漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018
 亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019
亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019
 亚洲足球联合会
亚洲足球联合会
 中北美洲及加勒比海足球协会
中北美洲及加勒比海足球协会
 南美洲足球协会
南美洲足球协会
 非洲足球协会
非洲足球协会
 国际足球联合会
国际足球联合会
 1990年世界杯足球赛
1990年世界杯足球赛
 1994年世界杯足球赛
1994年世界杯足球赛
 1998年世界杯足球赛
1998年世界杯足球赛
 2002年世界杯足球赛
2002年世界杯足球赛
 2006年世界杯足球赛
2006年世界杯足球赛
 2010年世界杯足球赛
2010年世界杯足球赛
 世界杯决赛队
世界杯决赛队
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 2022年世界杯足球赛
2022年世界杯足球赛

 2026年世界杯足球赛
2026年世界杯足球赛
 2013年国际足联联合会杯
2013年国际足联联合会杯
 2017年国际足联联合会杯
2017年国际足联联合会杯
 1991年女子世界杯足球
1991年女子世界杯足球
 1995年女子世界杯足球
1995年女子世界杯足球
 1999年女子世界杯足球
1999年女子世界杯足球
 2003年女子世界杯足球
2003年女子世界杯足球
 2007年女子世界杯足球
2007年女子世界杯足球
 2011年女子世界杯足球
2011年女子世界杯足球
 2015年女子世界杯足球赛
2015年女子世界杯足球赛
 2019年女子世界杯足球赛
2019年女子世界杯足球赛
 大洋洲足球联合会
大洋洲足球联合会
 瑞士
瑞士
 苏黎世
苏黎世

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足联女子世界杯
(F)国际足联女子世界杯

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足球联赛
(F)国际足球联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)亚洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)非洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)非洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)中北美洲及加勒比海地区足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)中北美洲及加勒比海地区足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)美洲解放杯
(F)美洲解放杯

 体育
体育
 (F)欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛
(F)欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛

 体育
体育
 (F)欧洲足球锦标赛
(F)欧洲足球锦标赛

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足联U-20世界杯
(F)国际足联U-20世界杯

 体育
体育
 (F)国际足联联合会杯
(F)国际足联联合会杯

 体育
体育
 (F)亚洲杯足球赛
(F)亚洲杯足球赛

 体育
体育
 (F)非洲国家杯
(F)非洲国家杯
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015/16
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2015/16
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2016/17
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2016/17
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017/18
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2017/18
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018/19
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2018/19
 欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019/20
欧洲足球俱乐部冠军联赛 2019/20
 欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2017/18
欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2017/18
 欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2018/19
欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2018/19
 欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2019/20
欧洲足球俱乐部联赛2019/20
 欧洲足联国家联赛
欧洲足联国家联赛
 欧洲足球协会联盟
欧洲足球协会联盟

