
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CAD/CAE/CAM/EDA/PDM/PLM
CAD/CAE/CAM/EDA/PDM/PLM


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CNC
CNC


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CRM/EAM/ERP/SRM/SCM/HCM/QM/XM/WFM
CRM/EAM/ERP/SRM/SCM/HCM/QM/XM/WFM


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Industrial Robot
Industrial Robot


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES
PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Science and technology
Science and technology


 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Big Data
Big Data


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing

 Science and technology
Science and technology



 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Big Data
Big Data


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 ***Metaverse
***Metaverse

 Science and technology
Science and technology

Cloud Computing (deutsch etwa Rechnen in der Wolke) ist primär der Ansatz, abstrahierte IT-Infrastrukturen (z. B. Rechenkapazität, Datenspeicher-, fertige Software- und Programmierumgebungen als Service) dynamisch an den Bedarf angepasst über ein Netzwerk zur Verfügung zu stellen.
Die Abrechnung erfolgt dabei nutzungsabhängig, da nur tatsächlich genutzte Dienste bezahlt werden müssen. Ein weiterer zentraler Punkt des Konzeptes ist, dass die Bereitstellung basierend auf der Kombination aus virtualisierten Rechenzentren und modernen Webtechnologien wie Webservices vollautomatisch erfolgen kann und somit keinerlei Mensch-Maschine-Interaktion mehr erfordert. Sekundär geht es bei „Cloud Computing“ auch darum, alles als dynamisch nutzbaren Dienst zur Verfügung zu stellen, sei es nun Rechenkapazität, Buchhaltung, einfachste von Menschen verrichtete Arbeit, eine fertige Softwarelösung oder beliebige andere Dienste (siehe auch XaaS). Im Zentrum steht dabei die Illusion der unendlichen Ressourcen, die völlig frei ohne jegliche Verzögerung an den tatsächlichen Bedarf angepasst werden können (siehe auch Skalierbarkeit)[1].
Der Zugriff auf die entfernten Systeme erfolgt über ein Netzwerk, beispielsweise das des Internets. Es gibt aber im Kontext von Firmen auch sogenannte „Private Clouds“, bei denen die Bereitstellung über ein firmeninternes Intranet erfolgt. Die meisten Anbieter von Cloudlösungen nutzen die Poolingeffekte, die aus der gemeinsamen Nutzung von Ressourcen entstehen, für ihr Geschäftsmodell.
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1999
Women's Soccer World Cup 1999

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
 United States
United States
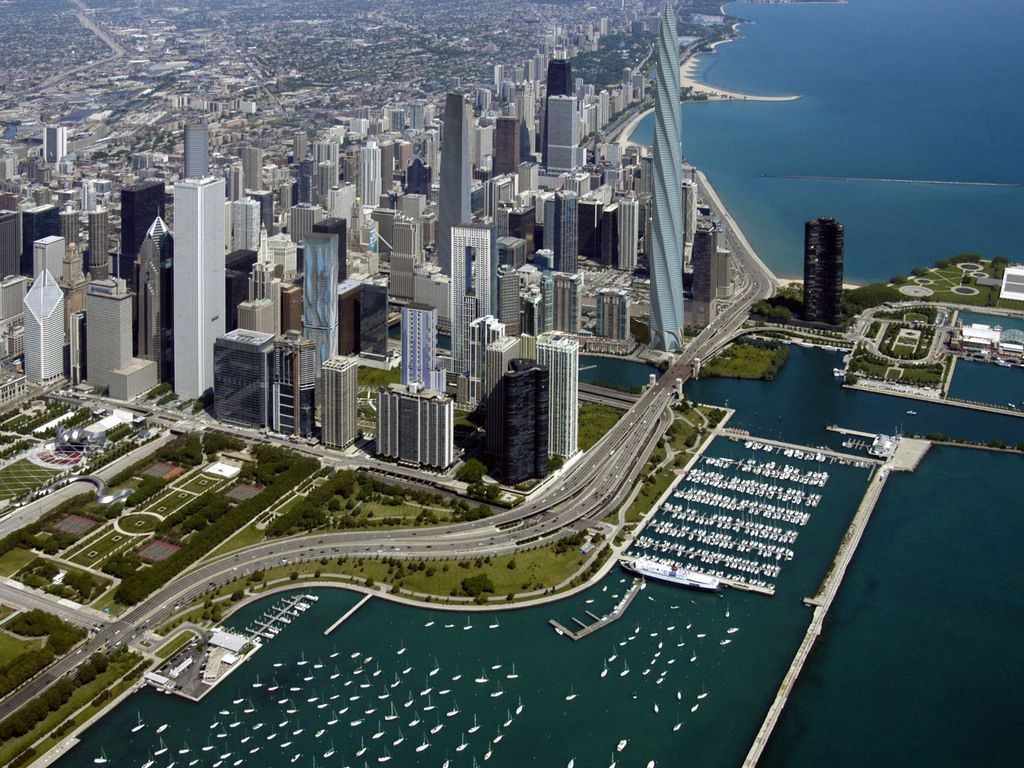


