world's most populous city from around 1831 to 1925.[50]
London contains four World Heritage Sites: the Tower of London; Kew Gardens; the site comprising the Palace of Westminster, Westminster Abbey, and St Margaret's Church; and the historic settlement of Greenwich (in which the Royal Observatory, Greenwich defines the Prime Meridian, 0° longitude, and GMT).[51] Other landmarks include Buckingham Palace, the London Eye, Piccadilly Circus, St Paul's Cathedral, Tower Bridge, Trafalgar Square and The Shard. London is home to numerous museums, galleries, libraries, sporting events and other cultural institutions, including the British Museum, National Gallery, Natural History Museum, Tate Modern, British Library and West End theatres.[52] The London Underground is the oldest underground railway network in the world.
 England
England
 Manchester
Manchester

 History
History
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 Important port
Important port
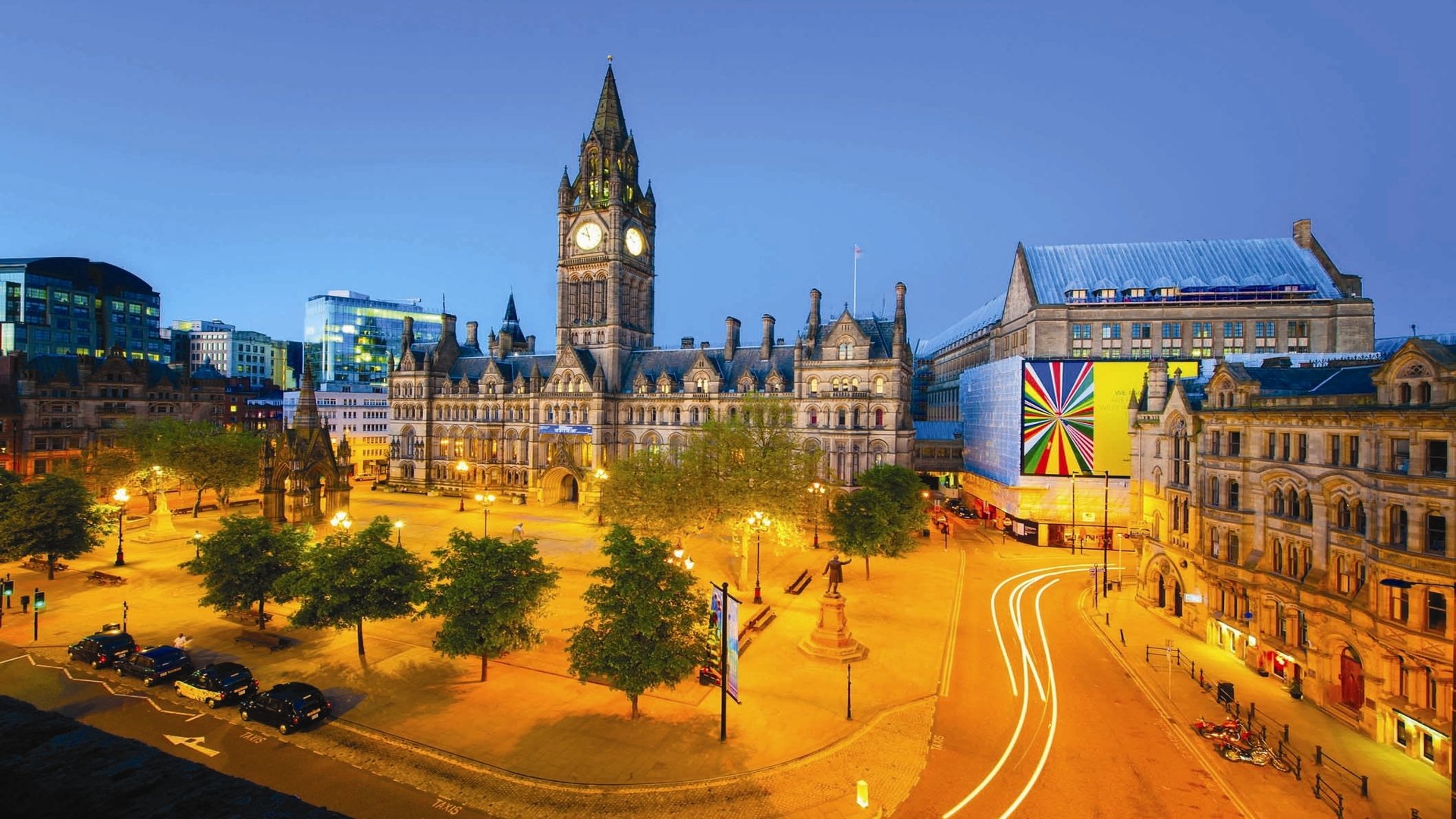

Manchester (/ˈmæntʃɪstər, -tʃɛs-/)[5][6] is a city and metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England, with a population of 545,500 as of 2017.[7] It lies within the United Kingdom's third-most populous metropolitan area, with a population of 3.2 million.[8] Manchester is fringed by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and an arc of towns with which it forms a continuous conurbation. The local authority is Manchester City Council.
