
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 2015年女子世界杯足球赛
2015年女子世界杯足球赛
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019
 亚洲足球联合会
亚洲足球联合会
 中北美洲及加勒比海足球协会
中北美洲及加勒比海足球协会
 南美洲足球协会
南美洲足球协会
 非洲足球协会
非洲足球协会
 国际足球联合会
国际足球联合会
 1990年世界杯足球赛
1990年世界杯足球赛
 1994年世界杯足球赛
1994年世界杯足球赛
 1998年世界杯足球赛
1998年世界杯足球赛
 2002年世界杯足球赛
2002年世界杯足球赛
 2006年世界杯足球赛
2006年世界杯足球赛
 2010年世界杯足球赛
2010年世界杯足球赛
 世界杯决赛队
世界杯决赛队
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 2022年世界杯足球赛
2022年世界杯足球赛

 2026年世界杯足球赛
2026年世界杯足球赛
 2013年国际足联联合会杯
2013年国际足联联合会杯
 2017年国际足联联合会杯
2017年国际足联联合会杯
 1991年女子世界杯足球
1991年女子世界杯足球
 1995年女子世界杯足球
1995年女子世界杯足球
 1999年女子世界杯足球
1999年女子世界杯足球
 2003年女子世界杯足球
2003年女子世界杯足球
 2007年女子世界杯足球
2007年女子世界杯足球
 2011年女子世界杯足球
2011年女子世界杯足球
 2015年女子世界杯足球赛
2015年女子世界杯足球赛
 2019年女子世界杯足球赛
2019年女子世界杯足球赛
 大洋洲足球联合会
大洋洲足球联合会
 瑞士
瑞士
 苏黎世
苏黎世

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足联女子世界杯
(F)国际足联女子世界杯

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足球联赛
(F)国际足球联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)非洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)非洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)中北美洲及加勒比海地区足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)中北美洲及加勒比海地区足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)美洲解放杯
(F)美洲解放杯

 体育
体育
 (F)欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)欧洲足球锦标赛
(F)欧洲足球锦标赛

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足联U-20世界杯
(F)国际足联U-20世界杯

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足联联合会杯
(F)国际足联联合会杯

 体育
体育
 (F)亚洲杯足球赛
(F)亚洲杯足球赛

 体育
体育
 (F)非洲国家杯
(F)非洲国家杯
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015/16
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015/16
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2016/17
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2016/17
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017/18
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017/18
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018/19
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018/19
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019/20
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019/20
 欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2017/18
欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2017/18
 欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2018/19
欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2018/19
 欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2019/20
欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2019/20
 欧洲足联国家联赛
欧洲足联国家联赛
 欧洲足球协会联盟
欧洲足球协会联盟

 重要的国际组织
重要的国际组织

Die Fédération Internationale de Football Association (deutsch Internationaler Verband des Association Football), kurz FIFA oder Fifa, ist ein privater Verband, der „die Kontrolle des Association Football in all seinen Formen“ zum Zweck hat.[3] Der Weltfußballverband ist ein gemeinnütziger Verein im Sinne der Artikel 60 ff. des Schweizerischen Zivilgesetzbuches mit Sitz in Zürich und im Handelsregister eingetragen.[4][5][6] Die FIFA muss als nicht steuerbefreiter Verein im Kanton Zürich eine reduzierte Gewinnsteuer von 4 % entrichten.[1][2]
Die FIFA erwirtschaftet in ihrer aktuellen Vierjahresertragsperiode 5,66 Milliarden Dollar, die zu 89 % aus der Vermarktung der von ihr organisierten Männer-Fußball-WM stammen. Darüber hinaus organisiert sie auch die Frauen-Fußball-WM und zahlreiche weitere Turniere. Ihr Präsident ist Gianni Infantino.
国际足球联合会(法语:Fédération Internationale de Football Association;英语:International Federation of Association Football[注 1]),简称国际足联(FIFA),是管理英式足球、室内五人足球和沙滩足球的国际体育组织,下辖211个会员协会。总部设于瑞士苏黎世。现任主席为吉安尼·因凡蒂诺。国际足联负责组织世界重大足球赛事,当中最著名的是4年举行一次的世界杯。[3]
国際サッカー連盟(こくさいサッカーれんめい、仏: Fédération Internationale de Football Association)は、サッカー(アソシエーション式フットボール)の国際競技連盟であり、スイスの法律に基づいた自立法人である。略称はFIFA(フランス語発音: [fifa] フィファ、英語発音: [ˈfiːfə] フィーファ)。本部はスイスのチューリッヒに置かれている。
2018年時点で全211の国内競技連盟が加盟し[1]、国際競技連盟としては世界最大である[3]。FIFAワールドカップ・FIFA女子ワールドカップの主催が、もっとも大きな任務となっている。
The Fédération Internationale de Football Association[a] (FIFA /ˈfiːfə/ FEE-fə; French for International Federation of Association Football; Spanish: Federación Internacional de Fútbol Asociación; German: Internationaler Verband des Association Football) is a non-profit organization which describes itself as an international governing body of association football, fútsal, beach soccer, and efootball. It is the highest governing body of football.
FIFA was founded in 1904[3] to oversee international competition among the national associations of Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland. Headquartered in Zürich, its membership now comprises 211 national associations. Member countries must each also be members of one of the six regional confederations into which the world is divided: Africa, Asia, Europe, North & Central America and the Caribbean, Oceania, and South America.
