漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 China
China
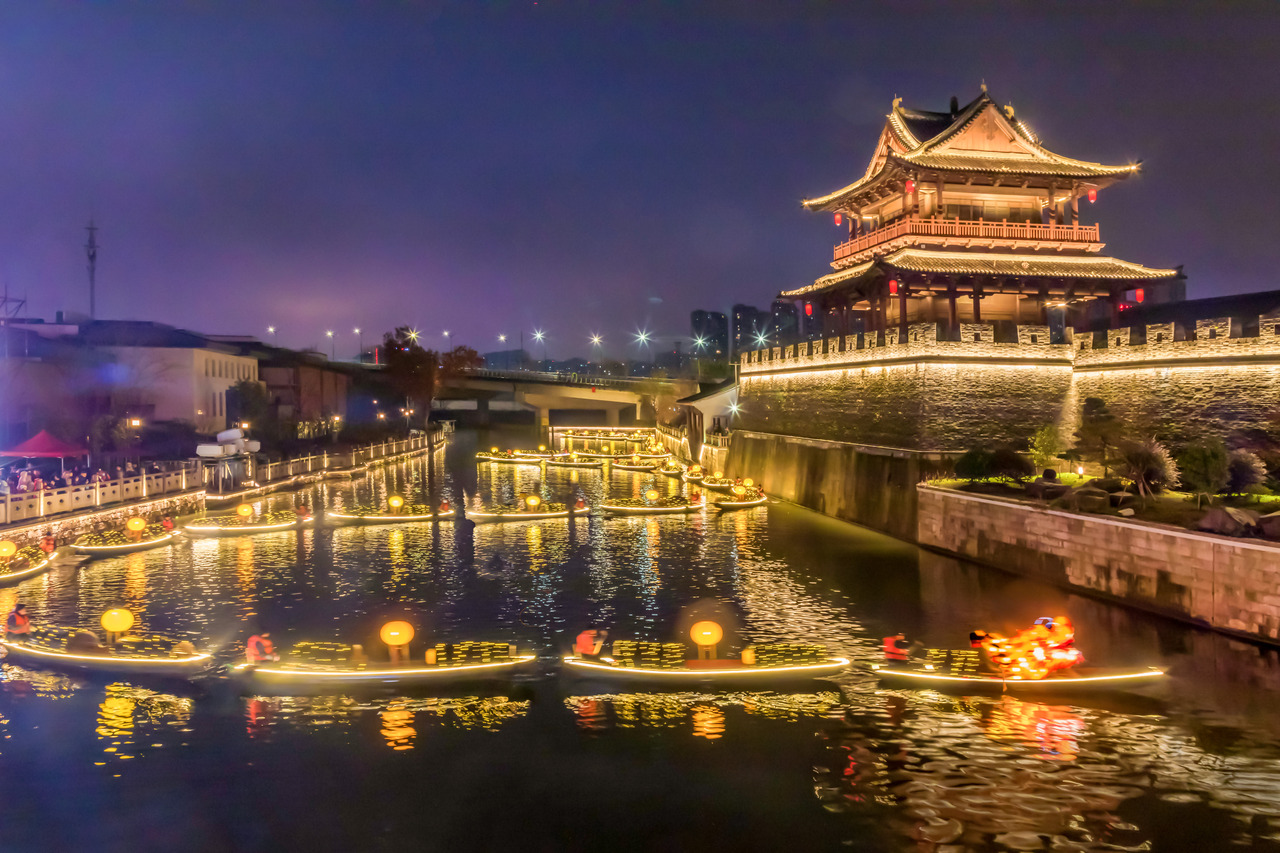
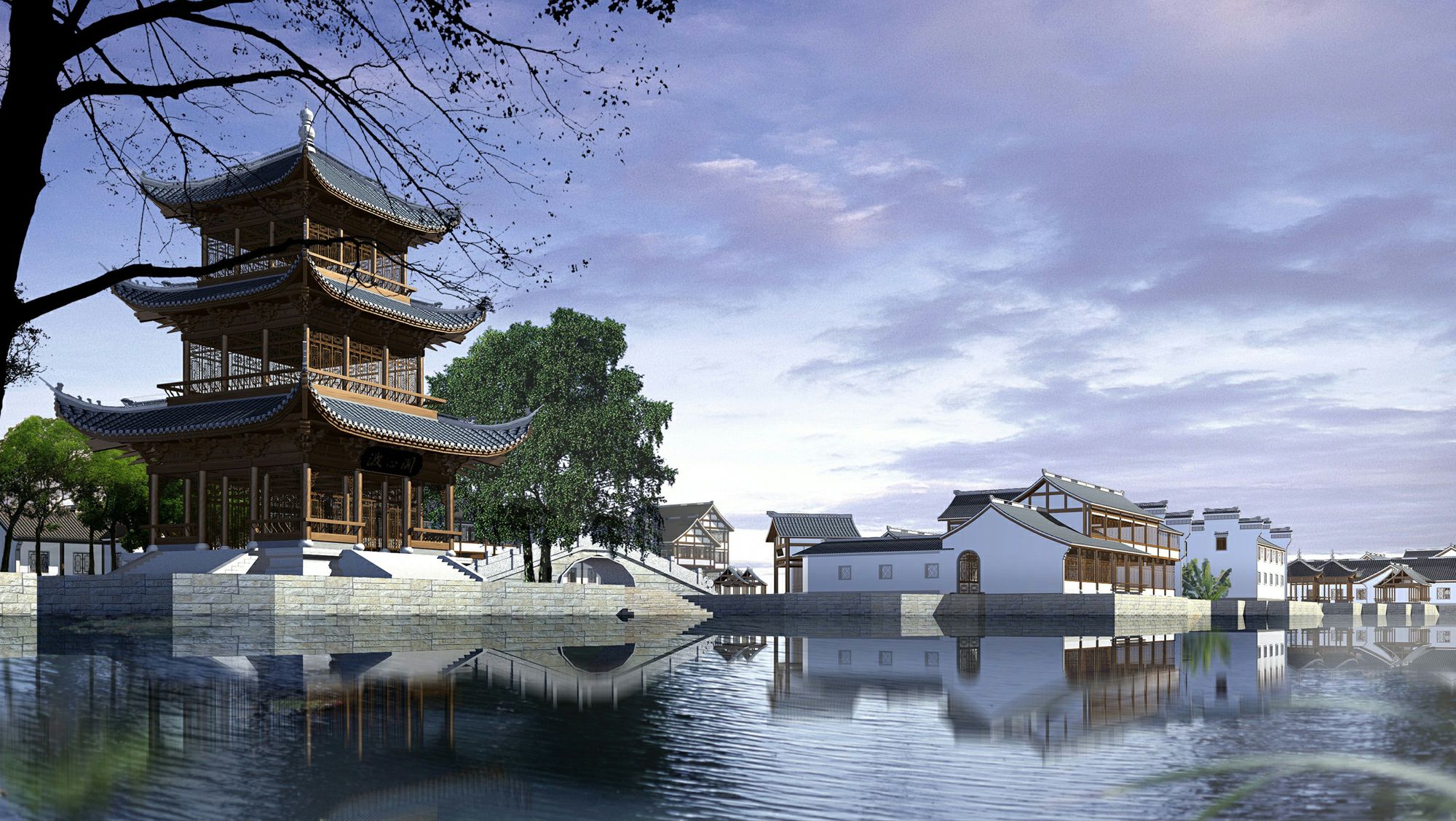










