漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书

Neil Alden Armstrong (* 5. August 1930 bei Wapakoneta, Ohio; † 25. August 2012 in Cincinnati, Ohio) war ein US-amerikanischer Testpilot und Astronaut. Er war Kommandant von Apollo 11, die mit Buzz Aldrin und Michael Collins zum Mond flog. Am 21. Juli 1969 betrat er als erster Mensch den Mond.
尼尔·奥尔登·阿姆斯特朗(英语:Neil Alden Armstrong,1930年8月5日—2012年8月25日)[1],美国宇航员、试飞员、海军飞行员和大学教授。在美国国家航空航天局服役时,阿姆斯特朗的首次太空任务是双子星8号,在这次任务中,他和大卫·斯科特执行了历史上第一次轨道对接。1969年7月21日,阿姆斯特朗在执行他的第二次也是最后一次太空任务阿波罗11号时,迈出了“人类的一大步”,成为第一个踏上月球的宇航员,也是在其他星球上留下足迹的第一人;他和其搭档巴兹·奥尔德林在月球表面共停留两个半小时。
成为宇航员之前,阿姆斯特朗曾是美国海军的飞机师,参与过朝鲜战争。他后来在国家航空咨询委员会(National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics,NACA)担任试飞员,飞行时间超过九百小时。作为试飞员,阿姆斯特朗飞过F-100“超级军刀”A型和C型、F-101“巫毒”以及F-104“星”式战斗机,他飞过的其他机型包括X-1B型、X-5、X-15、F-105“雷公”、F-106“三角标枪”、B-47“同温层喷气”、以及KC-135“同温层加油机”。
距离阿波罗11号登月点五十公里的阿姆斯特朗环形山就是以他的名字命名的。

Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (* 1. Juni 1796 in Paris; † 24. August 1832 in Paris) war ein französischer Physiker und Ingenieur, der mit seiner theoretischen Betrachtung der Dampfmaschine (Carnot-Prozess) einen neuen Zweig der Wissenschaft, die Thermodynamik, begründete.

Nikolaus August Otto (* 10. Juni 1832[1] in Holzhausen an der Haide im Taunus; † 26. Januar 1891 in Köln) war ein Erfinder vieler heute noch in Verbrennungsmotoren verwendeter Details und ein Miterfinder des Viertaktprinzips. Der heutige Begriff Ottomotor bezeichnet aber nicht seinen damaligen Motor, sondern wurde zu seiner Ehrung 1936 vom VDI für alle Hubkolbenmotoren mit Fremdzündung vorgeschlagen und 1946 in einer DIN-Norm eingeführt. Er war Autodidakt und absolvierte nie ein Hochschulstudium, erhielt aber später die Ehrendoktorwürde.


