
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Italien
Italien

 Architektur
Architektur
 Römische Architektur
Römische Architektur

 Architektur
Architektur
 Griechische Architektur
Griechische Architektur
 Italien
Italien

 Sicilia
Sicilia

 Weltkulturerbe
Weltkulturerbe

 Zivilisation
Zivilisation
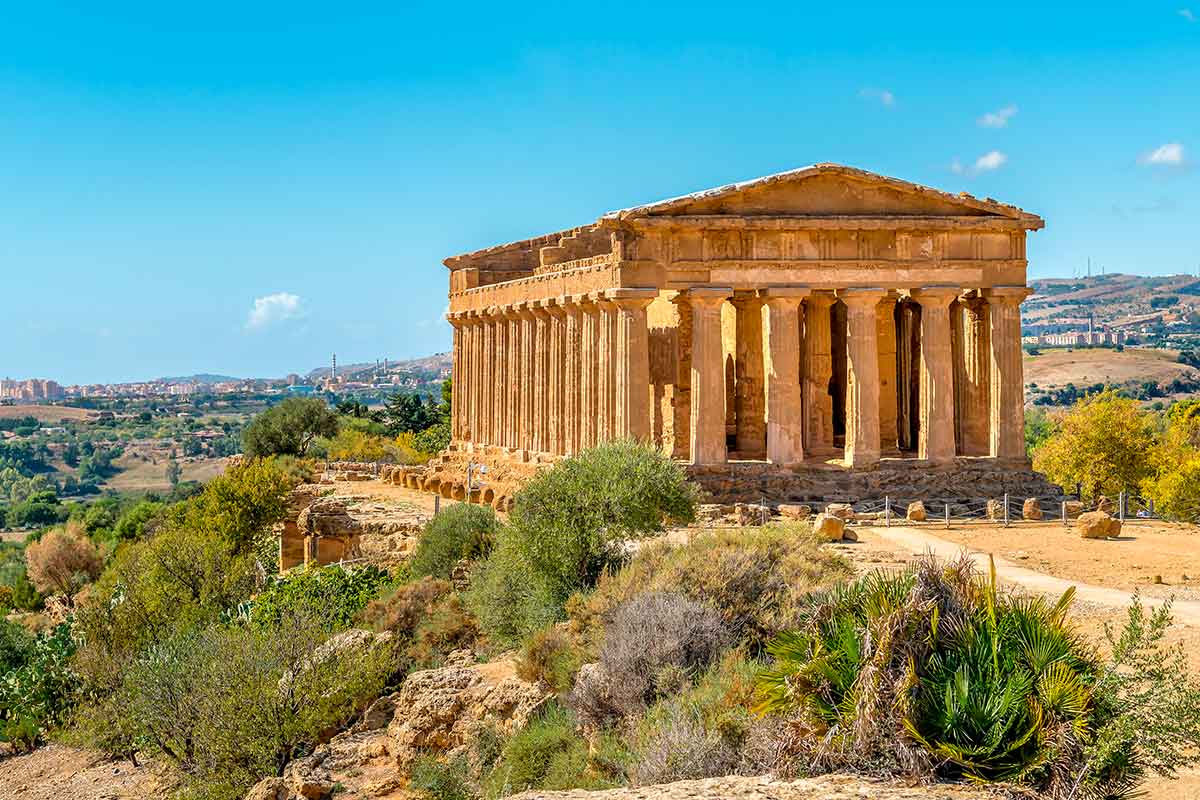



辛普朗隧道 (SimplonTunnel)在瑞士、意大利交界处。从意大利伊塞莱(Iselle)到瑞士布里格(Brig)。十三世纪起,已是北欧与南欧的重要贸易 通道,1905年建成隧道,第一次世界大战时被毁,1921年修复。山口海拔2,009米,隧道开凿在海拔700米处。长19.8公里,为世界最长隧道之 一。从瑞士伯尔尼到意大利米兰铁路由此通过。

 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Belarus
Belarus
 Berlin
Berlin

 Brandenburg
Brandenburg

 Bremen
Bremen
 China
China
 Deutschland
Deutschland
 Frankreich
Frankreich
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Iran
Iran
 Italien
Italien
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Niederlande
Niederlande

 Niedersachsen
Niedersachsen
 Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX

 Nordrhein-Westfalen
Nordrhein-Westfalen
 Polen
Polen
 Portugal
Portugal
 Russland
Russland