Die über 2 500 Jahre alte Stadt Shaoxing liegt im Süden des Jangtse-Deltas zwischen den Städten Hangzhou und Ningbo in der Provinz Zhejiang. Sie zählt im Innenstadtbereich 640 000 Einwohner. Zum Verwaltungsgebiet gehören jedoch rund 4,3 Millionen Menschen. Shaoxing ist eine der beliebtesten Touristenstädte Chinas.
Stadt der Brücken und Kanäle
Die Stadt der Brücken und Kanäle zählt im Reich der Mitte zur ersten Liga der bekannten historischen Kulturstädte. Sie hat neben vielen Ruhezonen und einer malerischen Altstadt aber auch überaus belebte Einkaufsstraßen, die alles bieten, was das Herz begehrt. Lebendige Märkte, große Kaufhäuser, unzählige kleine Geschäfte und große Hotels sowie ein Meer an Restaurants und Kneipen prägen das Stadtbild.
Shaoxing ist der wichtigste Produktionsstandort für Reiswein. Die staatliche Shaoxing County Winery China produziert jährlich rund 30 000 Tonnen Reiswein.
(Quelle: http://www.bayreuth.de/partnerstaedte/shaoxing_558.html)
Shaoxing (chinesisch 紹興市 / 绍兴市, Pinyin Shàoxīng Shì, W.-G. Shao-hsing) ist eine bezirksfreie Stadt in der chinesischen Provinz Zhejiang in der Ningshao-Ebene, 65 Kilometer entfernt von der Provinzhauptstadt Hangzhou.
Das Verwaltungsgebiet Shaoxings hat eine Fläche von 8.256 km² und ca. 4,99 Millionen Einwohner (Ende 2016). In dem eigentlichen städtischen Siedlungsgebiet von Shaoxing leben 1.725.726 Menschen (Zensus 2010). Die Durchschnittstemperatur beträgt 16 °C. Im Stadtbezirk Yuecheng gibt es eine Altstadt mit Kanälen und Brücken und verwinkelten Gassen.
绍兴市(普通话:Shào Xīng;吴语:Zau Shin),简称越,是中华人民共和国浙江省下辖的地级市,浙江第四大城市。旧称会稽、山阴,越文化中心。现在是中华人民共和国纺织业与小电机、节能光电工业的中心。
绍兴是浙江的文化中心之一,首批国家历史文化名城之一,是中国历史最悠久的城市之一,是有名的水乡、酒乡、桥乡,绍兴风景秀丽、人才辈出,著名的文化古迹包括兰亭、禹陵、鲁迅故里(包括鲁迅故居、三味书屋、咸亨酒店、百草园等)、蔡元培故居,周恩来祖居,秋瑾故居,马寅初故居,王羲之故居,贺知章故居等名人故居,东湖、沈园、吼山、新昌大佛寺等,古代越王“卧薪尝胆”的故事更是家喻户晓。
绍兴纺织业、小电机、节能照明、生物酿造业极发达,纺织业出口产品占世界纺织面料交易额的60%,绍兴中国轻纺城是世界最大的纺织品交易市场。另外,绍兴出产的黄酒(又称绍酒)更是闻名遐迩,成为国宴专用酒。根据酿制工艺和口感不同,绍兴黄酒又分加饭酒、花雕酒、善酿酒等。
绍兴市是浙江省辖地级市,位于浙江省中北部、杭州湾南岸,是具有江南水乡特色的文化和生态旅游城市 、长三角城市群重要城市、环杭州湾大湾区核心城市 、杭州都市圈副中心城市 。东连宁波市,南临台州市和金华市,西接杭州市,北隔钱塘江与嘉兴市相望,位于东经119°53′03"至121°13′38"、北纬29°13′35"至30°17′30"之间,属于亚热带季风气候,温暖湿润,四季分明。全市面积为8274.79平方千米(包含钱塘江水域面积,钱塘江河海分界线采用海盐澉浦—余姚西三闸连线),东西跨度130.68千米,南北跨度119.83千米 ,市辖区总面积2942平方公里,人口216.1万(2013年11月数据) 。
绍兴已有2500多年建城史 ,是首批国家历史文化名城、联合国人居奖城市,中国优秀旅游城市,国家森林城市,中国民营经济最具活力城市,也是著名的水乡、桥乡、酒乡、书法之乡、名士之乡。绍兴素称“文物之邦、鱼米之乡”。著名的文化古迹有兰亭、禹陵、鲁迅故里、沈园、柯岩、蔡元培故居、周恩来祖居、秋瑾故居、马寅初故居、王羲之故居、贺知章故居等。
紹興市(しょうこうし)は中華人民共和国浙江省に位置する地級市。
旧名は越州。南宋の紹興元年(1131年)、会稽・山陰方面を治める事を目的として越州に府が置かれたために元号に因んで命名された。以後、府・路名として行政区分に用いられて都市名として定着した。
日本では紹興酒の産地としてよく知られており、また近代中国の文豪魯迅の生家がある。魯迅が日本に留学した折の恩師である藤野厳九郎の出身地・福井県あわら市とは友好都市の関係を結んでいる。
Shaoxing ([ʂâuɕíŋ] ( listen); Chinese: 绍兴) is a prefecture-level city on the southern shore of Hangzhou Bay in eastern Zhejiang province, China. It was formerly known as Kuaiji and Shanyin and abbreviated in Chinese as 越 (Yuè) from the area's former inhabitants. Located on the south bank of the Qiantang River estuary, it borders Ningbo to the east, Taizhou to the southeast, Jinhua to the southwest, and Hangzhou to the west. As of 2010, its population was 4,912,339 inhabitants. Among which, 1,914,683 (Keqiao and Yuecheng districts) lived in the built-up metropolitan area of Hangzhou-Shaoxing, with a total of 8,156,154 inhabitants.
listen); Chinese: 绍兴) is a prefecture-level city on the southern shore of Hangzhou Bay in eastern Zhejiang province, China. It was formerly known as Kuaiji and Shanyin and abbreviated in Chinese as 越 (Yuè) from the area's former inhabitants. Located on the south bank of the Qiantang River estuary, it borders Ningbo to the east, Taizhou to the southeast, Jinhua to the southwest, and Hangzhou to the west. As of 2010, its population was 4,912,339 inhabitants. Among which, 1,914,683 (Keqiao and Yuecheng districts) lived in the built-up metropolitan area of Hangzhou-Shaoxing, with a total of 8,156,154 inhabitants.
Notable residents of Shaoxing include Wang Xizhi, the parents of Zhou Enlai, Lu Xun, and Cai Yuanpei. It is also noted for Shaoxing wine, meigan cai, and stinky tofu, and was recently featured on A Bite of China. Its local variety of Chinese opera sung in the local dialect and known as Yue or Shaoxing opera is second in popularity only to Peking opera. In 2010, Shaoxing celebrated the 2,500th anniversary of the founding of the city.
Economically, the city's driven by manufacturing of textiles, electronics, and energy-efficient lighting. Zhejiang has the fifth highest per capita GDP in the nation, with the city itself at 32nd nationally by GDP per capita.
Shaoxing (chinois simplifié : 绍兴市 ; pinyin : shàoxīng shì) est une ville-préfecture du sud-est de la Chine, dans la province du Zhejiang.
Avec ses hutongs et ses canaux, Shaoxing a su garder sa nonchalance malgré ses presque cinq millions d'habitants et la proximité de Shanghai. Les maisonnettes blanches, dépouillées, sont typiques du sud de la Chine. Capitale à la période des Royaumes combattants, la ville se découvre au fil de l'eau, sur des barques noires aux airs de gondoles, les wupeng3.
C'est la ville de naissance de Zeng Peiyan, qui appartient au Bureau politique et au Conseil d'État.
Shaoxing est aussi la ville de naissance de l'écrivain Lu Xun (1881-1936).
Shaoxing (cinese: 绍兴; pinyin: Shàoxīng) è una città-prefettura della Cina nella provincia dello Zhejiang.
Shaoxing (en chino: 绍兴市, pinyin: Shàoxīng shì). Es una ciudad-prefectura en la provincia de Zhejiang, República Popular de China. Limita al norte con el Río Qiantang, al sur con Jinhua, al oeste con Hangzhou y al este con Ningbo. Su área es de 8256 km² y su población es cerca de 5 millones. La ciudad se volvió mundialmente famosa por el Vino de Shaoxing.
Шаосин (кит. упр. 绍兴, пиньинь: Shàoxīng) — городской округ в провинции Чжэцзян КНР.
Одна из достопримечательностей — мавзолей Юя Великого, заложенный в 6 в. н. э. Шаосин — родина выдающегося китайского литератора Лу Синя.
DeepSeek-V3 Capabilities
DeepSeek-V3 achieves a significant breakthrough in inference speed over previous models.
It tops the leaderboard among open-source models and rivals the most advanced closed-source models globally.
| Benchmark (Metric) | DeepSeek V3 | DeepSeek V2.5 | Qwen2.5 | Llama3.1 | Claude-3.5 | GPT-4o | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0905 | 72B-Inst | 405B-Inst | Sonnet-1022 | 0513 | |||
| Architecture | MoE | MoE | Dense | Dense | - | - | |
| # Activated Params | 37B | 21B | 72B | 405B | - | - | |
| # Total Params | 671B | 236B | 72B | 405B | - | - | |
| English | MMLU (EM) | 88.5 | 80.6 | 85.3 | 88.6 | 88.3 | 87.2 |
| MMLU-Redux (EM) | 89.1 | 80.3 | 85.6 | 86.2 | 88.9 | 88.0 | |
| MMLU-Pro (EM) | 75.9 | 66.2 | 71.6 | 73.3 | 78.0 | 72.6 | |
| DROP (3-shot F1) | 91.6 | 87.8 | 76.7 | 88.7 | 88.3 | 83.7 | |
| IF-Eval (Prompt Strict) | 86.1 | 80.6 | 84.1 | 86.0 | 86.5 | 84.3 | |
| GPQA-Diamond (Pass@1) | 59.1 | 41.3 | 49.0 | 51.1 | 65.0 | 49.9 | |
| SimpleQA (Correct) | 24.9 | 10.2 | 9.1 | 17.1 | 28.4 | 38.2 | |
| FRAMES (Acc.) | 73.3 | 65.4 | 69.8 | 70.0 | 72.5 | 80.5 | |
| LongBench v2 (Acc.) | 48.7 | 35.4 | 39.4 | 36.1 | 41.0 | 48.1 | |
| Code | HumanEval-Mul (Pass@1) | 82.6 | 77.4 | 77.3 | 77.2 | 81.7 | 80.5 |
| LiveCodeBench (Pass@1-COT) | 40.5 | 29.2 | 31.1 | 28.4 | 36.3 | 33.4 | |
| LiveCodeBench (Pass@1) | 37.6 | 28.4 | 28.7 | 30.1 | 32.8 | 34.2 | |
| Codeforces (Percentile) | 51.6 | 35.6 | 24.8 | 25.3 | 20.3 | 23.6 | |
| SWE Verified (Resolved) | 42.0 | 22.6 | 23.8 | 24.5 | 50.8 | 38.8 | |
| Aider-Edit (Acc.) | 79.7 | 71.6 | 65.4 | 63.9 | 84.2 | 72.9 | |
| Aider-Polyglot (Acc.) | 49.6 | 18.2 | 7.6 | 5.8 | 45.3 | 16.0 | |
| Math | AIME 2024 (Pass@1) | 39.2 | 16.7 | 23.3 | 23.3 | 16.0 | 9.3 |
| MATH-500 (EM) | 90.2 | 74.7 | 80.0 | 73.8 | 78.3 | 74.6 | |
| CNMO 2024 (Pass@1) | 43.2 | 10.8 | 15.9 | 6.8 | 13.1 | 10.8 | |
| Chinese | CLUEWSC (EM) | 90.9 | 90.4 | 91.4 | 84.7 | 85.4 | 87.9 |
| C-Eval (EM) | 86.5 | 79.5 | 86.1 | 61.5 | 76.7 | 76.0 | |
| C-SimpleQA (Correct) | 64.1 | 54.1 | 48.4 | 50.4 | 51.3 | 59.3 |
 China
China
 Chinese Super League 2019
Chinese Super League 2019

