
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
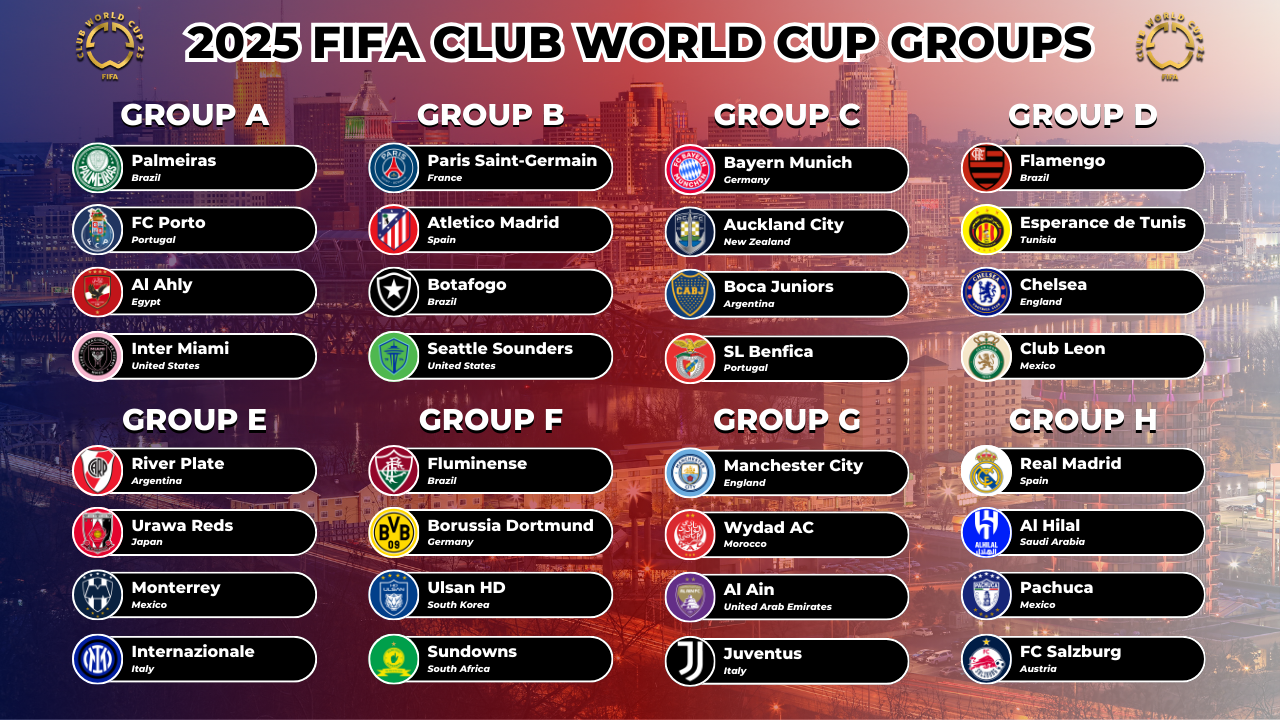
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025
 FIFA
FIFA
 FIFA Club World Cup
FIFA Club World Cup
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 (F)AFC Champions League
(F)AFC Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)CAF Champions League
(F)CAF Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Champions League
(F)UEFA Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Copa Libertadores
(F)Copa Libertadores

 Sport
Sport
 (F)CONCACAF Champions League
(F)CONCACAF Champions League

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN
 United States
United States

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA
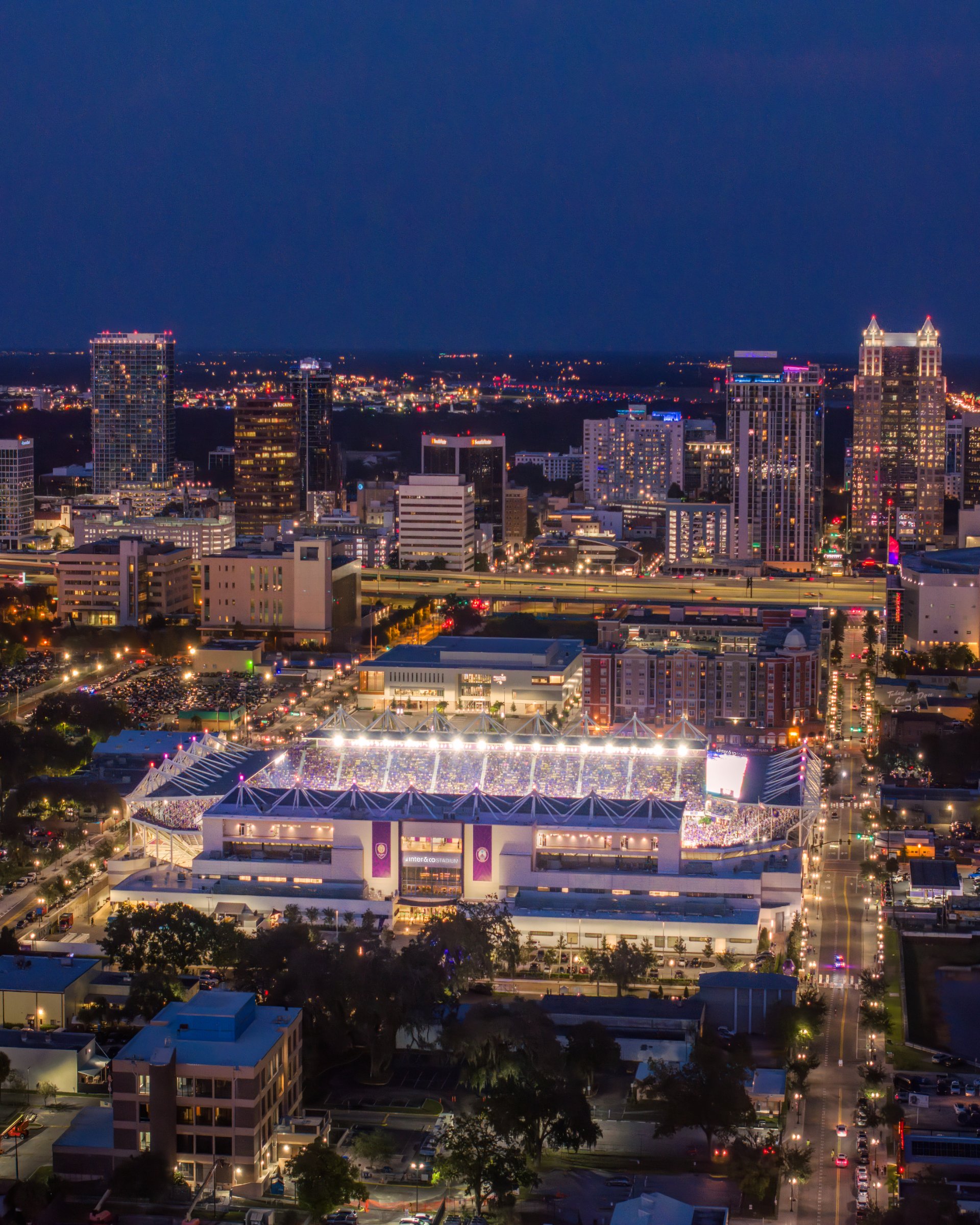


Heimspielbetrieb Orlando City (MLS, seit 2017) Orlando City B (USL, seit 2017) Orlando Pride (NWSL, seit 2017) Veranstaltungen Spiele von Orlando City Spiele der Orlando City B Spiele von Orlando Pride NCAA Division I Women’s Soccer Championship 2017 MLS All-Star Game 2019 SheBelieves Cup 2018, 2020, 2021
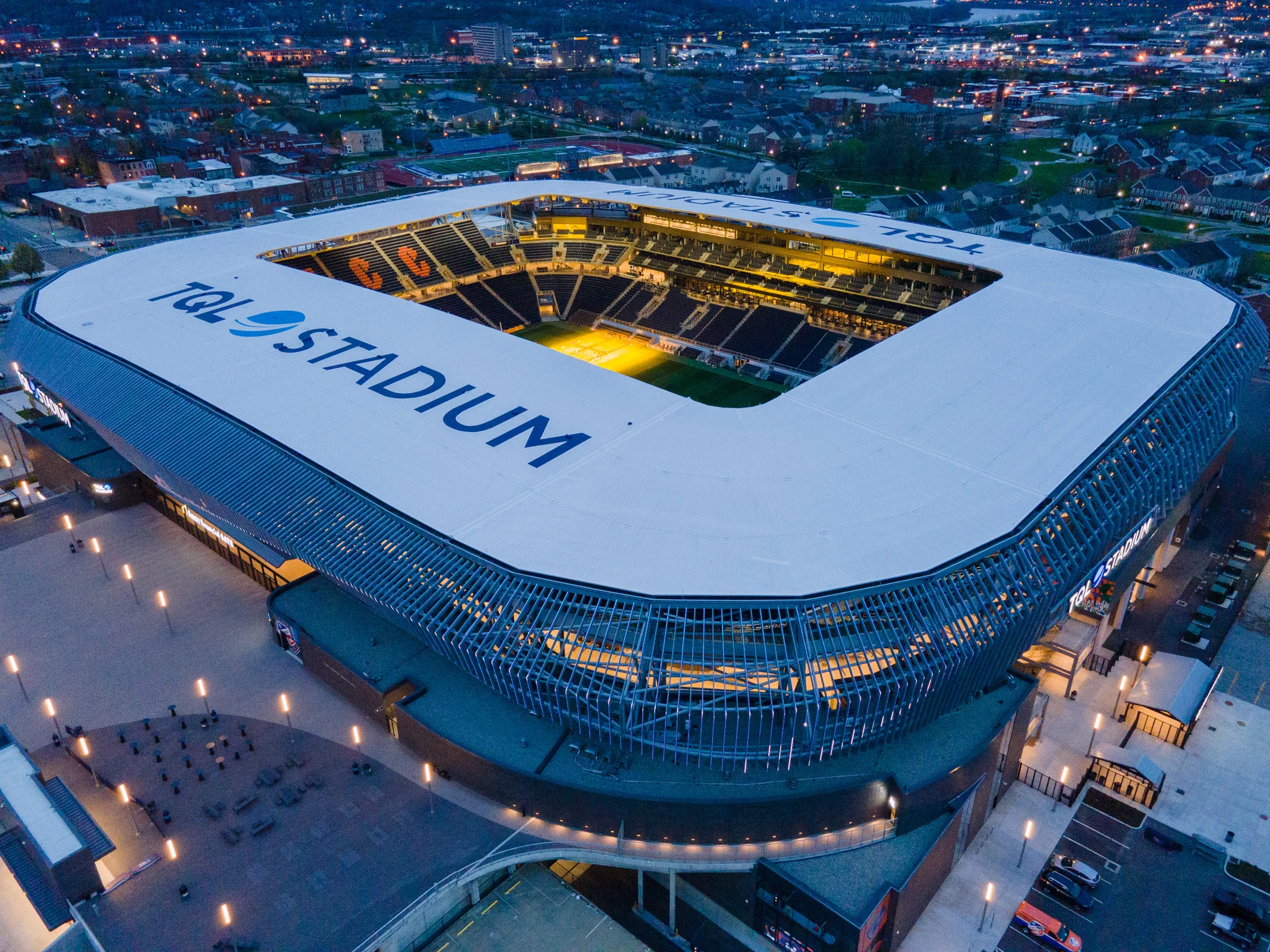