The recorded history of Manchester began with the civilian settlement associated with the Roman fort of Mamucium or Mancunium, which was established in about AD 79 on a sandstone bluff near the confluence of the rivers Medlock and Irwell. It was historically a part of Lancashire, although areas of Cheshire south of the River Mersey were incorporated in the 20th century.[9] Throughout the Middle Ages Manchester remained a manorial township but began to expand "at an astonishing rate" around the turn of the 19th century. Manchester's unplanned urbanisation was brought on by a boom in textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution,[10] and resulted in it becoming the world's first industrialised city.[11]
Manchester achieved city status in 1853. The Manchester Ship Canal opened in 1894, creating the Port of Manchester and directly linking the city to the Irish Sea, 36 miles (58 km) to the west. Its fortune declined after the Second World War, owing to deindustrialisation, but the IRA bombing in 1996 led to extensive investment and regeneration.[12]
In 2014, the Globalization and World Cities Research Network ranked Manchester as a beta world city, the highest-ranked British city apart from London.[13] Manchester is the third-most visited city in the UK, after London and Edinburgh.[14] It is notable for its architecture, culture, musical exports, media links, scientific and engineering output, social impact, sports clubs and transport connections. Manchester Liverpool Road railway station was the world's first inter-city passenger railway station; scientists first split the atom, developed the stored-program computer and produced graphene in the city. Manchester hosted the 2002 Commonwealth Games.


 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon

 Important port
Important port
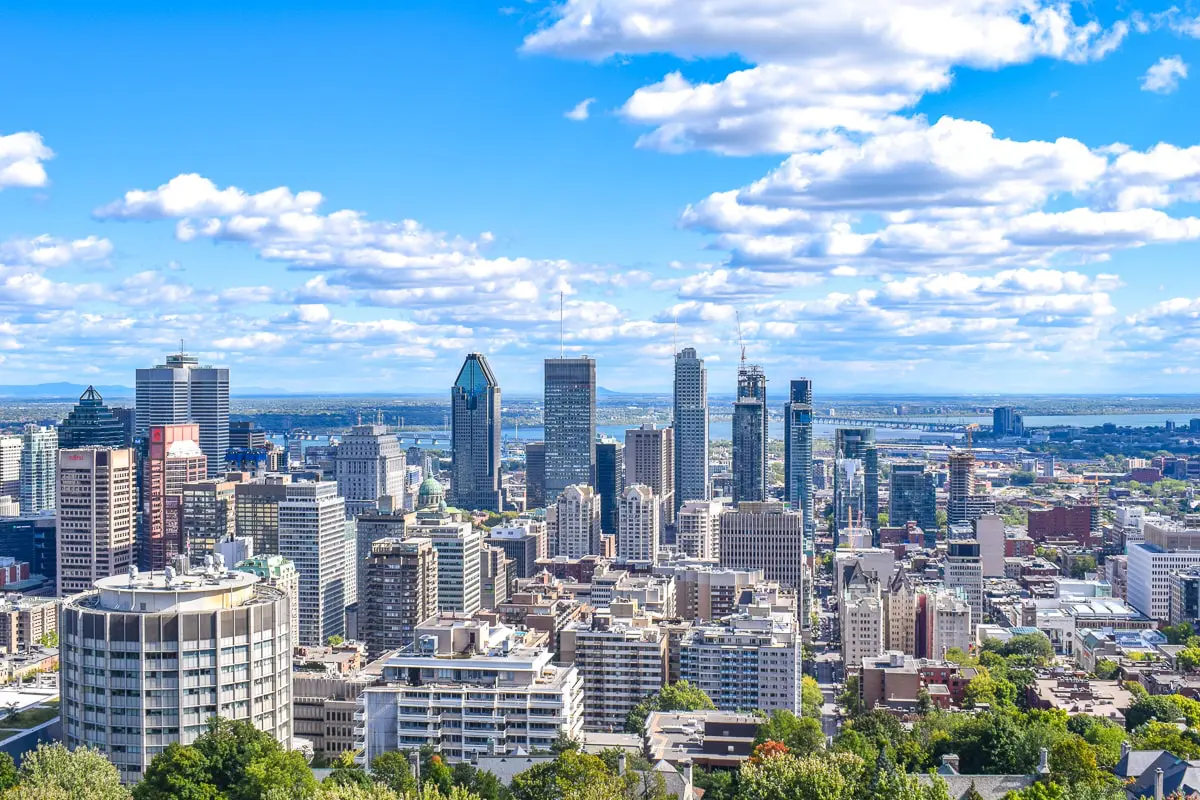

Montreal (/ˌmʌntriˈɔːl/ ( listen) MUN-tree-AWL;[14] French: [mɔ̃ʁeal] (