 Finanz
Finanz
 ***Globales Finanzzentrum/Global Financial Center
***Globales Finanzzentrum/Global Financial Center

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 N 2000 - 2100 nach Christus
N 2000 - 2100 nach Christus
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD

 Internationale Städte
Internationale Städte
 ***Globale wirtschaftliche Wettbewerbsfähigkeit der Städte
***Globale wirtschaftliche Wettbewerbsfähigkeit der Städte
 Special Economic Zone
Special Economic Zone

 Sport
Sport
 The Ocean Race
The Ocean Race
 Urlaub und Reisen
Urlaub und Reisen

 Wichtiger Hafen
Wichtiger Hafen
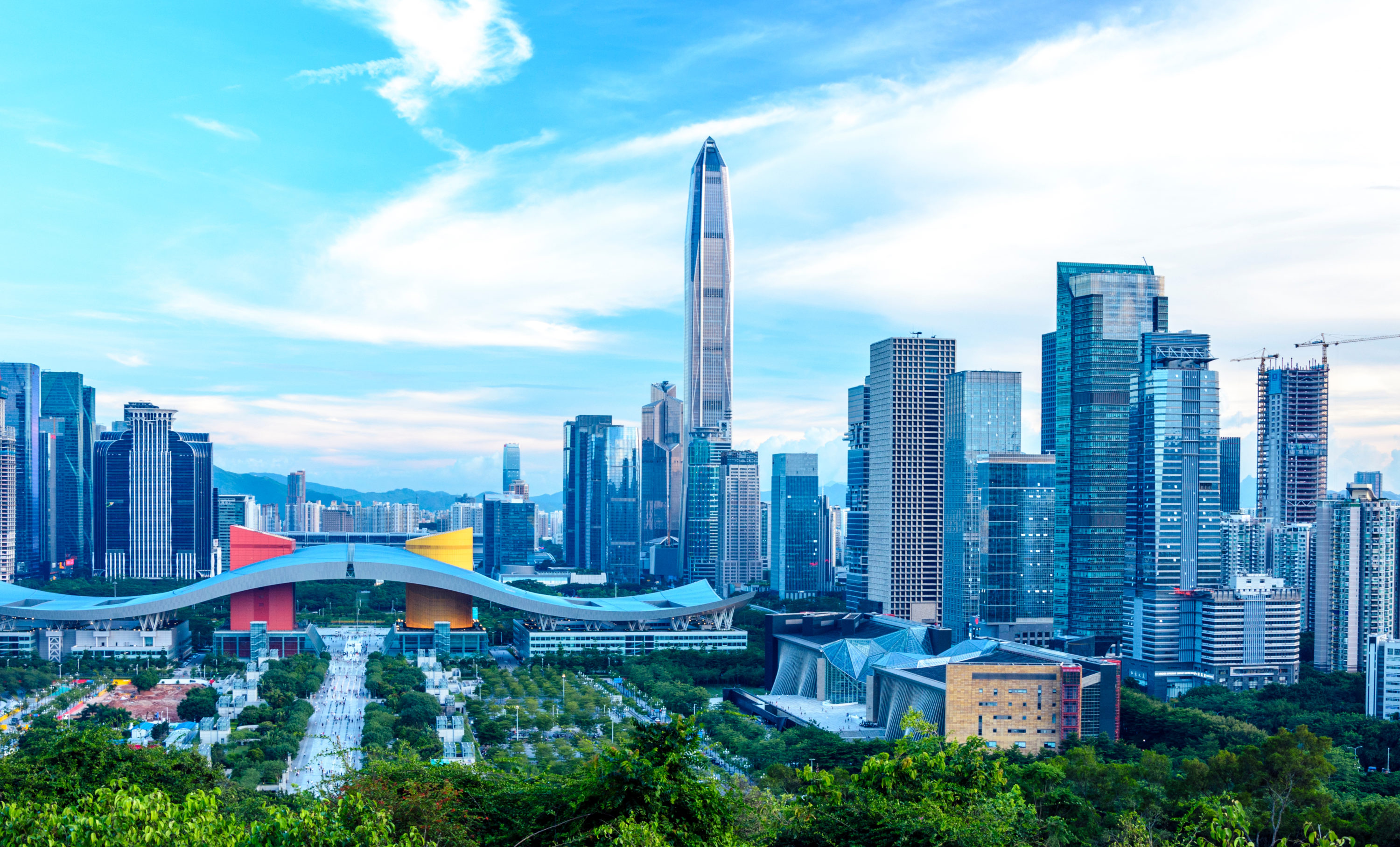

Shenzhen (chin. 深圳市, Shēnzhèn Shì) ist eine Unterprovinzstadt in der Provinz Guangdong der Volksrepublik China. Shenzhen liegt im Süden der Provinz, nur durch einen Fluss von Hongkong getrennt. Die Stadt gilt als eine der bedeutendsten Städte für ausländische Investitionen und ist eine der am schnellsten wachsenden Städte der Welt. Im Jahr 1979 lebten im heutigen Stadtgebiet gerade einmal 30.000 Einwohner. Heute ist Shenzhen eine moderne Metropole mit über 12 Millionen Einwohnern[3], die fast genauso schnell wächst wie Shanghai. Shenzhen ist die Stadt mit dem höchsten Pro-Kopf-Einkommen in China (ohne Hongkong und Macao). Tragsäule der lokalen Wirtschaft ist die Elektronik- und Telekommunikationsindustrie.(Quelle:Wikipedia)
Shenzhen (chinesisch 深圳市, Pinyin ) ist eine Unterprovinzstadt in der Provinz Guangdong der Volksrepublik China.
Shenzhen liegt im Süden der Provinz und grenzt südlich an die Sonderverwaltungszone Hongkong. Die Planstadt gilt aufgrund ihres Status als Sonderwirtschaftszone als eine bedeutende Stadt für ausländische Investitionen und ist eine der am schnellsten wachsenden Städte der Welt. Shenzhen ist die Stadt mit dem höchsten Pro-Kopf-Einkommen in China (ohne Hongkong und Macau). Tragende Säulen der lokalen Wirtschaft sind die Elektronik- und die Telekommunikationsindustrie.
Seit 2008 ist Shenzhen als UNESCO City of Design Teil des Creative Cities Network.
深圳市,简称深,别称鹏城,是位于中华人民共和国广东省的地级市,同时是副省级计划单列市、经济特区及国家综合配套改革试验区,1979年1月在原宝安县的基础上设立,为中国的证券资本市场中心、以及重要的国际经济中心[6]。深圳全市均划入深圳经济特区范围。南边与香港接壤,北与惠州市、东莞市毗邻。
深圳因改革开放而快速发展,在中国的制度创新、扩大开放等方面承担着试验和示范的重要使命。1980年,中国第一个经济特区——深圳经济特区在此成立[7]。自1999年起,中国国际高新技术成果交易会每年定期在深圳举行。2010年,前海深港现代服务业合作区获中央政府批准成立,将作为深圳与香港合作的先导区。2011年,深圳主办第26届世界大学生夏季运动会[8]。2016年,深圳市生产总值超越广州市成为中国内地经济总量第三大城市。
深圳是中国南方重要的高新技术研发和制造基地。深圳港集装箱吞吐量连续多年居于世界第三,外贸出口总额连续20余年居中国大陆第一位,深圳宝安国际机场是中国大陆第五大民航机场。深圳证券交易所的首次公开募股数量自2009年至2015年居世界第一位,是中国企业重要的融资平台[9]。
深圳市(しんせんし、簡体字: 深圳市、拼音: 、英語: Shenzhen)は中華人民共和国広東省に位置する副省級市。
深圳市は香港の新界と接し、経済特区に指定されている。北京市、上海市、広州市と共に、中国本土の4大都市と称される「北上広深」の一つであり、「一線都市」に分類されている[2]。中国屈指の世界都市であり、金融センターとしても重要な機能を果たしている。2010年の近郊を含む都市的地域の人口は1,447万人であり、世界第15位である[3]。アメリカのシンクタンクが2017年に発表した総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界80位の都市と評価された[4]。中国本土では北京市、上海市に次ぐ3位である。
住民構成の特徴としては移民都市であることがあげられる。元来は宝安県として一集落に過ぎなかったものが、改革開放経済の過程で外部より労働人口が流入して都市が形成され、広東省でありながら広東語が使われる比率が極めて低い地域となっている。また深圳市には政府主導で新興事業発展のためのインフラが整えられていることから、スタートアップ企業や製造工場が数多く存在し、「中国のシリコンバレー」等とも呼ばれている。
なお、原住民もある程度存在し、主には農業・漁業に従事する。原住民は香港の新界地域と同じく、大きく客家語を話す客家と広東語を話す囲頭人の2つのグループに分ける。客家は主に北東部の竜崗区と宝安区の東部、福田区の北部、南山区の北部などの丘陵区域に分布し、囲頭人は主に羅湖区、福田区の中南部、南山区の中南部、宝安区の中西部などの平原地域に居住する[5][6]。
Shenzhen ([ʂə́n.ʈʂə̂n] (![]() listen)) is a major city in Guangdong Province, China, which forms part of the Pearl River Delta megalopolis north of Hong Kong. It holds sub-provincial administrative status, with powers slightly less than a province.
listen)) is a major city in Guangdong Province, China, which forms part of the Pearl River Delta megalopolis north of Hong Kong. It holds sub-provincial administrative status, with powers slightly less than a province.
Shenzhen, which roughly follows the administrative boundaries of Bao'an County, was made a city in 1979, and was named after the former county town, whose train station was the last stop on the Mainland Chinese section of the Kowloon–Canton Railway.[7] In 1980 Shenzhen was designated China's first Special Economic Zone.[8] Shenzhen's registered population in 2017 is estimated to be at 12,905,000.[1] However, officials estimate that the population of Shenzhen is about 20 million due to the large unregistered floating migrant population living in the city.[9][10] Shenzhen was one of the fastest-growing cities in the world in the 1990s and the 2000s.[11]
Shenzhen's cityscape is the result of its vibrant economy made possible by rapid foreign investment since the institution of the policy of "reform and opening" in 1979.[12] The city is a leading global technology hub, dubbed the next Silicon Valley.[13][14][15]