Heimspielbetrieb FC Cincinnati (MLS, seit 2021) Veranstaltungen Länderspiel der US-amerikanischen Fußballnationalmannschaft

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
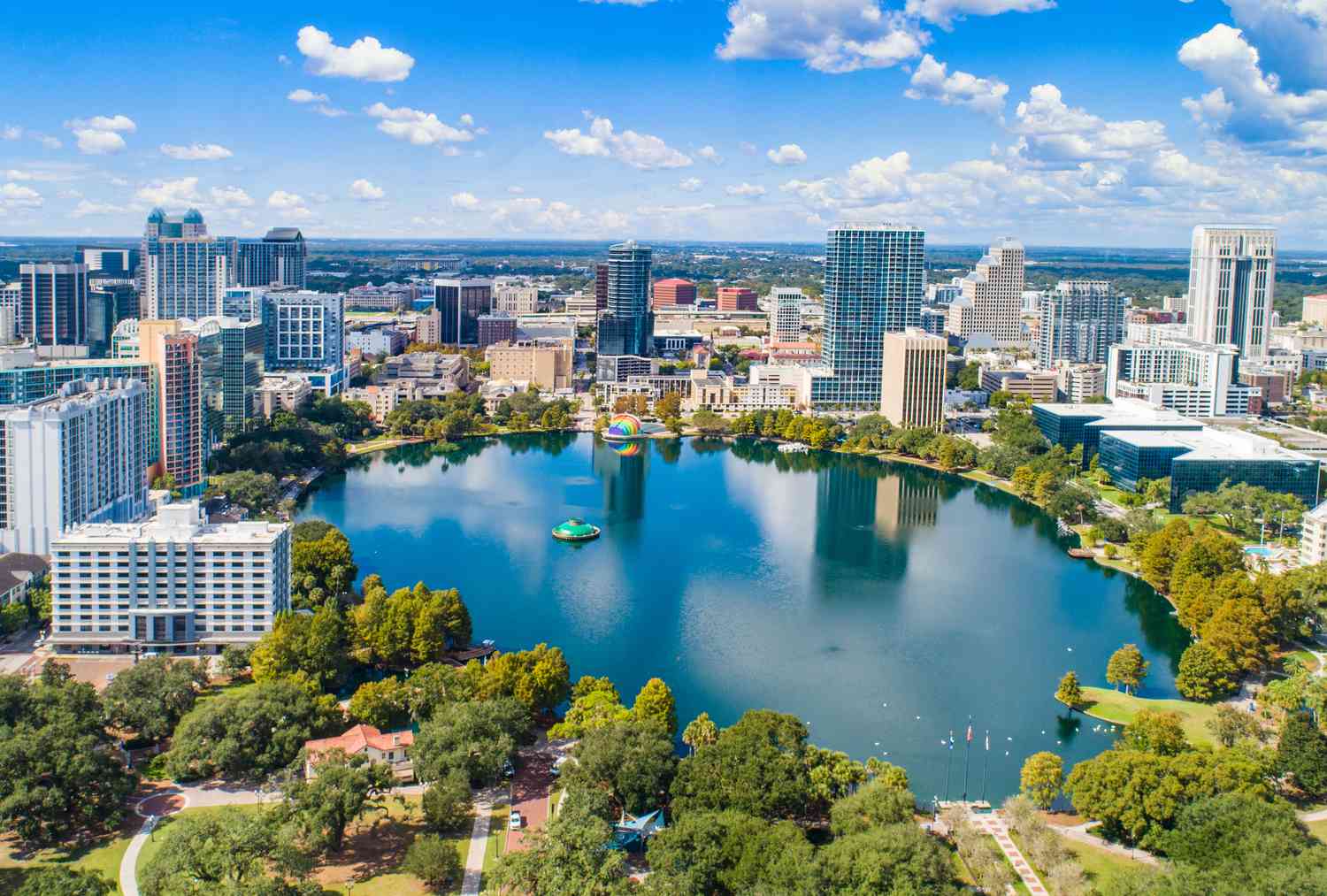