 重要的国际组织
重要的国际组织

Die Fédération Internationale de Football Association (deutsch Internationaler Verband des Association Football), kurz FIFA oder Fifa, ist ein privater Verband, der „die Kontrolle des Association Football in all seinen Formen“ zum Zweck hat.[3] Der Weltfußballverband ist ein gemeinnütziger Verein im Sinne der Artikel 60 ff. des Schweizerischen Zivilgesetzbuches mit Sitz in Zürich und im Handelsregister eingetragen.[4][5][6] Die FIFA muss als nicht steuerbefreiter Verein im Kanton Zürich eine reduzierte Gewinnsteuer von 4 % entrichten.[1][2]
Die FIFA erwirtschaftet in ihrer aktuellen Vierjahresertragsperiode 5,66 Milliarden Dollar, die zu 89 % aus der Vermarktung der von ihr organisierten Männer-Fußball-WM stammen. Darüber hinaus organisiert sie auch die Frauen-Fußball-WM und zahlreiche weitere Turniere. Ihr Präsident ist Gianni Infantino.
国际足球联合会(法语:Fédération Internationale de Football Association;英语:International Federation of Association Football[注 1]),简称国际足联(FIFA),是管理英式足球、室内五人足球和沙滩足球的国际体育组织,下辖211个会员协会。总部设于瑞士苏黎世。现任主席为吉安尼·因凡蒂诺。国际足联负责组织世界重大足球赛事,当中最著名的是4年举行一次的世界杯。[3]
国際サッカー連盟(こくさいサッカーれんめい、仏: Fédération Internationale de Football Association)は、サッカー(アソシエーション式フットボール)の国際競技連盟であり、スイスの法律に基づいた自立法人である。略称はFIFA(フランス語発音: [fifa] フィファ、英語発音: [ˈfiːfə] フィーファ)。本部はスイスのチューリッヒに置かれている。
2018年時点で全211の国内競技連盟が加盟し[1]、国際競技連盟としては世界最大である[3]。FIFAワールドカップ・FIFA女子ワールドカップの主催が、もっとも大きな任務となっている。
The Fédération Internationale de Football Association[a] (FIFA /ˈfiːfə/ FEE-fə; French for International Federation of Association Football; Spanish: Federación Internacional de Fútbol Asociación; German: Internationaler Verband des Association Football) is a non-profit organization which describes itself as an international governing body of association football, fútsal, beach soccer, and efootball. It is the highest governing body of football.
FIFA was founded in 1904[3] to oversee international competition among the national associations of Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland. Headquartered in Zürich, its membership now comprises 211 national associations. Member countries must each also be members of one of the six regional confederations into which the world is divided: Africa, Asia, Europe, North & Central America and the Caribbean, Oceania, and South America.
Today, FIFA outlines a number of objectives in the organizational Statues, including growing football internationally, providing efforts to ensure football is accessible to everyone, and advocating for integrity and fair play.[4] FIFA is responsible for the organization and promotion of football's major international tournaments, notably the World Cup which commenced in 1930 and the Women's World Cup which commenced in 1991. Although FIFA does not solely set the rules of football, that being the responsibility of the International Football Association Board of which FIFA is a member, it applies and enforces the rules across all FIFA competitions.[5] All FIFA tournaments generate revenue from sponsorship; in 2018, FIFA had revenues of over US $4.6 billion, ending the 2015–2018 cycle with a net positive of US$1.2 billion, and had cash reserves of over US$2.7 billion.[6]
Reports by investigative journalists have linked FIFA leadership with corruption, bribery, and vote-rigging related to the election of FIFA president Sepp Blatter and the organization's decision to award the 2018 and 2022 World Cups to Russia and Qatar, respectively. These allegations led to the indictments of nine high-ranking FIFA officials and five corporate executives by the U.S. Department of Justice on charges including racketeering, wire fraud, and money laundering. On 27 May 2015, several of these officials were arrested by Swiss authorities, who were launching a simultaneous but separate criminal investigation into how the organization awarded the 2018 and 2022 World Cups. Those among these officials who were also indicted in the U.S. are expected to be extradited to face charges there as well.[7][8][9] Many officials were suspended by FIFA's ethics committee including Sepp Blatter[10] and Michel Platini.[11] In early 2017 reports became public about FIFA president Gianni Infantino attempting to prevent the re-elections[12] of both chairmen of the ethics committee, Cornel Borbély and Hans-Joachim Eckert, during the FIFA congress in May 2017.[13][14] On 9 May 2017, following Infantino's proposal,[15] FIFA Council decided not to renew the mandates of Borbély and Eckert.[15] Together with the chairmen, 11 of 13 committee members were removed.[16]