Shenzhen is home to the Shenzhen Stock Exchange as well as the headquarters of numerous multinational companies such as JXD, Vanke, Hytera, CIMC, Shenzhen Airlines, Nepstar, Hasee, Ping An Bank, Ping An Insurance, China Merchants Bank, Tencent, ZTE, Huawei and BYD.[16] Shenzhen ranks 22nd in the 2017 Global Financial Centres Index.[17] It also has one of the busiest container ports in the world.[18]
Shenzhen (chinois : 深圳市 ; pinyin : ; cantonais Jyutping : sam¹ zan³ si⁵ ; cantonais Yale : sàm jan si⁵) est une ville sous-provinciale de la province du Guangdong en Chine.
Située en bordure de Hong Kong, la municipalité est encore largement rurale dans les années 1970. En 1980, une partie de son territoire acquiert le statut de zone économique spéciale et devient l'un des principaux lieux d'expérimentation de la politique d'ouverture aux investissements étrangers. Bénéficiant de sa position géographique privilégiée, elle connaît un essor économique et démographique spectaculaire. En 2010, elle compte environ 10 millions d'habitants et constitue une des Municipalités les plus riches de Chine (en). Elle fait partie de la mégalopole chinoise du delta de la Rivière des Perles.
La population, en grande partie immigrée, vient de diverses régions chinoises. Le mandarin, la « langue commune », est autant parlé que le cantonais, langue traditionnelle de la région.
Shenzhen (IPA ʂə́n.ʈʂə̂n, 深圳S, ShēnzhènP) è una città sub-provinciale della Repubblica Popolare Cinese appartenente alla provincia di Guangdong nella Cina continentale meridionale. Shenzhen, trovandosi immediatamente a nord della Regione Amministrativa Speciale di Hong Kong, detiene lo stato amministrativo sub-provinciale che gli attribuisce poteri leggermente diversi e limitati rispetto alla Provincia di appartenenza.
Shenzhen era semplicemente una Città-Mercato composta da 30 mila persone lungo la rotta ferroviaria di Kowloon-Canton. Nel 1979 fu ufficialmente nominata città e successivamente, nel Maggio 1980, Deng Xiaoping decise di lanciare uno dei più audaci esperimenti economici mai tentati prima.
Con Shenzhen, si dà inizio al piano sperimentale per trasformare il modello economico Cinese tradizionale in un modello più liberale e aperto a investimenti provenienti da compagnie estere e permettere a quest'ultime di potersi insediare e operare all'interno della prima "zona economica speciale" in Cina (SEZ)
Shenzhen (pronunciado [ʂə́n.ʈʂə̂n/Shén-Zhen](![]() escuchar) (chino: 深圳市, pinyin: Shēnzhèn) es una ciudad-subprovincia de 12 millones de habitantes localizada en el delta del río de las Perlas, en la costa sur de la provincia de Cantón, en la República Popular China.
escuchar) (chino: 深圳市, pinyin: Shēnzhèn) es una ciudad-subprovincia de 12 millones de habitantes localizada en el delta del río de las Perlas, en la costa sur de la provincia de Cantón, en la República Popular China.
El nombre de la ciudad tiene su origen en la denominación que daban los habitantes de la zona a las zanjas de los arrozales a las que llamaban zhen o chon. Shénzhen significa "zanjas profundas", debido a que la zona en que la ciudad se asienta es una región atravesada por ríos y en la cual existen profundas zanjas en los arrozales.4
Hoy en día se la considera el "Silicon Valley" de China5.
Шэньчжэ́нь (кит. упр. 深圳, пиньинь: Shēnzhèn, буквально — «глубокая межа») — город субпровинциального значения в провинции Гуандун на юге Китайской Народной Республики, граничит с Гонконгом. Население по переписи 2000 года составляло 7 008 831 человек[2], а согласно переписи 2010 года — 10 357 938 человек[2] (по данным ООН, Шэньчжэнь входит в первую пятёрку городов мира по темпам прироста населения[3]). Благодаря масштабным иностранным и государственным инвестициям за довольно короткий период времени город превратился в крупный промышленный, финансовый и транспортный центр экономического региона дельты Жемчужной реки и всей страны в целом. Сегодня Шэньчжэнь является одним из наиболее динамично развивающихся городов Китая, четвёртым из числа наиболее конкурентоспособных городов страны, крупнейшим среди китайских городов по объёму экспорта и служит своеобразными воротами для привлечения инвестиций, новых технологий и культуры ведения бизнеса[4][5].
Фактически город был основан в 1979 году на месте уезда Баоань, переименованного в Шэньчжэнь, но городское поселение прослеживается на данной территории с IV века. В 2008 году Шэньчжэнь был выбран ЮНЕСКО «Творческим городом дизайна»[6], в 2011 году принимал XXVI Всемирную летнюю Универсиаду, благодаря которой существенно обновил и расширил свою инфраструктуру. Шэньчжэнь знаменит, прежде всего, своей высотной архитектурой, тематическими парками, отраслевыми выставками и, конечно же, как один из крупнейших центров электронной и электротехнической промышленности (например, большая часть популярных iPhone и iPad производится именно здесь[7]).
Согласно рейтингу сайта Tech Insider (подразделение портала Business Insider), Шэньчжэнь входит в число самых технологичных городов мира[8].





