
English Encyclopedia
 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织


The Australian Institute of International Affairs (AIIA) is an Australian research institute and think tank which focuses on International relations. It publishes the Australian Journal of International Affairs. It is one of the oldest active private research institutes in Australia.
The Brookings Institution, often simply called Brookings, is an American research group founded in 1916. Located on Think Tank Row in Washington, D.C.,[3] the organization conducts research and education in the social sciences, primarily in economics (and tax policy), metropolitan policy, governance, foreign policy, global economy, and economic development.[4][5] Its stated mission is to "provide innovative and practical recommendations that advance three broad goals: strengthen American democracy; foster the economic and social welfare, security and opportunity of all Americans; and secure a more open, safe, prosperous, and cooperative international system."[3]
Brookings has five research programs at its Washington campus: Economic Studies,[6] Foreign Policy,[7] Governance Studies,[8] Global Economy and Development,[9] and Metropolitan Policy.[10] It also established and operates three international centers which are based in Doha, Qatar (Brookings Doha Center, and since 2021, the Middle East Council on Global Affairs or MECGA);[11] Beijing, China (Brookings-Tsinghua Center for Public Policy, and since 2020, the Brookings-Tsinghua China Office at Tsinghua University);[12] and New Delhi, India (Brookings India, and since 2020, the Centre for Social and Economic Progress or CSEP).[13]
The University of Pennsylvania's Global Go To Think Tank Index Report has named Brookings "Think Tank of the Year" and "Top Think Tank in the World" every year since 2008.[14] The Economist describes Brookings as "perhaps America’s most prestigious think-tank."[15]
Brookings states that its staff "represent diverse points of view" and describes itself as nonpartisan,[16] and various media outlets have alternately described Brookings as centrist,[17] liberal,[18] or right-wing.[19] An academic analysis of congressional records from 1993 to 2002 found that Brookings was cited by conservative politicians almost as often as by liberal politicians, earning a score of 53 on a 1–100 scale, 100 representing the most liberal score.[20] The same study found Brookings to be the most frequently cited think tank by U.S. media and politicians.

The Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) is a think tank based in Washington, D.C., in the United States.[5] CSIS was founded as the Center for Strategic and International Studies of Georgetown University in 1962. The center conducts policy studies and strategic analyses of political, economic and security issues throughout the world, with a specific focus on issues concerning international relations, trade, technology, finance, energy and geostrategy.[6]
In the University of Pennsylvania's 2019 Global Go To Think Tanks Report, CSIS is ranked the number one think tank in the United States across all fields, the "Top Defense and National Security Think Tank" in the world, and the 4th best think tank in the world overall.[7][8] CSIS has been named the number one think tank for Defense and National Security for the past seven years, and has been declared the 'Center of Excellence'.[8]
Since its founding, CSIS "has been dedicated to finding ways to sustain American prominence and prosperity as a force for good in the world", according to its website.[9] CSIS is officially a bipartisan think tank with scholars that represent varying points of view across the political spectrum. The think tank is known for inviting well-known foreign policy and public service officials from the U.S. Congress and the executive branch, including those affiliated with either the Democratic or the Republican Party as well as foreign officials of varying political backgrounds. It has been labeled a "centrist" think tank by U.S. News & World Report.[10]
The center hosts the Statesmen's Forum, a bipartisan venue for international leaders to present their views. Past speakers have included UN Secretary General Ban Ki Moon and National Security Advisor Tom Donilon.[11] The center also conducts the CSIS-Schieffer School Dialogues, a series of discussions hosted by Bob Schieffer, of CBS News, in addition to the Global Security Forum, with keynote addresses by Defense Department officials including former Secretary of Defense Chuck Hagel.