Orlando ist eine Stadt und zudem der County Seat des Orange County im US-Bundesstaat Florida mit 238.300 Einwohnern (Stand: 2010). Nach Jacksonville, Miami, Tampa und Saint Petersburg ist Orlando die fünftgrößte Stadt Floridas. Die Stadt ist Teil der Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) Orlando–Kissimmee–Sanford (kurz auch Greater Orlando) mit rund 2,1 Millionen Einwohnern.
Am meisten ist Orlando durch die Themenparks von Walt Disney World und Universal Studios bekannt. Orlando gilt als die „Touristen-Hauptstadt der USA“[1] und war im Jahr 2014 mit über 62 Millionen Besuchern aus aller Welt das meistbesuchte Touristenziel der Vereinigten Staaten.[2]
奥兰多(英语:Orlando)是位于美国佛罗里达州中部的一座城市,也是橙县(又译奥兰治县)的县治所在,根据美国人口调查局2006年统计,人口共220,186人。2016年3月都会区已上升至2,387,138人。
奥兰多位于中佛罗里达州,是一座休闲城市。湖泊众多,干净的街道、友善的居民及温暖的气候为健行、露营、水上活动、蜜月及家庭旅行的最佳去处。走在奥兰多具有历史性的 Lock Haven 区内,奥兰多自然中心(Orlando Science Center)显眼的铝质圆顶印入眼帘,该自然中心提供个年龄层儿童互动性的展览。在Lock Haven 区内还有奥兰多艺术博物馆(Orlando Museum of Art)、橙县历史博物馆(Orange County Historical Museum)及附近的哈利花园(Harry P. Leu Gardens)。在奥兰多还有老少咸宜的主题乐园,如华德迪士尼世界(Walt Disney World)、环球影城(Universal Studio)、冒险岛乐园(Islands of Adventure), 海洋世界(Sea World)及无数的旅馆,造就了它的观光地位。
由华纳兄弟与环球影城公司合作兴建的哈利波特的魔法世界,位在两大电影制片商在奥兰多面积达787英亩的主题公园园址,霍格华兹城堡与人工白雪覆盖的霍格莫德村,将哈利波特书中的魔法世界真实呈现。于2009年完工,造价数十亿美元。
就像在阳光地带的各大城市,奥兰多在1980年代和进入21世纪的第一个十年迅速发展。奥兰多是中佛罗里达大学的本部所在地,按大学生和硕博士研究生数量算几乎都是全美国最大的大学,主要在培育在肯尼迪航天中心和卡纳维拉尔角空军基地,以支持美国的太空计划的理工人才。在全球城市研究小组的名单上奥兰多被列为“伽马”级世界城市。2009年根据皮尤研究中心研究,基于人们所希望的生活,奥兰多被列为第四大最流行的美国城市。
オーランド(Orlando, 英語発音: [ɔrˈlændoʊ] オランドウ、オァランドウ)は、アメリカ合衆国フロリダ州中央部、オレンジ郡の郡庁所在地であり、全米屈指の観光・保養都市として知られる。
日本語ではオルランドやオランドーの表記も見られる。
2009年現在の推計人口で、市域人口は235,860人、都市圏 (MSA) の人口は2,082,421人で全米27位、広域都市圏(CSA)の人口は2,747,614人である。フロリダ州最大の内陸都市。そして、南東フロリダ大都市圏(マイアミ・フォートローダーデール・ウェストパームビーチ)、タンパ湾大都市圏(タンパ・セントピーターズバーグ・クリアウォーター)に次ぐ、州第3の大都市圏となっており、2000年の国勢調査と比較しても40万人以上の人口増加となっている。
また、オーランドはアメリカで第2の規模を誇る州立総合大学 University of Central Florida がキャンパスを構える。
オーランドは全米屈指の観光・保養都市として知られる。市近郊にはウォルト・ディズニー・ワールド・リゾート、ユニバーサル・オーランド・リゾート、シーワールドなど幾つものテーマパーク・遊園地を有している。またゴルフ場も100ヶ所以上を数える。豪華なリゾートホテルが林立し、郊外には幾つものショッピングセンターやアウトレットモールがある。
手つかずの自然も多く残り、自然保護区が多数指定されている。デイトナビーチなど近郊の海岸にはビーチリゾートが発展しており、世界中から多くの観光客が訪れる。スーパーボーイズグループ、バックストリート・ボーイズのホームタウンでもある。
Orlando (/ɔːrˈlændoʊ/) is a city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Orange County. Located in Central Florida, it is the center of the Orlando metropolitan area, which had a population of 2,509,831, according to U.S. Census Bureau figures released in July 2017. These figures make it the 23rd-largest metropolitan area[8] in the United States, the sixth-largest metropolitan area in the Southern United States, and the third-largest metropolitan area in Florida. As of 2015, Orlando had an estimated city-proper population of 280,257, making it the 73rd-largest city in the United States, the fourth-largest city in Florida, and the state's largest inland city.
The City of Orlando is nicknamed "The City Beautiful," and its symbol is the fountain at Lake Eola. Orlando is also known as "The Theme Park Capital of the World" and in 2016 its tourist attractions and events drew more than 72 million visitors.[9] The Orlando International Airport (MCO or OIA) is the thirteenth-busiest airport in the United States and the 29th-busiest in the world.[10]
As one of the world's most visited tourist destinations, Orlando's famous attractions form the backbone of its tourism industry. The two most significant of these attractions are Walt Disney World, opened by the Walt Disney Company in 1971, and located approximately 21 miles (34 km) southwest of Downtown Orlando in Bay Lake; and the Universal Orlando Resort, opened in 1990 as a major expansion of Universal Studios Florida. With the exception of Walt Disney World, most major attractions are located along International Drive with one of these attractions being the famous Orlando Eye. The city is also one of the busiest American cities for conferences and conventions; the Orange County Convention Center is the second-largest convention facility in the United States.
Like other major cities in the Sun Belt, Orlando grew rapidly from the 1980s up into the first decade of the 21st century. Orlando is home to the University of Central Florida, which is the largest university campus in the United States in terms of enrollment as of 2015. In 2010, Orlando was listed as a "Gamma−" level global city in the World Cities Study Group's inventory.[11] Orlando ranks as the fourth-most popular American city based on where people want to live according to a 2009 Pew Research Center study.[12]
Orlando est une ville des États-Unis, siège du comté d'Orange, en Floride. La ville compte 280 257 habitants en 20171. Son agglomération comprend quant à elle 1 800 000 personnes selon des estimations de 2004 effectuées par le Bureau du recensement des États-Unis. C'est la sixième ville de Floride, et la première située à l'intérieur des terres de l'État. Orlando et ses environs constituent à présent l'une des zones métropolitaines américaines à la croissance la plus rapide.
Elle est surtout connue pour son complexe de loisirs Walt Disney World Resort créé par la Walt Disney Company en 1971, ainsi que pour l'Universal Orlando Resort (1991) composé de deux grands parcs, le premier sur le cinéma Universal Studios le deuxième avec des attractions en rapport avec les héros de comics Islands of Adventure. Sans oublier City Walk, lieu composé de restaurants, bars, cinémas et discothèques aux thèmes divers. La zone consacrée au monde magique de la saga Harry Potter n'est pas un parc à part entière mais un land du parc Universal Studios et un land d'Islands of Adventure. On trouve également dans la ville un SeaWorld, parc d'attractions dont le concept est basé sur des spectacles avec des animaux. Pour la partie restauration, une avenue nommée International Drive regroupe tous les thèmes de restauration possibles avec notamment le McDonald's avec l'aire de jeu la plus grande du monde. Le centre de la ville est en cours de restauration, avec la création d'un nouveau parc à thème, Gatorland. Orlando attire 52 millions de touristes par an et est la deuxième ville hôtelière du pays. Orlando est une des villes qui a connu le plus important apport de population des États-Unis d'Amérique, nombre de retraités étant venus s'installer à Orlando pour sa douceur de vivre, sa situation géographique et son climat, caractères qu'elle partage avec le reste de la Sun Belt.Le symbole d'Orlando est la fontaine du lac Eola (en).
Orlando (AFI: /orˈlando/[2]; in inglese americano [ɔːɹˈlændoʊ̯][3]) è una città degli Stati Uniti d'America, capoluogo della Contea di Orange, in Florida. Secondo il censimento del 2000 la popolazione era di 185.951 (area metropolitana 1.644.561). Una stima del 2006 parla di 220.186 abitanti (2.633.282 l'area metropolitana) facendone la sesta città più grande della Florida. È inoltre a capo dell'Area Statistica Metropolitana (MSA) Orlando-Kissimee. Orlando ospita la seconda più grande università della Florida, la University of Central Florida.
La città è conosciuta dai turisti per le numerose attrazioni in zona, in particolar modo la vicina Walt Disney World Resort, che si trova al di fuori dei confini cittadini di Orlando. Altre aree di attrazione sono SeaWorld e Universal Orlando Resort. Nonostante si trovi lontano dalle principali attrazioni turistiche Orlando sta vivendo un momento di rilancio in tal senso con molti progetti in costruzione o in pianificazione. Per Orlando si stimano 52 milioni di turisti l'anno. Orlando è la seconda città nel paese per numero di stanze d'albergo. Orlando è anche nota per la sua ampia schiera di campi da golf disponibili per golfisti di ogni livello.
Il soprannome della città è "The city beautiful", il suo simbolo è la fontana del lago Eola ed il sindaco attuale è il democratico Buddy Dyer.
La ciudad de Orlando es la sede del condado de Orange y es ciudad central de la zona metropolitana del mismo nombre, así como también cabecera de la región conocida como Florida Central, en el estado de Florida, del sudeste de Estados Unidos. Según el censo estadounidense de 2000, la ciudad tenía una población de 185.951 habitantes (la población en el área metropolitana es de 1.644.561). Un censo local de la población en 2003 arrojó un resultado de 199.336 habitantes (1,8 millones en el área metropolitana). Es la sexta ciudad más grande de Florida y la ciudad no costera más grande. Es además la cabecera de la tercera área metropolitana más grande del estado, detrás de Miami-Fort Lauderdale y Tampa-San Petersburgo.
La ciudad es principalmente conocida por sus hoteles y sus muchas atracciones turísticas de interés infantil y juvenil, particularmente Walt Disney World Resort y Universal Orlando Resort. Otra atracción incluye SeaWorld. El centro de la ciudad de Orlando, más conocido como Downtown Orlando, ha sido objeto de continua reestructuración, a pesar de estar alejada de las principales atracciones turísticas. Es sede de Orlando Sentinel, uno de los periódicos más grandes del estado, de los Orlando Magic, un equipo de baloncesto profesional de la NBA, y del Orlando City Soccer Club de la Major League Soccer; además alberga el torneo de golf Arnold Palmer Invitational del PGA Tour.
Орла́ндо[1] (англ. Orlando) — четвёртый по величине город штата Флорида и самый крупный внутренний город полуострова Флорида с населением 2 387 138 человек (2016) во всей агломерации, что делает её 24-м по величине в США, шестым по величине мегаполисом в южной части Соединённых Штатов и третьим по величине мегаполисом в штате Флорида. По оценке Бюро переписи населения США, в 2010 году в городе проживало 238 300 человек, по оценке 2016 года — 277 173 человека, что делает город 73-м в списке городов США по численности населения, четвертым по величине городом во Флориде и самым крупным внутренним городом штата. Орландо был назван в честь Орландо Ривса, по одному из предположений, солдата армии США, который участвовал во второй войне с семинолами и погиб в этой области.
Орландо известен как мировая столица тематических парков; в 2014 году его достопримечательности, парки, конференции и конвенции посетило более 62 миллионов посетителей[2]. Международный аэропорт Орландо (MCO) является тринадцатым по загруженности аэропорт в Соединённых Штатах и 29 самых оживленных в мире[3].
Наиболее известные и самые посещаемые[4] в США и за их пределами достопримечательности Орландо образуют основу индустрии туризма: Диснейуорлд, расположенный примерно в 34 км к юго-западу от Орландо в Лейк-Буэна-Виста, который разместился на территории в 24 тысячи гектаров (год открытия — 1971); Юнивёрсал Резорт, открывшийся в 1999 году как расширение Юнивёрсал Студиос Флорида; SeaWorld; Gatorland; и Wet 'N Wild. За исключением Walt Disney World, большинство основных достопримечательностей расположены вдоль улицы Интернешнл Драйв. Город также является одним из самых оживленных американских городов для проведения конференций и конвенций.
Город долгое время являлся небольшим поселением в тропической заболоченной сельве, кишащей москитами и аллигаторами. Однако, как и другие крупные города «солнечного пояса», Орландо быстро рос в течение 1980-х годов и в первом десятилетии 21-го века. В Орландо расположен Университет Центральной Флориды, являющийся вторым по количеству студентов в Соединенных Штатах. Орландо занимает четвёртое место в списке наиболее привлекательных для проживания американских городов[5].
В расовом отношении город также претерпел сильные изменения. В 2000 году 50,8 % населения составляли белые, 17,5 % — латиноамериканцы, 26,9 % — афроамериканцы, 2,7 % — азиаты[6].