Shennongjia ist eine der besterhaltensten Urwald-Zonen in China. Im üppigen Biotop von Shennongjia leben und wachsen zahlreiche Wildtier- und Pflanzenarten, darunter gibt es viele Arten aus uralter Zeit. Daher wird Shennongjia auch als ,,Zufluchtsstätte der Lebewesen" bezeichnet.
Shennongjia liegt im gebirgigen Nordwesten der zentralchinesischen Provinz Hubei. Sein Urwald erstreckt sich über eine Fläche von mehr als 3000 Quadratkilometern. Überall in den hohen Bergen und tiefen Schluchten gedeiht eine üppige Vegetation. Heute ist Shennongjia eines der Gebiete der Welt, in denen das Ökosystem der subtropischen Urwälder am besten erhalten ist. Dank dieser guten natürlichen Voraussetzungen ist Shennongjia ein Paradies für das Überleben einer Vielzahl von Tier- und Pflanzenarten geworden.
(Quelle:http://www.bjrundschau.com/uic/txt/2010-02/25/content_248478.htm)
 China
China
 Fujian Sheng-FJ
Fujian Sheng-FJ
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hainan Sheng-HI
Hainan Sheng-HI
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH

 Urlaub und Reisen
Urlaub und Reisen
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ


 China
China

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 M 1500 - 2000 nach Christus
M 1500 - 2000 nach Christus
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN

