A college endowment refers to all the money that an institution receives in donations. However, endowment funds are not ‘no-questions-asked’ cash boosts for the college. Instead, endowments are tightly controlled investments that are supposed to be grown so that the interest can be used to upgrade facilities, hire new staff, provide scholarships or aid the college or its students in some way.
Over the past three decades, the total market value of the 20 largest college endowments has grown nearly tenfold — from $30.6 billion to $302.1 billion. As the size of college endowments has increased, so too has the debate over their purpose, management and ethical obligations.
To get a better idea of how college endowments have changed over the last 30 years, DegreeQuery looked at the market value of the 20 largest U.S. college endowments from 1990 to 2020.
30 Years of U.S. college endowments
Based on the most recent NACUBO survey of 810 universities, the total market value of endowments in 2018 was $624.3 billion. 48.3% of that is held by just 20 colleges. But why the huge growth in market value over the past 30 years? It might be something to do with how much of the endowment the university chooses to spend on operations or the return rates of the endowment’s investment portfolio. Due to their often wealthy donor base and long-term investment horizons, the largest university endowments can invest in a diverse array of asset classes, and often grow faster than the economy as a whole.
From 1990 to 2020, the market value of the 20 largest college endowments grew at an average annual rate of 8.5% — faster than the 6.6% average annual growth rate for the Fortune 500 over the same period. The universities with the fastest growth over the past 30 years include the University of Michigan, Duke University and the University of Notre Dame. Meanwhile, the endowments with the slowest growth include Emory University, Rice University and Washington University in St. Louis.
1. U.S. college endowments in the 1990s
From 1990 to 1999, the market value of the 20 largest U.S. college endowments grew at an average annual rate of 12.5% — the fastest of the last three decades. As you can see from our graph, over this period, the University of Michigan endowment rose from the 20th largest to the 17th largest, and the University of Pennsylvania rose from the 16th largest to the 12th largest. Meanwhile, the Columbia University endowment fell from the sixth-largest to the 11th largest. Although the University of Texas System endowment had the slowest growth of the 20 largest endowments over this period, it remained the second-largest endowment overall.
2. U.S. college endowments in the 2000s
Endowment growth is closely connected with the overall health of the economy. As of 2018, just 4% of endowment assets were held as cash, the rest invested in equities, fixed income instruments and alternative investment vehicles. In the lead up to the 2008 financial crisis — university endowments had increasingly invested in high-risk, illiquid investments like private equity, real estate and hedge funds. As a result, endowments lost tens of billions of dollars in value, with some schools losing more than 25% of their total endowment value. From 2008 to 2009, the total value of the 20 largest endowments fell 3.4%. Yale posted the largest percentage decline, losing 28.6% of its market value. Other university endowments that posted big losses from the recession include Harvard, Duke and Stanford.