listen) MUN-tree-AWL;[14] French: [mɔ̃ʁeal] ( listen); officially Montréal) is the most populous municipality in the Canadian province of Quebec and the second-most populous municipality in Canada. Originally called Ville-Marie, or "City of Mary",[15] it is named after Mount Royal,[16] the triple-peaked hill in the heart of the city. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which took its name from the same source as the city,[17][18] and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. It has a distinct four-season continental climate with warm to hot summers and cold, snowy winters.[19]
listen); officially Montréal) is the most populous municipality in the Canadian province of Quebec and the second-most populous municipality in Canada. Originally called Ville-Marie, or "City of Mary",[15] it is named after Mount Royal,[16] the triple-peaked hill in the heart of the city. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which took its name from the same source as the city,[17][18] and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. It has a distinct four-season continental climate with warm to hot summers and cold, snowy winters.[19]
In 2016, the city had a population of 1,704,694,[9] with a population of 1,942,044 in the urban agglomeration, including all of the other municipalities on the Island of Montreal.[9] The broader metropolitan area had a population of 4,098,927.[11] French is the city's official language[20][21] and is the language spoken at home by 49.8% of the population of the city, followed by English at 22.8% and 18.3% other languages (in the 2016 census, not including multi-language responses).[9] In the larger Montreal Census Metropolitan Area, 65.8% of the population speaks French at home, compared to 15.3% who speak English.[11] The agglomeration Montreal is one of the most bilingual cities in Quebec and Canada, with over 59% of the population able to speak both English and French.[9] Montreal is the second-largest primarily French-speaking city in the world, after Paris.[22][23][24][25] It is situated 258 kilometres (160 mi) south-west of Quebec City.