Today, FIFA outlines a number of objectives in the organizational Statues, including growing football internationally, providing efforts to ensure football is accessible to everyone, and advocating for integrity and fair play.[4] FIFA is responsible for the organization and promotion of football's major international tournaments, notably the World Cup which commenced in 1930 and the Women's World Cup which commenced in 1991. Although FIFA does not solely set the rules of football, that being the responsibility of the International Football Association Board of which FIFA is a member, it applies and enforces the rules across all FIFA competitions.[5] All FIFA tournaments generate revenue from sponsorship; in 2018, FIFA had revenues of over US $4.6 billion, ending the 2015–2018 cycle with a net positive of US$1.2 billion, and had cash reserves of over US$2.7 billion.[6]
Reports by investigative journalists have linked FIFA leadership with corruption, bribery, and vote-rigging related to the election of FIFA president Sepp Blatter and the organization's decision to award the 2018 and 2022 World Cups to Russia and Qatar, respectively. These allegations led to the indictments of nine high-ranking FIFA officials and five corporate executives by the U.S. Department of Justice on charges including racketeering, wire fraud, and money laundering. On 27 May 2015, several of these officials were arrested by Swiss authorities, who were launching a simultaneous but separate criminal investigation into how the organization awarded the 2018 and 2022 World Cups. Those among these officials who were also indicted in the U.S. are expected to be extradited to face charges there as well.[7][8][9] Many officials were suspended by FIFA's ethics committee including Sepp Blatter[10] and Michel Platini.[11] In early 2017 reports became public about FIFA president Gianni Infantino attempting to prevent the re-elections[12] of both chairmen of the ethics committee, Cornel Borbély and Hans-Joachim Eckert, during the FIFA congress in May 2017.[13][14] On 9 May 2017, following Infantino's proposal,[15] FIFA Council decided not to renew the mandates of Borbély and Eckert.[15] Together with the chairmen, 11 of 13 committee members were removed.[16]
La Fédération internationale de football association2 (souvent désignée par l'acronyme FIFA) est la fédération sportive internationale du football, du futsal et du football de plage. Association des fédérations nationales fondée le 21 mai 1904 à Paris, elle a pour vocation de gérer et de développer le football dans le monde. La Coupe du monde de football est créée en 1924 par Jules Rimet3, président de la fédération internationale de 1920 à 1954. Le terme Football Association est le nom originel du football, utilisé pour le distinguer des autres sports de ballon.
Fondée par les fédérations d'Allemagne, de Belgique, du Danemark, d'Espagne, de France, des Pays-Bas, de Suède et de Suisse, elle compte au 13 mai 2016 211 associations nationales affiliées à travers le monde, qui doivent être reconnues par l'une des six confédérations continentales. Son siège est situé depuis 1932 à Zurich, en Suisse.
Bien qu'étant officiellement une association à but non lucratif, la FIFA brasse un chiffre d'affaires très important du fait de l'organisation des compétitions et de leur sponsoring. En 2013, la FIFA génère 1,3 milliard de dollars de chiffre d'affaires, et dispose de réserves évaluées à 1,4 milliard de dollars4. La FIFA est chargée de l'organisation des grands tournois mondiaux, et notamment des Coupes du monde masculines, depuis le 13 juillet 1930, et féminines, depuis le 30 novembre 1991.
Après plusieurs années de rumeurs et d'enquêtes de journalistes sur les affaires financières au sein de la FIFA, notamment autour de l'attribution de l'organisation des Coupes du monde de 2018 et 2022 à la Russie et au Qatar, une enquête lancée par le département de la Justice des États-Unis pour des faits de corruption aboutit à un grand scandale en 2015, à la suite duquel le président Sepp Blatter, le 2 juin 2015, trois jours après sa réélection pour un cinquième mandat, annonce qu'il convoque un congrès extraordinaire, prévu en février 2016, afin de remettre son mandat de président à disposition. Le 8 octobre 2015, la commission d'éthique de la FIFA suspend Sepp Blatter de manière provisoire, pendant 90 jours5. Le 21 décembre 2015, la commission suspend Sepp Blatter pour 8 ans6. Cette suspension est ramenée à six ans le 24 février 2016, peu avant l'élection de son successeur, Gianni Infantino, le 26 février 2016.
La Fédération Internationale de Football Association (in italiano "Federazione internazionale di calcio"[Nota 1]), più nota con l'acronimo FIFA, è la federazione internazionale che governa gli sport del calcio, del calcio a 5 e del beach soccer. La sua sede si trova a Zurigo, in Svizzera, e il presidente è Gianni Infantino, eletto nel 2016.
La federazione fu fondata a Parigi il 21 maggio 1904 e si occupa dell'organizzazione di tutte le manifestazioni intercontinentali degli sport sopraccitati, tra le quali la più importante è sicuramente il Campionato mondiale di calcio, che premia il vincitore con il trofeo della Coppa del Mondo. Tale torneo viene disputato ogni quattro anni dal 1930, eccetto che per il 1942 e il 1946 a causa della Seconda guerra mondiale, e la federazione ha il compito di scegliere il paese organizzatore che ospita la fase finale della manifestazione.
La Fédération Internationale de Football Association2 (en español: Federación Internacional de Fútbol Asociación),3 universalmente conocida por sus siglas FIFA, es la institución que gobierna las federaciones de fútbol en todo el planeta. Se fundó el 21 de mayo de 1904 y tiene su sede en Zúrich, Suiza. Forma parte del IFAB, organismo encargado de modificar las reglas del juego. Además, la FIFA organiza la Copa Mundial de Fútbol, los otros campeonatos del mundo en sus distintas categorías, ramas y variaciones de la disciplina, y los Torneos Olímpicos a la par del COI.