Wie die meisten amerikanischen Städte ist Chicago am Reißbrett entworfen worden. Das Schachbrettmuster kann man z.B. von der Aussichtsplattform des Sears-Towers gut erkennen. Die Aussicht von diesem Punkt aus ist atemberaubend. Genießen Sie das Panorama des Lake Michigan und beobachten Sie die Flugzeuge die am Chicago-International-Airport landen.
Chicago (deutsche Schreibweise: Chikago,[1] Aussprache: [ʃɪˈkɑːgoʊ]; ) ist eine Stadt am Südwestufer des Michigansees im Bundesstaat Illinois in den Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika. Mit einer Einwohnerzahl von 2.722.389 (2014)[2] ist sie die drittgrößte Stadt der Vereinigten Staaten. In der Agglomeration leben 8,7 Millionen, in der Metropolregion Chicago 9,7 Millionen Menschen (2007).[3]
Chicago ist seit der Mitte des 19. Jahrhunderts eine wichtige Handelsstadt in den Vereinigten Staaten. Diese Funktion wird durch ihre Eigenschaft als Eisenbahnknotenpunkt und ihre Lage an der Mündung des Illinois Waterways begünstigt. Die Stadt liegt an wichtigen Eisenbahnstrecken, die die Ost- mit der Westküste verbinden und ist über die Großen Seen und den Sankt-Lorenz-Seeweg bzw. den Eriekanal mit dem Atlantik und mit New York City verbunden. Der Illinois Waterway stellt über den Mississippi die Verbindung zum Golf von Mexiko her.
Chicago ist Sitz der Chicago Mercantile Exchange, der größten Warenterminbörse der Vereinigten Staaten, und der Chicago Board of Trade, der größten Rohstoff-, Futures- und Optionsbörse der Vereinigten Staaten. Außerdem befindet sich hier die größte Regionalbörse der Vereinigten Staaten, die Chicago Stock Exchange.
Die Metropolregion von Chicago erbrachte 2016 eine Wirtschaftsleistung von 651,2 Milliarden US-Dollar.[4] Bei einer Studie aus dem Jahr 2014 belegte Chicago Platz 9 unter den wirtschaftsstärksten Metropolregionen weltweit und Platz 3 innerhalb der Vereinigten Staaten.[5]
十七世纪时为法国皮毛商交易地,后归美国。1834年建市。1848年伊利诺伊·密歇根运河开通和铁路相继修建后,发展极速。全国最大的铁路 枢纽,32条干线交会于此。现为全国性的重要农畜产品贸易市场和钢铁冶炼基地。肉类加工、面粉、罐头、冷冻食品加工等发达。此外还有农机制造、机车、货 车、电话机、电视机、收音机、印刷、塑料等。包括卫星城市格里、南芝加哥,为美国第二个重工业地带。多大银行、商业企业,有芝加哥大学(1891年建)与 科学研究机构等。
芝加哥市内保存着早期传统式的西欧古建筑,又有壮观巍峨的现代摩天大楼。市区沿着宽阔壮丽的大道连绵数十公里,规划布局井井有条。现在的城市是 1871年的大火之后重建的,新城各种形状新奇、色彩各异的高层建筑使其成为一建筑艺术博物馆。芝加哥市区内摩天大楼之多,仅次于纽约。
芝加哥市内保存着早期传统式的西欧古建筑,又有壮观巍峨的现代摩天大楼。市区沿着宽阔壮丽的大道连绵数十公里,规划布局井井有条。现在的城市是1871年 的大火之后重建的,新城各种形状新奇、色彩各异的高层建筑使其成为一建筑艺术博物馆。芝加哥市区内摩天大楼之多,仅次于纽约。当今全世界5座最高的摩天大 楼有3座在芝加哥,市中心的西尔斯大厦是美国第一高楼,有110层,高443米。
19世纪开通的伊利诺伊-密歇根运河,把处于内陆的芝加哥同五大湖和大西洋连接起来,变为港口城市。海洋巨轮从加拿大的圣劳伦斯湾直驶芝加哥码 头。芝加哥是美国的铁路枢纽,几十条铁路交汇于此,连接美国各大城市;它还有世界上最繁忙国际机场之一的奥黑尔国际机场;因此,芝加哥可以称得上美国东西 交通、水、陆、空运输的中心。
シカゴ(英: Chicago [ʃɨˈkɑːɡoʊ, ʃɨˈkɔːɡoʊ, tʃɨˈkɑːɡoʊ] (![]() 音声ファイル)))は、アメリカ合衆国イリノイ州にある都市。同州最大の都市であり、国内では、ニューヨーク、ロサンゼルスに次ぐ人口を持つ。
音声ファイル)))は、アメリカ合衆国イリノイ州にある都市。同州最大の都市であり、国内では、ニューヨーク、ロサンゼルスに次ぐ人口を持つ。
シカゴはクック郡内にあり、同郡の郡庁所在地である。同郡には他にアーリントンハイツなどが含まれる。2012年の人口は271万人。
19世紀後半から20世紀中盤まで、アメリカ国内における鉄道・航空・海運の拠点として、また五大湖工業地帯の中心として発展し、ニューヨークに次ぐアメリカ第2の都市となっていた歴史を持つ。摩天楼がそびえ立つアメリカ型都市の発祥とされ、ダウンタウンの高層建築は、シカゴ派として知られ、近代建築史における重要局面をなした。1973年に建てられたシアーズ・タワー(現在はウィリス・タワーに改称)は、1998年まで世界一の高層建築であった。マコーミック・プレイスコンプレックスは、北米最大のコンベンション・センターであり、オヘア空港は全米有数の過密な空港として知られる。
アメリカのシンクタンクが2017年に発表した総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界12位の都市と評価された[1]。アメリカの都市ではニューヨーク、ロサンゼルスに次ぐ3位である。2017年3月の調査によると、世界7位の金融センターである[2]。2014年の都市の経済規模(GDP)では、世界9位となっている[3]。
日本語の漢字表記は「市俄古」。また、シカゴに住む人々は「Chicagoans(シカゴアンズ)」と呼ばれている[4]。
Chicago (/ʃɪˈkɑːɡoʊ/ (![]() listen), locally also /-ˈkɔː-/), officially the City of Chicago, located on the shores of freshwater Lake Michigan, is the third most populous city in America after New York and Los Angeles. As of the 2017 census-estimate, Chicago has a population of 2,716,450, which makes it the most populous city in both the state of Illinois and the Midwestern United States. It is the county seat of Cook County, the second most populous county in the U.S. Chicago is the principal city of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is often referred to as "Chicagoland." The Chicago metropolitan area has nearly 10 million people, is the third-largest in the United States, the fourth largest in North America, and the third largest metropolitan area in the world by land area. Chicago is the birthplace of the skyscraper, and considered the most influential architectural city of the 20th century.[6] In finance, the city saw the creation of the first standardized futures contracts at the Chicago Board of Trade; which today is the largest and most diverse derivatives market in the world, generating 20% of all volume in commodities and financial futures.[7]