Chatham House, also known as the Royal Institute of International Affairs, is an independent policy institute headquartered in London. Its mission is to provide authoritative commentary on world events and offer solutions to global challenges. It is the originator of the Chatham House Rule.
 *欧洲联盟
*欧洲联盟
 比利时
比利时
 比利时
比利时
 丹麦
丹麦
 联邦德国
联邦德国
 爱沙尼亚
爱沙尼亚

 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟
 欧共体成员国
欧共体成员国
 芬兰
芬兰
 法国
法国
 希腊
希腊
 手拉手
手拉手
 荷兰
荷兰
 爱尔兰
爱尔兰
 意大利
意大利
 克罗地亚
克罗地亚
 拉脱维亚
拉脱维亚
 立陶宛
立陶宛
 卢森堡
卢森堡
 马耳他
马耳他
 诺贝尔奖
诺贝尔奖
 2012
2012
 诺贝尔奖
诺贝尔奖
 诺贝尔和平奖
诺贝尔和平奖
 奥地利
奥地利

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团
二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 七国集团
七国集团
 波兰
波兰
 葡萄牙
葡萄牙
 罗马尼亚
罗马尼亚
 瑞典
瑞典
 斯洛伐克
斯洛伐克
 斯洛文尼亚
斯洛文尼亚
 西班牙
西班牙
 捷克
捷克
 匈牙利
匈牙利