La FIFA agrupa 211 asociaciones o federaciones de fútbol de distintos países, contando con 17 países afiliados más que la Organización de las Naciones Unidas, tres menos que la Asociación Internacional de Federaciones de Atletismo y dos menos que la Federación Internacional de Baloncesto.45
Междунаро́дная федера́ция футбо́ла[1] (фр. Fédération Internationale de Football Association, сокращённо FIFA, в русской транслитерации — ФИФА́) — главная футбольная организация, являющаяся крупнейшим международным руководящим органом в футболе, мини-футболе и пляжном футболе. Штаб-квартира ФИФА находится в швейцарском городе Цюрихе.
Под эгидой ФИФА проходят все футбольные турниры всемирного масштаба, в числе которых чемпионат мира ФИФА, аналогичный турнир среди женщин, молодёжные и юношеские турниры, Кубок конфедераций и клубный чемпионат мира.
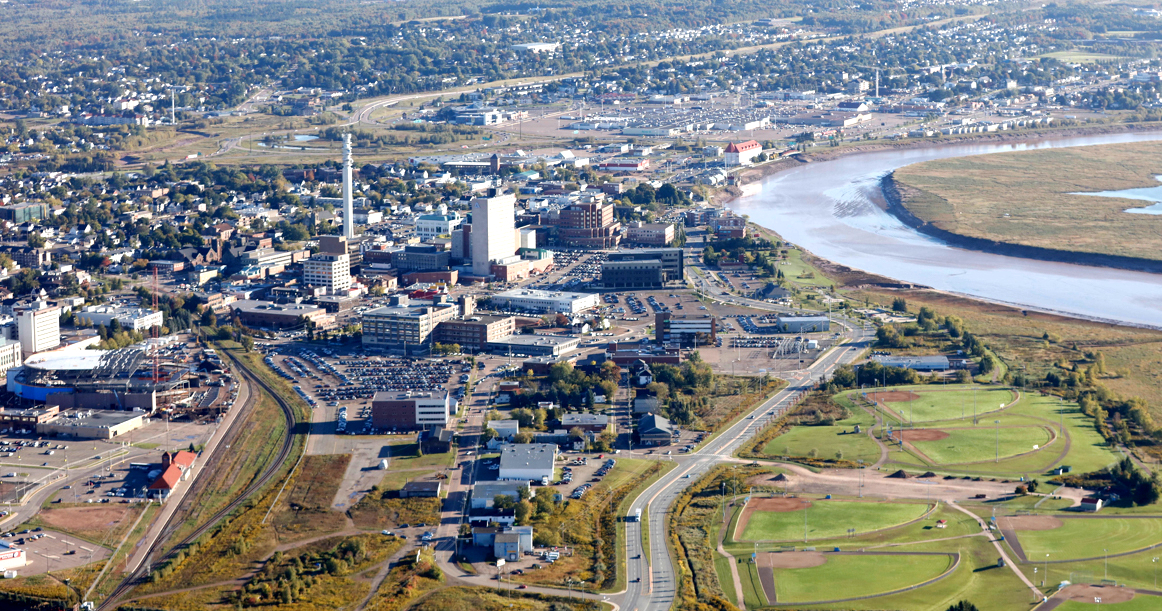

蒙克顿(Moncton,发音: /ˈmʌŋktən/)是加拿大新不伦瑞克省威斯特摩兰县的一个城市,位于该省东南部,座落珀蒂克的克河(Petitcodiac River)畔。蒙克顿处于加拿大海洋省份的中心地带,因此发展成该地区的陆路运输枢纽,并得“枢纽之城”(Hub City)的外号。据2011人口普查所示,蒙克顿市内有69,074名居民,而都会区人口则达138,644人,是全国人口增长速度最高的普查都会区之一。
欧洲裔移民于1733年首度进驻蒙克顿一带,而来自宾夕法尼亚的德裔美国人则于1766年在此建立居民点。当时蒙克顿为一农业社区,但该带的造船业于19世纪中叶陆续兴旺,而蒙克顿亦于1855年建制为镇。然而,造船业于1860年代转衰,蒙克顿亦于1862年失去其城镇资格。1871年,加拿大殖民地际铁路将其总部设于蒙克顿,刺激该带经济,蒙克顿亦于1875年恢复建制,再于1890年升格为市。加拿大国家铁路公司的蒙克顿车厂于1980年代末关闭后,区内经济再度受创,但后来仍能复苏。时至今日,蒙克顿的经济趋向多方面发展,除了运输、物流和零售等传统行业外,也被教育、医疗、金融、资讯科技和保险等行业支撑。
Moncton ist eine Stadt in der kanadischen Provinz New Brunswick an der Ostküste des Landes. Mit 71.889 Einwohnern (Stand 2016) ist sie vor Saint John (67.575 Einwohner) die größte Stadt der Provinz. Ihre Fläche beträgt 142 km². Den Spitznamen „Hub City“ bekam die Stadt, da sie zentral in den Maritimes gelegen ist und einen bedeutenden Verkehrsknotenpunkt für Bahn- und Straßenverbindungen darstellt.