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025
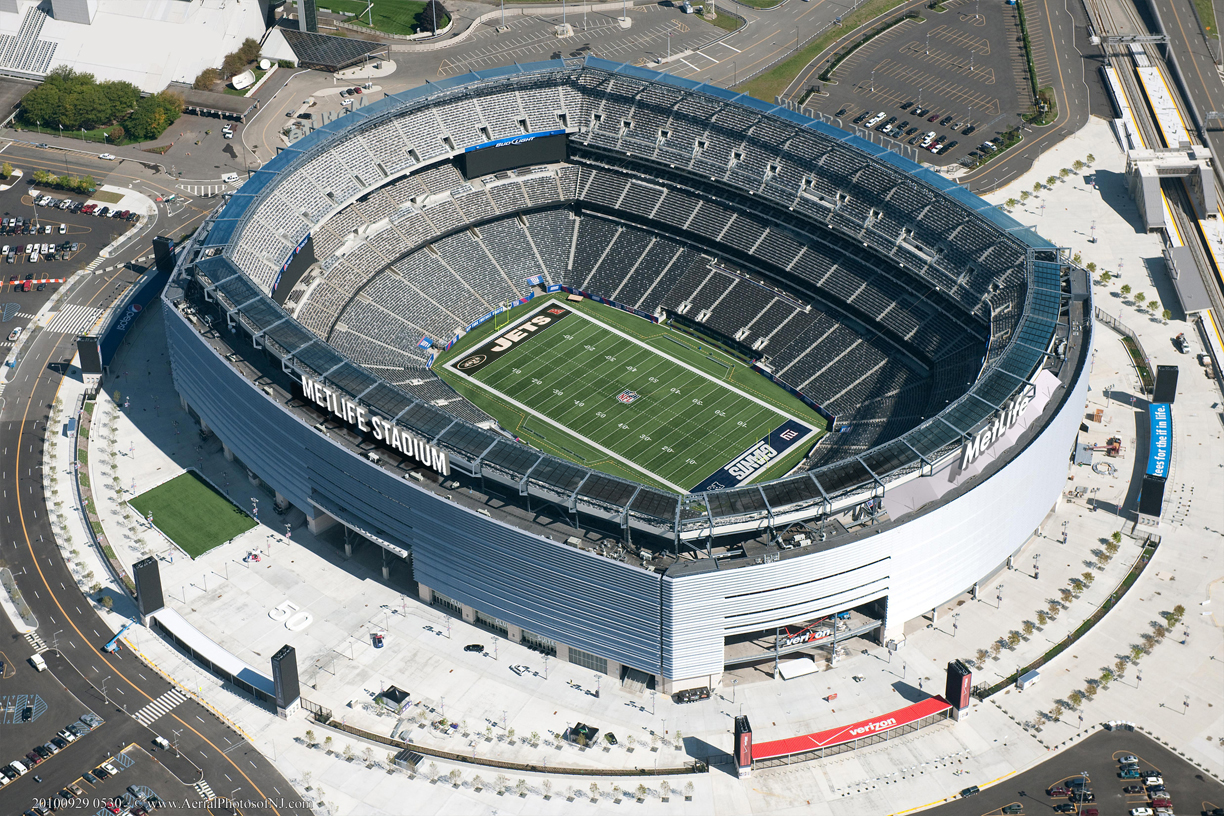
 National Football League 2018
National Football League 2018

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 Sport
Sport
 United States
United States

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1999
Women's Soccer World Cup 1999


 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2003
Women's Soccer World Cup 2003

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA
 United States
United States