 Museum
Museum

 Urlaub und Reisen
Urlaub und Reisen

 Weltkulturerbe
Weltkulturerbe
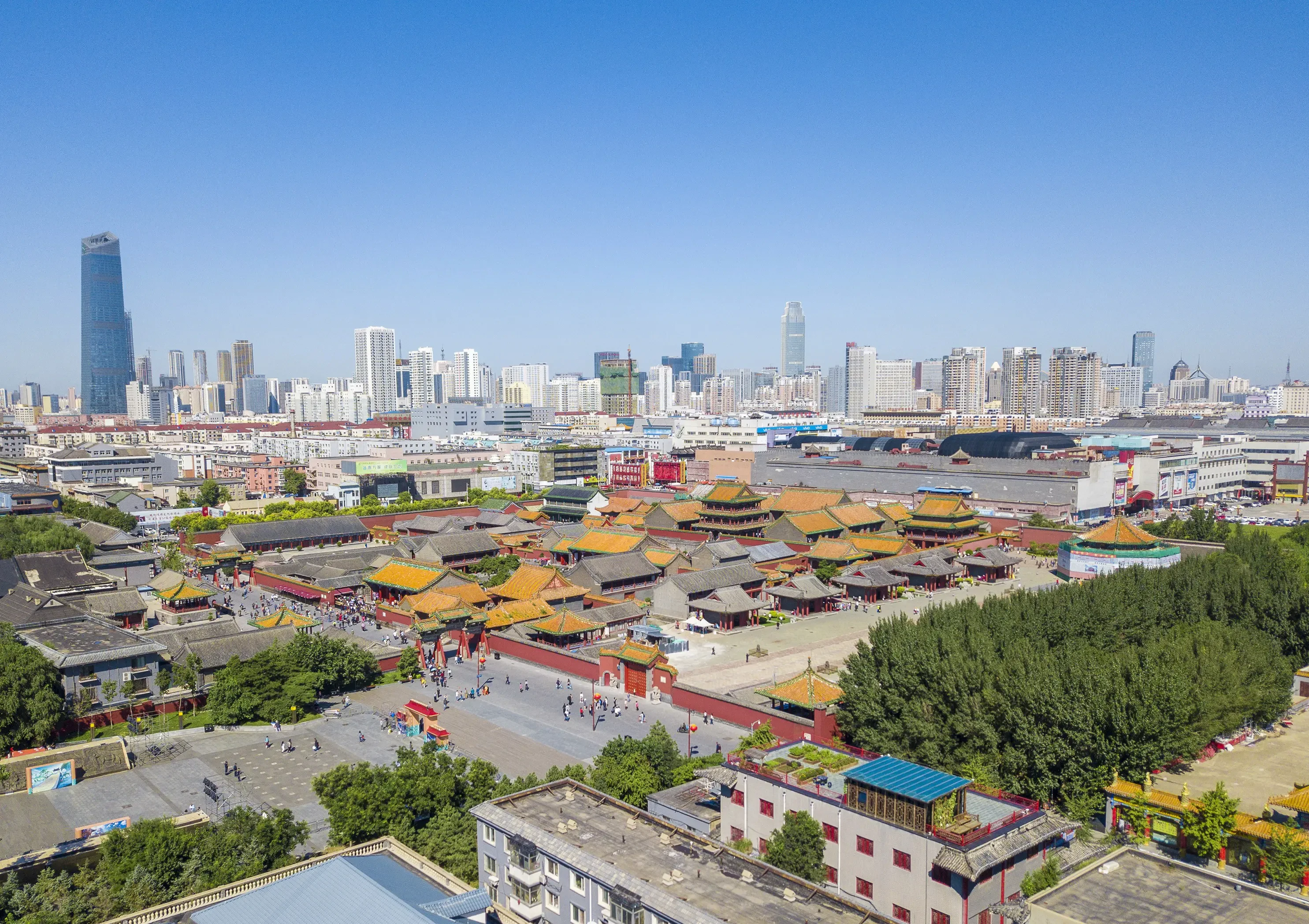
沈阳故宫,位于沈阳市沈河区明清旧城中心,是后金、满清入关前的沈阳(盛京)皇宫,满清入关迁都北京后改为盛京行宫(或称奉天行宫) ,始建于1625年。乾隆帝时期又有较大规模的改建与增修,占地约6万平方米。1926年以后,其建筑群陆续辟作博物馆(现称沈阳故宫博物院) 。
入关前
后金天命十年(1625年)三月,后金汗努尔哈赤将都城从东京迁移至明沈阳中卫城,同年开始在沈阳中卫城中心部位偏东南角的位置修筑宫殿[1],即现存的大政殿和十王亭。这组建筑主要是作为理政和朝贺的场所,努尔哈赤居住的寝宫在原沈阳城的北门——安定门。
1626年,皇太极继承后金汗位。从1631年起,用5年的时间对盛京城和皇宫进行改建。他在其原来王府的基础上修建新的大内宫殿,并将原沿袭自沈阳中卫城的十字形街道系统改为井字形街道系统,从而将皇宫置于城池的中央[2]。
1636年,皇太极在此去汗号称帝,改国号为清 ,对沈阳宫殿各主要建筑分别正式命名:“定宫殿名,中宫为清宁宫、东宫为关雎宫、西宫为麟趾宫、次东宫为衍庆宫、次西宫为永福宫、台东楼为翔凤楼、台西楼为飞龙阁、正殿为崇政殿、大门为大清门、东门为东翼门、西门为西翼门、大殿为笃恭殿”[3]。此后又在大清门前东、西两侧分别建文德坊、武功坊两座牌坊,因坊心有“崇德二年孟春吉日立” ,可知建成于1637年。这也是清入关前唯一有确切年代记载的宫殿。
入关后
顺治元年八月二十日,清世祖离开盛京前往北京。在清朝入关定都北京后,沈阳故宫失去了作为皇宫的地位,成为陪都行宫。康熙帝和乾隆帝东巡祭祖期间,曾在此居住。乾隆四十六年,即1780年,增建了西路建筑,包括戏台嘉荫堂和用于储藏四库全书的文溯阁,并在中路修建了东所、西所和盛京太庙。以及对某些入关前宫殿的局部进行改造,其中比较重要的一处是崇政殿,因皇帝东巡时在此举行典礼,但殿内屏风宝座等均系皇太极时遗留,不便使用,所以乾隆皇帝命重新制作。乾隆九年,又命于殿前增设日晷、嘉量。文溯阁等西路宫殿建成后,直到终清之时这里的建筑未再有明显变化。
The Mukden Palace (simplified Chinese: 盛京宫殿; traditional Chinese: 盛京宮殿; pinyin: Shèngjīng Gōngdiàn), or Shenyang Imperial Palace (simplified Chinese: 沈阳故宫; traditional Chinese: 瀋陽故宮; pinyin: Shěnyáng Gùgōng), was the former imperial palace of the early Manchu-led Qing dynasty. It was built in 1625, and the first three Qing emperors lived there from 1625 to 1644. Since the collapse of imperial rule in China, the palace has been converted to a museum that now lies in the center of Shenyang, Liaoning.
Le palais de Mukden (chinois simplifié : 盛京宫殿 ; chinois traditionnel : 盛京宮殿 ; pinyin : ) ou palais de Moukden ou Shenyang Gugong (chinois simplifié : 沈阳故宫 ; chinois traditionnel : 瀋陽故宮 ; pinyin : ), également connu sous le nom de palais impérial de Shenyang, est le premier palais occupé par les empereurs de la dynastie Qing, avant leur installation dans la Cité interdite de Pékin. Il est construit en 1625 et les trois premiers empereurs de la dynastie Qing y vivent de 1625 a 1644. Depuis la fin du régime impérial chinois, le palais a été converti en un musée, qui accueille chaque année 1.6 million de visiteurs2. Il est situé à Shenyang (Moukden en mandchou) en Chine.