La Fédération internationale de football association2 (souvent désignée par l'acronyme FIFA) est la fédération sportive internationale du football, du futsal et du football de plage. Association des fédérations nationales fondée le 21 mai 1904 à Paris, elle a pour vocation de gérer et de développer le football dans le monde. La Coupe du monde de football est créée en 1924 par Jules Rimet3, président de la fédération internationale de 1920 à 1954. Le terme Football Association est le nom originel du football, utilisé pour le distinguer des autres sports de ballon.
Fondée par les fédérations d'Allemagne, de Belgique, du Danemark, d'Espagne, de France, des Pays-Bas, de Suède et de Suisse, elle compte au 13 mai 2016 211 associations nationales affiliées à travers le monde, qui doivent être reconnues par l'une des six confédérations continentales. Son siège est situé depuis 1932 à Zurich, en Suisse.
Bien qu'étant officiellement une association à but non lucratif, la FIFA brasse un chiffre d'affaires très important du fait de l'organisation des compétitions et de leur sponsoring. En 2013, la FIFA génère 1,3 milliard de dollars de chiffre d'affaires, et dispose de réserves évaluées à 1,4 milliard de dollars4. La FIFA est chargée de l'organisation des grands tournois mondiaux, et notamment des Coupes du monde masculines, depuis le 13 juillet 1930, et féminines, depuis le 30 novembre 1991.
Après plusieurs années de rumeurs et d'enquêtes de journalistes sur les affaires financières au sein de la FIFA, notamment autour de l'attribution de l'organisation des Coupes du monde de 2018 et 2022 à la Russie et au Qatar, une enquête lancée par le département de la Justice des États-Unis pour des faits de corruption aboutit à un grand scandale en 2015, à la suite duquel le président Sepp Blatter, le 2 juin 2015, trois jours après sa réélection pour un cinquième mandat, annonce qu'il convoque un congrès extraordinaire, prévu en février 2016, afin de remettre son mandat de président à disposition. Le 8 octobre 2015, la commission d'éthique de la FIFA suspend Sepp Blatter de manière provisoire, pendant 90 jours5. Le 21 décembre 2015, la commission suspend Sepp Blatter pour 8 ans6. Cette suspension est ramenée à six ans le 24 février 2016, peu avant l'élection de son successeur, Gianni Infantino, le 26 février 2016.
La Fédération Internationale de Football Association (in italiano "Federazione internazionale di calcio"[Nota 1]), più nota con l'acronimo FIFA, è la federazione internazionale che governa gli sport del calcio, del calcio a 5 e del beach soccer. La sua sede si trova a Zurigo, in Svizzera, e il presidente è Gianni Infantino, eletto nel 2016.
La federazione fu fondata a Parigi il 21 maggio 1904 e si occupa dell'organizzazione di tutte le manifestazioni intercontinentali degli sport sopraccitati, tra le quali la più importante è sicuramente il Campionato mondiale di calcio, che premia il vincitore con il trofeo della Coppa del Mondo. Tale torneo viene disputato ogni quattro anni dal 1930, eccetto che per il 1942 e il 1946 a causa della Seconda guerra mondiale, e la federazione ha il compito di scegliere il paese organizzatore che ospita la fase finale della manifestazione.
La Fédération Internationale de Football Association2 (en español: Federación Internacional de Fútbol Asociación),3 universalmente conocida por sus siglas FIFA, es la institución que gobierna las federaciones de fútbol en todo el planeta. Se fundó el 21 de mayo de 1904 y tiene su sede en Zúrich, Suiza. Forma parte del IFAB, organismo encargado de modificar las reglas del juego. Además, la FIFA organiza la Copa Mundial de Fútbol, los otros campeonatos del mundo en sus distintas categorías, ramas y variaciones de la disciplina, y los Torneos Olímpicos a la par del COI.
La FIFA agrupa 211 asociaciones o federaciones de fútbol de distintos países, contando con 17 países afiliados más que la Organización de las Naciones Unidas, tres menos que la Asociación Internacional de Federaciones de Atletismo y dos menos que la Federación Internacional de Baloncesto.45
Междунаро́дная федера́ция футбо́ла[1] (фр. Fédération Internationale de Football Association, сокращённо FIFA, в русской транслитерации — ФИФА́) — главная футбольная организация, являющаяся крупнейшим международным руководящим органом в футболе, мини-футболе и пляжном футболе. Штаб-квартира ФИФА находится в швейцарском городе Цюрихе.
Под эгидой ФИФА проходят все футбольные турниры всемирного масштаба, в числе которых чемпионат мира ФИФА, аналогичный турнир среди женщин, молодёжные и юношеские турниры, Кубок конфедераций и клубный чемпионат мира.
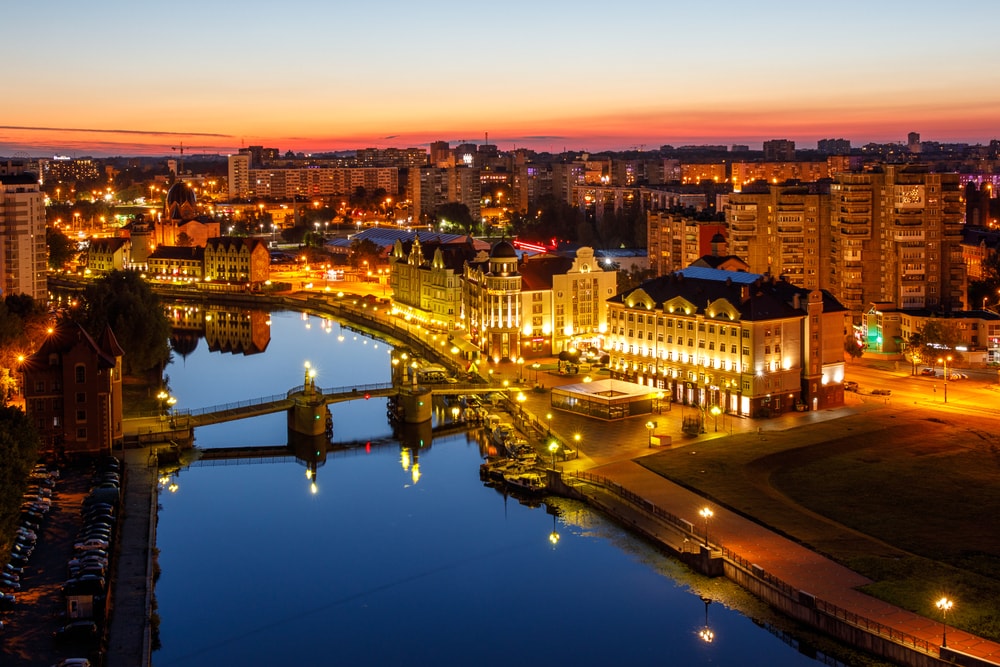