 Important port
Important port
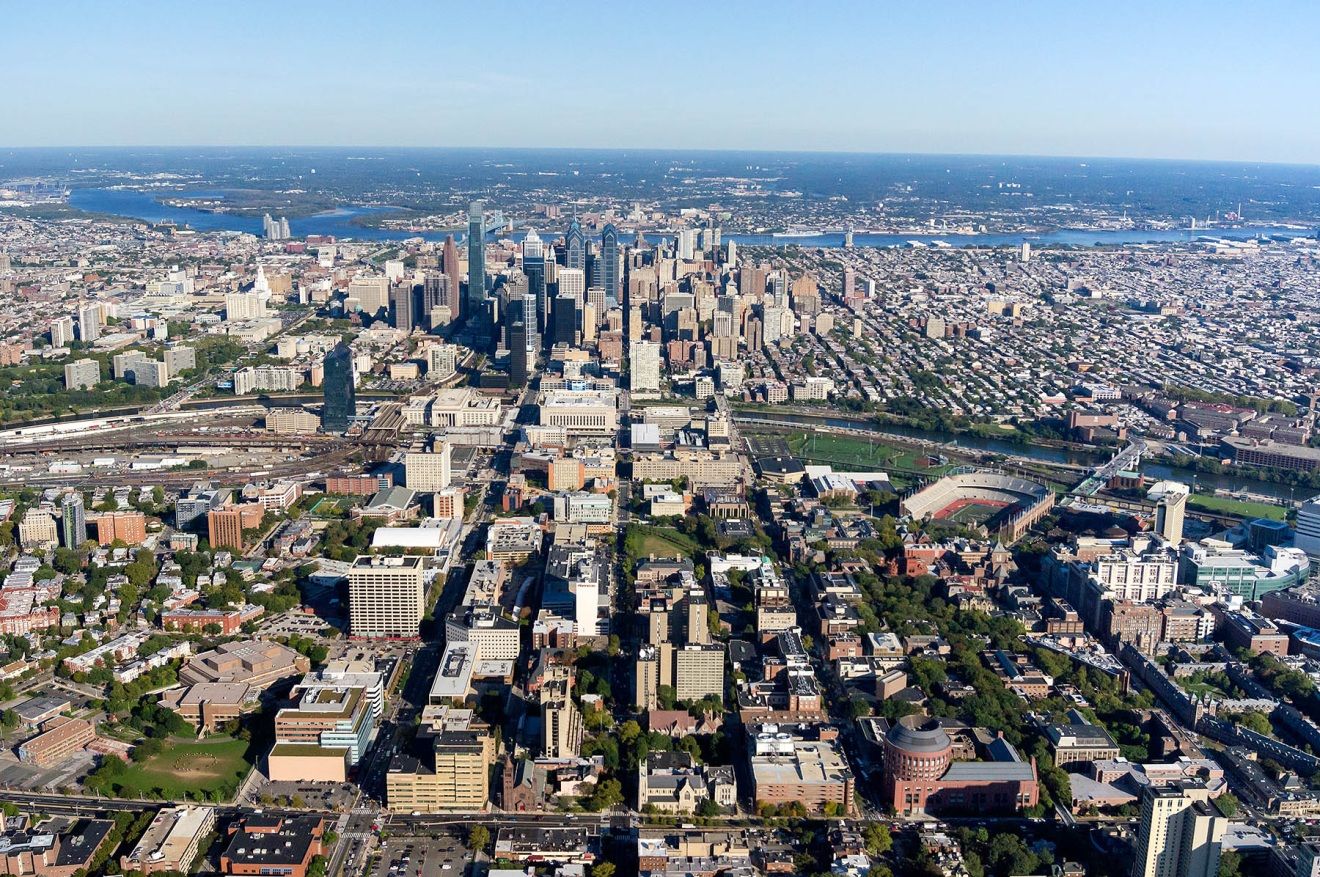

Philadelphia ist eine Stadt im US-Bundesstaat Pennsylvania. Mit rund 1,6 Millionen Einwohnern (Stand: 2016, Schätzung des U.S. Census Bureau) ist sie die sechstgrößte Stadt der Vereinigten Staaten[1] und die größte des Bundesstaates Pennsylvania. An der Ostküste ist Philadelphia nach New York City die zweitgrößte Stadt. Die Stadt liegt am Delaware River im Zentrum der Metropolregion Delaware Valley.
In der Geschichte der USA ist Philadelphia eine der bedeutendsten Städte. Nach New York und vor Washington war sie 1790 bis 1800 Nationalhauptstadt und damals die größte Stadt der USA sowie nach London die zweitgrößte englischsprachige Stadt der Welt. In Philadelphia tagte der erste und teilweise auch der zweite Kontinentalkongress sowie der Verfassungskonvent von 1787, die Amerikanische Unabhängigkeitserklärung wurde hier verkündet und die Verfassung beschlossen.
Philadelphia wird umgangssprachlich Philly oder City of Brotherly Love genannt, was von einer Übersetzung des griechischen Namens Philadelphia herrührt (φιλíα philía ‚Liebe‘ und ἀδελφός adelphós ‚Bruder‘ → φιλαδελφία philadelphía ‚Bruderliebe‘).
费城(英语:Philadelphia),即费利德菲亚,也常被简称为费利(或菲利,英语:Philly) ,中文又音译为非拉铁非和菲拉德尔斐亚,是美国宾夕法尼亚州人口最多、面积最大的都市,同时是美国第五大城。根据2010年人口普查数据,费城人口为1,526,006人。费城市中心的人口在全美国排名第五,仅次于纽约、洛杉矶、芝加哥和休斯顿。以现在美国官方的定义而言,费城都会区的面积大小排名全美第四,共约620万人居住其中,但若以其他定义来衡量,费城排名第六,次于旧金山湾区与华盛顿-巴尔的摩都会区。费城是德拉瓦河谷都会区的中心城市。
费利德菲亚即希腊文“友爱”的意思,是传教士命名的,费城是美国最老、最具历史意义的城市,它在美国史上有非常重要的地位。在18世纪时,费城是美国第二大城与人口最多的城市,在当时,它的政治与社会重要性超过纽约与波士顿。本杰明·富兰克林对费城的兴起贡献良多。从1854年起,费城市和费城县为两个并行的地方政府,而从1952年起,市与县共有一个政府组织,但费城县仍属宾州州政府下的一个独立的县。
自从1854年通过“合并法案”(Act of Consolidation)后,费城市的边界就与费城县相同。在此之前,费城市只在南街(South Street)、葡萄街(Vine Street)与德拉瓦河与斯库基尔河(Schuylkill River)之间的区域。费城后来扩张至周围的西费城(West Philadelphia)、北费城(North Philadelphia)与东北费城(Northeast Philadelphia),同时也包括了几个小型的聚落如罗布鲁(Roxborough)、马拉扬克(Manayunk)、艾利山(Mount Airy)与栗树丘(Chestnut)。费城同时是全美最大的大学城(college town)之一,拥有许多高等学府,其中包括常春藤盟校的宾夕法尼亚大学,国家第一所医学院和法学院兼缘于此校。有超过120,000名大学生就读市区的学院与大学,周遭的都会区也有接近300,000名的大学与学院学生。
フィラデルフィア(英語: Philadelphia)は、アメリカ合衆国ペンシルベニア州南東部にある都市。同州の最大都市かつ北米有数の世界都市である。市内の人口は156万7442人(2015年推計[1])で全米第5位。
名門のペンシルベニア大学や工学系に強いドレクセル大学、日本にもキャンパスを置く州立大学のテンプル大学を抱える学術都市である。市内に約12万人、都市圏全体で約30万人と、全米で最も多くの学生を持つ都市のひとつである。
漢字の当て字和名は費拉特費、また短縮して費府。
なお、フィラデルフィア都市圏の治安は概ね良好であるが、デラウェア川の対岸にあるニュージャージー州カムデンは、デトロイトやセントルイスなどと並んで、全米で最も危険な都市のひとつとされる。
独立記念館や自由の鐘があり、近郊にはバレーフォージがある合衆国建国ゆかりの地である。
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the U.S. state and Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, and the sixth-most populous U.S. city, with a 2017 census-estimated population of 1,580,863.[6] Since 1854, the city has been coterminous with Philadelphia County, the most populous county in Pennsylvania and the urban core of the eighth-largest U.S. metropolitan statistical area, with over 6 million residents as of 2017.[4] Philadelphia is also the economic and cultural anchor of the greater Delaware Valley, located along the lower Delaware and Schuylkill Rivers, within the Northeast megalopolis. The Delaware Valley's population of 7.2 million ranks it as the eighth-largest combined statistical area in the United States.[5]
William Penn, an English Quaker, founded the city in 1682 to serve as capital of the Pennsylvania Colony.[8] Philadelphia played an instrumental role in the American Revolution as a meeting place for the Founding Fathers of the United States, who signed the Declaration of Independence in 1776 at the Second Continental Congress, and the Constitution at the Philadelphia Convention of 1787. Several other key events occurred in Philadelphia during the Revolutionary War including the First Continental Congress, the preservation of the Liberty Bell, the Battle of Germantown, and the Siege of Fort Mifflin. Philadelphia was one of the nation's capitals during the revolution, and served as temporary U.S. capital while Washington, D.C., was under construction. In the 19th century, Philadelphia became a major industrial center and a railroad hub. The city grew from an influx of European immigrants, most of whom came from Ireland, Italy and Germany—the three largest reported ancestry groups in the city as of 2015.[9] In the early 20th century, Philadelphia became a prime destination for African Americans during the Great Migration after the Civil War,[10] as well as Puerto Ricans.[11] The city's population doubled from one million to two million people between 1890 and 1950.
The Philadelphia area's many universities and colleges make it a top study destination, as the city has evolved into an educational and economic hub.[12][13] According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis, the Philadelphia area had a gross domestic product of US$431 billion in 2016, the eighth-largest metropolitan economy in the United States.[14] Philadelphia is the center of economic activity in Pennsylvania and is home to five Fortune 1000 companies. The Philadelphia skyline is expanding, with a market of almost 81,900 commercial properties in 2016,[15] including several nationally prominent skyscrapers.[16] Philadelphia has more outdoor sculptures and murals than any other American city.[17][18] Fairmount Park, when combined with the adjacent Wissahickon Valley Park in the same watershed, is one of the largest contiguous urban park areas in the United States.[19] The city is known for its arts, culture, cuisine, and colonial history, attracting 42 million domestic tourists in 2016 who spent US$6.8 billion, generating an estimated $11 billion in total economic impact in the city and surrounding four counties of Pennsylvania.[20] Philadelphia has also emerged as a biotechnology hub.[21]
Philadelphia is the birthplace of the United States Marine Corps,[22][23] and is also the home of many U.S. firsts, including the first library (1731),[24] hospital (1751),[24] medical school (1765),[25] national capital (1774),[26] stock exchange (1790),[24] zoo (1874),[27] and business school (1881).[28] Philadelphia contains 67 National Historic Landmarks and the World Heritage Site of Independence Hall.[29] The city became a member of the Organization of World Heritage Cities in 2015,[30] as the first World Heritage City in the United States.[13] Although Philadelphia is rapidly undergoing gentrification, the city actively maintains mitigation strategies to minimize displacement of homeowners in gentrifying neighborhoods.[31]