Les édifices qui le composent sont inscrits au patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO et sont également protégés en Chine, par la liste des sites historiques et culturels majeurs protégés au niveau national, au Liaoning sous le no 1-112.
Il Palazzo Mukden (in cinese: 盛京宮殿T, 盛京宫殿S, Shěngjīng GōngdiànP), chiamato anche Shenyang Gugong (瀋陽故宮T, 沈阳故宫S, Shěnyáng GùgōngP), è l'antico palazzo imperiale della dinastia Qing (1616 - 1910). Si trova nel centro della città cinese di Mukden, oggi Shenyang, in Manciuria.
Il palazzo si estende su una superficie di circa 70.000 metri quadrati e consta di 70 edifici, a loro volta composti da 300 stanze.
El Palacio Mukden (en chino tradicional, 盛京宮殿; en chino simplificado, 盛京宫殿; pinyin, Shěngjīng Gōngdiàn) o Shenyang Gugong (en chino tradicional, 瀋陽故宮; en chino simplificado, 沈阳故宫; pinyin, Shěnyáng Gùgōng), también conocido como el Palacio Imperial Shenyang, es un antiguo palacio imperial de la nueva Dinastía Qing (1616-1910) de China.
Fue construido en 1625 y los tres primeros emperadores Qing vivieron allí de 1625 a 1644. Está situado en el centro de la ciudad de Shenyang, Manchuria, China.
Мукденский дворец (кит. трад. 瀋陽故宮, упр. 沈阳故宫) — дворец первых императоров Маньчжурской династии Китая — Нурхаци и Абахая. Заложен Нурхаци в 1625 году в Шэньяне (он же Мукден; исторически Южная Маньчжурия, к северо-востоку от Пекина). Первые здания по архитектурному решению напоминали юрты. К 1631 году строительство дворцового комплекса с учётом дополнительных построек Абахая в основном завершилось. Это комбинация элементов маньчжурской, китайской и тибетской архитектуры.
После завоевания Пекина в 1644 году император переехал в Запретный город, однако он и его наследники продолжали ежегодно посещать Мукден.
В 1780 году дворцовый комплекс был расширен императором Цяньлуном и приобрёл в большей степени облик традиционного китайского дворцового комплекса.
В 1900 году дворец был занят российской армией под командованием Деана Субботича, направленной против повстанцев-ихэтуаней.
В 1955 году объявлен национальным музеем. В 2004 году вошёл в число памятников Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО как часть комплексного объекта «Дворцы императоров династий Мин и Цин в Пекине и Шэньяне».
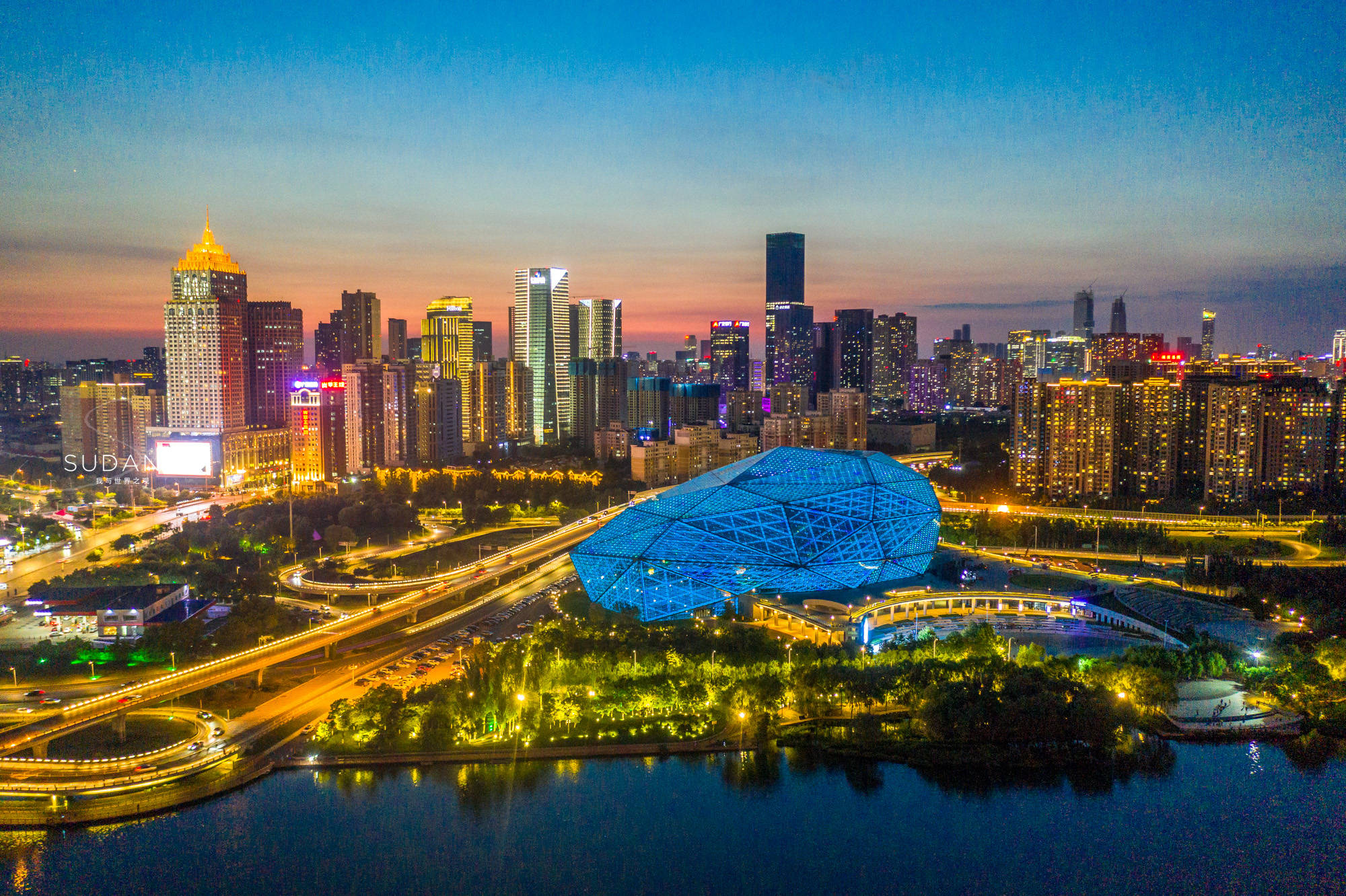