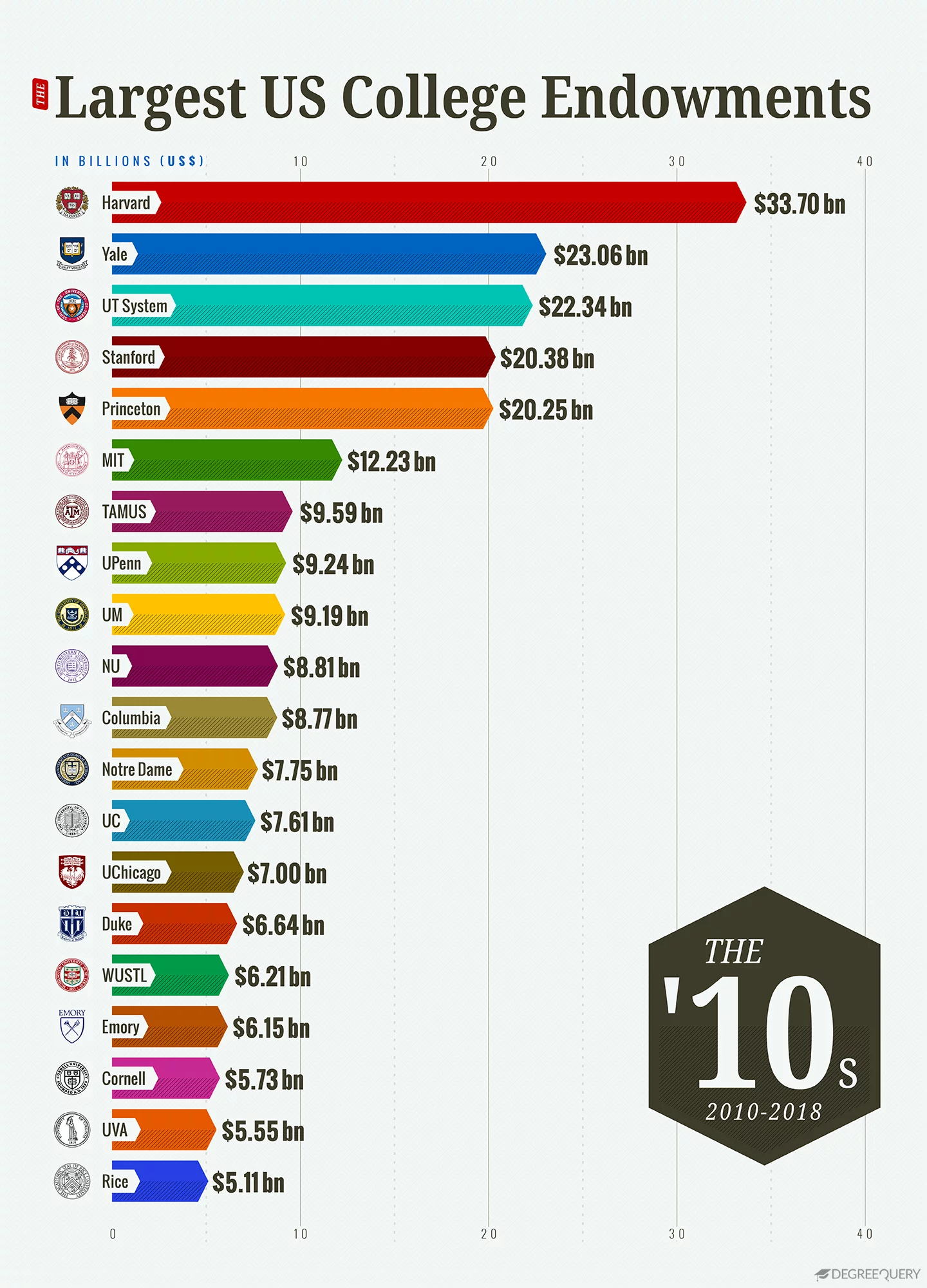
3. U.S. college endowments in the 2010s
Endowment growth rates rebounded in the wake of the Great Recession, although growth was still slow compared to the 1990s. From 2010 to 2018, the market value of the 20 largest endowments grew at an average annual rate of 7.6%. This is more than the 3.5% average annual growth rate for 2000 to 2009, yet less than the 12.5% rate for 1990 to 1999. During this period, the biggest winners were the University of Pennsylvania, rising from 11th to 7th largest, and the Texas A&M University System, which rose from 10th to 8th largest. Lackluster performance at some of the wealthiest schools has prompted some universities to make major changes to their endowment management. In 2017, for example, Harvard announced it would lay off roughly half of its 230-person staff in the wake of poor investment performance.
As you can see, university endowments were big business over the past 30 years. Nowadays, students, policymakers and the general public are increasingly involved in the conversation surrounding their management, mission and societal impact. For example, the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which imposed a 1.4% tax on the net investment income of the wealthiest endowments, recently sparked a wave of criticism from university administrators. Elsewhere on campus, protesting students demanded their universities divest from fossil fuel companies.
As the debate rages on and endowments continue to grow, these visualizations help us see how we got to this point.
Methodology
To get a better idea of how college endowments have changed over the last 30 years, DegreeQuery looked at the market value of the 20 largest U.S. college endowments from 1990 to 2018. Data on endowment asset value by university came from the National Association of College and University Business Officers (NACUBO) and is unadjusted for inflation. In years when certain universities did not participate in the NACUBO survey, we estimated the endowment value based on the compound annual growth rate for all available years. Estimated figures include the market value of the endowment assets for the Texas A&M University System for 1990, as well as the market value of the endowment assets for the University of California system for the years 1990 through 1992.
SOURCES
Fortune 500. (n.d.) Fortune 500 2018. fortune.com
NACUBO. (2019). Detailed Asset Allocations for U.S. College and University Endowments and Affiliated Foundations, FY18. nacubo.org
Miller, C. & Fabrikant, G. (2008). Universities retrench as endowments suffer from financial crisis. nytimes.com
Humphreys, J. et al. (2010). Educational Endowments and the Financial Crisis: Social Costs and Systemic Risks in the Shadow Banking System. tellus.org
Plender, J. (2014). There is a history lesson to be learnt from Yale endowment. ft.com
Fabrikant, G. (2017). Harvard Makes Changes in Managing a Lagging Endowment. nytimes.com
Tax Policy Center. (n.d.). What is the tax treatment of college and university endowments? taxpolicycenter.org