 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness

 New York-NY
New York-NY
 Silk road
Silk road
 United States
United States

 Important port
Important port

New York City (AE: [nuːˈjɔɹk ˈsɪɾi], kurz: New York, deutsch veraltet: Neuyork,[1] Abk.: NYC) ist eine Weltstadt an der Ostküste der Vereinigten Staaten. Sie liegt im Bundesstaat New York und ist mit rund 8,5 Millionen Einwohnern die bevölkerungsreichste Stadt der Vereinigten Staaten.[2]
Die Metropolregion New York mit 18,9 Mio. Einwohnern[3] ist einer der bedeutendsten Wirtschaftsräume und Handelsplätze der Welt, Sitz vieler internationaler Konzerne und Organisationen wie der Vereinten Nationen sowie wichtiger See- und Binnenhafen an der amerikanischen Ostküste und dem Hudson. Die Stadt genießt mit ihrer großen Anzahl an Sehenswürdigkeiten, den 500 Galerien, etwa 200 Museen, mehr als 150 Theatern und mehr als 18.000 Restaurants Weltruf auch in den Bereichen Kunst und Kultur und verzeichnet jedes Jahr etwa 50 Mio. Besucher, davon knapp 12 Mio. aus dem Ausland.[4][5] Laut Forbes Magazine ist New York City die Stadt mit den höchsten Lebenshaltungskosten in den Vereinigten Staaten sowie eine der teuersten Städte weltweit.[6]
Nachdem 1524 Giovanni da Verrazano und 1609 Henry Hudson die Gegend des heutigen New Yorks erforscht hatten, siedelten ab 1610 niederländische Kaufleute an der Südspitze der Insel Manna-Hatta und bald darauf an der Westspitze von Long Island, dem heutigen Brooklyn. Erst 1626 kaufte Peter Minuit den Einheimischen, wahrscheinlich Lenni-Lenape-Indianern, die Insel „Manna-hatta“ für Waren im Wert von 60 Gulden ab. Die damit begründete Siedlung erhielt danach den Namen Nieuw Amsterdam und war zunächst Hauptstadt der Kolonie Nieuw Nederland, bis sie 1664 von den Briten erobert wurde und die Stadt den seither gültigen Namen bekam.[7] Ihr Aufstieg zur Weltstadt begann 1825 mit der Fertigstellung des Eriekanals.
Die Metropolregion New York erbrachte 2016 eine Wirtschaftsleistung von 1,657 Billionen US-Dollar. Unter den Städten der Welt belegt es damit den zweiten Rang hinter Tokio und wäre als eigener Staat gezählt unter den 20 größten Volkswirtschaften der Welt.[8]
美国纽约(NewYork)是美国乃至美洲最大的城市,全市由由五个区组成:曼哈顿(Manhattan)、布 鲁克林(Brooklyn)、皇 后区(Queens)、布郎克斯(Bronxs)和斯塔滕岛(Staten Island)。光是一个曼哈顿(Manhattan)就超过旧金山的大小,曼哈顿区是纽约市的精华所在,分成上中下城的曼哈顿区,拥有最流行最金融和最 颓废的风情。美国最大的500家公司中,有三分之一以上把总部设在曼哈顿。这里还能领略到著名的自由女神像、联合国总部、时代广场、大都会艺术博物馆、中央公园、苏活(soho)商业区、小意大利、第五大道商业区、格林威治村、华尔街、洛克菲勒中心、百老汇剧院区、唐人街等等人们印象中的纽约。
纽约是美国文化、艺术、音乐和出版中心,有众多的博物馆、美术馆、图书馆、科学研究机构和艺术中心,美国三大广播电视网和一些有影响的报刊、通讯社的总部都设在这里。(Quelle:http://www.ghl.com.cn)
纽约市(英语:New York City,简写为NYC),通称纽约,是位于美国纽约州的城市,为美国人口最多的城市、纽约都会区的核心、以及世界最大的城市之一,是对全球的经济、商业、金融、媒体、政治、教育和娱乐具有极大影响力的国际大都会。纽约还是联合国总部所在地[5],因此也被认为是世界外交的中心[6]。纽约还被称为“世界文化之都”[7][8],名列世界三大国际都会“纽伦港”之一。[9]
纽约位于东北部,濒临大西洋海岸,坐拥世界上最大的天然港口之一的纽约港[10]。纽约市共有曼哈顿区、皇后区、布鲁克林区、布朗克斯区、斯塔滕岛区等5个行政区,每一个行政区也各自是纽约州的一个县[11]。1898年,五个行政区被合并为现在的纽约市[12]。纽约也是全美国人口最密集的主要城市[13],2012年约有8,336,697人[14]居住于302.64平方英里(783.8平方千米)的土地上[15]。纽约都市区在全美的都会区中也高居第一,人口达到1980万[16],同时也是全美最大的联合统计区的一部分,在大区中人口达到2340万[17]。纽约也是语言和人口族群最为多元化的城市[18][19],在此使用的语言达到800种[20][21],而在2005年,全市有36%的人口是非美国出生的。
纽约的历史可以追溯至1624年,荷兰殖民者在这时候在此地建立贸易站,名为新阿姆斯特丹[22]。1664年,纽约及其周边地区为英国所占[22][23][24]。美国建国后,纽约在1785年至1790年为首都[25],1790年,纽约取代费城成为美国第一大城市[26]。纽约市的标志自由女神像在19世纪末20世纪初迎接了数百万移民的到来[27],它同时也是美国及其民主制度的象征[28]。
每年来到纽约的游客达到近5500万[29],许多区域和地标为人们所熟知。纽约还被不同媒体选为世界上被拍照最多的城市[30][31][32]。时报广场位于百老汇剧院区枢纽[33],被称作“世界的十字路口”[34],是世界上行人来往最密集的步行地段之一[35][36]和世界娱乐产业的中心之一[37]。城中的许多桥梁、高楼[38]和公园世界闻名。纽约的金融区,以曼哈顿下城的华尔街为龙头,被称为世界的金融中心[39][40],世界上最大的证券交易所(按上市公司市值)纽约证券交易所也位于此地[41]。曼哈顿的房地产是世界上最为昂贵的之一[42],其唐人街是西半球最为密集的华人聚居地[43][44]。纽约地铁是世界上最为发达的城市交通系统之一,提供24小时不间断的服务[45]。纽约同时还是许多高等学府的所在地[46],其中包括哥伦比亚大学、纽约大学和洛克菲勒大学等排名位于世界前35的学校[47]。
ニューヨーク市(英: New York City)は、アメリカ合衆国ニューヨーク州にある都市。
1790年以来、同国最大の都市であり[4]、市域人口は800万人を超え、都市圏人口では定義にもよるが2000万人以上である[2][5]。2015年の市内総生産は6625億ドルであり[6]、全米最大、東京に続き世界2位である。
ロンドンと並ぶ世界トップクラスの世界都市[7]、金融センターであり[8]、国際連合の本部所在地でもあり、世界の政治、経済、文化、ファッション、エンターテインメントなどに多大な影響を及ぼしている。
The City of New York, often called New York City (NYC) or simply New York, is the most populous city in the United States.[9] With an estimated 2017 population of 8,622,698[7] distributed over a land area of about 302.6 square miles (784 km2),[10][11] New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the United States.[12] Located at the southern tip of the state of New York, the city is the center of the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban landmass[13] and one of the world's most populous megacities,[14][15] with an estimated 20,320,876 people in its 2017 metropolitan statistical area and 23,876,155 residents in its combined statistical area.[4][5] A global power city,[16] New York City has been described uniquely[17] as the cultural,[18][19][20][21] financial,[22][23] and media capital of the world,[24][25] and exerts a significant impact upon commerce,[23] entertainment, research, technology, education, politics, tourism, art, fashion, and sports. The city's fast pace[26][27] has inspired the term New York minute.[28] Home to the headquarters of the United Nations,[29] New York is an important center for international diplomacy.[30][31]