Gemeinsam mit den Nachbarstädten Dieppe, Riverview sowie den Gemeinden Westmorland und Albert Counties bildet Moncton eine Metropolregion mit rund 108.620 Einwohnern (2016). Etwa 65 % der Einwohner sprechen Englisch, 35 % Französisch. Die Bevölkerung ist fast ausschließlich weiß. Vom 4. bis zum 12. April 2009 fanden in dem 7000 Sitzplätze fassenden Moncton Coliseum die Curling-Weltmeisterschaften der Männer statt.
モンクトン(Moncton)は、カナダのニューブランズウィック州ウェストモーランド郡の都市。
州の南東でプチコーディアック渓谷内にあり、大西洋岸諸州の中で地理的に中央部に位置する。歴史的にも大西洋諸州の中央部で鉄道などの陸上輸送のハブとして機能したため、「ハブ・シティー」と言うニックネームがある。
人口も大都市圏で12万人を超え、州内最大の都市部、大西洋諸州内ではハリファックス、セントジョンズに次ぐ第三の都市圏を形成している。
モンクトンは現在急成長している都市圏の一つで、トロント以東では最も急成長している都市圏である。
Moncton (/ˈmʌŋktən/; French pronunciation: [mɔŋktœn]) is the largest city in the Canadian province of New Brunswick. Situated in the Petitcodiac River Valley, Moncton lies at the geographic centre of the Maritime Provinces. The city has earned the nickname "Hub City" due to its central inland location in the region and its history as a railway and land transportation hub for the Maritimes.
The city proper has a population of 71,889 (2016) and has a land area of 142 km2 (55 sq mi). The Moncton CMA has a population of 144,810 (2016), making it the largest city[8] and CMA in New Brunswick, and the second-largest city and CMA in the Maritime Provinces. The CMA includes the neighbouring city of Dieppe and the town of Riverview, as well as adjacent suburban areas in Westmorland and Albert counties.[9]
Although the Moncton area was first settled in 1733, Moncton is considered to have been officially founded in 1766 with the arrival of Pennsylvania Dutch immigrants from Philadelphia. Initially an agricultural settlement, Moncton was not incorporated until 1855. The city was named for Lt. Col. Robert Monckton, the British officer who had captured nearby Fort Beauséjour a century earlier. A significant wooden shipbuilding industry had developed in the community by the mid-1840s, allowing for the civic incorporation in 1855, but the shipbuilding economy collapsed in the 1860s, causing the town to lose its civic charter in 1862. Moncton regained its charter in 1875 after the community's economy rebounded, mainly due to a growing railway industry. In 1871, the Intercolonial Railway of Canada had chosen Moncton to be its headquarters, and Moncton remained a railway town for well over a century until the closure of the Canadian National Railway (CNR) locomotive shops in the late 1980s.
Although the economy of Moncton was traumatized twice—by the collapse of the shipbuilding industry in the 1860s and by the closure of the CNR locomotive shops in the 1980s—the city was able to rebound strongly on both occasions. The city adopted the motto Resurgo after its rebirth as a railway town. The city's economy is stable and diversified, primarily based on its traditional transportation, distribution, retailing, and commercial heritage, and supplemented by strength in the educational, health care, financial, information technology, and insurance sectors. The strength of Moncton's economy has received national recognition and the local unemployment rate is consistently less than the national average.
Moncton (prononcé en français : /mɔŋktœn/, en anglais : /ˈmʌŋktən/) est une ville canadienne située dans le comté de Westmorland, dans le Sud-Est du Nouveau-Brunswick.
Moncton è una città del Canada, nella provincia del Nuovo Brunswick, con 69.074 abitanti (2011). La sua area metropolitana ne conta 138.644 (2011) ed è una delle prime trenta del Canada, comprendendo anche Dieppe e Riverview. Moncton è un centro urbano bilingue: l'inglese e il francese sono entrambe riconosciute come lingue ufficiali. Un terzo circa della popolazione utilizza il francese nei suoi rapporti familiari, il resto l'inglese e, in minor misura, altri idiomi parlati dagli immigrati asiatici ed europei.
Moncton es una ciudad canadiense ubicada en el condado de Westmorland, al sureste de la provincia de Nuevo Brunswick.
De acuerdo a los datos del penúltimo censo, el área metropolitana de Moncton es la región urbana con mayor crecimiento al este de Toronto y una de las 10 ciudades canadienses con mayor crecimiento, con un aumento de la población de 6,5 % entre 2001 y el 2006. Su región metropolitana, denominada Gran Moncton, incluye a las ciudades de Dieppe y de Riverview y porciones de los condados de Westmorland y de Albert.1
La ciudad de Moncton es la primera ciudad en población de la provincia, con 71.889 habitantes en el 2016,2 algo más que la ciudad de Saint John con 67.575. La región metropolitana de Moncton es también la aglomeración más poblada de Nuevo Brunswick con 144.810 habitantes, que sobrepasa a la población de la región metropolitana de Saint John (126.202).