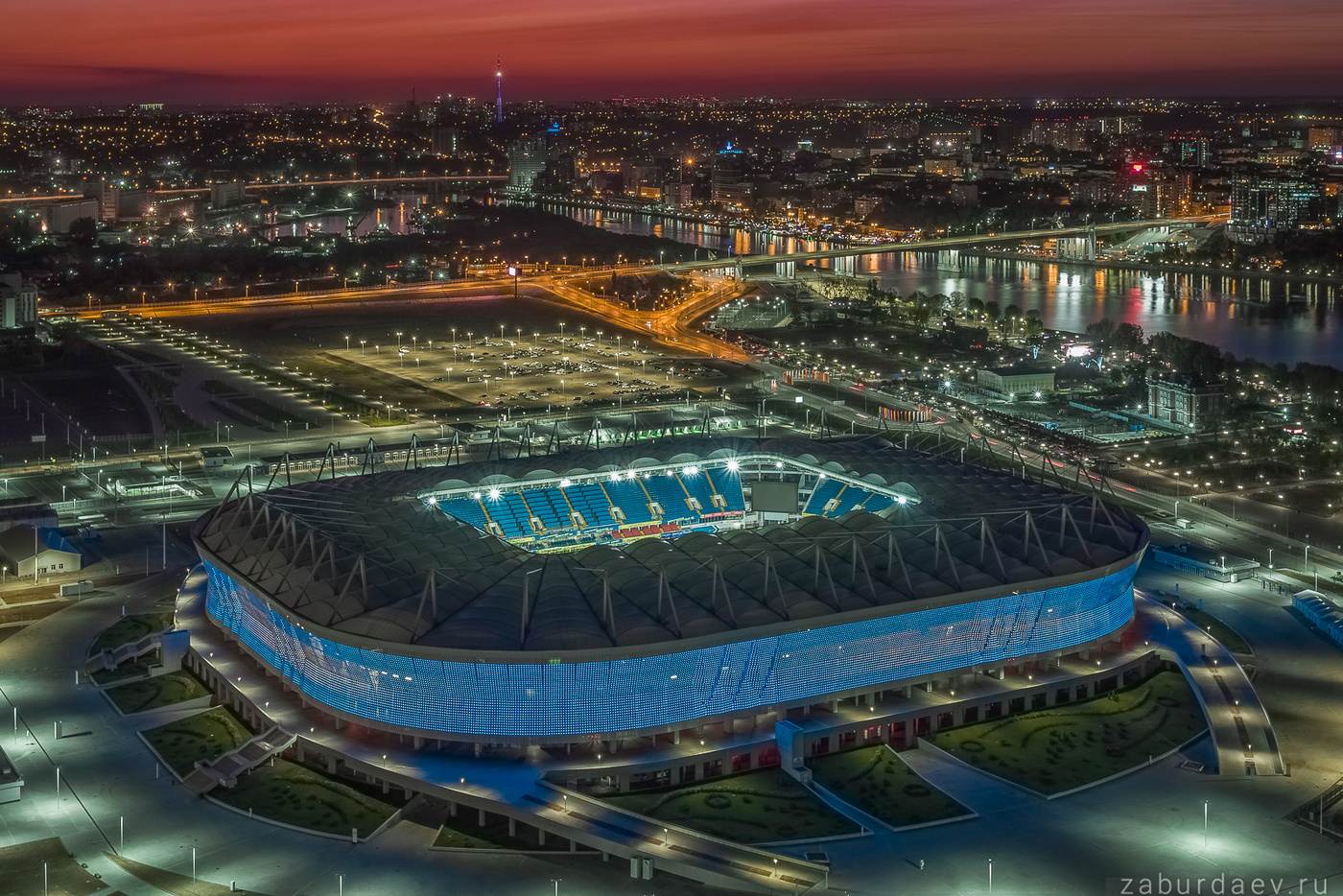
Kaliningrad [kaˈliːniːnɡʀaːt] (seit 1946 russisch Калинингра́д [kəlʲɪnʲɪnˈɡrat], bis 1946 Königsberg) ist die Hauptstadt der Oblast Kaliningrad. Die vormals deutsche Stadt Königsberg wurde als Ergebnis des Zweiten Weltkrieges unter dem Namen Kaliningrad, wie der gesamte Nordteil Ostpreußens (außer dem Memelland), Teil der Russischen Sowjetrepublik, der größten Unionsrepublik der Sowjetunion. Benannt wurde die Stadt nach dem ehemaligen sowjetischen Staatsoberhaupt Kalinin. Seit der Unabhängigkeit der baltischen Staaten 1991 ist die Oblast Kaliningrad – von der Erreichbarkeit über die internationalen Gewässer der Ostsee abgesehen – eine Exklave Russlands zwischen Polen und Litauen.
加里宁格勒(俄语:Калининград,拉丁字母转写:Kaliningrad),旧名哥尼斯堡(德语:Königsberg,在德文中意指“国王之山”;俄语:Кёнигсберг;古普鲁士语:Twangste, Kunnegsgarbs, Knigsberg;波兰语:Królewiec;立陶宛语:Karaliaučius),是俄罗斯加里宁格勒州的首府,为濒临波罗的海的海港城市,市区面积215.7平方千米,2010年人口为431,402人。
此地最早是古普鲁士人的定居点,1255年条顿骑士团于北方十字军入侵期间在此建立据点,并出于对普热米斯尔·奥托卡二世国王的敬意取名“哥尼斯堡”。之后,该城一直是条顿骑士团国、普鲁士和德国东普鲁士的一部分,直到二战末期的1945年,苏联红军占领整个东普鲁士为止。二战结束后,根据《波茨坦协定》,东普鲁士约三分之一的面积划归给苏联,其余部分划归给波兰。1946年7月4日,苏联把划归给其的东普鲁士部分领土,取名为加里宁格勒州,以纪念当时刚逝世的最高苏维埃主席团主席米哈伊·加里宁,哥尼斯堡也同步更改为现名,并成为该州之首府至今。
カリーニングラード(ロシア語:Калининград〔カリニングラート〕、ラテン文字転写の例:Kaliningrad )は、ロシア連邦西部にあるカリーニングラード州の州都である。バルト海に接する港湾都市で、人口は約42万人。カリーニングラード州はポーランドとリトアニアに挟まれたロシアの飛地領で人口はおよそ95万人、世界有数の琥珀の産地である。
カリーニングラードはもともと1255年にドイツ人の東方植民によって建設された都市で、1946年まで使われていた旧名はケーニヒスベルク(Königsberg;ドイツ語で「王の山」の意)。20世紀前半まではドイツの東北辺境の重要都市であった。
Kaliningrad (Russian: Калининград, IPA: [kəlʲɪnʲɪnˈɡrat]) is a city in the administrative centre of Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave between Poland and Lithuania on the Baltic Sea.
In the Middle Ages it was the site of the Old Prussian settlement Twangste. In 1255, during the Northern Crusades, a new fortress named Königsberg was built by the Teutonic Knights. Königsberg became the capital of the Duchy of Prussia, a fiefdom of Poland from 1525 to 1657, and later East Prussia, Germany. It was heavily damaged during World War II, and its population fled or were removed by force. Königsberg became a Russian city, renamed Kaliningrad in 1946.
Kaliningrad (en russe : Калининград, en polonais : Królewiec, en lituanien : Karaliaučius), anciennement Königsberg en Prusse-Orientale, est une ville de Russie située dans une enclave territoriale, l'oblast de Kaliningrad, totalement isolée du reste du territoire russe, entre la Pologne et la Lituanie. Sa population s'élève à 441 376 habitants en 2013.
En 2018, la ville accueille quelques matchs de la Coupe du monde de football.
Kaliningrad (in russo Калининград; AFI: [kəlʲɪnʲɪnˈgrat]; ex denominazione in tedesco: Königsberg; in Yiddish: קעניגסבערג, Kenigsberg; tr. russa: Кёнигсберг, Kjonigsberg; in antico prussiano: Twangste, Kunnegsgarbs, Knigsberg; in latino: Regiomontum) è una città della Russia di 475 056 abitanti.
Essa è il capoluogo e centro principale dell'oblast’ omonima, exclave russa tra Polonia e Lituania con accesso al mar Baltico, di cui è uno dei maggiori porti. Il nome è un omaggio a Michail Ivanovič Kalinin, primo capo di Stato dell'URSS.
La città, che si trova in Prussia Orientale, un tempo territorio sotto sovranità tedesca, ha tale nome dal 4 giugno 1946; originariamente si chiamava Königsberg, letteralmente Monte del Re o Regiomonte, ed era stata la patria del filosofo Immanuel Kant. Nel 1992 passò alla Russia dall'Unione Sovietica, che l'aveva annessa nel maggio 1945. Essa è nota anche con gli esonimi Królewiec (in polacco), Kenigsberg (in lingua yiddish) e Karaliaučius (in lituano); prima di ricevere il nome attuale, in russo era nota come Kënigsberg.