Historically the commercial capital of Canada, Montreal was surpassed in population and in economic strength by Toronto in the 1970s.[26] It remains an important centre of commerce, aerospace, transport, finance, pharmaceuticals, technology, design, education, art, culture, tourism, food, fashion, gaming, film, and world affairs. Montreal has the second-highest number of consulates in North America,[27] serves as the location of the headquarters of the International Civil Aviation Organization, and was named a UNESCO City of Design in 2006.[28][29] In 2017, Montreal was ranked the 12th most liveable city in the world by the Economist Intelligence Unit in its annual Global Liveability Ranking,[30] and the best city in the world to be a university student in the QS World University Rankings.[31]
Montreal has hosted multiple international conferences and events, including the 1967 International and Universal Exposition and the 1976 Summer Olympics.[32][33] It is the only Canadian city to have held the Summer Olympics. In 2018, Montreal was ranked as an Alpha− world city.[34] As of 2016 the city hosts the Canadian Grand Prix of Formula One,[35] the Montreal International Jazz Festival[36] and the Just for Laughs festival.[37]
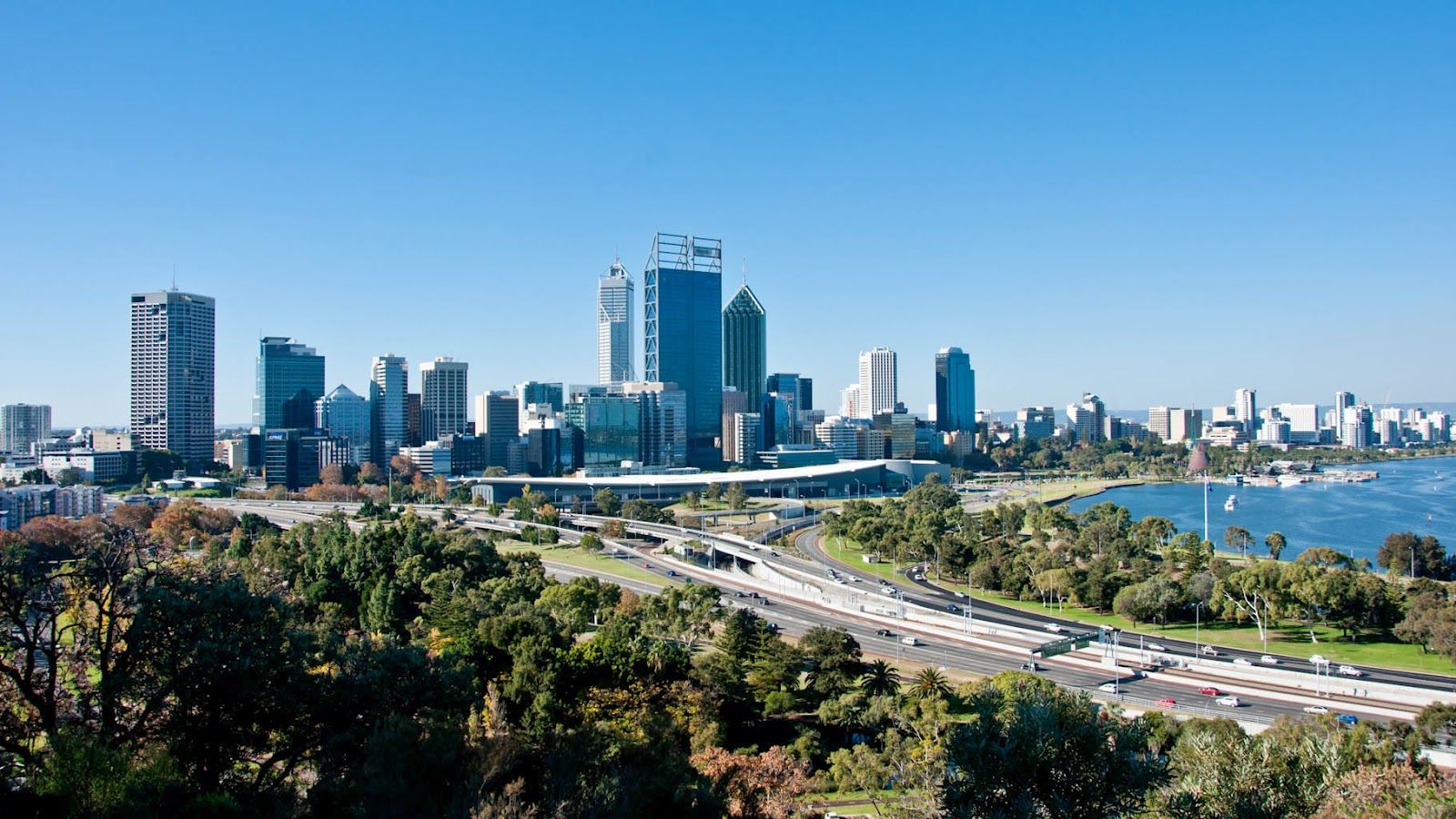

Perth (/pɜːrθ/ ( listen)) is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia (WA).[8] It is the fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020.[1] Perth is part of the South West Land Division of Western Australia, with most of the metropolitan area on the Swan Coastal Plain between the Indian Ocean and the Darling Scarp. The city has expanded outward from the original British settlements on the Swan River, upon which the city's central business district and port of Fremantle are situated. Perth is located on the traditional lands of the Whadjuk Noongar people, where Aboriginal Australians have lived for at least 38,000 years.