Philadelphie (en anglais Philadelphia, prononcé [ˌfɪləˈdɛlfiə]), surnommée Philly, est une ville du Commonwealth de Pennsylvanie, située dans le Nord-Est des États-Unis, entre New York et Washington DC. Le nom de la ville, choisi par William Penn, signifie « amitié fraternelle2 » en grec, car elle devait être un îlot de tolérance religieuse.
Cinquième ville du pays selon le recensement fédéral de 2010 (après New York, Los Angeles, Chicago et Houston) et sixième agglomération3, Philadelphie compte 1 526 006 habitants dans la municipalité (Philadelphia City) et 5 965 343 habitants dans son aire métropolitaine (PMSA de Philadelphie–Camden–Wilmington)4.
Centre historique, culturel et artistique majeur aux États-Unis, Philadelphie est également un grand port industriel sur le fleuve Delaware qui se jette dans l’océan Atlantique. Fondée en 1682, elle fut jusqu'à 1790 la ville la plus peuplée d'Amérique du Nord. Entre 1774 et 1800, le Congrès des États-Unis s'est réuni en plusieurs endroits, le plus souvent à Philadelphie, faisant de celle-ci la capitale temporaire du pays, jusqu'à ce que Washington devienne la capitale définitive. Par ailleurs, Philadelphie entretient pendant quelques décennies une rivalité financière et politique avec New York, avant d'être éclipsée par sa rivale.
À présent, Philadelphie est la principale métropole de l'État de Pennsylvanie, dont la capitale est Harrisburg, et le siège du comté de Philadelphie.
Filadelfia[1][2] (in inglese: Philadelphia, informalmente anche Philly[3]) è la sesta città per popolazione degli Stati Uniti d'America e la più importante dello stato della Pennsylvania. Nel 2014 contava 1 560 297 abitanti; mentre la sua area metropolitana, estesa anche su parti dei vicini stati del Delaware e del New Jersey, raggiungeva i 5,8 milioni di abitanti.
Fondata nel 1682 dal quacchero William Penn, Filadelfia è una delle più antiche città degli Stati Uniti d'America, e fra la fine del XVIII secolo e l'inizio del XIX fu la città più grande del Paese. In quell'epoca vi furono redatte la dichiarazione di Indipendenza (1776) e la costituzione statunitense.
Filadelfia sorge sulla riva occidentale del fiume Delaware, ed è attraversata da un suo affluente, lo Schuylkill; il centro storico della città è compreso fra questi due fiumi.
Filadelfia3 (en inglés, Philadelphia, también apodada coloquialmente Philly) es la mayor ciudad del estado de Pensilvania, Estados Unidos. Está ubicada sobre la orilla derecha del río Delaware —poco antes de su desembocadura en la bahía de Delaware—, que la separa del estado de Nueva Jersey, y en un punto intermedio entre las importantes ciudades de Nueva York y Washington D. C. Es la quinta ciudad del país por población y la 51.ª del mundo. El condado de Filadelfia, del que es sede, tiene 1 526 000 habs. (Philadelphia City) y su área metropolitana (Valle de Delaware) alcanza los 6 millones de habs. (censo de 2014).
Es un gran centro histórico, cultural y artístico en los Estados Unidos, y de la misma forma un importante puerto industrial sobre el río Delaware, que se extiende hasta el océano Atlántico. Fundada en 1682, fue durante el siglo XVIII la ciudad más poblada de las Trece Colonias y la tercera ciudad más poblada del Imperio británico (tras Londres y Dublín), antes de convertirse provisionalmente en la ciudad capital de los Estados Unidos. Fue velozmente superada por Nueva York y le cedió su estatus de capital a la flamante ciudad de Washington D.C. Hoy, Filadelfia es la principal metrópolis del estado de Pensilvania, aunque la capital y sede del gobierno es Harrisburg.
El nombre de la ciudad, elegido por William Penn, significa "la ciudad del amor fraternal" (compuesta de philos (φίλος) "amor", y adelphos (ἀδελφός) "hermano"), pues se deseaba que fuese un refugio de tolerancia religiosa.
Establecida en 1682, es una de las ciudades más antiguas del país, y, como capital original y ciudad más grande de la época colonial, gozaba de una importancia política y social mayor que Boston o Nueva York. En 1776, el Congreso Continental de las Trece Colonias se reunió en Filadelfia y en el 4 de julio de ese año, declaró la independencia de Gran Bretaña. Quizás el ciudadano más famoso de Filadelfia fue Benjamin Franklin, escritor, científico y político.
Filadelfia es fundamental para la historia afroamericana, su gran población negra es anterior a la Gran Migración.
Филаде́льфия (англ. Philadelphia [ˌfɪləˈdɛlfiə], общеупотр. сокр. «Фи́л(л)и», англ. Philly [ˈfɪli])[1][2] — один из старейших городов США, пятый по величине населения город страны и самый населённый город штата Пенсильвания, с населением 1 526 006 жителей (согласно переписи 2010 года). Население агломерации вместе с пригородами составляет 6 034 678 жителей. Расположен на реке Делавэр у побережья Атлантического океана[3].
Филадельфия богата историей и культурой. В исторической части города до сих пор царит атмосфера маленького и тихого городка, каким была и Филадельфия, и другие колониальные города во время образования государства Соединённые Штаты Америки.
Основан в 1682 году Уильямом Пенном. Имеет прозвище «Город братской любви» (Φιλαδέλφεια на греческом языке означает 'братолюбие'), это связано с тем, что город основан переселенцами, принадлежавшими к протестантской общине квакеров (в США и сейчас его неофициально называют Квакертаун - 'город квакеров'). В 1776 году в Филадельфии Второй континентальный конгресс тринадцати североамериканских штатов принял Декларацию независимости. В 1776, 1777, 1778—1783 и 1790—1800 Филадельфия была временной столицей США.
Одним из известных жителей города был Бенджамин Франклин.
 FIFA
FIFA
 FIFA Club World Cup
FIFA Club World Cup
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025