Situated on one of the world's largest natural harbors,[32][33] New York City consists of five boroughs, each of which is a separate county of the State of New York.[34] The five boroughs – Brooklyn, Queens, Manhattan, The Bronx, and Staten Island – were consolidated into a single city in 1898.[35] The city and its metropolitan area constitute the premier gateway for legal immigration to the United States.[36] As many as 800 languages are spoken in New York,[37][38][39] making it the most linguistically diverse city in the world.[38][40][41] New York City is home to more than 3.2 million residents born outside the United States,[42] the largest foreign-born population of any city in the world.[43] In 2017, the New York metropolitan area produced a gross metropolitan product (GMP) of US$1.73 trillion.[44] If greater New York City were a sovereign state, it would have the 12th highest GDP in the world.[45]
New York City traces its origins to a trading post founded by colonists from the Dutch Republic in 1624 on Lower Manhattan; the post was named New Amsterdam in 1626.[46] The city and its surroundings came under English control in 1664[46] and were renamed New York after King Charles II of England granted the lands to his brother, the Duke of York.[47] New York served as the capital of the United States from 1785 until 1790.[48] It has been the country's largest city since 1790.[49] The Statue of Liberty greeted millions of immigrants as they came to the Americas by ship in the late 19th and early 20th centuries[50] and is a world symbol of the United States and its ideals of liberty and peace.[51] In the 21st century, New York has emerged as a global node of creativity and entrepreneurship,[52] social tolerance,[53] and environmental sustainability,[54][55] and as a symbol of freedom and cultural diversity.[56]
Many districts and landmarks in New York City are well known, with the city having three of the world's ten most visited tourist attractions in 2013[57] and receiving a record 62.8 million tourists in 2017.[58] Several sources have ranked New York the most photographed city in the world.[59][60] Times Square, iconic as the world's "heart"[61] and its "Crossroads",[62] is the brightly illuminated hub of the Broadway Theater District,[63] one of the world's busiest pedestrian intersections,[64][65] and a major center of the world's entertainment industry.[66] The names of many of the city's landmarks, skyscrapers,[67] and parks are known around the world. Manhattan's real estate market is among the most expensive in the world.[68][69] New York is home to the largest ethnic Chinese population outside of Asia,[70][71] with multiple signature Chinatowns developing across the city.[72][73][74] Providing continuous 24/7 service,[75] the New York City Subway is the largest single-operator rapid transit system worldwide, with 472 rail stations.[76][77][78] Over 120 colleges and universities are located in New York City, including Columbia University, New York University, and Rockefeller University, which have been ranked among the top universities in the world.[79][80] Anchored by Wall Street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan, it has been called both the most economically powerful city and the leading financial center of the world,[23][81][82][83] and the city is home to the world's two largest stock exchanges by total market capitalization, the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ.[84][85]
New Yorka (prononciation en anglais américain /nuːˈjɔɹk/ ; Écouter), officiellement nommée City of New York, connue également sous les noms et abréviations de New York City ou NYC, est la plus grande ville des États-Unis en termes d'habitants et l'une des plus importantes du continent américain. Elle se situe dans le Nord-Est des États-Unis, sur la côte atlantique, à l'extrémité sud-est de l'État de New York. La ville de New York se compose de cinq arrondissements appelés boroughs : Manhattan, Brooklyn, Queens, le Bronx et Staten Island. Ses habitants s'appellent les New-Yorkais (en anglais : New Yorkers).
New York exerce un impact significatif sur le commerce mondial, la finance, les médias, l'art, la mode, la recherche, la technologie, l'éducation et le divertissement. Regroupant l'ensemble des caractéristiques d'une ville mondiale, elle est parfois considérée comme « la capitale du monde ». Si elle n'est plus la capitale fédérale des États-Unis depuis plus de deux siècles (elle occupe cette fonction de 1785 à 17902), New York alimente pendant quelques décennies une rivalité financière et politique avec Philadelphie.
Il n'en reste pas moins que New York est la ville la plus peuplée du pays depuis 1790, avec 8 550 405 habitants selon le Bureau du recensement des États-Unis (estimations de 20153,4). Elle est aussi la troisième plus grande ville du continent américain derrière Mexico et São Paulo. Située au cœur de la mégalopole du BosWashb, l'agglomération new-yorkaise (20 182 305 habitants5) s'étend sur plusieurs comtés de l'État de New York (banlieues est et nord) et empiète sur deux États limitrophes. En effet, l'État du New Jersey comprend ses banlieues ouest et sud, et celui du Connecticut comprend ses banlieues nord-est. Son aire urbaine quant à elle comptait 24 millions d'habitants en 20156.