listen)) is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia (WA).[8] It is the fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020.[1] Perth is part of the South West Land Division of Western Australia, with most of the metropolitan area on the Swan Coastal Plain between the Indian Ocean and the Darling Scarp. The city has expanded outward from the original British settlements on the Swan River, upon which the city's central business district and port of Fremantle are situated. Perth is located on the traditional lands of the Whadjuk Noongar people, where Aboriginal Australians have lived for at least 38,000 years.
Captain James Stirling founded Perth in 1829 as the administrative centre of the Swan River Colony. It was named after the city of Perth in Scotland, due to the influence of Stirling's patron Sir George Murray, who had connections with the area. It gained city status in 1856, although the Perth City Council currently governs only a small area around the central business district. The city's population increased substantially as a result of the Western Australian gold rushes in the late 19th century. It has grown steadily since World War II due to a high net migration rate. Post-war immigrants were predominantly from Britain and Southern Europe, while more recent arrivals have led to a large population of Asian descent. Several mining booms in other parts of Western Australia in the late 20th and early 21st centuries saw Perth become the regional headquarters for large mining operations.
Perth contains a number of important public buildings as well as various historic sites. Notable government buildings include Parliament House, Government House, the Supreme Court Buildings and the Perth Mint. The city is served by Fremantle Harbour and Perth Airport. It was a naval base for the Allies during World War II and the Royal Australian Navy's Fleet Base West is located on Garden Island. All five of Western Australia's universities are based in Perth. The city has been ranked as one of the world's most liveable cities, and was classified by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network in 2020 as a Beta global city.[9]
As of 2021, Perth is divided into 30 local government areas and consists of more than 350 suburbs. The metropolitan boundaries stretch 123 kilometres (76 mi) from Two Rocks in the north to Singleton in the south,[10] and 62 kilometres (39 mi) east inland to The Lakes. Outside of the central business district, important urban centres within the metropolitan area include Armadale, Fremantle, Joondalup, Midland, and Rockingham. Most of those were originally established as separate settlements and retained a distinct identity after being subsumed into the wider metropolitan area. Mandurah, Western Australia's second-largest city, forms a conurbation with Perth along the coast, though for most purposes it is still considered a separate city.