listen), locally also /-ˈkɔː-/), officially the City of Chicago, located on the shores of freshwater Lake Michigan, is the third most populous city in America after New York and Los Angeles. As of the 2017 census-estimate, Chicago has a population of 2,716,450, which makes it the most populous city in both the state of Illinois and the Midwestern United States. It is the county seat of Cook County, the second most populous county in the U.S. Chicago is the principal city of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is often referred to as "Chicagoland." The Chicago metropolitan area has nearly 10 million people, is the third-largest in the United States, the fourth largest in North America, and the third largest metropolitan area in the world by land area. Chicago is the birthplace of the skyscraper, and considered the most influential architectural city of the 20th century.[6] In finance, the city saw the creation of the first standardized futures contracts at the Chicago Board of Trade; which today is the largest and most diverse derivatives market in the world, generating 20% of all volume in commodities and financial futures.[7]
Chicago was incorporated as a city in 1837 near a portage between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River watershed and grew rapidly in the mid-nineteenth century.[8] After the Great Chicago Fire of 1871, which destroyed several square miles and left more than 100,000 homeless, the city made a concerted effort to rebuild.[9] The construction boom accelerated population growth throughout the following decades, and by 1900 Chicago was one of the five largest cities in the world.[10] During this period, Chicago made noted contributions to urban planning and zoning standards, which included creating new construction styles (including the Chicago School of architecture), the development of the City Beautiful Movement, and the steel-framed skyscraper.[11]
Positioned along Lake Michigan, the city is an international hub for finance, commerce, industry, technology, telecommunications, and transportation. O'Hare International Airport is the one of the busiest airports in the world, and the region also has the largest number of U.S. highways and railroad freight.[12] In 2012, Chicago was listed as an alpha global city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network,[13] and it ranked seventh in the entire world in the 2017 Global Cities Index.[14] Chicago has the fourth-largest gross metropolitan product in the world — generating about $670.5 billion according to September 2017 estimates — ranking it after the metropolitan areas of Tokyo, New York City, and Los Angeles, and ranking ahead of number five London and number six Paris.[15] Chicago has one of the world's largest and most diversified and balanced economies, not being dependent on any one industry, with no single industry employing more than 14% of the workforce.[16]
Chicago was the second most visited city in the United States with 55 million domestic and international visitors,[17][18] not far behind the 62 million visitors to New York City in 2017.[19] The city ranked first place in the 2018 Time Out City Life Index, a global quality of life survey of 15,000 people in 32 cities.[20][21][22][23][24] Landmarks in the city include Millennium Park, Navy Pier, the Magnificent Mile, the Art Institute of Chicago, Museum Campus, the Willis (Sears) Tower, the Museum of Science and Industry, and Lincoln Park Zoo. Chicago's culture includes the visual arts, literature, film, theater, comedy (especially improvisational comedy), food, and music, particularly jazz, blues, soul, hip-hop, gospel,[25] and electronic dance music including house music. There are many colleges and universities in the Chicago area, of which the University of Chicago, Northwestern University, and the University of Illinois at Chicago are classified as "highest research" doctoral universities.
Chicago has professional sports teams in each of the major professional leagues, including two Major League Baseball teams. The city has had several nicknames throughout its history such as the Windy City, Chi-Town, Second City, and the City of the Big Shoulders, referring to its numerous towers and skyscrapers.[26]
Chicago (en anglais [ʃɪˈkɑːɡoʊ] ou [ʃɪˈkɔːɡoʊ]) est la troisième ville des États-Unis par sa population et se situe dans le nord-est de l'État de l'Illinois. C'est la plus grande ville de la région du Midwest, dont elle forme le principal centre économique et culturel2. Chicago se trouve sur la rive sud-ouest du lac Michigan, un des cinq Grands Lacs d'Amérique du Nord. Les rivières Chicago et Calumet traversent la ville.
Comptoir commercial fondé à la fin du XVIIIe siècle par Jean Baptiste Pointe du Sable, un mulâtre d'origine française, Chicago devient une municipalité en 18333 et acquiert officiellement le statut de ville en 18374. Elle est le siège du comté de Cook. Chicago est aussi le siège d'une paroisse catholique francophone, signe de son histoire liée à la France5.