New York accueille quelque 50 millions de visiteurs annuellement7,8,9. Times Square, « The Crossroads of the World »10,11,12, est l'une des intersections les plus populaires du monde13, et le quartier des théâtres de Broadway14 est la plaque tournante du spectacle dans le pays tout entier et un centre majeur de l'industrie du divertissement dans le monde15. La ville abrite un grand nombre de ponts et tunnels (78916 en 2012), gratte-ciel et parcs de renommée mondiale17.
New York se place en tête dans la triade des grands centres financiers mondiaux avec Londres et Hong Kong, ces trois villes étant appelées par les médias anglophones « Nylonkong »18. Le quartier financier de New York, ancré par Wall Street dans le Lower Manhattan, fonctionne ainsi comme la « capitale financière du monde »19,20,21,22,23,24 et est le foyer du New York Stock Exchange (Bourse de New York)25, tandis que le nouveau One World Trade Center est le plus haut gratte-ciel d'Amérique du Nord. De plus, le marché immobilier de Manhattan est parmi les plus chers dans le monde26.
New York est frappée le 11 septembre 2001 par le plus grave attentat ayant jamais touché les États-Unis, deux avions de ligne détournés par des terroristes membres d'Al-Qaïda percutèrent les tours jumelles du World Trade Center et les détruisirent entièrement. En 2018, le quartier est toujours en reconstruction. New York est l'une des villes les plus cosmopolites du monde, par ses nombreux quartiers ethniques. Les plus connus sont Little Italy, ou encore Chinatown qui intègre la plus forte concentration de population chinoise des Amériques27,28,29,30. Enfin, New York accueille des institutions d'importance mondiale. On peut notamment citer le siège de l'ONU, mais aussi de nombreux sièges de multinationales31 et des centres culturels tels que le Metropolitan Museum of Art, le Brooklyn Museum, le Museum of Modern Art, le Lincoln Center. De nombreuses universités réputées sont situées à New York, notamment l'université de la ville de New York, l'université Columbia, l'université de New York, et l'université Rockefeller, qui sont classées dans le top 50 des universités dans le monde32.
New York (AFI: /njuˈjɔrk/[6], in inglese americano [nuː ˈjɔɹk], in italiano conosciuta anche come Nuova York) è una città degli Stati Uniti d'America. Viene detta New York City per distinguerla dall'omonimo Stato federato.
Conosciuta nel mondo anche come "grande mela" (Big Apple), un paragone le cui origini risalgono al libro The Wayfarer in New York scritto da Edward S. Martin nel 1909,[7][8] è situata nello Stato omonimo e sorge su un'area di circa 785 km² alla foce del fiume Hudson, sull'oceano Atlantico, mentre l'area metropolitana comprende anche località situate nei due adiacenti stati del New Jersey e del Connecticut.
È la città più popolosa degli Stati Uniti (tanto che la sua popolazione di 8,5 milioni di abitanti supera il doppio dei 4 milioni di Los Angeles, seconda città nazionale), nonché uno dei centri economici più importanti del mondo, riconosciuta come città globale. L'agglomerato urbano conta 18.223.567 abitanti,[9] quello metropolitano è di 23.019.036 abitanti, che la rendono, secondo le stime, dalla terza alla sesta area urbana più popolata del mondo, e tra le prime tre dell'emisfero boreale e del continente americano (in concorrenza con Città del Messico e San Paolo). New York è anche stimata come diciottesima città più popolata al mondo, tra le città africane di Kinshasa e Lagos, nonché la più popolosa città anglofona del mondo.
Situata sulla cosiddetta baia di New York (New York Bay), in parte sul continente e in parte su isole, è amministrativamente divisa in cinque distretti (borough): Manhattan, The Bronx, Queens, Brooklyn e Staten Island. Di essi, uno è nel continente (il Bronx, situato a nord di Manhattan), tre si trovano su isole: (Staten Island, di fronte al New Jersey; Queens e Brooklyn, rispettivamente nell'estremità nord-occidentale e sud-occidentale dell'isola di Long Island) e uno, Manhattan, sull'appendice inferiore della penisola su cui si trova anche il Bronx e che da esso è separato dall'Harlem River, fiume-canale che collega l'Hudson all'East River. I cinque distretti sono sedi di contea metropolitana: la contea di New York propriamente detta occupa il territorio di Manhattan, quella di Kings il territorio di Brooklyn e quella di Richmond il territorio di Staten Island; le altre due contee (Bronx e Queens) sono omonime dei distretti e si sovrappongono al loro territorio amministrativo. New York è inoltre riconosciuta come una delle città con i panorami urbani più impressionanti del mondo.
Non appartengono a New York, né fanno parte della sua area metropolitana, ma gravitano intorno ad essa per ragioni economiche e culturali, alcune città del confinante Stato del New Jersey, come Jersey City, Newark e Hoboken, situate sulla riva occidentale dell'Hudson, di fronte a Manhattan. La citata