 Sport
Sport
 (F)AFC Champions League
(F)AFC Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)CAF Champions League
(F)CAF Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)CONCACAF Champions League
(F)CONCACAF Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Copa Libertadores
(F)Copa Libertadores

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Champions League
(F)UEFA Champions League


国际足联俱乐部世界杯(英语:FIFA Club World Cup),或译为世界俱乐部杯、俱乐部冠军杯,简称世俱杯。由该项赛事的前身国际足联俱乐部世锦赛(英语:FIFA Club World Championship)与洲际杯(又名丰田杯,英语:Intercontinental Cup)合并而来[1][2]。是一项由国际足联主办,来自六大洲最顶级俱乐部参与的国际足球锦标赛。
Die FIFA-Klub-Weltmeisterschaft ist die offizielle Weltmeisterschaft für Fußball-Vereinsmannschaften, bei der die Sieger der sechs kontinentalen Meisterwettbewerbe im Vereinsfußball gegeneinander antreten. Nach einem ersten Versuch im Jahr 2000 in Brasilien wird sie seit 2005 regelmäßig gegen Ende des Jahres ausgespielt. Sie gilt als Nachfolger des Weltpokals, der auf europäische und südamerikanische Mannschaften begrenzt war.
Startberechtigt sind sieben Klubs, neben den Gewinnern der UEFA Champions League (Europa) und der Copa Libertadores (Südamerika) auch die Gewinner der CAF Champions League (Afrika), der AFC Champions League (Asien), des CONCACAF Champions Cups (Nord- und Mittelamerika) und der OFC Champions League (Ozeanien) sowie ein Team aus dem Gastgeberland.
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2003
Women's Soccer World Cup 2003

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD
 United States
United States
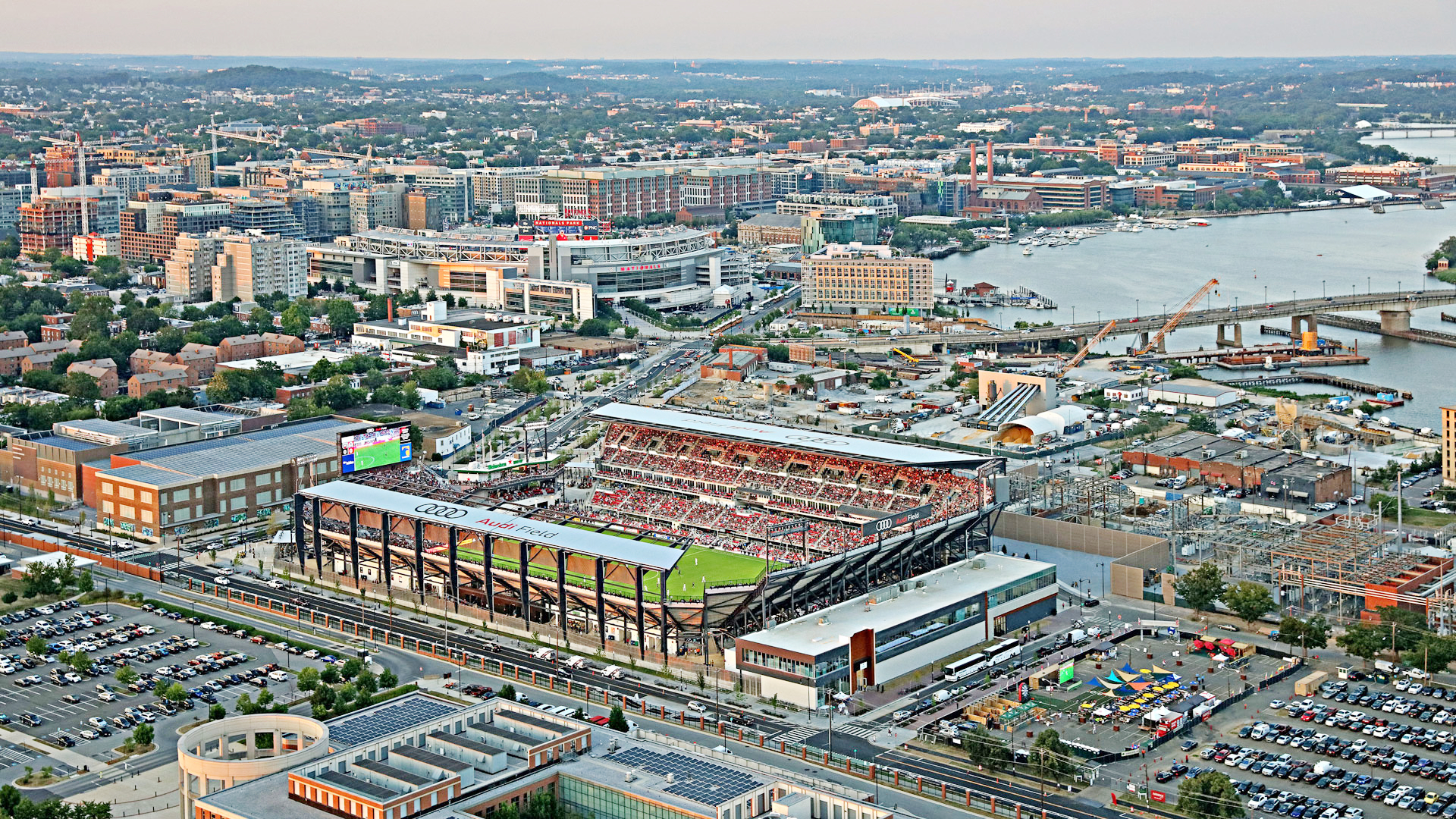
 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
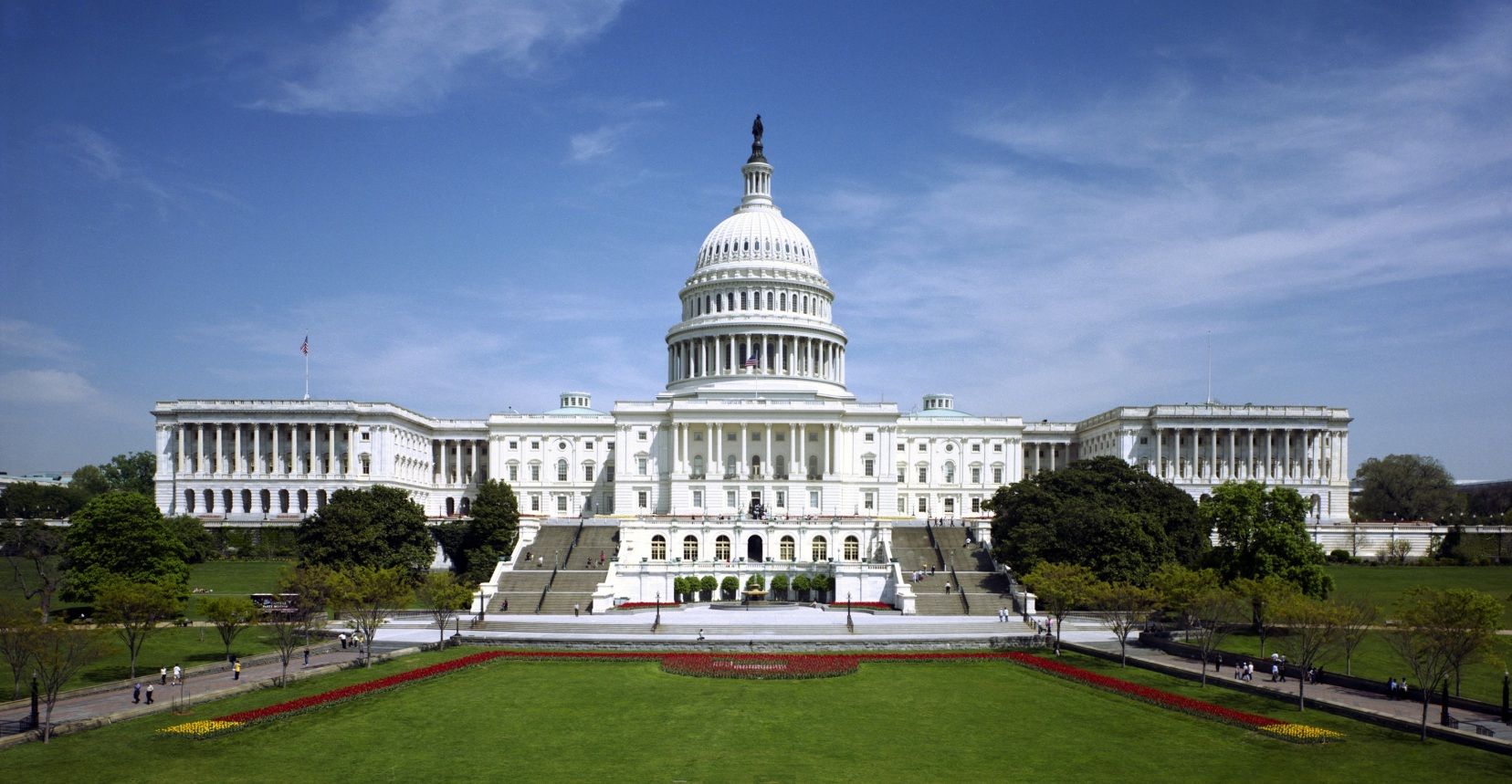