 经济和贸易
经济和贸易
 自由贸易区
自由贸易区
 塞浦路斯
塞浦路斯
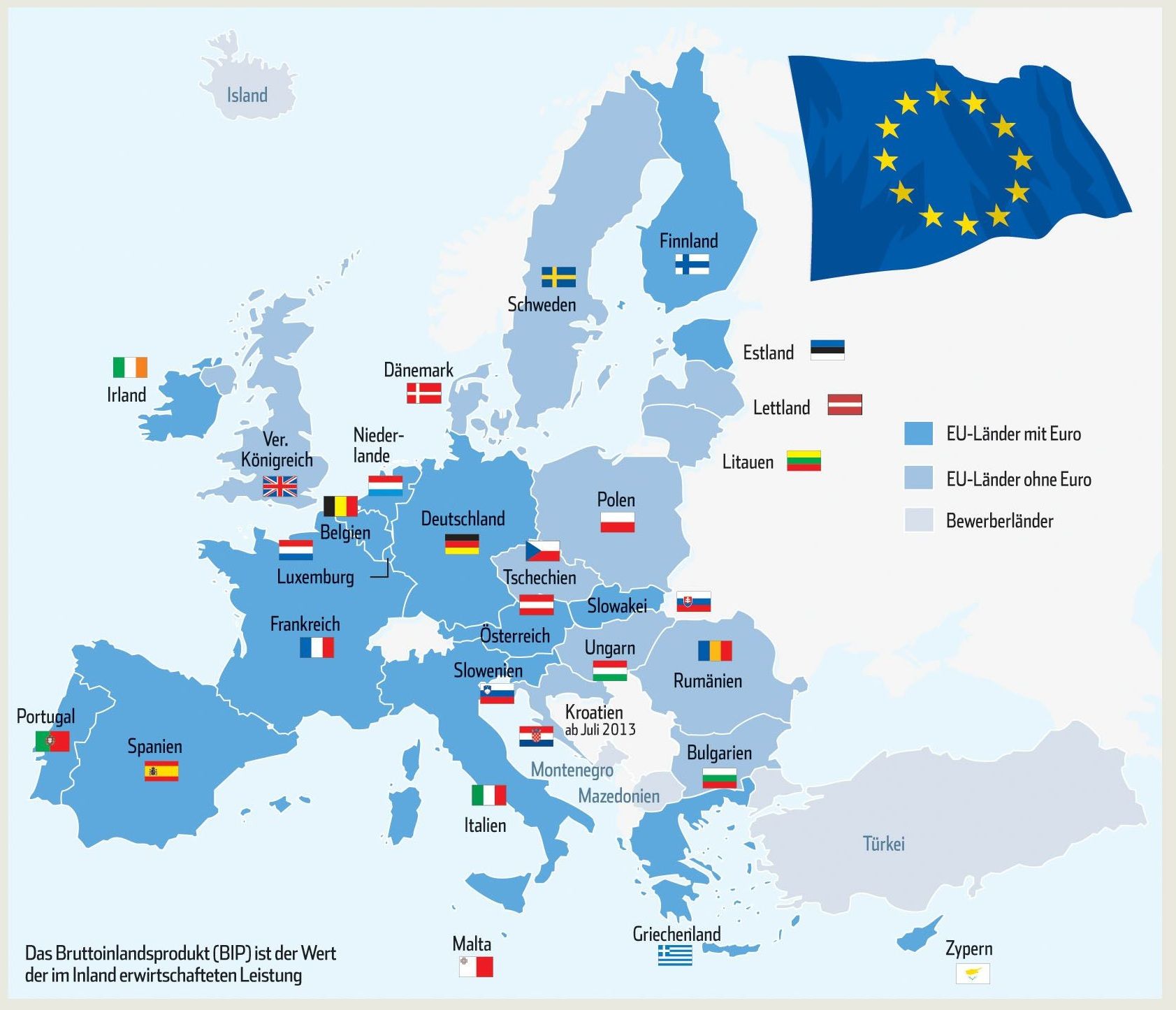
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 28 member states that are located primarily in Europe.[13] It has an area of 4,475,757 km2 (1,728,099 sq mi) and an estimated population of over 510 million. The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters (only) where members have agreed to act as one. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market,[14] enact legislation in justice and home affairs and maintain common policies on trade,[15] agriculture,[16] fisheries and regional development.[17] For travel within the Schengen Area, passport controls have been abolished.[18] A monetary union was established in 1999 and came into full force in 2002 and is composed of 19 EU member states which use the euro currency.
The EU and European citizenship were established when the Maastricht Treaty was enacted in 1993.[19] The EU traces its origins to the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) and the European Economic Community (EEC), established, respectively, by the 1951 Treaty of Paris and 1957 Treaty of Rome. The original members of what came to be known as the European Communities were the Inner Six: Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany. The Communities and its successors have grown in size by the accession of new member states and in power by the addition of policy areas to its remit. The latest major amendment to the constitutional basis of the EU, the Treaty of Lisbon, came into force in 2009. While no member state has left the EU or its predecessors, the United Kingdom signified an intention to leave after a membership referendum in June 2016 and is negotiating its withdrawal.
The European Union provides more foreign aid than any other economic union.[20] Covering 7.3% of the world population,[21] the EU in 2017 generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of 19.670 trillion US dollars, constituting approximately 24.6% of global nominal GDP[22] and 16.5% when measured in terms of purchasing power parity.[23] Additionally, 27 out of 28 EU countries have a very high Human Development Index, according to the United Nations Development Programme. In 2012, the EU was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize.[24] Through the Common Foreign and Security Policy, the EU has developed a role in external relations and defence. The union maintains permanent diplomatic missions throughout the world and represents itself at the United Nations, the World Trade Organization, the G7 and the G20. Because of its global influence, the European Union has been described as an emerging superpower.[25]
 阿根廷
阿根廷
 澳大利亚
澳大利亚
 巴西
巴西

 中国
中国
 联邦德国
联邦德国
 英格兰
英格兰

 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟
 法国
法国

 汉堡州
汉堡州

 手拉手
手拉手
 印度
印度
 印度尼西亚
印度尼西亚
 意大利
意大利
 日本
日本
 墨西哥
墨西哥
 尼古拉·萨科齐
尼古拉·萨科齐

 俄亥俄州
俄亥俄州

 安大略
安大略

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团
二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团