The Philadelphia, Newtown and New York Railroad was a railroad in southeastern Pennsylvania that is now a part of the SEPTA commuter rail system as the Fox Chase Branch. Despite the name, it only ever extended between Philadelphia and Newtown, Pennsylvania.
 Bark
Bark
 Three-masted barque
Three-masted barque

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Royal Navy
Royal Navy
 Segelschiff
Segelschiff
 Bark/Barque/Barc
Bark/Barque/Barc
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom





Ernest Miller Hemingway, [ˈɜːnɪst ˈmɪlə ˈhɛmɪŋwɛɪ] (BrE) oder [ˈɜrnɪst ˈmɪɫəʳ ˈhɛmɪŋweɪ] (AmE), (* 21. Juli 1899 in Oak Park, Illinois; † 2. Juli 1961 in Ketchum, Idaho) war einer der erfolgreichsten und bekanntesten US-amerikanischen Schriftsteller des 20. Jahrhunderts. 1953 erhielt Hemingway den Pulitzer-Preis für seine Novelle Der alte Mann und das Meer und 1954 den Literaturnobelpreis.
Hemingway betätigte sich nicht nur als Schriftsteller, sondern war auch Reporter und Kriegsberichterstatter, zugleich Abenteurer, Hochseefischer und Großwildjäger, was sich in seinem Werk niederschlägt. Dieses ist vornehmlich Verarbeitung eigener Erlebnisse und Ereignisse seiner Zeit.[1]
欧内斯特·米勒·海明威(Ernest Miller Hemingway,1899年7月21日-1961年7月2日),美国记者和作家,被认为是20世纪最著名的小说家之一。海明威出生于美国伊利诺伊州芝加哥市郊区的奥克帕克,晚年在爱达荷州凯彻姆的家中自杀身亡。海明威一生中的感情错综复杂,先后结过四次婚,是美国“迷失的一代”(Lost Generation)作家中的代表人物,作品中对人生、世界、社会都表现出了迷茫和彷徨。
1939年至1960年间,海明威在古巴定居,并称自己为“普通的古巴人”。在这段期间海明威写下了闻名于世的代表作《老人与海》。古巴革命成功以后,海明威曾与古巴革命的领导人菲德尔·卡斯特罗会面。2002年11月11日,卡斯特罗更亲自出席了海明威故居博物馆的落成仪式。
在海明威一生之中曾荣获不少奖项。他在第一次世界大战期间被授予银制勇敢勋章;1953年,他以《老人与海》一书获得普立兹奖;1954年,《老人与海》又为海明威夺得诺贝尔文学奖。2001年,海明威的《太阳照样升起》(The Sun Also Rises)与《永别了,武器》两部作品被美国现代图书馆列入“20世纪中的100部最佳英文小说”中。
海明威的写作风格以简洁著称,对美国文学及20世纪文学的发展有极深远的影响;他的很多作品至今仍极具权威。
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia

 European Union
European Union
 Member States of the European Union
Member States of the European Union
 Finland
Finland
 France
France

 History
History

 History
History

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD
 Greece
Greece
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malta
Malta
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Peace Prize
Nobel Peace Prize
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 2012
2012
 Austria
Austria