Der District of Columbia oder Washington, D.C. [ˈwɔʃɪŋtn̩] ist Bundesdistrikt, Regierungssitz und seit 1800 die Hauptstadt der Vereinigten Staaten. Der Distrikt ist kein Bundesstaat und gehört auch zu keinem, er ist vielmehr dem Kongress der Vereinigten Staaten direkt unterstellt. Trotz Namensgleichheit mit dem Bundesstaat Washington wird Washington, D.C. im deutschen Sprachraum meist nur „Washington“ genannt. D.C. steht dabei für District of Columbia.
Bei der Volkszählung 2010 hatte Washington, D.C. 601.723 Einwohner.[1] Das United States Census Bureau schätzte die Einwohnerzahl zum 1. Juli 2015 auf 672.228 Einwohner, nach einem stetigen Abfall der Bevölkerung seit 1950 der erste größere Zuwachs.[2] Der Großraum Washington[3] hatte 5.582.170 Einwohner. Zusammen mit dem benachbarten Großraum Baltimore hatte die Region laut Zensus insgesamt 8.572.971 Einwohner.[4]
Mit dem Weißen Haus als Amts- und Wohnsitz des Präsidenten und dem Kapitol, das den Kongress (bestehend aus Senat und Repräsentantenhaus) beherbergt, sowie dem Obersten Gerichtshof befinden sich die Spitzen aller drei verfassungsmäßigen Gewalten in der Stadt. Washington ist darüber hinaus Sitz des Internationalen Währungsfonds, der Weltbank und der Organisation Amerikanischer Staaten.
华盛顿哥伦比亚特区(英语:Washington, D.C.),是美国的首都,原称哥伦比亚特区[注 1](District of Columbia,缩写为 D.C.),以及简称华盛顿(Washington)、特区(the District)等。中文通常简称华府。华盛顿哥伦比亚特区是大多数美国联邦政府机关、与各国驻美大使馆的所在地,也是世界银行、国际货币基金、美洲国家组织等国际组织总部的所在地,并拥有为数众多的博物馆与文化史迹。哥伦比亚特区是美国最富裕、财富高度集中的地区;该地区2015年的人均生产总值为181,185美元,冠绝全美。
1776年美国独立时的首都是费城,之后因独立战争和国家新立而屡有变迁,到1785年开始纽约被定为美国的首都。1790年7月1日,国会通过《首都选址法》,决定将首都从纽约迁至波多马克河和安那考斯迪亚河汇合处附近;但完成正式迁都前先由费城暂代首都。1800年,美国联邦政府部门从临时首都的费城迁往建设完成的华盛顿,华盛顿开始作为美国首都正式运作至今[3]。华盛顿哥伦比亚特区实际上是由美国国会直接管辖的联邦地区,因此不属于美国的任何州份。
华盛顿哥伦比亚特区位于美国东岸的中大西洋地区,属马里兰州和弗吉尼亚州的交界处,两州界河波多马克河由西北向东南流贯特区,形成特区西面的天然界限。成立之初,哥伦比亚特区是一个边长10英里(16千米)的长方形区域,不仅包括了特区现在的全部范围,还包括波多马克河西岸弗吉尼亚州亚历山德里亚县,即今日的阿灵顿县以及亚历山德里亚市。特区成立后不久,西岸的居民就因为国会过度重视东岸以及蓄奴等问题,发起了回归弗吉尼亚的运动,经他们多次请愿,美国国会于1846年7月9日通过法案,并经弗吉尼亚人民大会批准,将波多马克河南岸的土地交还南方的弗吉尼亚州。特区设立早期,波多马克河北岸有乔治城镇、华盛顿市及华盛顿县三个分开的行政区划;其中建立于1791年的华盛顿市乃为彰显乔治·华盛顿对美国建国的贡献而命名,后来发展为特区中的核心城市。依据一项1871年的立法,前述三区于1878年合并为华盛顿市,而联邦管辖的特区及华盛顿市地方政府从此辖区重叠,因此产生今日使用的“华盛顿哥伦比亚特区”合称。
ワシントンD.C.(ワシントン・ディーシー、英: Washington, D.C.)は
同国東海岸、メリーランド州とヴァージニア州に挟まれたポトマック川河畔に位置する。
現代の主要都市としては狭隘で人口もさほど多くないが、超大国の政府所在地として国際的に強大な政治的影響力を保持する世界都市であり、また金融センターとしても高い重要性を持つ。首都としての機能を果たすべく設計された、計画都市である[† 1]。
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington or D.C., is the capital of the United States of America.[4] Founded after the American Revolution as the seat of government of the newly independent country, Washington was named after George Washington, first President of the United States and Founding Father.[5] Washington is the principal city of the Washington metropolitan area, which has a population of 6,131,977.[6] As the seat of the United States federal government and several international organizations, the city is an important world political capital.[7] Washington is one of the most visited cities in the world, with more than 20 million annual tourists.[8][9]
The signing of the Residence Act on July 16, 1790, approved the creation of a capital district located along the Potomac River on the country's East Coast. The U.S. Constitution provided for a federal district under the exclusive jurisdiction of the Congress and the District is therefore not a part of any state. The states of Maryland and Virginia each donated land to form the federal district, which included the pre-existing settlements of Georgetown and Alexandria. Named in honor of President George Washington, the City of Washington was founded in 1791 to serve as the new national capital. In 1846, Congress returned the land originally ceded by Virginia; in 1871, it created a single municipal government for the remaining portion of the District.
Washington had an estimated population of 693,972 as of July 2017, making it the 20th largest American city by population. Commuters from the surrounding Maryland and Virginia suburbs raise the city's daytime population to more than one million during the workweek. The Washington metropolitan area, of which the District is the principal city, has a population of over 6 million, the sixth-largest metropolitan statistical area in the country.
All three branches of the U.S. federal government are centered in the District: U.S. Congress (legislative), President (executive), and the U.S. Supreme Court (judicial). Washington is home to many national monuments and museums, which are primarily situated on or around the National Mall. The city hosts 177 foreign embassies as well as the headquarters of many international organizations, trade unions, non-profit, lobbying groups, and professional associations, including the Organization of American States, AARP, the National Geographic Society, the Human Rights Campaign, the International Finance Corporation, and the American Red Cross.
A locally elected mayor and a 13‑member council have governed the District since 1973. However, Congress maintains supreme authority over the city and may overturn local laws. D.C. residents elect a non-voting, at-large congressional delegate to the House of Representatives, but the District has no representation in the Senate. The District receives three electoral votes in presidential elections as permitted by the Twenty-third Amendment to the United States Constitution, ratified in 1961.
Washington, dans le district de Columbia (en anglais : Washington, District of Columbia), souvent appelée Washington, D.C., The District, ou simplement D.C. (pour éviter la confusion avec l'État de Washington), est une ville indépendante américaine, capitale des États-Unis. Selon les dernières estimations (2013), elle compte 646 449 habitants intra-muros sur une superficie de 177 km2 ; son aire urbaine en compte environ 5,8 millions, la septième des États-Unis.
En tant que capitale fédérale, elle ne fait pas partie des cinquante États de l'Union et dépend directement du gouvernement fédéral. À ce titre, la ville est le siège de nombreuses institutions américaines, telles que la Maison-Blanche, résidence officielle du président ; le Capitole, siège du Congrès (constitué de ses deux chambres : celle des représentants et le Sénat), ainsi que le siège de la Banque mondiale (BM), de la Cour suprême et d'autres organismes fédéraux, comme la Réserve fédérale des États-Unis (Fed). Elle accueille en outre 176 ambassades et représentations diplomatiques.
Washington est créée à la suite de la signature du Residence Act en 1790, qui prévoit la création d'une capitale fédérale. Elle est fondée en janvier 1791, sur les rives du fleuve Potomac, à proximité des villes de Georgetown et d'Alexandria. Nommée en hommage au premier président des États-Unis, George Washington, elle est construite ex nihilo selon un plan hippodamien de l'ingénieur franco-américain Pierre Charles L'Enfant. L'urbanisme diffère de la plupart des autres villes américaines car la construction de gratte-ciel y est interdite : l'architecture de Washington est marquée par une faible hauteur et un héritage de l'architecture coloniale. Peu peuplée durant la première moitié du XIXe siècle, ce n'est qu'à la fin de la guerre de Sécession qu'elle acquiert sa légitimité en tant que capitale, devenant le symbole de l'unité retrouvée.
Située sur la côte atlantique du nord-est du pays, entre le Maryland et la Virginie, la ville se trouve à soixante kilomètres au sud de Baltimore, à deux cents kilomètres de Philadelphie et trois cents kilomètres de New York. Elle marque l'extrémité méridionale de la mégalopole américaine, appelée également BosWash. Les coordonnées géographiques de la ville correspondent au point zéro, d'où sont calculées toutes les distances routières aux États-Unis. Son climat est de type subtropical humide, avec de fortes variations de température entre l'été et l'hiver.
En tant que siège de la plupart des institutions fédérales, l'économie est fortement dépendante des activités gouvernementales, qui représentent jusqu'à 50 % de son PIB au milieu du XXe siècle. Aujourd'hui, l'économie est diversifiée, notamment dans l'industrie de l'armement et de l'informatique.
La population de la ville se stabilise de nos jours autour de 600 000 habitants, après avoir connu une baisse importante depuis la Seconde Guerre mondiale, essentiellement en raison du départ des Blancs pour les banlieues environnantes. Devenue une ville en majorité composée d'Afro-Américains (50,1 %), Washington comprend historiquement plusieurs ghettos — dont certains connaissent actuellement un processus de gentrification — et est depuis sa fondation un bastion du Parti démocrate.
La ville compte plusieurs universités, dont la prestigieuse université de Georgetown, ainsi que la Bibliothèque du Congrès, plus grande bibliothèque au monde.
Washington dispose de services de polices dépendant de la municipalité ; ainsi que la Garde nationale du district de Columbia (en) qui en tant que force fédérale dépend du président lui-même. Le district de Columbia ne dispose donc pas de forces autonomes comme les Polices d'État ou les Forces de défense d'État existant dans les États de l'Union.
Washington D.C. (AFI: /ˈwɔʃʃinton/[2]; in inglese [ˈwɒʃɪŋtən]) è la capitale degli Stati Uniti d'America, con una popolazione di 672 228 abitanti[1] (5 582 170 abitanti nell'area metropolitana)[3]. Si trova sulla costa orientale degli Stati Uniti a circa 50 km dal mare, a sud dello stato del Maryland, a nord dello stato della Virginia e a 374 km circa a sud di New York.
La città di Washington coincide territorialmente e politicamente con il Distretto di Columbia[4] (in inglese: District of Columbia, in sigla D.C., distretto federale previsto dalla Costituzione dell'Unione e formalizzato dal District of Columbia Organic Act del 1801), di cui è parte integrante. Infatti, mentre in origine il distretto comprendeva le contee di Washington (donata dallo stato del Maryland) ed Alexandria (donata dallo stato della Virginia), in seguito ad un referendum del 1846 quest'ultima è tornata allo stato della Virginia e ha cambiato nome in Contea di Arlington.
Di conseguenza con il District of Columbia Organic Act del 1871,[5] il Congresso ha ufficialmente soppresso la contea di Washington, che comprendeva l'attuale città di Washington, sottoponendo l'intero territorio dapprima ad un unico governatore di nomina presidenziale, poi, dal 1845, ad un triumvirato composto da due politici e un ingegnere. Da quel momento la Città di Washington e il Distretto di Columbia divennero la stessa entità, condidivendo la personalità giuridica.[6]
Ciononostante, l'area metropolitana di Washington deborda dai confini del distretto, estendendosi anche su 7 contee del Maryland (Anne Arundel, Calvert, Charles, Frederick, Howard, Montgomery e Prince George's), su 5 contee della Virginia (Arlington, ossia l'ex Contea di Alexandria, Fairfax, Loudon, Prince William e Stafford) e su 5 città autonome dello stesso Stato (Alexandria, Fairfax, Falls Church, Manassas e Manassas Park). Gran parte dell'area è collegata da un servizio di metropolitana.
Nel 1973 le richieste per una maggiore democrazia nel distretto portarono all'approvazione del District of Columbia Home Rule Act,[7] la legge che soppresse il triumvirato e affidò l'amministrazione cittadina a un sindaco eletto dal popolo, il Mayor, e a un Consiglio comunale, il Council of the District. Il distretto, che gode di 3 voti nel collegio dei Grandi elettori del Presidente dell'Unione, non prevede nella propria legislazione la pena di morte.
Hanno sede a Washington le principali istituzioni di governo degli Stati Uniti (Presidente, Congresso, Corte Suprema), molti ministeri ed enti federali, e alcune organizzazioni internazionali, tra cui la Banca Mondiale, il Fondo Monetario Internazionale e l'Organizzazione degli Stati Americani.
Washington D. C. (/ˈwɑʃɪŋtən diˈsi/ en inglés), oficialmente denominado Distrito de Columbia (District of Columbia), es la capital de los Estados Unidos de América. Se administra como distrito federal, una entidad diferente a los cincuenta estados que componen dicha nación, y depende directamente del gobierno federal. El Distrito de Columbia fue fundado el 16 de julio de 1790, y en 1791 se oficializó, dentro del distrito, una nueva ciudad denominada Washington, al este de la ya existente Georgetown. En 1871 se unificaron los gobiernos de estas dos ciudades y del resto de poblaciones del distrito en una sola entidad, D. C.
Se localiza a orillas del río Potomac y está rodeada por los estados de Virginia al oeste, y de Maryland al norte, este y sur.
La ciudad de Washington nació como una ciudad planificada, y fue desarrollada a finales del siglo XVIII para servir como la capital nacional permanente, después de que diversas localidades ostentaran dicha posición desde la independencia del país, en 1776; en tanto, el distrito federal fue formado para marcar la diferencia entre la capital nacional y los estados. La ciudad fue nombrada en honor a George Washington, el primer presidente de los Estados Unidos. El nombre del distrito, Columbia, es el nombre poético de Estados Unidos, en referencia a Cristóbal Colón (en inglés Christopher Columbus), primer explorador en llegar a América. La ciudad es llamada comúnmente Washington, the District (el Distrito) o simplemente D. C. En el siglo XIX también se la conoció como Ciudad Federal o Ciudad de Washington.
Los centros de las tres ramas del Gobierno de los Estados Unidos se ubican en el Distrito. También situadas en la ciudad están las sedes del Banco Mundial, el FMI, la OEA, el BID, y otras instituciones nacionales e internacionales, incluyendo asociaciones profesionales y sindicatos. Debido a su importancia a nivel político, Washington es un lugar de frecuentes manifestaciones y protestas, particularmente en el National Mall. Además es un destino popular entre los turistas, debido a los numerosos monumentos y lugares de interés nacional. La ciudad es un centro de la historia y cultura estadounidense, y en ella se encuentra el complejo de museos más grande del mundo (el Instituto Smithsoniano), además de galerías de arte, universidades, catedrales, centros e instituciones de arte dramático, y escenarios de música nativa.
El Distrito de Columbia y la ciudad de Washington son gobernados por un solo gobierno municipal. Para cuestiones prácticas son considerados como la misma entidad. Éste no siempre ha sido el caso: hasta 1871 —cuando Georgetown dejó de ser una ciudad separada— había múltiples jurisdicciones dentro del Distrito.3 A pesar de que hay un gobierno municipal y un alcalde, el Congreso tiene la autoridad suprema sobre la ciudad y el distrito, lo que resulta en que los ciudadanos tengan menos autogobierno que los residentes de los estados. El Distrito tiene un delegado en el Congreso, que participa en los debates pero no tiene derecho a voto.
La población del Distrito de Columbia es de 646 449 habitantes en 2013 según estimaciones de la Oficina del Censo de los Estados Unidos.1 El área metropolitana de Washington D. C. es la octava más grande de Estados Unidos, con más de 5 millones de residentes,2 y el área metropolitana que forma junto a la cercana Baltimore tiene una población que excede los 8 millones. Si Washington D. C. fuera un estado, estaría último en cuanto a superficie (por detrás de Rhode Island), en penúltimo lugar en cuanto a población (por delante de Wyoming), en el lugar n.º 35 en cuanto a producto interno bruto y primero en densidad de población.
Aunque el Distrito de Columbia no tiene un miembro votante del Congreso los residentes todavía están obligados a pagar impuestos al gobierno federal. Esto es diferente de los territorios de Estados Unidos, como Puerto Rico, cuyos ciudadanos en general no pagan impuestos sobre la renta individual. Los residentes protestan por la falta de derechos de voto, sobre todo porque la falta de representación en el Parlamento británico fue una de las principales razones para la independencia del país del Reino Unido. La ciudad adoptó una frase de la Guerra de la Independencia, «No hay tributación sin representación», para protestar por la falta de derechos de voto.4 El eslogan también aparece en las placas de automóvil expedidas por la ciudad.5

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025
 National Football League 2018
National Football League 2018

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Sport
Sport

 Architecture
Architecture
 International cities
International cities