La ville de Chicago compte 2 716 450 habitants et s'étend sur une superficie de 606 km2. Ses habitants s'appellent les Chicagoans6 (ou plus rarement Chicagolais7). Troisième ville des États-Unis par sa population, l'agglomération de Chicago est également la troisième du pays avec une population de 8 711 000 habitants s'étendant sur 5 498 km2. L'aire métropolitaine de Chicago (Chicago metropolitan area), communément appelée « Chicagoland », compte 9 526 434 habitants et s'étend sur 28 163 km28,9 à travers trois États (Illinois, Indiana et Wisconsin), ce qui en fait la quatrième aire urbaine d'Amérique du Nord après Mexico, New York et Los Angeles10.
Chicago est une ville de classe mondiale alpha11. Elle constitue le deuxième centre industriel des États-Unis et appartient à la « Ceinture des industries » (Manufacturing Belt), mais la ville est aussi une des principales places financières du monde12 et la première bourse de matières premières agricoles au monde13. C'est à Chicago que sont fixés les prix du blé et du soja aux États-Unis14. La ville se classe au troisième rang national pour le nombre d'entreprises implantées dans son agglomération15, dont les plus importantes sont Motorola, Boeing, United Airlines, McDonald's, Sears, Kraft Foods, Mondelēz ou encore les laboratoires Abbott. D'autres entreprises y ont été créées, comme Hertz, l'une des plus grandes enseignes de location de voitures. L'industrie emploie plus d'un million de personnes dans l'agglomération de Chicago15.
Grâce à sa situation exceptionnelle, la ville constitue un centre de communication majeur de voies terrestres (l'un des plus importants en Amérique du Nord), et de transports aériens avec ses deux aéroports internationaux, O'Hare et Midway. Elle acquiert une grande renommée culturelle grâce à son architecture moderne de gratte-ciel16 et attire des millions de visiteurs chaque année17. En effet, la Willis Tower (appelée « Sears Tower » jusqu'au mois de juillet 2009) a été de 1973 à 1998, le plus haut gratte-ciel du monde18 et est à ce jour le deuxième immeuble le plus haut du continent américain après le One World Trade Center à New York. Enfin, la ville compte de nombreux établissements d'enseignement supérieur, des musées prestigieux, des théâtres réputés et un orchestre symphonique de renommée mondiale.
Chicago (AFI: /ʧiˈkaɡo/[4]; in inglese /ʃɪˈkɑɡoʊ/) è la più grande città dell'Illinois, la più grande metropoli dell'entroterra statunitense e la terza per popolazione di tutti gli Stati Uniti d'America dopo New York e Los Angeles, con i suoi 2.722.389 abitanti.[3] La sua area metropolitana (detta Chicagoland) conta 9.554.598 abitanti distribuiti in un'ampia area pianeggiante situata lungo le rive del lago Michigan. Trasformatasi da cittadina in una importante metropoli, Chicago è stata definita come una delle 10 città più influenti al mondo. Oggi è una città multietnica, nonché un importante centro finanziario e industriale ed uno dei maggiori centri fieristico/espositivi mondiali.
Il centro della città (denominato "the Loop") è dominato da imponenti grattacieli che arrivano anche ai 108 piani (per un'altezza di 442 m) della Willis Tower. Questa tipologia architettonica è nata proprio a Chicago che, se da tempo ha dovuto perdere il primato di città con più grattacieli nel paese a favore di New York, vanta ancora oggi il secondo grattacielo più alto statunitense (dopo il nuovo World Trade Center) e tre grattacieli nella classifica dei primi 15 al mondo. Venti dei suoi grattacieli superano i 200 metri d'altezza e ben 240 superano i 100 metri. La città si estende per 50 km sul lago Michigan da nord a sud.
Chicago è la città con il maggior numero di ponti mobili al mondo (attualmente 45) ed è un punto di riferimento mondiale per il blues.
La città di Chicago ha diversi soprannomi, tra i quali "Windy City" e "Second City".
Chicago, conocida coloquialmente como «la Segunda Ciudad» o «la Ciudad de los Vientos», es la tercera ciudad con mayor número de habitantes en Estados Unidos, detrás de Nueva York y Los Ángeles.
Chicago se encuentra en el estado de Illinois, a lo largo de la costa suroeste del lago Míchigan, y es la sede del condado de Cook.2 Forma parte del área metropolitana de Chicago, una conurbación integrada además por los condados periféricos.
Чика́го (англ. Chicago, МФА: [ʃɪˈkɑːgoʊ] или [ʃɪˈkɔːgoʊ]) — третий по числу жителей (после Нью-Йорка и Лос-Анджелеса) город США, второй по значимости финансовый центр страны (после Нью-Йорка) и крупнейший транспортный узел Северной Америки. Расположен на юго-западном побережье озера Мичиган в штате Иллинойс; административный центр округа Кук.
Население Чикаго (по данным переписи 2010 года) составляет 2 695 000 человек. Агломерация Чикаго (с различными пригородами) называется «Большой Чикаго» или «Страна Чикаго» (англ. Chicagoland; название предложено газетой Chicago Tribune в начале XX века); в ней проживает более 9 млн человек. Агломерация Чикаго занимает 37-е место в мире по числу жителей.
Чикаго по праву считается экономической, промышленной, транспортной и культурной столицей Среднего Запада. Неофициально его иногда также называют «Второй Город» и «Город ветров». Впервые Чикаго был назван «Городом ветров» в статье в Chicago Tribune за 1858 год.