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Sweden
Sweden
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Hungary
Hungary

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Free trade agreement
Free trade agreement
 Cyprus
Cyprus
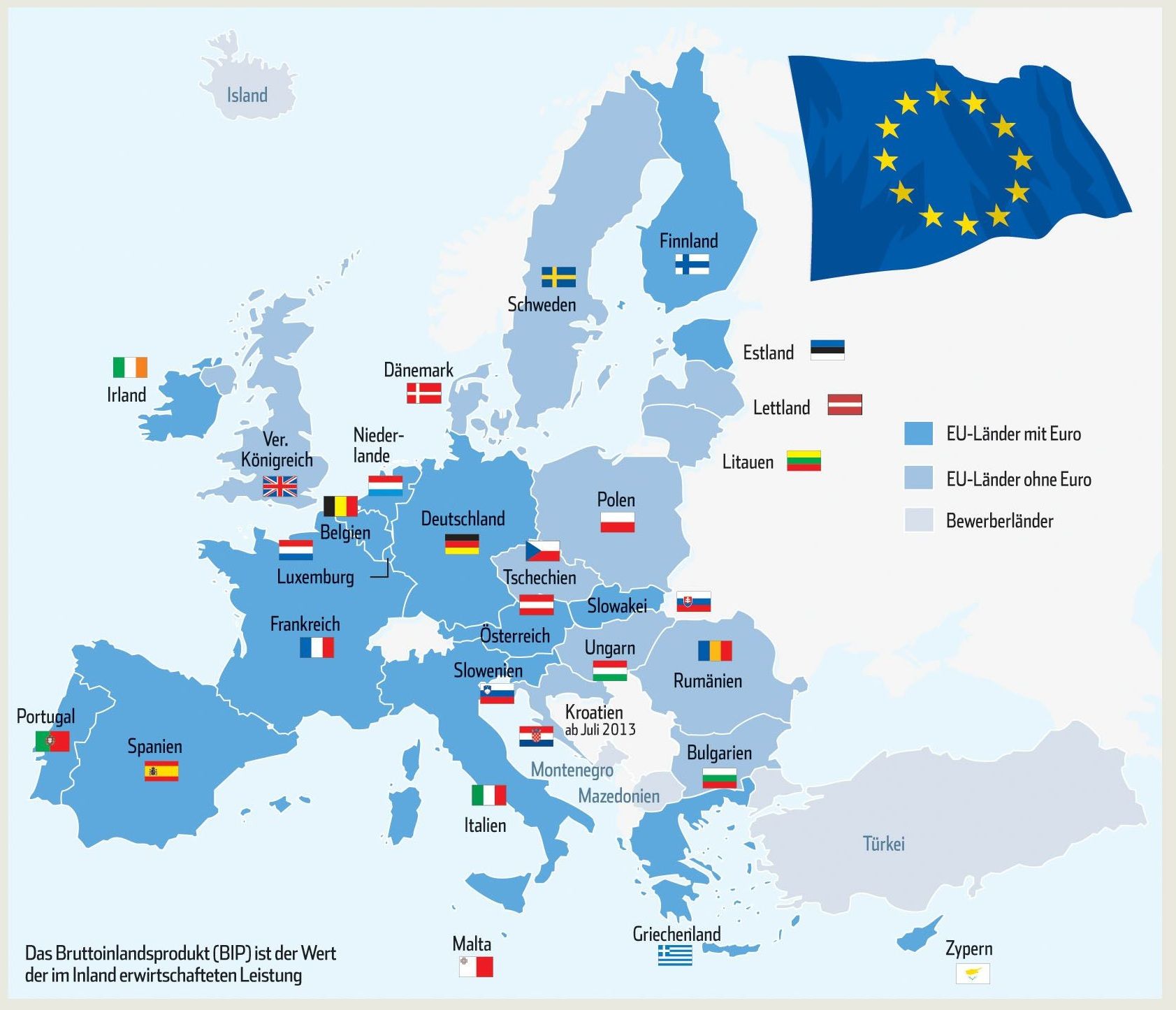
Die Europäische Union (EU) ist ein Verbund von derzeit 28 Mitgliedstaaten. Außerhalb von Europa umfasst die EU auch einige Überseegebiete. Sie hat insgesamt mehr als eine halbe Milliarde Einwohner. Gemessen am Bruttoinlandsprodukt ist der EU-Binnenmarkt der größte gemeinsame Wirtschaftsraum[7] der Erde. Die EU stellt eine eigenständige Rechtspersönlichkeit dar und hat daher Einsichts- und Rederecht bei den Vereinten Nationen.[8] Die verbreitetsten Sprachen in der EU sind Englisch, Deutsch und Französisch. Im Jahre 2012 wurde die Europäische Union mit dem Friedensnobelpreis ausgezeichnet.[9]
Das politische System der EU, das sich im Zuge der europäischen Integration herausgebildet hat, basiert auf dem Vertrag über die Europäische Union und dem Vertrag über die Arbeitsweise der Europäischen Union. Es enthält sowohl überstaatliche als auch zwischenstaatliche Elemente. Während im Europäischen Rat und im Rat der Europäischen Union die einzelnen Staaten mit ihren Regierungen vertreten sind, repräsentiert das Europäische Parlament bei der Rechtsetzung der EU unmittelbar die Unionsbürger. Die Europäische Kommission als Exekutivorgan und der EU-Gerichtshof als Rechtsprechungsinstanz sind ebenfalls überstaatliche Einrichtungen.
Die Anfänge der EU gehen auf die 1950er-Jahre zurück, als zunächst sechs Staaten die Europäische Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft (EWG) gründeten. Eine gezielte wirtschaftliche Verflechtung sollte militärische Konflikte für die Zukunft verhindern und durch den größeren Markt das Wirtschaftswachstum beschleunigen und damit den Wohlstand der Bürger steigern. Im Lauf der folgenden Jahrzehnte traten in mehreren Erweiterungsrunden weitere Staaten den Gemeinschaften (EG) bei. Ab 1985 wurden mit dem Schengener Übereinkommen die Binnengrenzen zwischen den Mitgliedsländern geöffnet. Nach dem Fall des Eisernen Vorhangs beziehungsweise der Auflösung des Ostblockes im Jahr 1989 änderte sich die geopolitische Lage in Europa grundlegend, womit sich Möglichkeiten zur Vertiefung der Integration, aber auch zur Vorbereitung von Erweiterungen im Osten ergaben. Mit dem Vertrag von Maastricht wurde 1992 die Europäische Union gegründet, die damit Zuständigkeiten in nichtwirtschaftlichen Politikbereichen bekam. In mehreren Reformverträgen, zuletzt im Vertrag von Lissabon, wurden die überstaatlichen Zuständigkeiten der EU ausgebaut und die demokratische Verankerung der politischen Entscheidungsprozesse auf Unionsebene nachgebessert, vor allem durch nochmalige Stärkung der Stellung des Europäischen Parlaments. Eine europäische Öffentlichkeit und Identität als Voraussetzung einer supranationalen Volkssouveränität bildet sich indes erst allmählich und nicht ohne Gegenströmungen heraus. Seit den 1980er-Jahren nahm mit den Kompetenzerweiterungen und dem damit einhergehenden Bedeutungsgewinn der EU auch die öffentliche Debatte über die Verfasstheit der EU an Intensität zu; dabei wurden auch EU-skeptische Positionen vermehrt artikuliert. Im Vertrag von Lissabon wurden im Jahr 2007 auch Austrittsszenarien geregelt.
Von den 28 EU-Staaten bilden 19 Staaten eine Wirtschafts- und Währungsunion. Im Jahr 2002 wurde eine gemeinsame Währung für diese Länder, der Euro, eingeführt. Im Rahmen des Raums der Freiheit, der Sicherheit und des Rechts arbeiten die EU-Mitgliedstaaten in der Innen- und Justizpolitik zusammen. Durch die gemeinsame Außen- und Sicherheitspolitik bemühen sie sich um ein gemeinsames Auftreten gegenüber Drittstaaten. Zukunftsbezogenes gemeinsames Handeln ist Gegenstand der Initiative Europa 2020, zu der unter anderem die Digitalpolitik gehört. Die Europäische Union hat Beobachterstatus in der G7, ist Mitglied in der G20 und vertritt ihre Mitgliedstaaten in der Welthandelsorganisation.
Die EU war 2016 der weltweit zweitgrößte Wirtschaftsraum nach nominalem (hinter den USA) sowie kaufkraftbereinigten Bruttoinlandsprodukt (hinter der Volksrepublik China). Als Staatenverbund ist sie der größte Güterproduzent und die größte Handelsmacht der Welt. Die Mitgliedsstaaten haben einen der höchsten Lebensstandards weltweit, wobei es jedoch auch innerhalb der EU deutliche Unterschiede zwischen einzelnen Ländern gibt. Im Index der menschlichen Entwicklung galten 2015 26 der 28 Mitgliedstaaten als „sehr hoch“ entwickelt.
Nach der Osterweiterung in den Jahren 2004 und 2007 ist die Europäische Union infolge der Finanzkrise ab 2007 und durch die Flüchtlingskrise ab 2015 in verschiedenen Mitgliedsstaaten einer zunehmenden EU-Skepsis von Teilen der Bevölkerung ausgesetzt, die sich unter anderem in dem Brexit-Referendum von 2016 niedergeschlagen hat. Unter dem Eindruck der Krisenerscheinungen und der Zunahme von rechtspopulistischen Tendenzen in den Mitgliedstaaten der Union wird die EU-Finalitätsdebatte neuerlich intensiv geführt. Einen auf die nähere Zukunft gerichteten, stark beachteten Reformplan hat der französische Staatspräsident Emmanuel Macron mit seiner Initiative für Europa vorgelegt.
欧洲联盟(英语:European Union;法语:Union européenne;德语:Europäische Union),简称欧盟(英语:EU;法语:UE;德语:EU),是根据1993年生效的《马斯特里赫特条约》(也称《欧洲联盟条约》)所建立的政治经济联盟,现拥有28个成员国,正式官方语言有24种。规范欧盟的条约经过多次修订,目前欧盟的运作方式依照《里斯本条约》。政治上所有成员国均为议会民主国家(2008年《经济学人》民主状态调查);经济上为仅次于以美国为首的北美自由贸易区的世界上第二大经济实体,德国、法国及意大利为欧盟三大核心成员国;军事上绝大多数欧盟成员国均为北大西洋公约组织成员。
欧盟的历史可追溯至1952年建立的欧洲煤钢共同体,当时只有六个成员国。1958年又成立了欧洲经济共同体和欧洲原子能共同体,1967年统合在欧洲各共同体之下,1993年又统合在欧洲联盟之下,欧盟已经渐渐地从贸易实体转变成经济和政治联盟。同时,欧洲经济共同体和后来的欧盟在1973年至2013年期间进行了八次扩大,成员国从6个增至28个。起初推动欧盟建立的动机,是渴望重建二战后损失惨重的欧洲,以及担忧欧洲会再度陷入战争泥潭。
欧盟的主要机构有欧洲委员会(成员国家首脑组成)、欧盟理事会(成员国家部长组成的欧盟的上议院)、欧盟委员会(欧盟的行政机构)、欧洲议会(欧盟的众议院,唯一的直接民选机构)、欧洲法院、欧洲中央银行等。此外,欧洲原子能共同体也在欧洲共同体的管辖范围之内,但在法律上是独立于欧盟的国际组织。
欧元由28个成员国中的19个采纳为流通货币;《申根条约》取消了部分成员国之间的边境管制,目前已有22个欧盟成员国和4个非成员国实施。