Монктон (англ. и фр. Moncton) — город в графстве Вестморленд, расположен на реке Птикодьяк в том месте, где река образует меандр Куд, на юго-востоке провинции Нью-Брансуик, Канада. Это первый по величине город провинции
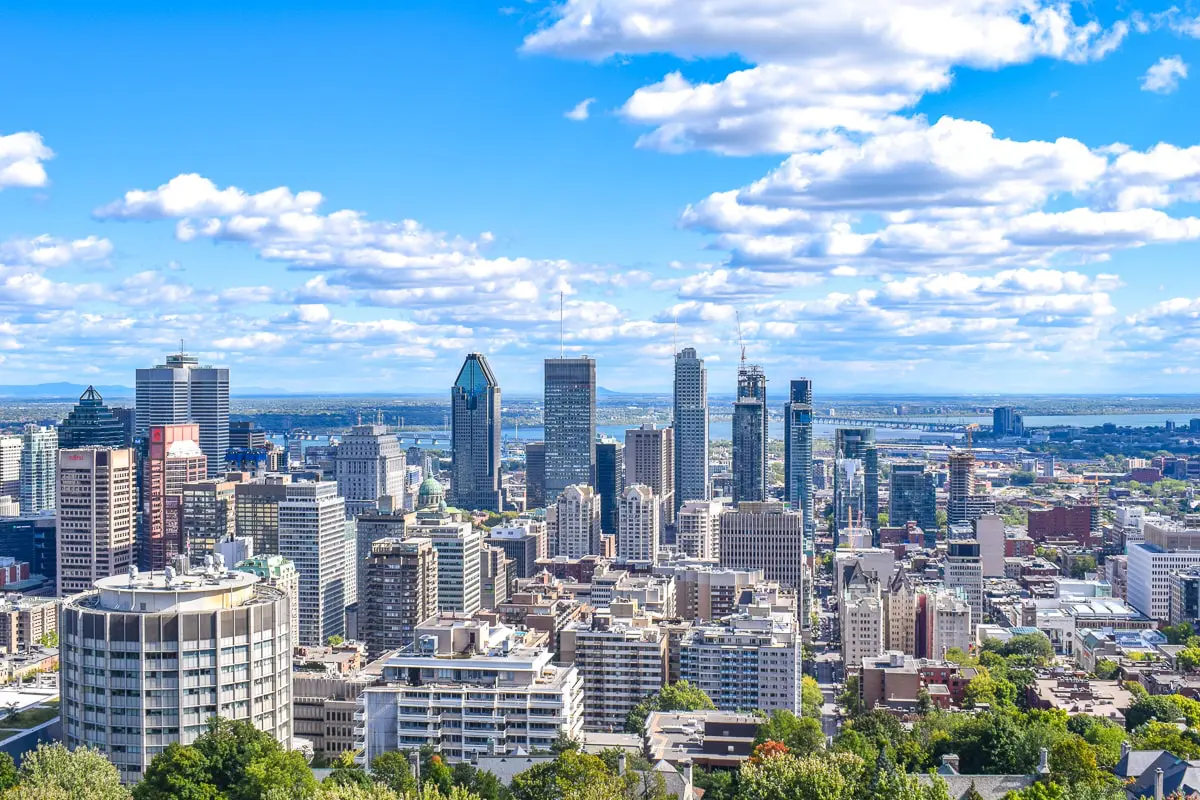



Montreal (deutsch [mɔntʁeˈa:l]) bzw. Montréal (französisch [mɔ̃ʁeˈal], englisch [ˌmʌntɹiːˈɒl]) ist eine Millionenstadt in Kanada. Sie liegt im Südwesten der Provinz Québec auf der Île de Montréal, der größten Insel im Hochelaga-Archipel, die vom Sankt-Lorenz-Strom und von Mündungsarmen des Ottawa umflossen wird. Die Nachbarprovinz Ontario liegt knapp 60 Kilometer westlich, die Grenze zu den USA etwas mehr als 50 Kilometer südlich. Das Stadtbild wird vom Mont Royal geprägt, einem 233 Meter hohen Hügelzug vulkanischen Ursprungs im Zentrum der Insel, von dem sich der Name der Stadt ableitet.
Als der französische Seefahrer Jacques Cartier im Jahr 1535 als erster Europäer die Gegend erforschte, lebten Sankt-Lorenz-Irokesen auf der Insel. 1642 gründeten Paul Chomedey de Maisonneuve und Jeanne Mance das Fort Ville-Marie, eine katholische Missionsstation. Daraus entwickelte sich in der Folge die Siedlung Montreal, die 1760 unter britische Herrschaft kam. Montreal erhielt 1832 die Stadtrechte. Die Stadt wuchs rasch und entwickelte sich zum wirtschaftlichen und kulturellen Zentrum des Landes, verlor aber im letzten Viertel des 20. Jahrhunderts diese führende Rolle an Toronto. Bedeutende Ereignisse von weltweiter Ausstrahlung waren die Weltausstellung Expo 67 und die Olympischen Sommerspiele 1976.
Die Wirtschaft Montreals ist stark diversifiziert. Wichtige Pfeiler des Dienstleistungssektors sind Finanzdienstleistungen, Medien, Handel und Design. Von großer Bedeutung ist auch der Tourismus, dies aufgrund der Sehenswürdigkeiten und des vielfältigen kulturellen Angebots, das neben Museen auch zahlreiche Festivals in den Bereichen Film, Theater und Musik umfasst. Mehr als 60 internationale Organisationen haben ihren Sitz in Montreal. Im Industriesektor sind Luftfahrt-, Pharma- und Spitzentechnologieunternehmen vorherrschend. Mit vier Universitäten und mehreren weiteren Hochschulen ist Montreal ein bedeutender Bildungsstandort. Außerdem ist die Stadt ein Knotenpunkt im Schienen- und Straßennetz und verfügt darüber hinaus über den größten Binnenhafen auf dem amerikanischen Kontinent.