 Sachsen
Sachsen

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Spanien
Spanien
 Türkei
Türkei
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Usbekistan
Usbekistan
 Vereinigtes Königreich
Vereinigtes Königreich
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
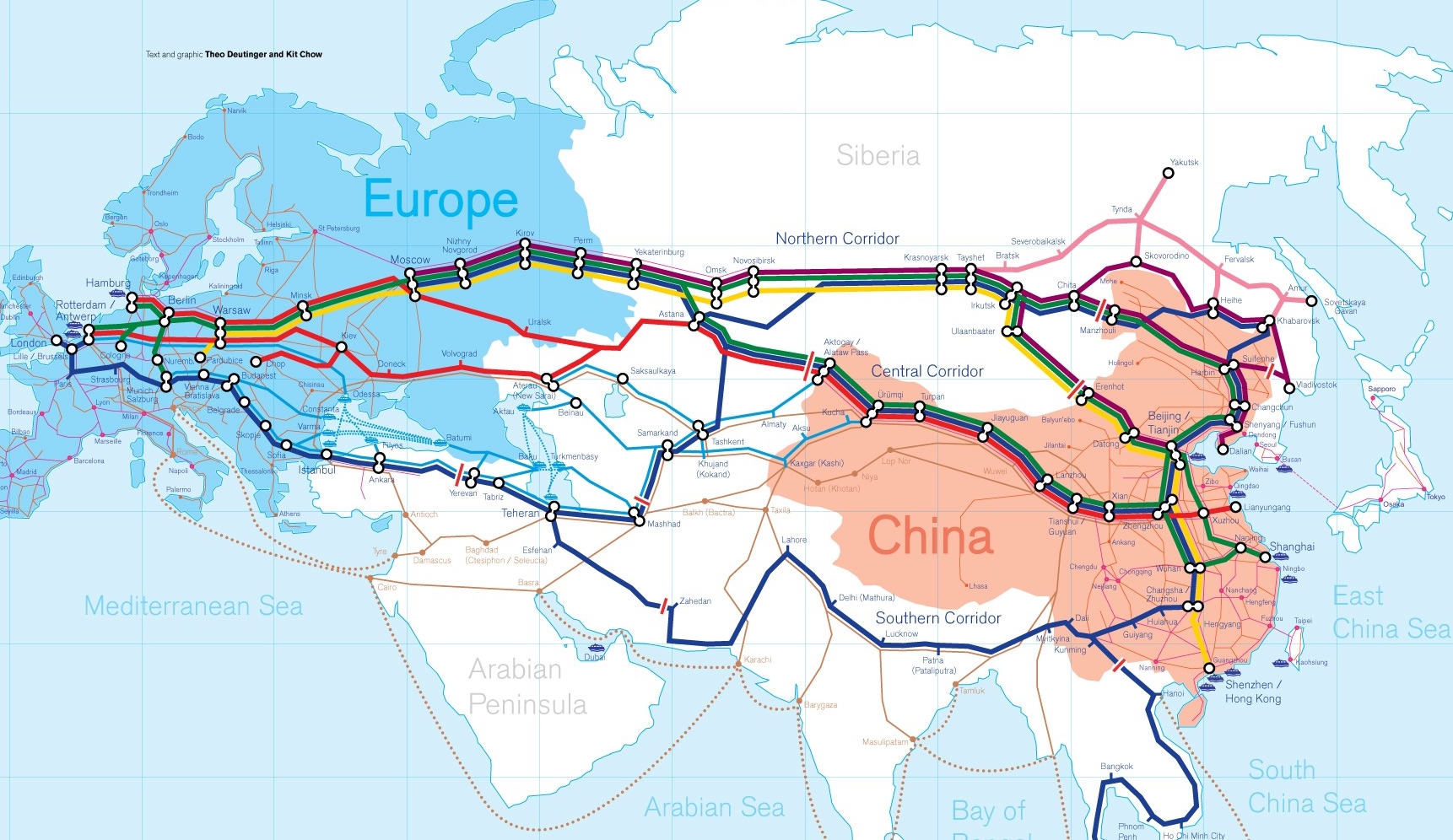
Die Neue eurasische Kontinentalbrücke (chinesisch 新亚欧大陆桥, Pinyin Xīn Yà-Ōu Dàlù Qiáo, englisch New Eurasian Continental Bridge), die auch Zweite eurasische Kontinentalbrücke (第二亚欧大陆桥, Dì'èr Yà-Ōu Dàlù Qiáo, englisch Second Eurasian Continental Bridge) genannt wird, ist eine 10.870 Kilometer[1] lange Eisenbahnverbindung, die Rotterdam in Europa mit der ostchinesischen Hafenstadt Lianyungang in der Provinz Jiangsu verbindet.
Sie besteht seit 1990 und führt durch die Dsungarische Pforte (Grenzbahnhof Alashankou). Die Lan-Xin-Bahn (chinesisch 兰新铁路, Pinyin Lán-Xīn Tiělù), also die Strecke von Lanzhou nach Ürümqi (in Xinjiang), ist ein Teil von ihr.
Es gibt eine nördliche, mittlere und südliche Route.[2] Die mittlere Strecke verläuft durch Kasachstan über Dostyk, Aqtogai, Astana, Samara, Smolensk, Brest, Warschau, Berlin zum Hafen von Rotterdam.[3] Vom slowakischen Košice soll auch eine Abzweigung in den Großraum Wien führen, siehe Breitspurstrecke Košice–Wien.
亚欧大陆桥,或新世纪亚欧大陆桥,是在中国大陆的新闻报道中经常出现的一个词语,特指从中国东部的沿海港口(有时特指连云港),沿陇海铁路、兰新铁路、北疆铁路,通过中亚、西亚到达欧洲的铁路路线。这条铁路在中国境外的具体走向,并没有任何官方文件精确指明,一说是经哈萨克斯坦、乌兹别克斯坦、土库曼斯坦、伊朗到达土耳其;一说是经俄罗斯、白俄罗斯、波兰、德国到达荷兰鹿特丹。全长10,800.32公里,1990年9月12日贯通。
The New Eurasian Land Bridge, also called the Second or New Eurasian Continental Bridge, is the southern branch of the Eurasian Land Bridge rail links running through China. The Eurasian Land Bridge is the overland rail link between Asia and Europe.
Due to a break-of-gauge between standard gauge used in China and the Russian gauge used in the former Soviet Union countries, containers must be physically transferred from Chinese to Kazakh railway cars at Dostyk on the Chinese-Kazakh border and again at the Belarus-Poland border where the standard gauge used in western Europe begins. This is done with truck-mounted cranes.[1] Chinese media often states that the New Eurasian Land/Continental Bridge extends from Lianyungang to Rotterdam, a distance of 11,870 kilometres (7,380 mi). The exact route used to connect the two cities is not always specified in Chinese media reports, but appears to usually refer to the route which passes through Kazakhstan.
All rail freight from China across the Eurasian Land Bridge must pass north of the Caspian Sea through Russia at some point. A proposed alternative would pass through Turkey and Bulgaria,[2] but any route south of the Caspian Sea must pass through Iran.[1]
Kazakhstan's President Nursultan Nazarbayev urged Eurasian and Chinese leaders at the 18th Shanghai Cooperation Organisation to construct the Eurasian high-speed railway (EHSRW) following a Beijing-Astana-Moscow-Berlin.[3]
The Eurasian Land Bridge (Russian: Евразийский сухопутный мост, Yevraziyskiy sukhoputniy most), sometimes called the New Silk Road (Новый шёлковый путь, Noviy shyolkoviy put'), or Belt and Road Initiative is the rail transport route for moving freight and passengers overland between Pacific seaports in the Russian Far East and China and seaports in Europe. The route, a transcontinental railroad and rail land bridge, currently comprises the Trans-Siberian Railway, which runs through Russia and is sometimes called the Northern East-West Corridor, and the New Eurasian Land Bridge or Second Eurasian Continental Bridge, running through China and Kazakhstan. As of November 2007, about 1% of the $600 billion in goods shipped from Asia to Europe each year were delivered by inland transport routes.[1]
Completed in 1916, the Trans-Siberian connects Moscow with Russian Pacific seaports such as Vladivostok. From the 1960s until the early 1990s the railway served as the primary land bridge between Asia and Europe, until several factors caused the use of the railway for transcontinental freight to dwindle. One factor is that the railways of the former Soviet Union use a wider rail gauge than most of the rest of Europe as well as China. Recently, however, the Trans-Siberian has regained ground as a viable land route between the two continents.[why?]
China's rail system had long linked to the Trans-Siberian via northeastern China and Mongolia. In 1990 China added a link between its rail system and the Trans-Siberian via Kazakhstan. China calls its uninterrupted rail link between the port city of Lianyungang and Kazakhstan the New Eurasian Land Bridge or Second Eurasian Continental Bridge. In addition to Kazakhstan, the railways connect with other countries in Central Asia and the Middle East, including Iran. With the October 2013 completion of the rail link across the Bosphorus under the Marmaray project the New Eurasian Land Bridge now theoretically connects to Europe via Central and South Asia.
Proposed expansion of the Eurasian Land Bridge includes construction of a railway across Kazakhstan that is the same gauge as Chinese railways, rail links to India, Burma, Thailand, Malaysia and elsewhere in Southeast Asia, construction of a rail tunnel and highway bridge across the Bering Strait to connect the Trans-Siberian to the North American rail system, and construction of a rail tunnel between South Korea and Japan. The United Nations has proposed further expansion of the Eurasian Land Bridge, including the Trans-Asian Railway project.
El Nuevo Puente de Tierra de Eurasia es también llamado el Segundo o Nuevo Puente Continental de Eurasia. Es la rama meridional de las conexiones ferroviarias del Puente de Tierra de Eurasia (también conocido como "Nueva Ruta de la Seda") que se extienden a través de la República Popular China, atravesando Kazajistán, Rusia y Bielorrusia. El Puente de Tierra de Eurasia es el enlace ferroviario terrestre entre Asia Oriental y Europa.
La Nueva Ruta de la Seda (en ruso, Новый шёлковый путь, Noviy shyolkoviy put), o Puente Terrestre Euroasiático, es la ruta de transporte ferroviario para el movimiento de tren de mercancías y tren de pasajeros por tierra entre los puertos del Pacífico, en el Lejano Oriente ruso y chino y los puertos marítimos en Europa.