Gothic Revival architecture grew in the mid-19th century and was one of the early styles of Victorian-era homes. The Gothic Revival style takes influence from Medieval Europe and was designed as a country home. Architects believed the asymmetrical design and ornamentation complemented the nature of rural America.
Gothic Revival homes can be identified by their:
- Pointed arch in windows, doors, and decoration
- Elaborate wood trim vergeboards and bargeboards
- Steeply pitched roofs and front-facing gables
- Towers and turrets resembling medieval castles
Gothic Revival architecture was a popular style for schools and churches as well as rural homes.




Colonial-style houses are simple rectangular homes that became popular in the 1600s as colonists settled the East Coast. These homes have many variations due to the fact that new communities all over the world built Colonial-style homes to suit their culture.
British Colonial style is the most common and recognizable Colonial home. Its key features include:
- A side-gabled roof
- Two floors
- A centered front door
- Symmetrical windows on either side of the door
The rectangular shape and interest in symmetry are seen in other Colonial house styles, too. Materials and decorative features can vary by region, as some Colonial houses sport brick exteriors and ornate trim, while others showcase shingle siding and simple shutters.
These are also some of the cheapest types of houses to build.
The French Colonial house style can be seen around the world and has significant variety among its sub-styles.
French Colonial houses have the same symmetry as other Colonial homes with these distinct features:
- Dormer windows, including one centered above the door
- External stairs to enter higher floors
- Iron stairs and balconies
- Slightly raised basements to support the floor
French Colonial houses are most similar to Spanish Colonial houses and easily identified by their elaborate iron balconies, stairs, and entrances.

The U.S. health system is a mix of public and private, for-profit and nonprofit insurers and health care providers. The federal government provides funding for the national Medicare program for adults age 65 and older and some people with disabilities as well as for various programs for veterans and low-income people, including Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program. States manage and pay for aspects of local coverage and the safety net. Private insurance, the dominant form of coverage, is provided primarily by employers. The uninsured rate, 8.5 percent of the population, is down from 16 percent in 2010, the year that the landmark Affordable Care Act became law. Public and private insurers set their own benefit packages and cost-sharing structures, within federal and state regulations.

The Parthenon in Centennial Park, in Nashville, Tennessee, is a full-scale replica of the original Parthenon in Athens. It was designed by architect William Crawford Smith and built in 1897 as part of the Tennessee Centennial Exposition.
Today the Parthenon, which functions as an art museum, stands as the centerpiece of Centennial Park, a large public park just west of downtown Nashville. Alan LeQuire's 1990 re-creation of the Athena Parthenos statue in the naos (the east room of the main hall) is the focus of the Parthenon just as it was in ancient Greece. Since the building is complete and its decorations were polychromed (painted in colors) as close to the presumed original as possible, this replica of the original Parthenon in Athens serves as a monument to what is considered the pinnacle of classical architecture. The plaster replicas of the Parthenon Marbles found in the Treasury Room (the west room of the main hall) are direct casts of the original sculptures which adorned the pediments of the Athenian Parthenon, dating back to 438 BC. The surviving originals are housed in the British Museum in London and at the Acropolis Museum in Athens.