Kaliningrado (en ruso: Калининград, transliterado: Kaliningrad, en alemán: Königsberg, en prusiano antiguo: Twangste, Kunnegsgarbs, Knigsberg, en lituano: Karaliaučius, en polaco: Królewiec y en bielorruso: Каралявец) la antigua Königsberg prusiana, es una ciudad portuaria de Europa Oriental perteneciente a Rusia tras su anexión en 1945 y situada en un enclave en la desembocadura del río Pregel, que desagua en el lago del Vístula, comunicado a su vez con el mar Báltico por el estrecho de Baltiysk.
Es capital del óblast de Kaliningrado, que ocupa 15 100 km² y tiene una población de 968 200 habitantes (2004).[cita requerida] Dicho óblast (región o provincia) se encuentra aislado del resto del territorio ruso, con fronteras al norte y al este con Lituania y al sur con Polonia, ambas miembros de la Unión Europea (UE).
Калинингра́д — российский город, который по решению Потсдамской конференции 1945 года вместе с северной частью немецкой провинции Восточная Пруссия был передан СССР[7]. До 4 июля 1946 года город имел название Кёнигсбе́рг (нем. Königsberg), ранее фигурировало название Короле́вец; в Польше его называли Круле́вец (польск. Królewiec), в Чехии — Кра́ловец (чеш. Královec), в Литве используется Караля́учюс (лит. Karaliaučius); до 1255 года — Твангсте́ (прусск. Twangste, Tuwangste, Twānksta).
Сегодня город Калининград — центр Калининградской области, являющийся самым западным областным центром Российской Федерации. Расположен при впадении реки Преголи в Калининградский залив. Население — 475 056[2] чел. (2018). По утверждениям городских властей, к ним добавляется ещё от 120 до 180 тыс. жителей области и приезжих из других регионов страны, живущих и работающих в Калининграде относительно легальным образом[8]. Калининград — второй по численности населения (первый — Санкт-Петербург) город Северо-Западного федерального округа, третий (после Риги и Вильнюса) — Прибалтики и седьмой среди городов побережья Балтийского моря. Калининград входит в шестёрку основных центров внутреннего миграционного притяжения в России за последние два десятилетия[9]. Город является ядром быстрорастущей Калининградской агломерации с населением свыше 715 тыс. человек[10][11].
Крупный транспортный узел: железные и шоссейные дороги; морской и речной порты; международный аэропорт Храброво. В Калининграде расположен штаб Балтийского флота ВМФ России. Калининград входит в число 25 крупнейших промышленных центров России[12].
В Калининграде расположены музеи (музей янтаря, историко-художественный, Мирового океана, Художественная галерея, музей фортификации и т. д.), театры, крупные библиотеки (в частности, фрагменты средневекового книжного собрания — библиотеки Валленродта), зоопарк, ботанический сад. В центре города расположен кафедральный собор в стиле кирпичной готики. До 2010 года Калининград имел статус «исторического города»[13]. В 2018 году в городе проведены матчи Чемпионата мира по футболу.
 阿根廷
阿根廷
 巴西
巴西
 联邦德国
联邦德国
 迭戈·弗兰
迭戈·弗兰
 世界杯决赛队
世界杯决赛队
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 2022年世界杯足球赛
2022年世界杯足球赛
 金球奖
金球奖
 法国
法国
 意大利
意大利
 克罗地亚
克罗地亚
 利昂内尔·梅西
利昂内尔·梅西
 卢卡·莫德里奇
卢卡·莫德里奇
 马拉多纳
马拉多纳
 奥利弗·卡恩
奥利弗·卡恩
 保罗·罗西
保罗·罗西
 罗马里奥
罗马里奥
 罗纳尔多
罗纳尔多
 萨尔瓦托雷·斯基拉奇
萨尔瓦托雷·斯基拉奇
 乌拉圭
乌拉圭
 齐内丁·齐达内
齐内丁·齐达内
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 B组
B组
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 C组
C组
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 F组
F组
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 H组
H组
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 B组
B组
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 C组
C组
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 F组
F组
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 H组
H组
 俄罗斯
俄罗斯