 普罗旺斯-阿尔卑斯-蓝色海岸
普罗旺斯-阿尔卑斯-蓝色海岸

 昆士兰州
昆士兰州
 韩国
韩国
 俄罗斯
俄罗斯
 沙特阿拉伯
沙特阿拉伯
 南非
南非
 土耳其
土耳其
 英国
英国
 华盛顿哥伦比亚特区
华盛顿哥伦比亚特区
 浙江省-浙
浙江省-浙
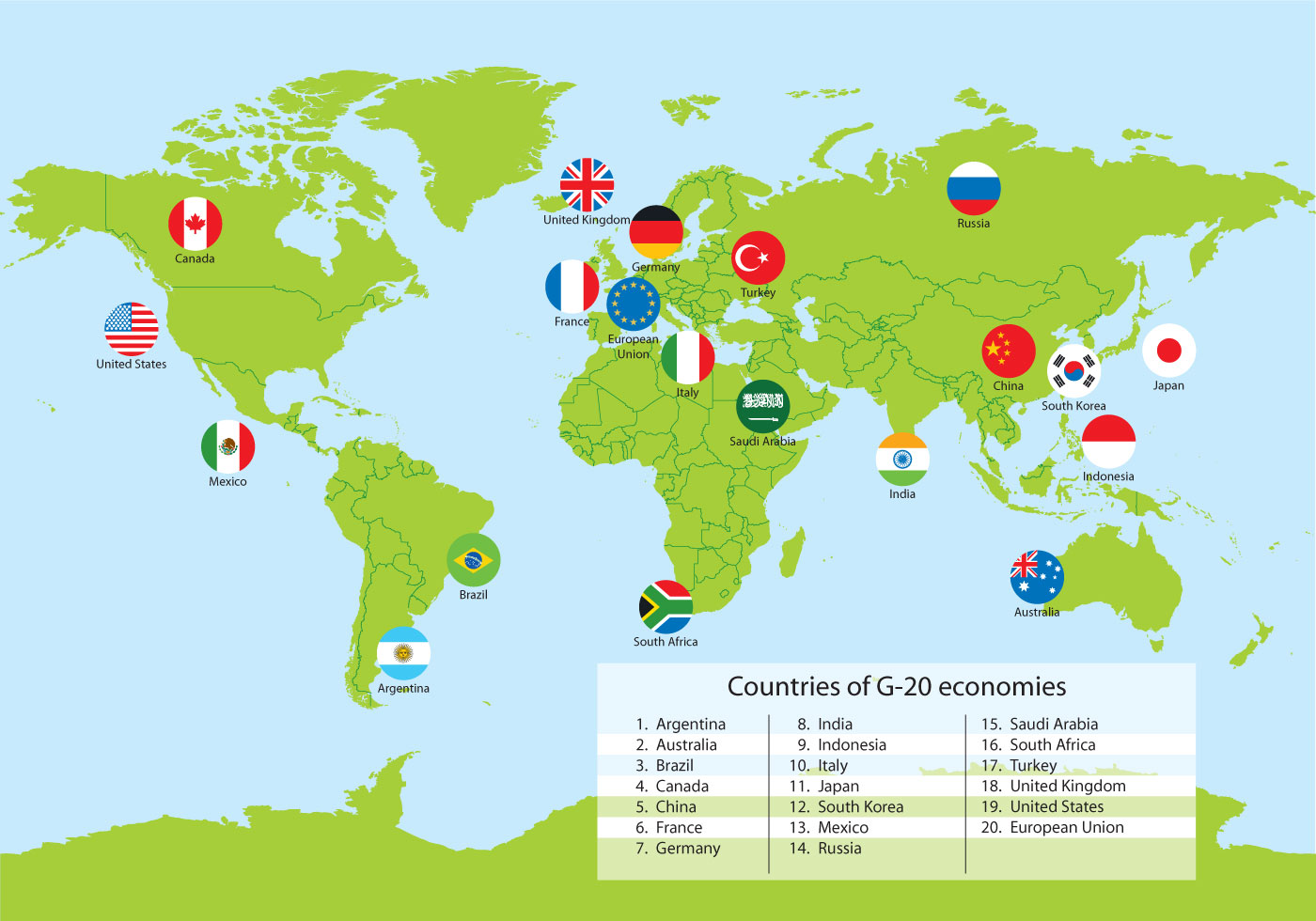
The G20 (or Group of Twenty) is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU). Founded in 1999 with the aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability,[3] the G20 has expanded its agenda since 2008 and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers, foreign ministers and think tanks[4], have periodically conferred at summits ever since. It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one organization.[3]
Membership of the G20 consists of 19 individual countries plus the European Union. The EU is represented by the European Commission and by the European Central Bank. Collectively, the G20 economies account for around 90%[5] of the gross world product (GWP), 80% of world trade (or, if excluding EU intra-trade, 75%), two-thirds of the world population,[2] and approximately half of the world land area.
With the G20 growing in stature[6] after its inaugural leaders' summit in 2008, its leaders announced on 25 September 2009 that the group would replace the G8 as the main economic council of wealthy nations.[7] Since its inception, the G20's membership policies have been criticized by some intellectuals,[8][9] and its summits have been a focus for major protests.[10][11]
The heads of the G20 nations held summits twice in 2009 and twice in 2010. Since the November 2011 Cannes summit, G20 summits have been held annually.[12]