Mit einer Bevölkerungszahl von 1.649.519 Einwohnern (Stand: 2011)[1] ist Montreal die zweitgrößte Stadt Kanadas nach Toronto und die größte der Provinz Québec. Die Verwaltungsregion, die alle Gemeinden auf der Insel umfasst, zählt 1.886.481 Einwohner (2011).[2] Der Ballungsraum Communauté métropolitaine de Montréal, der urbane Gebiete im näheren Umkreis miteinbezieht, zählt 3.824.221 Einwohner (2011).[3] Französisch ist Montreals Amtssprache und die Hauptsprache von 56,9 % der Bevölkerung, während 18,6 % hauptsächlich Englisch sprechen. Der Rest entfällt auf verschiedene Sprachen von Einwanderern, womit Montreal eine multikulturelle Bevölkerung besitzt.[4]
Montreal ist die zweitgrößte Stadt der Welt nach Paris, in der Französisch als Muttersprache gesprochen wird.[5][6][7][8] Montreal gehört auch weltweit zu den größten Städten, in denen Französisch die offizielle Sprache ist. Die Stadt stand früher an zweiter Stelle nach Paris, hat aber diesen Rang in den letzten Jahren an Kinshasa[9] und Abidjan[10] abgegeben.
蒙特利尔(法语:Montréal,[mɔ̃ʁeal] ![]() 聆听;英语:Montreal,/ˌmʌntriːˈɒl/ (
聆听;英语:Montreal,/ˌmʌntriːˈɒl/ (![]() 聆听)),蒙特利尔,港澳称为满地可,台湾称为蒙特娄[5][6]、蒙特利尔[6],是一座位于加拿大魁北克省西南部的城市,主要位于圣劳伦斯河和渥太华河汇合处的蒙特利尔岛及周边小岛上。根据2011年人口普查,蒙特利尔人口约为342万[9],是魁北克省内最大城市、加拿大第二大城市及北美第十五大城市。“蒙特利尔”一词来源于中古法语“Mont Royal”,意思为“皇家山”,至今蒙特利尔城中心的地标皇家山仍以此命名。法语是蒙特利尔的官方语言,也是城市里最常用的语言,使用人口占城市总人口的60.5%,使得蒙特利尔成为世界上仅次于巴黎的第二大法语城市。
聆听)),蒙特利尔,港澳称为满地可,台湾称为蒙特娄[5][6]、蒙特利尔[6],是一座位于加拿大魁北克省西南部的城市,主要位于圣劳伦斯河和渥太华河汇合处的蒙特利尔岛及周边小岛上。根据2011年人口普查,蒙特利尔人口约为342万[9],是魁北克省内最大城市、加拿大第二大城市及北美第十五大城市。“蒙特利尔”一词来源于中古法语“Mont Royal”,意思为“皇家山”,至今蒙特利尔城中心的地标皇家山仍以此命名。法语是蒙特利尔的官方语言,也是城市里最常用的语言,使用人口占城市总人口的60.5%,使得蒙特利尔成为世界上仅次于巴黎的第二大法语城市。
蒙特利尔曾经是加拿大经济首都,拥有最多的人口及最发达的经济,但是在1976年蒙特利尔奥运会后被安大略省的多伦多超过。今天蒙特利尔仍然是加拿大最重要的经济中心之一,航空工业、金融、设计、电影工业等行业发达。蒙特利尔被认为是世界最佳宜居城市,并被联合国教育、科学及文化组织认定为设计之城。1999年第35届国际技能竞赛在这里举行。
モントリオール(英語: Montreal [ˌmɒntrɪˈɔːl] (![]() 音声ファイル))、モンレアル(フランス語: Montréal[mɔ̃ʁeal] (
音声ファイル))、モンレアル(フランス語: Montréal[mɔ̃ʁeal] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、カナダ・ケベック州の都市。セントローレンス川沿いに位置し、アメリカ合衆国との国境や、カナダのオンタリオ州との州境に近い。
音声ファイル))は、カナダ・ケベック州の都市。セントローレンス川沿いに位置し、アメリカ合衆国との国境や、カナダのオンタリオ州との州境に近い。
モントリオール市は、カナダではオンタリオ州のトロントに次ぎ人口・経済規模で第二の都市である[5]。ケベック州では最大の都市である。2015年、アメリカのシンクタンクが公表したビジネス・人材・文化・政治などを対象とした総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界第24位の都市と評価された[6]。
住民の大半がフランス系カナダ人を中心にしたヨーロッパ系だが、市内の人口の31.7%は非白人と世界各地からの移民も多い多民族都市である。
周辺地域を含むモントリオール大都市圏の人口は約380万人であり、これは北米で15番目、世界でも第77位の規模。面積は約4千km2。モントリオール大都市圏の住民の7割弱が第一言語をフランス語とし、フランス語圏ではパリとキンシャサ[7]に次ぐ規模である。
フランス文化の薫り高い異国的な雰囲気、美食の町、石造りの住宅街、街中にある数多くの教会、石畳のヨーロッパ調の旧市街の街並みなどから観光客向けに「北米のパリ」と宣伝される。一方では、都市圏の住民の1割強の第一言語は英語であり、19世紀の終わりから20世紀の始めにかけて英国系移民によって街が発展してきたことからヴィクトリア朝の建物が多いなど英国文化も色濃く残り、北米文化と混合している側面も持つ。
Montreal (/ˌmʌntriˈɔːl/ ( listen) MUN-tree-AWL;[14] French: [mɔ̃ʁeal] (
listen) MUN-tree-AWL;[14] French: [mɔ̃ʁeal] ( listen); officially Montréal) is the most populous municipality in the Canadian province of Quebec and the second-most populous municipality in Canada. Originally called Ville-Marie, or "City of Mary",[15] it is named after Mount Royal,[16] the triple-peaked hill in the heart of the city. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which took its name from the same source as the city,[17][18] and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. It has a distinct four-season continental climate with warm to hot summers and cold, snowy winters.[19]
listen); officially Montréal) is the most populous municipality in the Canadian province of Quebec and the second-most populous municipality in Canada. Originally called Ville-Marie, or "City of Mary",[15] it is named after Mount Royal,[16] the triple-peaked hill in the heart of the city. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which took its name from the same source as the city,[17][18] and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. It has a distinct four-season continental climate with warm to hot summers and cold, snowy winters.[19]
In 2016, the city had a population of 1,704,694,[9] with a population of 1,942,044 in the urban agglomeration, including all of the other municipalities on the Island of Montreal.[9] The broader metropolitan area had a population of 4,098,927.[11] French is the city's official language[20][21] and is the language spoken at home by 49.8% of the population of the city, followed by English at 22.8% and 18.3% other languages (in the 2016 census, not including multi-language responses).[9] In the larger Montreal Census Metropolitan Area, 65.8% of the population speaks French at home, compared to 15.3% who speak English.[11] The agglomeration Montreal is one of the most bilingual cities in Quebec and Canada, with over 59% of the population able to speak both English and French.[9] Montreal is the second-largest primarily French-speaking city in the world, after Paris.[22][23][24][25] It is situated 258 kilometres (160 mi) south-west of Quebec City.