 文化遗产
文化遗产
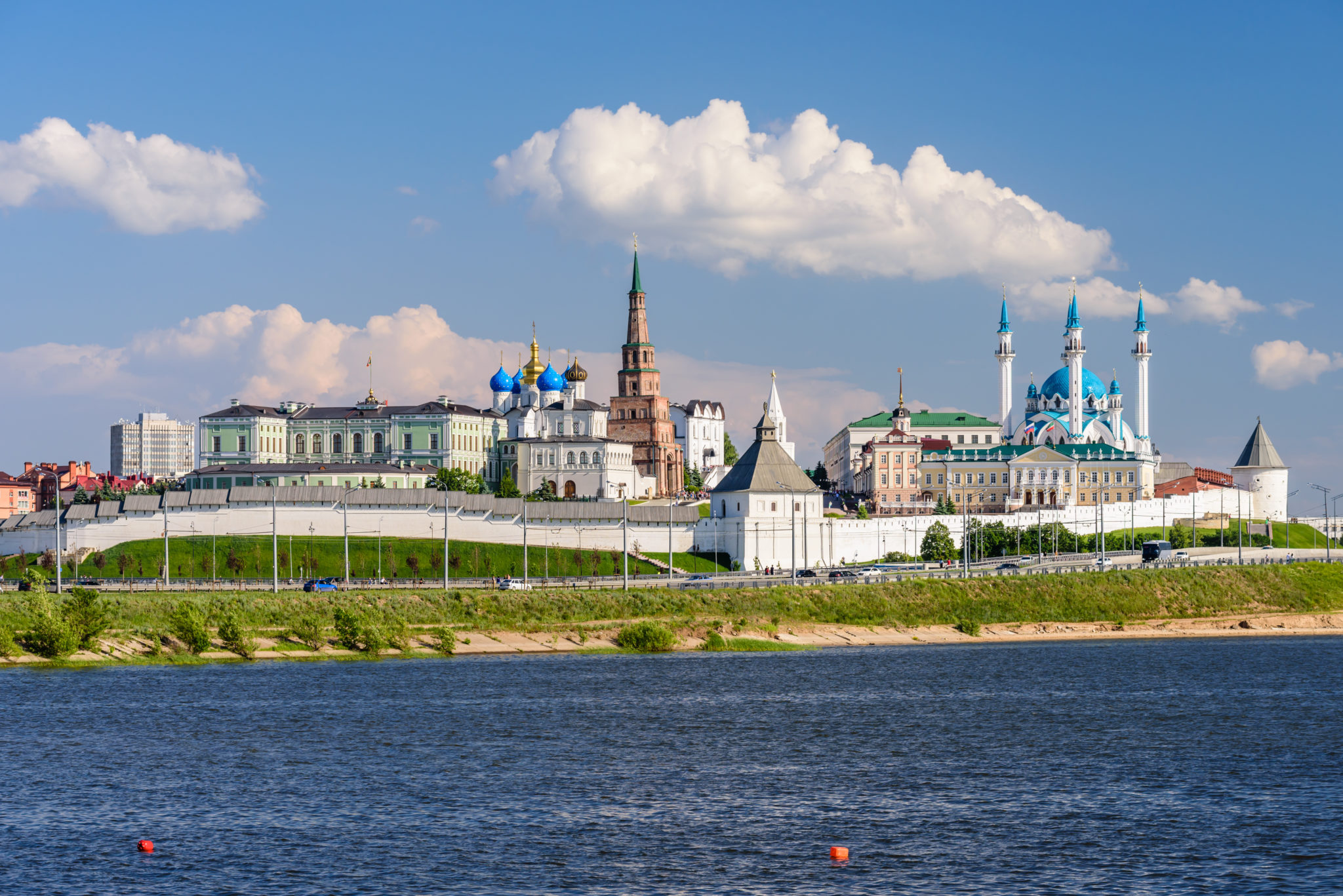
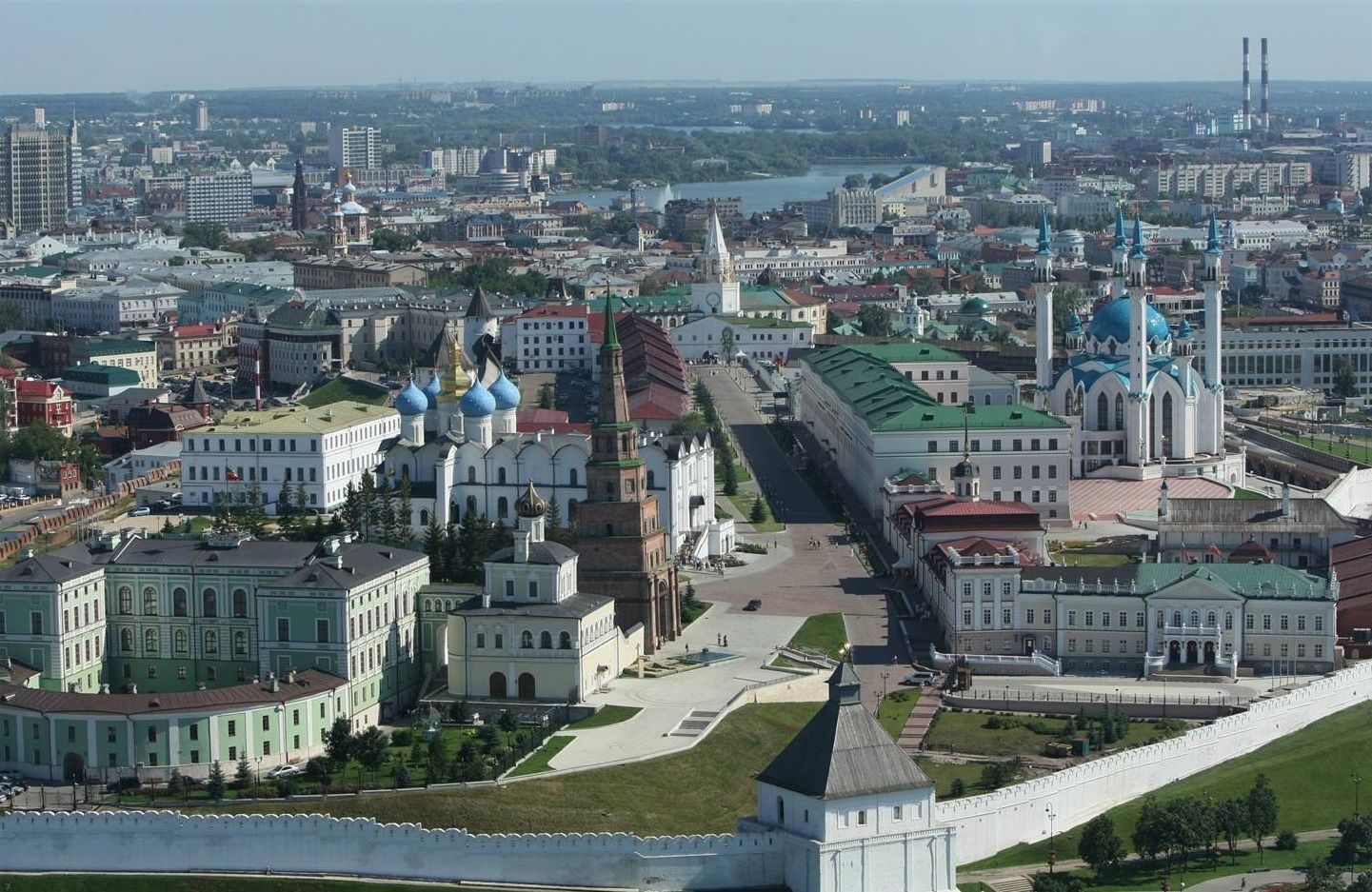