La ruta, un ferrocarril transcontinental y puente terrestre, actualmente comprende el ferrocarril Transiberiano, que se extiende a través de Rusia, y el nuevo puente de tierra de Eurasia o segundo puente continental de Eurasia, que discurre a través de China y Kazajistán, también se van a construir carreteras entre las ciudades de la ruta. A partir de noviembre de 2007, aproximadamente el 1% de los 600 millones de dólares en bienes enviados desde Asia a Europa cada año se entregaron por vías de transporte terrestre.1
Terminado en 1916, el tren Transiberiano conecta Moscú con el lejano puerto de Vladivostok en el océano Pacífico, el más largo del mundo en el Lejano Oriente e importante puerto del Pacífico. Desde la década de 1960 hasta principios de 1990 el ferrocarril sirvió como el principal puente terrestre entre Asia y Europa, hasta que varios factores hicieron que el uso de la vía férrea transcontinental para el transporte de carga disminuyese.
Un factor es que los ferrocarriles de la Unión Soviética utilizan un ancho de vía más ancho en los rieles que la mayor parte del resto de Europa y China, y el transporte en barcos de carga por el canal de Suez en Egipto, construido por Inglaterra. El sistema ferroviario de China se une al Transiberiano en el noreste de China y Mongolia. En 1990 China añadió un enlace entre su sistema ferroviario y el Transiberiano a través de Kazajistán. China denomina a su enlace ferroviario ininterrumpido entre la ciudad portuaria de Lianyungang y Kazajistán como el «Puente terrestre de Nueva Eurasia» o «Segundo puente continental Euroasiático». Además de Kazajistán, los ferrocarriles conectan con otros países de Asia Central y Oriente Medio, incluyendo a Irán. Con la finalización en octubre de 2013 de la línea ferroviaria a través del Bósforo en el marco del proyecto Marmaray el puente de tierra de Nueva Eurasia conecta ahora teóricamente a Europa a través de Asia Central y del Sur.
La propuesta de ampliación del Puente Terrestre Euroasiático incluye la construcción de un ferrocarril a través de Kazajistán con el mismo ancho de vía que los ferrocarriles chinos, enlaces ferroviarios a la India, Birmania, Tailandia, Malasia y otros países del sudeste asiático, la construcción de un túnel ferroviario y un puente de carretera a través del estrecho de Bering para conectar el Transiberiano al sistema ferroviario de América del Norte, y la construcción de un túnel ferroviario entre Corea del Sur y Japón. Las Naciones Unidas ha propuesto una mayor expansión del Puente Terrestre Euroasiático, incluyendo el proyecto del ferrocarril transasiático.
Новый шёлковый путь (Евразийский сухопутный мост — концепция новой паневразийской (в перспективе — межконтинентальной) транспортной системы, продвигаемой Китаем, в сотрудничестве с Казахстаном, Россией и другими странами, для перемещения грузов и пассажиров по суше из Китая в страны Европы. Транспортный маршрут включает трансконтинентальную железную дорогу — Транссибирскую магистраль, которая проходит через Россию и второй Евразийский континентальный мост[en], проходящий через Казахстан[1]. Поезда по этому самому длинному в мире грузовому железнодорожному маршруту из Китая в Германию будут идти 15 дней, что в 2 раза быстрее, чем по морскому маршруту через Суэцкий канал[2].
Идея Нового шёлкового пути основывается на историческом примере древнего Великого шёлкового пути, действовавшего со II в. до н. э. и бывшего одним из важнейших торговых маршрутов в древности и в средние века. Современный НШП является важнейшей частью стратегии развития Китая в современном мире — Новый шёлковый путь не только должен выстроить самые удобные и быстрые транзитные маршруты через центр Евразии, но и усилить экономическое развитие внутренних регионов Китая и соседних стран, а также создать новые рынки для китайских товаров (по состоянию на ноябрь 2007 года, около 1 % от товаров на 600 млрд долл. из Азии в Европу ежегодно доставлялись наземным транспортом[3]).
Китай продвигает проект «Нового шёлкового пути» не просто как возрождение древнего Шёлкового пути, транспортного маршрута между Востоком и Западом, но как масштабное преобразование всей торгово-экономической модели Евразии, и в первую очередь — Центральной и Средней Азии. Китайцы называют эту концепцию — «один пояс — один путь». Она включает в себя множество инфраструктурных проектов, которые должны в итоге опоясать всю планету. Проект всемирной системы транспортных коридоров соединяет Австралию и Индонезию, всю Центральную и Восточную Азию, Ближний Восток, Европу, Африку и через Латинскую Америку выходит к США. Среди проектов в рамках НШП планируются железные дороги и шоссе, морские и воздушные пути, трубопроводы и линии электропередач, и вся сопутствующая инфраструктура. По самым скромным оценкам, НШП втянет в свою орбиту 4,4 миллиарда человек — более половины населения Земли[4].
Предполагаемое расширение Евразийского сухопутного моста включает в себя строительство железнодорожных путей от трансконтинентальных линий в Иран, Индию, Мьянму, Таиланд, Пакистан, Непал, Афганистан и Малайзию, в другие регионы Юго-Восточной Азии и Закавказья (Азербайджан, Грузия). Маршрут включает тоннель Мармарай под проливом Босфор, паромные переправы через Каспийское море (Азербайджан-Иран-Туркменистан-Казахстан) и коридор Север-Юг.Организация Объединенных Наций предложила дальнейшее расширение Евразийского сухопутного моста, в том числе проекта Трансазиатской железной дороги (фактически существует уже в 2 вариантах).
Для развития инфраструктурных проектов в странах вдоль Нового шёлкового пути и Морского Шёлкового пути и с целью содействия сбыту китайской продукции в декабре 2014 года был создан инвестиционный Фонд Шёлкового пути[5].
8 мая 2015 года было подписано совместное заявление Президента РФ В. Путина и Председателя КНР Си Цзиньпина о сотрудничестве России и Китая, в рамках ЕАЭС и трансевразийского торгово-инфраструктурного проекта экономического пояса «Шёлковый путь». 13 июня 2015 года был запущен самый длинный в мире грузовой железнодорожный маршрут Харбин — Гамбург (Германия), через территорию России.
 Italien
Italien
 Italienische Marine
Italienische Marine