目前欧盟的主要议题有英国脱欧、欧盟的扩大、落实《里斯本条约》、全球暖化问题、非欧元区成员国加入欧元区、主权债务危机、移民危机等。
欧州連合(おうしゅうれんごう、英: European Union、略称:EU)は、マーストリヒト条約により設立されたヨーロッパの地域統合体。
欧州連合では欧州連合条約の発効前に調印されていた単一欧州議定書によって市場統合が実現し、またシェンゲン協定により域内での国境通過にかかる手続きなどの負担を大幅に削減した。さらに欧州連合条約発効後によって外交・安全保障分野と司法・内務分野での枠組みが新たに設けられ、ユーロの導入による通貨統合が進められている。このほかにも欧州議会の直接選挙が実施されたり、欧州連合基本権憲章が採択されたりするなど、欧州連合の市民の概念が具現化されつつある。加盟国数も欧州経済共同体設立を定めたローマ条約発効時の6か国から、2013年7月のクロアチア加盟により28か国にまで増えている。
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 28 member states that are located primarily in Europe.[13] It has an area of 4,475,757 km2 (1,728,099 sq mi) and an estimated population of over 510 million. The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters (only) where members have agreed to act as one. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market,[14] enact legislation in justice and home affairs and maintain common policies on trade,[15] agriculture,[16] fisheries and regional development.[17] For travel within the Schengen Area, passport controls have been abolished.[18] A monetary union was established in 1999 and came into full force in 2002 and is composed of 19 EU member states which use the euro currency.
The EU and European citizenship were established when the Maastricht Treaty was enacted in 1993.[19] The EU traces its origins to the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) and the European Economic Community (EEC), established, respectively, by the 1951 Treaty of Paris and 1957 Treaty of Rome. The original members of what came to be known as the European Communities were the Inner Six: Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany. The Communities and its successors have grown in size by the accession of new member states and in power by the addition of policy areas to its remit. The latest major amendment to the constitutional basis of the EU, the Treaty of Lisbon, came into force in 2009. While no member state has left the EU or its predecessors, the United Kingdom signified an intention to leave after a membership referendum in June 2016 and is negotiating its withdrawal.
The European Union provides more foreign aid than any other economic union.[20] Covering 7.3% of the world population,[21] the EU in 2017 generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of 19.670 trillion US dollars, constituting approximately 24.6% of global nominal GDP[22] and 16.5% when measured in terms of purchasing power parity.[23] Additionally, 27 out of 28 EU countries have a very high Human Development Index, according to the United Nations Development Programme. In 2012, the EU was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize.[24] Through the Common Foreign and Security Policy, the EU has developed a role in external relations and defence. The union maintains permanent diplomatic missions throughout the world and represents itself at the United Nations, the World Trade Organization, the G7 and the G20. Because of its global influence, the European Union has been described as an emerging superpower.[25]
L'Union européenne (UE)Note 4 est une association politico-économique sui generis de vingt-huit États européens qui délèguent ou transmettent par traité l’exercice de certaines compétences à des organes communautaires5,6. Elle s'étend sur un territoire de 4,5 millions de kilomètres carrés7, est peuplée de plus de 512 millions d'habitants3 et est la deuxième puissance économique mondiale en termes de PIB nominal derrière les États-Unis8,9,10. L’Union européenne est régie par le traité de Maastricht (TUE) et le traité de Rome (TFUE), dans leur version actuelle, depuis le 1er décembre 2009 et l'entrée en vigueur du traité de Lisbonne. Sa structure institutionnelle est en partie supranationale et en partie intergouvernementale : le Parlement européen est élu au suffrage universel direct, tandis que le Conseil européen et le Conseil de l'Union européenne (informellement le « Conseil des ministres ») sont composés de représentants des États membres. Le président de la Commission européenne est pour sa part élu par le Parlement sur proposition du Conseil européen. La Cour de justice de l'Union européenne est chargée de veiller à l'application du droit de l'Union européenne.
La déclaration du 9 mai 1950 de Robert Schuman, alors ministre français des Affaires étrangères, est considérée comme le texte fondateur de la construction européenne. Sous l’impulsion de personnalités politiques surnommées les « pères de l'Europe »11, comme Konrad Adenauer, Jean Monnet et Alcide De Gasperi, six États créent en 1951 la Communauté européenne du charbon et de l'acier. Après l’échec d'une Communauté européenne de défense en 1954, une Communauté économique européenne est instaurée en 1957 par le traité de Rome. La coopération économique est approfondie par l’Acte unique européen en 1986. En 1992, le traité de Maastricht prend la suite de l’Acte unique et institue une union politique qui prend le nom d’Union européenne et qui prévoit la création d'une union économique et monétaire dotée d’une monnaie unique : l’euro. Instituée en 1999, la zone euro compte dix-neuf États en 2017. De nouvelles réformes institutionnelles sont introduites en 1997 et en 2001. À la suite de l’échec d’un projet de constitution européenne après le refus par référendum des peuples français et néerlandais, les institutions sont à nouveau réformées en 2009 par le traité de Lisbonne pour y intégrer les mesures prévues par ce projet de constitution.