Kasan (russisch Каза́нь; tatarisch Казан) ist die Hauptstadt der Republik Tatarstan in Russland. Mit 1,32 Millionen Einwohnern (Stand 2024)[2] und knapp 2 Millionen im Ballungsraum ist Kasan die fünftgrößte Stadt Russlands und die größte Stadt an der Wolga, sowie im Wolga-Föderationskreis. Sie liegt etwa 720 km Luftlinie östlich von Moskau an der Mündung der Kasanka in die Wolga.
Historisch gesehen war Kasan die Hauptstadt des Khanats von Kasan und wurde im 16. Jahrhundert von Iwan dem Schrecklichen erobert, woraufhin die Stadt Teil des russischen Zarenreichs wurde. Während des Pugatschow-Aufstands (1773–1775) erobert und weitgehend zerstört, wurde Kasan später während der Herrschaft von Katharina der Großen wiederaufgebaut. In den folgenden Jahrhunderten entwickelte sich Kasan zu einem wichtigen industriellen, kulturellen und religiösen Zentrum Russlands, insbesondere für den Islam. Nachdem Sowjetrussland 1920 Teil der Sowjetunion geworden war, wurde Kasan zur Hauptstadt der Tatarischen Autonomen Sozialistischen Sowjetrepublik (Tatarische ASSR). Nach der Auflösung der Sowjetunion blieb Kasan die Hauptstadt der Republik Tatarstan.
Kasan ist bekannt für seine lebendige Mischung aus tatarischer und russischer Kultur und ein beliebtes Touristenziel. So besuchten im Jahr 2023 4 Millionen Touristen die Stadt. Der Kasaner Kreml wurde im Jahr 2000 zum UNESCO-Weltkulturerbe erklärt und die 2005 errichtete Kul-Scharif-Moschee gilt als die zweitgrößte Moschee Europas. Im April 2009 verlieh das russische Patentamt Kasan das Recht, sich als „Dritte Hauptstadt Russlands“ zu bezeichnen, was die Bedeutung der Stadt hinter den internationalen Aushängeschildern Moskau und St. Petersburg verdeutlicht. Kasan war Gastgeber der Sommeruniversiade 2013 und einer der Austragungsorte der FIFA Fußball-Weltmeisterschaft 2018.
Kazan (/kəˈzæn, -ˈzɑːn/; Tatar: Qazan, قزان[14]; Russian: Каза́нь, IPA: [kɐˈzanʲ]; Tatar: Казан) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan, Russia. With a population of 1,243,500,[15] it is the sixth most populous city in Russia. Kazan is one of the largest religious, economic, political, scientific, educational, cultural and sports centers in Russia. Kazan lies at the confluence of the Volga and Kazanka Rivers in European Russia, about 715 kilometres (444 mi) east from Moscow. The Kazan Kremlin is a World Heritage Site.
The millennium of Kazan was celebrated in 2005.
In April 2009, the Russian Patent Office granted Kazan the right to brand itself as the "Third Capital" of Russia.[16] In 2009 it was chosen as the "sports capital of Russia"[17] and it still is referred to as such.[18] In 2011, the European Weightlifting Championships were held here. The city hosted the 2013 Summer Universiade, 2014 World Fencing Championships, the 2015 World Aquatics Championships, and is one of the host cities for the 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup and, for the first time in Russia, the official stage of the Red Bull Air Race World Championship under the auspices of the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI). Kazan has also held the World Wushu Championships. In 2018, Kazan became one of the cities where the 2018 FIFA World Cup was held.
In 2015, 2.1 million tourists visited Kazan, a 20% increase in comparison with 2014. In 2015 1.5 million tourists visited the Kazan Kremlin, and one million visited the city's hotel and entertainment complex with an aquapark called "Kazan Riviera".[19]
Kazan (en russe, Казань ; en tatar : Казан) est une ville de Russie et la capitale de la république du Tatarstan, une des subdivisions de la Russie. Sa population s'élevait à 1 231 878 habitants en 2017 ce qui en fait la sixième ville de Russie. Kazan est un grand centre industriel et universitaire ainsi qu'un important nœud de communication. Kazan est située sur le cours moyen de la Volga à environ 700 km à l'est de Moscou. Kazan comme la république dont elle fait partie est pour moitié peuplée de tatars ce qui lui vaut de bénéficier d'une autonomie politique plus importante que d'autres sujets de la Russie.
Kazàn' (in russo: Казань?; in tàtaro Казан /qɑˈzɑn/; in latino: Casanum o Cazanum) è la capitale della repubblica russa del Tatarstan e la sesta città della Russia per popolazione, con una popolazione di 1 243 500 abitanti.
È un importante centro di commercio, industria e cultura, ed è il più importante sito della cultura tatara. Si trova alla confluenza del Volga con la Kazanka, nella Russia europea centrale. La città è stata sede della XXVII Universiade dal 6 al 17 luglio 2013, e della XVI edizione dei Campionati mondiali di nuoto dal 24 luglio al 9 agosto 2015.
Fino al 28 giugno 2017 ha ospitato la Confederations Cup, mentre nel 2018 ha ospitato i Campionati Mondiali di calcio.
Kazán (en ruso: Казань, Kazan; en tártaro: Казан) es la capital y ciudad más poblada de la República de Tartaristán, en Rusia. La ciudad se encuentra a orillas del Volga, en la confluencia del río Kazanka. Es la octava ciudad más poblada de Rusia, con una población en su área metropolitana de 1,57 millones de habitantes.
Каза́нь (тат. Казан, Qazan, قزان) — город в Российской Федерации, столица Республики Татарстан, крупный порт на левом берегу реки Волги, при впадении в неё реки Казанки. Один из крупнейших религиозных, экономических, политических, научных, образовательных, культурных и спортивных центров России. Казанский кремль входит в число объектов Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО.
Исторически столица (центр) Казанского ханства, Казанского царства, Казанской губернии и Татарской АССР.
Город имеет зарегистрированный бренд «Третья столица России»[6].
В 2005 году было отпраздновано тысячелетие Казани.
Казань неоднократно принимала международные соревнования высокого уровня по различным видам спорта, в том числе XXVII Всемирную летнюю Универсиаду в 2013 году, а также ряд матчей чемпионата мира по футболу 2018 года.
В 2014 году в рейтинге сайта о путешествиях TripAdvisor в качестве самых быстро развивающихся туристических направлений столица Татарстана заняла 8-е место в мире и 3-е место в Европе[7][8].
В 2017—2018 годах в рейтинге Airbnb Казань заняла 3-е место в рейтинге самых популярных у туристов городов России[9].
Городской округ граничит с Зеленодольским, Высокогорским, Пестречинским, Лаишевским районами, по акватории Куйбышевского водохранилища — с Верхнеуслонским районом.
 世界杯决赛队
世界杯决赛队
 2018年世界杯足球赛
2018年世界杯足球赛
 D组
D组
 2022年世界杯足球赛
2022年世界杯足球赛
 2022年世界杯足球赛
2022年世界杯足球赛
 F组
F组
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2016
欧洲足球锦标赛 2016
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
 E组
E组