 Militär,Verteidigung und Ausrüstung
Militär,Verteidigung und Ausrüstung
 Segelschiff
Segelschiff
 Vollschiff/Full rigged ship
Vollschiff/Full rigged ship
 Toscana
Toscana

 Ägypten
Ägypten
 Australien
Australien
 Belgien
Belgien
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Deutschland
Deutschland
 Dschibuti
Dschibuti
 Frankreich
Frankreich
 Griechenland
Griechenland
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Indien
Indien
 Indonesien
Indonesien


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Spätklassik, Romantik (Früh, Mittel, Spät)
Spätklassik, Romantik (Früh, Mittel, Spät)
 Italien
Italien
 Japan
Japan
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Marokko
Marokko
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Oman
Oman
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Philippinen
Philippinen
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republik Korea
Republik Korea
 Saudi-Arabien
Saudi-Arabien
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Singapur
Singapur
 Singapur
Singapur
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Thailand
Thailand
 Türkei
Türkei
 Vereinigte Arabische Emirate
Vereinigte Arabische Emirate
 Vereinigtes Königreich
Vereinigtes Königreich
 Vietnam
Vietnam
 Zypern
Zypern


 Abruzzo
Abruzzo

 Basilicata
Basilicata

 Calabria
Calabria
 Campania
Campania

 Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna
 Italien
Italien

 Lazio
Lazio

 Liguria
Liguria

 Lombardia
Lombardia

 Marche
Marche

 Molise
Molise

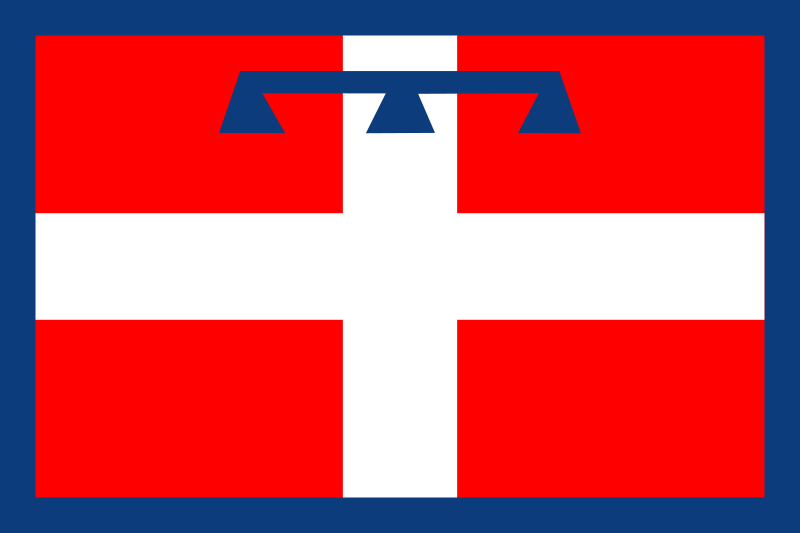 Piemonte
Piemonte

 Puglia
Puglia

 Sicilia
Sicilia

 Toscana
Toscana

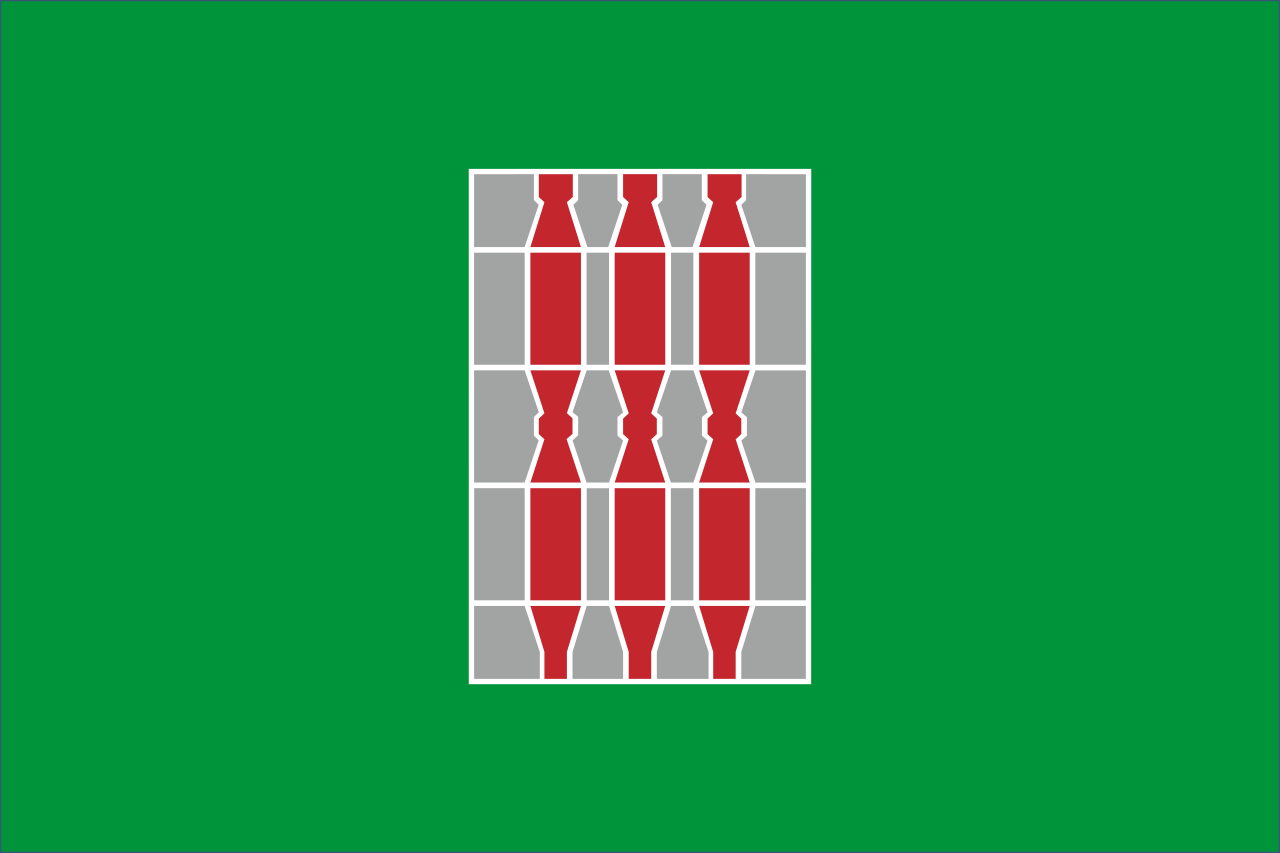 Umbria
Umbria
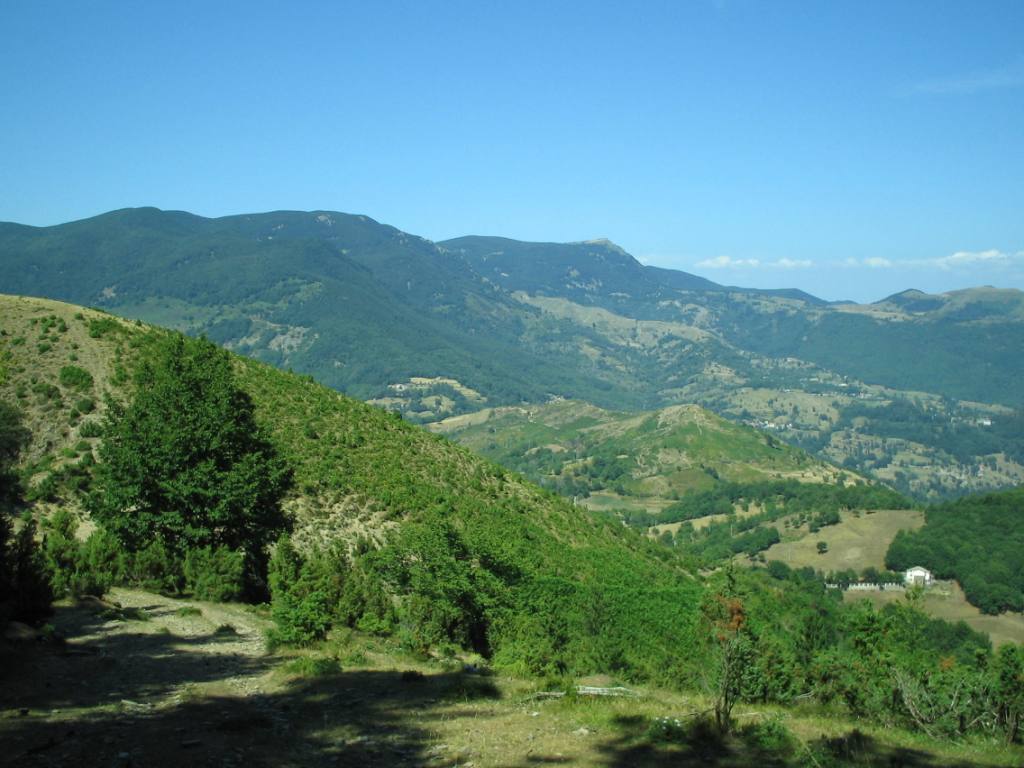