智能制造(英语:Smart manufacturing)[1]是指引入电脑整合制造以及数字信息技术的制造业。智能工厂就是典型的智能制造。智能制造中有可互操作的系统、智能自动化机器人、强大的网络安全以及联网的传感器。
Smart manufacturing[1] is a broad category of manufacturing that employs computer-integrated manufacturing, high levels of adaptability and rapid design changes, digital information technology, and more flexible technical workforce training.[2] Other goals sometimes include fast changes in production levels based on demand,[3][1] optimization of the supply chain,[3] efficient production and recyclability.[4] In this concept, as smart factory has interoperable systems, multi-scale dynamic modelling and simulation, intelligent automation, strong cyber security, and networked sensors.
The broad definition of smart manufacturing covers many different technologies. Some of the key technologies in the smart manufacturing movement include big data processing capabilities, industrial connectivity devices and services, and advanced robotics.[

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies
Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CNC
CNC


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CRM/EAM/ERP/SRM/SCM/HCM/QM/XM/WFM
CRM/EAM/ERP/SRM/SCM/HCM/QM/XM/WFM


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CAD/CAE/CAM/EDA/PDM/PLM
CAD/CAE/CAM/EDA/PDM/PLM


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Industrial Robot
Industrial Robot


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES
PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES
 United States
United States

| Technology | Location | |
|---|---|---|
| National Additive Manufacturing Innovation Institute (NAMII) | 3D printing | Youngstown, Ohio |
| Digital Manufacturing and Design Innovation Institute (DMDII) | Digital manufacturing | Chicago, Illinois |
| Lightweight Materials Manufacturing Innovation Institute (ALMMII) | Lightweight materials | Detroit, Michigan |
| Next Generation Power Electronics Institute (PowerAmerica) | Wide-bandgap semiconductors | Raleigh, North Carolina |
| Institute for Advanced Composites Manufacturing Innovation (IACMI) | Composite materials | Knoxville, Tennessee |
| American Institute for Manufacturing Integrated Photonics (AIM Photonics) | Photonic integrated circuits | Rochester, New York |
| Flexible Hybrid Electronics Manufacturing Innovation Institute | Flexible electronics | San Jose, California |
| Advanced Functional Fabrics of America (AFFOA) | Textiles | Cambridge, Massachusetts |
| Smart Manufacturing Innovation Institute | Smart manufacturing | Los Angeles, California |