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC

 Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Winter Olympics
Winter Olympics
 Ski vacation
Ski vacation

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon

 Important port
Important port
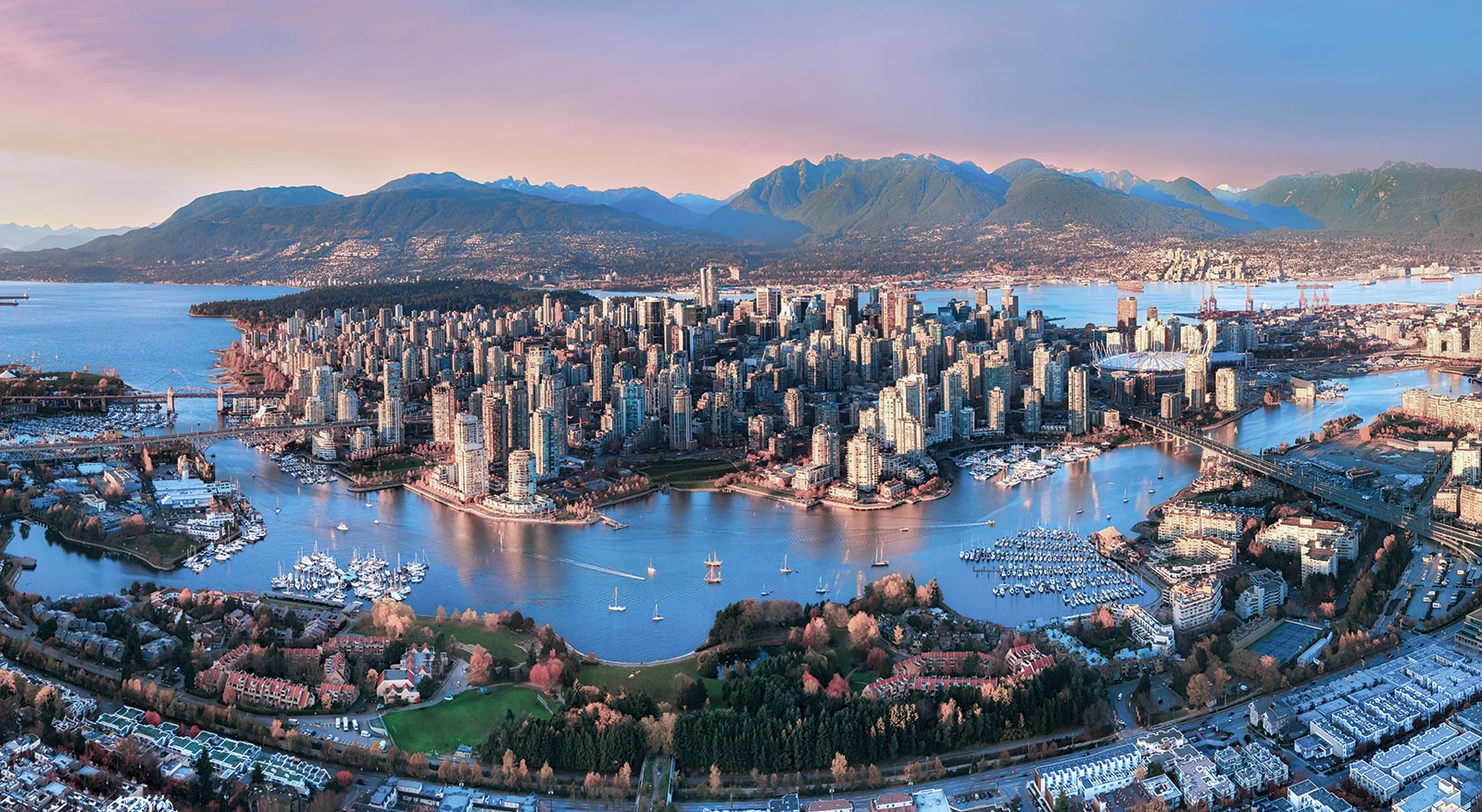 Vancouver (/vænˈkuːvər/ (
Vancouver (/vænˈkuːvər/ ( listen)) is a coastal seaport city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2016 census recorded 631,486 people in the city, up from 603,502 in 2011. The Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2,463,431 in 2016, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada with over 5,400 people per square kilometre,[5][6] which makes it the fifth-most densely populated city with over 250,000 residents in North America behind New York City, Guadalajara, San Francisco,[7] and Mexico City according to the 2011 census. Vancouver is one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities in Canada according to that census; 52% of its residents have a first language other than English.[8][9] Roughly 30% of the city's inhabitants are of Chinese heritage.[10] Vancouver is classed as a Beta global city.
listen)) is a coastal seaport city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2016 census recorded 631,486 people in the city, up from 603,502 in 2011. The Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2,463,431 in 2016, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada with over 5,400 people per square kilometre,[5][6] which makes it the fifth-most densely populated city with over 250,000 residents in North America behind New York City, Guadalajara, San Francisco,[7] and Mexico City according to the 2011 census. Vancouver is one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities in Canada according to that census; 52% of its residents have a first language other than English.[8][9] Roughly 30% of the city's inhabitants are of Chinese heritage.[10] Vancouver is classed as a Beta global city.