Historically the commercial capital of Canada, Montreal was surpassed in population and in economic strength by Toronto in the 1970s.[26] It remains an important centre of commerce, aerospace, transport, finance, pharmaceuticals, technology, design, education, art, culture, tourism, food, fashion, gaming, film, and world affairs. Montreal has the second-highest number of consulates in North America,[27] serves as the location of the headquarters of the International Civil Aviation Organization, and was named a UNESCO City of Design in 2006.[28][29] In 2017, Montreal was ranked the 12th most liveable city in the world by the Economist Intelligence Unit in its annual Global Liveability Ranking,[30] and the best city in the world to be a university student in the QS World University Rankings.[31]
Montreal has hosted multiple international conferences and events, including the 1967 International and Universal Exposition and the 1976 Summer Olympics.[32][33] It is the only Canadian city to have held the Summer Olympics. In 2018, Montreal was ranked as an Alpha− world city.[34] As of 2016 the city hosts the Canadian Grand Prix of Formula One,[35] the Montreal International Jazz Festival[36] and the Just for Laughs festival.[37]
Montréal [ˈmɔ̃ˌʁeal]3 Écouter est la deuxième ville la plus peuplée du Canada. Elle se situe principalement sur l’île fluviale de Montréal, sur le fleuve Saint-Laurent (entre Québec et le lac Ontario) dans le Sud de la province de Québec, dont elle est la métropole4.
En 2016, la ville comptait 1 704 694 habitants1 et son aire urbaine (appelée Région métropolitaine de Montréal) plus de 4 millions, soit environ la moitié de la population du Québec5. Montréal est ainsi la 19e agglomération la plus peuplée d'Amérique du Nord6 et la 122e ville la plus peuplée du monde7.
Ville francophone la plus peuplée d'Amérique8, Montréal est considérée comme ayant la deuxième population francophone au monde après ParisNote 1,9,10. En 2011, environ 50 % de la population de Montréal était de langue maternelle française, 13 % était de langue anglaise et 33 % était d'une autre langue11, ce qui fait d'elle l'une des villes les plus cosmopolites du monde12.
Montréal est le 3e plus grand centre financier d'Amérique du Nord et le 12e au monde13. Cœur économique du Québec, Montréal est aussi la seconde place financière du Canada et possède une économie fortement diversifiée14 par le commerce, l’éducation, les technologies de l'information et les industries aérospatiale, pharmaceutique, du tourisme et du cinéma. La ville est la 3e en importance dans l'industrie mondiale du jeu vidéo15. Classée ville mondiale en 2012, Montréal est la deuxième ville consulaire d'Amérique du Nord, abrite le siège de l'Organisation de l'aviation civile internationale et est le siège de plus de 65 organisations internationales gouvernementales et non gouvernementales16, ce qui fait d'elle la 3e ville en importance en Amérique du Nord pour ce qui est du nombre de siège sociaux d'organisations internationales, derrière New York et Washington17. De plus, la ville est la première d'Amérique du Nord pour le nombre de congrès internationaux18. En 2017, Montréal est consacrée « meilleure ville étudiante » au monde19 et est considérée comme la « Métropole universitaire du Canada, avec six universités et 450 centres de recherche »20.
Montréal a accueilli plusieurs événements internationaux d'envergure, dont l'Exposition universelle de 1967 et les Jeux olympiques d'été de 1976. Hôte du Grand Prix de Formule 1 du Canada, elle accueille annuellement de nombreux festivals, tels le Festival international de jazz de Montréal, les FrancoFolies, et le festival Juste pour rire. Le club de hockey des Canadiens de Montréal y a élu domicile dès sa création en 1909.