The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM).
As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field. Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve pro bono as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code.
Founded in 1863 as a result of an Act of Congress that was approved by Abraham Lincoln, the NAS is charged with "providing independent, objective advice to the nation on matters related to science and technology. … to provide scientific advice to the government 'whenever called upon' by any government department."[2]
The Academy receives no compensation from the government for its services.[3]
The Academy currently has 2,984 members and international members. Existing members elect new members for life. Up to 120 members are elected every year; up to 30 foreign citizens may be elected as international members annually. The election process begins with a formal nomination, followed by a vetting period, and culminates in a final ballot at the Academy's annual meeting in April each year. Members are affiliated with a section -- a specific scientific field -- in one of six so-called "classes": (1) Physical and Mathematical Sciences; (2) Biological Sciences; (3) Engineering and Applied Sciences; (4) Biomedical Sciences; (5) Behavioral and Social Sciences; and (6) Applied Biological, Agricultural, and Environmental Sciences.[6] Since its founding, the Academy has elected 6,457 members. Harvard University is associated with the most members (329), some 5% of the all-time total. The top ten institutions, half of which are Ivy League universities, account for nearly 28% of all members ever elected.[11]
| Top 10 Primary Institutions | Members (1963-2022) |
|---|---|
| Harvard University | 329 |
| Stanford University | 250 |
| University of California, Berkeley | 242 |
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology | 206 |
| Yale University | 132 |
| Princeton University | 128 |
| California Institute of Technology | 126 |
| Columbia University | 125 |
| University of Chicago | 120 |
| University of Pennsylvania | 83 |

Queen Anne homes were popularized in the later Victorian era, beginning around 1880. This style is the quintessential Victorian home for many, with ornate woodworking and decor inside and out.
Queen Anne homes have key regional differences across the country, but maintain these essentials:
- Textured walls with decorative shingles or half-timbering
- Large round or polygonal tower at the home’s corner
- Steeply pitched and asymmetrical roof
- Decorative spindles on porches and trim
- Decorative single-pane or stained glass windows
Queen Anne architecture is most common in homes, but can also be seen in schools, churches, and office buildings.





The American Farmhouse is a simple and timeless style. Farmhouses are designed to be practical first and foremost. They’re common across the US and often showcase regional variations, like wrap-around porches in the South.
Farmhouses have evolved with time and location, but often feature these elements:
- Rectangular floor plan
- Large front porches
- Natural wood and stone materials
- Few and small windows
- Formal front rooms separated from family rooms
Of course, the easiest way to identify a farmhouse is that they’ll often be situated on a large plot of farmland.





The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin,[1] Andrew Oliver, and other Founding Fathers of the United States.[2] It is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Membership in the academy is achieved through a thorough petition, review, and election process.[3] The academy's quarterly journal, Dædalus, is published by MIT Press on behalf of the academy.[4] The academy also conducts multidisciplinary public policy research.
The Academy was established by the Massachusetts legislature on May 4, 1780, charted in order "to cultivate every art and science which may tend to advance the interest, honor, dignity, and happiness of a free, independent, and virtuous people."[6] The sixty-two incorporating fellows represented varying interests and high standing in the political, professional, and commercial sectors of the state. The first class of new members, chosen by the Academy in 1781, included Benjamin Franklin and George Washington as well as several international honorary members. The initial volume of Academy Memoirs appeared in 1785, and the Proceedings followed in 1846. In the 1950s, the Academy launched its journal Daedalus, reflecting its commitment to a broader intellectual and socially-oriented program.[7]
Since the second half of the twentieth century, independent research has become a central focus of the Academy. In the late 1950s, arms control emerged as one of its signature concerns. The Academy also served as the catalyst in establishing the National Humanities Center in North Carolina. In the late 1990s, the Academy developed a new strategic plan, focusing on four major areas: science, technology, and global security; social policy and education; humanities and culture; and education. In 2002, the Academy established a visiting scholars program in association with Harvard University. More than 75 academic institutions from across the country have become Affiliates of the Academy to support this program and other Academy initiatives.[8]
The Academy has sponsored a number of awards and prizes,[9] throughout its history and has offered opportunities for fellowships and visiting scholars at the Academy.[10]
In July 2013, the Boston Globe exposed then president Leslie Berlowitz for falsifying her credentials, faking a doctorate, and consistently mistreating her staff.[11] Berlowitz subsequently resigned.