Vancouver is consistently named as one of the top five worldwide cities for livability and quality of life,[11][12] and the Economist Intelligence Unit acknowledged it as the first city ranked among the top-ten of the world's most well-living cities[13] for five consecutive years.[14] Vancouver has hosted many international conferences and events, including the 1954 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, UN Habitat I, Expo 86, the World Police and Fire Games in 1989 and 2009; and the 2010 Winter Olympics and Paralympics which were held in Vancouver and Whistler, a resort community 125 km (78 mi) north of the city.[15] In 2014, following thirty years in California, the TED conference made Vancouver its indefinite home. Several matches of the 2015 FIFA Women's World Cup were played in Vancouver, including the final at BC Place.[16]
The original settlement, named Gastown, grew up on clearcuts on the west edge of the Hastings Mill logging sawmill's property, where a makeshift tavern had been set up on a plank between two stumps and the proprietor, Gassy Jack, persuaded the curious millworkers to build him a tavern, on July 1, 1867. From that first enterprise, other stores and some hotels quickly appeared along the waterfront to the west. Gastown became formally laid out as a registered townsite dubbed Granville, B.I. ("B.I" standing for "Burrard Inlet"). As part of the land and political deal whereby the area of the townsite was made the railhead of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), it was renamed "Vancouver" and incorporated shortly thereafter as a city, in 1886. By 1887, the Canadian Pacific transcontinental railway was extended westward to the city to take advantage of its large natural seaport to the Pacific Ocean, which soon became a vital link in a trade route between the Orient / East Asia, Eastern Canada, and Europe.[17][18] As of 2014, Port Metro Vancouver is the third-largest port by tonnage in the Americas (recently displacing New York City), 27th in the world,[19] the busiest and largest in Canada, and the most diversified port in North America.[20] While forestry remains its largest industry, Vancouver is well known as an urban centre surrounded by nature, making tourism its second-largest industry.[21]
Major film production studios in Vancouver and nearby Burnaby have turned Greater Vancouver and nearby areas into one of the largest film production centres in North America,[22][23] earning it the nickname "Hollywood North".[24][25][26]
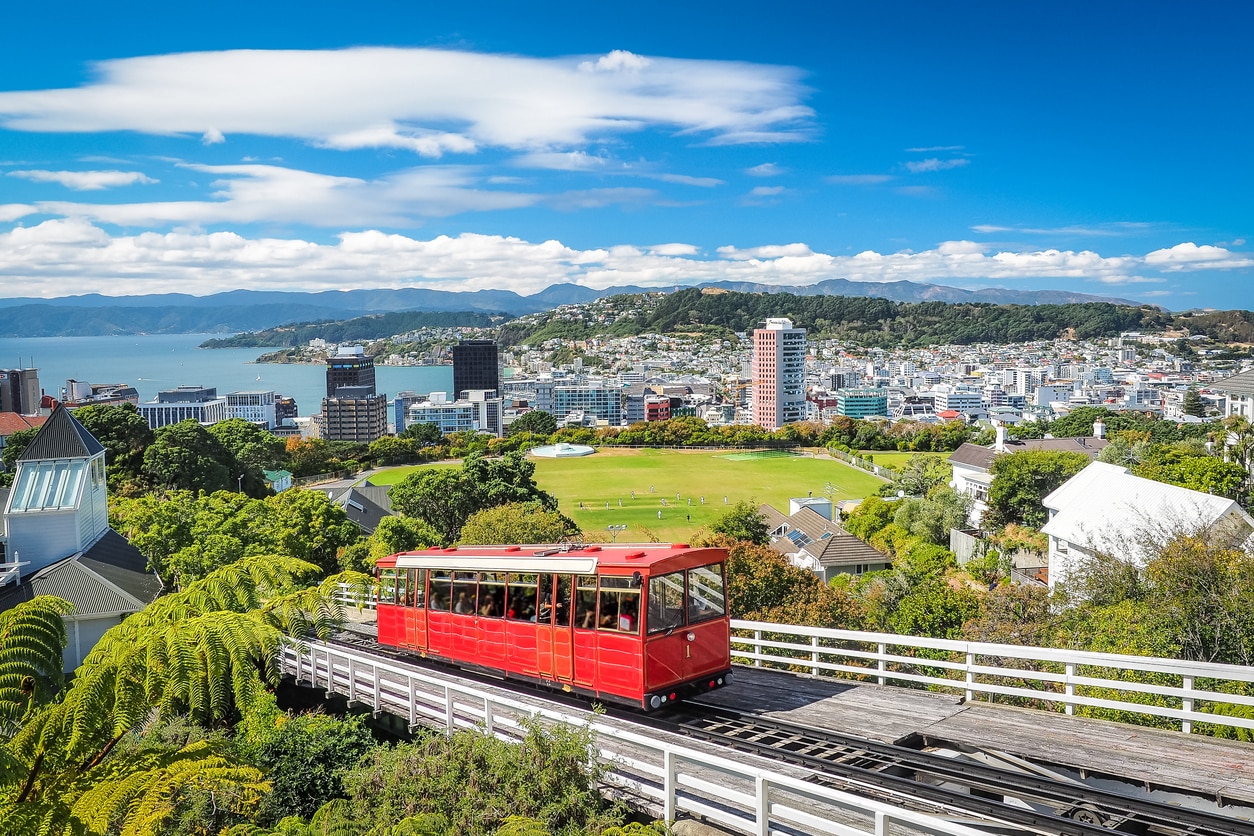