Montréal (in francese, pronuncia: /mɔ̃ʁeal/ ascolta[?·info]) o Montreal (pronuncia: [ˈmɔntreal][2]; in inglese: /mʌntriːˈɒl/ ascolta[?·info]), in italiano Monreale, è una città del Canada. È il centro più popoloso della provincia del Québec e il suo più importante polo economico, oltre a essere la seconda città più popolosa del Canada. Montréal è anche la seconda agglomerazione urbana del paese dopo quella di Toronto. In francese viene detta la Métropole e la sua area metropolitana conta all'incirca 4 milioni di abitanti[3]. Il centro storico di Montréal è il Vieux-Montréal (Vecchia Montréal).
Montreal (Montréal1 en la grafía oficial de la ciudad, en francés; pronunciación en francés: /mɔ̃.ʀe.al/ (![]() escuchar), pronunciación en inglés: /ˌmʌn.tɹiˈɒːl/ (
escuchar), pronunciación en inglés: /ˌmʌn.tɹiˈɒːl/ (![]() escuchar)) es la mayor ciudad de la provincia de Quebec, en Canadá y la segunda más poblada del país.2 Es también una región administrativa de Quebec. Se sitúa en la isla del mismo nombre entre el río San Lorenzo y la Rivière des Prairies. Es uno de los principales centros industriales, comerciales y culturales de Norteamérica.
escuchar)) es la mayor ciudad de la provincia de Quebec, en Canadá y la segunda más poblada del país.2 Es también una región administrativa de Quebec. Se sitúa en la isla del mismo nombre entre el río San Lorenzo y la Rivière des Prairies. Es uno de los principales centros industriales, comerciales y culturales de Norteamérica.
Montreal es la cuarta ciudad francófona más poblada del mundo, detrás de París, Kinshasa y Abiyán.34 Sin embargo, Montreal también tiene una considerable comunidad anglófona,5 y un creciente número de personas cuyo idioma materno no es ni el francés ni el inglés.
La palabra «Montreal» es la versión arcaica, en francés antiguo, de «Mont-Royal» (cuando «royal» se decía y se escribía «real» sin acento, como en castellano), un monte localizado en la ciudad, en el centro de la isla.67 Montreal es uno de los centros culturales más importantes de Canadá, puesto que acoge varios acontecimientos nacionales e internacionales. Entre ellos, podemos citar el festival Juste pour Rire, uno de los mayores festivales de humor del mundo, el Festival de Jazz de Montréal, uno de los mayores festivales de jazz del mundo, y el Grand Prix de Montréal. La ciudad, en total, acoge más de 70 eventos internacionales al año.
La población de Montreal es de las mejor formadas del mundo, poseyendo la mayor concentración de estudiantes universitarios per cápita de toda Norte América. La ciudad posee cuatro universidades —dos francófonas y dos anglófonas— y doce facultades. Es un centro de la industria de alta tecnología, especialmente en el área de medicina y de la industria aeroespacial.8
Fundada en 1642, Montreal fue una de las primeras ciudades de Canadá. Desde entonces, y hasta la década de 1960, fue el principal centro financiero e industrial de Canadá, así como la mayor ciudad del país. Considerada hasta entonces la capital económica de Canadá, también era considerada una de las ciudades más importantes del mundo. Sin embargo, durante la década de 1970, la anglófona Toronto le arrebató el puesto de capital financiera e industrial del país. En 2001, los 27 municipios de la isla de Montreal fueron fusionados con la ciudad de Montreal. En 2004, tras los resultados de un referéndum, 15 de estos municipios nuevamente volvieron a ser ciudades independientes.
Монреа́ль (фр. Montréal, [mɔ̃ʁeˈal], англ. Montreal) — самый крупный город в провинции Квебек и второй по величине город в Канаде. Первоначально назывался Вилль-Мари — город Марии. Название Монреаль произошло от горы Мон-Руаяль (Королевская гора)[2], находящейся в центре города[3][4], форма Монреаль возникла под влиянием окситанского языка части первых поселенцев.
По данным 2016 года, население Большого Монреаля составляло 4 098 927 человек[5]. Население самого города Монреаль составляет в 1 704 694 человек[6].
Единственный официальный язык в городе — французский, для 59,8 % жителей города этот язык является родным, затем по количеству носителей следует английский язык — 19,4 %[7][8]. В Большом Монреале доля носителей французского составляет 67,9 % от населения, второе место занимает английский — 16,5 %[9]. Больше половины населения города владеет в той или иной степени обоими языками[10]. До 2014 года Монреаль был вторым по населению франкоязычным городом мира после Парижа, но к 2015 году на 3-ю позицию его сместил африканский Абиджан[11]. Также в мире есть и другие крупные франкоязычные города — африканские Киншаса, Касабланка, Алжир, но в этих городах французский используется преимущественно в письменном виде или же в качестве второго языка[12][13].
Монреаль обыкновенно занимает самые высокие места в рейтинге самых удобных для жизни городов в мире. Журнал Monocle Magazine назвал город «культурной столицей Канады», а недавно ЮНЕСКО назвало Монреаль городом дизайна[14][15]. Уступив в середине 70-х титул экономической столицы Торонто, Монреаль остается важным деловым, промышленным и культурным центром Канады. В числе наиболее значимых отраслей: аэрокосмическая, биотехнологическая, фармацевтическая, отрасль информационных технологий, туризм, киноиндустрия, а также развитая индустрия компьютерных игр[16][нет в источнике].







 国际城市
国际城市
 新不伦瑞克省
新不伦瑞克省
 建筑艺术
建筑艺术
 魁北克省
魁北克省

 重要港口
重要港口