 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *****Energy storage
*****Energy storage

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Electrical power
*Electrical power

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *****Electronic electricity meters
*****Electronic electricity meters

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Technology concepts
Technology concepts

智能电网(英语:Smart grid、smart electric grid、或intelligent grid),一种现代化的输电网络。利用信息及通信技术,以数字或类比[1]信号侦测与收集供应端的电力供应状况,与使用端的电力使用状况。再用这些信息来调整电力的生产与输配,或调整家电及企业用户的耗电量,以此达到节约能源、降低损耗、增强电网可靠性的目的。[2]。智能电网雏型是20世纪产生的,由一些中心发电机向大量用户传输电能的电网的简单升级。在传统电网的基础上,电能的传输拓扑网络更加优化以满足更大范围的各种用电状况,如在用电量低的时段给电池充电,然后在高峰时反过来给电网提供电能。
智能电网包含了一个智能电表基础建设(Advanced Metering Infrastructure,AMI),用于记录系统所有电能的流动。通过智能电表(Smart meter),它会随时监测电力使用的状况。[3]智能电网包括超导传输线以减少电能的传输损耗,还具有集成新能源,如风能、太阳能等的能力。当电能便宜时,消费者可以开启某些家用电器,如洗碗机,工厂可以启动在任何时间段都可以进行的生产过程。在电能需求的高峰期,它可以关闭一些非必要的用电设备来降低需求。其他的智能电网发展方向包括电网之故障侦测、判断、自动试送电等。智能电网之最基础建设在于电网上的设备由人工在地监测,进化到遥测、遥控,再进化到自动判断调整控制。
智能电网政策在欧洲被组织为智能电网欧洲技术平台。 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 China
China

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 Aerospace
Aerospace
 Missions to Mars
Missions to Mars



 Aerospace
Aerospace
 *CNSA
*CNSA
 Ministerium für Informationsindustrie
Ministerium für Informationsindustrie

 Atomic bomb
Atomic bomb
 BRICS summit
BRICS summit
 China
China

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History

 History
History

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nuclear Weapon
Nuclear Weapon

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 BRICS
BRICS
 Silk road
Silk road
 Shanghai Cooperation Organization
Shanghai Cooperation Organization

 States of Asia
States of Asia

 United Nations
United Nations
 United Nations Security Council
United Nations Security Council
 Hydrogen bomb
Hydrogen bomb