 欧洲足球锦标赛 2024
欧洲足球锦标赛 2024
 克罗地亚
克罗地亚

 体育
体育
 (F)欧洲足联国家联赛
(F)欧洲足联国家联赛
 欧洲足联国家联赛
欧洲足联国家联赛
 联赛A - 小组4
联赛A - 小组4

Ort ul. Lužniki 24 Russland 119048 Moskau, Russland Klassifikation 4 Eigentümer Stadt Moskau Baubeginn 1955 Eröffnung 31. Juli 1956 11. November 2017 Renovierungen 1978–1980 1995–1997 2014–2017 Oberfläche Naturrasen Kapazität 80.000 Plätze Spielfläche 105 × 68 m Veranstaltungen Eishockey-Weltmeisterschaft 1957 Olympische Sommerspiele 1980 Leichtathletik-Europacup 1985 Moscow Music Peace Festival 1989 Russisches Pokalfinale 1993, 1994, 1995, 1998, 1999, 2002, 2006, 2007 Finale UEFA-Pokal 1999 Finale der UEFA Champions League 2008 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften 2013 Fußball-Weltmeisterschaft 2018 Konzerte


 建筑艺术
建筑艺术

 国际城市
国际城市
 加里宁格勒州
加里宁格勒州
 重要港口
重要港口