Der Apennin (auch im Plural die Apenninen; italienisch gli Appennini) ist ein rund 1500 km langer Gebirgszug in Italien (sowie zu sehr kleinen Teilen in San Marino), der einen großen Teil des Staatsgebiets durchzieht, überwiegend in Nordwest-Südost-Richtung. Über den Apennin verläuft die Hauptwasserscheide Italiens. Er ist Teil des Alpidischen Gebirgssystems. Der Großteil des Gebirges liegt auf der Apenninhalbinsel.
Der Apennin beginnt im Nordwesten Italiens und bildet im Ligurischen Apennin die Fortsetzung der Ligurischen Alpen. Die Grenze zwischen Alpen und Apennin bildet der Col di Cadibona (436 m). Von dort reicht der Apennin Richtung Osten über die Apuanischen Alpen bis zur Adriaküste, wo er sich nach Süden wendet und im Abruzzischen Apennin mit dem Massiv des Gran Sasso d’Italia (2912 m) seine größte Höhe erreicht.
Weiter südwärts teilt sich der Apennin in einzelne kleinere Gebirgsteile wie die Sila und den Aspromonte auf und findet seine Fortsetzung in den Gebirgen Nordsiziliens.
Im Apennin herrscht typisches Gebirgsklima mit niedrigen Temperaturen, jedoch starken Temperaturschwankungen und hohen Niederschlägen. Im Hügelland und den Vorgebirgen ist das Klima mediterran beeinflusst, mit Niederschlagsmengen von etwa 800 mm und einer deutlichen Sommertrockenheit. In den subalpinen Regionen steigt die Niederschlagsmenge auf über 1300 mm, wobei ein deutlicher West-Ost-Unterschied besteht.
亚平宁山脉(意大利语:Appennini[1]),位于亚平宁半岛东侧,是亚平宁半岛的主干山脉,北起阿尔卑斯山南麓,南至亚平宁半岛南端,全长超过1000公里。全境属意大利管辖。


 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Ägypten
Ägypten
 Armenien
Armenien
 Aserbaidschan
Aserbaidschan
 Äthiopien
Äthiopien
 Australien
Australien
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Dänemark
Dänemark
 Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
 Deutschland
Deutschland
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Finanz
Finanz
 Internationale Bank für Zusammenarbeit
Internationale Bank für Zusammenarbeit
 Finnland
Finnland
 Frankreich
Frankreich
 Georgien
Georgien
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Indien
Indien
 Indonesien
Indonesien
 Iran
Iran
 Irland
Irland
 Island
Island
 Israel
Israel
 Italien
Italien
 Jordanien
Jordanien
 Kambodscha
Kambodscha
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kirgisistan
Kirgisistan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxemburg
Luxemburg
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta
 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 Neuseeland
Neuseeland
 Niederlande
Niederlande
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Oman
Oman
 Österreich
Österreich
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Philippinen
Philippinen
 Polen
Polen
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republik Korea
Republik Korea
 Russland
Russland
 Samoa
Samoa
 Saudi-Arabien
Saudi-Arabien
 Schweden
Schweden
 Schweiz
Schweiz
 Singapur
Singapur
 Spanien
Spanien
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Südafrika
Südafrika
 Tadschikistan
Tadschikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Türkei
Türkei
 Ungarn
Ungarn
 Usbekistan
Usbekistan
 Vereinigte Arabische Emirate
Vereinigte Arabische Emirate
 Vereinigtes Königreich
Vereinigtes Königreich
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Wichtige internationale Organisationen
Wichtige internationale Organisationen

 Wirtschaft und Handel
Wirtschaft und Handel
 Wirtschafts- und Politikforschung
Wirtschafts- und Politikforschung
 Zypern
Zypern