Die Volksrepublik China (chinesisch 中华人民共和国, Pinyin Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó ![]() [tʂʊŋ˥xua˧˥ʐɛn˧˥mɪn˧˥kʊŋ˥˩xə˧˥kuɔ˧˥]), allgemein als China bezeichnet, ist ein am 1. Oktober 1949 gegründeter sozialistischer Staat in Ostasien. Mit rund 1,4 Milliarden Einwohnern stellt China das bevölkerungsreichste und gemessen an seiner Gesamtfläche das viertgrößte Land der Erde dar.[7]
[tʂʊŋ˥xua˧˥ʐɛn˧˥mɪn˧˥kʊŋ˥˩xə˧˥kuɔ˧˥]), allgemein als China bezeichnet, ist ein am 1. Oktober 1949 gegründeter sozialistischer Staat in Ostasien. Mit rund 1,4 Milliarden Einwohnern stellt China das bevölkerungsreichste und gemessen an seiner Gesamtfläche das viertgrößte Land der Erde dar.[7]
Gemäß ihrer Verfassung steht die Volksrepublik China „unter der demokratischen Diktatur des Volkes“, wird jedoch seit 1949 autoritär von der Kommunistischen Partei Chinas (KPCh) regiert. Wirtschaftlich weist China seit vielen Jahren eine hohe Dynamik auf. Auf Grundlage ihrer Reform- und Öffnungspolitik entwickelte sich China beginnend ab 1978 zu einer wirtschaftlichen und technologischen Großmacht.[8] Von der Weltbank wird das Land seit 2016 zu den Staaten mit einem Einkommensniveau im oberen Mittelfeld gerechnet. Seit 2010 ist China der Staat mit der umfangreichsten Warenausfuhr und gemessen an der Kaufkraftparität seit 2016 die größte Volkswirtschaft der Welt. Das jährliche Wirtschaftswachstum lag zwischen 2010 und 2017 im Durchschnitt bei 6,7 Prozent.[9]
Die Volksrepublik China zählt zu den offiziellen Atommächten, ist ständiges Mitglied des Weltsicherheitsrates sowie unter anderem Mitglied der Welthandelsorganisation, Weltbank, APEC, ASEAN, BRICS, UNESCO, Interpol, G20.
中华人民共和国,通称中国[13],是位于东亚的社会主义国家,首都位于北京[14]。中国领土陆地面积约960万平方千米,是世界上纯陆地[注 13]面积第二大、陆地[注 14]面积第三大、总面积第三大或第四大的国家[注 15][15],其分为23个省份[注 16]、5个自治区、4个直辖市和2个特别行政区。被视为亚洲地区重要地域大国,也被视为潜在超级大国[16][17][18]。是世界上人口最多的国家,约有13.9亿人[8],同时也是一个多民族国家,共有已确认的民族56个,其中汉族人口占91.51%[19]。以普通话和规范汉字为国家通用语言文字,少数民族地区可使用自己民族的语言文字。
中国地势西高东低而呈现三级阶梯分布,大部分地区属于温带、副热带季风气候,地理景致与气候型态丰富多样,有冰川、丹霞、黄土、沙漠、喀斯特等多种地貌[20],北方有干草原和荒漠,南方有热带雨林,西部和西南边境则有天山山脉、帕米尔高原、喀喇昆仑山脉和喜马拉雅山脉。东临太平洋,领海由渤海(内海)以及黄海、东海、南海三大边海组成[21],水域面积约470万平方千米,分布有大小岛屿7600个[22]。
科技方面,中国在航天航空、高速铁路、新能源、核技术、超级计算机、量子网络等领域有较强实力,研发经费则位居世界第二[23]。国防预算为世界第二高,拥有世界规模最大的常备部队及三位一体的核打击能力[24][25]。自1986年实行九年义务教育制度,就读公立学校的学生由政府提供其间学费。1978年改革开放后,中国成为经济增长最快的经济体之一[26][27]。当前,中国对外贸易额世界第一,是世界上最大的商品出口国及第二大的进口国,依国内生产总值按购买力平价位列世界第一、而国际汇率则排名世界第二[28]。2017年,中国人均国内生产总值依购买力平价为18,119美元,列全球第76位;依国际汇率则为8,643美元,列全球第72位,均尚低于世界水平[10]。改革开放以来,尽管贫困问题得到极大改善,但收入差距较大,且区域间发展不均——东部沿海地区的经济较中西部及东北地区发达——的问题仍极需解决[29][30]。
1949年中国共产党在内战中取得优势,终结了中国国民党在中国大陆的统治,于同年10月1日建立了中华人民共和国中央人民政府,并与退守台湾地区的中华民国政府形成两岸分治的政治格局。遵循和平共处五项原则的外交政策,在1971年取得在联合国的中国代表权后,成为联合国安全理事会常任理事国并加入了许多国际组织。
中華人民共和国(ちゅうかじんみんきょうわこく、簡体字: 中华人民共和国、繁体字: 中華人民共和國、拼音: 、英語: People's Republic of China, PRC)、通称中国(ちゅうごく、拼音: 、英語: China)は、東アジアに位置する主権国家。首都・北京市を政庁所在地とし、13億8千万人以上の人口で世界一人口が多い国でもある。
中華人民共和国憲法第一条で社会主義国家であることを明言しており、政治は中国共産党が指導的地位を有するヘゲモニー政党制を採用している[4]。
中華人民共和国は、中華民国統治下の中国で1921年に結党された中国共産党が、ソビエト連邦の支援を受けながら国共合作・抗日戦争(八路軍・新四軍)・国共内戦を経て国民政府を台湾島へ放逐[5]し、1949年10月1日に北京市で建国式典(中華人民共和国開国大典)を開催したことで成立した。
同国は国共内戦の延長で1954年に「台湾解放宣言」[6]を出し、第一次台湾海峡危機(1954年~1955年)と金門砲戦(1958年~1979年)を起こしたが武力による台湾占領には至らなかった。同国は2010年代に入ると一つの中国による台湾問題の解決を「(自国の)核心的利益の一つ」と規定するようになり、基本的には九二共識の合意に基づいた平和的な中国統一を目指しているが、一方で人民解放軍の武力による台湾制圧の可能性も指摘されている[7]。
計測方法によるが、同国は陸地面積では世界第2位[8]、総面積では世界第3位又は第4位である。同国の地形は、乾燥した北の森林ステップ、ゴビ砂漠、タクラマカン砂漠から、多湿な南の亜熱帯の森林まで広大かつ多様である。ヒマラヤ山脈、カラコルム山脈、パミール高原、天山山脈により、同国は南及び中央アジアから切り離されている。長さ世界第3位の長江及び同世界第6位の黄河は、チベット高原から人口密度の高い東の沿岸地域に流れ、古代には黄河文明や長江文明を興してきた。同国の太平洋に沿った海岸線は14,500kmの長さで、渤海、黄海、東シナ海、南シナ海に囲まれている。同国の国土は、22省級行政区、5自治区、北京市・天津市・上海市・重慶市の4直轄市、大部分が自治的な香港・マカオの2特別行政区によって構成されている。
中国は、繁栄と衰退の繰り返しだと考えられる過去2000年間の大部分で世界最大かつ最も複雑な経済を有した[9][10]。1978年における改革開放の導入以来、外資流入の勢いが増してゆき、産業構造が政策から転換して、中国は世界で最も成長率が高い主要経済大国の1つになった(#経済)。ソ連の純粋な社会主義体制と距離をとり、「経済面は有限な資本主義、政治面は一党独裁を守る」のような国家形態に変更したのである(中国特色社会主義)。