The Heritage Foundation (abbreviated to Heritage)[1][2] is an American conservative think tank based in Washington, D.C., primarily geared towards public policy. The foundation took a leading role in the conservative movement during the presidency of Ronald Reagan, whose policies were taken from Heritage's policy study Mandate for Leadership.[4]
Historically, the Heritage Foundation has had significant influence in U.S. public policy making. It is among the most influential conservative public policy organizations in the United States.

LSE IDEAS is a foreign policy think tank at the London School of Economics and Political Science. IDEAS was founded as a think tank for Diplomacy and Strategy in February 2008, succeeding the Cold War Studies Centre founded in 2004. The Chair is Professor Michael Cox and its Directors are Professor Christopher Coker and Professor Christopher Alden. The 2018 and 2017 Global Go To Think Tank Index run by the University of Pennsylvania's Think Tank and Civil Societies Program ranked LSE IDEAS as the number one European university-affiliated think tank, and the number two university-affiliated think tank in the world.[1][2]
IDEAS runs seven research projects, hosts public and private events (43 in 2017-2018), and publishes analysis of international affairs. From 2017 to 2018, it released 75 publications and held 43 fellowships and scholarships. In addition, IDEAS houses the LSE Executive MSc International Strategy and Diplomacy, a programme designed to enhance the strategic vision of mid-career professionals.

Midterm elections in the United States are the general elections that are held near the midpoint of a president's four-year term of office, on Election Day on the Tuesday after the first Monday in November. Federal offices that are up for election during the midterms include all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives, and 33 or 34 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate.
In addition, 34 of the 50 U.S. states elect their governors for four-year terms during midterm elections, while Vermont and New Hampshire elect governors to two-year terms in both midterm and presidential elections. Thus, 36 governors are elected during midterm elections. Many states also elect officers to their state legislatures in midterm years. There are also elections held at the municipal level. On the ballot are many mayors, other local public offices, and a wide variety of citizen initiatives.
Special elections are often held in conjunction with regular elections,[1] so additional Senators, governors and other local officials may be elected to partial terms.
Midterm elections historically generate lower voter turnout than presidential elections. While the latter have had turnouts of about 50–60% over the past 60 years, only about 40% of those eligible to vote go to the polls in midterm elections.[2][3] Historically, midterm elections often see the president's party lose seats in Congress, and also frequently see the president's opposite-party opponents gain control of one or both houses of Congress.
The RAND Corporation ("research and development")[7] is an American nonprofit global policy think tank[1] created in 1948 by Douglas Aircraft Company to offer research and analysis to the United States Armed Forces. It is financed by the U.S. government and private endowment,[6] corporations,[8] universities[8] and private individuals.[8]
The company has grown to assist other governments, international organizations, private companies and foundations with a host of defense and non-defense issues, including healthcare. RAND aims for interdisciplinary and quantitative problem solving by translating theoretical concepts from formal economics and the physical sciences into novel applications in other areas, using applied science and operations research.
 财政金融
财政金融
 加利福尼亚州
加利福尼亚州