Anlass zur Initiative der Gründung war insbesondere die Unzufriedenheit Chinas über eine Dominanz der US-Amerikaner im Internationalen Währungsfonds, der keine faire Verteilung der globalen Machtverhältnisse aus Sicht Chinas widerspiegelte.[2] Da sich die US-Amerikaner strikt weigerten, eine Änderung der Stimmverhältnisse zu implementieren, begann China 2013 mit der Gründung der Initiative. Neben den 21 Gründungsmitgliedern haben im Jahr 2015 auch unter anderem Deutschland, Italien, Frankreich und das Vereinigte Königreich ihr Interesse bekundet, als nicht-regionale Mitglieder die neue Entwicklungsbank zu unterstützen.[3]
Die Gründungsurkunde der AIIB wurde am 29. Juni 2015 von Vertretern aus 57 Ländern in Peking unterzeichnet.[4] Die Bank nahm im Januar 2016 ihre Arbeit ohne Beteiligung der USA und Japan auf.[5]
Joachim von Amsberg ist der "Vizepräsident für Politik und Strategie".
亚洲基础设施投资银行(英语:Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank,縮寫:AIIB),简称亚投行,是一个愿意向亚洲国家和地區的基础设施建设提供资金支持的政府间性质的亚洲区域多边开发机构,成立的目的是促进亚洲区域的互联互通建设和经济一体化的进程,並且加大中國與其他亚洲國家和地区的合作力度。总部设在中国北京,法定资本为1,000亿美元。[2]
中华人民共和国主席习近平于2013年10月2日在雅加达同印度尼西亚总统苏西洛举行会谈时首次倡议筹建亚投行。[3]2014年10月24日,中国、印度、新加坡等21国在北京正式签署《筹建亚投行备忘录》。[2]2014年11月25日,印度尼西亚签署备忘录,成为亚投行第22个意向创始成员国。[4]
2015年3月12日,英国正式申请作为意向创始成员国加入亚投行,[5]成为正式申请加入亚投行的首个欧洲国家、主要西方国家。[6]随后法国、意大利、德国等西方国家纷纷以意向创始成员国身份申请加入亚投行。[7]接收新意向创始成员国申请截止日期3月31日临近,韩国[8]、俄罗斯[9]、巴西[10]等域内国家和重要新兴经济体也抓紧申请成为亚投行意向创始成员国。
各方商定将于2015年年中完成亚投行章程谈判并签署,年底前完成章程生效程序,正式成立亚投行。[11]
アジアインフラ投資銀行(アジアインフラとうしぎんこう、英: Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB、中: 亚洲基础设施投资银行,亞洲基礎設施投資銀行)は、国際開発金融機関のひとつである。
中華人民共和国が2013年秋に提唱し主導する形で発足した[1]。「合計の出資比率が50%以上となる10以上の国が国内手続きを終える」としていた設立協定が発効条件を満たし、2015年12月25日に発足し[2][3]、2016年1月16日に開業式典を行った[1][4]。
57か国を創設メンバーとして発足し[1][5]、2017年3月23日に加盟国は70カ国・地域となってアジア開発銀行の67カ国・地域を超え[6][7]、一方で日本、アメリカ合衆国などは2017年の現時点で参加を見送っている[8]。 創設時の資本金は1000億ドルである[9]。
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) is a multilateral development bank that aims to support the building of infrastructure in the Asia-Pacific region. The bank currently has 93 members from around the world [7]. The bank started operation after the agreement entered into force on 25 December 2015, after ratifications were received from 10 member states holding a total number of 50% of the initial subscriptions of the Authorized Capital Stock.[8]
The United Nations has addressed the launch of AIIB as having potential for "scaling up financing for sustainable development"[9] and to improve the global economic governance.[10] The starting capital of the bank was $100 billion, equivalent to 2⁄3 of the capital of the Asian Development Bank and about half that of the World Bank.[11]
The bank was proposed by China in 2013[12] and the initiative was launched at a ceremony in Beijing in October 2014.[13] It received the highest credit ratings from the three biggest rating agencies in the world, and is seen as a potential rival to the World Bank and IMF.[14][15]
La Banque asiatique d'investissement dans les infrastructures (BAII ou AIIB), est une banque d'investissement proposée par la République populaire de Chine dans le but de concurrencer le Fonds monétaire international, la Banque mondiale et la Banque asiatique de développement1 pour répondre au besoin croissant d'infrastructures en Asie du Sud-Est et en Asie centrale. Cette banque s'inscrit dans la stratégie de la nouvelle route de la soie, développée par la Chine.
La Banca Asiatica d'Investimento per le infrastrutture (AIIB), fondata a Pechino nell'ottobre 2014, è un'istituzione finanziaria internazionale proposta dalla Repubblica Popolare Cinese. Si contrappone al Fondo Monetario Internazionale, alla Banca Mondiale e all'Asian Development Bank[1], le quali si trovano sotto il controllo del capitale e delle scelte strategiche dei paesi sviluppati come gli Stati Uniti d'America.[2] Scopo della Banca è fornire e sviluppare progetti di infrastrutture nella regione Asia-Pacifico attraverso la promozione dello sviluppo economico-sociale della regione e contribuendo alla crescita mondiale.
El Banco Asiático de Inversión en Infraestructura (Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank o AIIB) es una institución financiera internacional propuesta por el gobierno de China. El propósito de este banco de desarrollo multilateral es proporcionar la financiación para proyectos de infraestructura en la región de Asia basado en un sistema financiero de préstamo1 y el fomento del sistema de libre mercado en los países asiáticos.
El AIIB está considerado por algunos como una versión continental del FMI y del Banco Mundial, y busca ser un rival por la influencia en la región del Banco de Desarrollo asiático (ADB), el cual esta alineado a los intereses de potencias, tanto regionales (Japón), como globales (Estados Unidos, la Unión Europea).2
El banco fue propuesto por Xi Jinping en 2013 e inaugurado con una ceremonia en Pekín en octubre de 2014. La ONU se a mostrado entusiasta con la propuesta china, a la que a descrito como el FMI del futuro y a señalado como "una gran propuesta para financiar el desarrollo sostenible" y "mejorar la gobernanza económica mundial". La entidad constó inicialmente con 100 mil millones de dolares, es decir, la mitad del dinero de que posee el Banco Mundial.
La entidad a recibido inversión por parte de corporaciones financieras estadounidenses como la Standard & Poor's, Moody's o Fitch Group34. Actualmente la entidad consta de 87 miembros, incluyendo los 57 miembros fundadores. Bélgica, Canadá, y Ucrania están barajando unirse al AIIB. Estados Unidos, Japón y Colombia no tienen intención de participar. China a prohibido a Corea del Norte unirse, instigando además una política de aislamiento contra esta por parte del AIIB.
Азиатский банк инфраструктурных инвестиций (АБИИ) (англ. Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB) — международная финансовая организация, создание которой было предложено Китаем. Основные цели, которые преследует АБИИ, — стимулирование финансового сотрудничества в Азиатско-Тихоокеанском регионе, финансирование инфраструктурных проектов в Азии от строительства дорог и аэропортов до антенн связи и жилья экономкласса[1].
По заявлениям вице-премьера России Игоря Шувалова, AБИИ не рассматривается как потенциальный конкурент МВФ, Всемирного банка и Азиатского банка развития (АБР). Однако эксперты рассматривают AIIB как потенциального конкурента базирующихся в США Международного валютного фонда (МВФ) и Всемирного банка. После сообщений об успехах AIIB американский министр финансов США Джейкоб Лью предупредил, что международным финансовым организациям в США, таким как ВБ и МВФ, грозит потеря доверия [2][3].
Китай, Индия и Россия возглавили организацию, оказавшись в тройке крупнейших владельцев голосов. При этом на важнейшие решения КНР имеет фактическое право вето[4].
 *Mittelmeer
*Mittelmeer

 Abruzzo
Abruzzo
 Albanien
Albanien
 Bernsteinstraße
Bernsteinstraße
 Bosnien-Herzegowina
Bosnien-Herzegowina

 Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna

 Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
 Italien
Italien
 Kroatien
Kroatien