2016年時点で、同国は名目GDP及び貿易輸入額のいずれにおいても世界第2位であり(2014年には国際通貨基金・世界銀行・CIAワールドファクトブックによると購買力平価は世界最大のGDPとなった[11][12][13])、購買力平価GDPと貿易輸出額は世界一位である[14]。同国は核保有国に認められ、世界第2位の防衛予算で世界最大の常備軍を有する。中華人民共和国は1971年以来国際連合加盟国であり、中華民国の後任として安全保障理事会常任理事国である。中国は多数の公式及び非公式の多国間機構加盟国であり、WTO、APEC、BRICs、上海協力機構、BCIM、G20がこれに該当する。中国はアジアの地域大国であり、多数の解説者により潜在的な超大国として特徴付けられてきた[15][16]。なお2017年7月現在、中華人民共和国の世界遺産はイタリアについで52件ある。国内には文化遺産が22件、自然遺産が4件、複合遺産が4件存在する。
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia and the world's most populous country, with a population of around 1.404 billion.[13] Covering approximately 9,600,000 square kilometers (3,700,000 sq mi), it is the third- or fourth-largest country by total area.[k][19] Governed by the Communist Party of China, the state exercises jurisdiction over 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four direct-controlled municipalities (Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, and Chongqing), and the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
China emerged as one of the world's earliest civilizations, in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. For millennia, China's political system was based on hereditary monarchies, or dynasties, beginning with the semi-legendary Xia dynasty in 21st century BCE.[20] Since then, China has expanded, fractured, and re-unified numerous times. In the 3rd century BCE, the Qin reunited core China and established the first Chinese empire. The succeeding Han dynasty, which ruled from 206 BC until 220 AD, saw some of the most advanced technology at that time, including papermaking and the compass,[21] along with agricultural and medical improvements. The invention of gunpowder and movable type in the Tang dynasty (618–907) and Northern Song (960–1127) completed the Four Great Inventions. Tang culture spread widely in Asia, as the new Silk Route brought traders to as far as Mesopotamia and Horn of Africa.[22] Dynastic rule ended in 1912 with the Xinhai Revolution, when a republic replaced the Qing dynasty. The Chinese Civil War resulted in a division of territory in 1949, when the Communist Party of China established the People's Republic of China, a unitary one-party sovereign state on Mainland China, while the Kuomintang-led government retreated to the island of Taiwan. The political status of Taiwan remains disputed.
Since the introduction of economic reforms in 1978, China's economy has been one of the world's fastest-growing with annual growth rates consistently above 6 percent.[23] As of 2016, it is the world's second-largest economy by nominal GDP and largest by purchasing power parity (PPP).[24] China is also the world's largest exporter and second-largest importer of goods.[25] China is a recognized nuclear weapons state and has the world's largest standing army and second-largest defense budget.[26][27] The PRC is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council as it replaced the ROC in 1971, as well as an active global partner of ASEAN Plus mechanism. China is also a leading member of numerous formal and informal multilateral organizations, including the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), WTO, APEC, BRICS, the BCIM, and the G20. In recent times, China has been widely characterized as a global superpower.[28][29][30]
La Chined, en forme longue la république populaire de Chine (ou République populaire de Chinee, RPC, chinois simplifié : 中华人民共和国 ; chinois traditionnel : 中華人民共和國 ; pinyin : , prononcé [tʂʊŋ˥xua˧˥ɻən˧˥mɪn˧˥kʊŋ˥˩xə˧˥kuɔ˧˥] Écouter), parfois appelée Chine populaire, est un pays d'Asie de l'Est. Avec près d'1,4 milliard d'habitants, soit environ un sixième de la population mondiale, elle est le pays le plus peuplé du monde6. Elle compte huit agglomérations de plus de dix millions d'habitants, dont la capitale Pékin,


 Geography
Geography
 Astronomy
Astronomy