Depuis la formation de la CEE, le nombre d'États membres est passé de 6 à 28. Les membres fondateurs de la Communauté économique européenne, en 1957, sont l'AllemagneNote 5, la Belgique, la France, l'Italie, le Luxembourg et les Pays-Bas. Ils sont rejoints en 1973 par trois membres de l'Association européenne de libre-échange : le Danemark, l'Irlande et le Royaume-Uni. L'Union s'élargit vers le sud avec d'abord l'adhésion de la Grèce en 1981, puis celle de l'Espagne et du Portugal en 1986. Entretemps, en 1985, le Groenland a décidé de se retirer en ratifiant le Traité sur le Groenland et a désormais le statut de pays et territoire d'outre-mer associé. Avec la fin de la Guerre froide, la partie orientale de l'Allemagne rejoint la Communauté économique européenne en 1990Note 6. L'Union européenne intègre en 1995 des États neutres : l'Autriche, la Finlande et la Suède. En 2004, dix nouveaux États, en majorité issus du bloc de l'Est, s'ajoutent aux quinze déjà membres : Chypre, l'Estonie, la Hongrie, la Lettonie, la Lituanie, Malte, la Pologne, la Slovaquie, la Slovénie et République tchèque. Deux États supplémentaires, la Bulgarie et la Roumanie, complètent en 2007 ce cinquième élargissement, Enfin, en 2013, la Croatie rejoint l'Union12. Le 23 juin 2016, les citoyens britanniques votent en majorité pour la sortie du Royaume-Uni de l'Union européenne dans le cadre d'un référendum. La procédure de retrait est enclenchée le 29 mars 2017 par l'activation de l'article 50 du traité sur l'Union européenne.
Le 12 octobre 2012, le prix Nobel de la paix est attribué à l'Union européenne pour « sa contribution à la promotion de la paix, la réconciliation, la démocratie et les droits de l'Homme en Europe »13.
L'Unione europea (abbreviata in UE o Ue, pron. /ˈue/[12]) è un'organizzazione internazionale politica ed economica a carattere sovranazionale, che comprende 28 paesi membri indipendenti e democratici. La sua formazione risale al trattato di Roma del 25 marzo 1957, la denominazione attuale al trattato di Maastricht del 7 febbraio 1992 (entrato in vigore il 1º novembre 1993), e l'istituzione ufficiale al 2002 con l'avvento della valuta unica ed il successivo trattato di Lisbona, dopo un lungo percorso intrapreso dalle Comunità europee precedentemente esistenti e attraverso la stipulazione di numerosi trattati, che hanno contribuito al processo di integrazione europea.
Questa garantisce la libera circolazione di persone, merci, servizi e capitali all'interno del suo territorio attraverso un mercato europeo comune e la cittadinanza dell'Unione europea, promuove la pace, i valori e il benessere dei suoi popoli, lotta contro l'esclusione sociale e la discriminazione, favorisce il progresso scientifico e tecnologico e mira alla stabilità politica, alla crescita economica e alla coesione sociale e territoriale tra gli stati membri[13], cercando di attenuare le differenze socio-economiche tra i vari stati membri e incrementarne il benessere socio-economico.
Le competenze dell'Unione europea spaziano dalle politiche economiche (agricoltura e commercio) agli affari esteri, alla difesa e alla protezione ambientale, con una politica agraria comune, una politica estera comune e la presenza di fondi strutturali per il raggiungimento degli obiettivi socio-economici preposti. In alcuni di questi campi tali funzioni la rendono dunque simile a una federazione di stati (per es. per quanto riguarda gli affari monetari o le politiche ambientali), mentre in altri settori l'Unione è più vicina a una confederazione (mancando di una Costituzione, ordinamento giuridico, politica interna e politica industriale comuni) o a un'organizzazione politica sovranazionale (come per la politica estera).
Le politiche di unione economica e monetaria dell'Unione europea hanno portato nel 2002 all'introduzione di una moneta unica, l'euro, attualmente adottato da 19 stati dell'Unione, che formano la cosiddetta eurozona, con una politica monetaria comune regolata dalla Banca centrale europea (BCE).
Il 12 ottobre 2012 è stata insignita del premio Nobel per la pace, con la seguente motivazione: «per oltre sei decenni ha contribuito all'avanzamento della pace e della riconciliazione, della democrazia e dei diritti umani in Europa».[14]
La Unión Europea (UE) es una comunidad política de derecho constituida en régimen sui géneris de organización internacional nacida para propiciar y acoger la integración y gobernanza en común de los Estados y los pueblos de Europa. Está compuesta por veintiocho Estados europeos y fue establecida con la entrada en vigor del Tratado de la Unión Europea (TUE) el 1 de noviembre de 1993.6
Con ese acto, la supraestructura «Unión Europea» aunaba y se fundaba sobre las tres Comunidades Europeas preexistentes —la Comunidad Europea del Carbón y del Acero (CECA), la Comunidad Europea de la Energía Atómica (Euratom) y la Comunidad Económica Europea (CEE/CE)— y les añadía la política exterior común y la cooperación judicial y policial, formando un sistema complejo conocido como «los tres pilares». Sin embargo, con la entrada en vigor el 1 de diciembre de 2009 del Tratado de Lisboa, la Unión Europea sucedió, por completo aunque con ciertas particularidades, a las Comunidades Europeas y asumió con ello su personalidad jurídica única como sujeto de derecho internacional.7
La Unión Europea ha desarrollado un sistema jurídico y político, el comunitario europeo, único en el mundo, que se rige por mecanismos y procedimientos de funcionamiento interno complejos, que se han extendido y evolucionado a lo largo de su historia hasta conformar, en la actualidad, un sistema híbrido de gobierno transnacional difícilmente homologable que combina elementos próximos a la cooperación multilateral, si bien fuertemente estructurada e institucionalizada, con otros de vocación netamente supranacional, regidos ambos por una dinámica de integración regional muy acentuada.
Todo esto desemboca en una peculiarísima comunidad de Derecho, cuya naturaleza jurídica y política es muy discutida, si bien sus elementos fundacionales y su evolución histórica, todavía abierta, apuntan, en el presente, a una especial forma de moderna confederación o gobernanza supranacional, acusadamente institucionalizada y con una inspiración histórico-política de vocación federal —en el sentido de un federalismo internacional n

 Aerospace
Aerospace
 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics

 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Literature
Literature