 Marche
Marche

 Molise
Molise
 Montenegro
Montenegro

 Puglia
Puglia
 Slowenien
Slowenien
 Veneto
Veneto
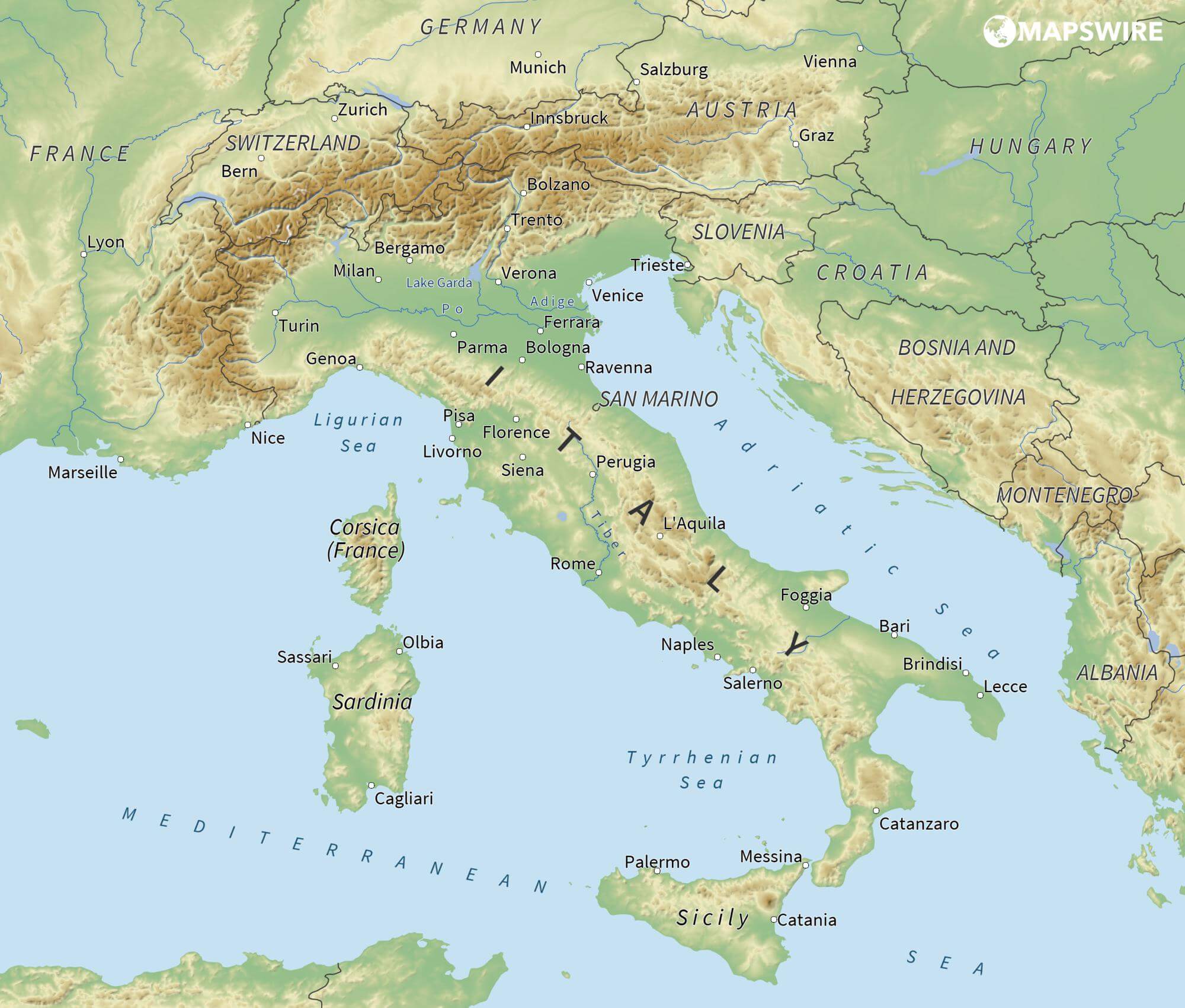
Das Adriatische Meer, kurz auch die Adria (lateinisch Mare Adriaticum; italienisch Mare Adriatico; bosnisch, kroatisch und serbisch Jadransko more oder kurz Jadran; slowenisch Jadransko morje; albanisch Deti Adriatik oder kurz Adriatiku), ist das lang gestreckte nördliche Seitenbecken des Mittelmeeres zwischen der Apenninhalbinsel und Balkanhalbinsel. Es ist nach der Stadt Adria in Italien (Provinz Rovigo) benannt. Zum Adriatischen Meer wird alles gerechnet, was nördlich der Straße von Otranto liegt.
亚得里亚海(意大利语:Mar Adriatico,斯洛文尼亚语:Jadransko morje,克罗地亚语:Jadransko more,阿尔巴尼亚语:Deti Adriatik),是地中海的一部分水域,分隔了意大利半岛(亚平宁半岛)和巴尔干半岛,也分隔了亚平宁山脉与狄那里克阿尔卑斯山脉及其临近地区。亚得里亚海西岸属于意大利,东岸则分别属于斯洛文尼亚、克罗地亚、波斯尼亚和黑塞哥维那、黑山和阿尔巴尼亚。亚得里亚海透过位于其南部的奥特朗托海峡与爱奥尼亚海相连。波河、阿迪杰河、奥凡托河等河流流入亚得里亚海;海中有近1200个岛屿,其中只有69个有人居住。
アドリア海(アドリアかい、英: Adriatic Sea ; イタリア語: Mar Adriatico ; クロアチア語: Jadransko more)は、地中海の海域の一つ。イタリア半島とバルカン半島に挟まれている。
The Adriatic Sea (/ˌeɪdriˈætɪk/) is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the northwest and the Po Valley. The countries with coasts on the Adriatic are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Italy, Montenegro and Slovenia. The Adriatic contains over 1,300 islands, mostly located along the Croatian part of its eastern coast. It is divided into three basins, the northern being the shallowest and the southern being the deepest, with a maximum depth of 1,233 metres (4,045 ft). The Otranto Sill, an underwater ridge, is located at the border between the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. The prevailing currents flow counterclockwise from the Strait of Otranto, along the eastern coast and back to the strait along the western (Italian) coast. Tidal movements in the Adriatic are slight, although larger amplitudes are known to occur occasionally. The Adriatic's salinity is lower than the Mediterranean's because the Adriatic collects a third of the fresh water flowing into the Mediterranean, acting as a dilution basin. The surface water temperatures generally range from 30 °C (86 °F) in summer to 12 °C (54 °F) in winter, significantly moderating the Adriatic Basin's climate.
The Adriatic Sea sits on the Apulian or Adriatic Microplate, which separated from the African Plate in the Mesozoic era. The plate's movement contributed to the formation of the surrounding mountain chains and Apennine tectonic uplift after its collision with the Eurasian plate. In the Late Oligocene, the Apennine Peninsula first formed, separating the Adriatic Basin from the rest of the Mediterranean. All types of sediment are found in the Adriatic, with the bulk of the material transported by the Po and other rivers on the western coast. The western coast is alluvial or terraced, while the eastern coast is highly indented with pronounced karstification. There are dozens of marine protected areas in the Adriatic, designed to protect the sea's karst habitats and biodiversity. The sea is abundant in flora and fauna—more than 7,000 species are identified as native to the Adriatic, many of them endemic, rare and threatened ones.
The Adriatic's shores are populated by more than 3.5 million people; the largest cities are Bari, Venice, Trieste and Split. The earliest settlements on the Adriatic shores were Etruscan, Illyrian, and Greek. By the 2nd century BC, the shores were under Rome's control. In the Middle Ages, the Adriatic shores and the sea itself were controlled, to a varying extent, by a series of states—most notably the Byzantine Empire, the Croatian Kingdom, the Republic of Venice, the Habsburg Monarchy and the Ottoman Empire. The Napoleonic Wars resulted in the First French Empire gaining coastal control and the British effort to counter the French in the area, ultimately securing most of the eastern Adriatic shore and the Po Valley for Austria. Following Italian unification, the Kingdom of Italy started an eastward expansion that lasted until the 20th century. Following World War I and the collapse of Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire, the eastern coast's control passed to Yugoslavia and Albania. The former disintegrated during the 1990s, resulting in four new states on the Adriatic coast. Italy and Yugoslavia agreed on their maritime boundaries by 1975 and this boundary is recognised by Yugoslavia's successor states, but the maritime boundaries between Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, and Montenegro are still disputed. Italy and Albania agreed on their maritime boundary in 1992.
Fisheries and tourism are significant sources of income all along the Adriatic coast. Adriatic Croatia's tourism industry has grown faster economically than the rest of the Adriatic Basin's. Maritime transport is also a significant branch of the area's economy—there are 19 seaports in the Adriatic that each handle more than a million tonnes of cargo per year. The largest Adriatic seaport by annual cargo turnover is the Port of Trieste, while the Port of Split is the largest Adriatic seaport by passengers served per year.
La mer Adriatique (du latin : Mare Hadriaticum ou Mare Adriaticum) est une mer séparant la péninsule italienne de la péninsule balkanique. L'Adriatique est le bras de la Méditerranée situé le plus au nord en s'étendant du canal d'Otrante (où elle rejoint la mer Ionienne) jusqu'aux villes de Venise et de Trieste et à l'embouchure du Pô. Les pays côtiers sont l'Italie, la Slovénie, la Croatie, la Bosnie-Herzégovine, le Monténégro et l'Albanie, ainsi que la Grèce par l'île de Corfou.
Il mare Adriatico è l'articolazione del mar Mediterraneo orientale situata tra la penisola italiana e la penisola balcanica; suddiviso in Alto Adriatico, Medio Adriatico e Basso Adriatico, bagna sei Paesi: Italia, Slovenia, Croazia, Bosnia ed Erzegovina, Montenegro e Albania, confinando a sud-est con il Mar Ionio.
El mar Adriático (del latín, Mare Hadriaticum) es un golfo estrecho y alargado que forma parte del mar Mediterráneo. Se encuentra situado entre la península Itálica, al oeste, y la península de los Balcanes, al este, con una anchura máxima de unos 200 km, y una longitud de unos 800 km. Su extremo meridional limita con el mar Jónico, del que lo separa el canal de Otranto. Su superficie total es de, aproximadamente, 160 000 km².
Las costas occidental, septentrional, y parte de la oriental corresponden a Italia (60% de la longitud de costa del Adriático), mientras que el resto de la costa oriental corresponde a Croacia, Eslovenia, Bosnia y Herzegovina, Montenegro y Albania. Algunos de los ríos que desembocan en el Adriático son el Reno, el Po, el Adigio, el Brenta, el Piave y el Neretva.
La costa del Adriático concentra un gran número de centros turísticos, como Venecia, que recibe el nombre de «Reina del Adriático». Tras la división de Yugoslavia, la costa croata se ha convertido también en un destino turístico muy popular.
Sus aguas sostienen industria pesquera, y se llevan a cabo prospecciones petrolíferas en este mar. Durante los años 1990, varias investigaciones revelaron que sus niveles de contaminación son muy altos.
En las últimas décadas el gobierno de Italia ha intentado hacer de él una barrera contra la inmigración ilegal, en su mayor parte proveniente de Albania.
Адриати́ческое мо́ре (итал. mare Adriatico, эмил.-ром. Mèr Adriâtic, вен. Mar Adriàtico, неап. Mar Adriateco, словен. Jadransko morje, сербохорв. Jadransko more/Јадранско море, алб. Deti Adriatik, лат. mare Hadriaticum), также Адриатика — полузамкнутое море, часть Средиземного моря между Апеннинским и Балканским полуостровами. Омывает берега Италии (более 1000 км), Словении (47 км), Хорватии (1777 км), Боснии и Герцеговины (20 км), Черногории (200 км), Албании (472 км).