Wellington (Māori: Te Whanganui-a-Tara [tɛ ˈfaŋanʉi a taɾa]) is the capital city and second most populous urban area of New Zealand, with 418,500 residents.[3] It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the major population centre of the southern North Island, and is the administrative centre of the Wellington Region, which also includes the Kapiti Coast and Wairarapa. Its latitude is 41°17′S, making it the world's southernmost capital of a sovereign state.[4] Wellington features a temperate maritime climate and is the world's windiest city, with an average wind speed of over 26 km/h (16 mph).[5]
The Wellington urban area comprises four local authorities: Wellington City, on the peninsula between Cook Strait and Wellington Harbour, contains the central business district and about half the population; Porirua on Porirua Harbour to the north is notable for its large Māori and Pacific Island communities; Lower Hutt and Upper Hutt are largely suburban areas to the northeast, together known as the Hutt Valley.
Situated near the geographic centre of the country, Wellington was well placed for trade. In 1839 it was chosen as the first major planned settlement for British immigrants coming to New Zealand. The settlement was named in honour of Arthur Wellesley, the first Duke of Wellington and victor of the Battle of Waterloo.
As the nation's capital since 1865, the New Zealand Government and Parliament, Supreme Court and most of the public service are based in the city. Architectural sights include the Government Building—one of the largest wooden buildings in the world—as well as the iconic Beehive. Wellington is also home to several of the largest and oldest cultural institutions in the nation such the National Archives, the National Library, the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa, and numerous theatres. It plays host to many artistic and cultural organisations, including the New Zealand Symphony Orchestra and Royal New Zealand Ballet. One of the world's most liveable cities, the 2014 Mercer Quality of Living Survey ranked Wellington 12th in the world.[6]
Wellington's economy is primarily service-based, with an emphasis on finance, business services, and government. It is the centre of New Zealand's film and special effects industries, and increasingly a hub for information technology and innovation,[7] with two public research universities. Wellington is one of New Zealand's chief seaports and serves both domestic and international shipping. The city is served by Wellington International Airport, the third busiest airport in the country. Wellington's transport network includes train and bus lines which reach as far as the Kapiti Coast and Wairarapa, and ferries connect the city to the South Island.
 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH
 Queensland-QLD
Queensland-QLD
 Western Australia-WA
Western Australia-WA