Shěnyáng (chin. 沈阳市/瀋陽市) liegt im Nordosten der Volksrepublik China und ist die Hauptstadt der Provinz Liaoning. Es ist das kulturelle und wirtschaftliche Zentrum Nordostchinas.
Großregion: Nordostchina
Provinz: Liaoning
Status: Unterprovinzstadt
Untergliederung: 9 Stadtbezirke, 3 Kreise, 1 kreisfreie Stadt
Einwohner: ca. 7,2 Mio. Einwohner
Fläche: 12.942 km²
Geschichte:
Von 1625 bis 1644 war Shenyang unter dem Namen Mukden (奉天 Fèngtiān) die Hauptstadt des Mandschurischen Staates. Deshalb steht dort der einzige kaiserliche Palast (故宫 Gùgōng) Chinas außerhalb der Verbotenen Stadt in Peking. Er wurde errichtet von Nurhachi und von seinem Sohn Huang Tai Chi (1592-1643) beendet. Von hier aus eroberte die Qing-Dynastie China und regierte es bis zum Ende des Kaiserreiches 1911. Die ersten Kaiser der Qing-Dynastie sind in bedeutenden Gräbern um Shenyang bestattet.1931 kam es hier zum Mukden-Zwischenfall, der der Auslöser für die Mandschurei-Krise war und als dessen Folge die Mandschurei von Japan besetzt und der Staat Mandschukuo gegründet wurde.(Quelle: http://christian-klinkert.de/shenyang.aspx)
 Architektur
Architektur

 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Unternehmen
Unternehmen

 Automobil
Automobil
 Messe
Messe
 Tierwelt
Tierwelt
 Geographie
Geographie
 Transport und Verkehr
Transport und Verkehr