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 Geographie
Geographie
 Religion
Religion
 Transport und Verkehr
Transport und Verkehr
 Schiffe und Nautik
Schiffe und Nautik
 Unternehmen
Unternehmen
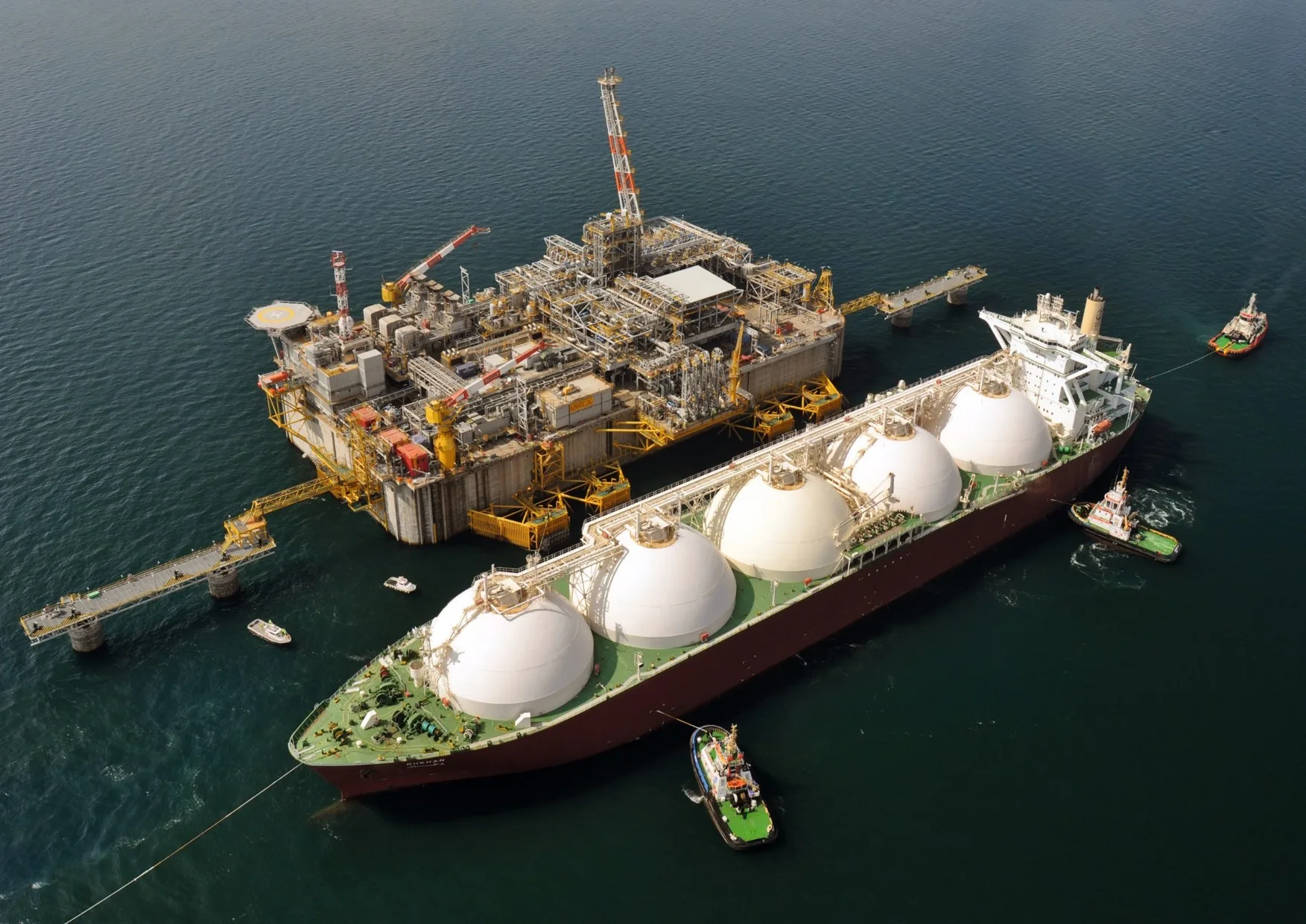
 Energieressource
Energieressource